Sea Clutter Spectral Parameters Prediction and Influence Factor Analysis Based on Deep Learning
-
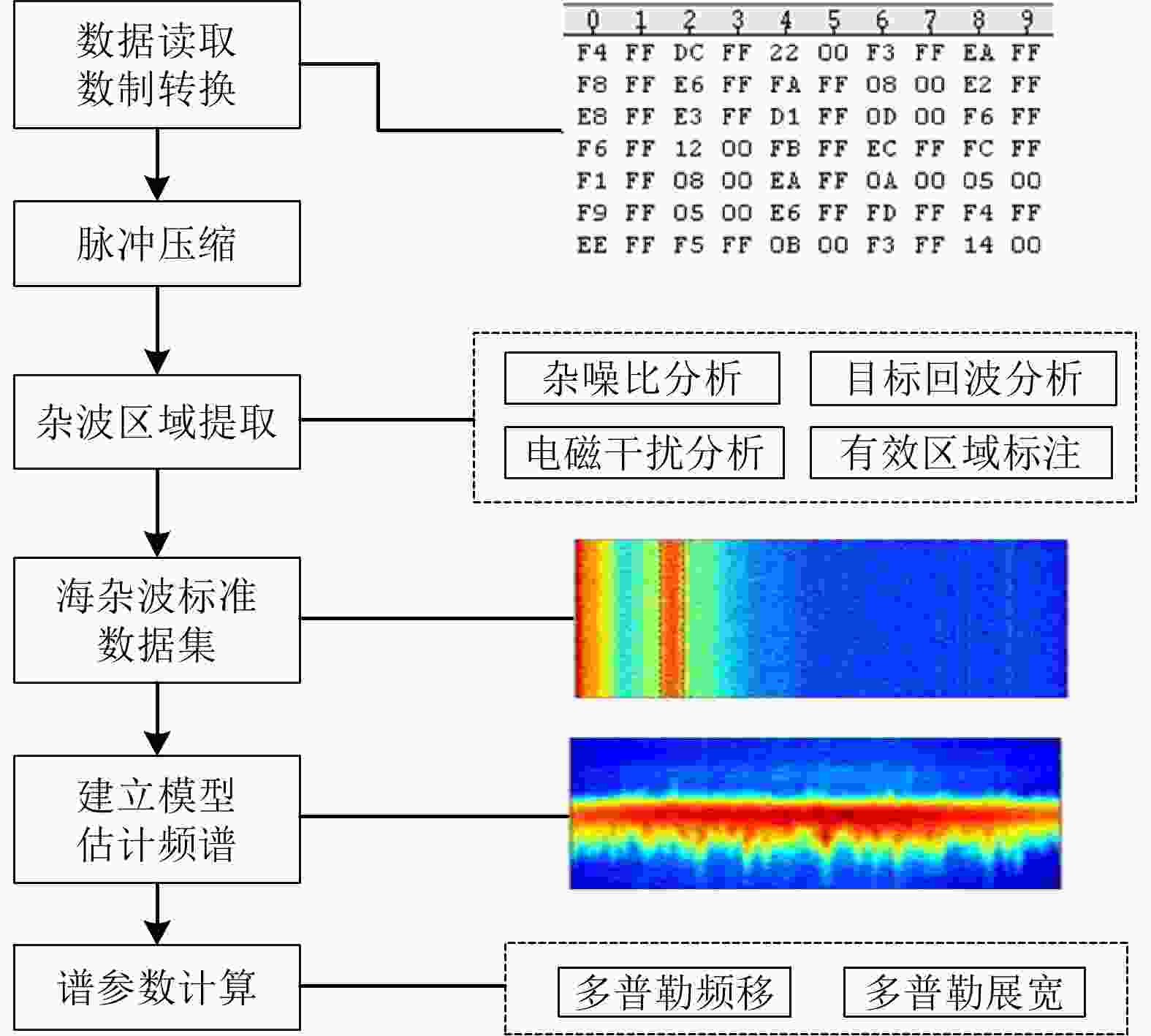
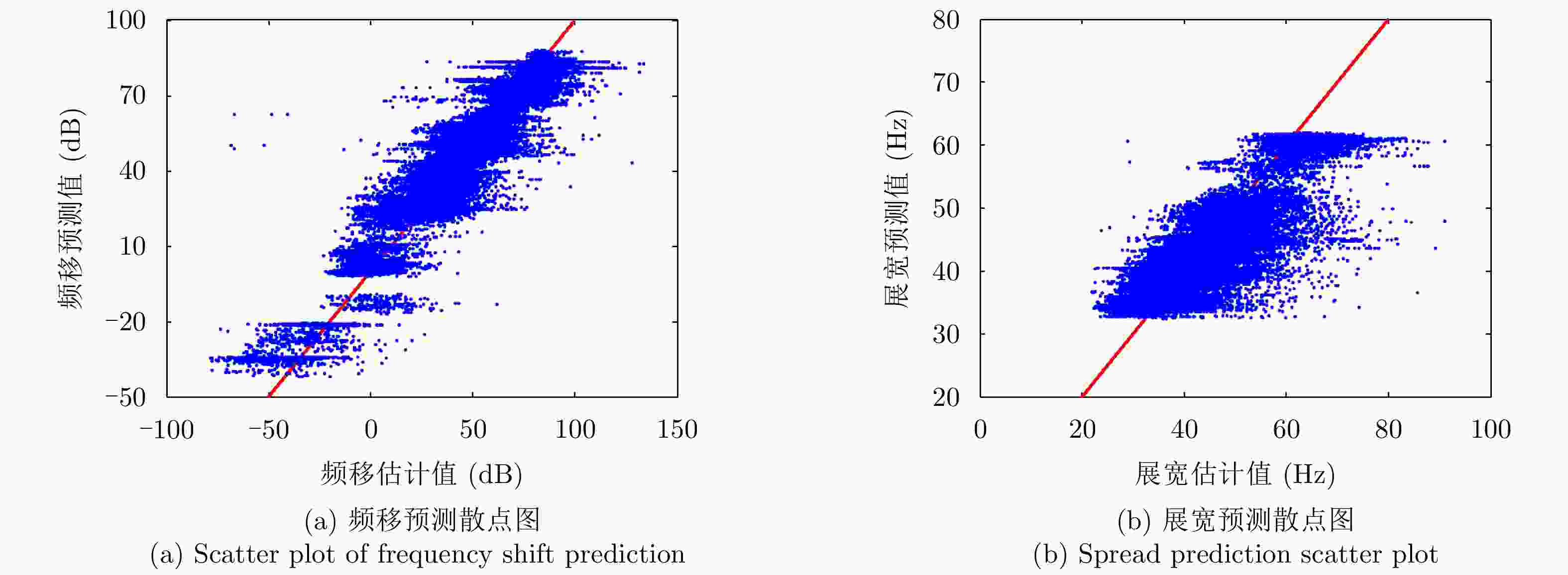
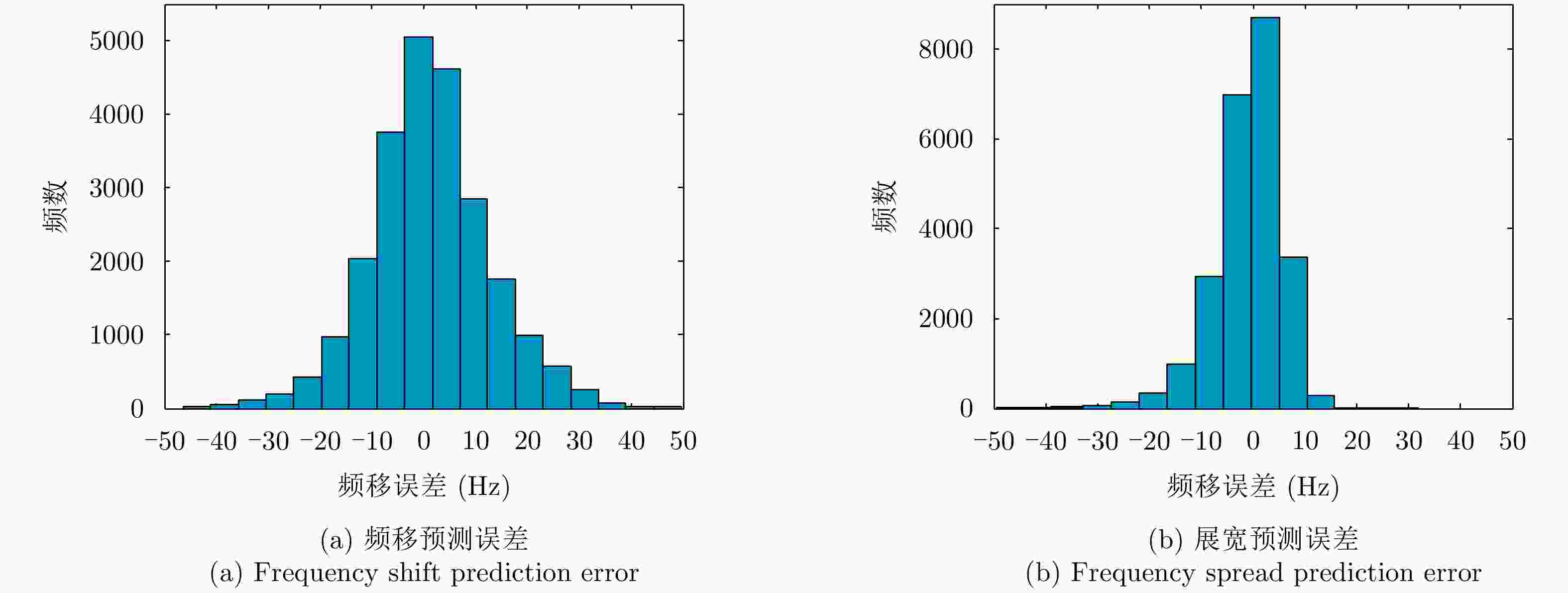
摘要: 该文基于不同雷达参数和海洋环境参数条件下的岸基雷达海杂波实测数据,利用深度神经网络(DNN)建模技术,建立了从多个测量条件参数出发的海杂波多普勒谱参数预测模型,实现了独立于杂波数据、基于环境特征的海杂波谱特征认知,谱频移和展宽的预测精度达90%以上。基于该预测模型,该文提出了一种基于参数循环递减认知的多普勒谱影响因素分析方法,分析了不同测量参数对海杂波多普勒谱预测的影响,得到了谱参数随主要影响因素的变化规律,结果对基于多普勒特征的海面目标检测应用具有重要意义。Abstract: Using Deep Neural Network (DNN) modeling technology, a prediction model of Doppler spectral parameters of sea clutter based on multiple measurement conditions is established based on measured data of sea clutter from shore-based radar under different radar parameters and marine environmental parameters. The recognition of sea clutter spectral characteristics based on environmental characteristics and independent of clutter data is realized. The spectral frequency shift and broadening prediction accuracy are greater than 90%. Based on the prediction model, an analysis method of Doppler spectrum influence factors based on the parameter cycle decreasing cognition is proposed. The influence of different measurement parameters on the Doppler spectrum prediction of sea clutter is analyzed, and the change law of spectrum parameters with the main influence factors is obtained. The results are of great significance to the application of sea surface target detection based on Doppler characteristics.
-
Key words:
- Sea clutter /
- Doppler spectrum /
- Deep Neural Network (DNN) /
- Influence factors /
- Prediction model
-
表 1 Ku波段海杂波数据集信息
Table 1. Ku band sea clutter dataset information
海情等级 HH极化(组) VV极化(组) 总数(组) 1 18675 16165 34840 2 28356 23726 52082 3 6942 11499 18441 合计 53973 51390 105363 表 2 海杂波谱参数预测训练数据集组成形式
Table 2. Composition of training data set for prediction of sea clutter spectral parameters
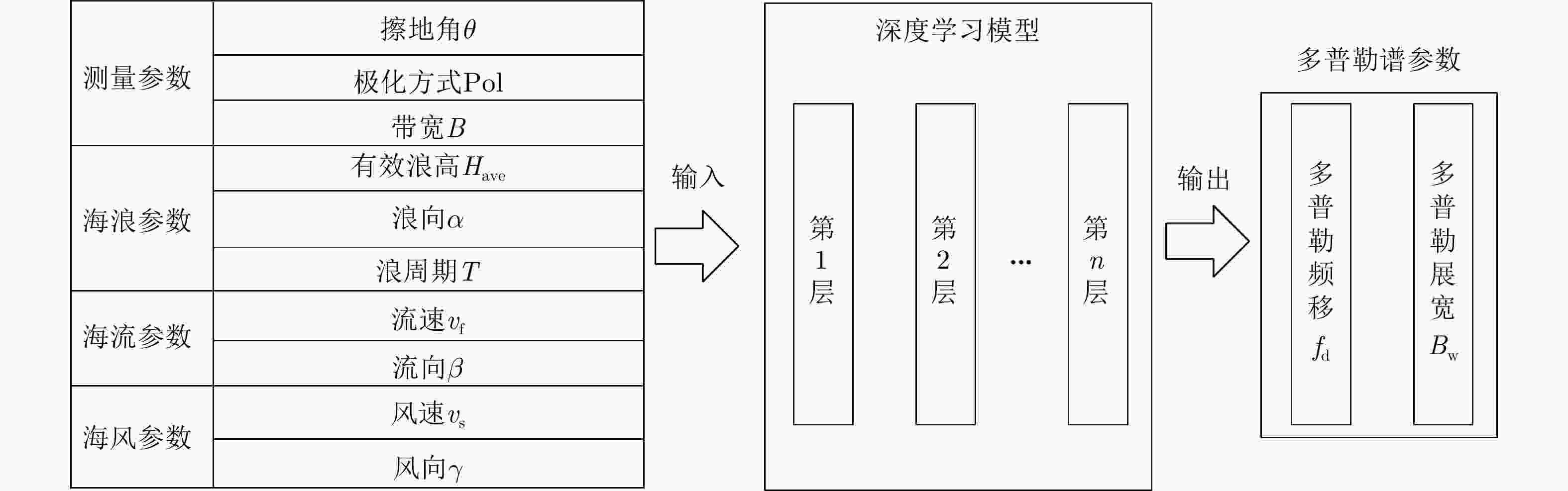
参数 符号 输入 擦地角 $ \theta $ 极化 Pol 带宽 B 有效浪高 $ {H_{{\text{ave}}}} $ 浪向 $ \alpha $ 浪周期 T 流速 $ {v_{\text{f}}} $ 流向 $ \beta $ 风速 ${v_{\rm{s}}}$ 风向 $ \gamma $ 输出 频移 $ {f_{\text{d}}} $ 展宽 $ {B_{\text{w}}} $ 表 3 不同网络的隐层参数设置
Table 3. Hidden layer parameter settings of different networks
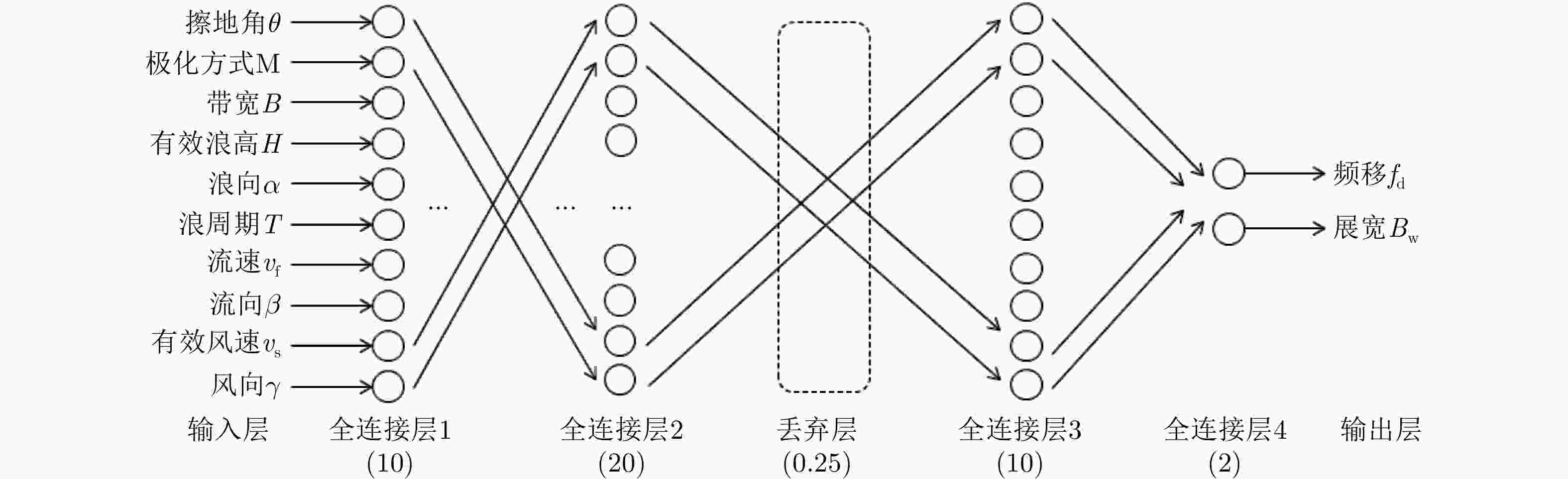
模型名称 隐藏层数 激活函数 损失函数 优化函数 DNN-5 5 Leaky ReLU 改进
Huber LossAdam函数 BPNN 2 ReLU RBFNN 2 RBF RNN 4 ReLU SVR 无须训练 KNN 表 4 各个模型的谱参数预测结果
Table 4. Prediction results of spectral parameters of each model
模型 MAE RMSE $ \eta $ PR $ {f_{\text{d}}} $ $ {B_{\text{w}}} $ $ {f_{\text{d}}} $ $ {B_{\text{w}}} $ $ {f_{\text{d}}} $ $ {B_{\text{w}}} $ $ {f_{\text{d}}} $ $ {B_{\text{w}}} $ SVR 17.46 5.10 22.37 6.78 0.815 0.892 0.749 0.780 KNN 9.87 5.06 12.63 6.69 0.889 0.911 0.926 0.792 DNN-5 8.50 4.58 11.57 6.16 0.913 0.953 0.941 0.827 BPNN 11.97 4.83 16.05 6.53 0.877 0.941 0.877 0.802 RBFNN 9.15 4.60 12.34 6.20 0.905 0.951 0.930 0.819 RNN 10.26 4.67 13.38 6.17 0.887 0.952 0.922 0.826 表 5 基于循环递减认知方法的DNN-5评价指标
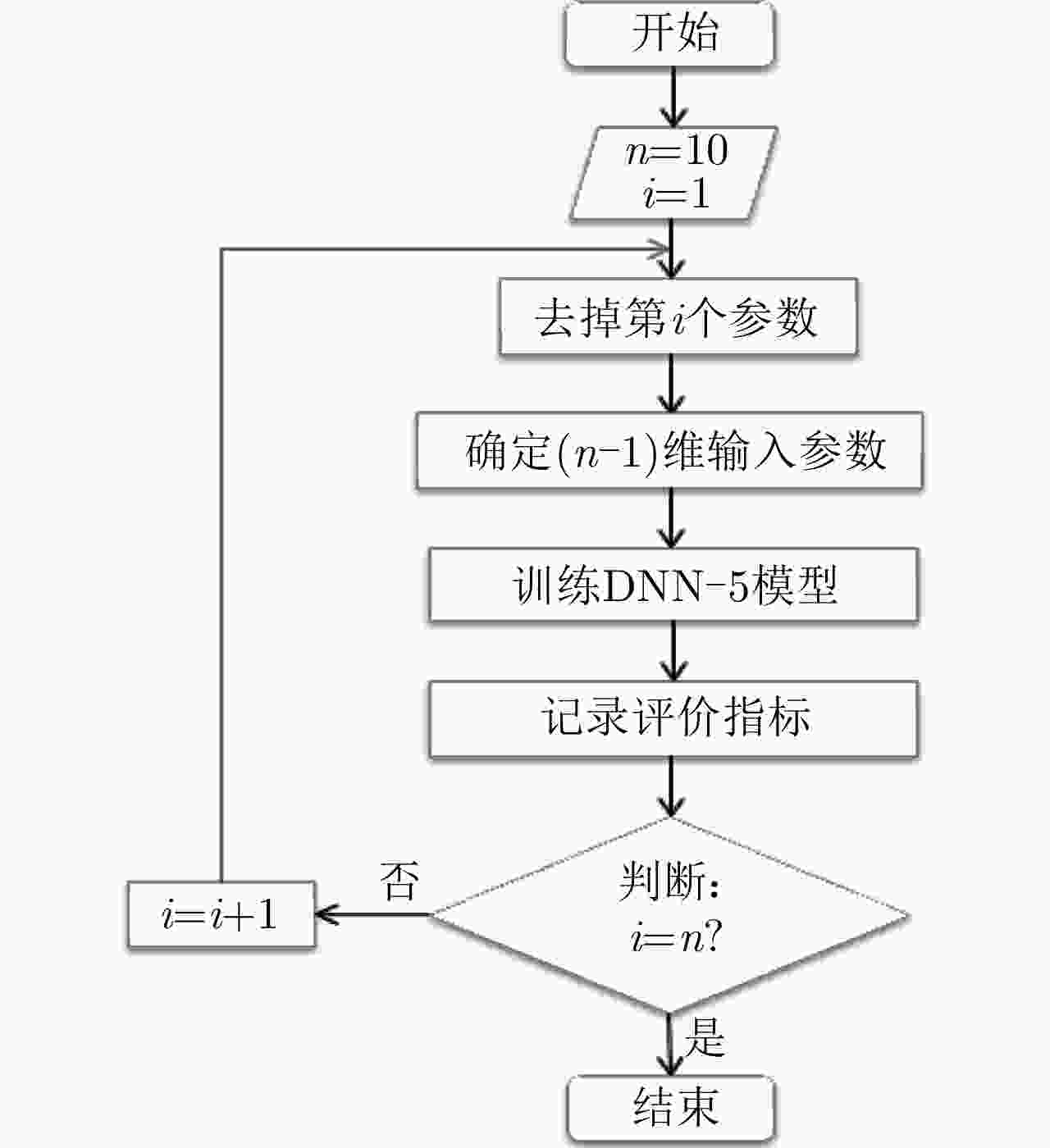
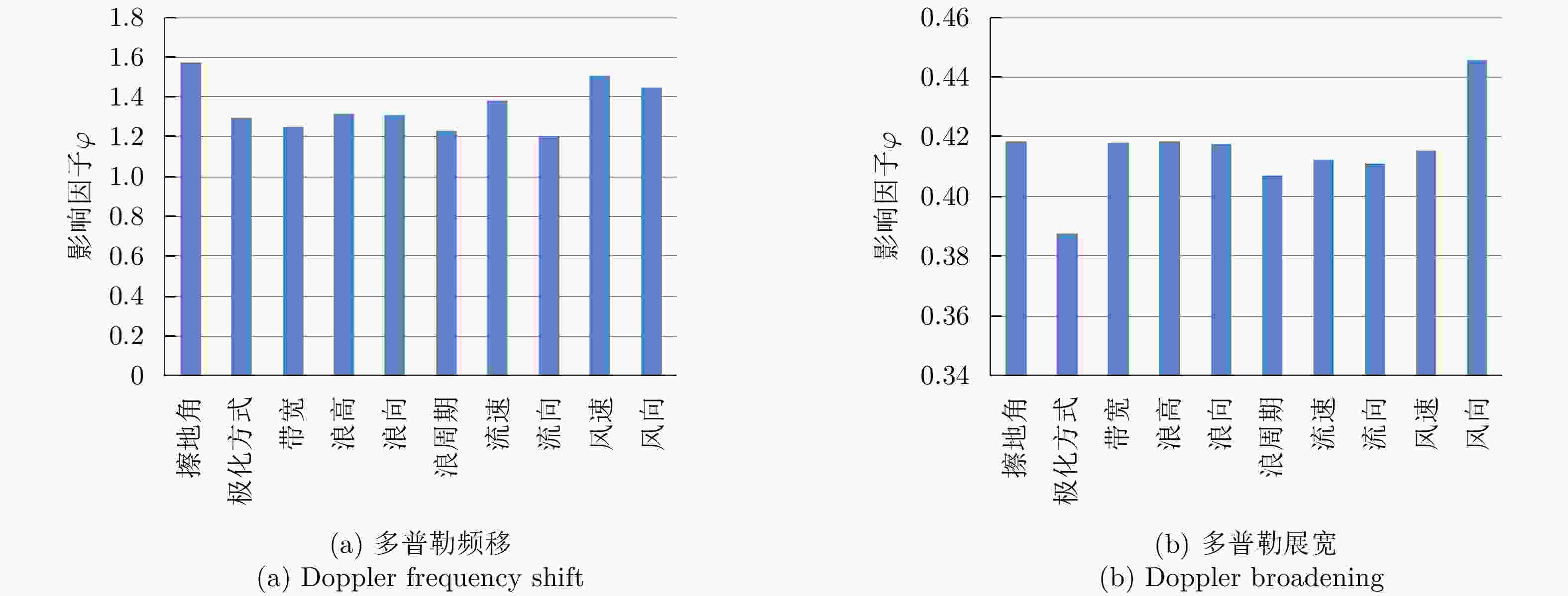
Table 5. Evaluation index of DNN-5 based on the cyclic decreasing cognition method
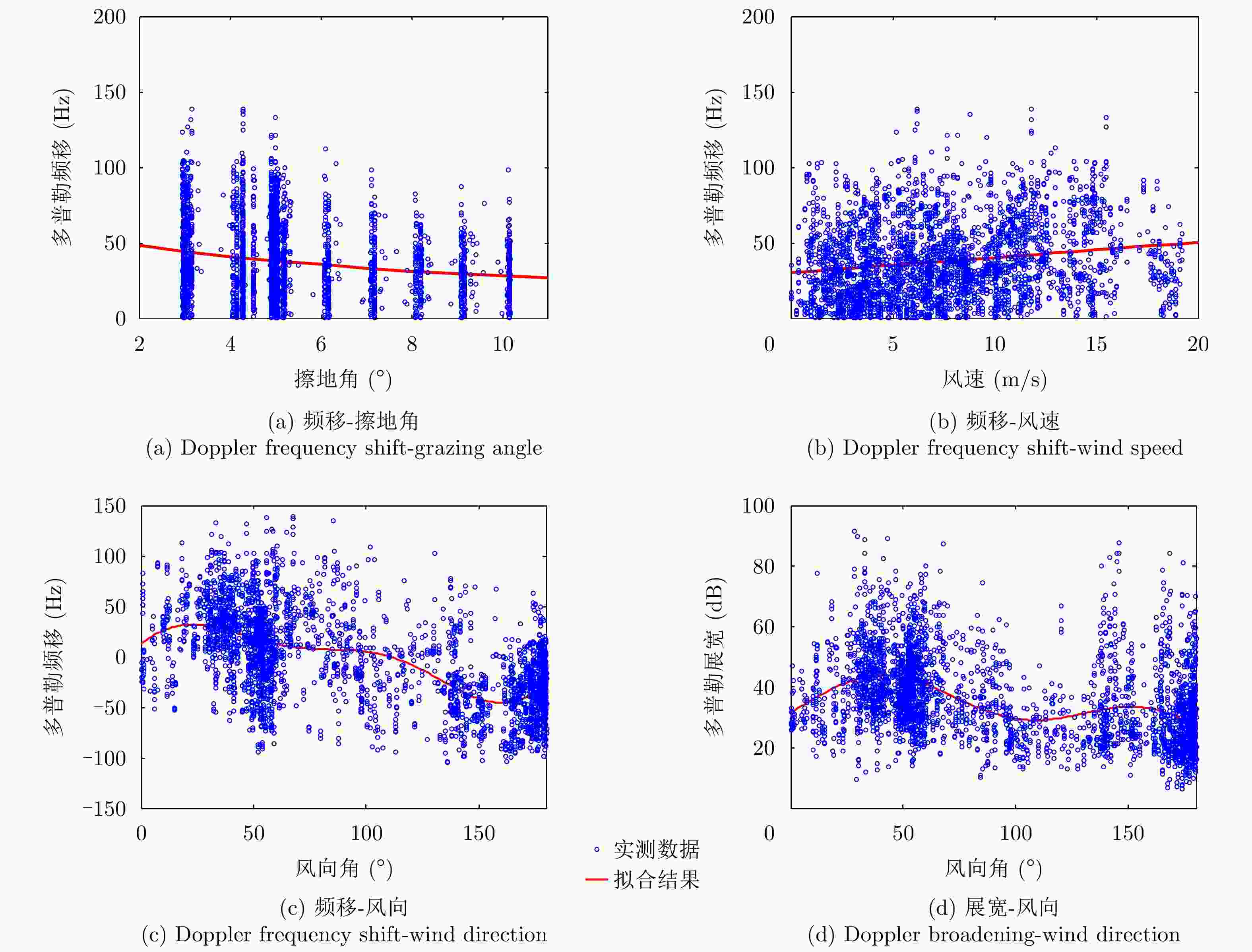
去掉参数 多普勒频移 多普勒展宽 MAE RMSE PR η $ \varphi $ MAE RMSE PR η $ \varphi $ 擦地角 9.62 13.48 0.916 0.902 1.57 4.87 6.55 0.803 0.949 0.418 极化方式 9.02 12.20 0.937 0.907 1.29 4.77 6.39 0.828 0.950 0.387 带宽 8.90 12.03 0.942 0.909 1.25 4.93 6.62 0.824 0.947 0.418 浪高 9.17 12.23 0.942 0.906 1.31 4.94 6.60 0.823 0.947 0.418 浪向 9.15 12.25 0.943 0.906 1.31 4.91 6.59 0.818 0.947 0.417 浪周期 8.90 11.83 0.942 0.909 1.23 4.90 6.51 0.827 0.948 0.407 流速 9.30 12.56 0.937 0.904 1.38 4.90 6.57 0.824 0.948 0.412 流向 8.76 11.77 0.944 0.910 1.20 4.90 6.57 0.826 0.948 0.411 风速 9.63 13.11 0.931 0.900 1.51 4.86 6.62 0.817 0.948 0.415 风向 9.54 12.75 0.932 0.902 1.45 5.08 6.79 0.819 0.945 0.446 -
[1] SHI Yanling, GUO Yaxing, YAO Tingting, et al. Sea-surface small floating target recurrence plots FAC classification based on CNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5115713. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3192986 [2] QU Qizhe, WANG Yongliang, LIU Weijian, et al. A false alarm controllable detection method based on CNN for sea-surface small targets[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4025705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3190865 [3] WARD K D, TOUGH R J A, and WATTS S. Sea Clutter: Scattering, The K Distribution and Radar Performance[M]. 2nd ed. London: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2013: 129–142. [4] 李清亮, 尹志盈, 朱秀芹, 等. 雷达地海杂波测量与建模[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 312–408.LI Qingliang, YIN Zhiying, ZHU Xiuqin, et al. Measurement and Modeling of Radar Clutter from Land and Sea[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 312–408. [5] 丁昊, 董云龙, 刘宁波, 等. 海杂波特性认知研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 499–516. doi: 10.12000/JR16069DING Hao, DONG Yunlong, LIU Ningbo, et al. Overview and prospects of research on sea clutter property cognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 499–516. doi: 10.12000/JR16069 [6] CROMBIE D D. Doppler spectrum of sea echo at 13.56 Mc./s.[J]. Nature, 1955, 175(4459): 681–682. doi: 10.1038/175681a0 [7] LEE P H Y, BARTER J D, BEACH K L, et al. Power spectral lineshapes of microwave radiation backscattered from sea surfaces at small grazing angles[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1995, 142(5): 252–258. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19952084 [8] WALKER D. Experimentally motivated model for low grazing angle radar Doppler spectra of the sea surface[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2000, 147(3): 114–120. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20000386 [9] ROSENBERG L and STACY N J. Analysis of medium grazing angle X-band sea-clutter Doppler spectra[C]. 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2008: 1–6. [10] ROSENBERG L. Parametric modeling of sea clutter Doppler spectra[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5105409. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3107950 [11] ZHANG Jinpeng, ZHANG Yushi, XU Xinyu, et al. Estimation of sea clutter inherent Doppler spectrum from shipborne S-band radar sea echo[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2020, 29(6): 068402. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/ab888a [12] WEN Liwu, DING Jinshan, ZHONG Chao, et al. Modeling of correlated complex sea clutter using unsupervised phase retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(1): 228–239. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2995892 [13] MCDONALD M K and CERUTTI-MAORI D. Clairvoyant radar sea clutter covariance matrix modelling[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(1): 154–160. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0103 [14] SHEN Yan and LI Guoqiang. The chaotic neural network is used to predict the sea clutter signal[C]. 2009 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence, Shanghai, China, 2009: 25–30. [15] FERNÁNDEZ J R M and DE LA CONCEPCIÓN BACALLAO VIDAL J. Improved shape parameter estimation in K clutter with neural networks and deep learning[J]. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence, 2016, 3(7): 96–103. doi: 10.9781/ijimai.2016.3714 [16] MA Liwen, WU Jiaji, ZHANG Jinpeng, et al. Sea clutter amplitude prediction using a Long short-term memory neural network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(23): 2826. doi: 10.3390/rs11232826 [17] SHUI Penglang, SHI Xiaofan, LI Xin, et al. GRNN-based predictors of UHF-band sea clutter reflectivity at low grazing angle[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 1502205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3076842 [18] 张晓峰, 王莉, 殷国东, 等. Ku波段地海杂波极化特性实验与分析[J]. 电波科学学报, 2019, 34(6): 676–686. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2019043003ZHANG Xiaofeng, WANG Li, YIN Guodong, et al. The experiments and analysis of polarization characteristics of the ground and sea clutters at Ku band[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2019, 34(6): 676–686. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2019043003 [19] MADSEN K, NIELSEN H B, and TINGLEFF O. Methods for Non-Linear Least Squares Problems[M]. 2nd ed. Lyngby: Informatics and Mathematical Modelling, Technical University of Denmark, 2004: 24–29. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: