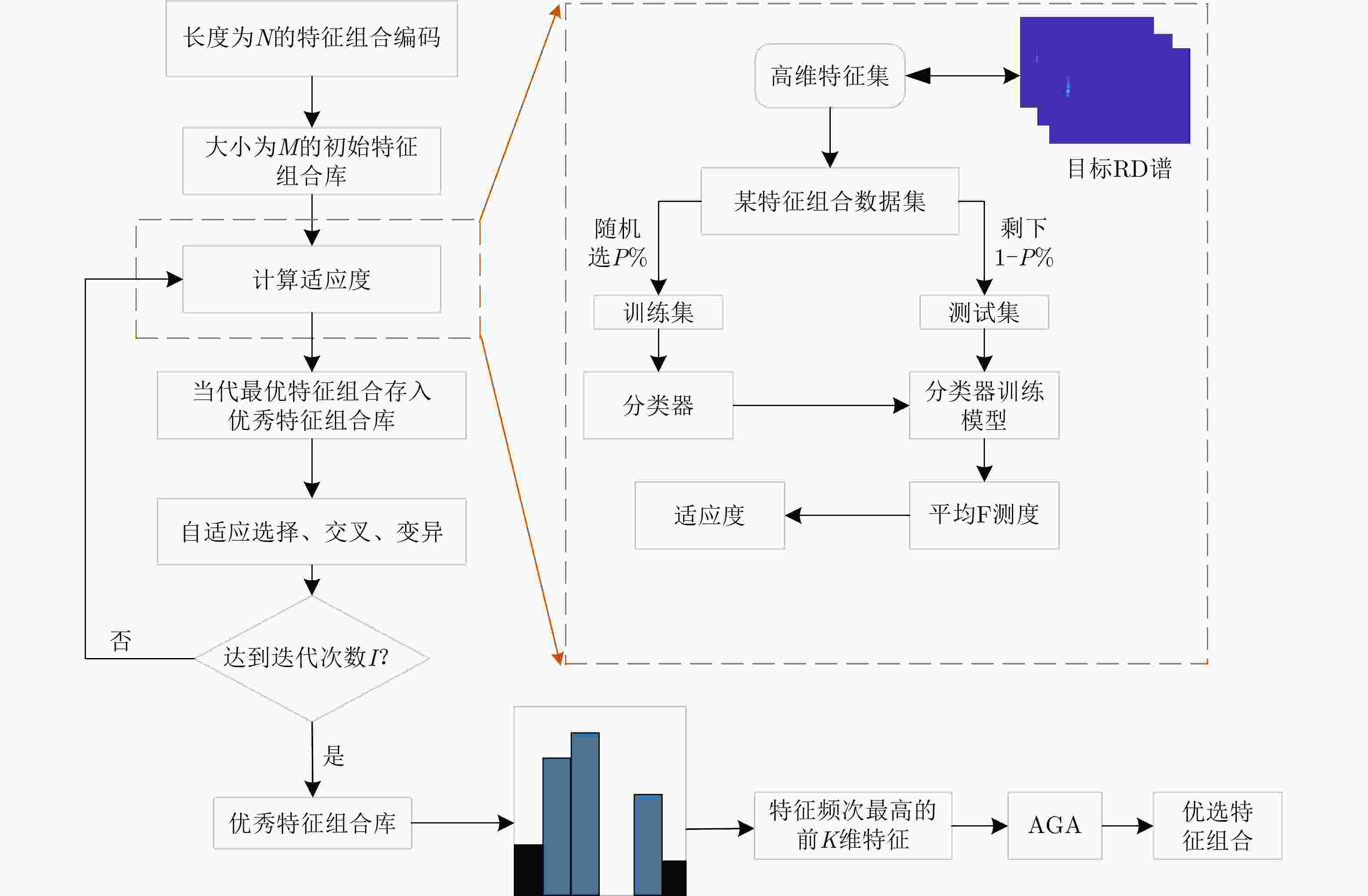
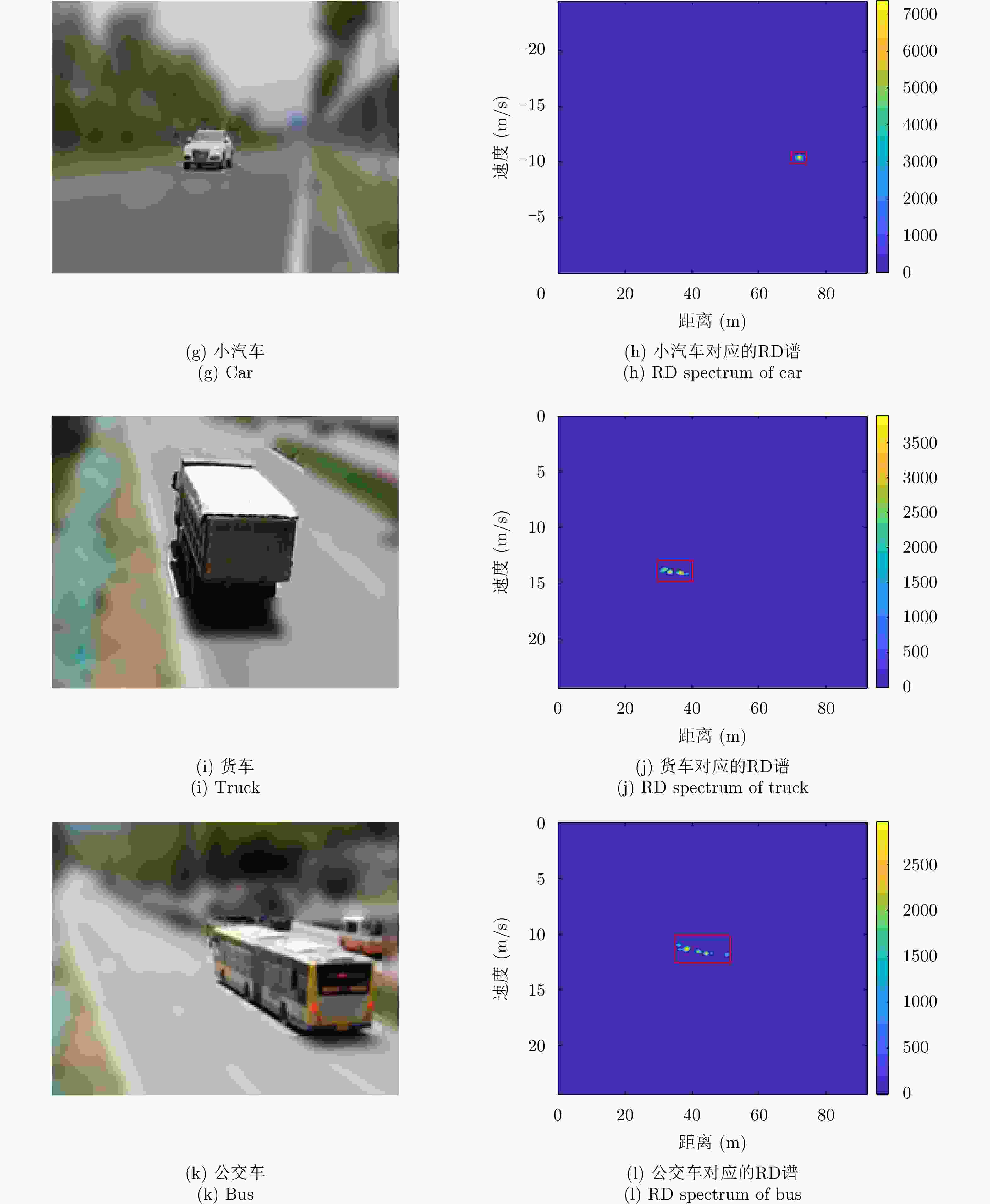
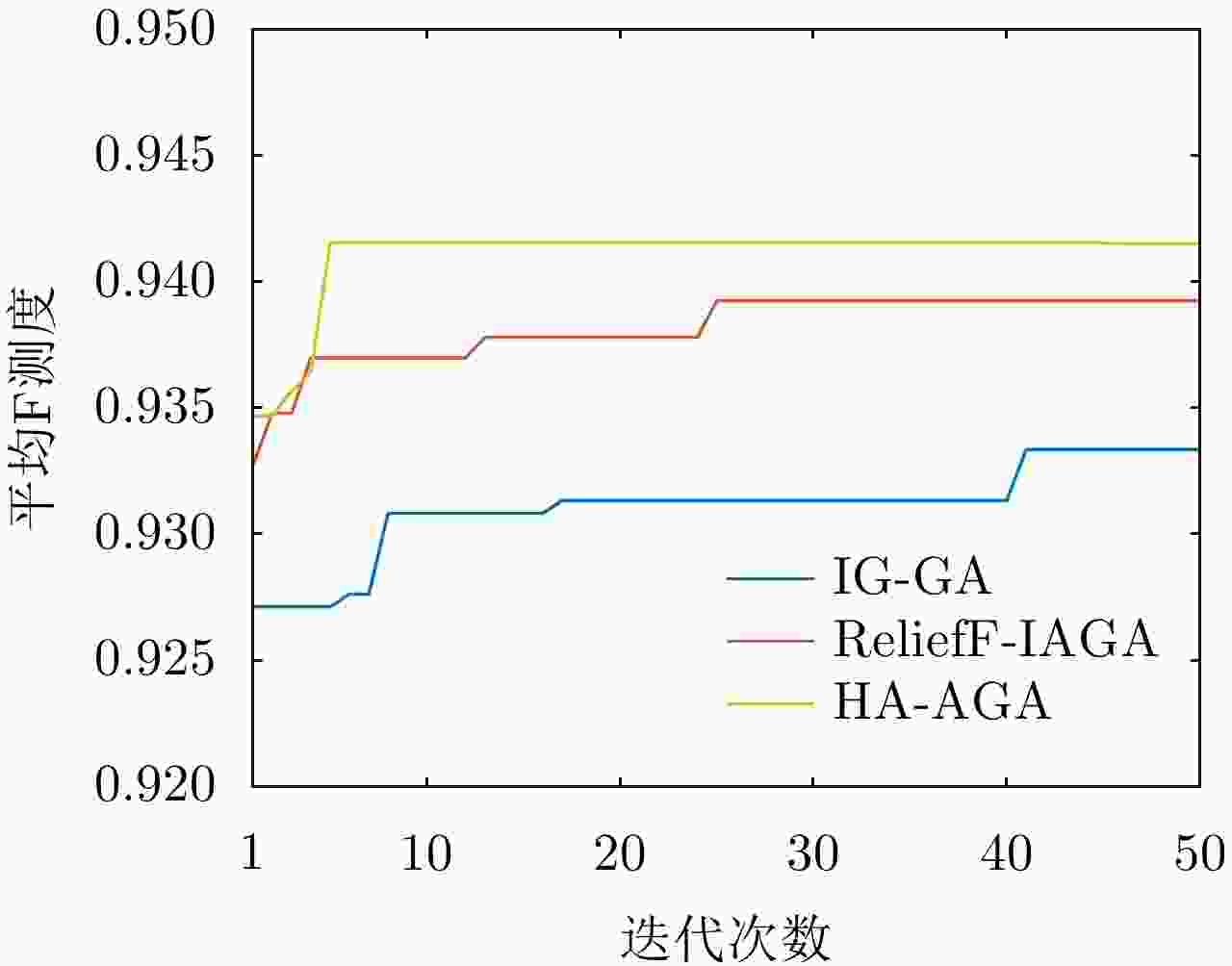
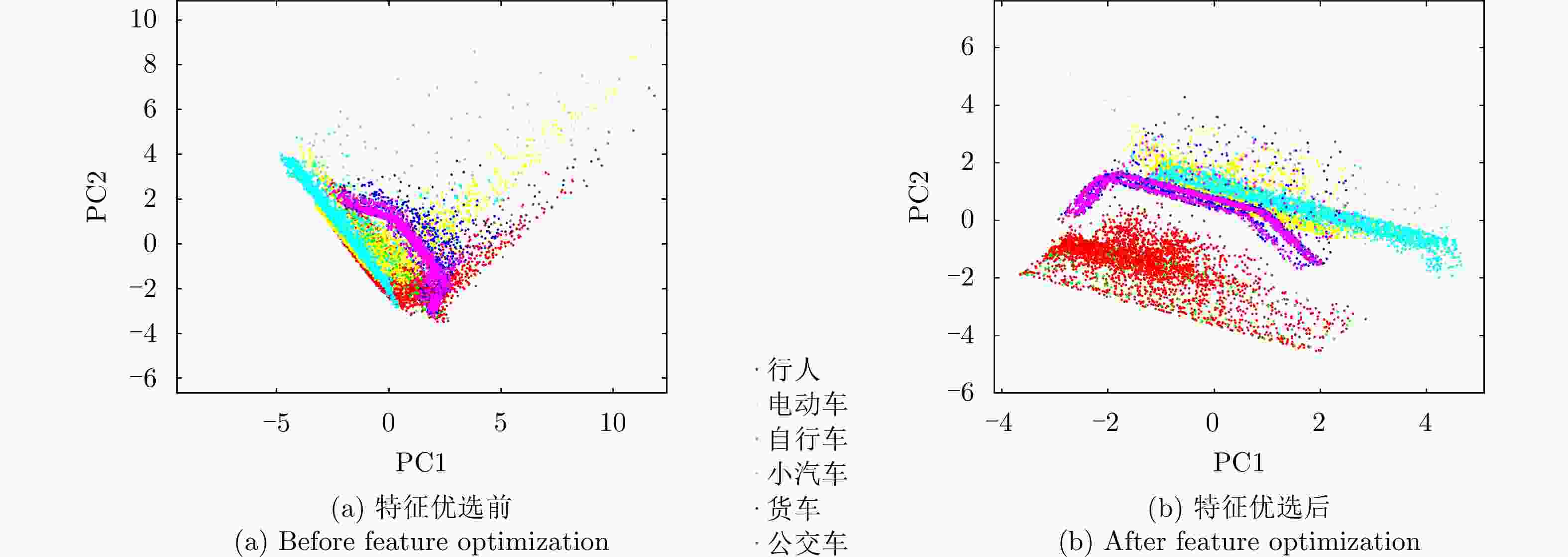
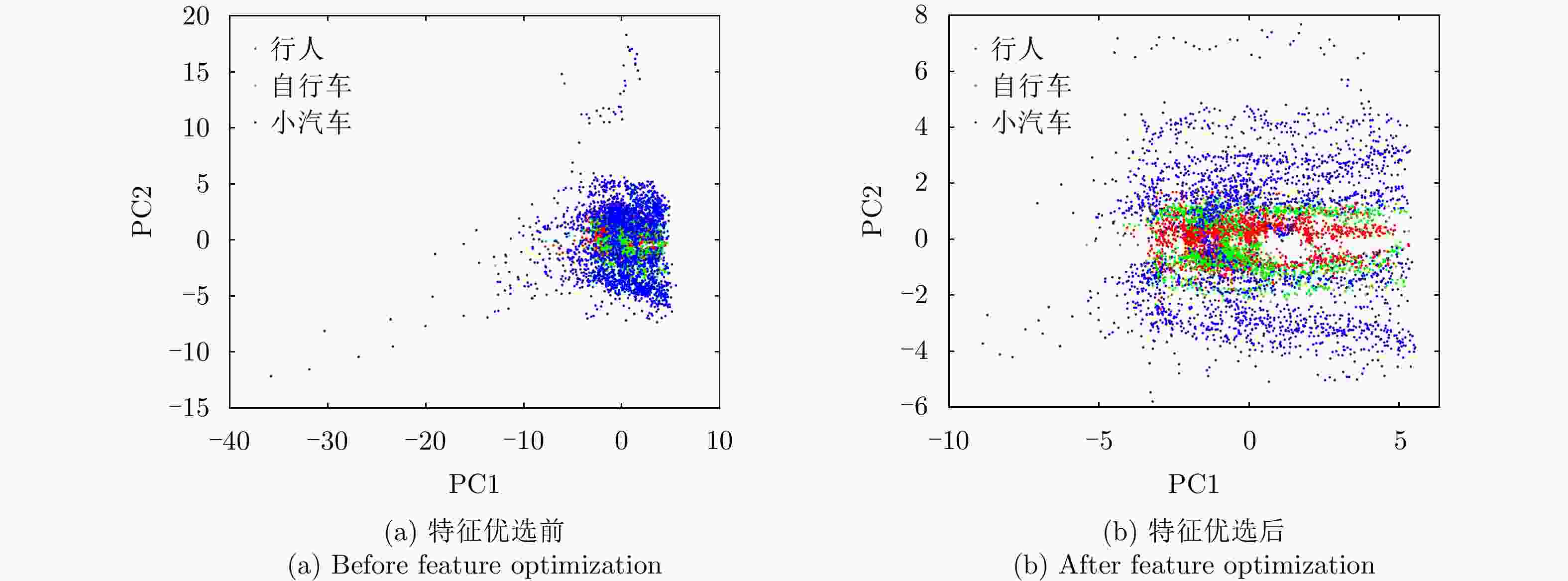
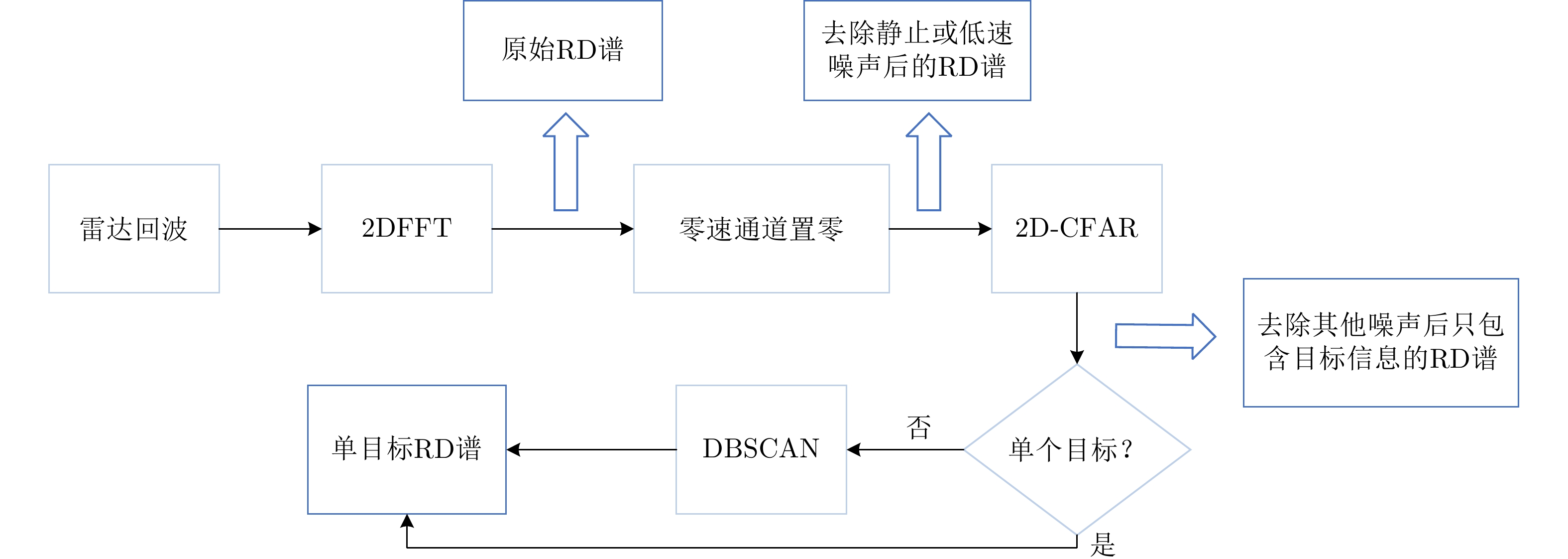
Feature Selection Method of Radar-based Road Target Recognition via Histogram Analysis and Adaptive Genetics
-
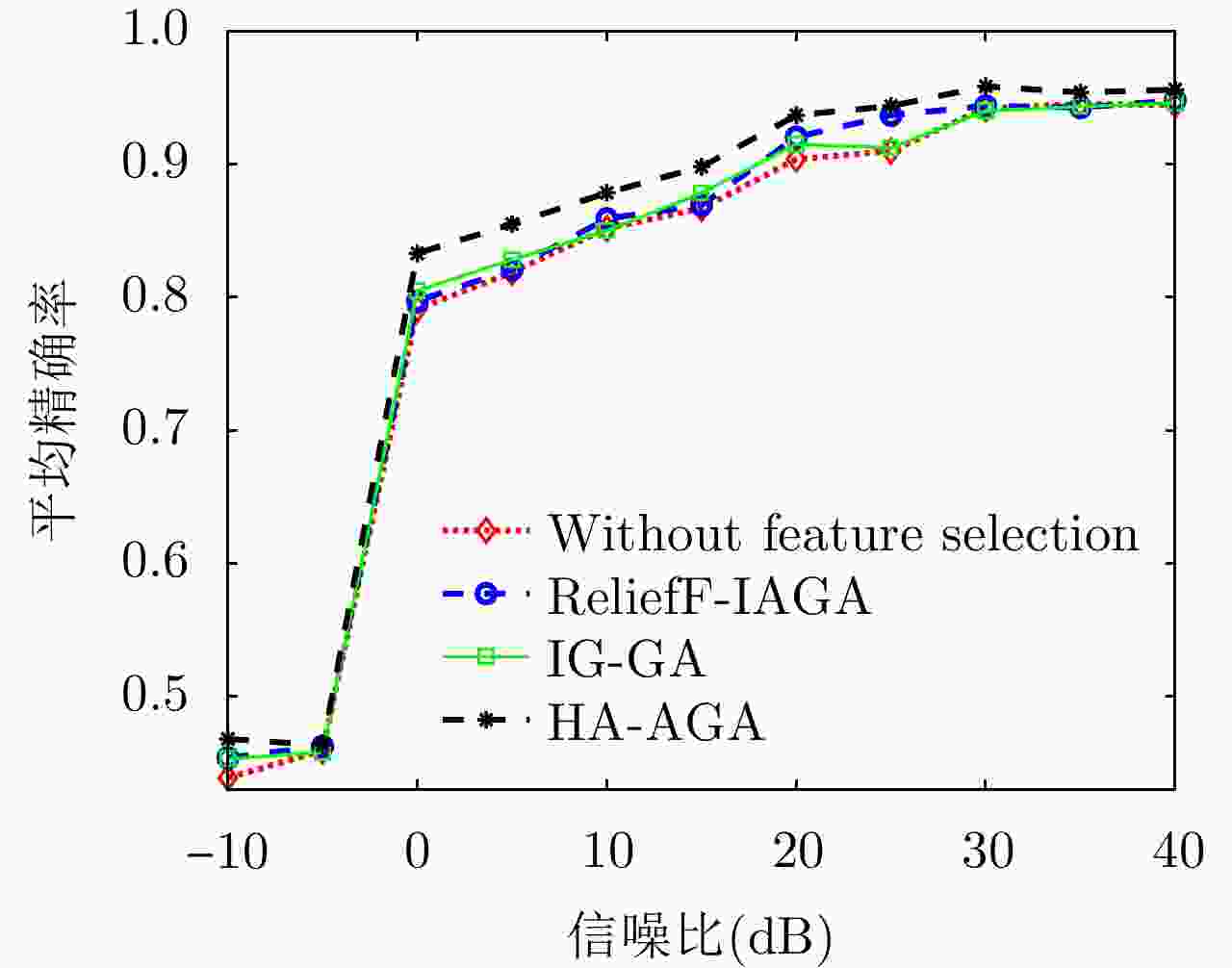
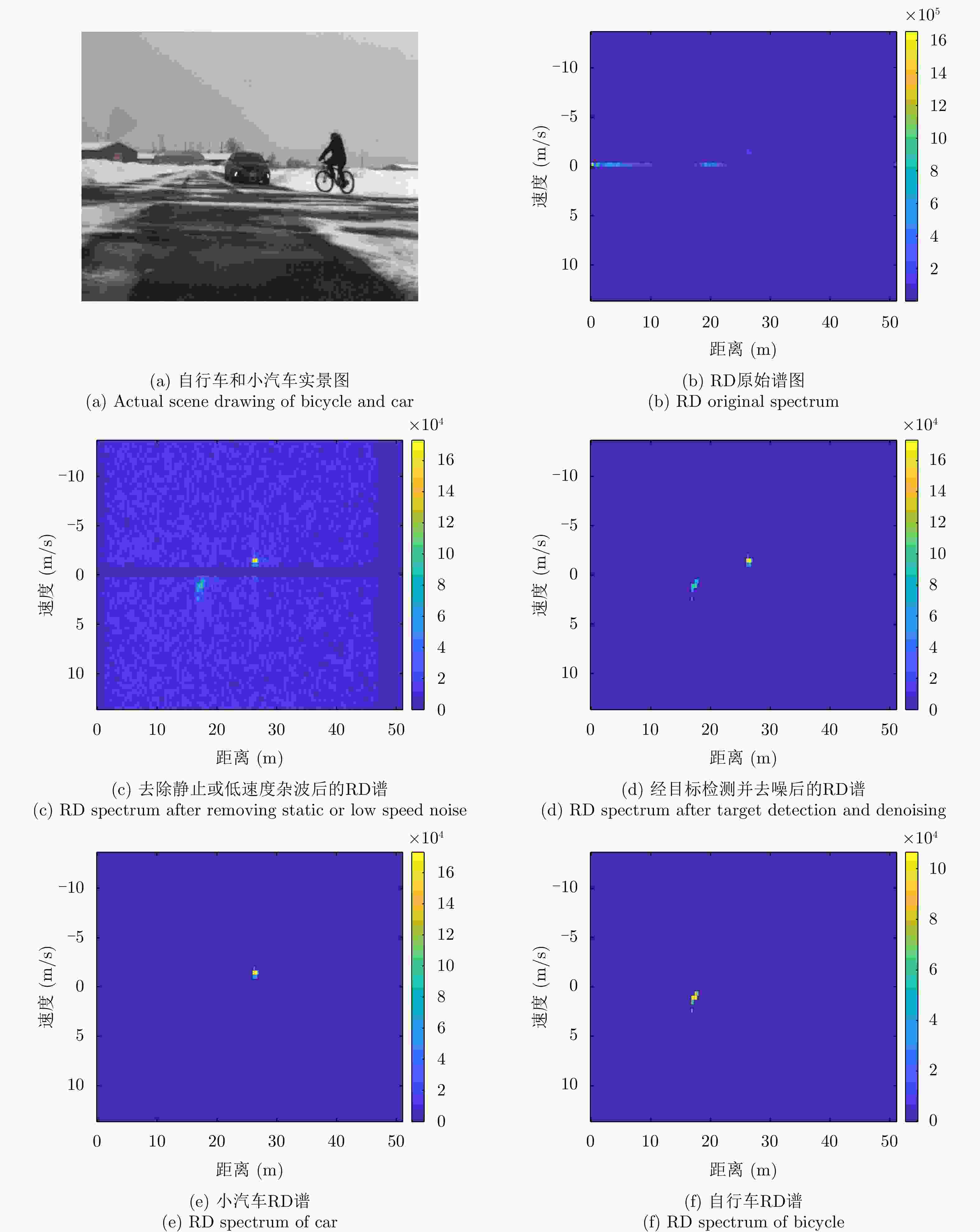
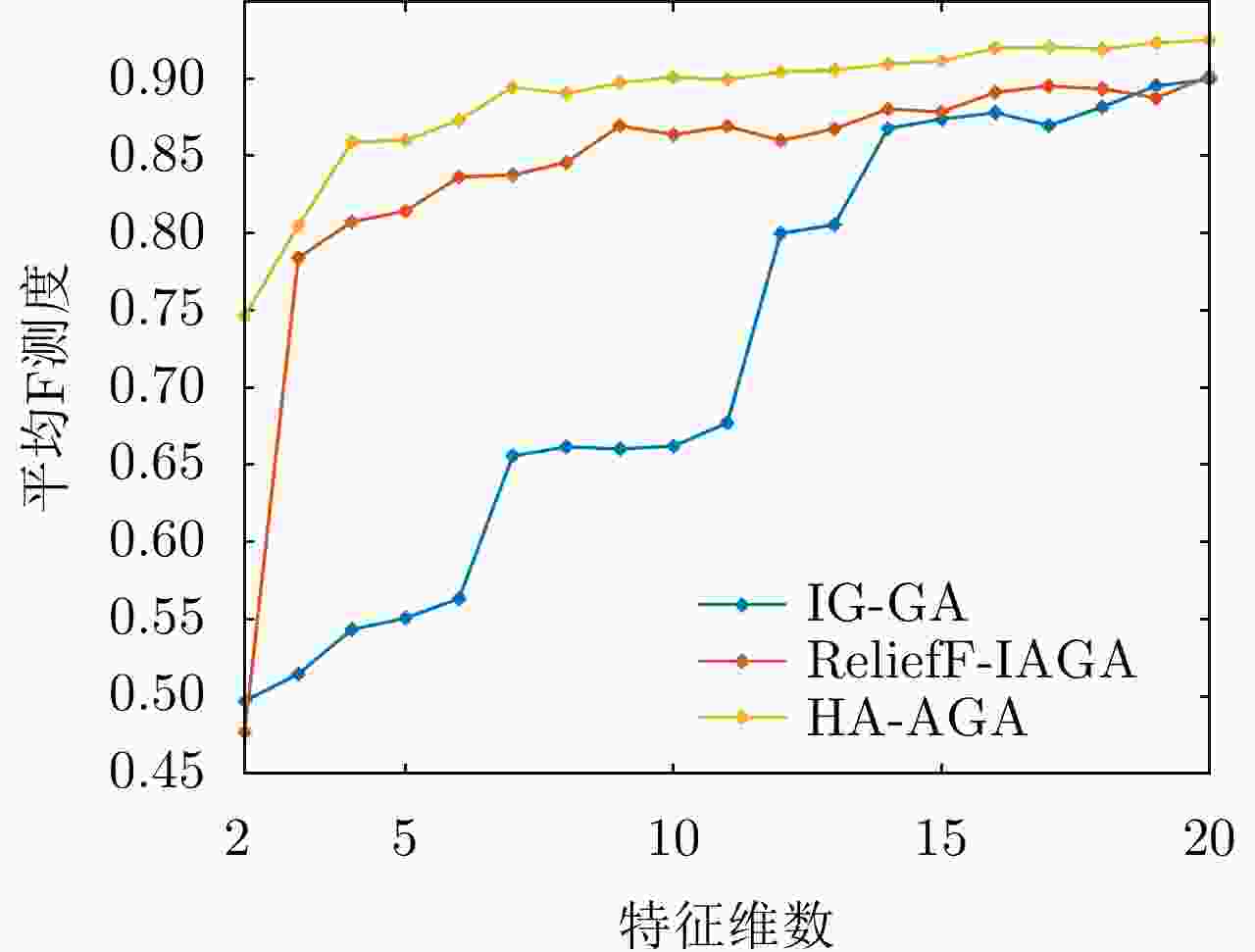
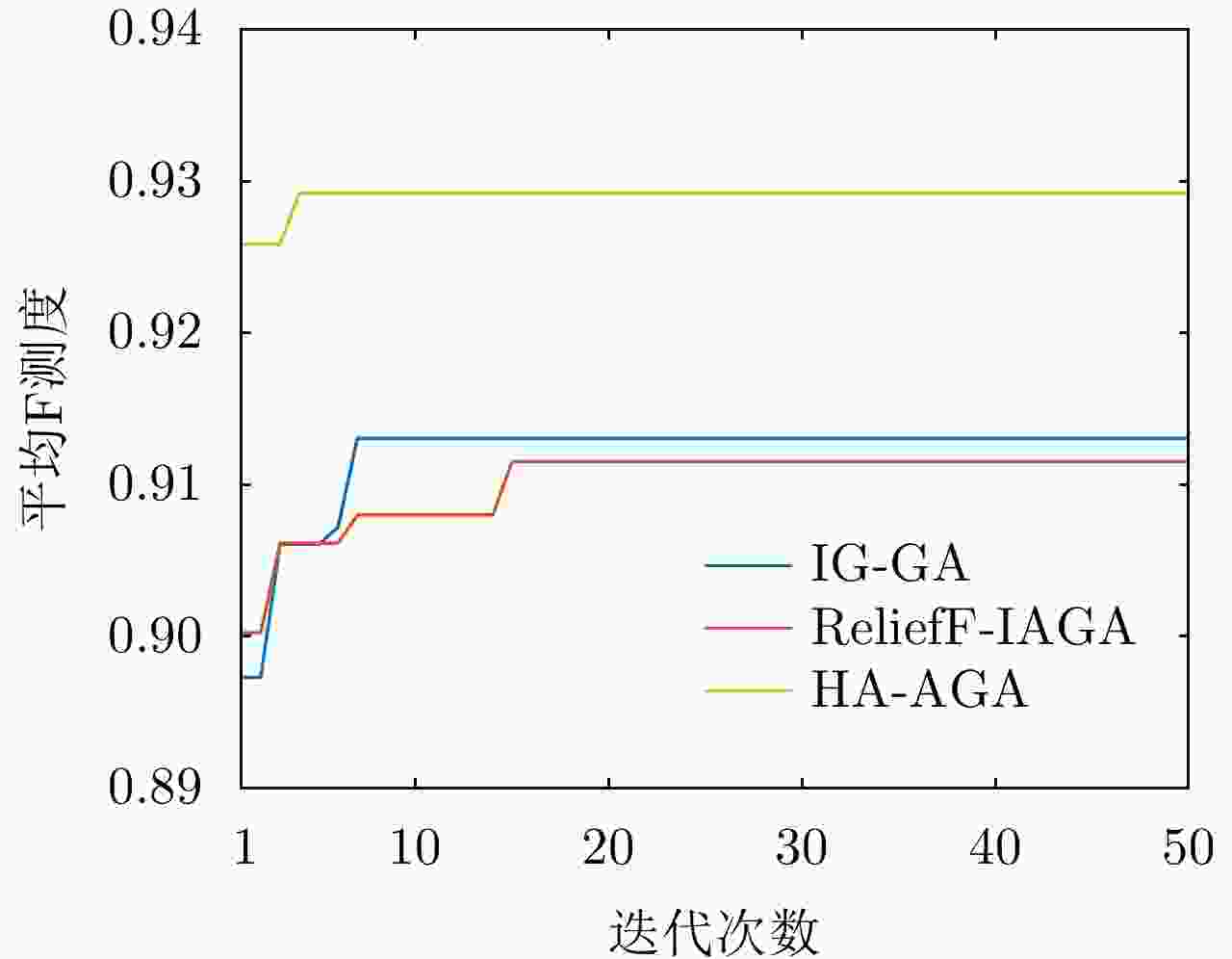
摘要: 在雷达道路目标识别领域,目标类别多变且特性相近时增加目标特征维数是一种提高识别性能常用的手段。然而特征维数的增多会导致特征冗余和维数灾难,因此需对提取的高维特征集进行优选,基于随机搜索的自适应遗传算法(AGA)是一种有效的特征优选方法。为提升AGA算法的特征优选效率和精度,现有方法通常通过引入特征与目标种类的先验相关度对高维特征集进行预降维,然而此类算法仅考虑了单个特征与目标的相关性,忽略了特征组合与目标类别的匹配度,使得优选出的特征集不一定是目标的最佳识别组合。针对该问题,该文通过引入直方图分析对不同特征组合与目标类别的匹配度加以研究,提出了一种新的改进自适应遗传(HA-AGA)特征优选方法,在提升特征优选效率和精度的同时提升目标的识别性能。基于毫米波雷达实测数据集的对比实验表明,所提出的HA-AGA方法的目标识别平均精确率可达到95.7%,分别比IG-GA, ReliefF-IAGA和改进RetinaNet方法提升了1.9%, 2.4%和10.1%。基于公共数据集CARRADA的对比实验表明,所提出的HA-AGA方法的目标识别平均精确率达到93.0%,分别比IG-GA和ReliefF-IAGA方法提升了1.2%和1.5%,验证了所提方法的有效性和优越性。此外,还进行了不同特征优选方法分别结合集成装袋树、精细树和K-最邻近(KNN)分类器的性能对比,实验结果表明所提方法结合不同分类器均具有明显优势,具有一定的广泛适用性。Abstract: In radar-based road target recognition, the increase in target feature dimension is a common technique to improve recognition performance when targets become diverse, but their characteristics are similar. However, the increase in feature dimension leads to feature redundancy and dimension disasters. Therefore, it is necessary to optimize the extracted high-dimensional feature set. The Adaptive Genetic Algorithm (AGA) based on random search is an effective feature optimization method. To improve the efficiency and accuracy of the AGA, the existing improved AGA methods generally utilize the prior correlation between features and targets for pre-dimensionality reduction of high-dimensional feature sets. However, such algorithms only consider the correlation between a single feature and a target, neglecting the correlation between feature combinations and targets. The selected feature set may not be the best recognition combination for the target. Thus, to address this issue, this study proposes an improved AGA via pre-dimensionality reduction based on Histogram Analysis (HA) of the correlation between different feature combinations and targets. The proposed method can simultaneously improve the efficiency and accuracy of feature selection and target recognition performance. Comparative experiments based on a real dataset of the millimeter-wave radar showed that the average accuracy of target recognition of the proposed HA-AGA method could reach 95.7%, which is 1.9%, 2.4%, and 10.1% higher than that of IG-GA, ReliefF-IAGA, and improved RetinaNet methods, respectively. Comparative experiments based on the CARRADA dataset showed that the average accuracy of target recognition of the proposed HA-AGA method could reach 93.0%, which is 1.2% and 1.5% higher than that of IG-GA and ReliefF-IAGA methods, respectively. These results verify the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method compared with existing methods. In addition, the performance of different feature optimization methods coupled with the integrated bagging tree, fine tree, and K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) classifier was compared. The experimental results showed that the proposed method exhibits evident advantages when coupled with different classifiers and has broad applicability.
-
表 1 特征及其公式
Table 1. Features and formulas
序号 特征 公式 序号 特征 公式 1 峰值点距离 $ {f_1} = {r_{\text{t}}} $ 16 最大距离点速度与
峰值点速度差$ {f_{16}} = {f_{14}} - {f_{11}} $ 2 平均距离 $ {f_2} = \dfrac{1}{s}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^s {{r_i}} $ 17 速度宽 $ {f_{17}} = \max ({v_i}) - \min ({v_i}) $ 3 最小距离点距离 $ {f_3} = {\text{min}}({r_i}) $ 18 速度维中值 $ {f_{18}} = \dfrac{{\max ({v_i}) + \min ({v_i})}}{2} $ 4 最大距离点距离 $ {f_4} = {\text{max}}({r_i}) $ 19 速度维方差 $ {f_{19}} = \dfrac{1}{G}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{g = 1}^G {{{({A_g} - {{\bar A}_G})}^2}} $ 5 峰值点距离与最小距离差 $ {f_5} = {f_1} - {f_3} $ 20 速度维熵 $ {f_{20}} = - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{g = 1}^G {{p_g}\lg \left( {{p_g}} \right)} $ 6 最大距离与峰值点距离差 $ {f_6} = {f_4} - {f_1} $ 21 散射点个数 $ {f_{21}} = s $ 7 距离宽 $ {f_7} = {\text{max}}({r_i}) - {\text{min}}({r_i}) $ 22 距离宽比速度宽 $ {f_{22}} = \dfrac{{{f_7}}}{{{f_{17}}}} $ 8 距离维中值 $ {f_8} = \dfrac{{\max ({r_i}) + \min ({r_i})}}{2} $ 23 能量密度 $ {f_{23}} = \dfrac{1}{s}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^s {A_i^2} $ 9 距离维方差 $ {f_9} = \dfrac{1}{G}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{g = 1}^G {{{({A_g} - {{\bar A}_G})}^2}} $ 24 波形熵 $ {f_{24}} = - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = 0}^{N - 1} {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{m = 0}^{M - 1} {{p_{n,m}}\lg \left( {{p_{n,m}}} \right)} } $ 10 距离维熵 $ {f_{10}} = - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{g = 1}^G {{p_g}\lg \left( {{p_g}} \right)} $ 25 2阶中心矩 $ {f_{25}} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = 0}^{N - 1} {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{m = 0}^{M - 1} {(n - \bar n)(m - \bar m)A\left( {n,m} \right)} } $ 11 峰值点速度 $ {f_{11}} = {v_{\text{t}}} $ 26 4阶中心矩 $ {f_{26}} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = 0}^{N - 1} {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{m = 0}^{M - 1} {{{(n - \bar n)}^2}{{(m - \bar m)}^2}A\left( {n,m} \right)} } $ 12 平均速度 $ {f_{12}} = \dfrac{1}{s}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^s {{v_i}} $ 27 信号幅值方差 $ {f_{27}} = \dfrac{1}{s}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^s {{{({A_i} - \bar A)}^2}} $ 13 最小距离点速度 $ {f_{13}} = {v_{{r_{\min }}}} $ 28 主分量能量 $ {f_{28}} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^n {{\text{main\_energ}}{{\text{y}}_j}} $ 14 最大距离点速度 $ {f_{14}} = {v_{{r_{\max }}}} $ 29 副分量能量 $ {f_{29}} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^s {A_i^2 - } \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^n {{\text{main\_energ}}{{\text{y}}_j}} $ 15 峰值点速度与最小
距离点速度差$ {f_{{\text{15}}}} = {f_{{\text{11}}}} - {f_{{\text{13}}}} $ 30 主副能量比 $ {f_{30}} = \dfrac{{{f_{28}}}}{{{f_{29}}}} $ 表 2 实测数据集描述
Table 2. The real radar dataset description
类别 标签 训练集(帧) 测试集(帧) 行人 1 2981 1278 电动车 2 2727 1169 自行车 3 111 48 小汽车 4 1756 753 货车 5 1162 499 公交车 6 1486 637 表 3 雷达参数
Table 3. Radar parameters
参数 数值 载频(GHz) 24 带宽(MHz) 207.32 波形斜率(MHz/μs) 0.80986 采样率(MHz) 1 每个脉冲采样点数 256 帧脉冲数 128 接收通道数 4 帧持续时长(ms) 32.768 表 4 各算法优选后的特征组合
Table 4. Feature combination of different algorithms after optimization
特征选择算法 优选后特征组合 IG-GA $ {f_2} $, $ {f_8} $, $ {f_{10}} $, $ {f_{11}} $, $ {f_{12}} $, $ {f_{22}} $, $ {f_{24}} $, $ {f_{26}} $, $ {f_{27}} $, $ {f_{28}} $, $ {f_{29}} $ ReliefF-IAGA $ {f_1} $, $ {f_2} $, $ {f_3} $, $ {f_4} $, $ {f_5} $, $ {f_6} $, $ {f_8} $, $ {f_{10}} $, $ {f_{12}} $, $ {f_{17}} $, $ {f_{18}} $, $ {f_{20}} $, $ {f_{22}} $, $ {f_{25}} $ HA-AGA $ {f_1} $, $ {f_3} $, $ {f_5} $, $ {f_7} $, $ {f_8} $, $ {f_{10}} $, $ {f_{11}} $, $ {f_{12}} $, $ {f_{14}} $, $ {f_{17}} $, $ {f_{20}} $, $ {f_{22}} $, $ {f_{23}} $, $ {f_{24}} $ 表 5 各算法结合集成装袋树优选后识别结果(实测数据集)(%)
Table 5. Recognition result of different algorithms combined with integrated bagging tree after optimization (Real radar dataset) (%)
类别 未优选 IG-GA ReliefF-IAGA HA-AGA 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 行人 99.0/95.7/97.3 98.3/96.7/97.5 98.4/96.6/97.5 99.0/96.8/97.9 电动车 94.3/99.1/96.6 95.3/98.2/96.7 95.5/98.1/96.8 95.5/98.8/97.1 自行车 87.2/70.8/78.2 92.5/77.1/84.1 85.7/75.0/80.0 95.0/79.2/86.4 小汽车 97.6/98.3/98.0 96.1/97.3/96.7 97.8/98.9/98.3 98.1/98.5/98.3 货车 94.8/85.4/90.0 91.2/84.1/87.5 91.4/84.3/87.7 93.5/89.5/91.5 公交车 90.4/95.9/93.1 89.1/92.2/90.7 89.2/93.2/91.2 92.9/94.9/93.9 平均值 93.9/91.1/92.2 93.8/90.9/92.2 93.3/91.0/91.9 95.7/93.0/94.2 表 6 各算法结合精细树优选后识别结果(实测数据集)(%)
Table 6. Recognition result of different algorithms combined with fine tree after optimization (Real radar dataset) (%)
类别 未优选 IG-GA ReliefF-IAGA HA-AGA 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 行人 99.1/94.3/96.6 99.1/94.2/96.6 99.5/94.0/96.7 99.3/94.7/97.0 电动车 92.3/98.9/95.6 92.5/99.0/95.6 92.5/98.9/95.7 92.7/99.0/95.7 自行车 75.6/64.6/70.0 84.6/68.8/75.9 88.4/70.2/78.2 89.5/70.8/79.1 小汽车 96.5/97.4/96.8 95.9/93.5/94.7 97.5/97.0/97.1 96.4/97.5/97.0 货车 86.2/76.7/81.2 83.7/84.9/84.3 88.6/78.6/83.3 89.6/80.4/84.8 公交车 82.9/90.0/86.3 88.4/89.2/88.8 85.3/91.6/88.3 86.8/91.4/89.0 平均值 88.7/87.0/87.8 90.7/88.3/89.3 92.0/88.3/89.9 92.4/89.0/90.4 表 7 各算法结合KNN优选后识别结果(实测数据集)(%)
Table 7. Recognition result of different algorithms combined with KNN after optimization (Real radar dataset) (%)
类别 未优选 IG-GA ReliefF-IAGA HA-AGA 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 行人 94.6/93.6/94.1 96.0/94.8/95.5 96.0/94.3/95.1 96.3/94.6/95.5 电动车 91.9/94.3/93.1 92.7/96.1/94.3 92.2/95.2/93.7 92.7/95.7/94.2 自行车 70.7/60.4/65.2 87.5/72.9/79.6 84.7/75.0/79.5 86.0/77.1/81.3 小汽车 96.7/96.6/96.7 96.7/95.8/96.3 96.1/97.0/96.5 96.7/97.1/97.0 货车 88.6/83.3/85.9 85.7/82.5/84.5 87.2/82.8/84.9 89.6/83.3/86.3 公交车 87.8/91.0/89.3 87.9/89.4/88.6 90.0/90.0/90.0 88.4/91.6/90.0 平均值 88.4/86.4/87.4 91.1/88.6/89.8 91.0/89.0/89.9 91.6/89.9/91.0 表 8 HA-AGA与改进的RetinaNet方法的识别结果(%)
Table 8. Recognition results of HA-AGA and the improved RetinaNet method (%)
类别 改进的RetinaNet HA-AGA 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 行人 98.1/95.6/96.8 99.0/96.8/97.9 电动车 87.4/92.0/89.6 95.5/98.8/97.1 自行车 81.8/56.3/66.7 95.0/79.2/86.4 小汽车 80.2/84.5/82.3 98.1/98.5/98.3 货车 82.3/67.1/73.9 93.5/89.5/91.5 公交车 83.8/88.7/86.2 92.9/94.9/93.9 平均值 85.6/80.7/82.6 95.7/93.0/94.2 参数 数值 载频(GHz) 77 带宽(GHz) 4 最大距离(m) 50 FFT距离分辨率(m) 0.20 最大径向速度(m/s) 13.43 FFT径向速度分辨率(m/s) 0.42 每个脉冲采样点数 256 帧脉冲数 64 表 10 CARRADA数据集描述
Table 10. CARRADA dataset description
类别 标签 训练集(帧) 测试集(帧) 行人 1 2383 1021 自行车 2 1309 561 小汽车 3 2393 1026 表 11 不同算法优选后的特征组合
Table 11. Feature combination of different algorithms after optimization
特征选择算法 优选后特征组合 IG-GA $ {f_2} $,$ {f_4} $,$ {f_7} $,$ {f_8} $,$ {f_{12}} $,$ {f_{13}} $,$ {f_{18}} $,$ {f_{20}} $,$ {f_{22}} $,$ {f_{23}} $,$ {f_{26}} $ ReliefF-IAGA $ {f_1} $,$ {f_4} $,$ {f_5} $,$ {f_7} $,$ {f_8} $,$ {f_{12}} $,$ {f_{13}} $,$ {f_{18}} $,$ {f_{23}} $,$ {f_{26}} $,$ {f_{27}} $,$ {f_{30}} $ HA-AGA $ {f_1} $,$ {f_2} $,$ {f_3} $,$ {f_4} $,$ {f_6} $,$ {f_7} $,$ {f_8} $,$ {f_{12}} $,$ {f_{13}} $,$ {f_{17}} $,$ {f_{18}} $,$ {f_{21}} $,$ {f_{23}} $,$ {f_{28}} $ 表 12 各算法结合集成装袋树优选后识别结果(CARRADA)(%)
Table 12. Recognition result of different algorithms combined with integrated bagging tree after optimization (CARRADA) (%)
类别 未优选 IG-GA ReliefF-IAGA HA-AGA 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 行人 90.3/93.3/91.8 90.5/94.4/92.4 89.8/94.4/92.1 91.7/95.2/93.4 自行车 85.1/83.4/84.3 87.2/83.6/85.4 87.2/82.4/84.7 89.5/85.4/87.4 小汽车 97.6/95.4/96.5 97.6/95.6/96.6 97.4/95.4/96.4 97.7/96.5/97.1 平均值 91.0/90.7/90.9 91.8/91.2/91.5 91.5/90.7/91.1 93.0/92.4/92.7 表 13 各算法结合精细树优选后识别结果(CARRADA)(%)
Table 13. Recognition result of different algorithms combined with fine tree after optimization (CARRADA) (%)
类别 未优选 IG-GA ReliefF-IAGA HA-AGA 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 行人 87.5/86.7/87.1 86.9/86.6/86.8 84.0/88.0/86.0 88.0/87.3/87.7 自行车 74.8/80.6/77.6 71.4/80.4/75.6 73.5/76.3/74.9 72.8/83.1/77.6 小汽车 95.5/92.4/93.9 96.5/90.2/93.2 96.2/89.8/92.9 97.6/90.9/94.2 平均值 85.9/86.6/86.2 84.9/85.7/85.2 84.5/84.7/84.6 86.0/87.1/86.5 表 14 各算法结合KNN优选后识别结果(CARRADA)(%)
Table 14. Recognition result of different algorithms combined with KNN after optimization (CARRADA) (%)
类别未优选 IG-GA ReliefF-IAGA HA-AGA 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 精确率/召回率/F测度 行人 84.9/86.2/85.5 88.1/87.5/87.8 86.5/84.4/85.5 88.7/88.7/88.7 自行车 76.4/75.4/75.9 76.7/75.6/76.2 74.1/75.9/75.0 76.9/79.1/78.0 小汽车 93.0/92.2/92.6 93.4/94.7/94.1 92.4/93.4/92.9 93.1/91.6/92.3 平均值 84.8/84.6/84.7 86.1/85.9/86.0 84.3/84.6/84.5 86.2/86.5/86.4 -
[1] PATOLE S M, TORLAK M, WANG Dan, et al. Automotive radars: A review of signal processing techniques[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34(2): 22–35. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2016.2628914 [2] 周刚, 吴杰. 汽车防撞毫米波雷达系统参数优化设计[J]. 电讯技术, 2011, 51(7): 77–80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2011.07.016ZHOU Gang and WU Jie. Parameters optimized design of automobile anti-collision millimeter wave radar system[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2011, 51(7): 77–80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2011.07.016 [3] 元志安, 周笑宇, 刘心溥, 等. 基于RDSNet的毫米波雷达人体跌倒检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 656–664. doi: 10.12000/JR21015YUAN Zhian, ZHOU Xiaoyu, LIU Xinpu, et al. Human fall detection method using millimeter-wave radar based on RDSNet[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 656–664. doi: 10.12000/JR21015 [4] ZHAO Yan, ZHAO Lingjun, XIONG Boli, et al. Attention receptive pyramid network for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2738–2756. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2997081 [5] MIAO Tian, ZENG Hongcheng, YANG Wei, et al. An improved lightweight RetinaNet for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 4667–4679. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3180159 [6] WANG Chenxi, CHEN Zhichao, CHEN Xin, et al. Detection of MMW radar target based on Doppler characteristics and deep learning[C]. IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Industrial Design, Guangzhou, China, 2021: 266–271. [7] ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, KE Xiao, et al. HOG-ShipCLSNet: A novel deep learning network with HOG feature fusion for SAR ship classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5210322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3082759 [8] SOROWKA P and ROHLING H. Pedestrian classification with 24 GHz chirp sequence radar[C]. 2015 16th International Radar Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2015: 167–173. [9] 余月琴. 车载毫米波雷达行人识别算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020: 11–15.YU Yueqin. Research on pedestrian recognition algorithm of automobile millimeter wave radar[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020: 11–15. [10] HEUEL S and ROHLING H. Pedestrian classification in automotive radar systems[C]. 2012 13th International Radar Symposium, Warsaw, Poland, 2012: 39–44. [11] LANDGREBE D A. Signal Theory Methods in Multispectral Remote Sensing[M]. Hoboken, USA: Wiley, 2003. [12] EL AKADI A, AMINE A, EL OUARDIGHI A E, et al. A two-stage gene selection scheme utilizing MRMR filter and GA wrapper[J]. Knowledge and Information Systems, 2011, 26(3): 487–500. doi: 10.1007/s10115-010-0288-x [13] TEKELI B, GURBUZ S Z, and YUKSEL M. Information-theoretic feature selection for human Micro-Doppler signature classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(5): 2749–2762. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2505409 [14] JOLLIFFE I T. Principal Component Analysis[M]. 2nd ed. New York, USA: Springer, 2002: 1–9. [15] WANG Zigeng, XIAO Xia, and RAJASEKARAN S. Novel and efficient randomized algorithms for feature selection[J]. Big Data Mining and Analytics, 2020, 3(3): 208–224. doi: 10.26599/BDMA.2020.9020005 [16] GÜRBÜZ S Z, TEKELI B, KARABACAK C, et al. Feature selection for classification of human Micro-Doppler[C]. IEEE International Conference on Microwaves, Communications, Antennas and Electronic Systems, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2013: 1–5. [17] WU Yanwei, JIANG Mian, PEI Xiaoshuai, et al. Feature selection and decision fusion methods in target recognition[C]. IET International Radar Conference, Chongqing, China, 2021: 687–690. [18] XIAO Peng, WANG Zigeng, and RAJASEKARAN S. Novel speedup techniques for parallel singular value decomposition[C]. 2018 IEEE 20th International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 16th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 4th International Conference on Data Science and Systems, Exeter, UK, 2018: 188–195. [19] CHANDRASHEKAR G and SAHIN F. A survey on feature selection methods[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2014, 40(1): 16–28. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2013.11.024 [20] WANG Yunyan, ZHUO Tong, ZHANG Yu, et al. Hierarchical polarimetric SAR image classification based on feature selection and Genetic algorithm[C]. 2014 12th International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Hangzhou, China, 2014: 764–768. [21] BHANU B and LIN Yingqiang. Genetic algorithm based feature selection for target detection in SAR images[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2003, 21(7): 591–608. doi: 10.1016/S0262-8856(03)00057-X [22] SENTHILNATH J, OMKAR S N, MANI V, et al. Multi-sensor satellite remote sensing images for flood assessment using swarm intelligence[C]. 2015 International Conference on Cognitive Computing and Information Processing, Noida, India, 2015: 1–5. [23] LIANG Kui, DAI Wei, and DU Rui. A feature selection method based on improved genetic algorithm[C]. 2020 Global Reliability and Prognostics and Health Management (PHM-Shanghai), Shanghai, China, 2020: 1–5. [24] LI Yinghao, SHI Kai, QIAO Fuqiang, et al. A feature subset selection method based on the combination of PCA and improved GA[C]. 2020 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data and Business Intelligence (MLBDBI), Taiyuan, China, 2020: 191–194. [25] YANG B S, HAN Tian, and YIN Zhongjun. Fault diagnosis system of induction motors using feature extraction, feature selection and classification algorithm[J]. JSME International Journal Series C:Mechanical Systems, Machine Elements and Manufacturing, 2006, 49(3): 734–741. doi: 10.1299/jsmec.49.734 [26] LIU Ming, DING Xiangqian, YU Shusong, et al. Research on feature selection in near-infrared spectroscopy classification based on improved adaptive genetic algorithm combined with ReliefF[C]. 2017 9th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics (IHMSC), Hangzhou, China, 2017: 403–406. [27] YANG Jianyong and YAN Ruqiang. A multidimensional feature extraction and selection method for ECG arrhythmias classification[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(13): 14180–14190. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3047962 [28] THEJASWEE M, SRILAKSHMI P, KARUNA G, et al. Hybrid IG and GA based feature selection approach for text categorization[C]. 2020 4th International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), Coimbatore, India, 2020, 1606–1613. [29] DELON J, DESOLNEUX A, LISANI J L, et al. A nonparametric approach for histogram segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(1): 253–261. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.884951 [30] OUAKNINE A, NEWSON A, REBUT J, et al. CARRADA dataset: Camera and automotive Radar with range- angle- Doppler annotations[C]. 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 2021: 5068–5075. [31] WHITLEY D. A genetic algorithm tutorial[J]. Statistics and Computing, 1994, 4(2): 65–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00175354 [32] SAITO T and REHMSMEIER M. The precision-recall plot is more informative than the ROC plot when evaluating binary classifiers on imbalanced datasets[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0118432. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118432 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: