-
摘要: 该文讨论了多输入多输出(MIMO)雷达发射波形和接收滤波器的联合优化问题,以确保与叠加的授权通信网络频谱兼容。考虑信号相关杂波的干扰,在发射能量、相似性和频谱兼容约束下,所提出的信干噪比(SINR)最大化的优化问题是NP-hard问题。为此,首先引入辅助变量对原问题进行修正,然后提出了一种基于乘子块连续上界极小化的原对偶(ABSUM)算法求解该问题。此外,利用内点法求解在ABSUM算法每个更新过程中涉及的二次规划问题。最后,仿真结果表明,ABSUM算法在输出SINR、波束图、频谱特性等方面优于现有方法。
-
关键词:
- 频谱兼容 /
- 多输入多输出雷达 /
- 收发联合设计 /
- 迭代分块连续上界最小化方法 /
- 基于交替方向乘子法
Abstract: This paper proposes a joint design method to optimize the transmit waveforms and receive filter bank in Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) structure ensuring spectral compatibility with the surrounding communication service network. Considering the signal-dependent clutter interference, under the constraints of transmission energy, waveform similarity and spectrum compatibility, the formulated optimization problem of the output Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio (SINR) maximization is NP-hard. Toward this end, an auxiliary variable is first introduced to modify the original problem, and then a primal-dual algorithm based on the Alternating Block Successive Upper-bound Minimization (ABSUM) method is developed to deal with the resulting problem. Furthermore, an interior point method is used to handle the quadratic programming problem involved in each update procedure of the devised ABSUM method. Finally, numerical simulations are performed to demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over state-of-the-art methods in terms of the optimized SINR, beampattern, computational complexity and ambiguity properties. -
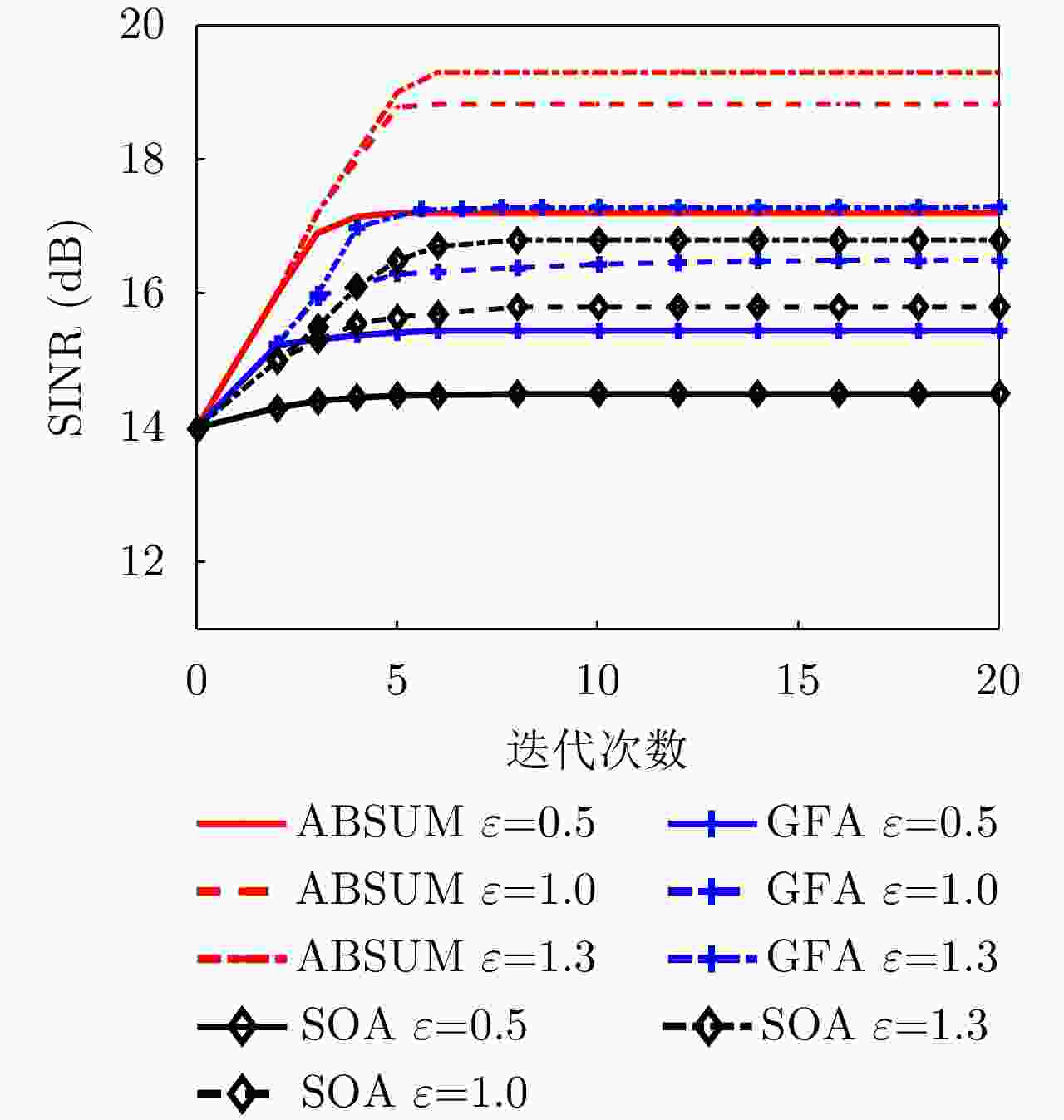
算法1 基于ABSUM的发射和接收联合设计算法 Alg. 1 ABSUM algorithm for solving transmit-receive design 输入:$k = 0$,初始化${\boldsymbol{c} }_{\rm{r}}^k$, ${\boldsymbol{t} }_{\rm{r}}^k$, ${{\boldsymbol{u}}^k}$, ${v^k}$和收敛参数$ {\epsilon}^{{\rm{abs}}} $, $ {\epsilon}^{{\rm{rel}}} $ 1:重复 2:$k = k + 1$ 3:通过求${\boldsymbol{\varPsi } }({ {\boldsymbol{c} }^k})$和${ {\boldsymbol{\varPsi } }_{{\rm{in}}} }({ {\boldsymbol{c} }^k})$的最大广义特征值来更新${{\boldsymbol{w}}^k}$。 4:使用内点法求解问题(16)和问题(18)更新${\boldsymbol{c} }_{\rm{r}}^k$和${\boldsymbol{t} }_{\rm{r}}^k$。 5:求解问题(12)更新${{\boldsymbol{u}}^k}$和${v^k}$ 6:如果满足收敛的终止条件,则算法停止迭代。 表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameter
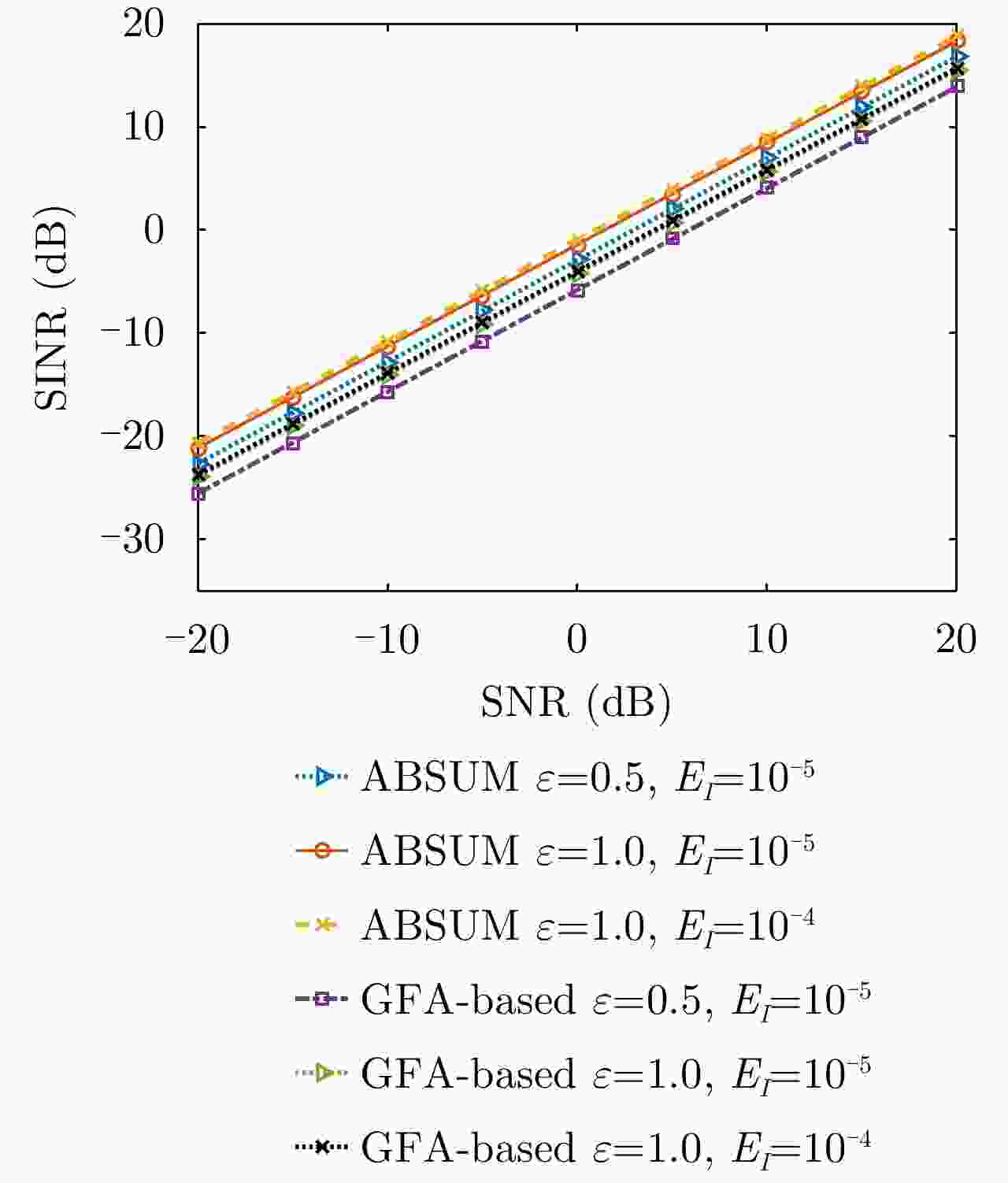
参数 数值 参数 数值 发射天线${N_{\rm{t}}}$ 4 接收天线${N_{\rm{r}}}$ 8 采样个数${N_{\rm{s}}}$ 64 干扰源角度${\theta _k}$ –50°, –10°, 40° 雷达目标角度${\theta _0}$ ${\text{1}}{5^ \circ }$ 无线网络归一化频率$f_{{\rm{lower}}}^i$, $f_{{\rm{upper}}}^i$ $[0.2,0.3]$
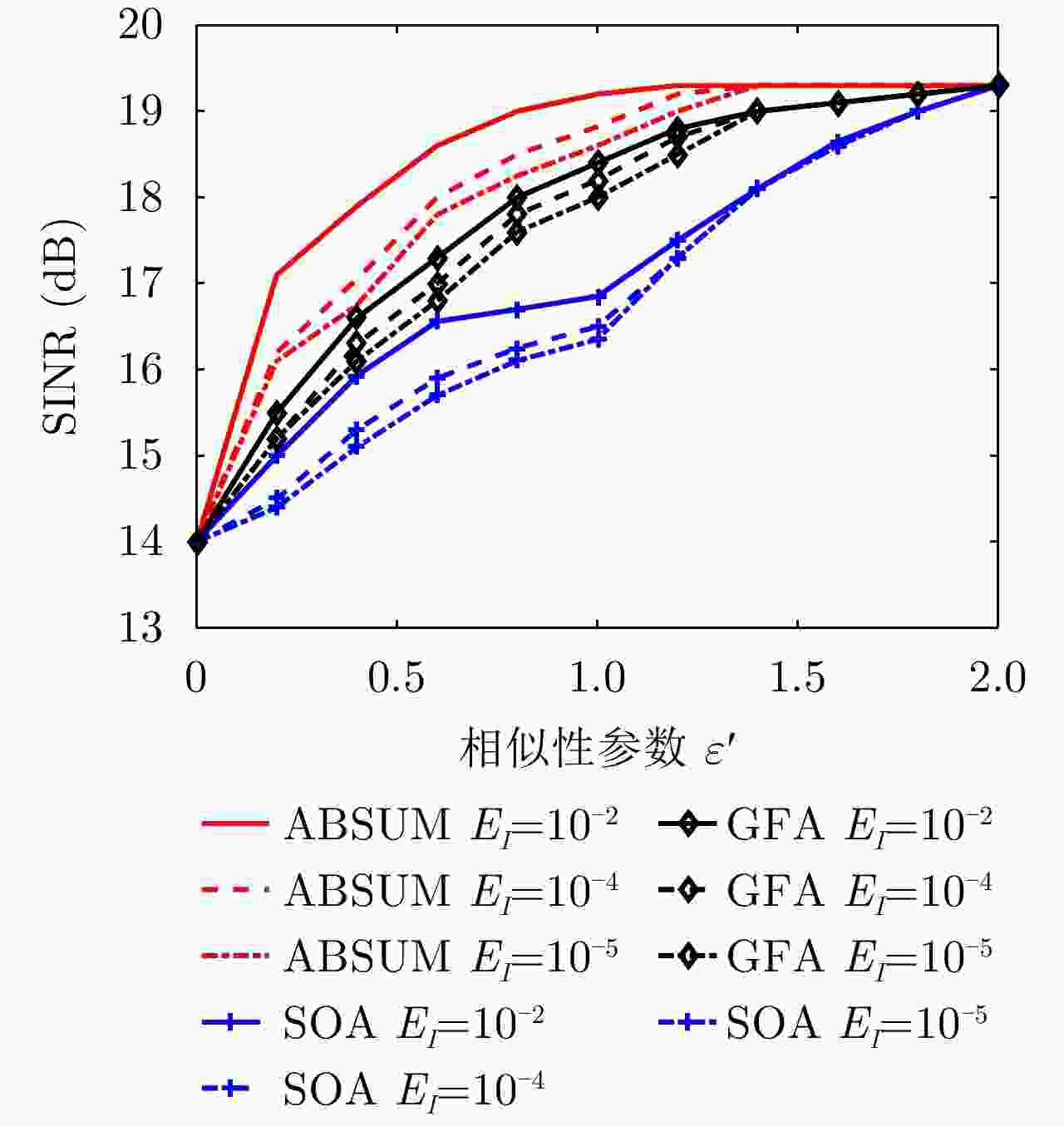
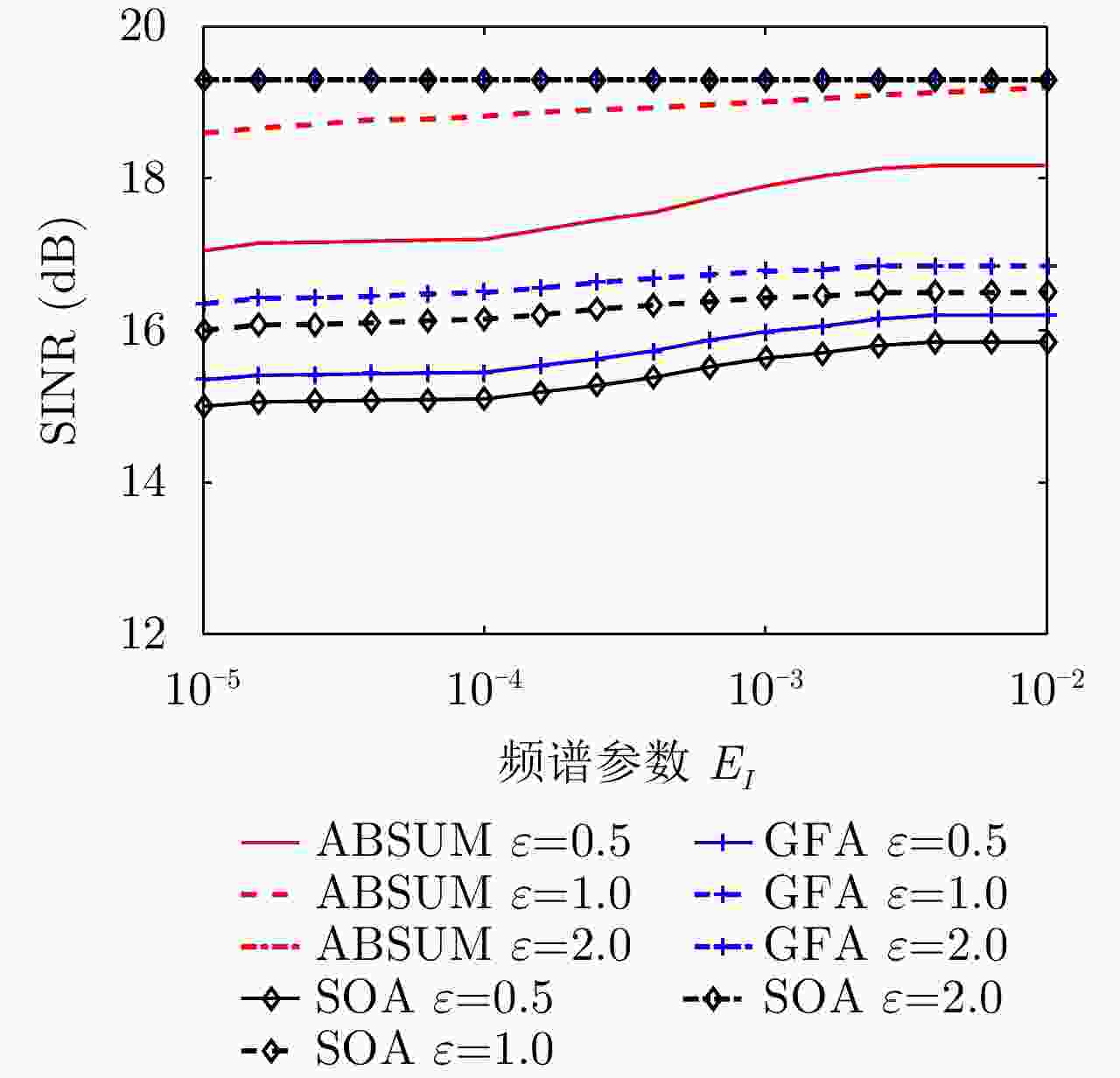
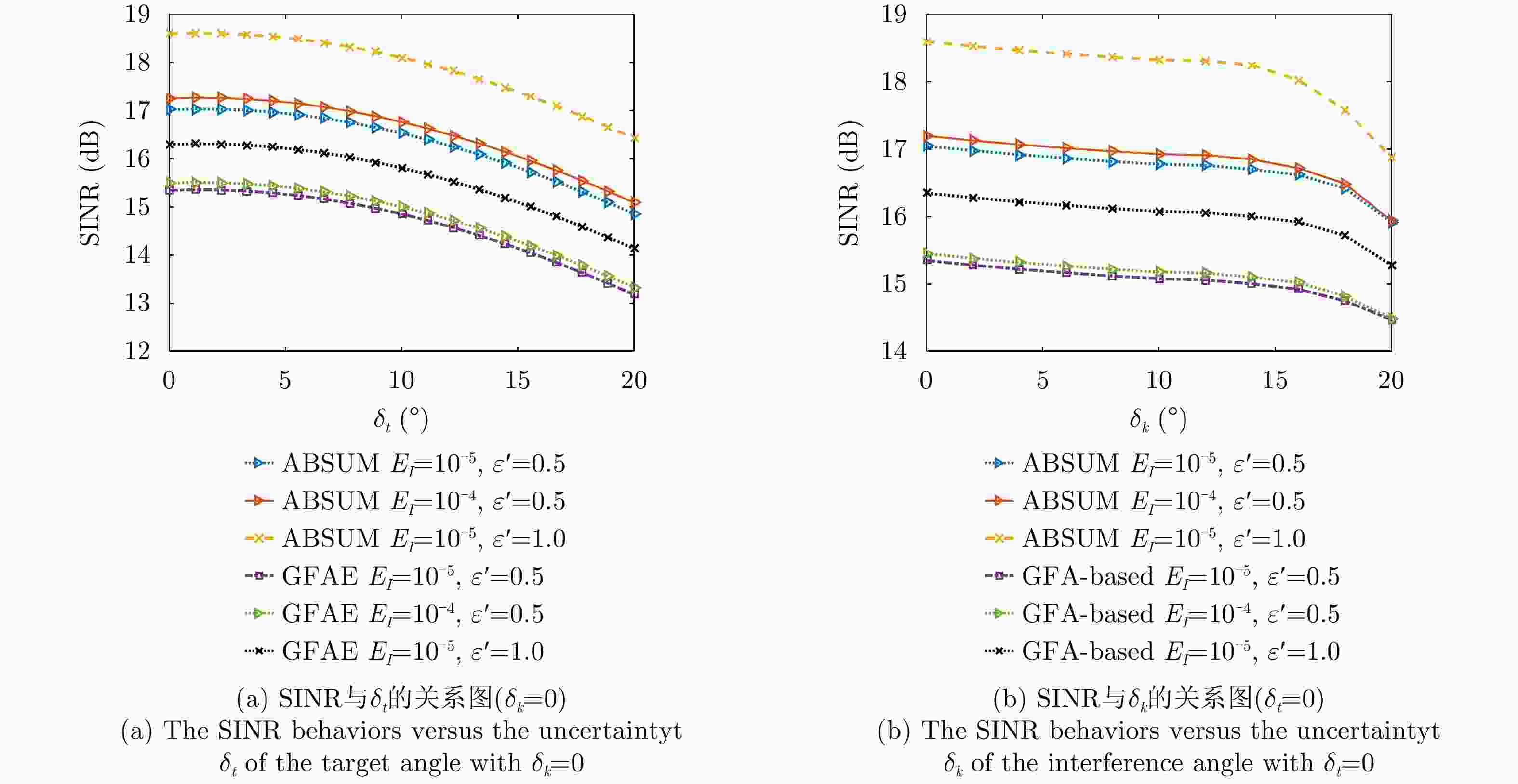
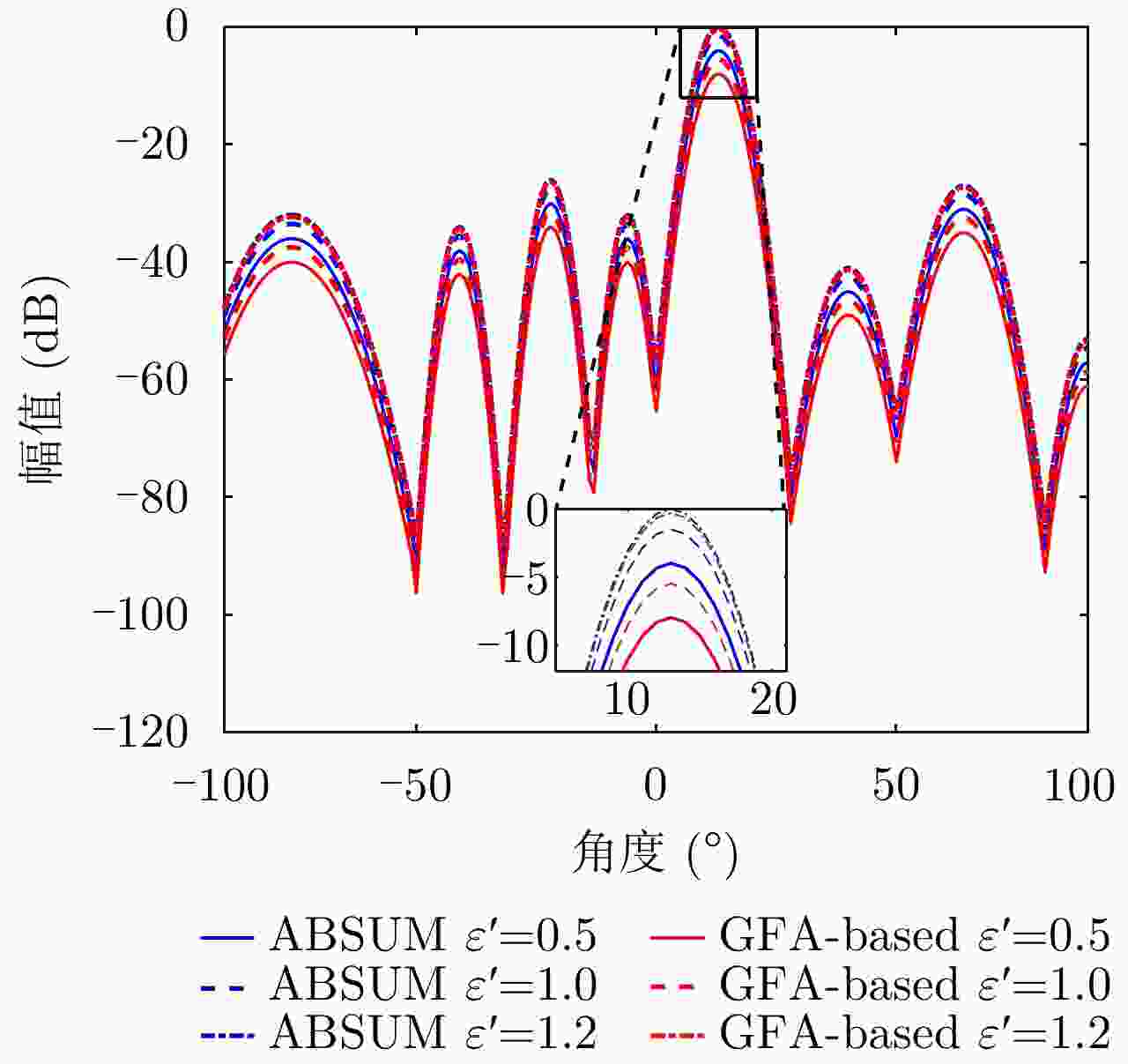
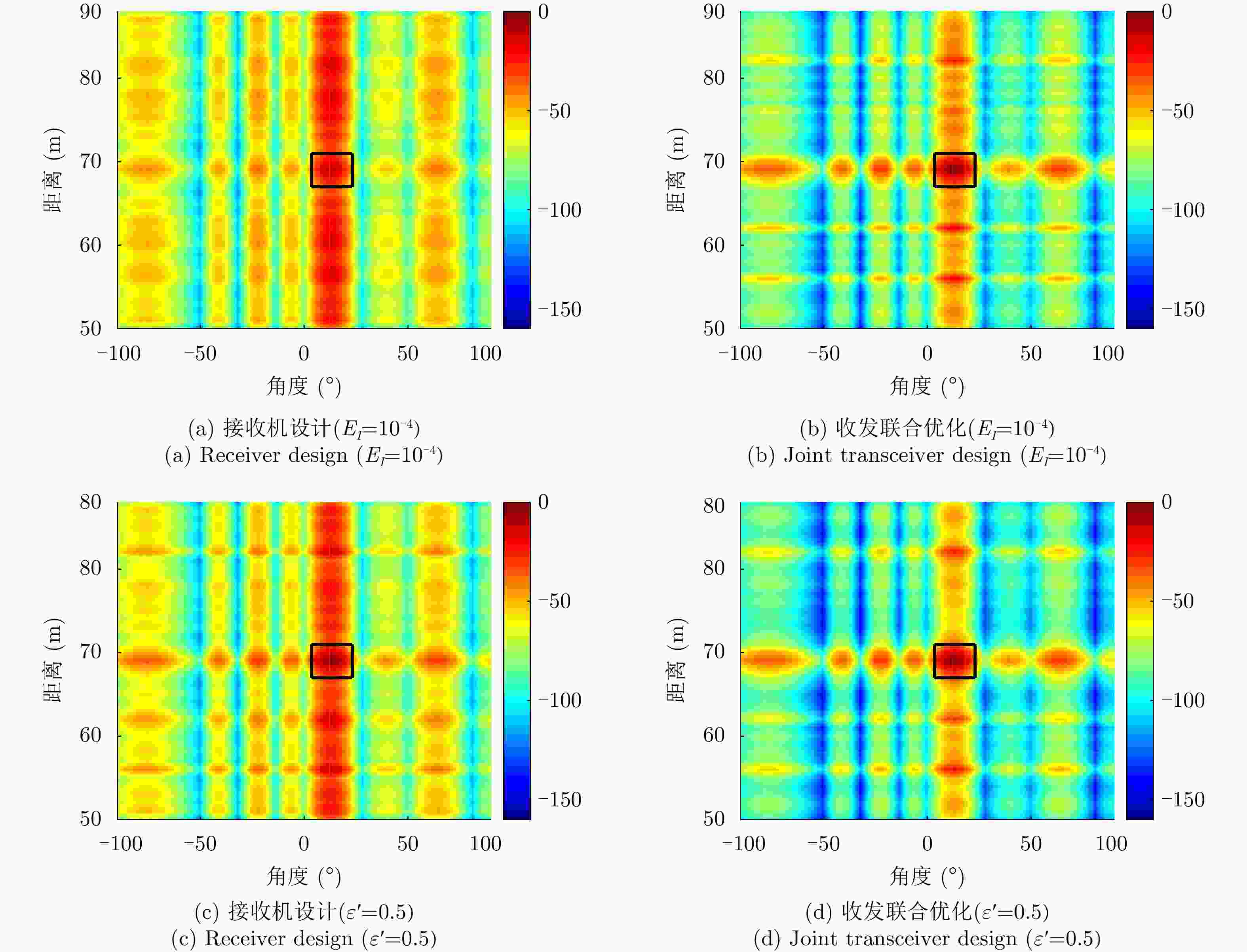
$[0.75,0.85]$最大干扰量${E_I}$ ${10}^{-2}, {10}^{-\text{3} }, {10}^{-\text{5} }$ 相似性参数$\varepsilon $ $0.5,0.8,1.0,2.0$ 表 2 ABSUM, GFA和SOA算法的优化SINR值(dB)和全局计算时间(s)
Table 2. SINR value (dB) and global computational times (s) for ABSUM, GFA and SOA
${\varepsilon'}$ ABSUM GFA SOA SINR Time SINR Time SINR Time 0.5 17.2 15.3 15.4 135.8 13.6 637.9 1.0 18.8 19.1 16.5 141.5 14.8 853.1 1.3 19.2 21.5 17.5 154.4 16.5 963.1 2.0 19.3 19.8 19.3 169.3 19.3 812.1 表 3 ABSUM、BCD、MM和GFA的SINR值(dB)和全局计算时间(s)
Table 3. SINR value (dB) and global computational times (s) for ABSUM, BCD, MM and GFA
${E_I}$ ABSUM SOA MM GFA SINR time SINR time SINR time SINR time ${10^{ - 2}}$ 19.2 14.3 16.7 45.3 19.1 10.2 16.8 120.8 ${10^{ - 3}}$ 19.0 16.2 16.8 55.2 18.9 13.4 16.7 134.5 ${10^{ - 4}}$ 18.8 19.1 16.8 66.8 18.6 15.7 16.5 141.5 -
[1] LI Jian and STOICA P. MIMO radar with colocated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2007, 24(5): 106–114. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2007.904812 [2] YU Xianxiang, CUI Guolong, YANG Jing, et al. MIMO radar transmit-receive design for moving target detection in signal-dependent clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(1): 522–536. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2951399 [3] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 杨婧, 等. 认知雷达波形优化设计方法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 537–557. doi: 10.12000/JR19072CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, YANG Jing, et al. An overview of waveform optimization methods for cognitive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 537–557. doi: 10.12000/JR19072 [4] AUBRY A, CAROTENUTO V, DE MAIO A, et al. Optimization theory-based radar waveform design for spectrally dense environments[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2016, 31(12): 14–25. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2016.150216 [5] STINCO P, GRECO M, GINI F, et al. Cognitive radars in spectrally dense environments[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2016, 31(10): 20–27. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2016.150193 [6] AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, GOVONI M A, et al. On the design of multi-spectrally constrained constant modulus radar signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 2231–2243. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2983642 [7] YAO Yu, WU Lenan, and LIU Haitao. Robust transceiver design in the presence of eclipsing loss for spectrally dense environments[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(3): 4334–4345. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.3024531 [8] YAO Yu, LIU Haitao, MIAO Pu, et al. MIMO radar design for extended target detection in a spectrally crowded environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021. [9] YAO Yu, LIU Haitao, and WU Lenan. Robust transmit waveform and receive filter design in the presence of eclipsing loss and signal-dependent interference[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 181: 107901. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107901 [10] CHEN Chunyang and VAIDYANATHAN P. MIMO radar waveform optimization with prior information of the extended target and clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(9): 3533–3544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2021632 [11] CUI Guoling, YU Xianxiang, CAROTENUTO V, et al. Space-time transmit code and receive filter design for colocated MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(5): 1116–1129. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2633242 [12] LIANG Junli, STOICA P, JING Yang, et al. Phase retrieval via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(1): 5–9. doi: 10.1109/lsp.2017.2767826 [13] ZHAO Licheng and PALOMAR D P. Maximin joint optimization of transmitting code and receiving filter in radar and communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(4): 850–863. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2016.2625267 [14] 付月, 崔国龙, 余显祥. 信号相关杂波背景下稳健的恒模序列与接收滤波器设计方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(3): 292–299. doi: 10.12000/JR16158FU Yue, CUI Guolong, and YU Xianxiang. Robust design of constant modulus sequence and receiver filter in the presence of signal-dependent clutter[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(3): 292–299. doi: 10.12000/JR16158 [15] AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, PIEZZO M, et al. Radar waveform design in a spectrally crowded environment via nonconvex quadratic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1138–1152. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120731 [16] WU Linlong, BABU P, and PALOMA D P. Transmit waveform/receive filter design for MIMO radar with multiple waveform constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(6): 1526–1540. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2017.2787115 [17] TANG Bo, LI Jian, and LIANG Junli. Alternating direction method of multipliers for radar waveform design in spectrally crowded environments[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 142: 398–402. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.08.003 [18] FAN Wen, LIANG Junli, LU Guangshan, et al. Spectrally-agile waveform design for wideband MIMO radar transmit beampattern synthesis via majorization-ADMM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1563–1578. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3052997 [19] AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, FARINA A, et al. Knowledge-aided (potentially cognitive) transmit signal and receive filter design in signal-dependent clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(1): 93–117. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6404093 [20] ALDAYEL O, MONGA V, and RANGASWAMY M. Successive QCQP refinement for MIMO radar waveform design under practical constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(14): 3760–3774. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2552501 [21] YANG Jing, AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, et al. Multi-spectrally constrained transceiver design against signal-dependent interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 1320–1332. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3144953 [22] SUN Ying, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Majorization-minimization algorithms in signal processing, communications, and machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(3): 794–816. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2601299 [23] TANG Bo and TANG Jun. Joint design of transmit waveforms and receive filters for MIMO radar space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(18): 4707–4722. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2569431 [24] CHENG Ziyang, HE Zishu, LIAO Bin, et al. MIMO radar waveform design with papr and similarity constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(4): 968–981. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2780052 [25] O’ROURKE S M, SETLUR P, RANGASWAMY M, et al. Quadratic semidefinite programming for waveform-constrained joint filter-signal design in STAP[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1744–1759. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2977271 [26] QIAN Junhui, LOPS M, ZHENG Le, et al. Joint system design for coexistence of MIMO radar and mimo communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(13): 3504–3519. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2831624 [27] CHENG Xu, AUBRY A, CIUONZO D, et al. Robust waveform and filter bank design of polarimetric radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(1): 370–384. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2650619 [28] HONG Mingyi, CHANG T H, WANG Xiangfeng, et al. A block successive upper-bound minimization method of multipliers for linearly constrained convex optimization[J]. Mathematics of Operations Research, 2020, 45(3): 833–861. doi: 10.1287/moor.2019.1010 [29] LUO Zhiquan, MA W K, SO A M C, et al. Semidefinite relaxation of quadratic optimization problems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(3): 20–34. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.936019 [30] RAZAVIYAYN M, HONG Mingyi, and LUO Zhiquan. A unified convergence analysis of block successive minimization methods for nonsmooth optimization[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2013, 23(2): 1126–1153. doi: 10.1137/120891009 [31] HONG Mingyi, RAZAVIYAYN M, LUO Zhiquan, et al. A unified algorithmic framework for block-structured optimization involving big data: With applications in machine learning and signal processing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2016, 33(1): 57–77. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2015.2481563 [32] GERSHMAN A B, SIDIROPOULOS N D, SHAHBAZPANAHI S, et al. Convex optimization-based beamforming[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(3): 62–75. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.936015 [33] CUI Guolong, LI Hongbin, and RANGASWAMY M. MIMO radar waveform design with constant modulus and similarity constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 62(2): 343–353. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288086 [34] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [35] 王璐璐. 基于信息论的自适应波形设计[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2015.WANG Lulu. Adaptive waveform design based on information theory[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2015. [36] 张钰. 基于最大互信息准则的认知雷达波形优化算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2012.ZHANG Yu. Study on the waveform design algorithm for cognitive radar based on maximum mutual information rule[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2012. [37] TANG Bo and LI Jian. Spectrally constrained MIMO radar waveform design based on mutual information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(3): 821–834. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2887186 [38] GRANT M and BOYD S. CVX package[EB/OL]. http://www.cvxr.com/cvx.r, 2012. [39] YU Xianxiang, ALHUJAILI K, CUI Guolong, et al. MIMO radar waveform design in the presence of multiple targets and practical constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1974–1989. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2979602 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: