SAR Elevation Control Point Extraction Combining Multistrategy ATLAS Data Preference and Image Matching
-
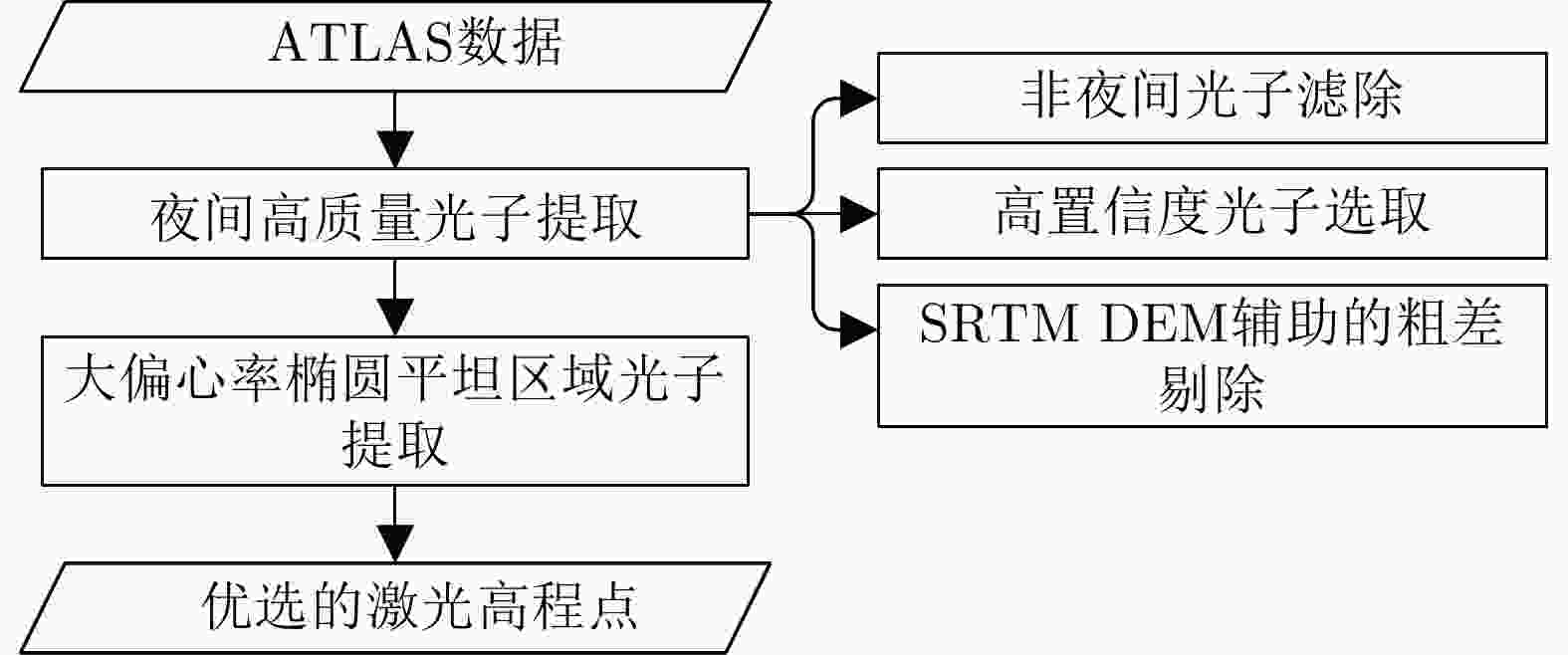
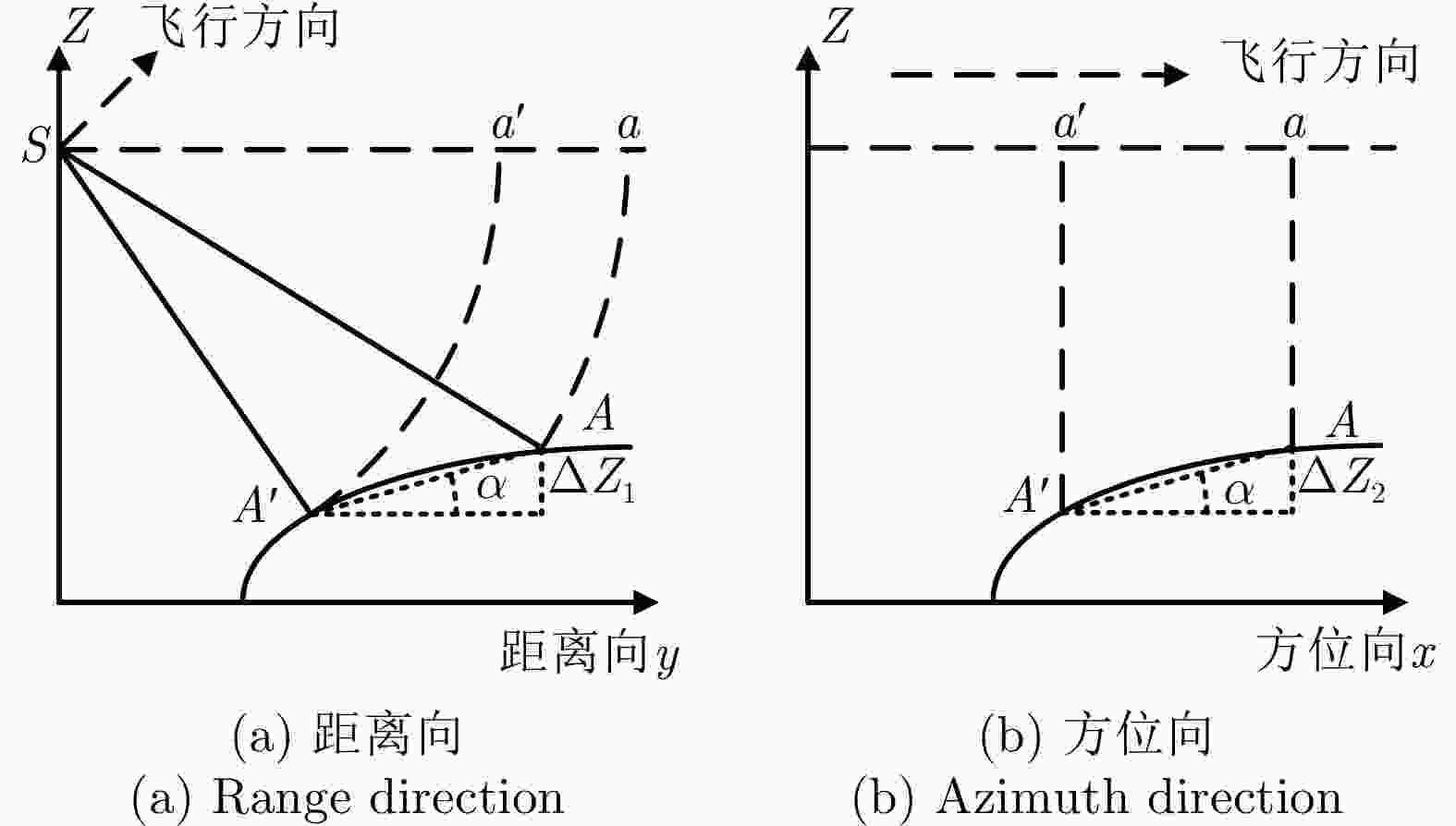
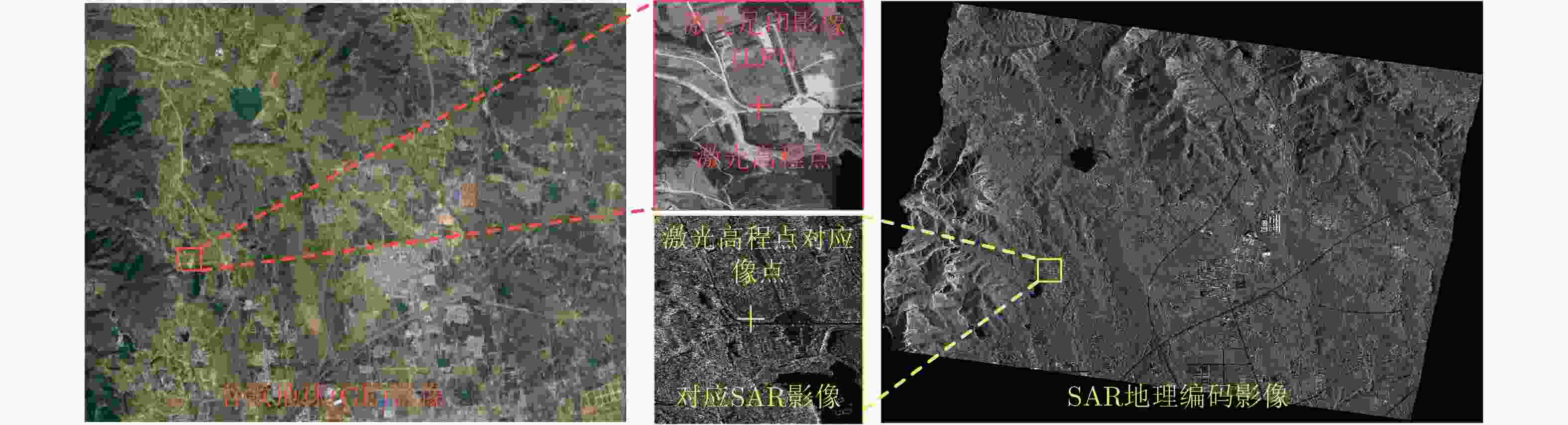
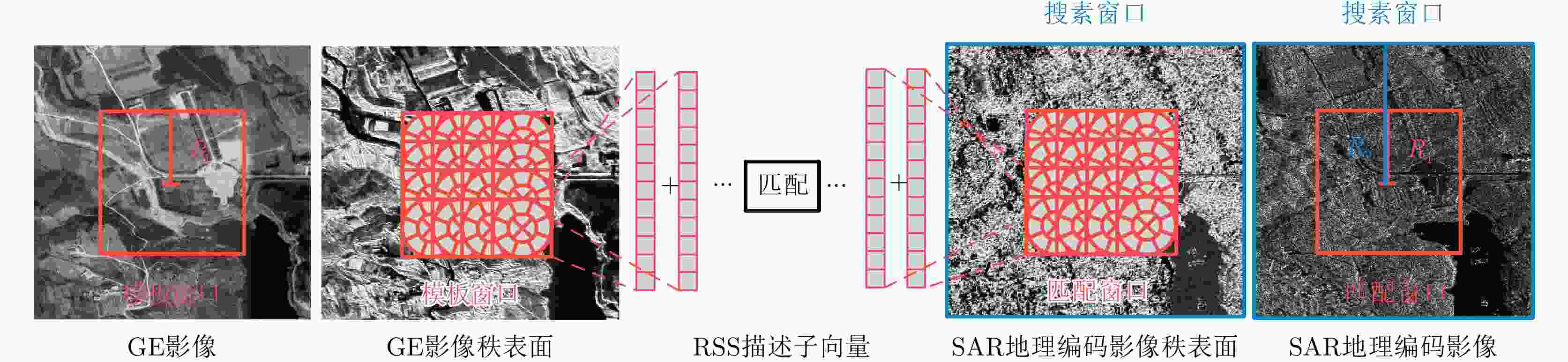
摘要: 为了精化星载SAR影像几何参数并提高立体定位精度,借鉴星载激光测高数据光学遥感影像高程控制点提取思路,设计了一种多策略高级地形激光测高系统(ATLAS)数据优选与影像匹配相结合的SAR高程控制点提取方法。该方法采用非夜间观测光子滤除、高置信度光子选取、SRTM DEM辅助的粗差剔除、大偏心率椭圆滤波核平坦区域光子筛选等多种策略,从ATLAS数据ATL03级产品中提取高质量、平坦区域的激光高程点,再依据SRTM DEM对斜距SAR影像进行地理编码,按激光高程点的平面坐标选取局部谷歌地球影像作为足印影像,采用秩自相似描述子进行足印影像与SAR地理编码影像的匹配,得到与激光高程点对应的SAR影像像点坐标,从而提取SAR高程控制点。采用中国登封市、日本横须贺市两个区域的ATLAS数据进行了高分三号SAR高程控制点提取实验,利用提取的高程控制点进行SAR影像几何参数精化,大幅提升了立体定位精度,验证了该文高程控制点提取方法的可行性和有效性。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达 /
- 高分三号 /
- 冰、云和陆地高程卫星-2 /
- 有理函数模型 /
- 定位
Abstract: To refine the geometric parameters of satellite-based SAR images and improve the stereo positioning accuracy, a method of SAR elevation control point extraction combining multistrategy ATLAS data preference and image matching has been developed. This method is based on the concept of optical remote sensing image elevation control point extraction from satellite-based laser altimetry data. The method employs various strategies, such as non-night observation photon filtering, high confidence photon selection, SRTM DEM-assisted coarse difference rejection, and large eccentricity elliptical filtering kernel flat area photon screening. To extract laser elevation points with high quality and flat area from ATLAS data for ATL03 level products. Then the geocoding of the slant range SAR images is performed using the SRTM DEM. The local Google Earth images are selected as the footprint images according to the plane coordinates of the laser elevation points. The rank self-similarity descriptor is used to match the footprint images with the SAR geocoded images. The coordinates of the SAR images corresponding to the laser elevation points are obtained. Thus, SAR elevation control points are extracted. The extraction of GF-3 SAR elevation control points was performed using ATLAS data from two regions: Dengfeng, China, and Yokosuka, Japan. The geometric parameter refinement of SAR images using extracted elevation control points significantly improved the accuracy of stereo positioning and verified that the method for extracting elevation control points described in this paper is feasible and effective. -
表 1 算法使用到的ATL03参数
Table 1. ATL03 parameters used by the algorithm
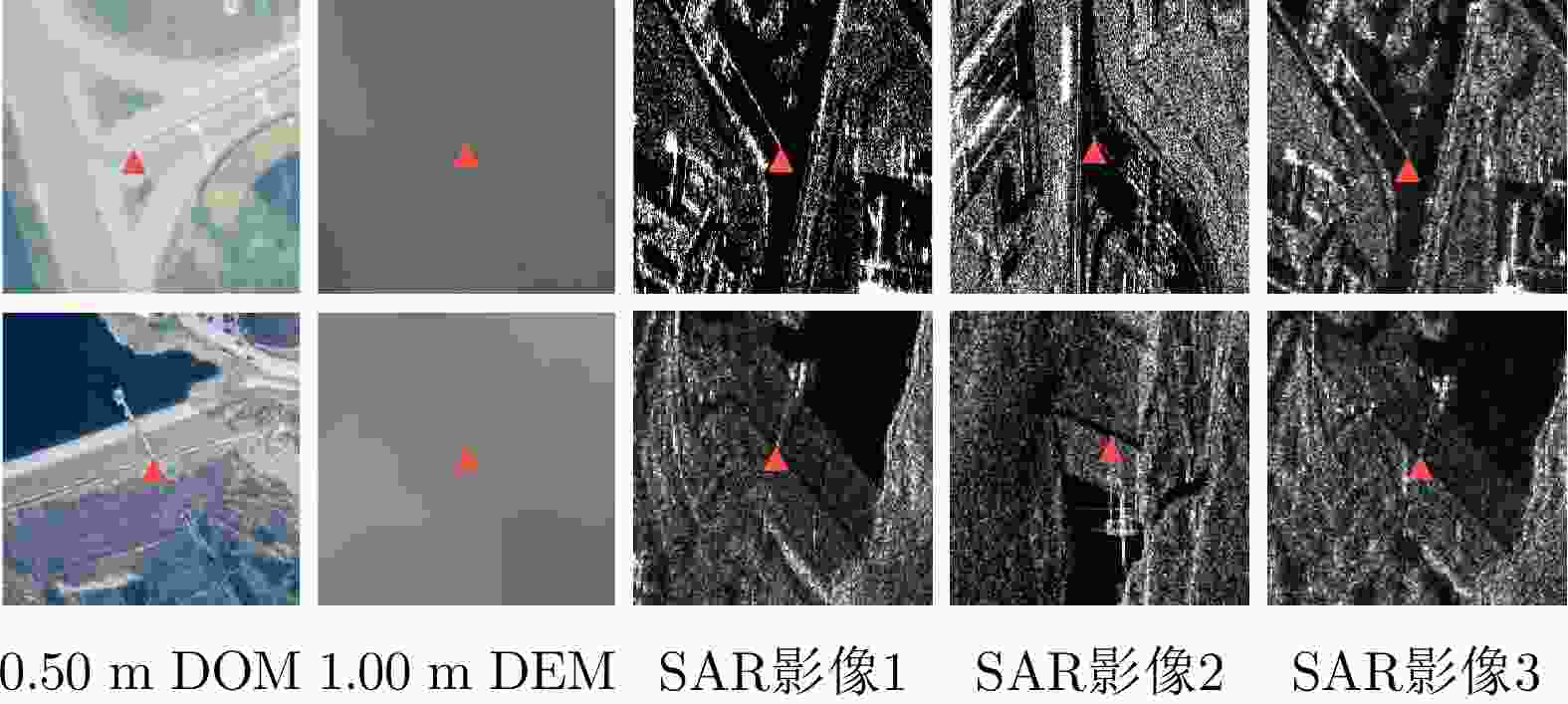
参数 含义 本文符号 lat_ph 每个接收光子纬度(WGS84) B lon_ph 每个接收光子经度(WGS84) L h_ph 每个接收光子高程(WGS84椭球高) H signal_conf_ph 每个接收光子置信度 C data_start_utc 数据开始时间 ${t_0}$ dist_ph_along 每个接收光子在该组中的沿轨距离 ${l_i}$ segment_length 每组沿轨距离(19.8~20.2 m) ${L_i}$ segment_ph_cnt 每组内光子数 ${w_i}$ 表 2 SAR影像数据基本参数
Table 2. Basic parameters of SAR image data
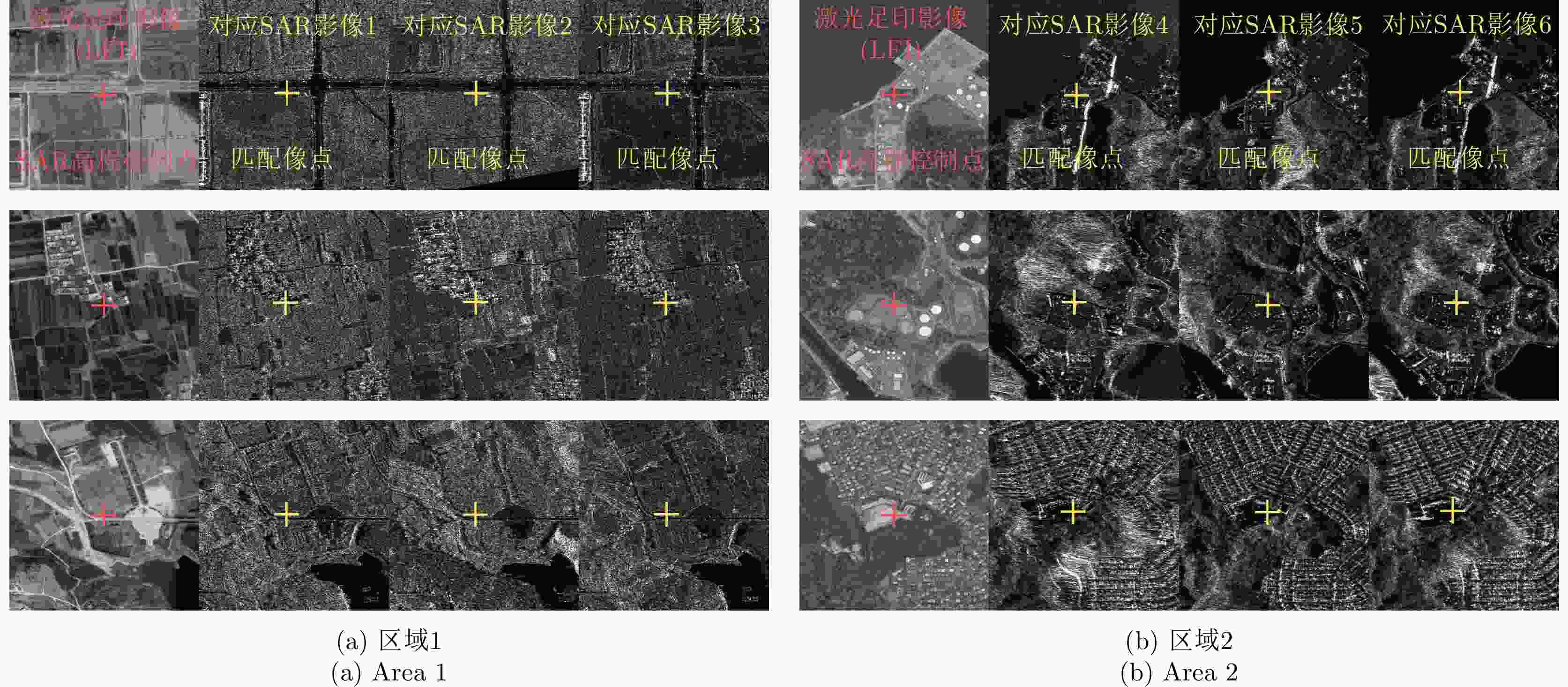
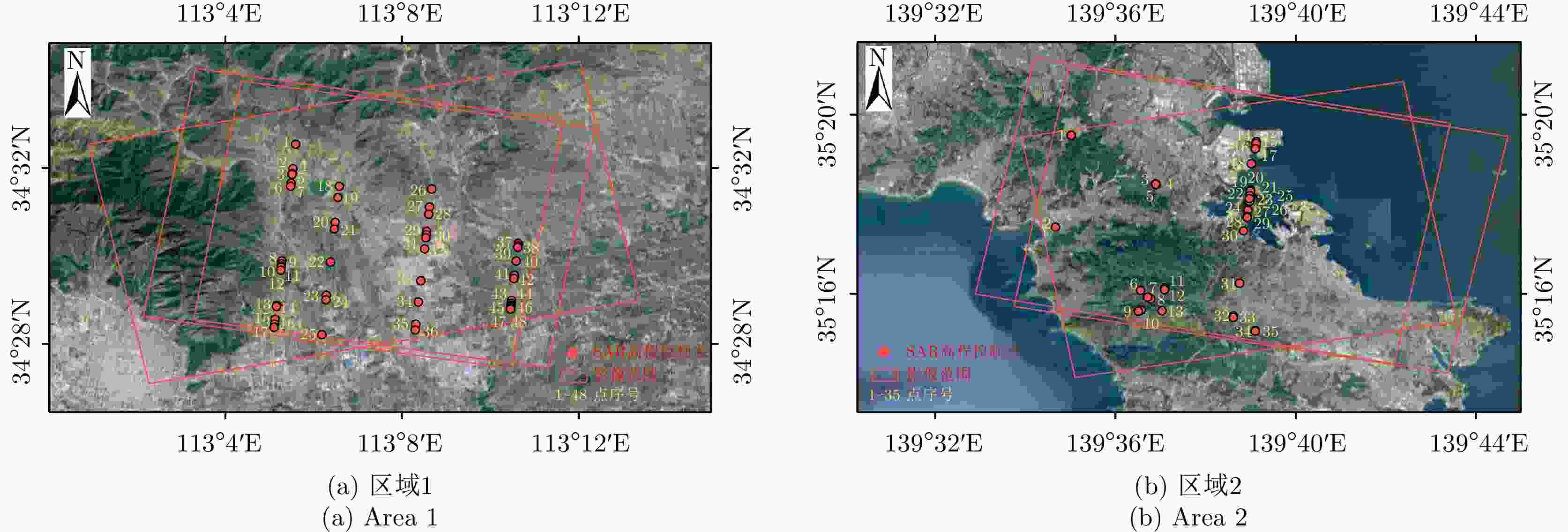
区域 序号 成像日期 轨道类型 入射角 尺寸(像素) 中心经纬度 区域1 影像1 20191021 升轨 23.31°~24.58° 32966$ \times $12576 (113.114°E, 34.514°N) 影像2 20191206 降轨 42.52°~43.18° 30944$ \times $15648 (113.120°E, 34.512°N) 影像3 20190829 降轨 46.24°~46.82° 28224$ \times $16056 (113.130°E, 34.511°N) 区域2 影像4 20190116 升轨 38.65°~39.38° 30558$ \times $14624 (139.645°E, 35.290°N) 影像5 20190116 降轨 25.16°~26.32° 31920$ \times $12576 (139.645°E, 35.296°N) 影像6 20190121 降轨 35.46°~36.25° 30638$ \times $13600 (139.642°E, 35.296°N) 表 3 不同筛选条件下光子数量
Table 3. The number of photons under different screening conditions
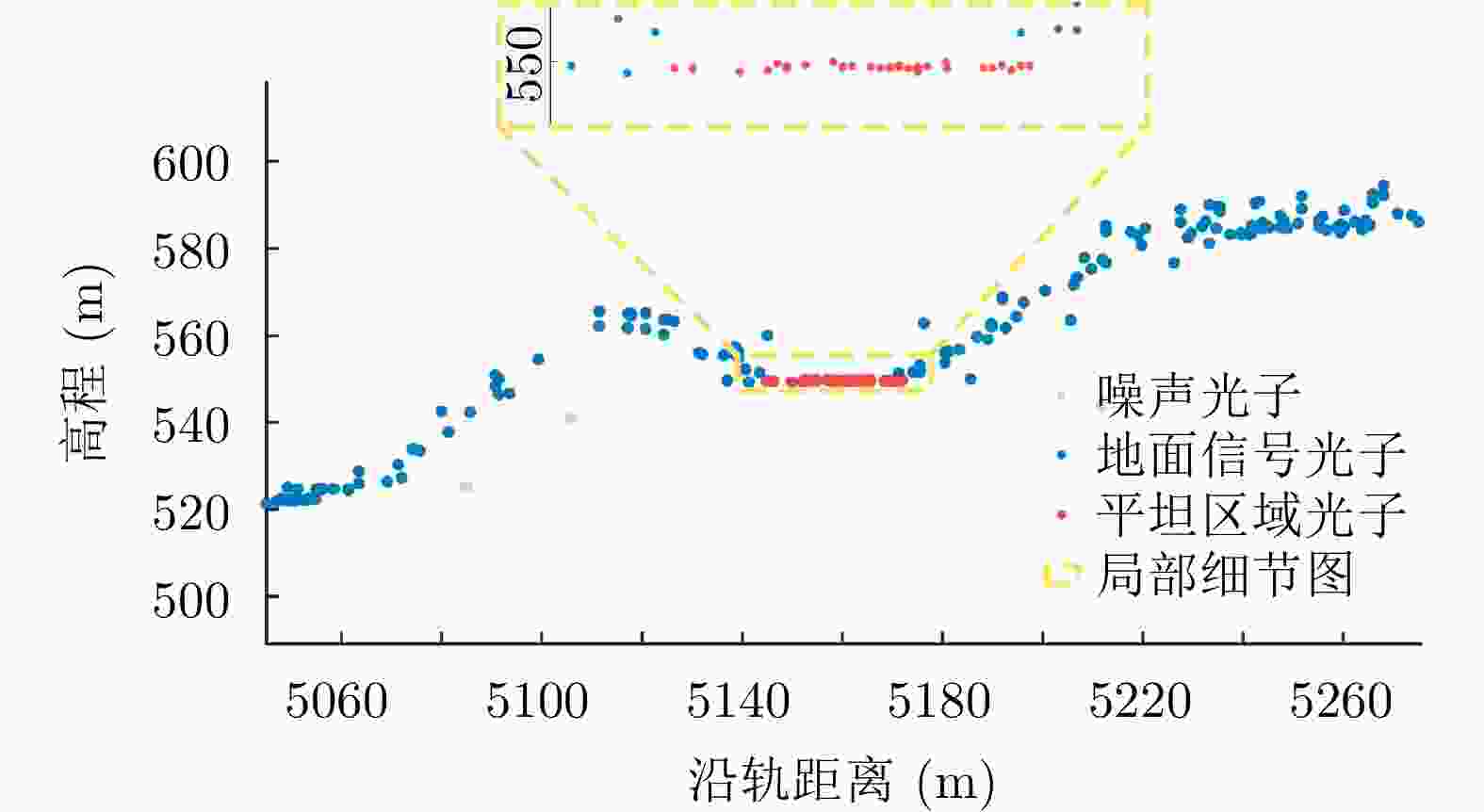
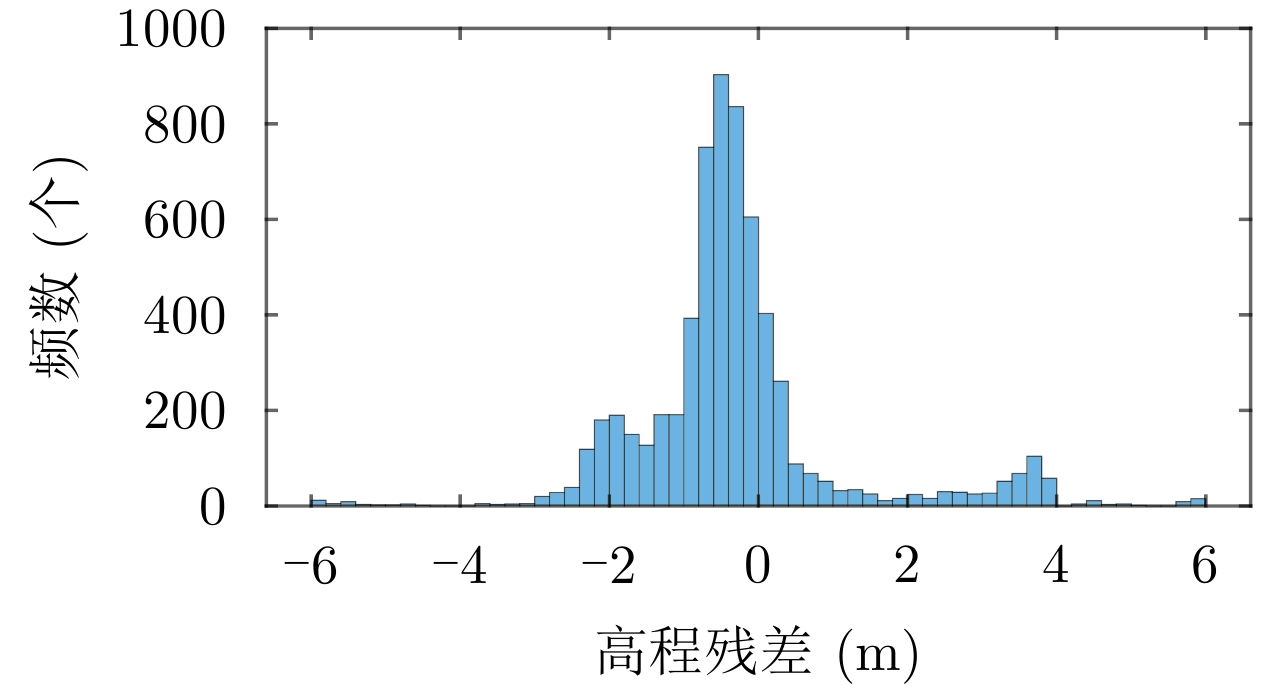
数据类型 区域1 区域2 光子数量(个) 数据剔除率(%) 光子数量(个) 数据剔除率(%) 原始数据 7 221 634 0 5 651 808 0 夜间观测数据 208 935 97.11 309 832 94.52 高置信度数据 171 242 18.04 276 938 10.62 粗差剔除数据 157 635 7.95 276 890 0.02 平坦区域数据 6 609 95.81 25 641 90.74 表 4 区域1 SAR高程控制点高程信息
Table 4. Elevation information of SAR elevation control points in area 1
序号 高程(m) 序号 高程(m) 序号 高程(m) 序号 高程(m) 序号 高程(m) 1 457.09 11 402.28 21 426.60 31 359.66 41 368.92 2 430.53 12 397.58 22 373.99 32 355.80 42 375.77 3 435.54 13 404.51 23 351.45 33 352.67 43 377.07 4 435.32 14 403.89 24 348.68 34 343.63 44 373.36 5 435.43 15 385.88 25 333.22 35 336.50 45 372.15 6 435.10 16 384.23 26 412.32 36 336.41 46 371.26 7 439.42 17 382.38 27 390.60 37 322.30 47 370.16 8 408.47 18 407.05 28 389.62 38 334.37 48 368.57 9 406.28 19 403.99 29 363.33 39 334.76 10 404.04 20 407.59 30 360.98 40 351.15 表 5 区域2 SAR高程控制点高程信息
Table 5. Elevation information of SAR elevation control points in area 2
序号 高程(m) 序号 高程(m) 序号 高程(m) 序号 高程(m) 序号 高程(m) 1 95.58 8 95.69 15 39.42 22 40.07 29 39.47 2 38.71 9 204.95 16 39.32 23 40.05 30 69.25 3 107.14 10 205.64 17 40.42 24 39.73 31 104.99 4 107.19 11 71.39 18 39.08 25 39.95 32 71.12 5 107.19 12 71.53 19 40.33 26 38.90 33 71.23 6 57.84 13 222.95 20 40.44 27 78.16 34 60.62 7 83.25 14 38.98 21 39.63 28 39.44 35 60.64 表 6 检查点信息
Table 6. Information of checkpoints
序号 经度(°) 纬度(°) 高程(m) 1 *.**3996 *.**7348 459.38 2 *.**0267 *.**2819 487.50 3 *.**6372 *.**4978 438.96 4 *.**2031 *.**1293 399.94 5 *.**9026 *.**1702 384.47 6 *.**7216 *.**9004 405.98 7 *.**4967 *.**1815 430.68 8 *.**3398 *.**2909 374.35 9 *.**8198 *.**0609 323.37 10 *.**9957 *.**5764 383.76 11 *.**2113 *.**4711 343.14 表 7 定位结果
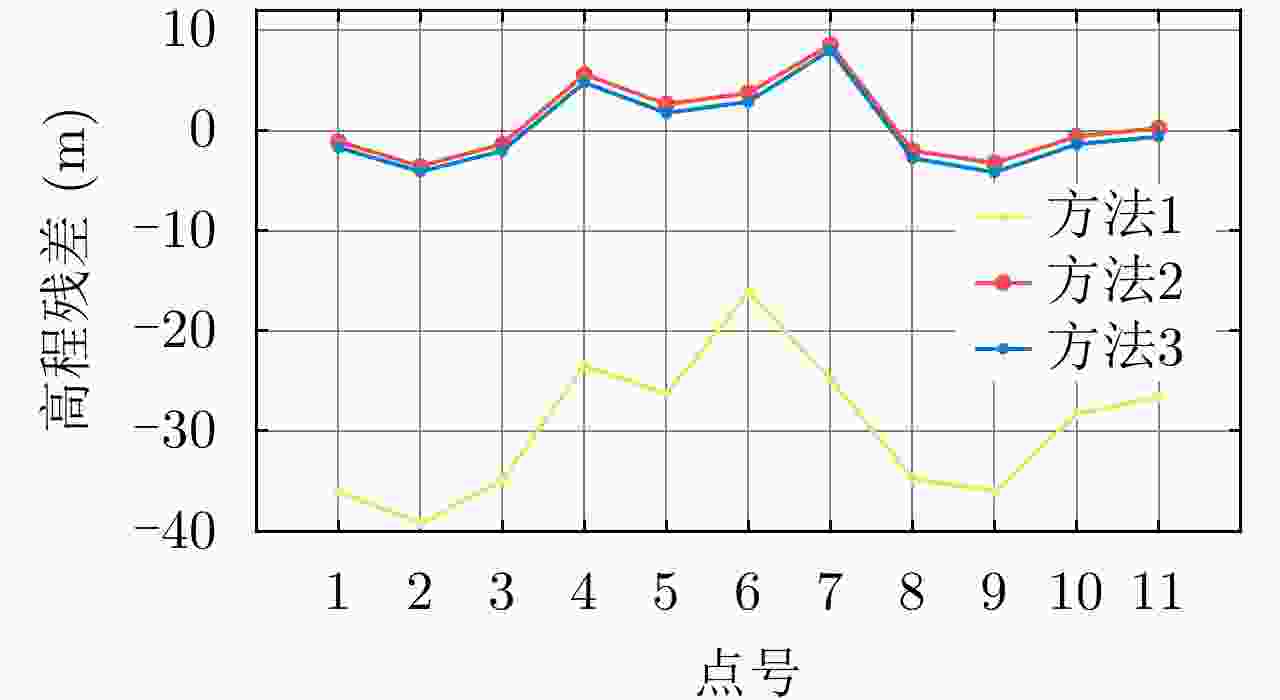
Table 7. Results of positioning
定位
方法SAR高程控制
点数(个)检查
点数(个)平面中
误差(m)高程中
误差(m)方法1 0 11 10.42 30.42 方法2 10 11 7.35 3.77 方法3 48 11 7.34 3.69 -
[1] WANG Taoyang, LI Xin, ZHANG Guo, et al. Large-scale orthorectification of GF-3 SAR images without ground control points for China’s land area[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1–17. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3142372 [2] 润一. 高分三号卫星在轨几何定标及与高分二号光学卫星影像联合定位[D]. [硕士论文], 武汉大学, 2017.RUN Yi. On-orbit geometric calibration of GF-3 satellite and joint-positioning of GF-3 and GF-2 satellite images[D]. [Master dissertation], Wuhan University, 2017. [3] 张红敏, 靳国旺, 徐青, 等. 利用单个地面控制点的SAR图像高精度立体定位[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 85–91. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13138ZHANG Hongmin, JIN Guowang, XU Qing, et al. Accurate positioning with stereo SAR images and one ground control point[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 85–91. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13138 [4] 魏钜杰, 张继贤, 赵争, 等. 稀少控制下TerraSAR-X影像高精度直接定位方法[J]. 测绘科学, 2011, 36(1): 58–60, 50. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2011.01.006WEI Jujie, ZHANG Jixian, ZHAO Zheng, et al. High-precisely direct geo-location method for TerraSAR-X image with sparse GCPs[J]. Science of Surveying and mapping, 2011, 36(1): 58–60, 50. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2011.01.006 [5] 张祖勋, 陶鹏杰. 谈大数据时代的“云控制”摄影测量[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(10): 1238–1248. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170337ZHANG Zuxun and TAO Pengjie. An overview on “cloud control” photogrammetry in big data era[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1238–1248. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170337 [6] 方勇, 龚辉, 张丽, 等. 从全球激光点云到三维数字地球空间框架: 全球精确测绘进阶之路[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(12): 1200002. doi: 10.3788/LOP202259.1200002FANG Yong, GONG Hui, ZHANG Li, et al. From global laser point cloud acquisition to 3D digital geospatial framework: The advanced road of global accurate mapping[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(12): 1200002. doi: 10.3788/LOP202259.1200002 [7] NEUMANN T A, MARTINO A J, MARKUS T, et al. The ice, cloud, and land elevation satellite-2 mission: A global geolocated photon product derived from the advanced topographic laser altimeter system[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 233: 111325. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111325 [8] XIE Huan, XU Qi, YE Dan, et al. A comparison and review of surface detection methods using MBL, MABEL, and ICESat-2 photon-counting laser altimetry data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 7604–7623. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3094195 [9] ICE, CLOUD, and land elevation satellite-2 (ICESat-2) algorithm theoretical basis document (ATBD) for global geolocated photons (ATL03)[EB/OL]. https://nsidc.org/sites/default/files/icesat2_atl03_atbd_r005_0.pdf, 2021. [10] LIN Xiaojuan, XU Min, CAO Chunxiang, et al. Estimates of forest canopy height using a combination of ICESat-2/ATLAS data and stereo-photogrammetry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(21): 3649. doi: 10.3390/rs12213649 [11] 张帅台, 李国元, 周晓青, 等. 基于多特征自适应的单光子点云去噪算法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2022, 51(6): 20210949. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210949ZHANG Shuaitai, LI Guoyuan, ZHOU Xiaoqing, et al. Single photon point cloud denoising algorithm based on multi-features adaptive[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(6): 20210949. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210949 [12] ZHU Xiaoxiao, NIE Sheng, WANG Cheng, et al. A ground elevation and vegetation height retrieval algorithm using micro-pulse photon-counting Lidar data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(12): 1962. doi: 10.3390/rs10121962 [13] MARKUS T, NEUMANN T, MARTINO A, et al. The ice, cloud, and land elevation satellite-2 (ICESat-2): Science requirements, concept, and implementation[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2017, 190: 260–273. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.12.029 [14] ROSIEK M R, KIRK R L, ARCHINAL B A, et al. Utility of Viking orbiter images and products for Mars mapping[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2005, 71(10): 1187–1195. doi: 10.14358/PERS.71.10.1187 [15] 何钰, 吴绍民, 邢帅. 基于RFM的嫦娥一号CCD影像区域网平差研究[J]. 测绘科学, 2013, 38(6): 5–6, 15. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2013.06.034HE Yu, WU Shaomin, and XING Shuai. Block adjustment of Chang’e-1 CCD images based on RFM[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2013, 38(6): 5–6, 15. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2013.06.034 [16] 耿迅. 火星形貌摄影测量技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 解放军信息工程大学, 2014.GENG Xun. Research on photogrammetric processing for Mars topographic mapping[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Information Engineering University, 2014. [17] 王晋, 张勇, 张祖勋, 等. ICESat激光高程点辅助的天绘一号卫星影像立体区域网平差[J]. 测绘学报, 2018, 47(3): 359–369. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20170425WANG Jin, ZHANG Yong, ZHNAG Zuxun, et al. ICESat laser points assisted block adjustment for mapping Satellite-1 stereo imagery[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2018, 47(3): 359–369. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20170425 [18] 张鑫磊, 邢帅, 徐青, 等. ATLAS数据与资源三号02星影像联合区域网平差[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49(S2): 20200194. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200194ZHANG Xinlei, XING Shuai, XU Qing, et al. Joint block adjustment for ATLAS data and ZY3-02 stereo imagery[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(S2): 20200194. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200194 [19] ZHANG Guo, JIANG Boyang, WANG Taoyang, et al. Combined block adjustment for optical satellite stereo imagery assisted by spaceborne SAR and laser altimetry data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(16): 3062. doi: 10.3390/rs13163062 [20] 谭建伟, 程春泉. 建筑影像高程控制点的激光测高全波形分解提取[J]. 测绘科学, 2021, 46(8): 1–7, 13. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2021.08.001TAN Jianwei and CHENG Chunquan. Extracting building image elevation control points by decomposing full waveform of laser altimetry[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(8): 1–7, 13. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2021.08.001 [21] 王密, 韦钰, 杨博, 等. ICESat-2/ATLAS全球高程控制点提取与分析[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2021, 46(2): 184–192. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20200531WANG Mi, WEI Yu, YANG Bo, et al. Extraction and analysis of global elevation control points from ICESat-2/ATLAS data[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(2): 184–192. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20200531 [22] 郑迎辉, 张艳, 王涛, 等. 基于ICESat-2数据的高程控制点提取和精度验证[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2022, 24(7): 1234–1244. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2022.210667ZHENG Yinghui, ZHANG Yan, WANG Tao, et al. Elevation control points extraction and accuracy validation based on ICESat-2 data[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2022, 24(7): 1234–1244. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2022.210667 [23] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 12341-2008 1: 25000 1: 50000 1: 100000 地形图航空摄影测量外业规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China and Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 12341-2008 Specifications for aerophotogrammetric field work of 1∶25000 1∶50000 1∶100000 topographic maps[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [24] 曹宁, 周平, 王霞, 等. 激光测高数据辅助卫星成像几何模型精化处理[J]. 遥感学报, 2018, 22(4): 599–610. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20187252CAO Ning, ZHOU Ping, WANG Xia, et al. Refined processing of laser altimeter data-aided satellite geometry model[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 22(4): 599–610. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20187252 [25] 唐新明, 刘昌儒, 张恒, 等. 高分七号卫星立体影像与激光测高数据联合区域网平差[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2021, 46(10): 1423–1430. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20210417TANG Xinming, LIU Changru, ZHANG Heng, et al. GF-7 satellite stereo images block adjustment assisted with laser altimetry data[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(10): 1423–1430. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20210417 [26] XIONG Xin, XU Qing, JIN Guowang, et al. Rank-based local self-similarity descriptor for optical-to-SAR image matching[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(10): 1742–1746. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2955153 [27] 王国安, 米鸿涛, 邓天宏, 等. 太阳高度角和日出日落时刻太阳方位角一年变化范围的计算[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2007, 30(S1): 161–164. doi: 10.16765/j.cnki.1673-7148.2007.s1.031WANG Guoan, MI Hongtao, DENG Tianhong, et al. Calculation of the change range of the sun high angle and the azimuth of sunrise and sunset in one year[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 2007, 30(S1): 161–164. doi: 10.16765/j.cnki.1673-7148.2007.s1.031 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: