-
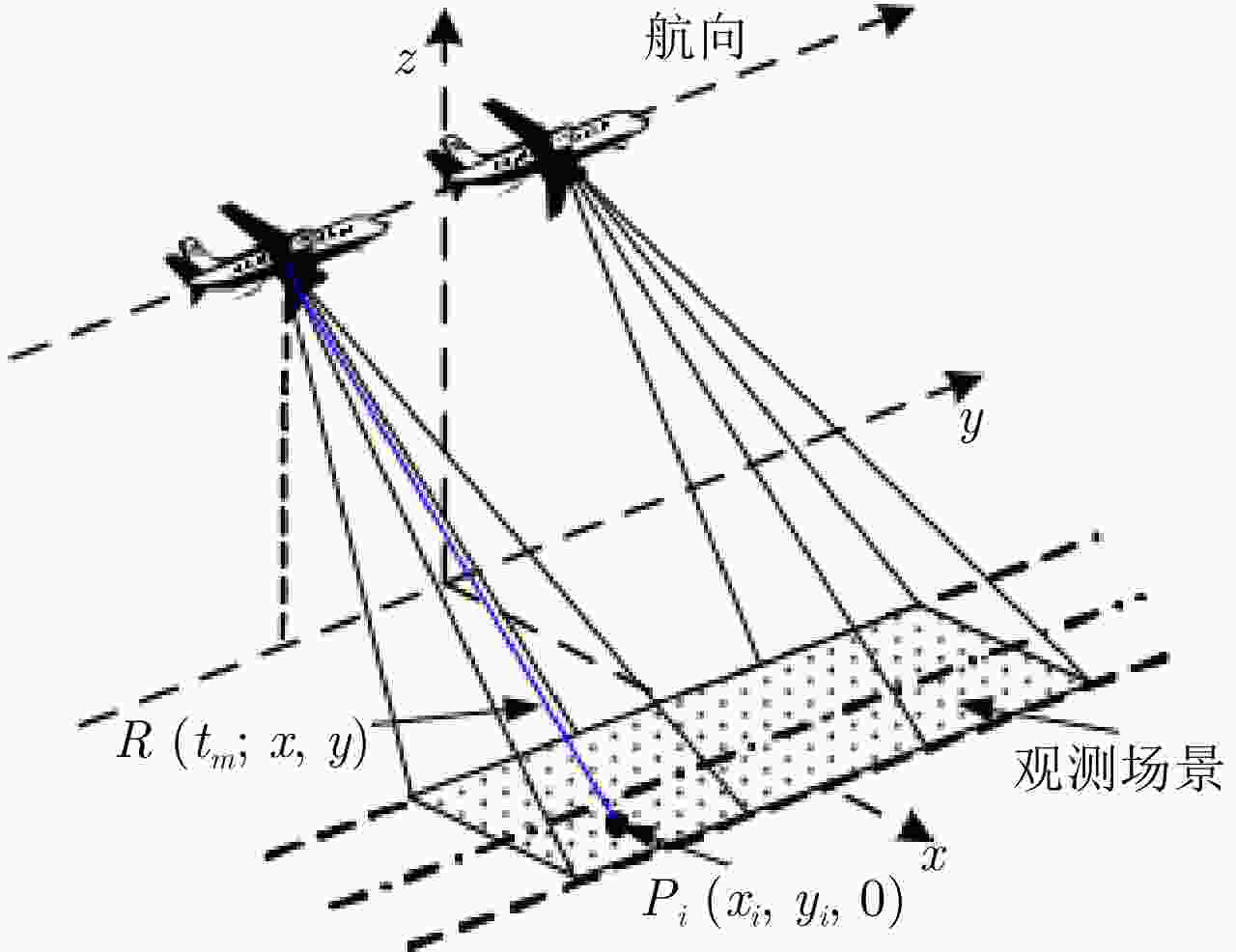
摘要: 针对合成孔径雷达(SAR)在稀疏采样条件下方位向分辨率低、易受噪声干扰等问题,提出改进的高分辨率SAR成像算法。该文在现有的L1/2正则化理论及其阈值迭代算法的基础上,改进了其表达式中的梯度算子,提高重构图像的求解精度,降低计算量。然后,在全采样和欠采样条件下,将原有L1/2阈值迭代算法与所提改进L1/2阈值迭代算法,分别结合近似观测模型对SAR回波信号进行成像处理和性能对比。实验结果表明,改进的算法具有更加优越的收敛性能,并且对于SAR图像方位向分辨率有一定的改善。Abstract: An improved Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging algorithm is proposed to address the issues of low azimuth resolution and noise interference in the sparse sampling condition. Based on the existing L1/2 regularization theory and iterative threshold algorithm, the gradient operator is modified, which can improve the solution accuracy of the reconstructed image and reduce the load of calculation. Then, under full sampling and under-sampling conditions, the original and improved L1/2 iterative threshold algorithm are combined with the approximate observation model to image SAR echo signals and compare their imaging performance. The experimental findings demonstrate that the improved algorithm improves the azimuth resolution of SAR images and has higher convergence performance.
-
表 1 SAR成像仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters of SAR imaging
参数 数值 载频(GHz) 5.3 飞行速度(m/s) 150 脉冲宽度(μs) 2.5 距离向采样率(MHz) 60 方位向采样率(Hz) 200 平台离场景中心斜距(km) 20 斜视角(°) 0 距离向调频率(MHz/μs) 20000 表 2 3种算法中5个点目标成像分辨率分析(m)
Table 2. Imaging resolution analysis of five targets in three algorithms (m)
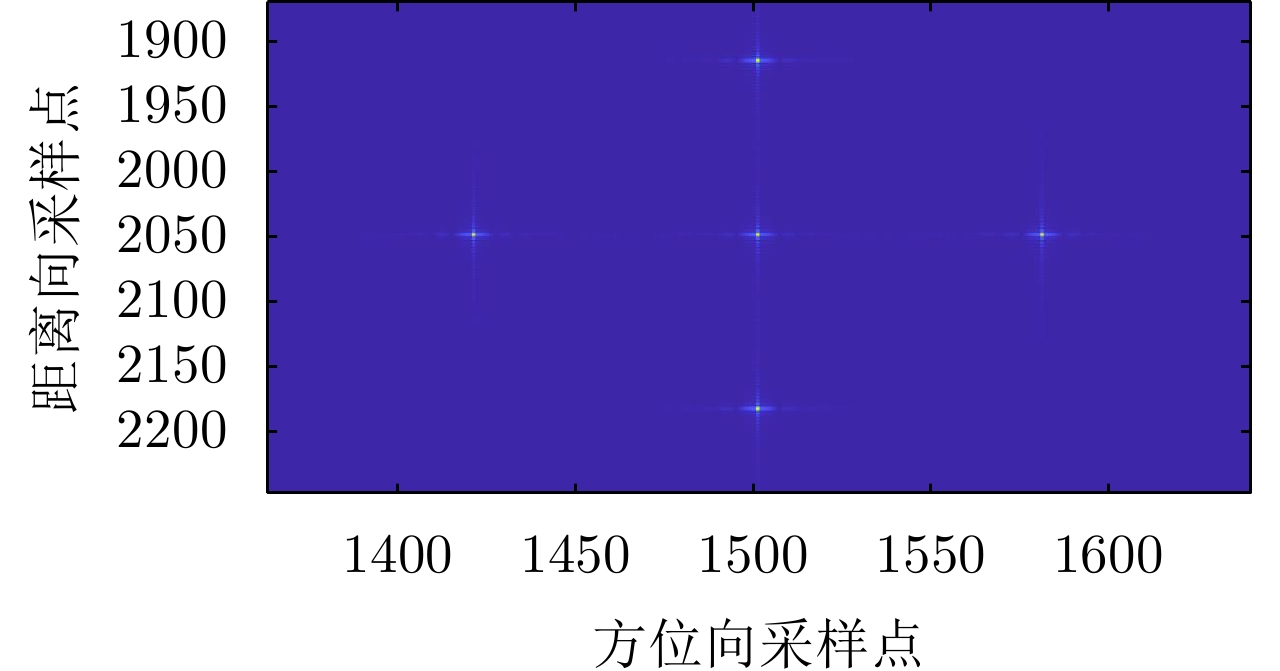
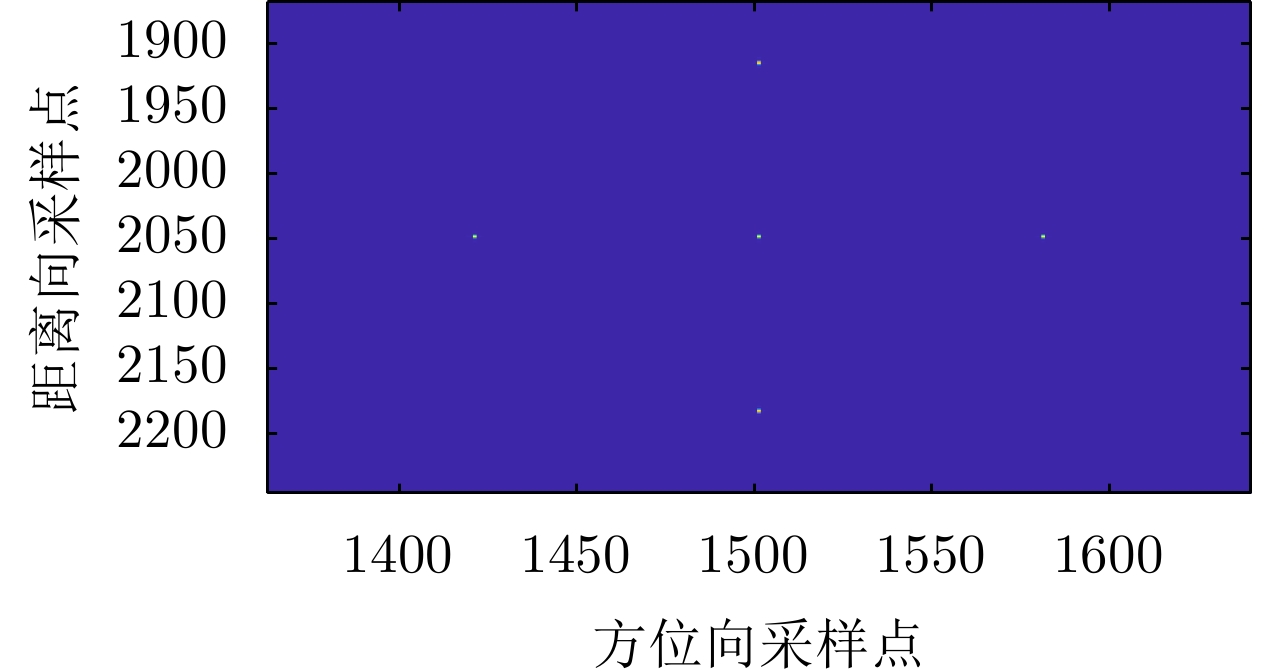
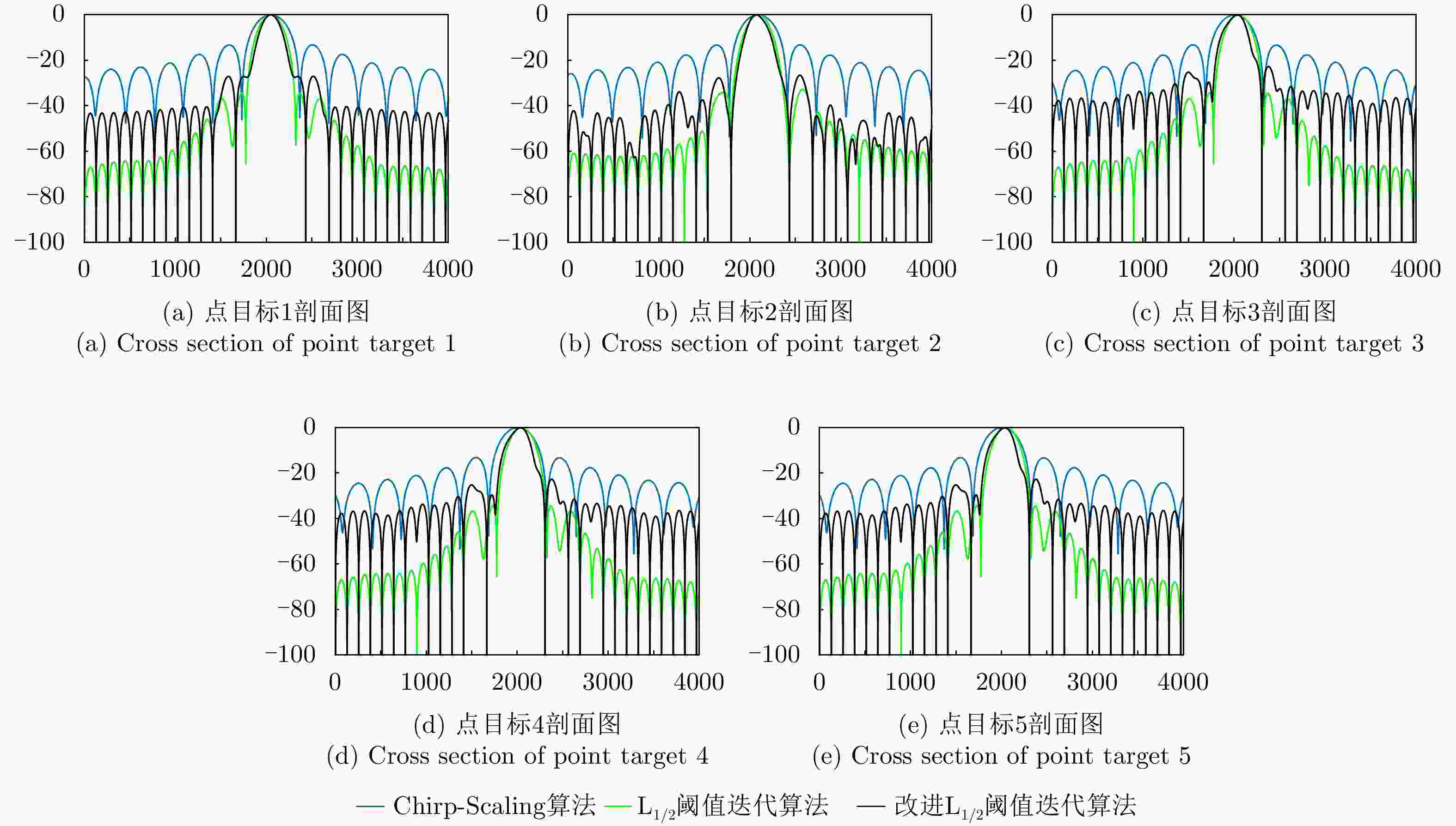
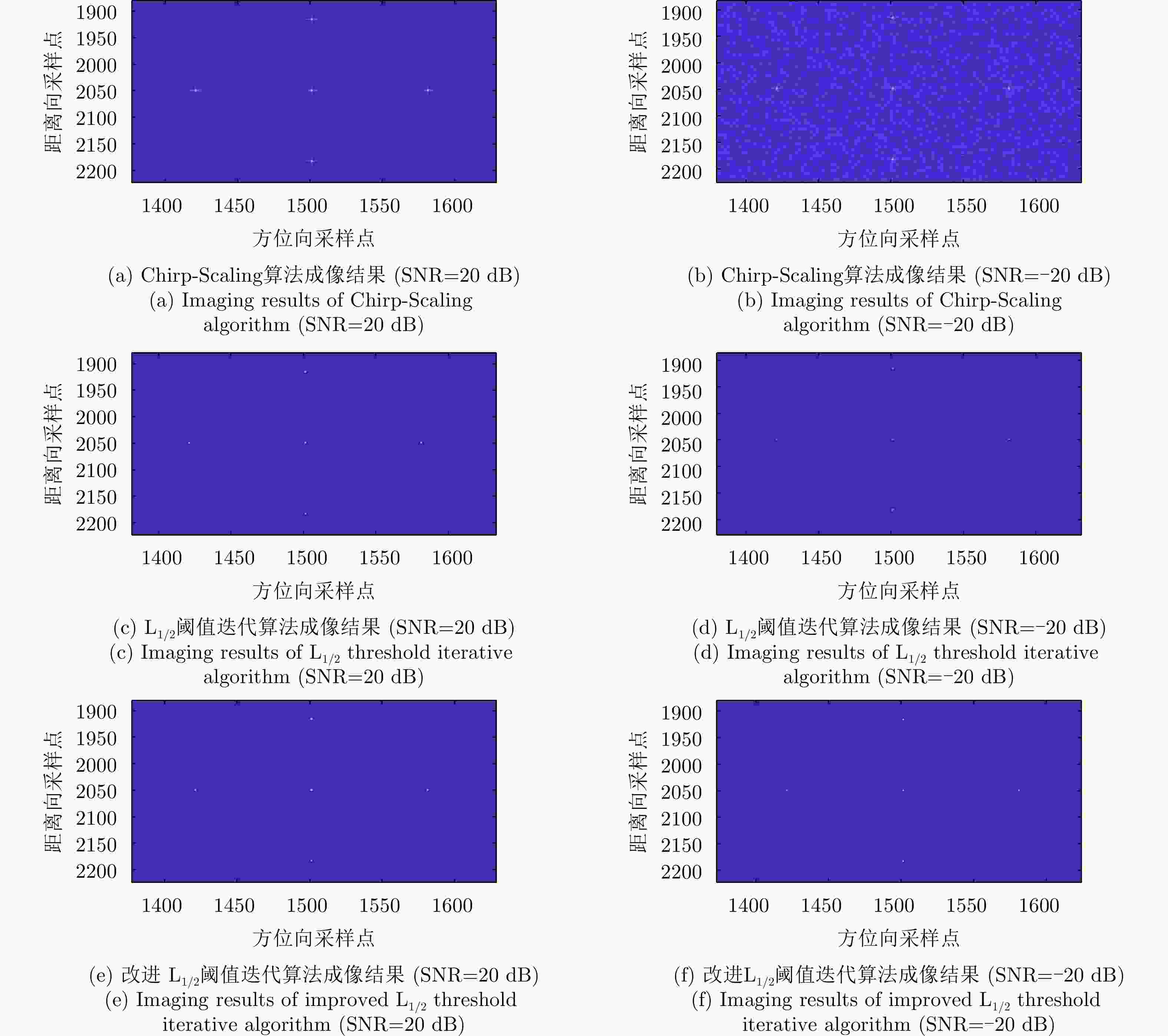
算法 点目标1 点目标2 点目标3 点目标4 点目标5 Chirp-Scaling算法 1.6104 1.6225 1.6235 1.6235 1.6235 L1/2阈值迭代算法 1.1425 1.1143 1.1425 1.1425 1.1425 改进L1/2阈值迭代算法 0.9389 0.9382 0.9623 0.9623 0.9623 表 3 3种算法中方位向数据缺失60%时5个点目标的分辨率(m)
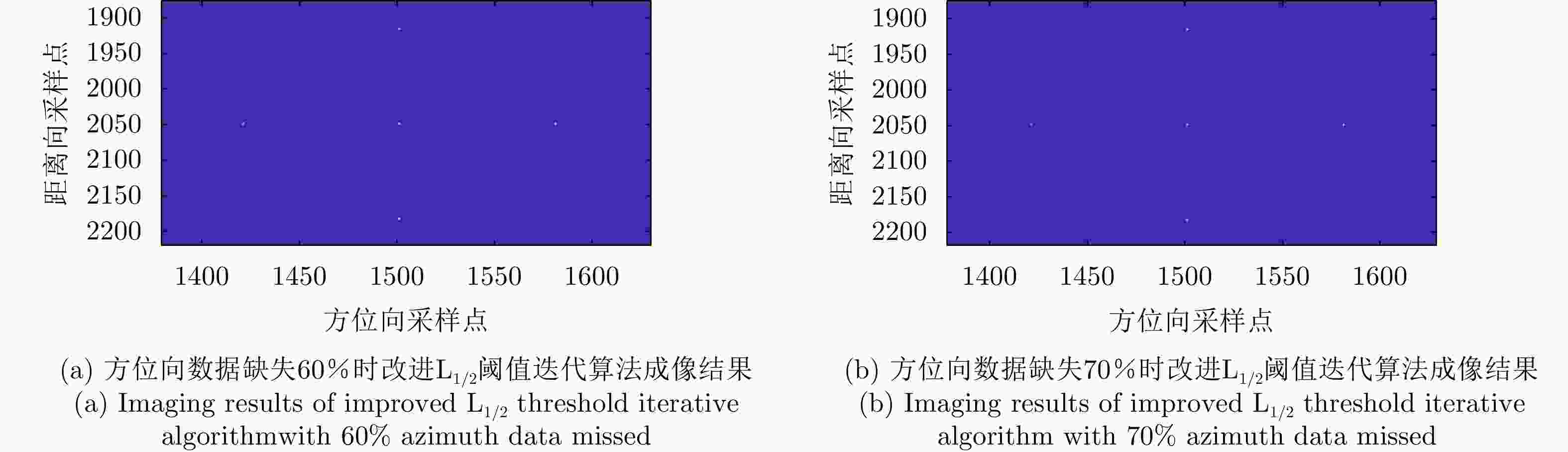
Table 3. The resolution of five targets with 60% azimuth data missed for three algorithms (m)
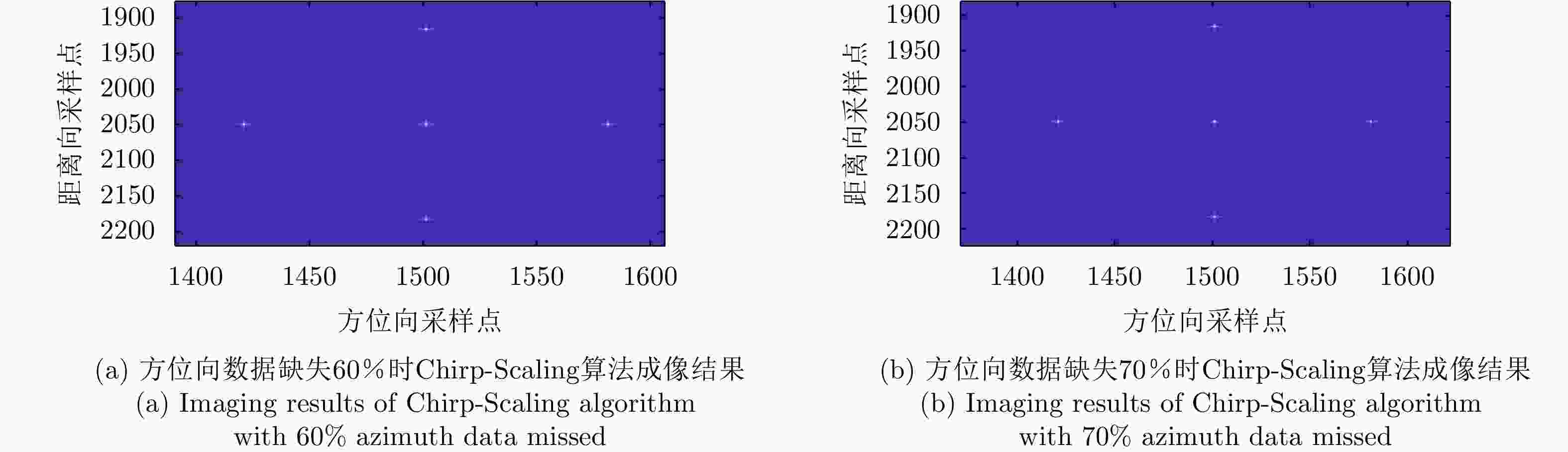
算法 点目标1 点目标2 点目标3 点目标4 点目标5 Chirp-Scaling算法 1.6619 1.6522 1.6484 1.6484 1.6484 L1/2阈值迭代算法 1.1494 1.1005 1.1494 1.1494 1.1494 改进L1/2阈值迭代算法 1.0759 1.0502 1.0599 1.0599 1.0599 表 4 3种算法中方位向数据缺失70%时5个点目标的分辨率(m)
Table 4. The resolution of five targets with 70% azimuth data missed for three algorithms (m)
算法 点目标1 点目标2 点目标3 点目标4 点目标5 Chirp-Scaling算法 1.6719 1.7801 1.7768 1.7768 1.7768 L1/2阈值迭代算法 1.1604 1.2054 1.1604 1.1604 1.1604 改进L1/2阈值迭代算法 1.1049 1.0619 1.0627 1.0627 1.0627 表 5 不同模型的运算量分析
Table 5. Calculation amount analysis of different models
性能分析 匹配滤波 精确观测模型 近似观测模型 空间复杂度 O(MN) O(M2N2) O(MN) 时间复杂度 O(MNlog2MN) O(IM2N2) O(IMNlog2MN) 表 6 不同采样率下两种算法重建点目标耗时时长(s)
Table 6. Time consuming of point target reconstruction by the two algorithms at different sampling rates (s)
算法 采样率100.0% 采样率75.0% 采样率50.0% 采样率25.0% 采样率12.5% L1/2阈值迭代算法 98.560592 74.146809 49.485751 25.464554 13.557194 改进L1/2阈值迭代算法 53.307587 40.525354 26.610069 13.761923 7.354359 表 7 RADARSAT-1卫星SAR成像参数
Table 7. Parameters of RADARSAT-1 satellite SAR imaging
参数 数值 载频(GHz) 5.3 飞行速度(m/s) 7062 脉冲宽度(μs) 41.75 距离向采样率(MHz) 32317 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 125.7 平台离场景中心斜距(km) 988.65 图像分辨率单元数(M×N) 2048×3000 距离向调频率(MHz/μs) 5000 成像场景大小(m) 10000×12000 表 8 3种算法实测数据成像耗时时长
Table 8. Time consuming of measured data imaging by the three algorithms
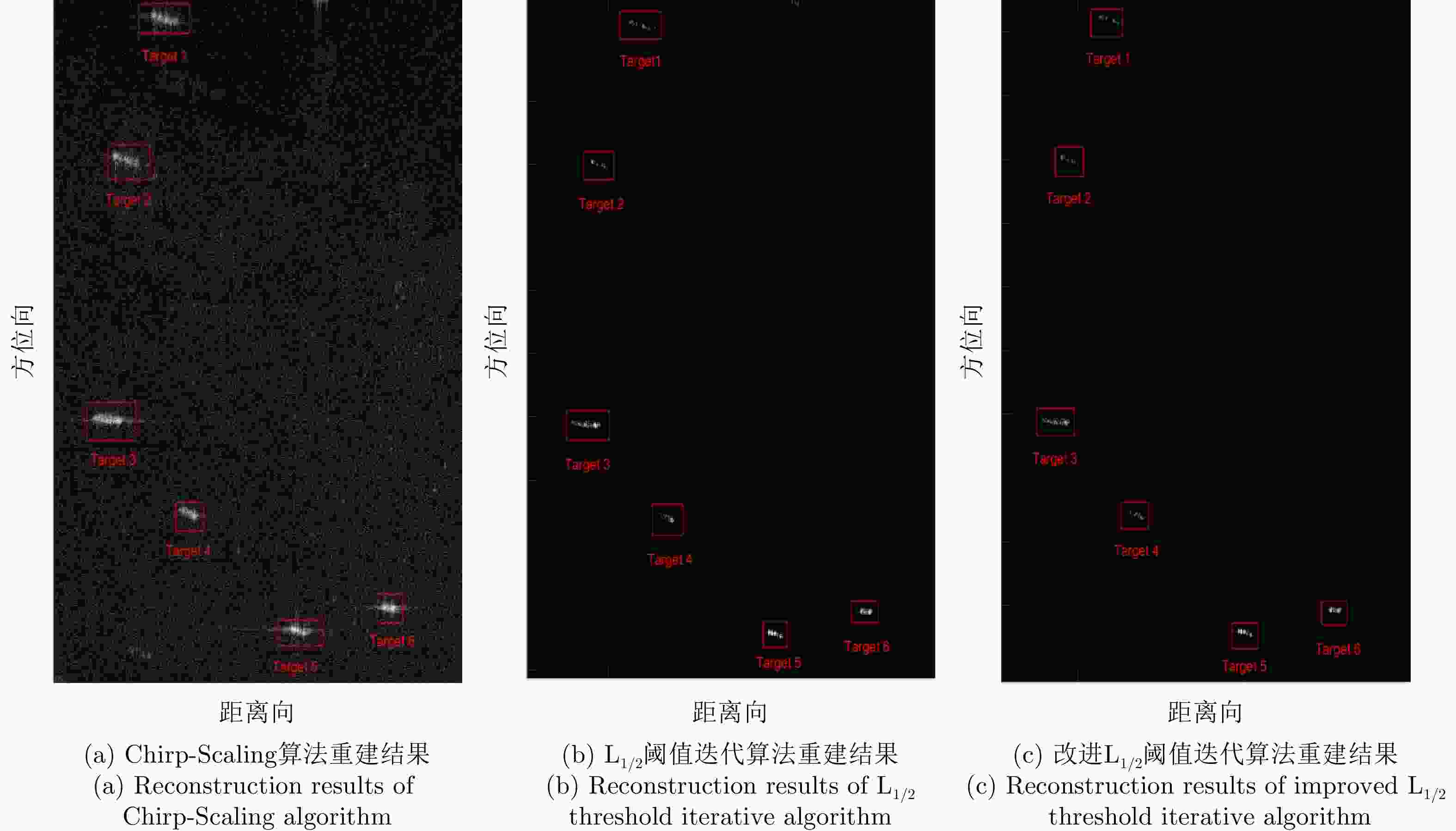
算法 重建耗时时长(s) Chirp-Scaling算法 3.143686 L1/2阈值迭代算法 14.176919 改进L1/2阈值迭代算法 10.074317 -
[1] GLENTIS G, ZHAO Kexin, JAKOBSSON A, et al. Non-parametric high-resolution SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(7): 1614–1624. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2232662 [2] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [3] 李清泉, 王欢. 基于稀疏表示理论的优化算法综述[J]. 测绘地理信息, 2019, 44(4): 1–9. doi: 10.14188/j.2095-6045.2019015LI Qingquan and WANG Huan. Sparse representation based optimization: A survey[J]. Journal of Geomatics, 2019, 44(4): 1–9. doi: 10.14188/j.2095-6045.2019015 [4] NI Jiacheng, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. Compressed sensing SAR imaging based on centralized sparse representation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(12): 4920–4932. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2831921 [5] JUNG D H, KIM H S, KIM C K, et al. Sparse scene recovery for high-resolution automobile FMCW SAR via scaled compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 10136–10146. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2931626 [6] 王天云, 刘冰, 魏强, 等. 压缩感知成像雷达研究进展[J]. 电光与控制, 2019, 26(7): 1–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2019.07.001WANG Tianyun, LIU Bing, WEI Qiang, et al. A review on research progresses of compressed sensing imaging radar[J]. Electronics Optics &Control, 2019, 26(7): 1–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2019.07.001 [7] JIANG Hai, JIANG Chenglong, ZHANG Bingchen, et al. Experimental results of spaceborne stripmap SAR raw data imaging via compressed sensing[C]. 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 202–205. [8] ALONSO M T, LOPEZ-DEKKER M, and MALLORQUI J J. A novel strategy for radar imaging based on compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4285–4295. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2051231 [9] ZENG Jinshan, FANG Jian, and XU Zongben. Sparse SAR imaging based on L1/2 regularization[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2012, 55(8): 1755–1775. doi: 10.1007/s11432-012-4632-5 [10] 史洪印, 贾宝京, 齐兆龙. 基于压缩感知的非均匀脉冲SAR欺骗性干扰抑制方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2016, 37(3): 525–532. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2016.03.007SHI Hongyin, JIA Baojing, and QI Zhaolong. Novel non-uniform pulse SAR deception jamming suppressing method based on compressive sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2016, 37(3): 525–532. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2016.03.007 [11] 段化军, 朱岱寅, 李勇, 等. 基于压缩感知的条带SAR缺失数据恢复成像方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2016, 38(5): 1025–1031. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2016.05.09DUAN Huajun, ZHU Daiyin, LI Yong, et al. Recovery and imaging method for missing data of the strip-map SAR based on compressive sensing[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(5): 1025–1031. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2016.05.09 [12] 李博, 刘发林, 周崇彬, 等. 基于近似观测的加权L1压缩感知SAR成像[J]. 微波学报, 2018, 34(6): 62–67. doi: 10.14183/j.cnki.1005-6122.201806014LI Bo, LIU Falin, ZHOU Chongbin, et al. Approximated observation-based weighted L1 compressed sensing SAR imaging[J]. Journal of Microwaves, 2018, 34(6): 62–67. doi: 10.14183/j.cnki.1005-6122.201806014 [13] 徐宗本, 吴一戎, 张冰尘, 等. 基于L1/2正则化理论的稀疏雷达成像[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(14): 1306–1319. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00372XU Zongben, WU Yirong, ZHANG Bingchen, et al. Sparse radar imaging based on L1/2 regularization theory[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(14): 1306–1319. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00372 [14] 杨卫星, 朱岱寅. 稀疏场景下SAR方位向随机丢失数据的迭代成像算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(7): 1748–1755. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.07.03YANG Weixing and ZHU Daiyin. Iterative imaging algorithm for SAR azimuth random missing data with sparse scenes[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(7): 1748–1755. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.07.03 [15] ZHANG Jian and GHANEM B. ISTA-net: Interpretable optimization-inspired deep network for image compressive sensing[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1828–1837. [16] 赵克祥, 毕辉, 张冰尘. 基于快速阈值迭代的SAR层析成像处理方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(5): 1019–1023. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.05.11ZHAO Kexiang, BI Hui, and ZHANG Bingchen. SAR tomography method based on fast threshold iteration iterative shrinkage-thresholding[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(5): 1019–1023. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.05.11 [17] BI Hui and BI Guoan. Performance analysis of iterative soft thresholding algorithm for L1 regularization based sparse SAR imaging[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, USA, 2019: 1–6. [18] XU Zhongming, WANG Qinghua, HE Yansong, et al. A monotonic two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding algorithm for sound source identification based on equivalent source method[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2018, 129: 386–396. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2017.07.012 [19] NESTEROV Y E. A method for solving the convex programming problem with convergence rate O (1/k2)[J]. Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, 1983, 269(3): 543–547. [20] BECK A and TEBOULLE M. A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(1): 183–202. doi: 10.1137/080716542 [21] 张倩, 李海洋. 一种改进的迭代软阈值算法及其应用[J]. 纺织高校基础科学学报, 2018, 31(2): 253–260. doi: 10.13338/j.issn.1006-8341.2018.02.020ZHANG Qian and LI Haiyang. An improved iterative soft thresholding algorithm and application[J]. Basic Sciences Journal of Textile Universities, 2018, 31(2): 253–260. doi: 10.13338/j.issn.1006-8341.2018.02.020 [22] XU Zongben. Data modeling: Visual psychology approach and L1/2 regularization theory[C]. International Congress of Mathematicians 2010 (ICM 2010), Hyderabad, India, 2010: 3151–3184. [23] XU Zongben, GUO Hailiang, WANG Yao, et al. Representative of L1/2 regularization among Lq ( 0<q≤ 1) regularizations: An experimental study based on phase diagram[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(7): 1225–1228. doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(11)60293-0 [24] XU Zongben, CHANG Xiangyu, XU Fengmin, et al. L1/2 regularization: A thresholding representation theory and a fast solver[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(7): 1013–1027. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2197412 [25] ZENG Jinshan, LIN Shaobo, WANG Yao, et al. L1/2 regularization: Convergence of iterative half thresholding algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(9): 2317–2329. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2309076 [26] BI Hui, ZHU Daiyin, BI Guoan, et al. FMCW SAR sparse imaging based on approximated observation: An overview on current technologies[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 4825–4835. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3017487 [27] FANG Jian, XU Zongben, ZHANG Bingchen, et al. Fast compressed sensing SAR imaging based on approximated observation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(1): 352–363. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2263309 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: