-
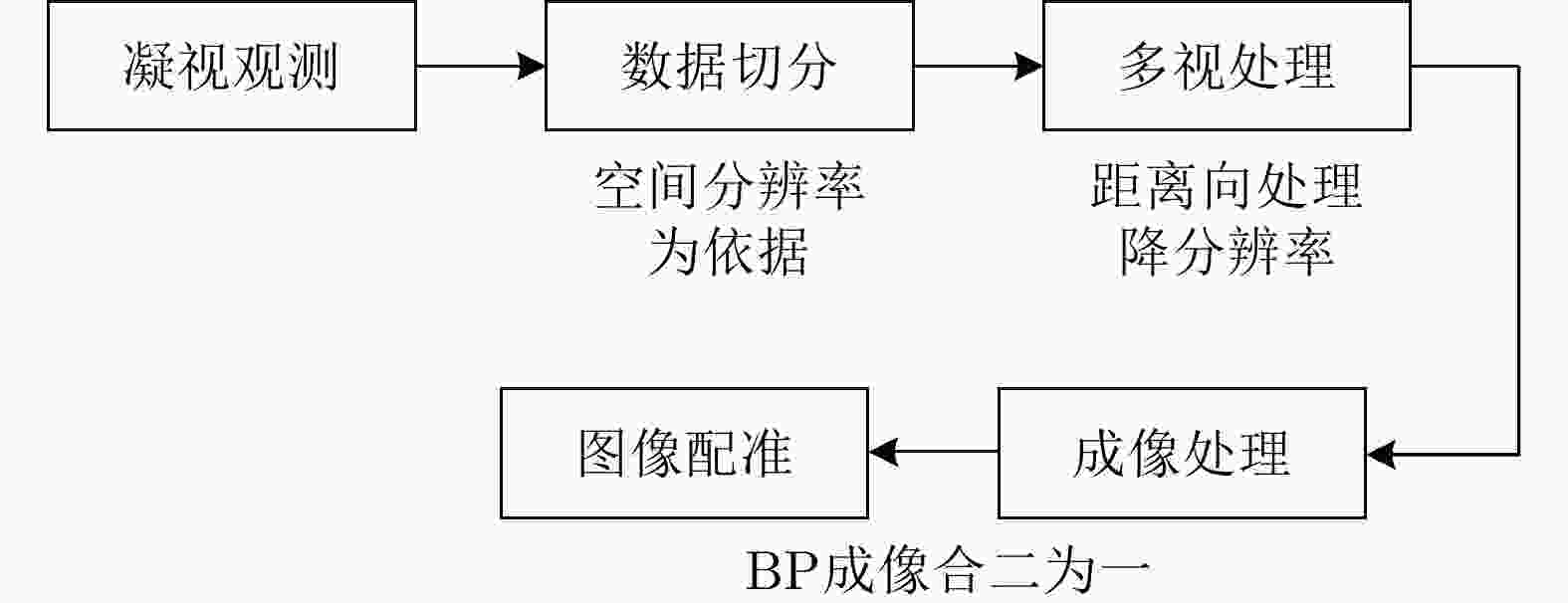
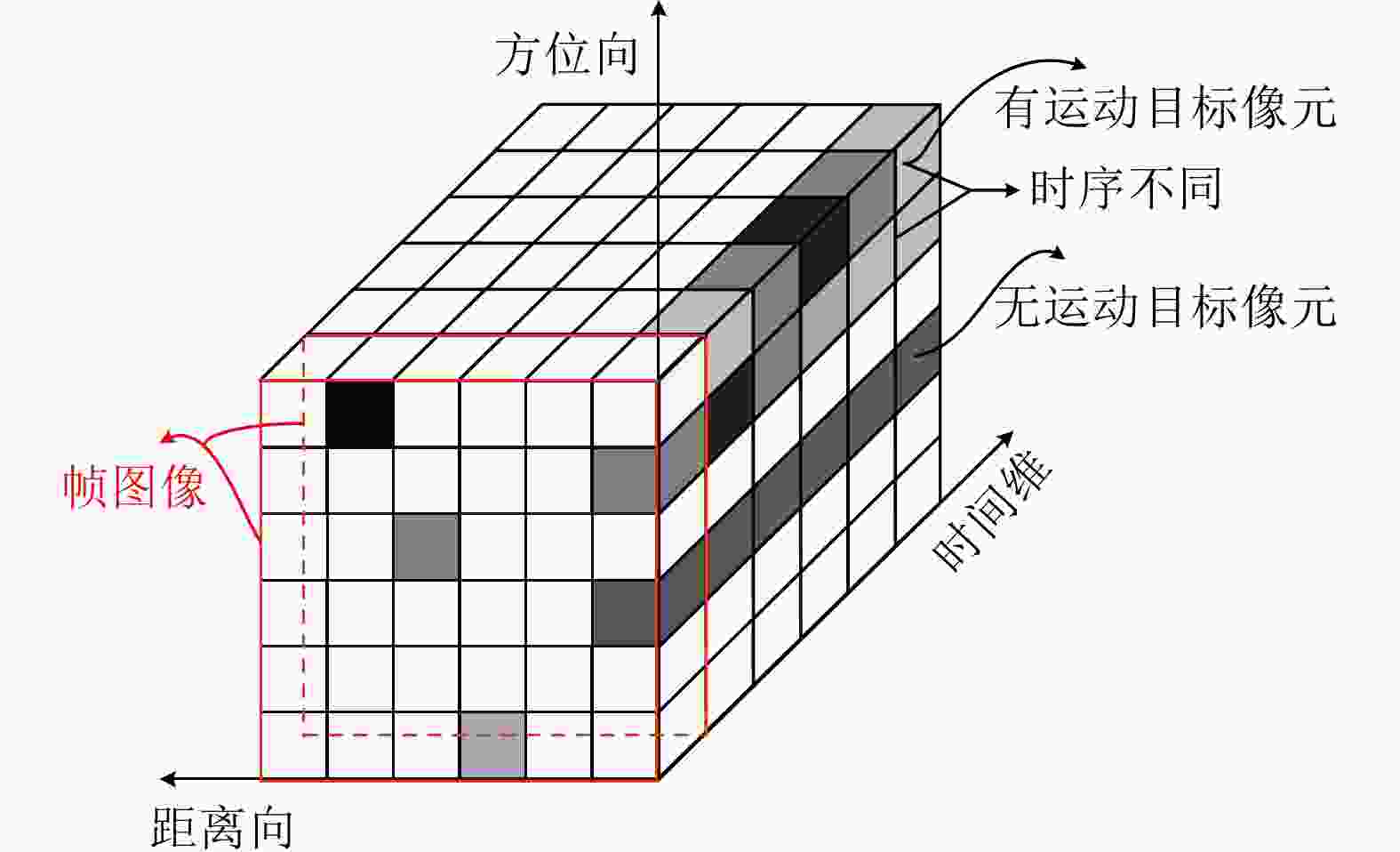
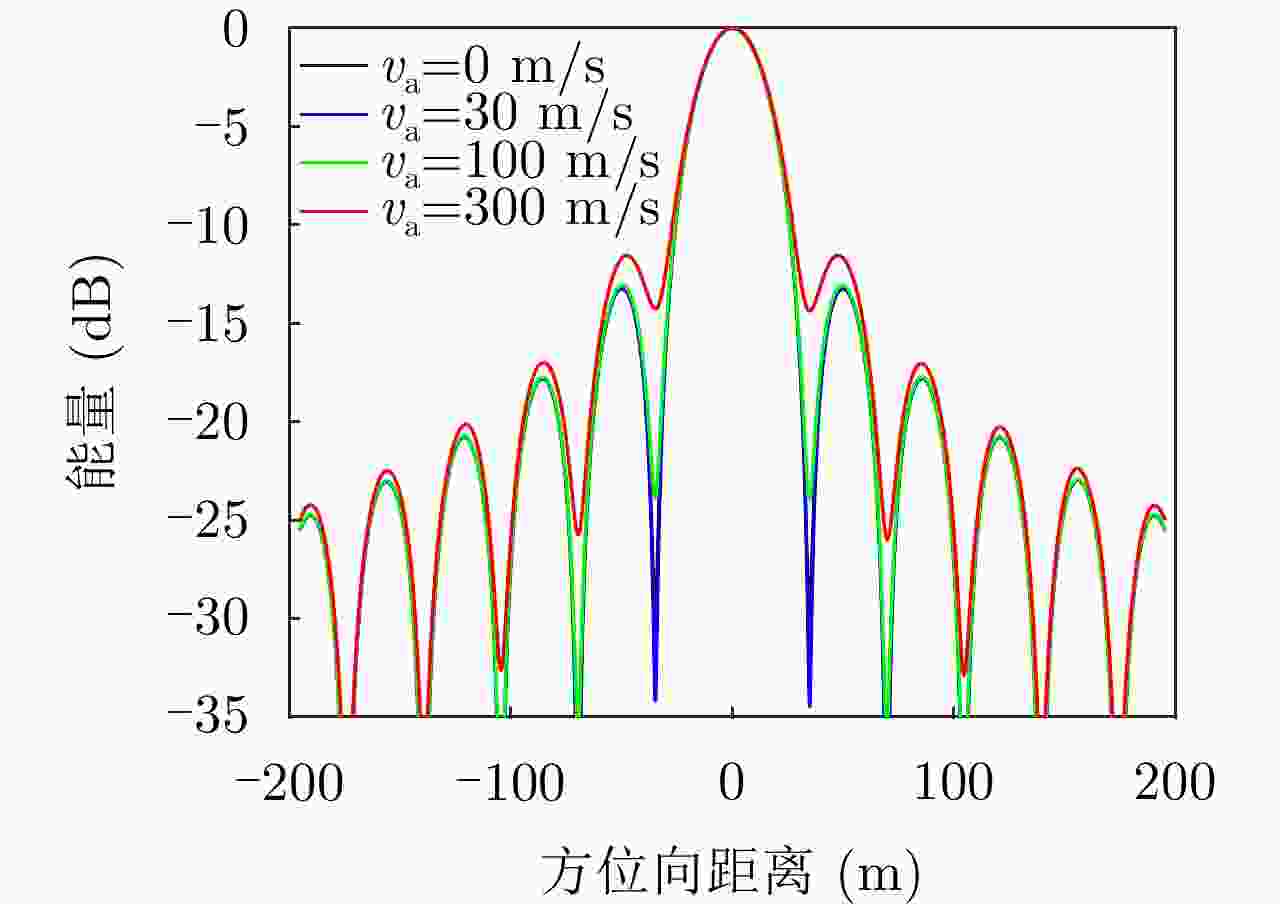
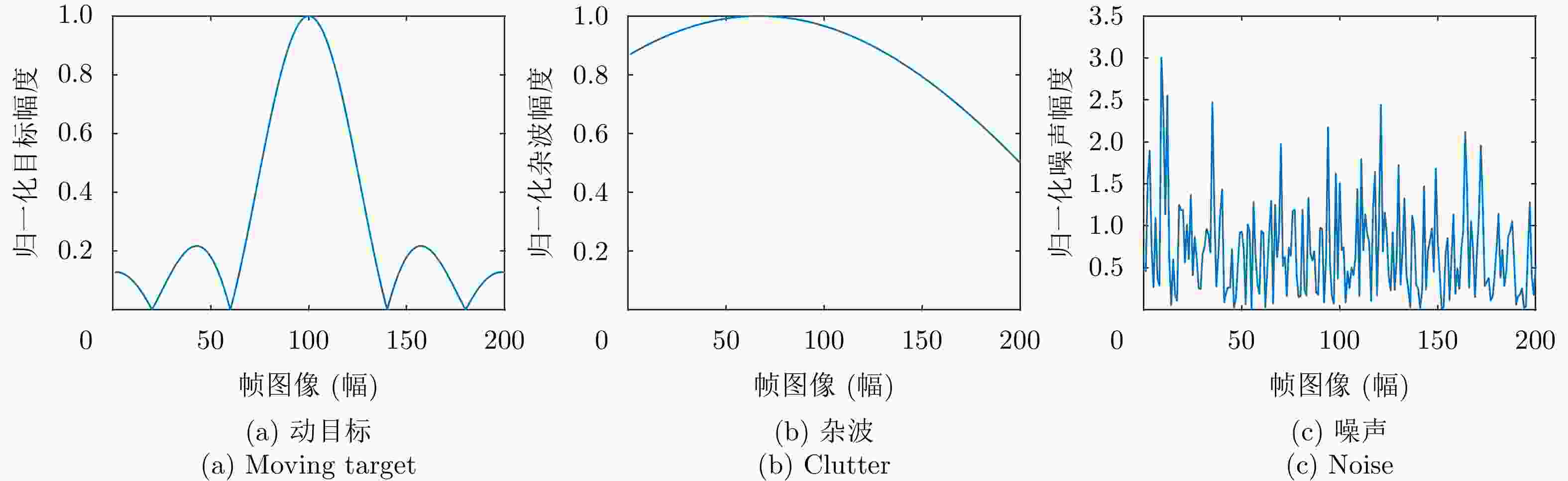
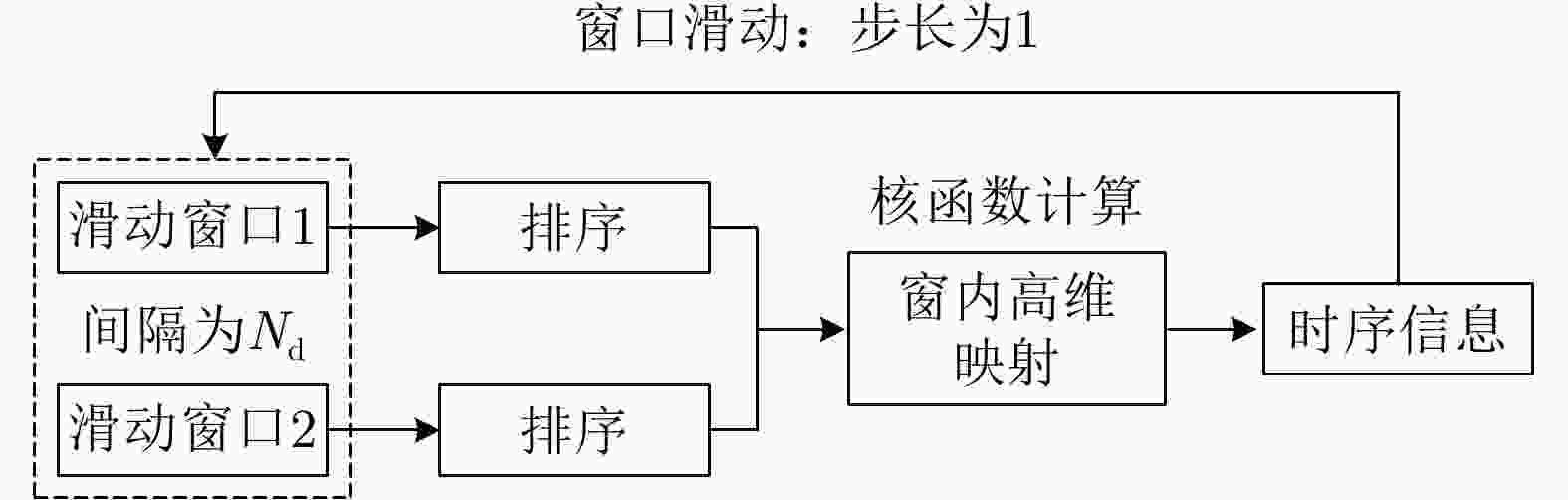
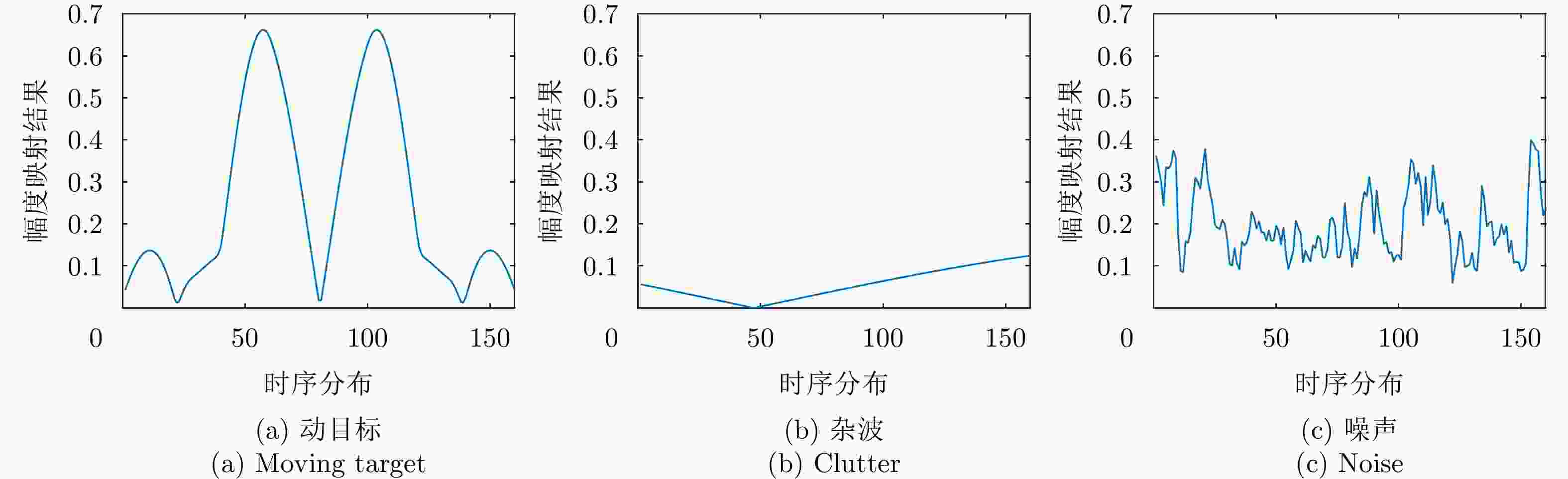
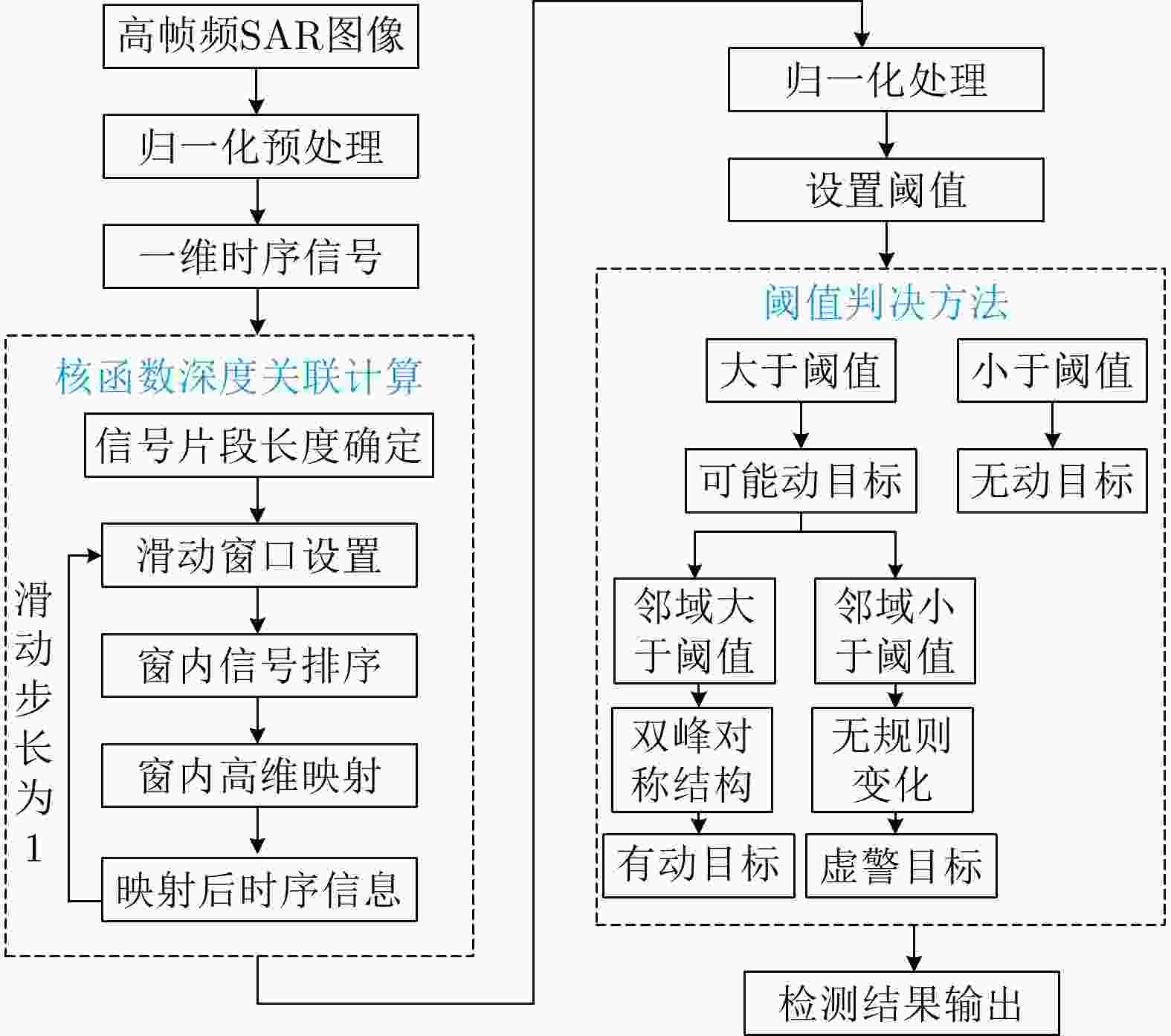
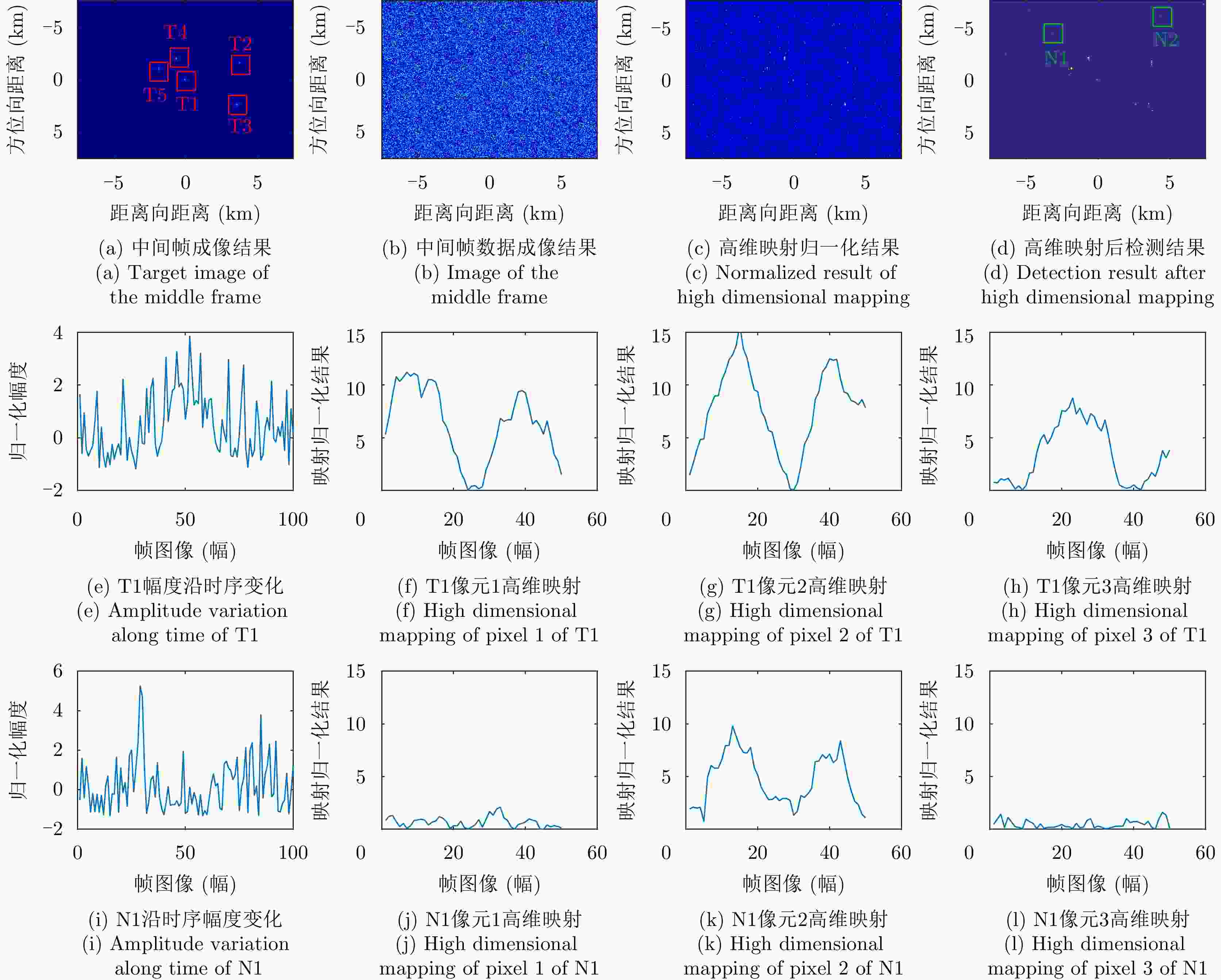
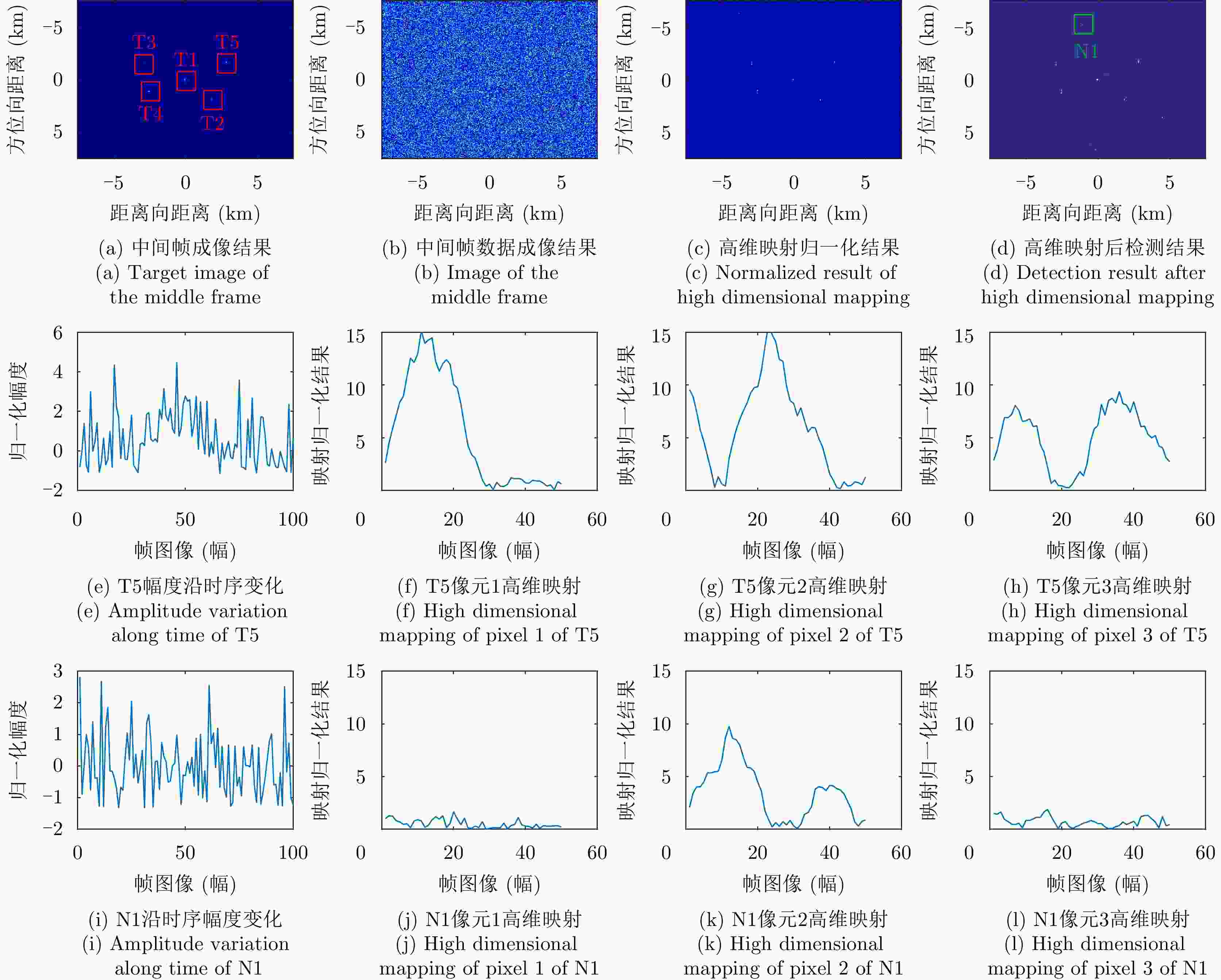
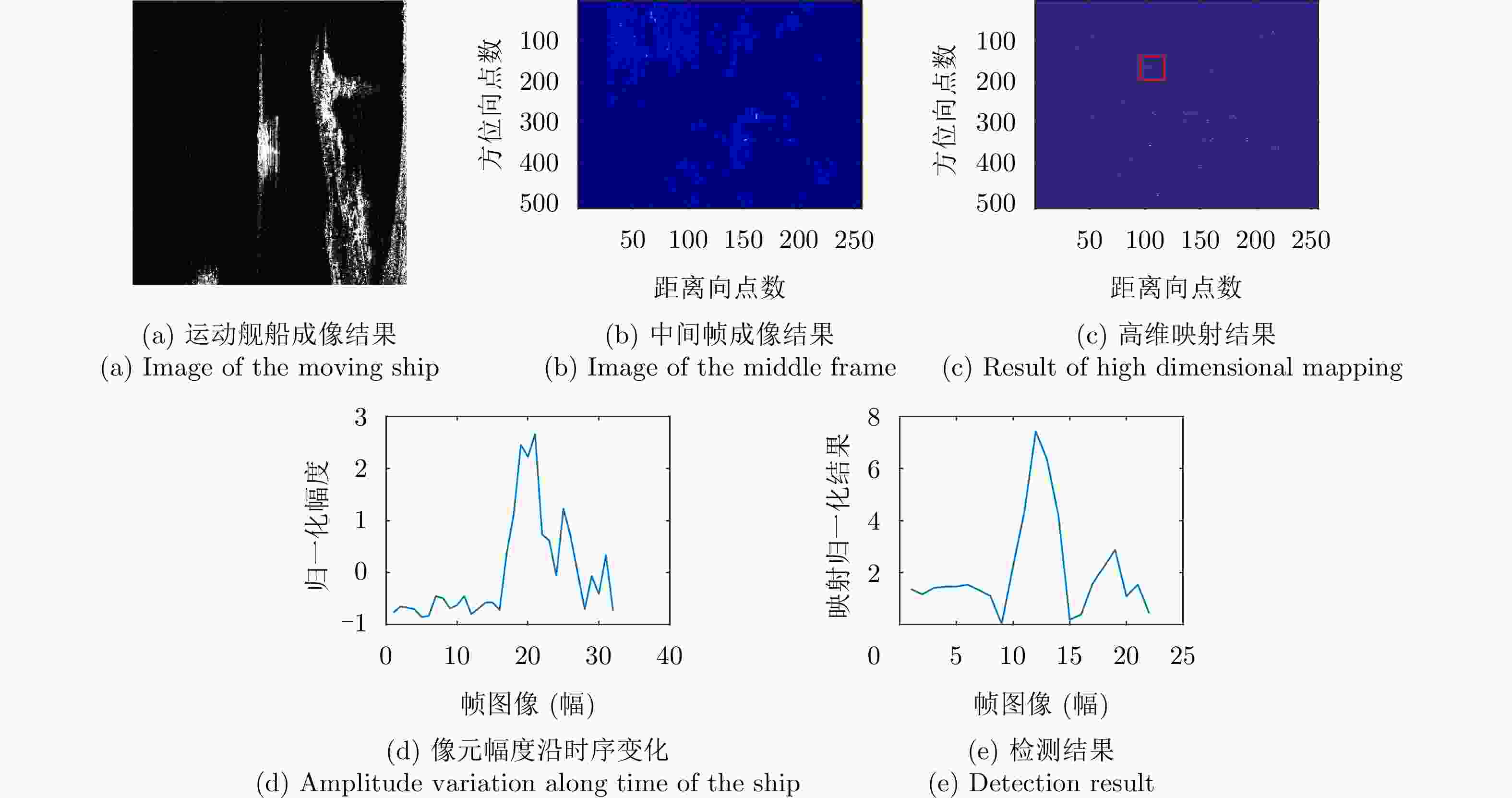
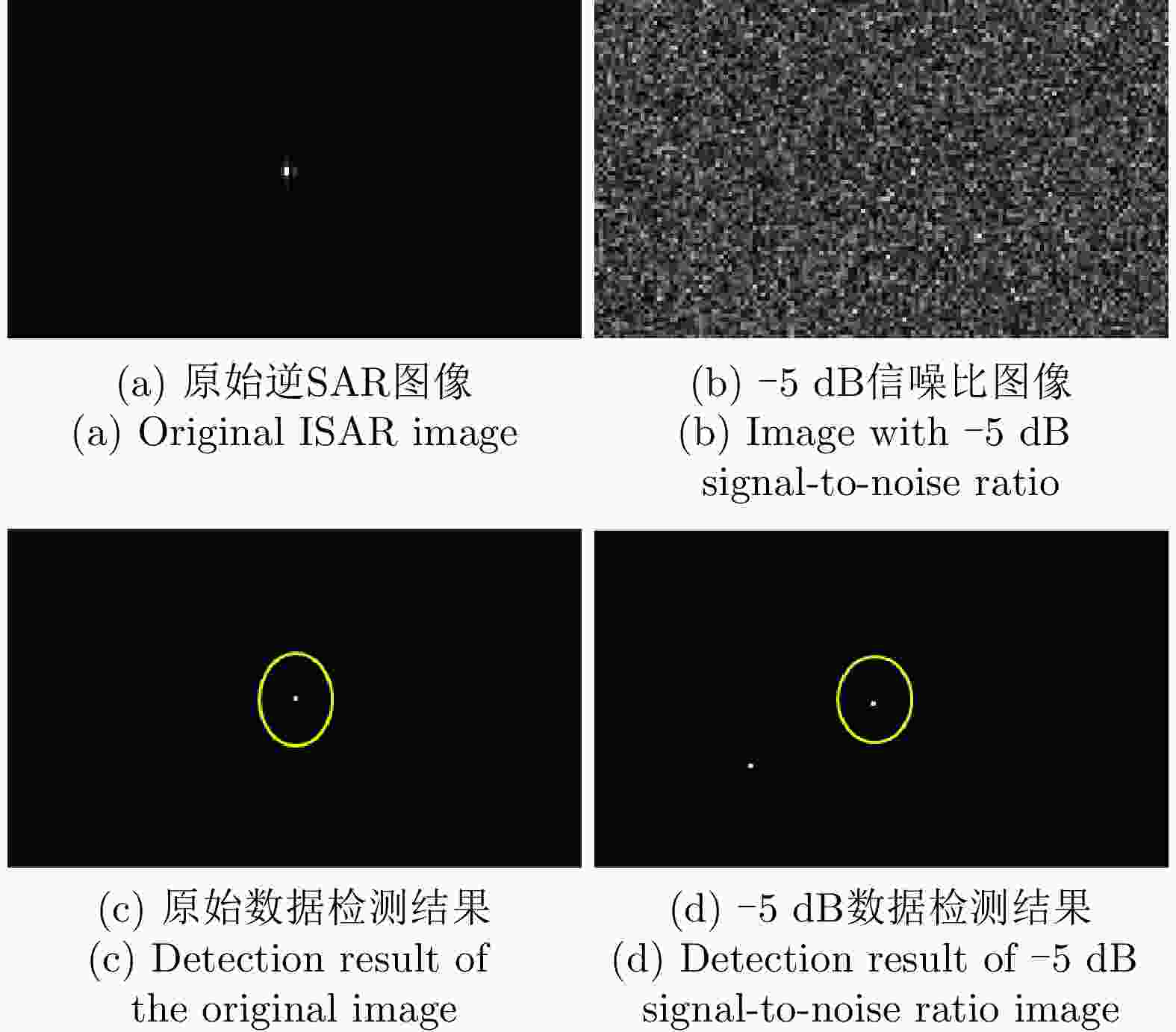
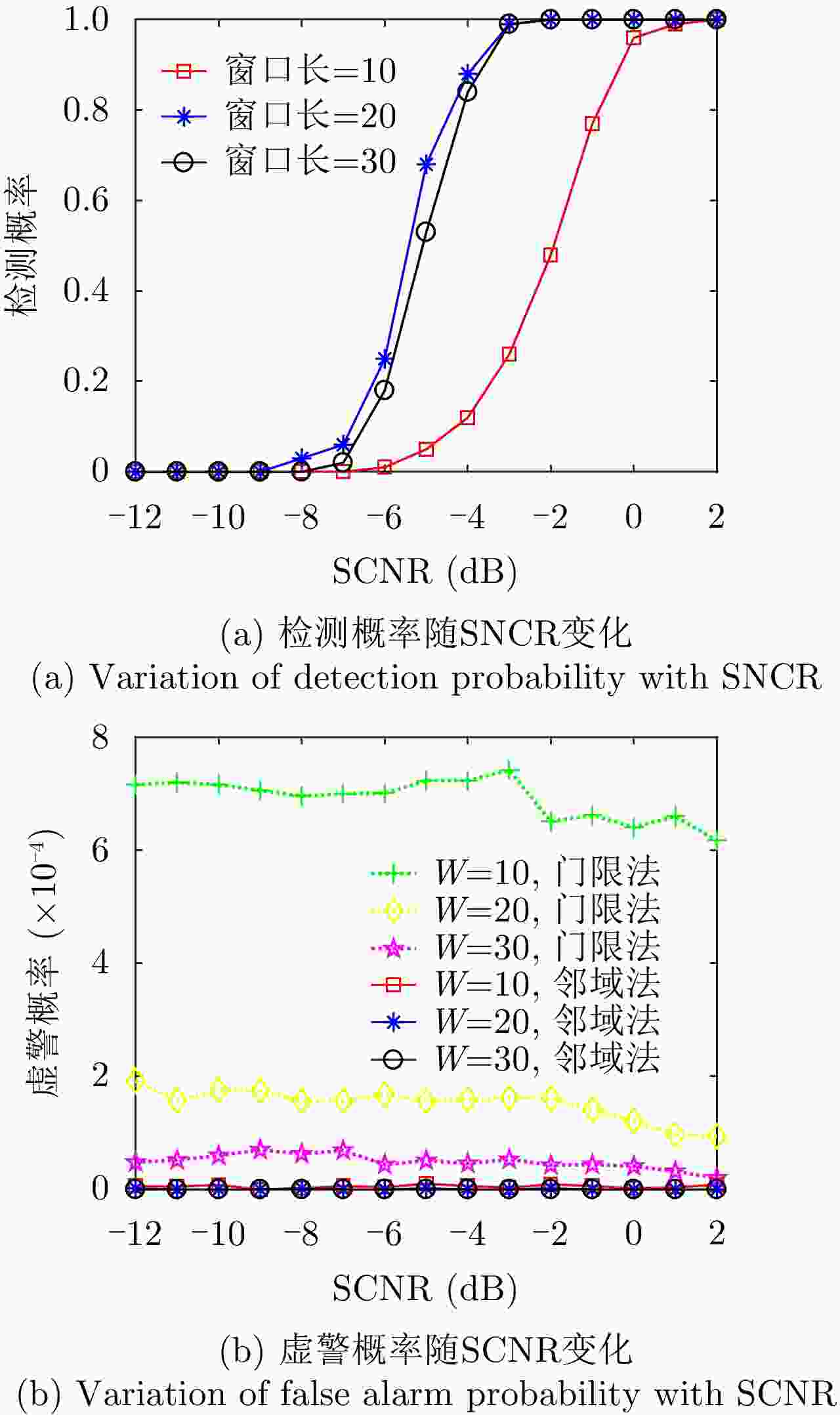
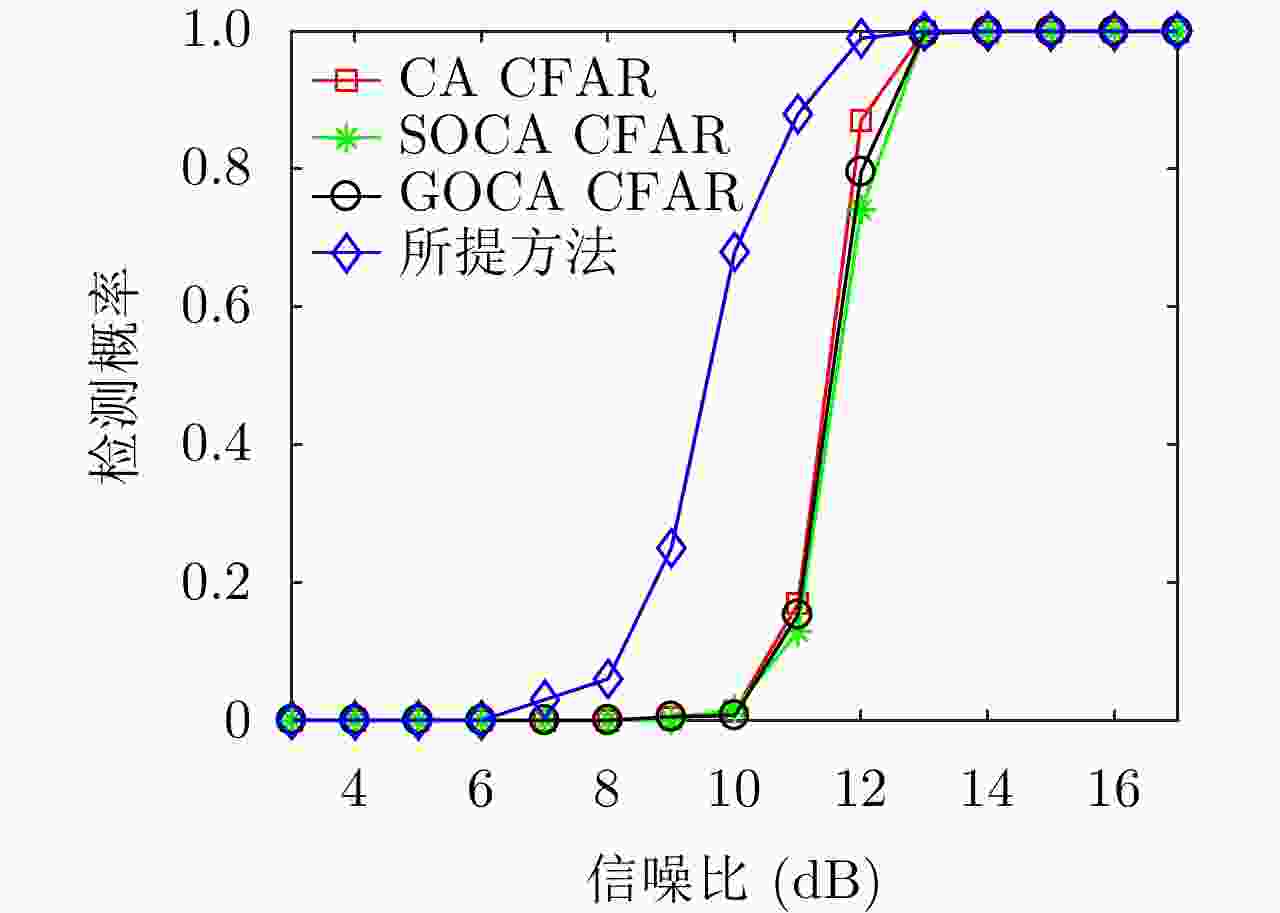
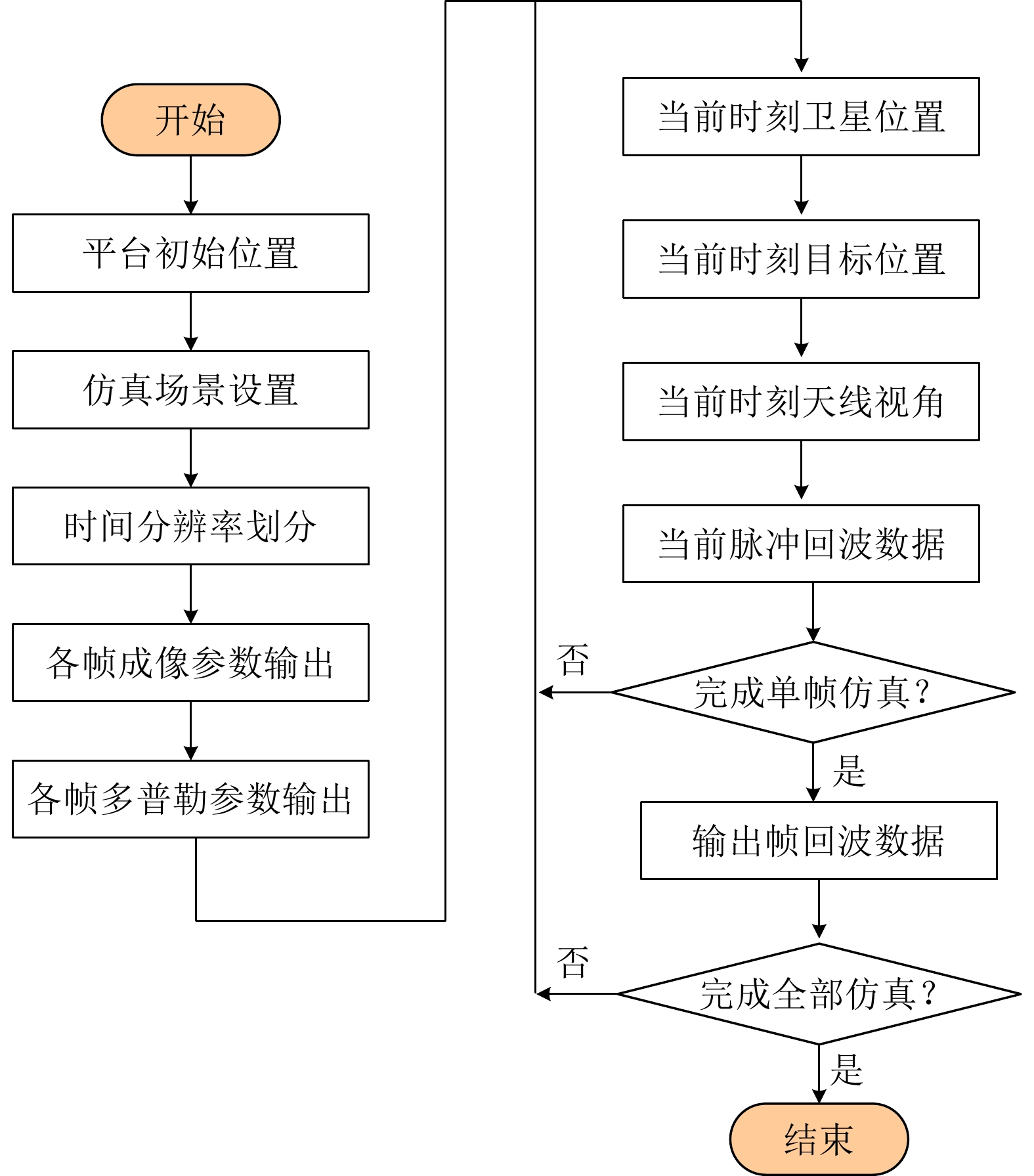
摘要: 该文针对低信杂噪比条件下运动目标检测难的现状,提出了高时相星载序贯合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像运动目标检测方法。首先,根据检测机理的不同将现有星载SAR运动目标检测方法分为3类,并进行了对比分析;其次,基于凝视观测模式建模分析了高帧频序贯SAR图像获取方式;在此基础上,将动目标检测等效为未知尺度、未知到达时间的一维瞬态微弱扰动信号检测,并理论分析了沿时间维高帧频序贯SAR图像间动目标幅度扰动的sinc函数形式,背景杂波幅度的缓变和系统噪声幅度的无规则快变状态;再次,为实现目标和杂波、噪声的可分性,基于核函数机理实现了动目标在高维空间的深度关联;最后,通过仿真和真实数据验证了所提方法的有效性,并分析了检测性能。性能分析结果表明在低信杂噪比条件下所提方法检测性能优于传统的恒虚警类方法。Abstract: To alleviate the difficulty in monitoring a moving target under a low signal-to-clutter-noise ratio, this paper proposes a moving target monitoring method with high frame-rate spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images. First, based on the detection mechanism, current spaceborne SAR moving target detection methods are divided into three categories, and a comparative analysis is performed. Second, the acquisition method of a high-frame-rate SAR image sequence is analyzed based on the staring observation mode. Then, the moving target detection is equated to one-dimensional transient weakly perturbed signal detection with unknown scale and arrival time. Next, the sinc-function form of moving target perturbation between high-frame-frequency SAR images, slowly changing background clutter, and irregular fast-changing state of system noise are analyzed theoretically. To separate the target, clutter, and noise, the deep correlation of the moving target in high-dimensional space is realized based on the kernel function mechanism. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by simulation experiments and real SAR data, and under a low signal-to-clutter-noise ratio, the detection performance of the proposed method is better than the traditional method of constant false alarm rate.
-
表 1 雷达系统仿真参数
Table 1. The simulation parameters of radar system
参数 数值 中心视角(°) 35.0 轨道高度(km) 1000.0 波长(m) 0.03125 天线长度(m) 4.0 天线高度(m) 1.8 轨道倾角(°) 97.44 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 4200 系统带宽(MHz) 420 采样率(MHz) 500 -
[1] FREEMAN A and CURRIE A. Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images of moving targets[J]. GEC Journal of Research, 1987, 5(2): 106–115. [2] BARBAROSSA S and FARINA A. A novel procedure for detecting and focusing moving objects with SAR based on the Wigner-Ville distribution[C]. IEEE International Conference on Radar, Arlington, USA, 1990: 44–50. [3] MOREIRA J R and KEYDEL W. A new MTI-SAR approach using the reflectivity displacement method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1995, 33(5): 1238–1244. doi: 10.1109/36.469488 [4] FIENUP J R. Detecting moving targets in SAR imagery by focusing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2001, 37(3): 794–809. doi: 10.1109/7.953237 [5] WEIHING D, HINZ S, MEYER F, et al. Detection of along-track ground moving targets in high resolution spaceborn SAR images[J]. International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing an Spetial Information Sciences, 2006, 36(7): 7. [6] ARII M. Efficient motion compensation of SAR imagery by refocusing approach[C]. Conference Proceedings of 2013 Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Tsukuba, Japan, 2013: 150–151. [7] ARII M. Efficient motion compensation of a moving object on SAR imagery based on velocity correlation function[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 936–946. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2245901 [8] 郑明洁, 杨汝良. 一种改进的DPCA运动目标检测方法[J]. 电子学报, 2004, 32(9): 1429–1432. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2004.09.005ZHENG Mingjie and YANG Ruliang. An improved DPCA moving targets detecting algorithm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2004, 32(9): 1429–1432. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2004.09.005 [9] CHEN Yi, QIAN Bo, and WANG Shengli. DPCA motion compensation technique based on multiple phase centers[C]. 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 711–714. [10] BUDILLON A, EVANGELISTA A, and SCHIRINZI G. GLRT detection of moving targets via multibaseline along-track interferometric SAR systems[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(3): 348–352. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2168381 [11] LEE J S, HOPPEL K W, MANGO S A, et al. Intensity and phase statistics of multilook polarimetric and interferometric SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(5): 1017–1028. doi: 10.1109/36.312890 [12] BRENNAN L E and REED L S. Theory of adaptive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1973, AES-9(2): 237–252. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1973.309792 [13] HONIG M L and GOLDSTEIN J S. Adaptive reduced-rank interference suppression based on the multistage wiener filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2002, 50(6): 986–994. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2002.1010618 [14] CRISTALLINI D and BURGER W. A robust direct data domain approach for STAP[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(3): 1283–1294. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2176335 [15] CERUTTI-MAORI D and SIKANETA I. A generalization of DPCA processing for multichannel SAR/GMTI radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 560–572. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2201260 [16] GIERULL C H, SIKANETA I, and CERUTTI-MAORI D. Two-step detector for RADARSAT-2’s experimental GMTI mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 436–454. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2201729 [17] CERUTTI-MAORI D, SIKANETA I, and GIERULL C H. Optimum SAR/GMTI processing and its application to the radar satellite RADARSAT-2 for traffic monitoring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(10): 3868–3881. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2186637 [18] KIRSCHT M. Detection and velocity estimation of moving objects in a sequence of single-look SAR images[C]. 1996 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Lincoln, USA, 1996: 333–335. [19] MITTERMAYER J, WOLLSTADT S, PRATS-IRAOLA P, et al. Bidirectional SAR imaging mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 601–614. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2202669 [20] YANG Wei, CHEN Jie, LIU Wei, et al. Moving target azimuth velocity estimation for the MASA mode based on sequential SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(6): 2780–2790. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2641744 [21] 申文杰, 韩冰, 林赟, 等. 多角度SAR动目标检测技术及其高分三号实验验证研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 304–320. doi: 10.12000/JR20021SHEN Wenjie, HAN Bing, LIN Yun, et al. Multi-aspect SAR-GMTI and experimental research on gaofen-3 SAR modes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 304–320. doi: 10.12000/JR20021 [22] 陈杰, 杨威, 王鹏波, 等. 多方位角观测星载SAR技术研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 205–220. doi: 10.12000/JR20015CHEN Jie, YANG Wei, WANG Pengbo, et al. Review of novel azimuthal multi-angle observation spaceborne SAR technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 205–220. doi: 10.12000/JR20015 [23] 李春升, 杨威, 王鹏波. 星载SAR成像处理算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 111–122. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20071LI Chunsheng, YANG Wei, and WANG Pengbo. A review of spaceborne SAR algorithm for image formation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 111–122. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20071 [24] MILLER J, BISHOP E, and DOERRY A. An application of backprojection for video SAR image formation exploiting a subaperature circular shift register[C]. Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XX, Baltimore, USA, 2013: 874609. [25] YANG Wei, CHEN Jie, LIU Wei, et al. A modified three-step algorithm for TOPS and sliding spotlight SAR data processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 6910–6921. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2735993 [26] WANG Yamin, CHEN Jie, LIU Wei, et al. A moving target velocity estimation method based on the MC-MASA SAR mode[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(9): 1632. doi: 10.3390/rs13091632 [27] 王亚敏, 陈杰, 杨威, 等. 基于Hybrid-TOPS的星载SAR运动目标监视新模式[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(6): 1256–1262. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0420WANG Yamin, CHEN Jie, YANG Wei, et al. New moving target monitoring mode with Hybrid-TOPS of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronsutics, 2016, 42(6): 1256–1262. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0420 [28] 赵嘉斐, 吴敬沄. 时空相关海杂波序列的仿真设计[J]. 电子设计工程, 2018, 26(15): 54–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2018.15.013ZHAO Jiafei and WU Jingyun. Simulation of correlated radar sea clutter[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2018, 26(15): 54–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2018.15.013 [29] 汪廷华, 陈峻婷. 核函数的选择研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2012, 33(3): 1181–1186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7024.2012.03.068WANG Tinghua and CHEN Junting. Survey of research on kernel selection[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2012, 33(3): 1181–1186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7024.2012.03.068 [30] SHAWE-TAYLOR J and CRISTIANINI N. Kernel Methods for Pattern Analysis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004: 60–70. [31] 肖建, 于龙, 白裔峰. 支持向量回归中核函数和超参数选择方法综述[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2008, 43(3): 297–303. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2008.03.001XIAO Jian, YU Long, and BAI Yifeng. Survey of the selection of kernels and hyper-parameters in support vector regression[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2008, 43(3): 297–303. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2008.03.001 [32] CAMPBELL C. An Introduction to Kernel Methods[M]. HOWLETT R J, JAIN L C, and KACPRZYK J. Radial Basis Function Networks 1: Recent Developments in Theory and Applications. Wien: Physica Verlag Rudolf Liebing KG, 2001: 155–192. [33] LANCKRIET G R G, DE BIE T, CRISTIANINI N, et al. A statistical framework for genomic data fusion[J]. Bioinformatics, 2004, 20(16): 2626–2635. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth294 [34] RAKOTOMAMONJY A, BACH F R, CANU S, et al. SimpleMKL[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9: 2491–2521. [35] GEBERT N, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Digital beamforming on receive: Techniques and optimization strategies for high-resolution wide-swath SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(2): 564–592. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5089542 [36] ROHLING H. Radar CFAR thresholding in clutter and multiple target situations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1983, AES-19(4): 608–621. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1983.309350 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: