-
摘要: 根据无人机蜂群构型自组织调整位置和权向量能够实现波束指向特定方向的任务需求,该文提出了一种新颖的任务驱动的自组织蜂群柔性阵列波束赋形算法。首先,建立以无人机蜂群距离为约束、以无人机机载天线坐标位置及权向量为优化变量的波束赋形数学模型。接着,应用Lawson准则简化目标函数,将天线坐标位置及权向量的两类变量优化问题简化为天线坐标位置的单类变量优化,解决了波束赋形模型优化变量耦合带来的求解难题。同时,引入辅助变量,进行约束和复杂目标函数的分离,并通过交替方向乘子法进行求解,降低了包含约束的高度非线性优化问题的求解难度。此外,该文将上述算法扩展至目标方向不精确的应用场景。仿真结果表明,该方法可有效降低波束赋形峰值旁边电平。Abstract: This paper proposes a novel task-driven flexible array beampattern synthesis model for self-organized drone swarms according to their task requirements so that they can adjust their positions appropriately and point in a specific direction. First, we formulate the novel beampattern synthesis model using the drone-swarm antenna position and weight vector as the optimization variables and the maximum driving distance as the constraint. Then, the Lawson criterion is used to simplify the objective function, and the two kinds of optimization variables of antenna position and weight vector are reduced to a single kind of variable optimization problem of antenna position, alleviating the optimization difficulty caused by the usage of coupled variables. Simultaneously, auxiliary variables are introduced to separate the constraints from the complex objective function, and the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM)is used to slove the problem, which reduces the difficulty of solving a highly nonlinear optimization problem with constraints,. In addition, we extend this method to a scenario in which the provided Direction Of Arrival (DOA)of interest is imprecise. Simulation results show that the proposed method can obtain lower sidelobe levels than previous methods.
-
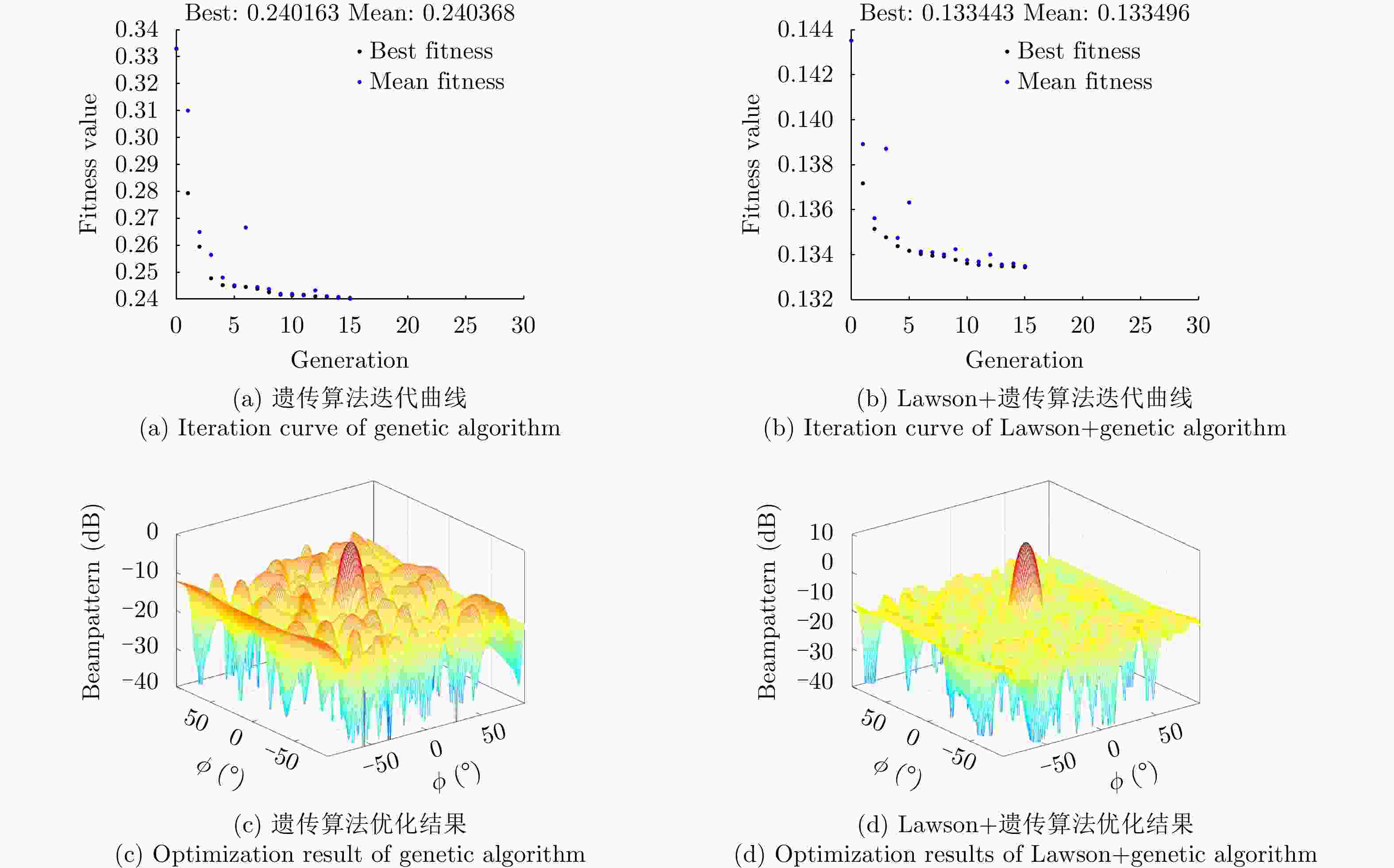
算法1 任务驱动的自组织蜂群柔性阵列波束赋形 Alg. 1 Task-driven flexible array beampattern synthesis for self-organized drone swarm 步骤1 随机初始化无人机坐标位置$\left\{ { {{\boldsymbol{p}}_n}(0)} \right\}$;设定波束指向方
向$ ({\theta _0},{\phi _0}) $和干扰方向$ ({\theta _l},{\phi _l}) $;初始化Lawson权值
$ {v_t}\left( {\theta ,\phi } \right) $为1,即$ {v_0}\left( {\theta ,\phi } \right) = 1,{\text{ }}\forall \left( {\theta ,\phi } \right) \in {\rm {Sidelobe}} $;设
外循环迭代变量为t;最大外循环次数$ {T_0} $;步骤2 随机初始化$ \{ {{\boldsymbol{q}}_n}(0),{{\boldsymbol{\lambda }}_n}(0)\} $,设内循环迭代变量为k;最
大内循环次数$ {K_0} $;根据式(9)计算权值矢量$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}_t} $;步骤2.1 应用式(13),式(14)确定$ \left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{p}}_n}(k + 1)} \right\}_{n = 1}^N $; 步骤2.2 应用式(17)确定$ \left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{q}}_n}(k + 1)} \right\}_{n = 1}^N $; 步骤2.3 应用式(18)更新拉格朗日乘子; 步骤2.4 重复步骤2.1—步骤2.3,直至达到最大迭代次
数$ {K_0} $;步骤3 应用式(5)进行权值更新; 步骤4 重复步骤2、步骤3,直至达到最大迭代次数$ {T_0} $。 输出:无人机权矢量$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}_t} $和坐标$ \left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{p}}_n}(k)} \right\} $ 算法2 目标方向不精确时的自组织蜂群柔性阵列波束赋形 Alg. 2 Flexible array beampattern synthesis for self-organized drone swarm with imprecise target direction 步骤1 初始化$ \{ {\boldsymbol{w}}(0),{{\boldsymbol{p}}_n}(0),{\lambda _m}(0),{\kappa _s}(0)\} $;循环迭代变量t;
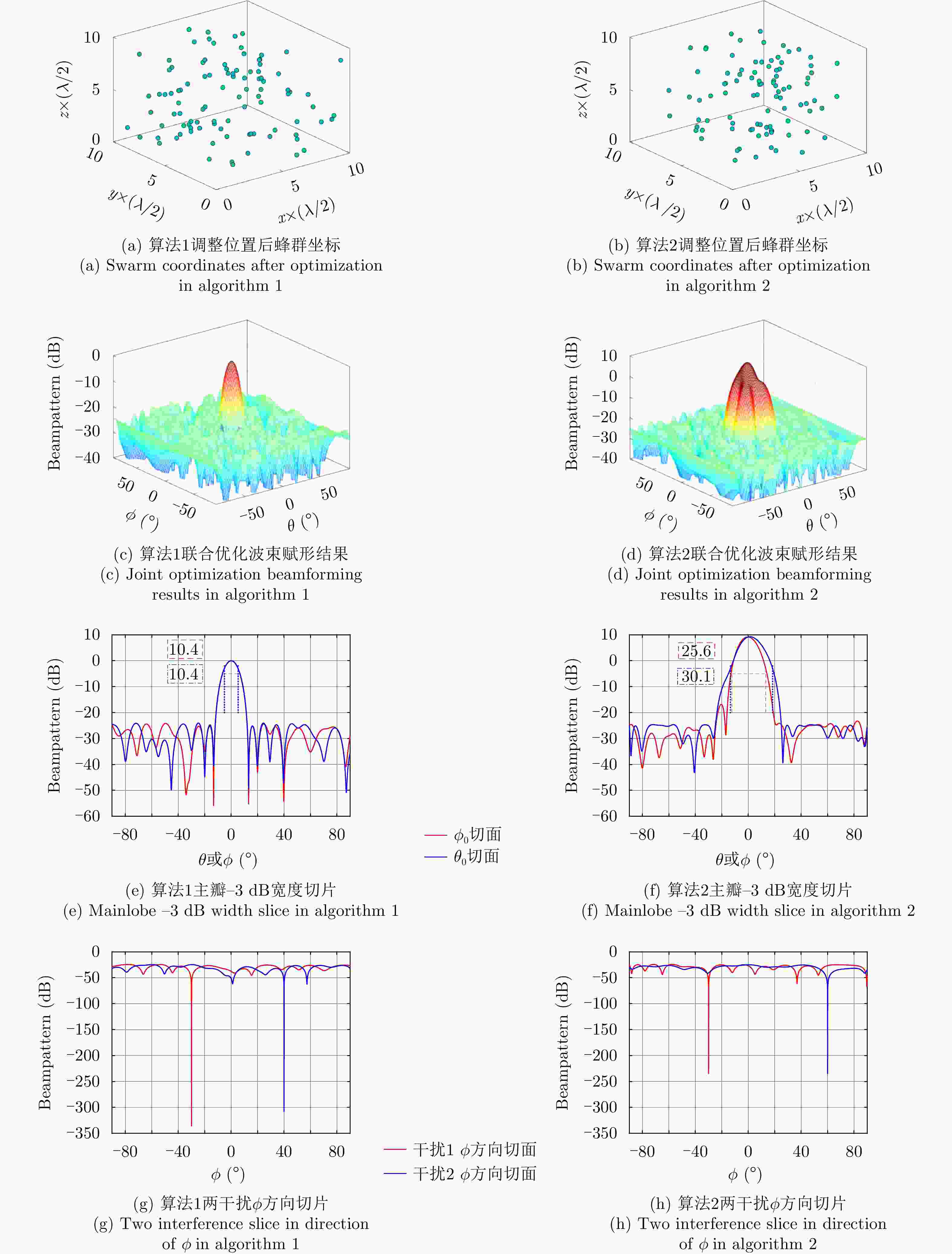
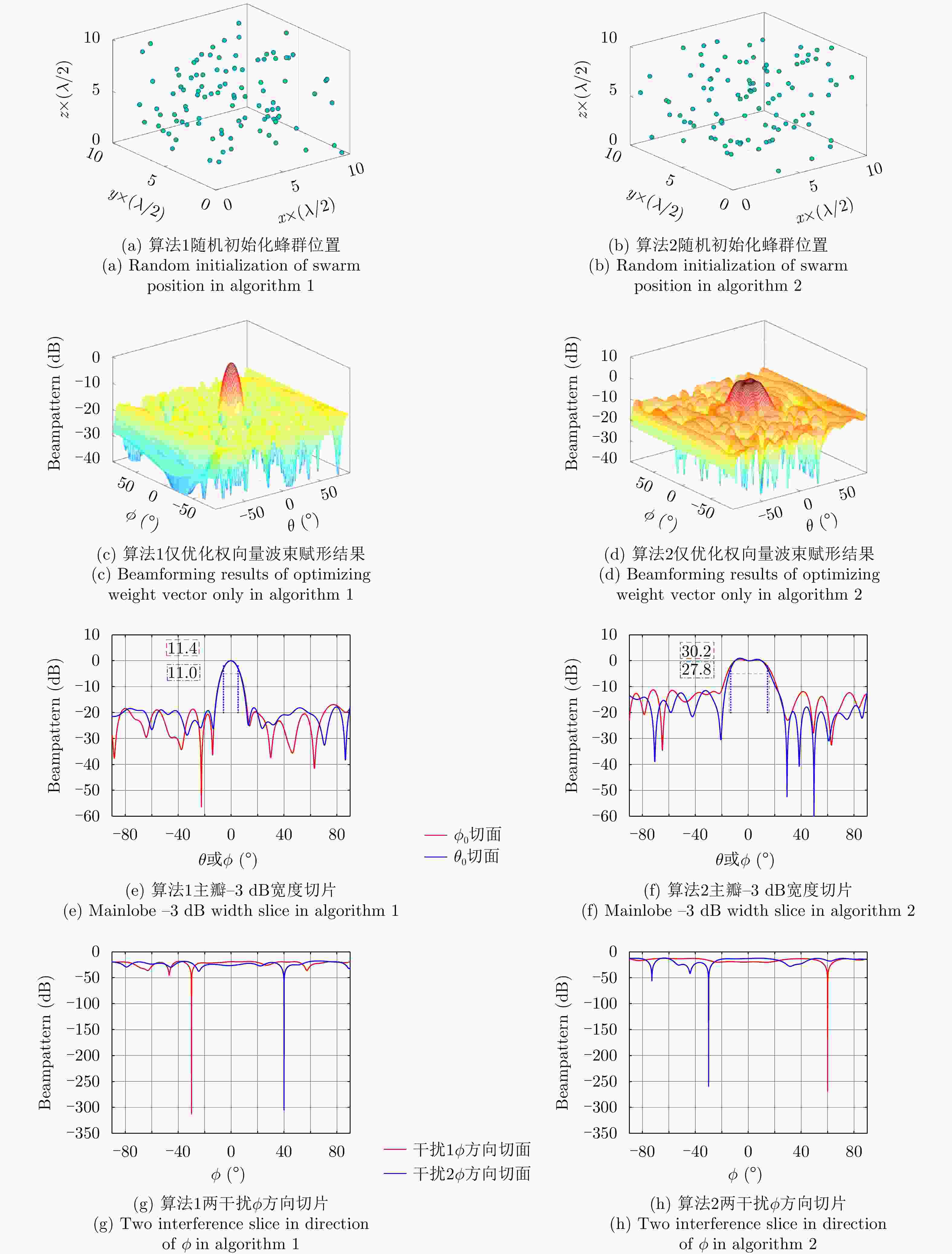
最大循环次数$ {T_0} $;步骤2 执行式(23)—式(25)获得$ \{ \varepsilon (t + 1),{u_m}(t + 1),{v_s}(t + 1)\} $; 步骤3 执行式(26)—式(36)获得$ {\boldsymbol{w}}(t + 1),{{\boldsymbol{p}}_n}(t + 1) $; 步骤4 执行式(37),式(38)进行拉格朗日乘子更新; 重复步骤2—步骤4,直至达到最大迭代次数$ {T_0} $。 输出:无人机权矢量$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}_t} $和坐标$ \left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{p}}_n}(k)} \right\} $ 表 1 算法1天线个数变化时PSL对比
Table 1. PSL comparison when the number of antennas changes in algorithm 1
天线个数 仅优化权向量时的PSL (dB) 联合优化时的PSL (dB) 50 –13.27 –15.56 100 –16.33 –23.13 150 –20.50 –25.21 表 2 算法2天线个数变化时PSL对比
Table 2. PSL comparison when the number of antennas changes in algorithm 2
天线个数 仅优化权向量时的PSL (dB) 联合优化时的PSL (dB) 50 –5.55 –15.82 100 –10.76 –24.45 150 –19.39 –28.04 表 3 算法1不同距离约束下PSL对比
Table 3. Comparison of PSL under different distance constraints in algorithm 1
距离约束 PSL (dB) 距离约束 PSL (dB) $0.2 \times \dfrac{\lambda}{2}$ –20.43 $2 \times \dfrac{\lambda}{2} $ –23.58 $0.5 \times \dfrac{\lambda}{2}$ –19.16 $5 \times \dfrac{\lambda}{2} $ –22.35 $1 \times \dfrac{\lambda}{2} $ –23.87 表 4 算法2不同距离约束下PSL对比
Table 4. Comparison of PSL under different distance constraints in algorithm 2
距离约束 PSL (dB) 距离约束 PSL (dB) $0.2 \times \dfrac{\lambda}{2}$ –14.65 $2 \times \dfrac{\lambda}{2}$ –17.27 $0.5 \times \dfrac{\lambda}{2}$ –21.34 $5 \times \dfrac{\lambda}{2}$ –11.73 $1 \times \dfrac{\lambda}{2}$ –24.45 -
[1] 董宇, 高敏, 张悦, 等. 美军蜂群无人机研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 飞航导弹, 2020(9): 37–42. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.20200158DONG Yu, GAO Min, ZHANG Yue, et al. Research progress and development trend of American drone swarm[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2020(9): 37–42. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.20200158 [2] ABBASI Q H, REHMAN M U, YANG Xiaodong, et al. Ultrawideband band-notched flexible antenna for wearable applications[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2013, 12: 1606–1609. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2013.2294214 [3] ASILI M, CHEN Pu, HOOD A Z, et al. Flexible microwave antenna applicator for chemo-thermotherapy of the breast[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2015, 14: 1778–1781. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2015.2423655 [4] SAEED S M, BALANIS C A, BIRTCHER C R, et al. Wearable flexible reconfigurable antenna integrated with artificial magnetic conductor[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2017, 16: 2396–2399. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2017.2720558 [5] MOGHADAS H, ZANDVAKILI M, SAMEOTO D, et al. Beam-reconfigurable aperture antenna by stretching or reshaping of a flexible surface[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2017, 16: 1337–1340. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2633964 [6] LIANG Junli, ZHANG Xuan, SO H C, et al. Sparse array beampattern synthesis via alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(5): 2333–2345. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2811778 [7] NAI S E, SER W, YU Zhuliang, et al. Beampattern synthesis for linear and planar arrays with antenna selection by convex optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(12): 3923–3930. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2078446 [8] LIU Foxiang, LIU Yanhui, XU Kaida, et al. Synthesizing uniform amplitude sparse dipole arrays with shaped patterns by joint optimization of element positions, rotations and phases[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(9): 6017–6028. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2920238 [9] BUCCI O M, D'ELIA G, MAZZARELLA G, et al. Antenna pattern synthesis: A new general approach[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1994, 82(3): 358–371. doi: 10.1109/5.272140 [10] EROKHIN A A. Frequency-invariant beam pattern nulling based on weighted pattern summation[J]. Technical Physics Letters, 2021, 47(4): 333–335. doi: 10.1134/S1063785021040064 [11] PENG Weilai, GU Tianyuan, ZHUANG Yangjingzhi, et al. Pattern synthesis with minimum mainlobe width via sparse optimization[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022, 128: 103632. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2022.103632 [12] AI Xiaoyu and GAN Lu. Precise array response control for beampattern synthesis with minimum pattern distortion[J]. Signal Processing, 2022, 192: 108395. doi: 10.1016/J.SIGPRO.2021.108395 [13] LIU Yanhui, BAI Jingjing, ZHENG Jinxiang, et al. Efficient shaped pattern synthesis for time modulated antenna arrays including mutual coupling by differential evolution integrated with FFT via least-square active element pattern expansion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(7): 4223–4228. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3045513 [14] GAO Renjing, TANG Yi, WANG Qi, et al. Pattern synthesis considering mutual coupling for peak sidelobe suppression and null controlling via element rotation and phase optimization[J]. Engineering Optimization, 2022, 54(1): 101–112. doi: 10.1080/0305215X.2020.1853716 [15] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [16] BERTSEKAS D P. Constrained Optimization and Lagrange Multiplier Methods[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1982. [17] LAWSON C L. Contributions to the theory of linear least maximum approximation[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of California, 1961. [18] RICE J R and USOW K H. The Lawson algorithm and extensions[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1968, 22(101): 118–127. doi: 10.2307/2004769 [19] ELLACOTT S and WILLIAMS J. Linear Chebyshev approximation in the complex plane using Lawson’s algorithm[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1976, 30(133): 35–44. doi: 10.2307/2005427 [20] BOYD S, PARIKH N, CHU E, et al. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends ® in Machine Learning, 2011, 3(1): 1–122. doi: 10.1561/2200000016 [21] GABAY D. Chapter IX applications of the method of multipliers to variational inequalities[J]. Studies in Mathematics and its Applications, 1983, 15: 299–331. doi: 10.1016/S0168-2024(08)70034-1 [22] ECKSTEIN J and BERTSEKAS D P. On the Douglas-Rachford splitting method and the proximal point algorithm for maximal monotone operators[J]. Mathematical Programming, 1992, 55(1): 293–318. doi: 10.1007/BF01581204 [23] HONG Mingyi, LUO Zhiquan, and RAZAVIYAYN M. Convergence analysis of alternating direction method of multipliers for a family of nonconvex problems[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brisbane, South Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 3836–3840. [24] XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Response vector constrained robust LCMV beamforming based on semidefinite programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(21): 5720–5732. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2460221 [25] LIANG Junli, SO H C, LI Jian, et al. Unimodular sequence design based on alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(20): 5367–5381. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2597123 [26] LIANG Junli, SO H C, LI Jian, et al. On optimizations with magnitude constraints on frequency or angular responses[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 145: 214–224. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.12.009 [27] YU Zhuliang, ER M H, and SER W. A novel adaptive beamformer based on semidefinite programming (SDP) with magnitude response constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2008, 56(5): 1297–1307. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2008.922644 [28] YU Zhuliang, SER W, M ER M H, et al. Robust adaptive beamformers based on worst-case optimization and constraints on magnitude response[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(7): 2615–2628. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2017004 [29] CHEN Zihao, LIANG Junli, WANG Tao, et al. Generalized MBI algorithm for designing sequence set and mismatched filter bank with ambiguity function constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 2918–2933. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3181346 [30] ZHOU Xin, WEN Xiangyong, WANG Zhepei, et al. Swarm of micro flying robots in the wild[J]. Science Robotics, 2022, 7(66): eabm5954. doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.abm5954 [31] 杨朝麟. 非均匀稀疏阵的阵列校准与稳健DOA估计算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2021.YANG Chaolin. Research on array calibration and robust estimation algorithm for non-uniform sparse array[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021. [32] 刘源, 纠博, 刘宏伟, 等. 基于杂波的收发分置MIMO雷达阵列位置误差联合校正方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(12): 2956–2963. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150347LIU Yuan, JIU Bo, LIU Hongwei, et al. Joint transmit and receive array position error calibration for bistatic MIMO radar based on clutter[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(12): 2956–2963. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150347 [33] 曹渊, 刘威, 崔东华. 适用于任意阵列的鲁棒波束形成算法[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2019, 39(12): 1263–1267, 1297. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.144CAO Yuan, LIU Wei, and CUI Donghua. A robust beamforming algorithm for arbitrary array[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2019, 39(12): 1263–1267, 1297. doi: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.144 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: