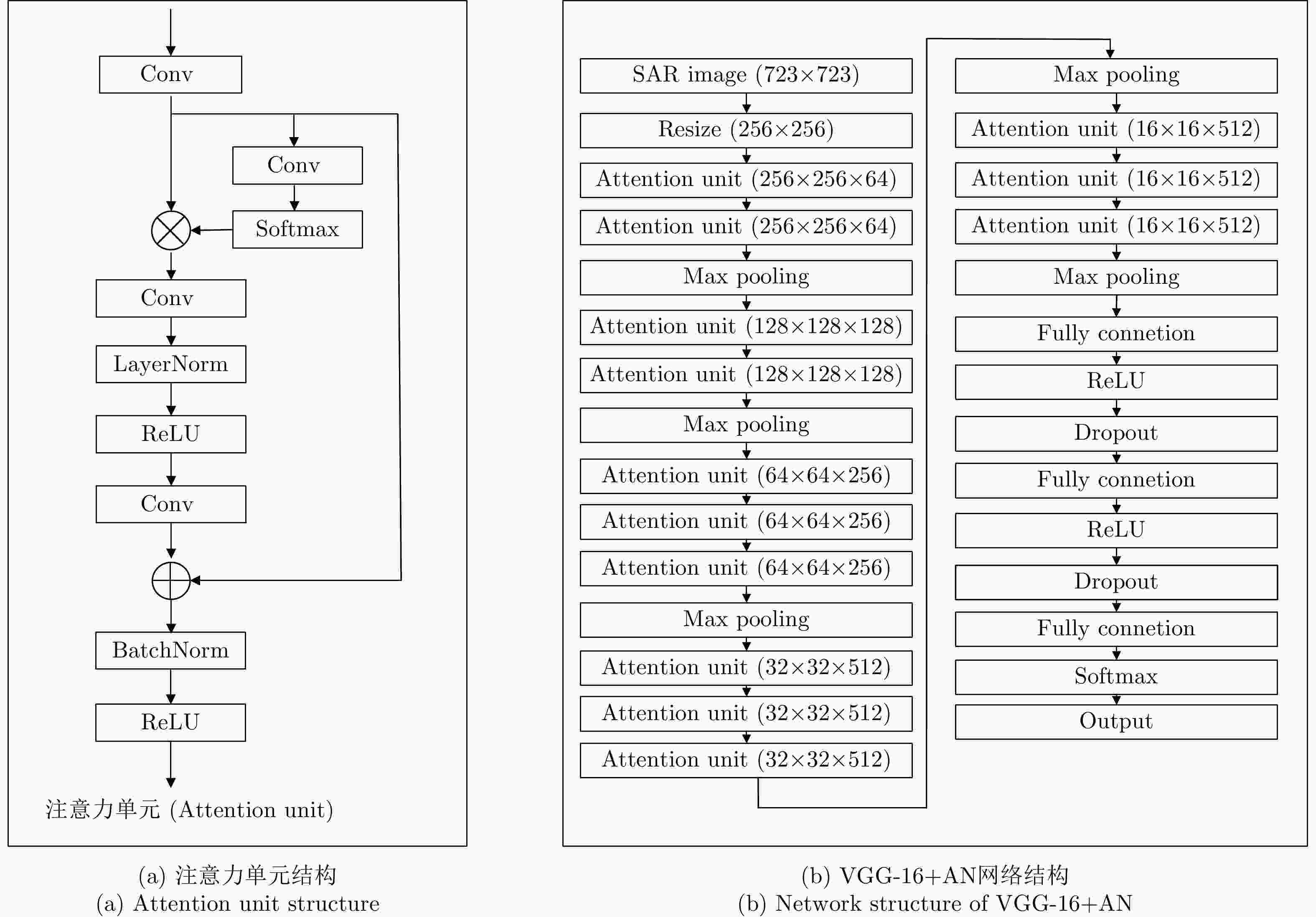
-
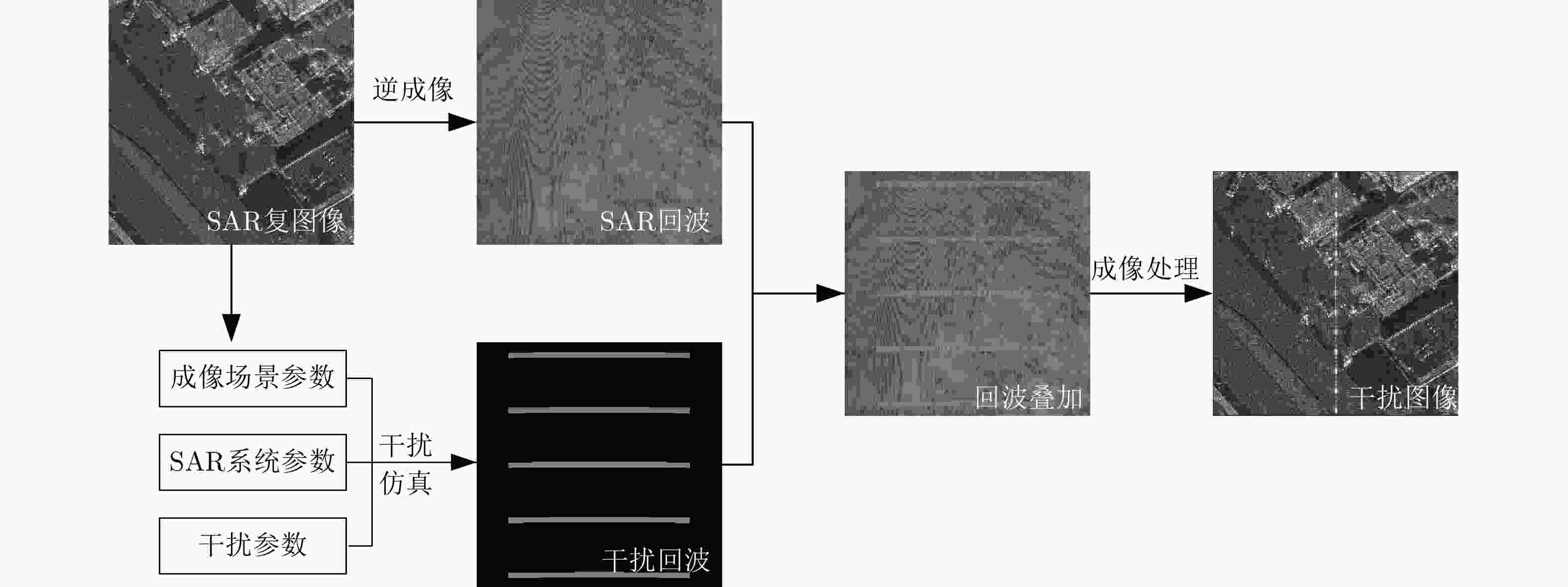
摘要: 合成孔径雷达(SAR)能够全天时全天候获取感兴趣区域的高分辨率雷达图像,在诸多领域获得了成功应用。在电子对抗博弈环境下,SAR图像解译与情报生成也面临复杂电磁干扰的严重影响。当前,国内外学者提出了许多SAR抗干扰技术方法。然而,作为抗干扰的前提,SAR图像干扰类型识别这一关键技术却鲜有报道。该文针对SAR图像典型有源干扰类型识别开展研究。首先,选取5种典型有源干扰样式,并根据干扰参数,细分为9种干扰类型,作为干扰识别对象。其次,开展干扰信号回波仿真,通过与MiniSAR实测数据进行回波域叠加和成像处理,构建了典型有源干扰类型样本集。在此基础上,提出了一种结合注意力机制的深度卷积神经网络(CNN)模型,并开展了对比实验验证。实验表明,对不同场景和不同干扰参数情形,相比于传统深度CNN模型,该文方法取得了更高的识别精度和更稳健的性能。Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) can acquire high-resolution radar images of region of interest under all-day and all-weather conditions, a capability that has been successfully applied in many fields. In the environment of military confrontation games, complex electromagnetic jamming severely impacts SAR image interpretation and intelligence generation. Scholars have proposed numerous SAR anti-jamming approaches to date. However, the recognition of SAR image jamming types, which is the prerequisite of anti-jamming, has rarely been reported. This work focuses on active jamming type recognition in SAR images. First, five typical active jamming modes are selected and further subdivided into nine jamming types based on various jamming parameters, which serve as the objects of jamming recognition. The typical active jamming datasets are then constructed based on the stacking of simulated jamming signal echoes and real-measured MiniSAR data in the echo domain and SAR imaging processing. Based on the jamming datasets, an attention-combining deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model has been proposed. Thereafter, comparative experiments are performed. Experiments show that, compared with traditional deep CNN models, the proposed method achieves more accurate recognition and more stable performance across various scenes and jamming parameter configurations.
-
Key words:
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) /
- Active jamming /
- Deep learning /
- Attention mechanism /
- Recognition
-
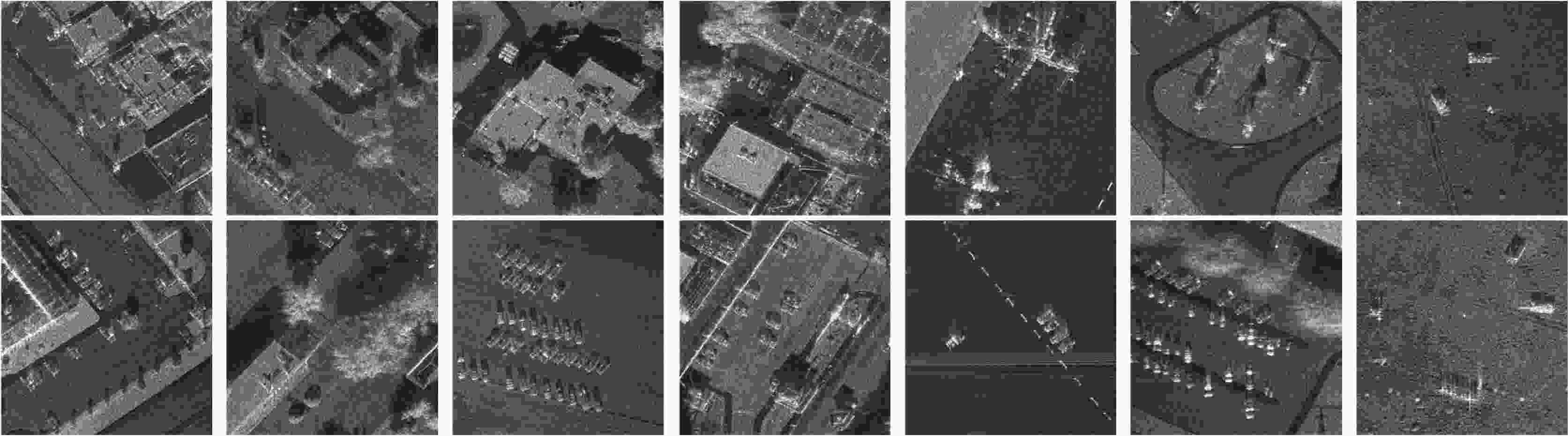
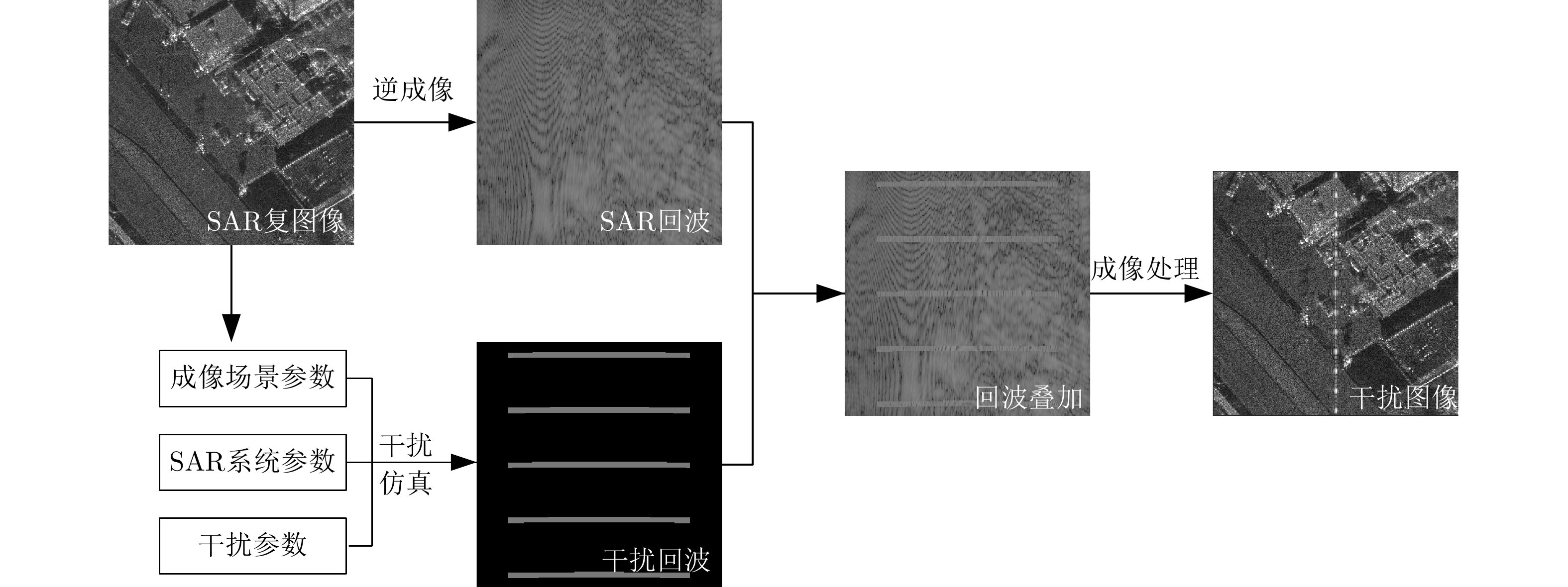
图 3 包含9种干扰类型和9种干扰机位置的车辆目标SAR图像切片((a) 噪声压制干扰,(b) 固定移频干扰,(c) 随机移频干扰,(d) 步进移频干扰,(e) 分段移频干扰,(f) 距离向间歇采样转发干扰,(g) 方位向间歇采样转发干扰,(h) 微动调制干扰,(i) 延迟多抽头干扰)
Figure 3. SAR image chips with vehicle targets containing 9 jamming types and 9 jammer positions((a) Noise suppression jamming, (b) Fixed shift-frequency jamming, (c) Random shift-frequency jamming, (d) Stepped shift-frequency jamming, (e) Blocked shift-frequency jamming, (f) Intermittent sampling repeater jamming in range, (g) Intermittent sampling repeater jamming in azimuth, (h) Micro-motion modulation jamming, (i) Delayed multi-taps jamming)
表 1 干扰参数设置
Table 1. Jamming parameter configuration
干扰类型 参数设置 噪声压制干扰 JSR=5.0, 7.5, 10.0, 12.5, 15.0, 17.5, 20.0, 22.5 dB 固定移频干扰 $R = 20$ 随机移频干扰 $R = 20$, $a = - 1$, $b = 1$ 步进移频干扰 $R = 20$, $ {f_{{{\text{d}}_{\text{0}}}}} = 0 $ 分段移频干扰 $R = 20$, $N = 3$, $ {f_1} = {f_{\text{d}}} $, $ {f_2} = 0 $,
$ {f_3} = - {f_{\text{d}}} $距离向间歇采样转发干扰 $R = 20$, ${D_{\rm r}} = 0.1$ 方位向间歇采样转发干扰 $R = 20$, ${D_{\rm r}} = 0.1$ 微动调制干扰 $R = 20$, $L = 100$ 延迟多抽头干扰 $R = 20$, $N = 2$ 表 2 实验1有源干扰类型识别结果(%)
Table 2. Active jamming type recognition results of experiment 1 (%)
测试集 方法 噪声干扰 固定移频 随机移频 分段移频 步进移频 距离向
间歇采样方位向
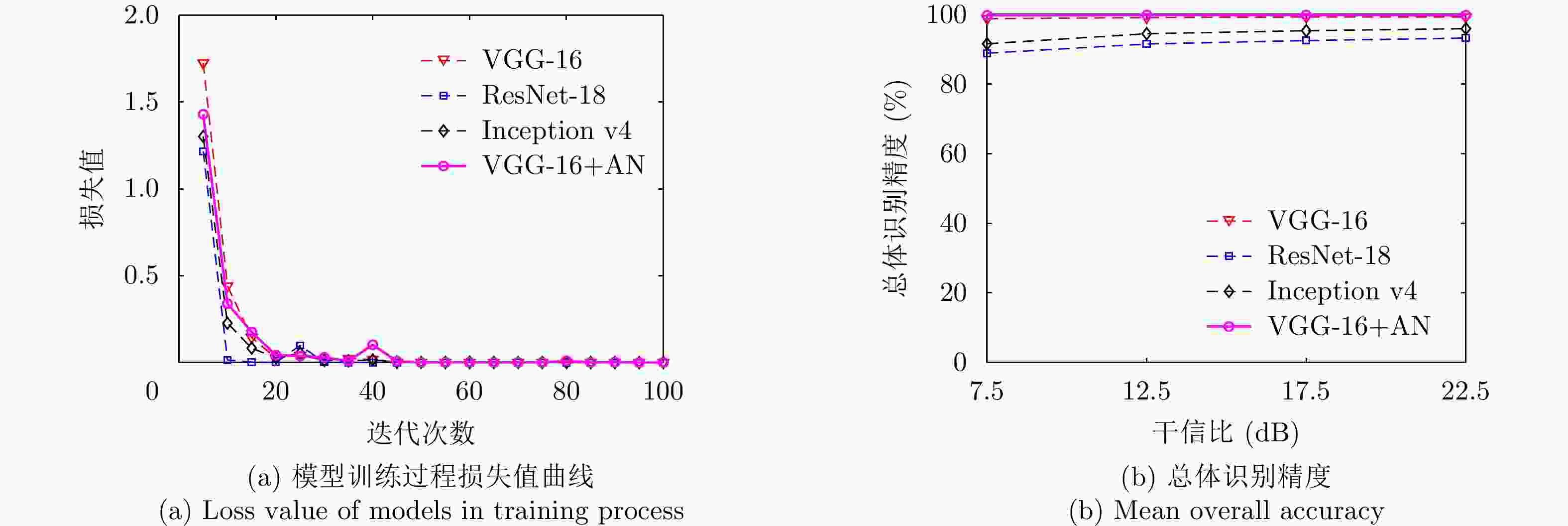
间歇采样延迟多抽头 微动干扰 OA JSR_7.5 VGG-16 100±0 98.41±2.46 100±0 97.46±2.15 99.68±0.63 100±0 100±0 94.29±4.33 99.37±0.78 98.80±0.70 ResNet-18 100±0 70.48±9.66 100±0 90.79±2.54 86.35±5.37 92.06±5.22 100±0 69.21±2.94 91.11±3.11 88.89±1.59 Inception v4 90.79±9.64 85.08±3.84 100±0 93.65±6.43 97.46±1.27 75.56±7.88 99.68±0.63 87.62±4.64 94.60±2.94 91.60±0.56 VGG-16+AN 100±0 99.68±0.63 100±0 99.05±0.78 100±0 100±0 100±0 99.37±0.78 100±0 99.79±0.13 JSR_12.5 VGG-16 100±0 99.15±0.98 100±0 98.31±1.93 99.89±0.21 100±0 100±0 95.56±3.61 99.47±0.67 99.15±0.63 ResNet-18 100±0 75.87±8.75 100±0 93.86±2.45 90.69±3.82 96.40±2.38 100±0 73.12±4.06 93.97±3.20 91.55±1.32 Inception v4 96.03±4.89 88.89±2.39 100±0 95.24±5.48 98.10±0.86 84.97±4.50 99.89±0.21 90.90±3.13 96.51±2.43 94.50±0.57 VGG-16+AN 100±0 99.89±0.21 100±0 99.58±0.40 99.79±0.42 100±0 100±0 99.58±0.62 100±0 99.87±0.11 JSR_17.5 VGG-16 100±0 99.37±0.74 100±0 98.65±1.60 99.92±0.16 100±0 100±0 96.03±3.33 99.60±0.50 99.29±0.55 ResNet-18 100±0 78.81±7.79 100±0 95.00±2.21 92.06±3.57 97.30±1.78 100±0 74.68±3.75 94.92±2.98 92.53±1.20 Inception v4 97.02±3.67 90.48±2.20 100±0 95.79±5.16 98.49±0.77 87.62±4.03 99.92±0.16 91.75±3.14 97.14±2.11 95.36±0.63 VGG-16+AN 100±0 99.92±0.16 100±0 99.68±0.30 99.84±0.32 100±0 100±0 99.44±0.59 100±0 99.88±0.10 JSR_22.5 VGG-16 100±0 99.49±0.59 100±0 98.92±1.28 99.94±0.13 99.24±0.25 100±0 96.44±3.08 99.68±0.40 99.30±0.51 ResNet-18 100±0 81.33±6.96 100±0 95.94±1.84 93.52±3.07 96.51±2.10 99.94±0.13 76.13±3.86 95.81±2.51 93.24±1.01 Inception v4 97.62±2.93 91.94±2.07 100±0 96.32±4.42 98.73±0.72 89.52±3.83 99.94±0.13 91.87±3.24 97.65±1.69 95.95±0.64 VGG-16+AN 100±0 99.94±0.13 100±0 99.75±0.24 99.87±0.25 99.49±0.52 100±0 99.37±0.57 100±0 99.82±0.12 表 3 实验2有源干扰类型识别结果(%)
Table 3. Active jamming type recognition results of experiment 2 (%)
测试集 方法 噪声
干扰固定
移频随机
移频分段
移频步进
移频距离向
间歇采样方位向
间歇采样延迟
多抽头微动
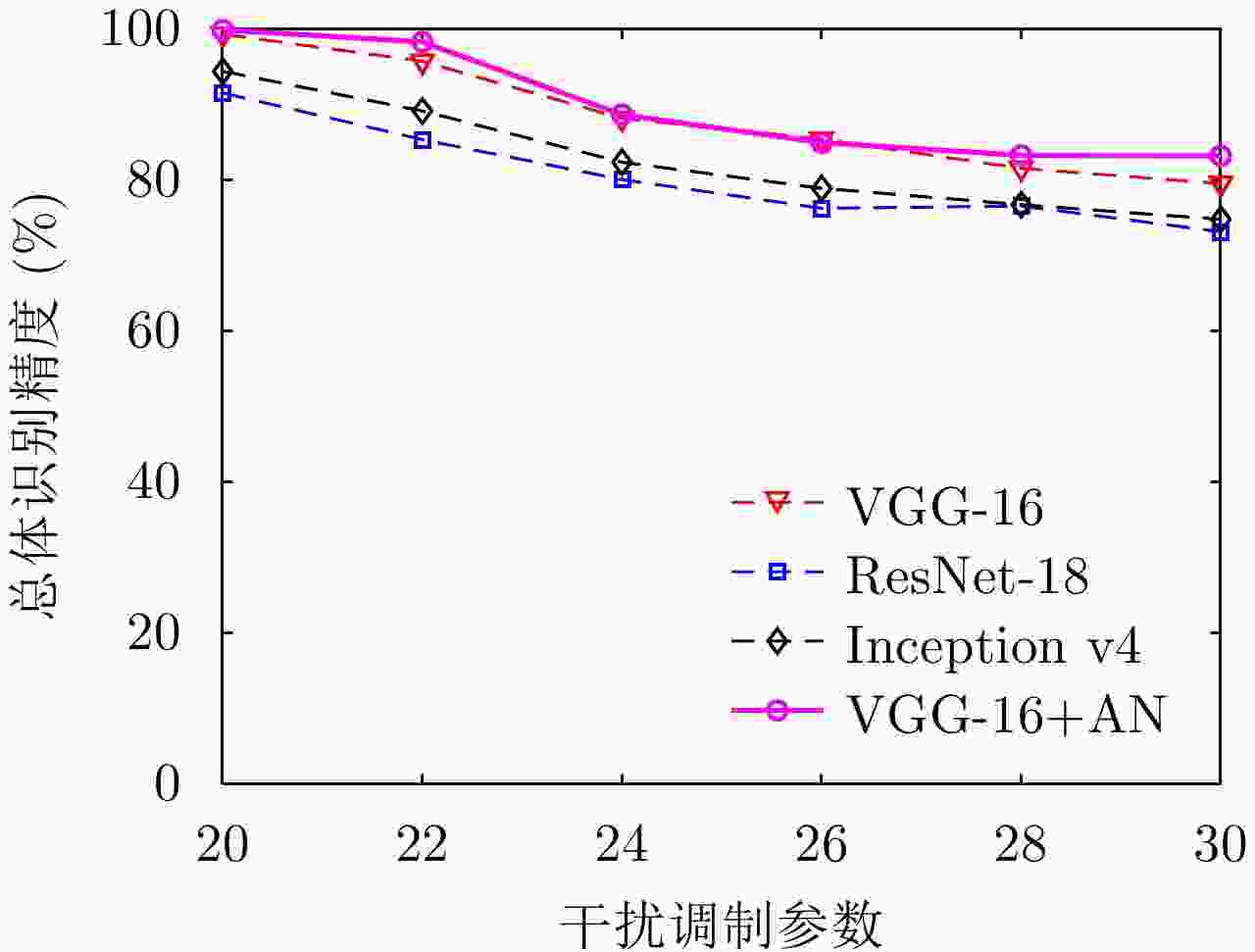
干扰OA Para_20 VGG-16 100±0 99.37±0.74 100±0 98.49±1.38 99.60±0.25 99.84±0.19 100±0 96.67±2.95 99.68±0.30 99.29±0.48 ResNet-18 99.86±0.28 77.94±7.19 100±0 93.89±2.47 91.11±3.30 94.37±2.51 100±0 72.86±3.31 93.65±2.50 91.52±1.27 Inception v4 94.03±3.11 89.92±2.87 100±0 94.76±5.05 98.10±1.16 84.44±5.12 99.44±0.59 91.67±3.65 96.98±1.41 94.37±0.77 VGG-16+AN 100±0 99.92±0.16 100±0 99.52±0.30 99.92±0.16 100±0 100±0 99.37±0.78 100±0 99.86±0.09 Para_22 VGG-16 100±0 98.89±0.95 100±0 93.10±5.64 99.84±0.19 99.76±0.32 100±0 87.30±5.42 82.38±7.44 95.70±1.41 ResNet-18 99.94±0.12 72.86±6.93 99.76±0.48 86.67±5.85 89.37±3.82 92.14±3.97 99.76±0.32 62.46±8.97 65.00±5.47 85.33±2.26 Inception v4 94.15±3.18 91.75±4.37 100±0 73.50±16.35 95.71±1.21 83.49±5.11 99.29±0.53 91.90±4.68 72.22±8.26 89.12±1.43 VGG-16+AN 100±0 99.44±0.69 100±0 96.59±4.34 99.60±0.35 99.84±0.19 100±0 95.16±6.31 93.81±2.85 98.27±1.14 Para_24 VGG-16 100±0 99.37±0.48 100±0 94.29±4.17 100±0 99.84±0.32 100±0 91.19±4.06 8.73±4.46 88.16±0.53 ResNet-18 99.98±0.04 72.54±7.96 99.84±0.32 88.57±5.84 89.37±4.85 94.05±3.47 100±0 60.95±5.30 15.16±2.61 80.05±2.31 Inception v4 94.21±3.38 92.46±2.81 100±0 76.11±9.43 96.35±2.67 83.41±5.06 98.49±0.85 91.11±8.15 8.89±6.80 82.34±0.64 VGG-16+AN 100±0 99.68±0.30 100.0±0 99.29±1.24 100±0 99.60±0.50 100±0 92.70±8.58 6.51±4.93 88.64±1.36 Para_26 VGG-16 100±0 99.37±0.89 100±0 95.71±4.74 99.44±0.78 99.68±0.39 100±0 69.60±16.78 4.76±6.06 85.40±2.01 ResNet-18 99.88±0.24 66.59±8.44 99.84±0.32 88.02±4.01 85.56±8.16 89.44±4.07 100±0 44.21±6.53 12.62±3.28 76.24±2.34 Inception v4 94.17±3.60 91.67±3.98 100±0 64.60±17.06 93.49±3.28 84.44±4.49 99.84±0.32 73.80±13.37 7.78±4.67 78.88±0.95 VGG-16+AN 100±0 99.84±0.32 100±0 92.5±12.77 99.05±1.17 98.33±2.39 100±0 73.40±23.68 1.19±1.20 84.94±3.68 Para_28 VGG-16 100±0 99.92±0.16 100±0 85.5±16.14 98.73±1.38 98.73±1.16 100±0 33.20±19.38 17.50±13.83 81.53±3.88 ResNet-18 99.88±0.24 71.1±10.00 99.76±0.32 81.03±5.15 84.05±7.81 84.44±6.63 100±0 38.41±3.30 30.08±4.91 76.54±1.47 Inception v4 94.07±3.67 92.46±3.21 100±0 49.1±22.05 93.73±4.39 81.59±5.35 99.60±0.43 52.90±17.55 26.90±11.50 76.72±2.78 VGG-16+AN 100±0 100±0 99.84±0.32 82.7±19.32 97.22±3.13 97.14±2.71 100±0 42.50±26.56 29.60±11.54 83.25±5.08 Para_30 VGG-16 100±0 99.21±0.75 100±0 73.3±26.03 96.75±4.36 94.76±6.04 99.92±0.16 20.30±16.48 31.20±17.88 79.51±5.44 ResNet-18 99.82±0.36 59.50±12.56 99.84±0.32 75.32±7.83 73.70±13.23 76.35±6.43 99.68±0.63 37.54±5.86 36.35±5.60 73.13±2.42 Inception v4 93.91±3.35 89.84±3.76 100±0 45.60±20.60 88.41±8.62 78.57±6.04 99.13±0.30 39.50±16.96 37.90±10.90 74.77±2.82 VGG-16+AN 100±0 99.84±0.19 99.84±0.32 79.7±19.91 94.92±4.77 93.25±6.03 99.92±0.16 34.30±26.16 46.67±7.65 83.17±4.71 -
[1] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005. [2] Bu-Chin Wang. Digital Signal Processing Techniques and Applications in Radar Image Processing[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. [3] 王雪松, 陈思伟. 合成孔径雷达极化成像解译识别技术的进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109WANG Xuesong and CHEN Siwei. Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interpretation and recognition: Advances and perspectives[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109 [4] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, XIAO Shunping, et al. Target Scattering Mechanism in Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar: Interpretation and Application[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2018. [5] 陈静. 雷达无源干扰原理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2009: 88–95.CHEN Jing. Principles of Radar Passive Jamming[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2009: 88–95. [6] 李永波, 黄成亮, 赵桥, 等. 伪装网的发展现状及趋势[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(S1): 576–577, 599.LI Yongbo, HUANG Chengliang, ZHAO Qiao, et al. The development status and trend of the camouflage mat[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(S1): 576–577, 599. [7] 肖冰, 李军念, 陈秦, 等. 国外军用伪装网技术的现状及发展趋势[J]. 四川兵工学报, 2003, 24(5): 64–66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0707.2003.05.022XIAO Bing, LI Junnian, CHEN Qin, et al. The status and developmental trend of the military camouflage net[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2003, 24(5): 64–66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0707.2003.05.022 [8] 李郝亮, 陈思伟, 王雪松. 海面角反射器的极化旋转域特性研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(7): 2065–2073. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.07.01LI Haoliang, CHEN Siwei, and WANG Xuesong. Study on characterization of sea corner reflectors in polarimetric rotation domain[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(7): 2065–2073. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.07.01 [9] 胡海, 张林, 张小东. 舰载充气式角反射体反导装备发展及运用[J]. 国防科技, 2018, 39(2): 74–77. doi: 10.13943/j.issn671-4547.2018.02.12HU Hai, ZHANG Lin, and ZHANG Xiaodong. A study on equipment developments and operational using of ship born gas-filled anti-missile multi-corner reflector[J]. Defense Technology Review, 2018, 39(2): 74–77. doi: 10.13943/j.issn671-4547.2018.02.12 [10] 张志远, 张介秋, 屈绍波, 等. 雷达角反射器的研究进展及展望[J]. 飞航导弹, 2014(4): 64–70. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.2014.04.021ZHANG Zhiyuan, ZHANG Jieqiu, QU Shaobo, et al. Research progress and prospect of radar corner reflector[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2014(4): 64–70. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.2014.04.021 [11] 秋云. 充气武器, 以假乱真迷惑敌人[J]. 科学启蒙, 2011(11): 27.QIU Yun. Inflatable weapons confuse the enemy with the real[J]. Science Initiation, 2011(11): 27. [12] 崔铁军. 电磁超材料——从等效媒质到现场可编程系统[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2020, 50(10): 1427–1461. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0123CUI Tiejun. Electromagnetic metamaterials—from effective media to field programmable systems[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2020, 50(10): 1427–1461. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0123 [13] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, and KUANG Gangyao. Radio frequency interference detection and localization in sentinel-1 images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(11): 9270–9281. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3049472 [14] 汪日超. 星载SAR压制式干扰与抗干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2017.WANG Richao. Research on spaceborne SAR compression interference and anti-jamming technology[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017. [15] 宋杰, 张华春, 郑慧芳. 基于微动调制的梳状谱灵巧噪声压制干扰[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2020, 18(5): 531–538, 545. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.05.011SONG Jie, ZHANG Huachun, and ZHENG Huifang. Suppression jamming of comb spectrum smart noise based on micro-motion modulation[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2020, 18(5): 531–538, 545. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.05.011 [16] 邓云凯, 郑远, 胡英辉. 合成孔径雷达转发式干扰分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(1): 69–74. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01636DENG Yunkai, ZHENG Yuan, and HU Yinghui. Analysis of synthetic aperture radar repeater jamming[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(1): 69–74. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01636 [17] 赵博, 杨军, 孙光才, 等. 一种虚假大场景SAR快速转发式欺骗干扰方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(4): 963–968. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.0050ZHAO Bo, YANG Jun, SUN Guangcai, et al. A method of SAR fast repeater deception jamming for large false scene[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(4): 963–968. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.0050 [18] 陈思伟, 代大海, 李永祯, 等. SAR二维余弦调相转发散射波干扰原理[J]. 电子学报, 2009, 37(12): 2620–2625. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.12.003CHEN Siwei, DAI Dahai, LI Yongzhen, et al. The theory of 2-D cosinusoidal phase-modulated repeater scatter-wave jamming to SAR[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2009, 37(12): 2620–2625. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.12.003 [19] 房明星, 毕大平, 沈爱国. 多通道SAR-GMTI二维余弦调相散射波干扰[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2018, 52(3): 356–364. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2018.03.015FANG Mingxing, BI Daping, and SHEN Aiguo. 2-D cosinusoidal phase-modulated scatter-wave jamming to multi-channel SAR-GMTI[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2018, 52(3): 356–364. doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2018.03.015 [20] 王雪松, 肖顺平, 李永祯, 等. 合成孔径雷达微动干扰[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.WANG Xuesong, XIAO Shunping, LI Yongzhen, et al. Micro-Motion Jamming of Sunthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. [21] 黄岩, 赵博, 陶明亮, 等. 合成孔径雷达抗干扰技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 86–106. doi: 10.12000/JR19113HUANG Yan, ZHAO Bo, TAO Mingliang, et al. Review of synthetic aperture radar interference suppression[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 86–106. doi: 10.12000/JR19113 [22] 赵宗锋. 基于信号波形设计的SAR抗干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2007.ZHAO Zongfeng. SAR anti-jamming based on waveform design[D]. [Master dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2007. [23] AXELSSON S R J. Noise radar using random phase and frequency modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(11): 2370–2384. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.834589 [24] ZHAO Bo, HUANG Lei, LI Jian, et al. Target reconstruction from deceptively jammed single-channel SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(1): 152–167. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2744178 [25] YANG Huizhang, HE Yaomin, DU Yanlei, et al. Two-dimensional spectral analysis filter for removal of LFM Radar interference in spaceborne SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5219016. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3132495 [26] YANG Huizhang, LI Kun, LI Jie, et al. BSF: Block subspace filter for removing narrowband and wideband radio interference artifacts in single-look complex SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5211916. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3096538 [27] 周超, 刘泉华, 胡程. 间歇采样转发式干扰的时频域辨识与抑制[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 100–106. doi: 10.12000/JR18080ZHOU Chao, LIU Quanhua, and HU Cheng. Time-frequency analysis techniques for recognition and suppression of interrupted sampling repeater jamming[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 100–106. doi: 10.12000/JR18080 [28] TAO Mingliang, ZHOU Feng, and ZHANG Zijing. Wideband interference mitigation in high-resolution airborne synthetic aperture Radar data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(1): 74–87. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2450754 [29] 陶臣嵩, 陈思伟, 肖顺平. 基于深度学习模型的SAR图像间歇采样转发干扰检测[J/OL]. 系统工程与电子技术. 待出版.TAO Chensong, CHEN Siwei, and XIAO Shunping. SAR image interrupted sampling repeater jamming detection based on deep learning models[J/OL]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, in press. [30] 黄洪旭, 黄知涛, 周一宇. 对合成孔径雷达的移频干扰研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2006, 27(3): 463–468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2006.03.027HUANG Hongxu, HUANG Zhitao, and ZHOU Yiyu. A study on the shift-frequency jamming to SAR[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2006, 27(3): 463–468. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2006.03.027 [31] 黄洪旭, 黄知涛, 周一宇. 对合成孔径雷达的随机移频干扰[J]. 信号处理, 2007, 23(1): 41–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2007.01.009HUANG Hongxu, HUANG Zhitao, and ZHOU Yiyu. Randomly-shift-frequency jamming style to SAR[J]. Signal Processing, 2007, 23(1): 41–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2007.01.009 [32] 黄洪旭, 黄知涛, 吴京, 等. 对合成孔径雷达的步进移频干扰[J]. 宇航学报, 2011, 32(4): 898–902. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2011.04.028HUANG Hongxu, HUANG Zhitao, WU Jing, et al. Stepped-shift-frequency jamming to SAR[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2011, 32(4): 898–902. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2011.04.028 [33] 吴晓芳, 邢世其, 王雪松, 等. 对合成孔径雷达的脉间分段移频干扰[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2010, 26(1): 53–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2010.01.016WU Xiaofang, XING Shiqi, WANG Xuesong, et al. Interpulse subsection-shift-frequency jamming to SAR[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2010, 26(1): 53–57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2010.01.016 [34] 王雪松, 刘建成, 张文明, 等. 间歇采样转发干扰的数学原理[J]. 中国科学E辑:信息科学, 2006, 36(8): 891–901. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7259.2006.08.007WANG Xuesong, LIU Jiancheng, ZHANG Wenming, et al. The mathematic principle of intermittent sampling repeater jamming[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2006, 36(8): 891–901. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7259.2006.08.007 [35] 吴晓芳, 柏仲干, 代大海, 等. 对SAR的方位向间歇采样转发干扰[J]. 信号处理, 2010, 26(1): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2010.01.001WU Xiaofang, BAI Zhonggan, DAI Dahai, et al. Azimuth intermittent sampling repeater jamming to SAR[J]. Signal Processing, 2010, 26(1): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2010.01.001 [36] 陈思伟, 王雪松, 刘阳, 等. 合成孔径雷达二维余弦调相转发干扰研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(8): 1862–1866. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01218CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, LIU Yang, et al. The 2-D cosinusoidal phase modulation repeater jamming of SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(8): 1862–1866. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2008.01218 [37] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. [38] CHEN Siwei and TAO Chensong. PolSAR image classification using polarimetric-feature-driven deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(4): 627–631. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2799877 [39] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [40] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [41] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]. The 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 4278–4284. [42] RUEGG M, MEIER E, and NUESCH D. Vibration and rotation in millimeter-wave SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(2): 293–304. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.887025 [43] CHEN, V C, LI Fayin, HO S S, et al. Micro-doppler effect in radar: Phenomenon, model, and simulation study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 2–21. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603402 [44] CAO Yue, XU Jiarui, LIN Stephen, et al. GCNet: Non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 1971–1980. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: