Nonlinear Trajectory Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging and Autofocus Algorithm Based on Sub-image Nonlinear Chirp Scaling
-
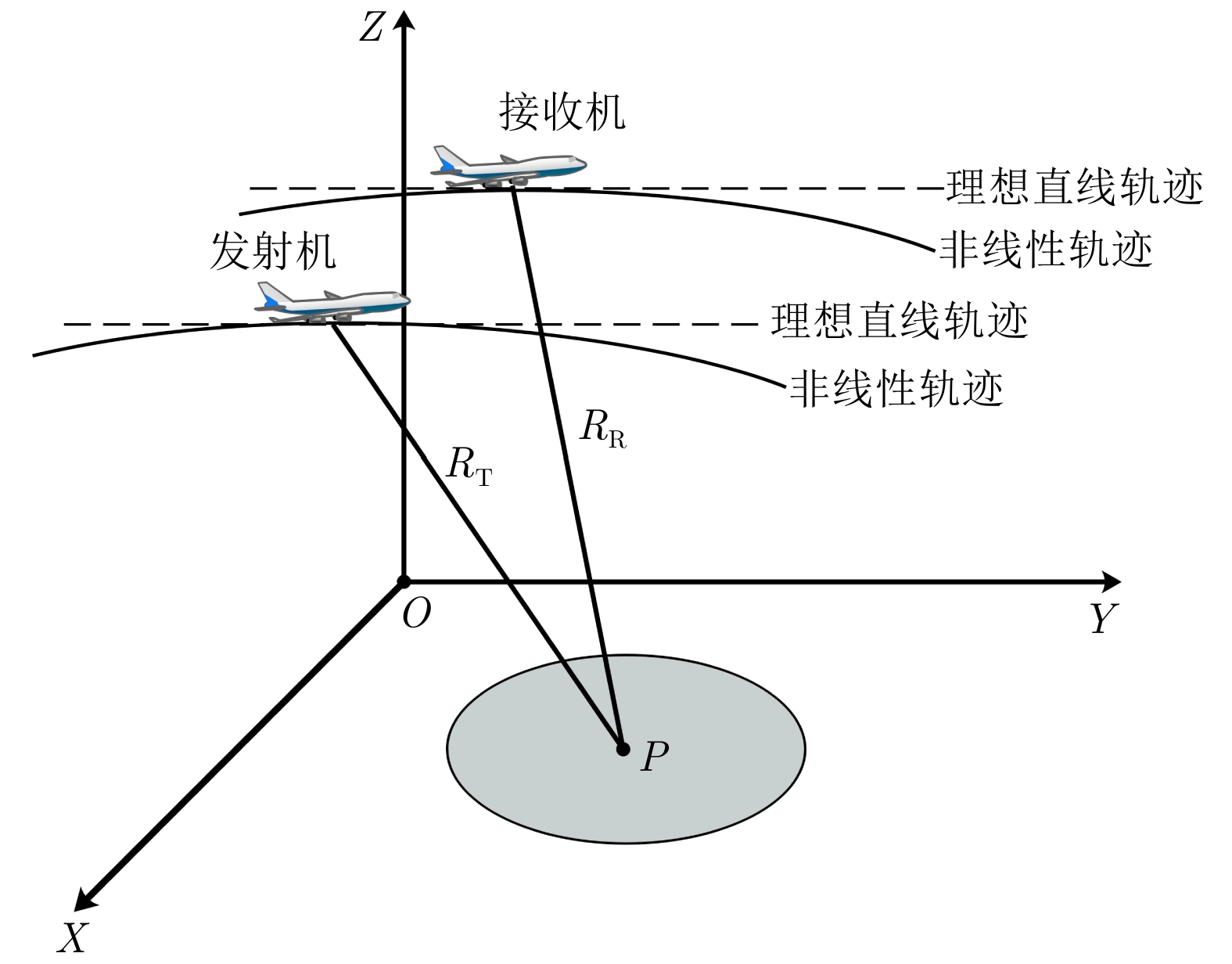
摘要: 合成孔径雷达(SAR)的非线性轨迹运动可能会在雷达回波信号中引入严重的二维空变特性,因此基于方位平移不变性假设的传统频域成像算法不再适用于非线性轨迹SAR的高精度成像。现有非线性轨迹SAR成像算法通常采用复杂的非线性变标(NCS)校正回波信号的方位空变特性,然而NCS参数过多导致算法复杂,使得其当存在较大平台运动测量误差时无法与现有自聚焦算法有效结合。针对该问题,该文提出一种基于子图像NCS的非线性轨迹SAR成像及其自聚焦方法,在保证成像精度的前提下能够减少NCS的参数数量,更有利于后续的自聚焦处理。仿真与实测数据处理验证了所提方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR) /
- 非线性轨迹 /
- 非线性变标(NCS) /
- 二维空变 /
- 自聚焦
Abstract: The radar echo signal may experience substantial two-dimensional spatial variance due to the nonlinear Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) trajectory. The traditional frequency-domain imaging algorithms based on the assumption of azimuth translational invariance are unsuitable for high-precision imaging of nonlinear trajectory SAR. Therefore, for nonlinear trajectory SAR imaging, the azimuth spatial variance of the echo signals is typically rectified using complex Nonlinear Chirp Scaling (NCS). However, when there are substantial motion errors, it cannot be effectively combined with the current autofocus algorithms considering the complexity of the algorithm due to too many NCS parameters. Thus, to address this issue, this study proposes a nonlinear trajectory SAR imaging and autofocus method according to the sub-image NCS, which can reduce the number of NCS parameters and ensure imaging accuracy; moreover, it is more conducive to the subsequent autofocus processing. The effectiveness of the suggested approach is confirmed by simulation and measured data processing. -
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters
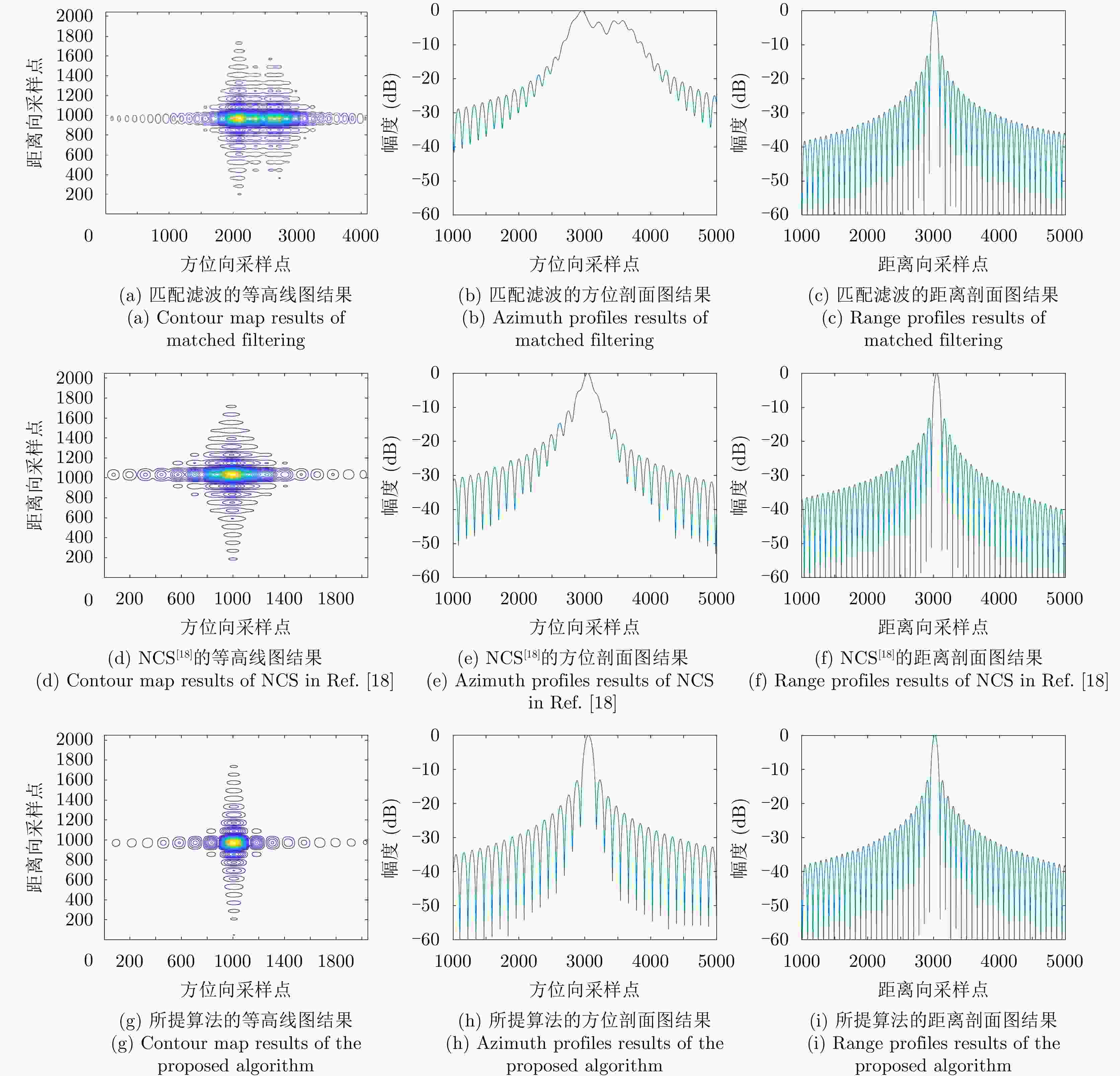
参数 发射机 接收机 初速度 (48.3, 13.6, 0) m/s (48.2, 13.5, 0) m/s 加速度 (–0.05, –0.01, 0) m/s2 (–0.05, –0.01, 0) m/s2 载频 16 GHz PRF 1000 Hz 带宽 1400 MHz 合成孔径时间 24 s 方位分辨率 0.1 m 最近斜距 17.5 km 工作模式 聚束 斜视角 0o 表 2 3种方法方位聚焦质量的定量评估结果
Table 2. Quantitative evaluation results of azimuth focusing quality for the three methods
方法 场景左端目标 场景右端目标 PSLR(dB) ISLR(dB) 熵值 PSLR(dB) ISLR(dB) 熵值 匹配滤波 –2.34 –5.11 8.487 –3.47 –4.88 8.512 NCS[18] –5.27 –7.24 8.391 –11.48 –8.91 8.344 子图像分割+NCS –13.14 –9.81 8.312 –13.20 –9.89 8.309 表 3 变标函数系数
${\boldsymbol{{\alpha _k},\beta}}$ 的估计算法Table 3. The estimation method of coefficients
${\boldsymbol{{\alpha _k},\beta}}$ 步骤1 求解第1个最优化问题,即式(17) 1.1 输入:two-step MoCo后的SAR图像 1.2 设$ \alpha = 0 $,参数$ \beta $的初始搜索区间为$\beta \in \left[ { {\beta _{\rm{s}}},{\beta _{\rm{e}}} } \right]$,迭 代终止阈值为$ \varepsilon {\text{ = }}0.01 $ 1.3 while $\max \left\{ {E\left( { {\beta _{\rm{s} } } } \right),E\left( { {\beta _{\rm{e} } } } \right)} \right\} > \varepsilon$ 引入式(8)中的4阶变标函数;采用黄金分割法不断 缩小$ \beta $的区间 1.4 End while 1.5 输出:$ \overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$}}{\beta } $及3阶误差校正后的图像 步骤2 求解第2个最优化问题,即式(18) 2.1 输入:$ \overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$}}{\beta } $及3阶误差校正后的图像 2.2 对图像进行分块处理,得到N个子图像 2.3 For k = 1:N (1) 设$ \beta = \overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$}}{\beta } $,参数$ {\alpha _k} $的初始搜索区间为
${\alpha _k} \in \left[ { {\alpha _{ {\rm{sk} } } } ,{ {\alpha _{ {\rm{ek} } } } } } \right]$,迭代终止阈值为$ \varepsilon {\text{ = }}0.01 $(2) while $\max \left\{ { {E_k}\left( { {\alpha _{{\rm{sk}}} } } \right),{E_k}\left( { {\alpha _{{\rm{ek}}} } } \right)} \right\} > \varepsilon$ 引入式(7)中的3阶变标函数;采用黄金分割法不断 缩小$ {\alpha _k} $的区间 (3) End while (4) 输出:$ {\overset{\lower0.5em\hbox{$\smash{\scriptscriptstyle\frown}$}}{\alpha } _k} $及2阶误差校正后的子图像 2.4 End 2.5 子图像拼接 表 4 图8局部细节图的熵值评估结果
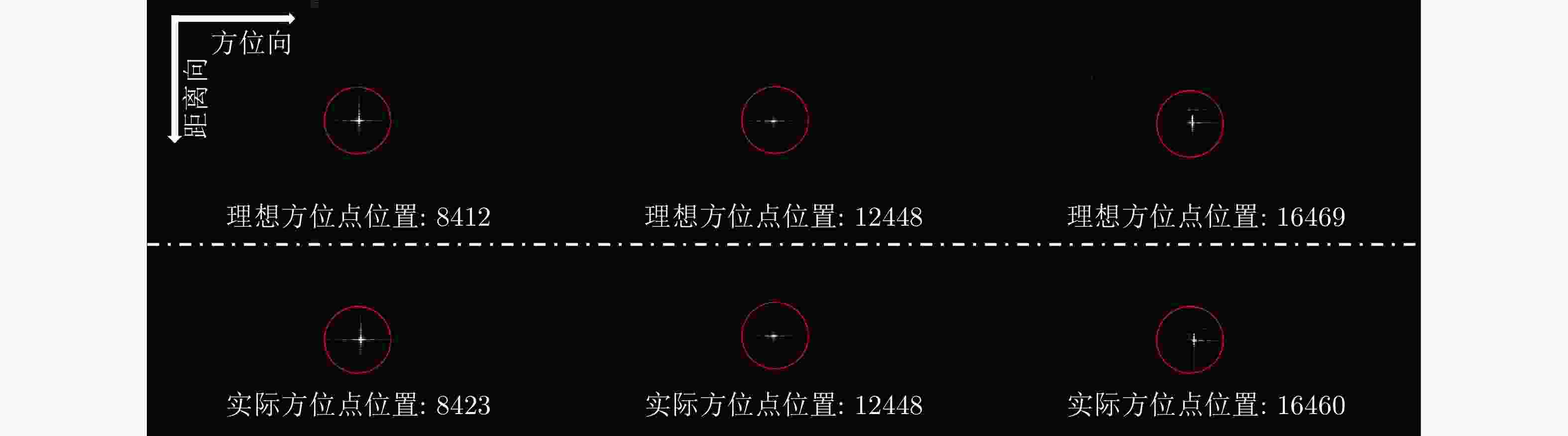
Table 4. Entropy evaluation results of local enlarged images in Fig. (8)
方法 场景左端 场景右端 匹配滤波 11.287 10.943 NCS[18] 11.161 10.867 子图像分割+NCS 11.160 10.852 -
[1] 邢孟道, 林浩, 陈溅来, 等. 多平台合成孔径雷达成像算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A review of imaging algorithms in multi-platform-borne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102 [2] 陈潇翔, 邢孟道. 基于空变运动误差分析的微波光子超高分辨SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(2): 205–214. doi: 10.12000/JR18121CHEN Xiaoxiang and XING Mengdao. An ultra-high-resolution microwave photonic-based SAR image method based on space-variant motion error analysis[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(2): 205–214. doi: 10.12000/JR18121 [3] 李根, 马彦恒, 熊旭颖. 基于二维空变运动补偿的机动平台大斜视SAR稀疏自聚焦方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(7): 1992–1999. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200456LI Gen, MA Yanheng, and XIONG Xuying. Sparse autofocus method for maneuvering platform high-squint SAR based on two-dimensional spatial-variant motion compensation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(7): 1992–1999. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200456 [4] 施天玥, 刘惠欣, 刘衍琦, 等. 基于先验相位结构信息的双基SAR两维自聚焦算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(6): 1045–1055. doi: 10.12000/JR20048SHI Tianyue, LIU Huixin, LIU Yanqi, et al. Bistatic synthetic aperture radar two-dimensional autofocus approach based on prior knowledge on phase structure[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(6): 1045–1055. doi: 10.12000/JR20048 [5] CHEN Jianlai, XING Mengdao, YU Hanwen, et al. Motion compensation/autofocus in airborne synthetic aperture radar: A review[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2022, 10(1): 185–206. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2021.3113982 [6] 别博文, 孙路, 邢孟道, 等. 基于局部直角坐标和子区域处理的弹载SAR频域成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(8): 1779–1786. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171107BIE Bowen, SUN Lu, XING Mengdao, et al. A frequency-domain algorithm based on local Cartesian coordinate and subregion processing for missile-borne SAR imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(8): 1779–1786. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171107 [7] CHEN Jianlai, ZHANG Junchao, JIN Yanghao, et al. Real-time processing of spaceborne SAR data with nonlinear trajectory based on variable PRF[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5205212. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3067945 [8] 李航, 刘文康, 孙光才, 等. 基于成像坐标系优化的中轨星载SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 856–864. doi: 10.12000/JR20098LI Hang, LIU Wenkang, SUN Guangcai, et al. MEO SAR imaging based on imaging coordinate system optimization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 856–864. doi: 10.12000/JR20098 [9] ASH J N. An autofocus method for backprojection imagery in synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(1): 104–108. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2161456 [10] XIONG Yi, LIANG Buge, YU Hanwen, et al. Processing of bistatic SAR data with nonlinear trajectory using a controlled-SVD algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 5750–5759. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3084619 [11] WU Junjie, LI Zhongyu, HUANG Yulin, et al. A generalized omega-K algorithm to process translationally variant bistatic-SAR data based on two-dimensional stolt mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6597–6614. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2299069 [12] PRATS P, CAMARA DE MACEDO K A, REIGBER A, et al. Comparison of topography- and aperture-dependent motion compensation algorithms for airborne SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2007, 4(3): 349–353. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2007.895712 [13] WONG F H, CUMMING I G, and NEO Y L. Focusing bistatic SAR data using the nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(9): 2493–2505. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.917599 [14] HUANG Lijia, QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, et al. Medium-earth-orbit SAR focusing using range Doppler algorithm with integrated two-step azimuth perturbation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(3): 626–630. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2353674 [15] ZHANG Tianyi, DING Zegang, TIAN Weiming, et al. A 2-D nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for high squint GEO SAR imaging based on optimal azimuth polynomial compensation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(12): 5724–5735. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2765353 [16] ZENG Tao, LI Yinghe, DING Zegang, et al. Subaperture approach based on azimuth-dependent range cell migration correction and azimuth focusing parameter equalization for maneuvering high-squint-mode SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(12): 6718–6734. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2447393 [17] LI Zhenyu, XING Mengdao, LIANG Yi, et al. A frequency-domain imaging algorithm for highly squinted SAR mounted on maneuvering platforms with nonlinear trajectory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(7): 4023–4038. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2535391 [18] QIU Xiaolan, HU Donghui, and DING Chibiao. An improved NLCS algorithm with capability analysis for one-stationary BiSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(10): 3179–3186. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.921569 [19] WANG Zhigui, LIU Mei, AI Gengting, et al. Focusing of bistatic SAR with curved trajectory based on extended azimuth nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(6): 4160–4179. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2961562 [20] CHEN Jianlai, ZHANG Junchao, YU Hanwen, et al. Blind NCS-based autofocus for airborne wide-beam SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2022, 8: 626–638. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2022.3194745 [21] PRATS-IRAOLA P, SCHEIBER R, RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, et al. On the processing of very high resolution spaceborne SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6003–6016. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2294353 [22] MOREIRA A and HUANG Yonghong. Airborne SAR processing of highly squinted data using a chirp scaling approach with integrated motion compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(5): 1029–1040. doi: 10.1109/36.312891 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: