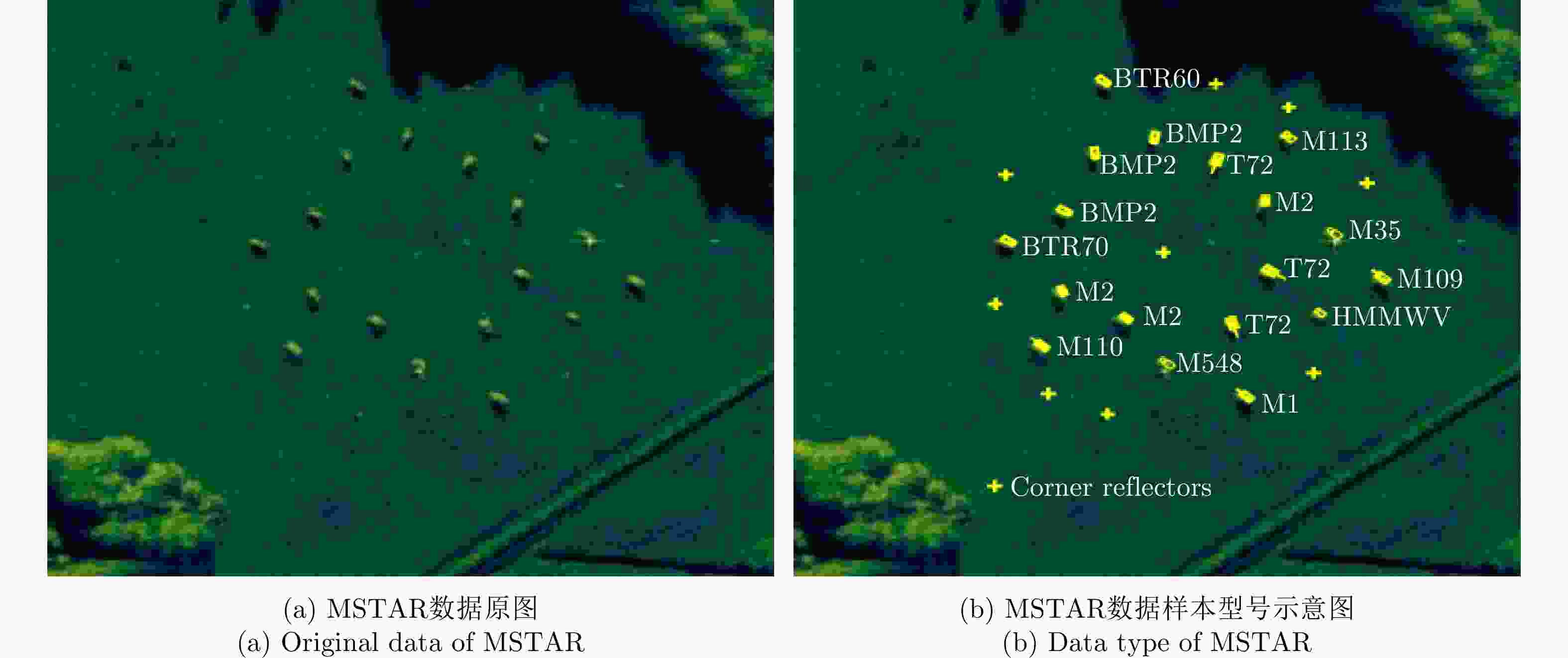
-
摘要:
自动目标识别(ATR)是一个和信号与信息处理、模式识别、人工智能等学科密切相关的特殊工程技术应用领域。由于ATR系统识别对象固有的不确定性,识别环境的复杂性,以及日益加剧的识别对抗性,使得ATR的发展一直面临着从理论到技术、到应用的系统性挑战。该文从工程视角出发,阐述了ATR的定义与内涵,简要回顾与分析了该领域发展动态,梳理了ATR的核心技术体系与系统开发模式,最后对未来的发展挑战做了分析。
Abstract:Automatic Target Recognition (ATR) is a special engineering application field which is closely related to signal and information processing, pattern recognition, artificial intelligence and other disciplines. Owing to the inherent uncertainty of ATR systems, the complexity of the recognition environment, and the increasingly adversarial nature of recognition, the development of ATR faces systematic challenges from theory to technology and applications. This paper presents the definition and connotation of ATR from an engineering perspective, briefly reviews and analyzes the developments in this field, explores the core technology system and system development model of ATR, and finally examines the future development challenges.
-
-
[1] TAIT P. Introduction to Radar Target Recognition[M]. London: IET Digital Library, 2005: 3–14. [2] RATCHES J A. Review of current aided/automatic target acquisition technology for military target acquisition tasks[J]. Optical Engineering, 2011, 50(7): 072001. doi: 10.1117/1.3601879 [3] BHANU B. Automatic target recognition: State of the art survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES-22(4): 364–379. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310772 [4] VERLY J G, DELANOY R L, and DUDGEON D E. Machine intelligence technology for automatic target recognition[J]. The Lincoln Laboratory Journal, 1989, 2(2): 277–311. [5] SCHACHTER B J. Automatic Target Recognition[M]. 3rd ed. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2018: 1–33. [6] BLACKNELL D and GRIFFITHS H. Radar Automatic Target Recognition (ATR) and Non-Cooperative Target Recognition (NCTR)[M]. London: IET Digital Library, 2013: 157–174. [7] 崔皓. 分布式架构原理与实践[M]. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2021: 117–169.CUI Hao. Principles and Practices of Distributed Architecture[M]. Beijing: Posts & Telecommunications Press, 2021: 117–169. [8] LIU Bing. Learning on the Job: Online lifelong and continual learning[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 13544–13549. [9] 郁文贤, 郭桂蓉. ATR的研究现状和发展趋势[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 1994, 16(6): 25–32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.1994.06.005YU Wenxian and GUO Guirong. The state of the arts of automatic target recognition[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 1994, 16(6): 25–32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.1994.06.005 [10] AFRL and DARPA. Sensor data management system website, MSTAR database[EB/OL]. https://www.sdms.afrl.af.mil/index.php?collection=mstar, 2022. [11] BRYANT A. Target recognition and adaption in contested environments (TRACE)[EB/OL]. https://www.darpa.mil/program/trace, 2022. [12] 郭炜炜, 杜小勇, 胡卫东, 等. 基于稀疏先验的SAR图像目标方位角稳健估计方法[J]. 信号处理, 2008, 24(6): 889–893. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2008.06.001GUO Weiwei, DU Xiaoyong, HU Weidong, et al. A robust target aspect estimation method from SAR images based on sparse prior[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2008, 24(6): 889–893. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2008.06.001 [13] 郁文贤, 李明国. 军事电子信息处理中的人工神经网络技术[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 1998, 20(3): 3–5.YU Wenxian and LI Mingguo. Applications of artificial neural networks technology to military electronic information processing[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 1998, 20(3): 3–5. [14] 黎湘, 郁文贤, 庄钊文, 等. 决策层信息融合的神经网络模型与算法研究[J]. 电子学报, 1997, 25(9): 117–120. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1997.09.030LI Xiang, YU Wenxian, ZHUANG Zhaowen, et al. Decision fusion for target recognition based on neural network model[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 1997, 25(9): 117–120. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1997.09.030 [15] KOVAR J J, KNECHT J, and CHENOWETH D. Automatic classification of infrared ship imagery[C]. SPIE 0292, Images and Data from Optical Sensors, San Diego, USA, 1981: 234–240. [16] AVCI E. A new method for expert target recognition system: Genetic wavelet extreme learning machine (GAWELM)[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2013, 40(10): 3984–3993. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2013.01.011 [17] 郭桂蓉. 模糊模式识别[M]. 长沙: 国防科技大学出版社, 1993: 134–168.GUO Guirong. FUZZY Pattern Recognition[M]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology Press, 1993: 134–168. [18] HU M K. Visual pattern recognition by moment invariant[J]. IRE Transactions on Information Theory, 1962, 8(2): 179–187. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1962.1057692 [19] 何友, 黄勇, 关键, 等. 海杂波中的雷达目标检测技术综述[J]. 现代雷达, 2014, 36(12): 1–9. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2014.12.004HE You, HUANG Yong, GUAN Jian, et al. An overview on radar target detection in sea clutter[J]. Modern Radar, 2014, 36(12): 1–9. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2014.12.004 [20] 艾小锋, 赵锋, 刘晓斌, 等. 双/多基地雷达目标探测与识别[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2020: 54–95.AI Xiaofeng, ZHAO Feng, LIU Xiaobin, et al. Bi-Station/Multi-Station Radar Target Detection and Recognition[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2020: 54–95. [21] BARTON D K. Radar System Analysis and Modeling[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005: 85–125. [22] CHUANG C W and MOFFATT D L. Natural resonances of radar targets via Prony’s method and target discrimination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1976, AES-12(5): 583–589. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1976.308260 [23] CHEN J S and WALTON E K. Comparison of two target classification techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES-22(1): 15–22. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310688 [24] 郭桂蓉, 郁文贤, 胡步法. 一种有效的舰船目标识别新方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 1990(6): 1–7, 15. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.1990.06.001GUO Guirong, YU Wenxian, and HU Bufa. A new effective method for ship target recognition[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 1990(6): 1–7, 15. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.1990.06.001 [25] 袁莉, 刘宏伟, 保铮. 基于中心矩特征的雷达HRRP自动目标识别[J]. 电子学报, 2004, 32(12): 2078–2081. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2004.12.036YUAN Li, LIU Hongwei, and BAO Zheng. Automatic target recognition of radar HRRP based on central moments features[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2004, 32(12): 2078–2081. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2004.12.036 [26] ZHANG Xuefeng, CHEN Bo, LIU Hongwei, et al. Infinite max-margin factor analysis via data augmentation[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 52: 17–32. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2015.10.020 [27] CHEN Jian, DU Lan, and LIAO Leiyao. Discriminative mixture variational autoencoder for semisupervised classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(5): 3032–3046. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3023019 [28] DU Chuan, CHEN Bo, XU Bin, et al. Factorized discriminative conditional variational auto-encoder for radar HRRP target recognition[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 158: 176–189. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.01.006 [29] COPSEY K and WEBB A. Bayesian gamma mixture model approach to radar target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(4): 1201–1217. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1261122 [30] DU Lan, CHEN Jian, HU Jing, et al. Statistical modeling with label constraint for radar target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(2): 1026–1044. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2925472 [31] 吴一戎, 朱敏慧. 合成孔径雷达技术的发展现状与趋势[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2000, 15(2): 121–123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2000.02.012WU Yirong and ZHU Minhui. The developing status and trends of synthetic aperture radar[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2000, 15(2): 121–123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2000.02.012 [32] HOLMES Q A, NUESCH D R, and SHUCHMAN R A. Textural analysis and real-time classification of sea-ice types using digital SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1984, GE-22(2): 113–120. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.1984.350602 [33] IKEUCHI K, WHEELER M D, YAMAZAKI T, et al. Model-based SAR ATR system[C]. SPIE 2757, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery III, Orlando, USA, 1996: 376–387. [34] ANAGNOSTOPOULOS G C. SVM-based target recognition from synthetic aperture radar images using target region outline descriptors[J]. Nonlinear Analysis:Theory,Methods&Applications, 2009, 71(12): e2934–e2939. doi: 10.1016/j.na.2009.07.030 [35] SAIDI M N, DAOUDI K, KHENCHAF A, et al. Automatic target recognition of aircraft models based on ISAR images[C]. 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009: IV-685–IV-688. [36] ZHENG Qinfen, DER S Z, and MAHMOUD H I. Model-based target recognition in pulsed ladar imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2001, 10(4): 565–572. doi: 10.1109/83.913591 [37] RUEL S, ENGLISH C E, MELO L, et al. Field testing of a 3D automatic target recognition and pose estimation algorithm[C]. SPIE 5426, Automatic Target Recognition XIV, Orlando, USA, 2004: 102–111. [38] GRONWALL C, GUSTAFSSON F, and MILLNERT M. Ground target recognition using rectangle estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(11): 3400–3408. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.881965 [39] VASILE A N. Pose independent target recognition system using pulsed ladar imagery[D]. [Master dissertation], Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2004. [40] ERNISSE B E, ROGERS S K, DESIMIO M P, et al. Complete automatic target cuer/recognition system for tactical forward-looking infrared images[J]. Optical Engineering, 1997, 36(9): 2593–2603. doi: 10.1117/1.601484 [41] INGGS M R and ROBINSON A D. Ship target recognition using low resolution radar and neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(2): 386–393. doi: 10.1109/7.766923 [42] NING Wu, CHEN Wugun, and ZHANG Xinggan. Automatic target recognition of ISAR object images based on neural network[C]. IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks and Signal Processing, Nanjing, China, 2003: 373–376. [43] 黄金, 梁彦, 程咏梅, 等. 基于序列图像的自动目标识别算法[J]. 航空学报, 2006, 27(1): 87–93. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2006.01.017HUANG Jin, LIANG Yan, CHEN Yongmei, et al. Automatic target recognition method based on sequential images[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2006, 27(1): 87–93. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2006.01.017 [44] 宋锐, 张静, 夏胜平, 等. 一种基于BP神经网络群的自适应分类方法及其应用[J]. 电子学报, 2001, 29(12A): 1950–1953. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2001.z1.055SONG Rui, ZHANG Jing, XIA Shengping, et al. An adaptive classification method of BP-NN group based classification system and its application[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2001, 29(12A): 1950–1953. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2001.z1.055 [45] AVCI E and COTELI R. A new automatic target recognition system based on wavelet extreme learning machine[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(16): 12340–12348. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2012.04.012 [46] 李明国, 郁文贤. 神经网络的函数逼近理论[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 1998, 20(4): 70–76.LI Mingguo and YU Wenxian. On neural networks founction approximation[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 1998, 20(4): 70–76. [47] 胡卫东, 郁文贤, 郭桂蓉. 一种有效的神经网络检测器[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 1997, 19(3): 18–22.HU Weidong, YU Wenxian, and GUO Guirong. An effective neural network detector[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 1997, 19(3): 18–22. [48] 路军, 郁文贤, 郭桂蓉, 等. 子波神经网络及其在自动目标识别中的应用[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 1995, 17(11): 11–18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.1995.11.003LU Jun, YU Wenxian, GUO Guirong, et al. Application of WNN in automatic target recognition[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 1995, 17(11): 11–18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.1995.11.003 [49] 夏胜平, 张乐锋, 虞华, 等. 基于RSOM树模型的机器学习原理与算法研究[J]. 电子学报, 2005, 33(5): 939–944. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2005.05.037XIA Shengping, ZHANG Lefeng, YU Hua, et al. Theory and algorithm of machine learning based on RSOM tree model[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2005, 33(5): 939–944. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2005.05.037 [50] 李予蜀, 余农, 吴常泳, 等. 红外航空图像自动目标识别的形态滤波神经网络算法[J]. 航空学报, 2002, 23(4): 368–372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2002.04.018LI Yushu, YU Nong, WU Changyong, et al. Morphological neural networks with applications to automatic target recognition in aeronautics infrared image[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2002, 23(4): 368–372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2002.04.018 [51] AVCI E, TÜRKOĞLU I, and POYRAZ M. A new approach based on wavelet nero genetic network for automatic target recognition with X-band Doppler radar[J]. Istanbul University Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, 2006, 6(2): 157–168. [52] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet Classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 [53] GAO Fei, HUANG Teng, SUN Jinping, et al. A new algorithm for SAR image target recognition based on an improved deep convolutional neural network[J]. Cognitive Computation, 2019, 11(6): 809–824. doi: 10.1007/s12559-018-9563-z [54] ZHU Pingping, ISAACS J, FU Bo, et al. Deep learning feature extraction for target recognition and classification in underwater sonar images[C]. IEEE 56th Annual Conference on Decision and Control, Melbourne, Australia, 2017: 2724–2731. [55] 田壮壮, 占荣辉, 胡杰民, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标识别研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037TIAN Zhuangzhuang, ZHAN Ronghui, HU Jiemin, et al. SAR ATR based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037 [56] CHEN Sizhe and WANG Haipeng. SAR target recognition based on deep learning[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics, Shanghai, China, 2014: 541–547. [57] 贺丰收, 何友, 刘准钆, 等. 卷积神经网络在雷达自动目标识别中的研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899HE Fengshou, HE You, LIU Zhunga, et al. Research and development on applications of convolutional neural networks of radar automatic target recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 119–131. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180899 [58] DING Baiyuan, WEN Gongjian, MA Conghui, et al. An efficient and robust framework for SAR target recognition by hierarchically fusing global and local features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(12): 5983–5995. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2863046 [59] ZHANG Jinsong, XING Mengdao, and XIE Yiyuan. FEC: A feature fusion framework for SAR target recognition based on electromagnetic scattering features and deep CNN features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(3): 2174–2187. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3003264 [60] LI Yi, DU Lan, and WEI Di. Multiscale CNN based on component analysis for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5211212. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3100137 [61] FENG Sijia, JI Kefeng, ZHANG Linbin, et al. SAR target classification based on integration of ASC parts model and deep learning algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 10213–10225. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3116979 [62] 王容川, 庄志洪, 王宏波, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的雷达目标HRRP分类识别方法[J]. 现代雷达, 2019, 41(5): 33–38. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.05.007WANG Rongchuan, ZHUANG Zhihong, WANG Hongbo, et al. HRRP classification and recognition method of Radar target based on convolutional neural network[J]. Modern Radar, 2019, 41(5): 33–38. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.05.007 [63] CHEVALIER M, THOME N, CORD M, et al. Low resolution convolutional neural network for automatic target recognition[C]. 7th International Symposium on Optronics in Defence and Security, Paris, France, 2016: 1–9. [64] 喻玲娟, 王亚东, 谢晓春, 等. 基于FCNN和ICAE的SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR18066YU Lingjuan, WANG Yadong, XIE Xiaochun, et al. SAR ATR based on FCNN and ICAE[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR18066 [65] ZHANG Zenghui, GUO Weiwei, ZHU Shengnan, et al. Toward arbitrary-oriented ship detection with rotated region proposal and discrimination networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(11): 1745–1749. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2856921 [66] ZHAO Juanping, ZHANG Zenghui, YU Wenxian, et al. A cascade coupled convolutional neural network guided visual attention method for ship detection from SAR images[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 50693–50708. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2869289 [67] KHELLAL A, MA Hongbin, and FEI Qing. Convolutional neural network based on extreme learning machine for maritime ships recognition in infrared images[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(5): 1490. doi: 10.3390/s18051490 [68] 史国军. 深度特征联合表征的红外图像目标识别方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(3): 20200399. doi: 10.3788/irla20200399SHI Guojun. Target recognition method of infrared imagery via joint representation of deep features[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(3): 20200399. doi: 10.3788/irla20200399 [69] PAN Mian, LIU Ailin, YU Yanzhen, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition model based on a stacked CNN–Bi-RNN with attention mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5100814. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3055061 [70] LI Rui, WANG Xiaodan, WANG Jian, et al. SAR target recognition based on efficient fully convolutional attention block CNN[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 19: 4005905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3037256 [71] OSAHOR U M and NASRABADI N M. Design of adversarial targets: Fooling deep ATR systems[C]. SPIE 10988, Automatic Target Recognition XXIX, Baltimore, USA, 2019: 82–91. [72] HUANG Teng, ZHANG Qixiang, LIU Jiabao, et al. Adversarial attacks on deep-learning-based SAR image target recognition[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2020, 162: 102632. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102632 [73] GOEL A, AGARWAL A, VATSA M, et al. DNDNet: Reconfiguring CNN for adversarial robustness[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 22–23. [74] DING Jun, CHEN Bo, LIU Hongwei, et al. Convolutional neural network with data augmentation for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 364–368. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2513754 [75] BAI Xueru, ZHOU Xuening, ZHANG Feng, et al. Robust pol-ISAR target recognition based on ST-MC-DCNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 9912–9927. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2930112 [76] ZHAI Yikui, DENG Wenbo, XU Ying, et al. Robust SAR automatic target recognition based on transferred MS-CNN with L2-regularization[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2019, 2019: 9140167. doi: 10.1155/2019/9140167 [77] 郭炜炜, 张增辉, 郁文贤, 等. SAR图像目标识别的可解释性问题探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, YU Wenxian, et al. Perspective on explainable SAR target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059 [78] HUANG Zhongling, PAN Zongxu, and LEI Bin. Transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network for SAR target classification with limited labeled data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(9): 907. doi: 10.3390/rs9090907 [79] MALMGREN-HANSEN D, KUSK A, DALL J, et al. Improving SAR automatic target recognition models with transfer learning from simulated data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1484–1488. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2717486 [80] ZHAO Siyuan, ZHANG Zenghui, ZHANG Tao, et al. Transferable SAR image classification crossing different satellites under open set condition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4506005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3159179 [81] ZHAO Siyuan, ZHANG Zenghui, GUO Weiwei, et al. An automatic ship detection method adapting to different satellites SAR images with feature alignment and compensation loss[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5225217. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3160727 [82] KARJALAINEN A I, MITCHELL R, and VAZQUEZ J. Training and validation of automatic target recognition systems using generative adversarial networks[C]. 2019 IEEE Sensor Signal Processing for Defence Conference (SSPD), Brighton, UK, 2019: 1–5. [83] YANG Shuang, SHI Xiaoran, and ZHOU Feng. Automatic target recognition for low-resolution SAR images based on super-resolution network[C]. IEEE 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–6. [84] AHMADIBENI A, JONES B, BOROOSHAK L, et al. Automatic target recognition of aerial vehicles based on synthetic SAR imagery using hybrid stacked denoising auto-encoders[C]. SPIE 11393, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXVII, 2020: 71–82. [85] ZELNIO E G. Advanced decision-making systems in future avionics: Automatic target recognition example[C]. 1998 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, Snowmass, USA, 1998: 309–313. [86] HUANG Lanqing, LIU Bin, LI Boying, et al. OpenSARShip: A dataset dedicated to Sentinel-1 ship interpretation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 195–208. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2755672 [87] 孙显, 王智睿, 孙元睿, 等. AIR-SARShip-1.0: 高分辨率SAR舰船检测数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097SUN Xian, WANG Zhirui, SUN Yuanrui, et al. AIR-SARShip-1.0: High-resolution SAR ship detection dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097 [88] 刘宁波, 董云龙, 王国庆, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, WANG Guoqing, et al. Sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089 [89] 回丙伟, 宋志勇, 王琦, 等. 空中弱小目标检测跟踪测试基准[J]. 航空兵器, 2019, 26(6): 56–59. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2019.0234HUI Bingwei, SONG Zhiyong, WANG Qi, et al. A benchmark for dim or small aircraft targets detection and tracking[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2019, 26(6): 56–59. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2019.0234 [90] 张静, 宋锐, 郁文贤. 雷达目标识别中的BP神经网络算法改进及应用[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2005, 27(4): 582–585. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2005.04.003ZHANG Jing, SONG Rui, and YU Wenxian. Improvements and applications of BP neural network algorithm in radar target recognition[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2005, 27(4): 582–585. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2005.04.003 [91] BLASCH E, SEETHARAMAN G, and DAREMA F. Dynamic data driven applications systems (DDDAS) modeling for automatic target recognition[C]. SPIE 8744, Automatic Target Recognition XXIII, Baltimore, USA, 2013: 165–174. [92] WILLIAMS D P, COUILLARD M, and DUGELAY S. On human perception and automatic target recognition: Strategies for human-computer cooperation[C]. 22nd IEEE International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, USA, 2014: 4690–4695. [93] TELLEZ O L. Human-in-the-loop for autonomous underwater threat recognition[C]. OCEANS 2018 MTS/IEEE Charleston, Charleston, USA, 2018: 1–5. [94] TELLEZ O L. Underwater threat recognition: Are automatic target classification algorithms going to replace expert human operators in the near future?[C]. OCEANS 2019-Marseille, Marseille, France, 2019: 1–4. [95] IRVINE J M. Evaluating assisted target recognition performance: An assessment of DARPA’s SAIP system[C]. SPIE 3721, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery VI, Orlando, USA, 1999: 693–704. [96] EVERSDEN A. DARPA issues solicitation for moving-target recognition project[EB/OL]. https://www.c4isrnet.com/home/2020/07/21/darpa-issues-solicitation-for-moving-target-recognition-project/, 2020. [97] BUSCHMANN F, MEUNIER R, ROHNERT H, et al. Pattern-Oriented Software Architecture, Volume 1, A System of Patterns[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1996: 3–7. [98] FORD N, PARSONS R, and KUA P. Building Evolutionary Architectures: Support Constant Change[M]. Beijing: O’Reilly Media, Inc. , 2017: 95–164. [99] 宋锐. 雷达舰船目标识别系统实现技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 2003.SONG Rui. Technology research on realization of radar ship target recognition system[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Defense Science and Technology, 2003. [100] 郁文贤, 计科峰, 柳彬. 星载SAR与AIS综合的海洋目标信息处理技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 164–200.YU Wenxian, JI Kefeng, and LIU Bin. Satellite Based SAR and AIS Synthetic Oceanic Target Information Processing Technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017: 164–200. [101] 郁文贤. 智能化识别方法及其在舰船雷达目标识别系统中的应用[D]. [博士论文], 国防科技大学, 1992.YU Wenxian. Intelligent recognition method and its application in ship radar target recognition system[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Defense Science and Technology, 1992. [102] 郁文贤, 郭桂蓉. 通用型对海监视雷达目标识别与综合显控系统[R]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2004.YU Wenxian and GUO Guirong. Universal sea-surveillance radar target recognition and comprehensive display and control system[R]. Changsha: University of Defense Science and Technology, 2004. [103] CALVO-FULLANA M, MOX D, PYATTAEV A, et al. ROS-NetSim: A framework for the integration of robotic and network simulators[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(2): 1120–1127. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3056347 [104] 张静. 岸对海雷达智能数据分析与目标判性系统研制报告[R]. 国防科技大学ATR重点实验室, 2003.ZHANG Jing. Shore-to-the-sea radar intelligent data analysis and target classification system report[R]. ATR Laboratory, University of Defense Science and Technology, 2003. [105] 郭桂蓉, 庄钊文. ATR柔性技术研究报告[R]. 国防科技大学, 1995.GUO Guirong and ZHUANG Zhaowen. ATR adaptive technology research report[R]. University of Defense Science and Technology, 1995. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
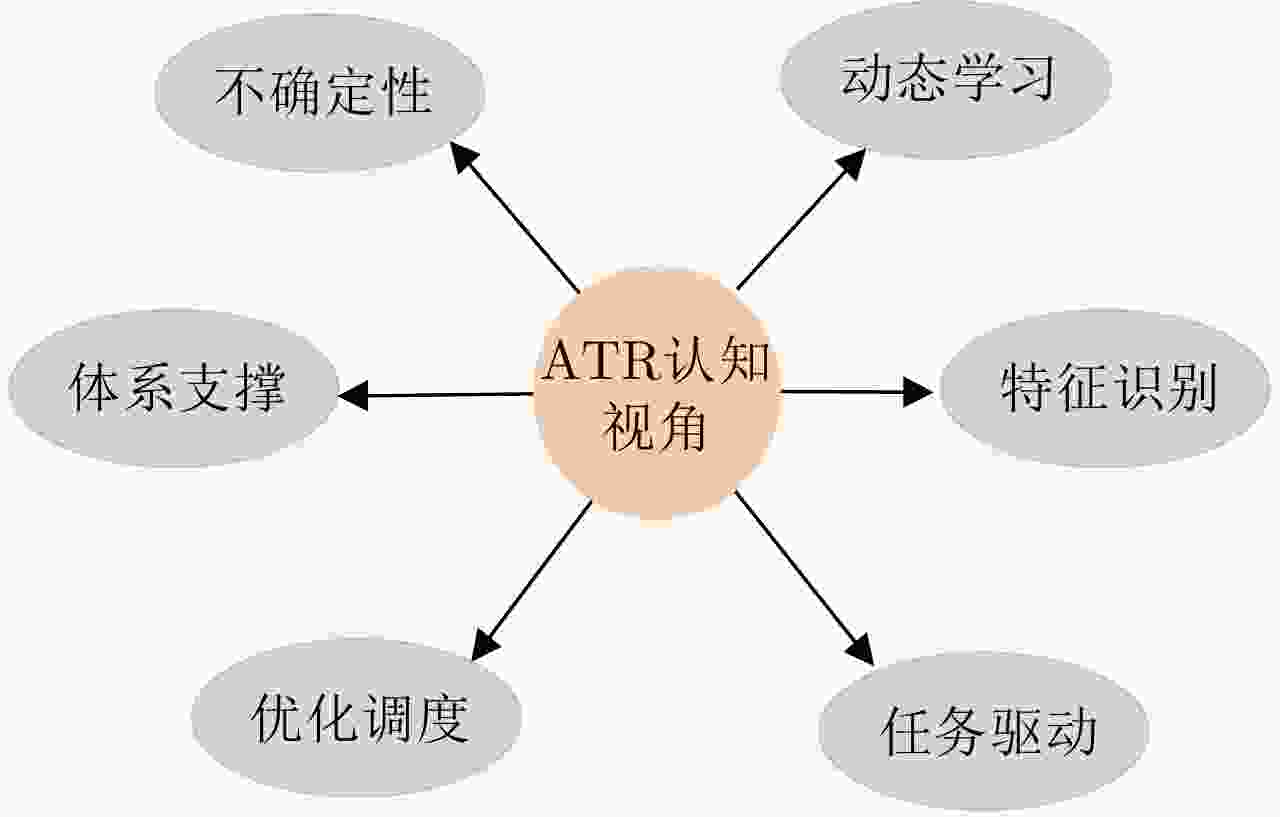
 下载:
下载: