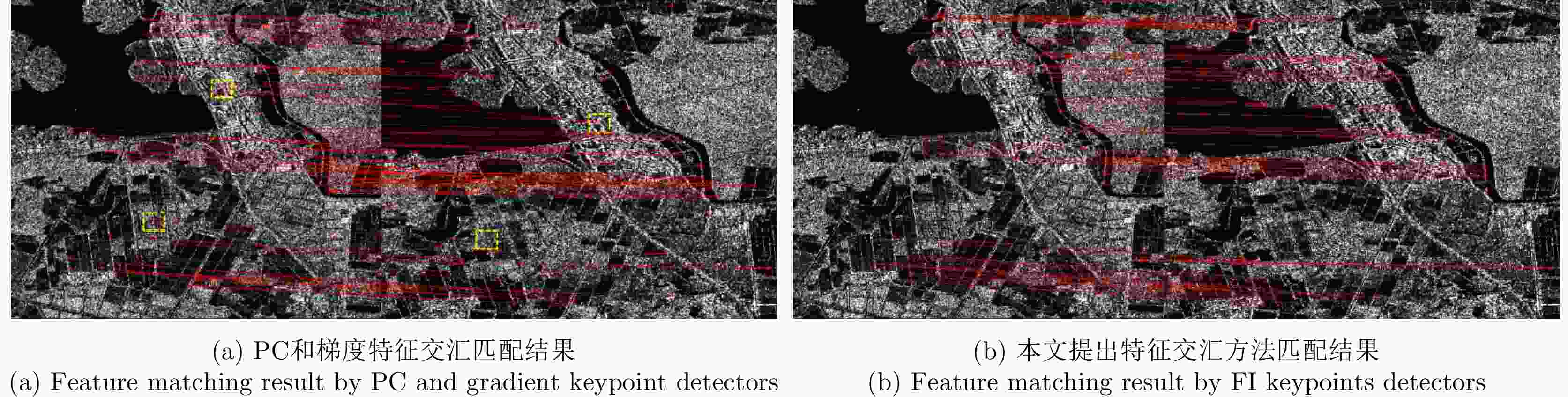
An Algorithm Based on a Feature Interaction-based Keypoint Detector and Sim-CSPNet for SAR Image Registration
-
摘要: 合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像存在固有的相干斑噪声和几何畸变,并且其成像过程中图像之间存在非线性辐射差异,因此SAR图像配准是近年来最具挑战性的任务之一。关键点的可重复性和特征描述符的有效性直接影响基于特征的配准方法精度。该文提出了一种新颖的基于特征交汇的关键点检测器,它包含3个并行的检测器,即相位一致性(PC)检测器、水平和垂直方向梯度检测器以及局部变异系数检测器。所提出的特征交汇关键点检测器不仅可以有效提取具有高重复性的关键点,而且大大减少了错误关键点的数量,从而降低了特征描述和匹配的计算成本。同时,该文设计了一种孪生跨阶段部分网络(Sim-CSPNet)来快速提取包含深层和浅层特征的特征描述符。与传统手工设计的浅层描述符相比,它可以用来获得更准确的匹配点对。通过对多组SAR图像进行配准实验,并与其他3种方法进行对比,验证了该方法具有很好的配准结果。Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) image registration has recently been one of the most challenging tasks because of speckle noise, geometric distortion and nonlinear radiation differences between SAR images. The repeatability of keypoints and the effectiveness of feature descriptors directly affect the registration accuracy of feature-based methods. In this paper, we propose a novel Feature Intersection-based (FI) keypoint detector, which contains three parallel detectors, i.e., a Phase Congruency (PC) detector, horizontal/vertical oriented gradient detectors, and a Local Coefficient of Variation (LCoV) detector. The proposed FI detector can effectively extract keypoints with high repeatabilityand greatly reduce the number of false keypoints, thus greatly reducing the computational cost of feature description and matching. We further propose the Siamese Cross Stage Partial Network (Sim-CSPNet) to rapidly extract feature descriptors containing deep and shallow features, which can obtain more correct matching point pairs than traditional synthetic shallow descriptors. Through the registration experiments on multiple sets of SAR images, the proposed method is verified to have better registration results than the three existing methods.
-
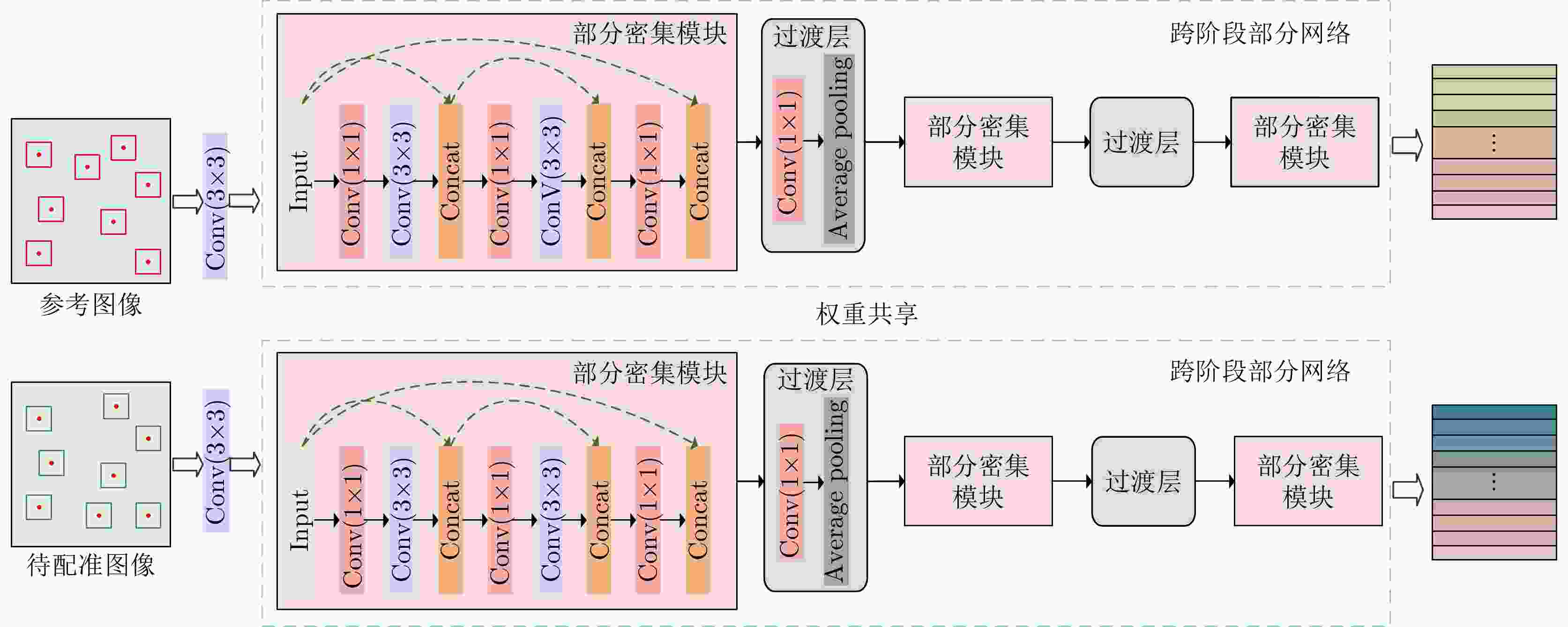
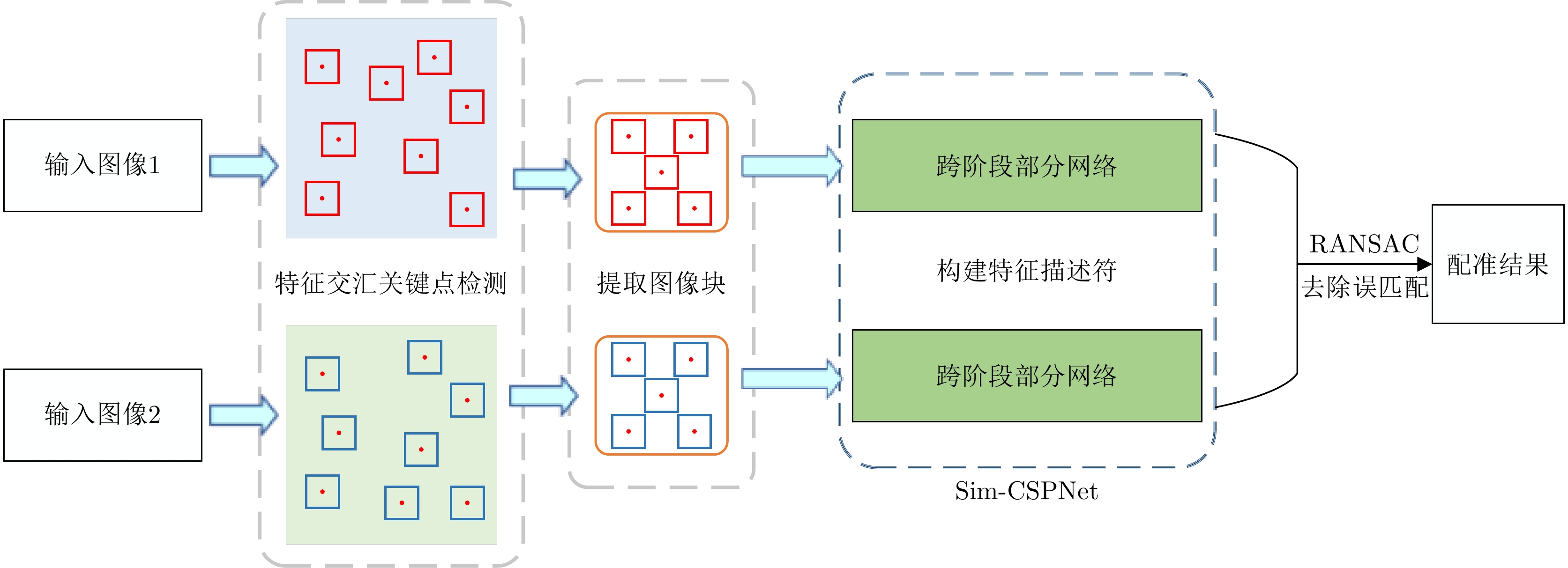
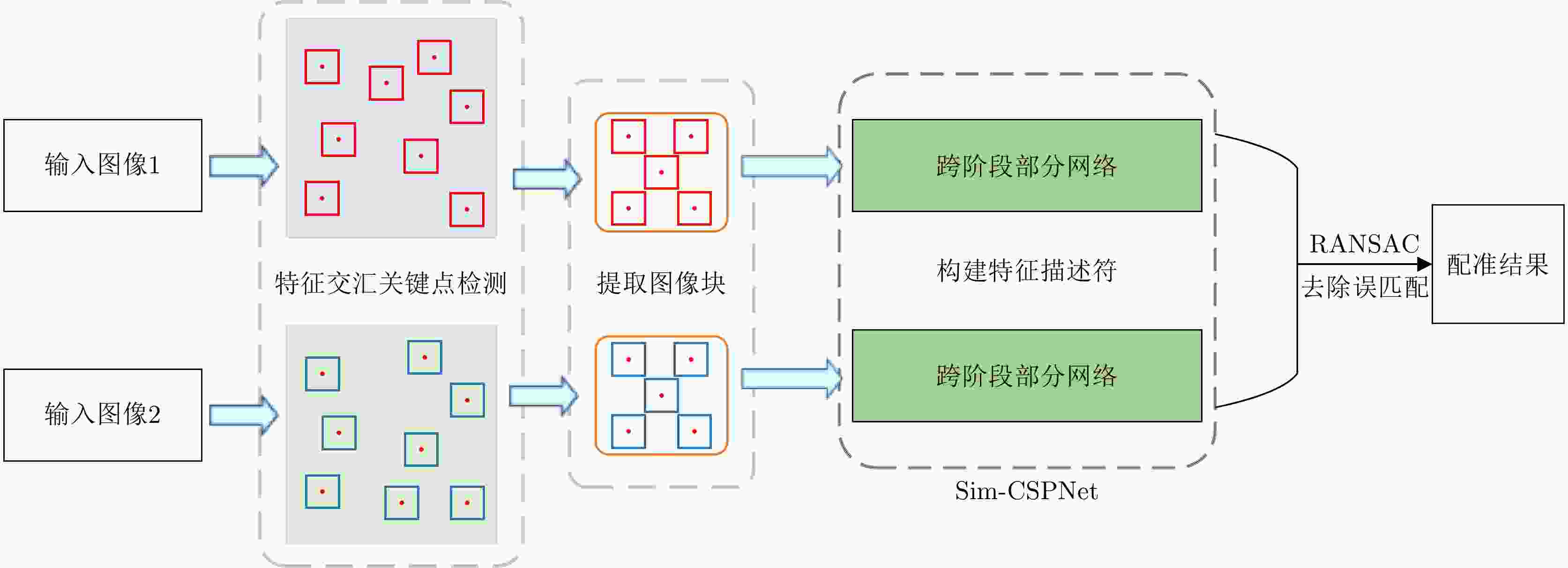
表 1 Sim-CSPNet模型结构
Table 1. Sim-CSPNet model structure
网络模块 网络层 输出尺寸 Input layer Input 64×64×1 Conv layer Conv(3×3), stride(2) 32×32×32 Block 1 Half of previous layer 32×32×16 Conv(1×1), stride(1) 32×32×48 Conv(3×3), stride(1) 32×32×12 Connect 32×32×28 Conv(1×1), stride(1) 32×32×48 Conv(3×3), stride(1) 32×32×12 Connect 32×32×40 Conv(1×1), stride(1) 32×32×20 Connect 32×32×36 Transition layer Conv(1×1), stride(1) 32×32×18 Average pooling(2×2), stride(2) 16×16×18 Block 2 16×16×25 Transition layer Conv(1×1), stride(1) 16×16×12 Average pooling(2×2), stride(2) 8×8×12 Block 3 8×8×21 Output layer Conv(8×8), stride(1) 256×1 表 2 实验使用的SAR图像对信息
Table 2. Information of SAR image pairs used in the experiment
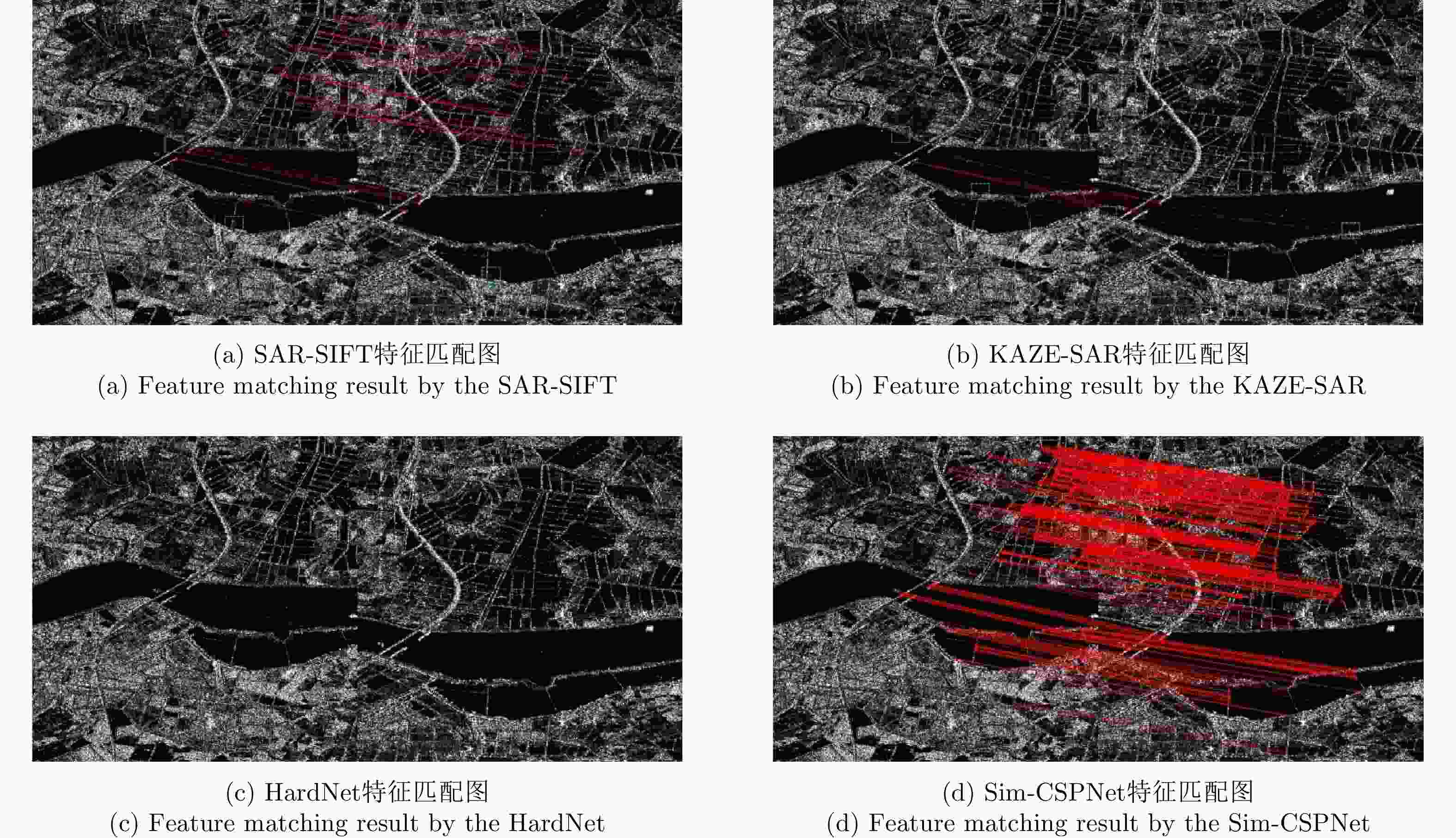
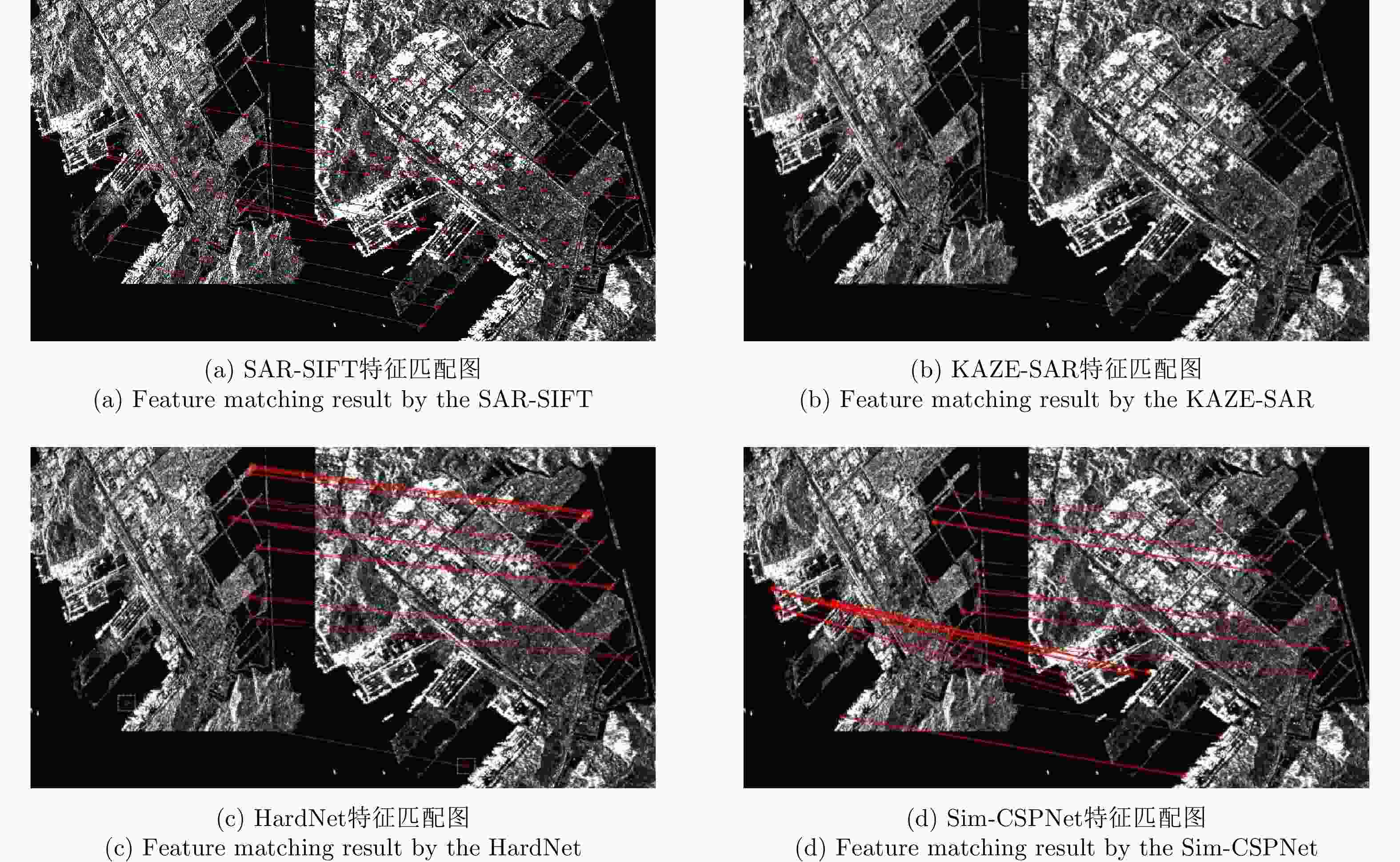
传感器 图像对编号 图像大小 分辨率(m) 获取时间 GF-3 Pair A 1214×1130(左) 2×6 20200715(左) 1480×1207(右) 20200726(右) Pair B 1000×1000(左) 2×6 20200715(左) 1000×1000(右) 20200726(右) Sentinel-1 Pair C 500×500(左) 11×14 20201010(左) 600×600(右) 20211222(右) Pair D 1374×1349(左) 11×14 20201010(左) 1597×1462(右) 20211222(右) 表 3 不同方法在4对SAR图像上的比较
Table 3. Comparison of different methods on four pairs of SAR images
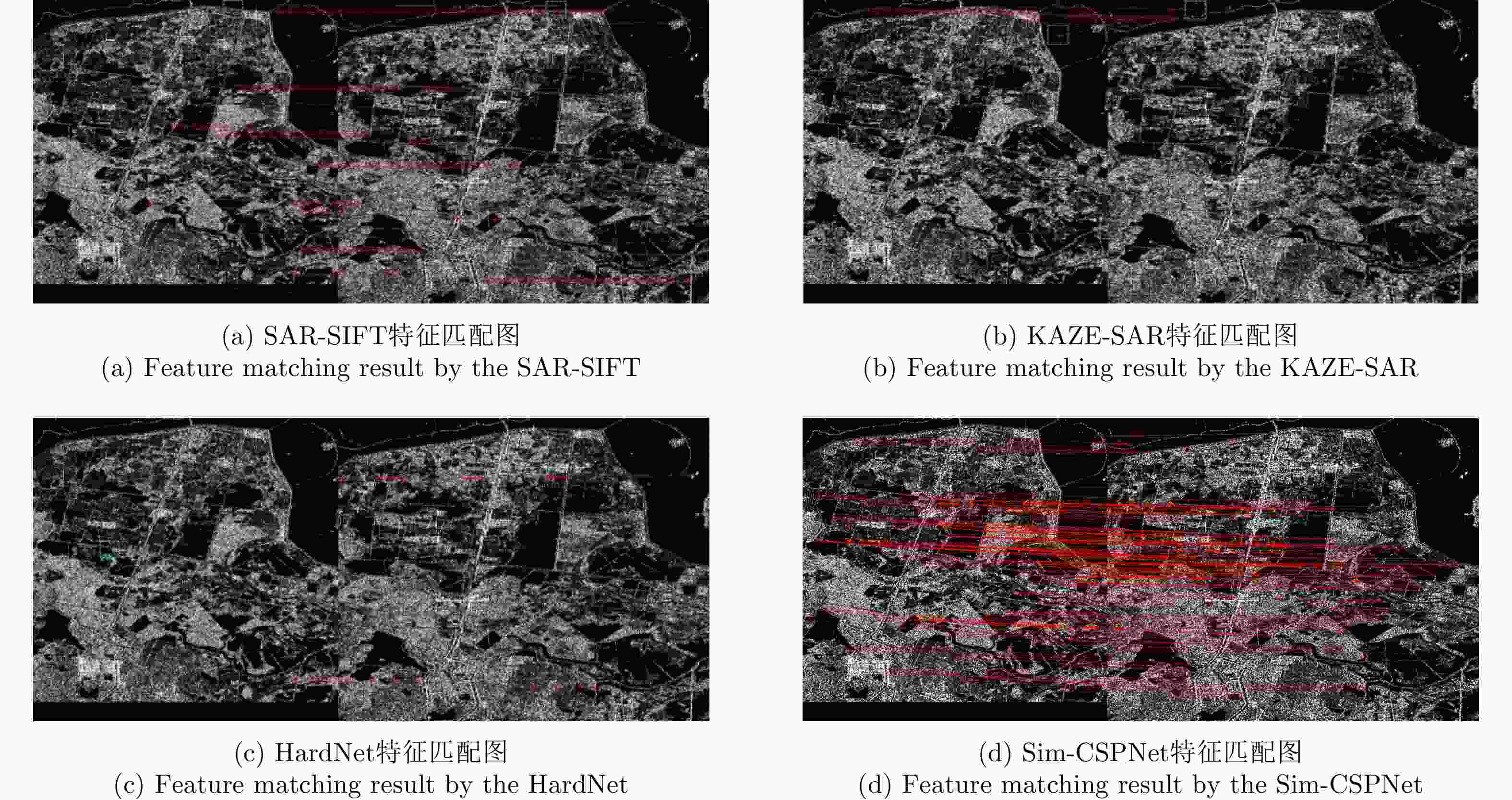
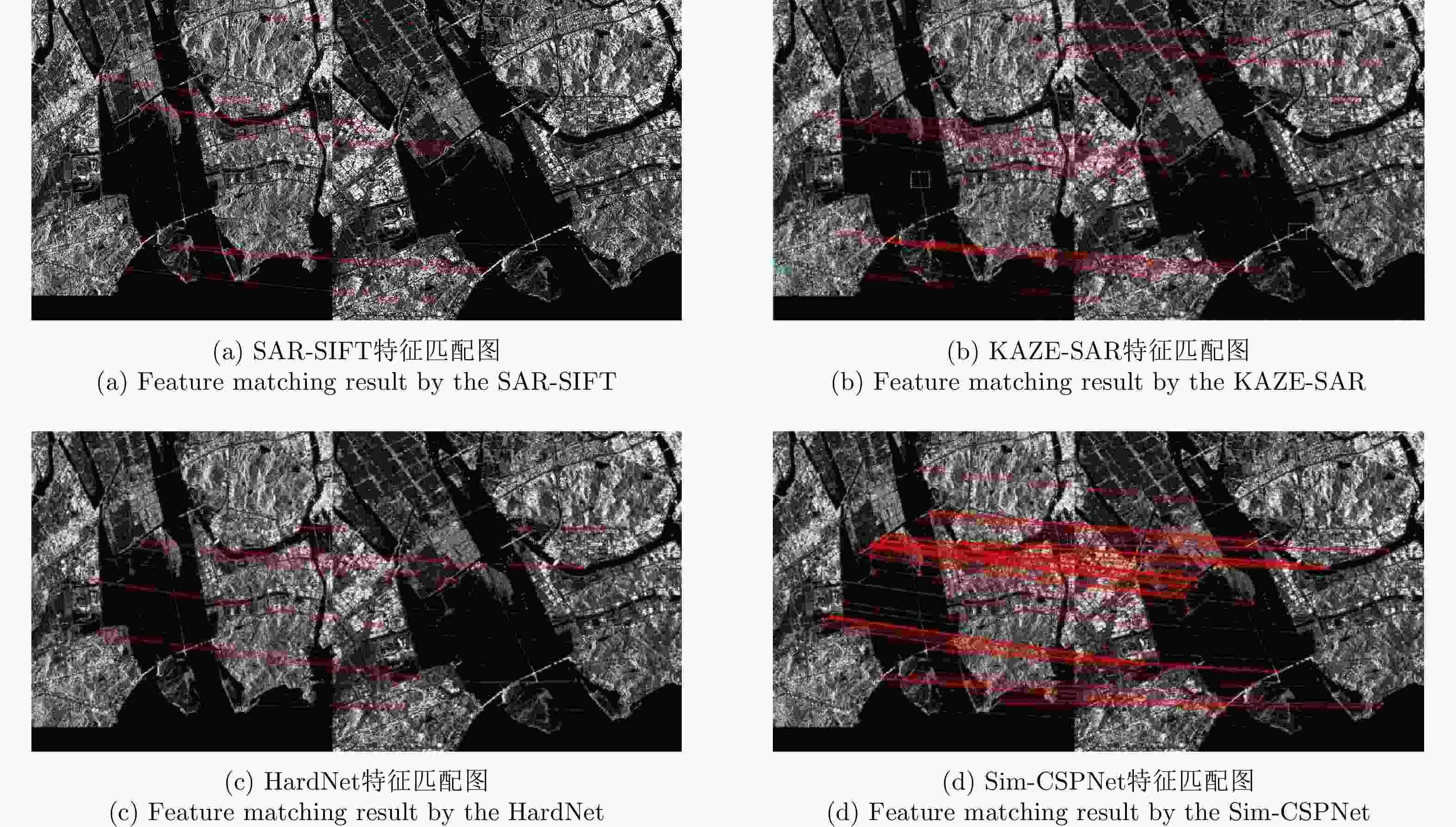
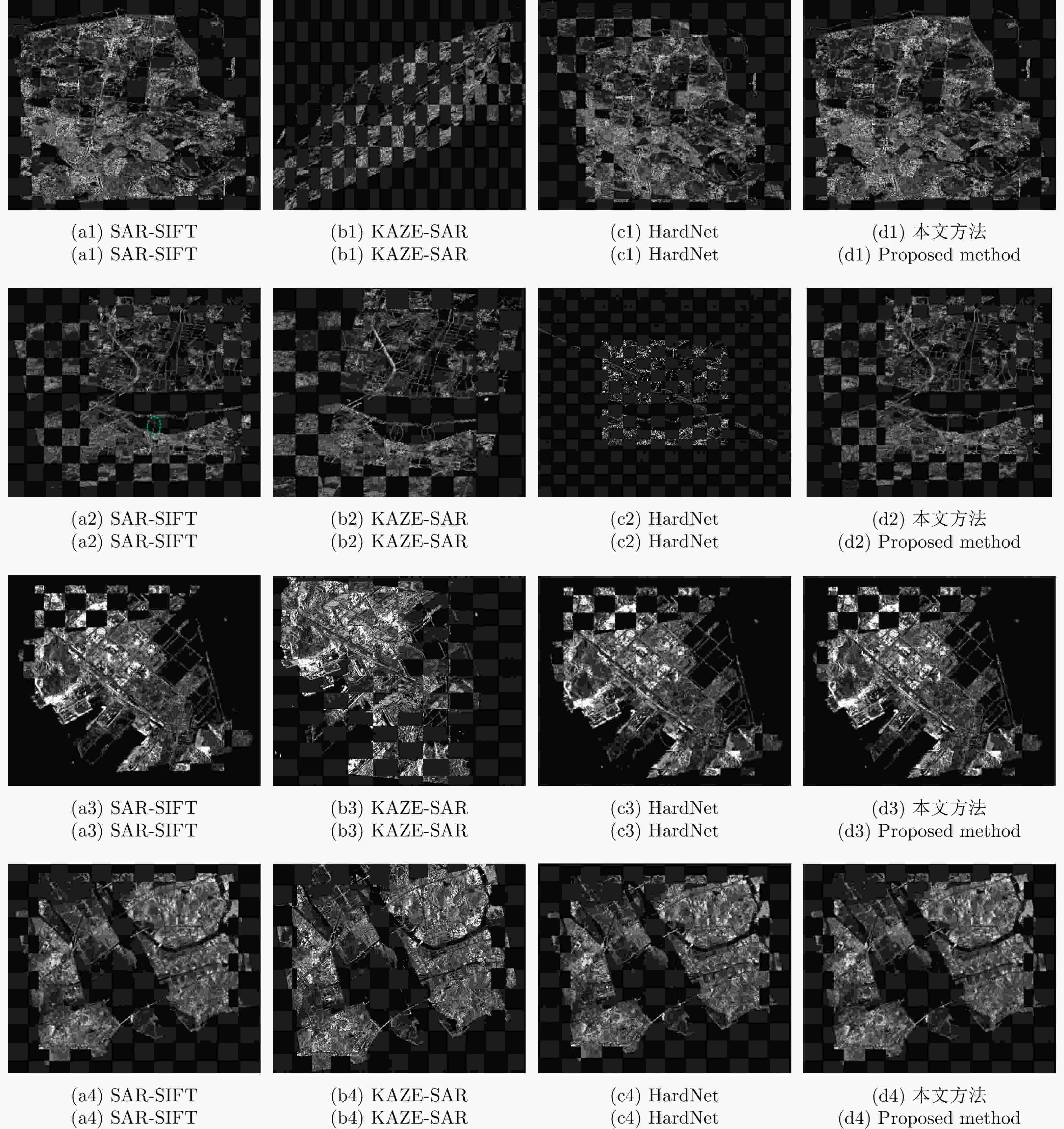
算法 Pair A Pair B Pair C Pair D RMSE NCM Time (s) RMSE NCM Time (s) RMSE NCM Time (s) RMSE NCM Time (s) SAR-SIFT 0.97 52 3215.9 0.89 51 1859.40 0.87 14 369.9 0.91 49 4232.1 KAZE-SAR – – 41.5 2.40 18 19.60 – – 5.7 4.80 61 79.2 HardNet 1.13 11 158.9 – – 63.50 0.80 21 28.9 0.96 65 146.2 本文方法 0.74 209 18.1 0.68 594 7.95 0.71 51 3.6 0.65 306 24.7 表 4 不同关键点检测器的定量比较
Table 4. Quantitative comparison of different keypoint detectors
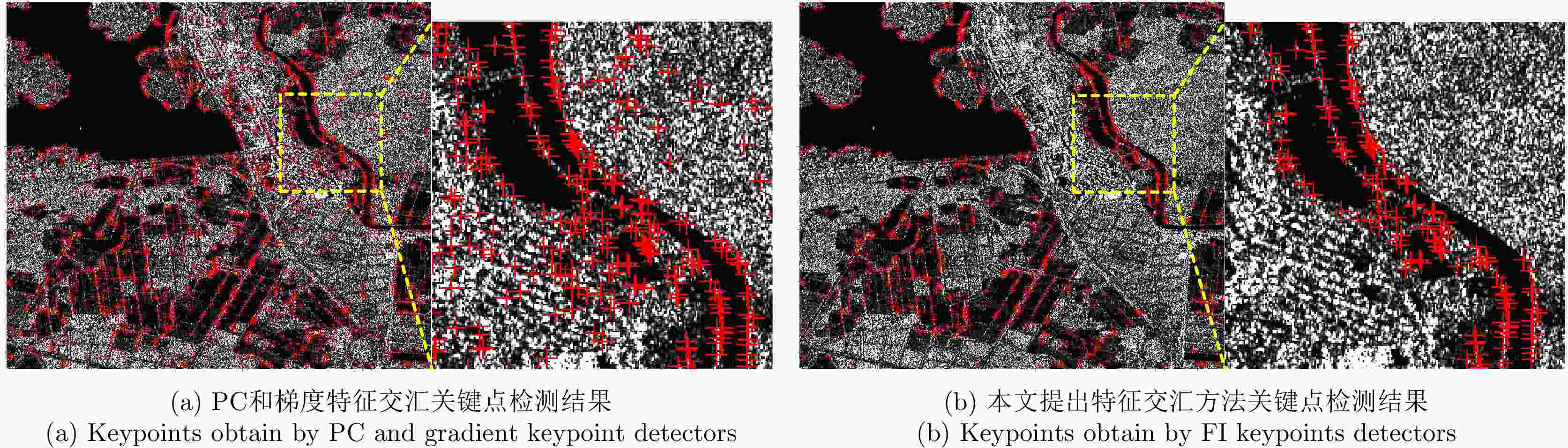
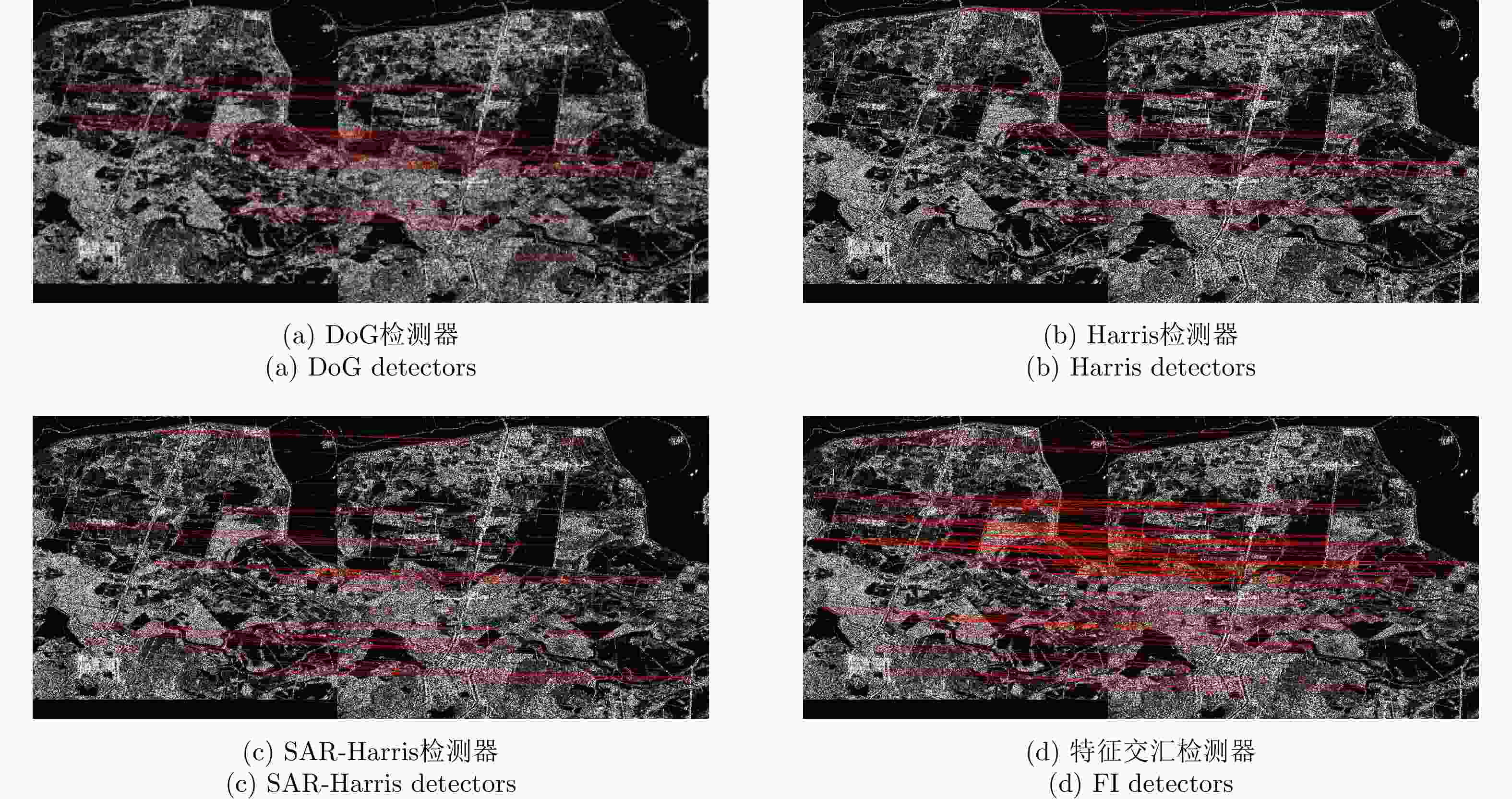
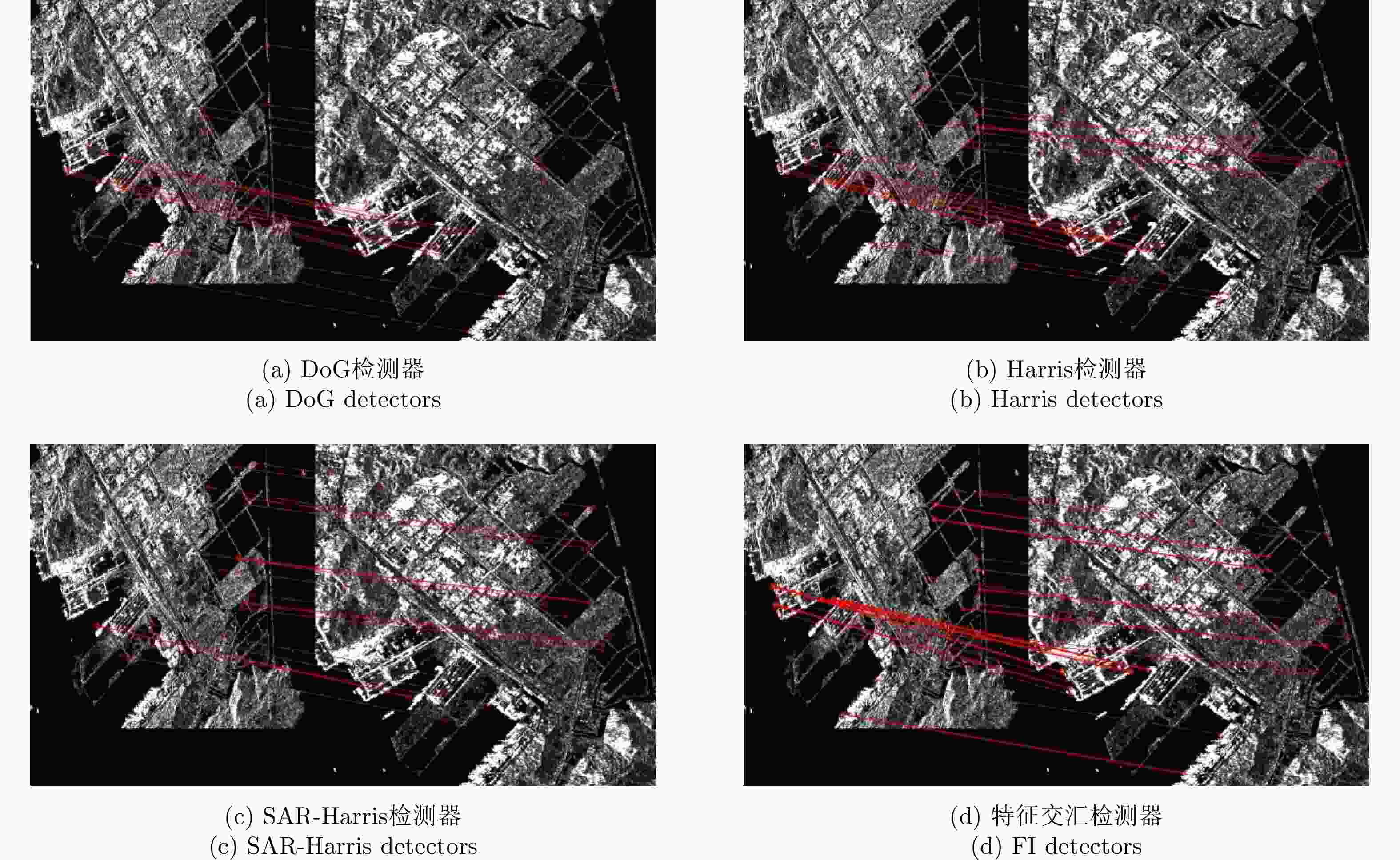
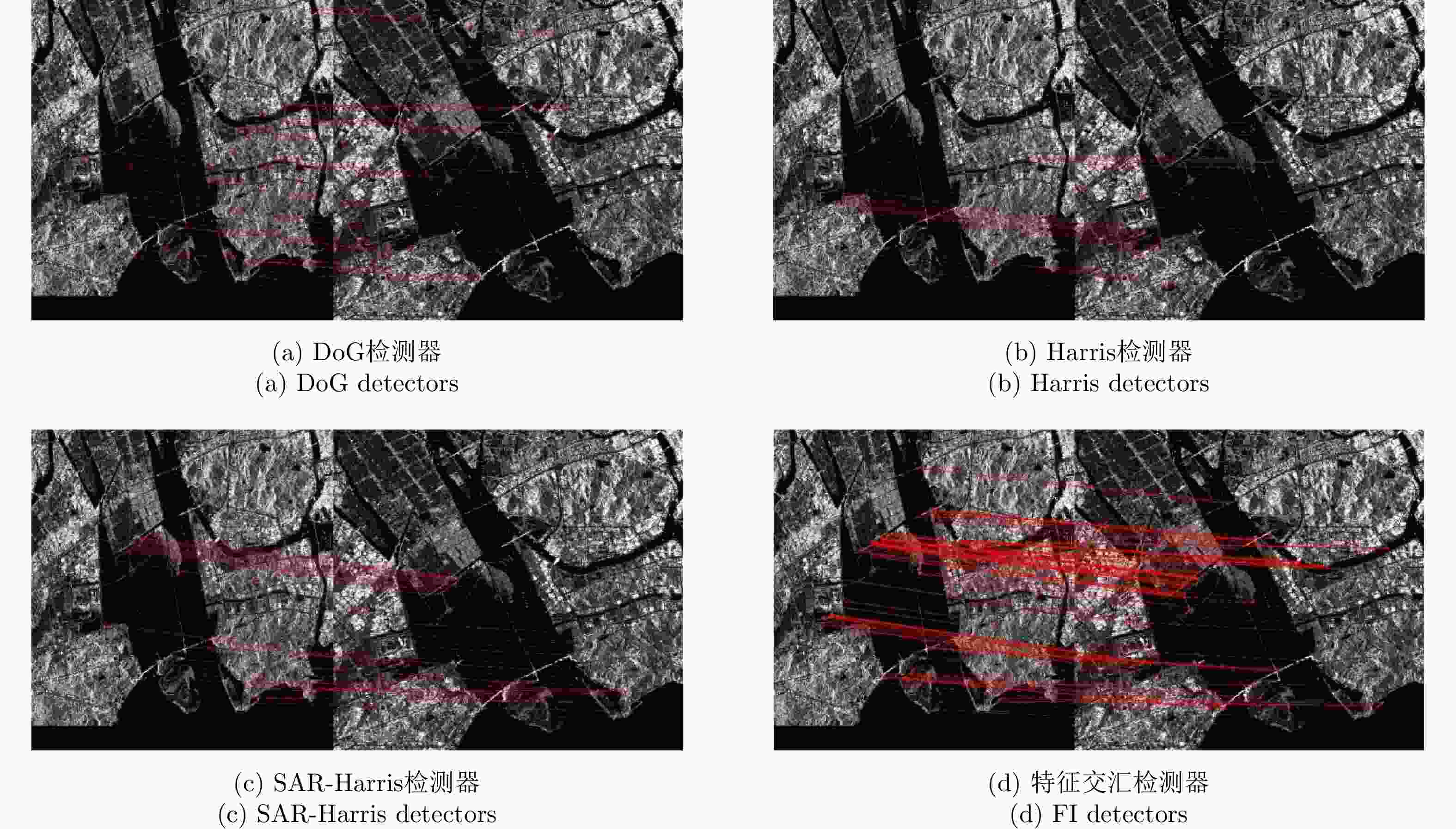
算法 指标 Pair A Pair B Pair C Pair D DoG 关键点数量(参考图像) 10651 3475 2992 13422 关键点数量(待配准图像) 19288 3383 4246 19923 时间(s) 14.9 6.64 3.56 21.28 NCM 81 17 36 128 RMSE 0.94 0.74 1.01 0.79 Harris 关键点数量(参考图像) 11513 8114 1867 14905 关键点数量(待配准图像) 14209 6370 2494 15053 时间(s) 12.47 6.79 3.39 13.32 NCM 60 40 25 49 RMSE 1.07 0.81 0.80 0.86 SAR-Harris 关键点数量(参考图像) 22746 9193 3391 23660 关键点数量(待配准图像) 32693 10215 5584 37767 时间(s) 49.4 11.31 7.6 34.68 NCM 134 132 39 164 RMSE 0.95 0.87 0.79 0.76 特征交汇检测器 关键点数量(参考图像) 7848 6133 752 10481 关键点数量(待配准图像) 7961 5424 715 11499 时间(s) 18.1 7.95 3.6 24.7 NCM 209 594 51 306 RMSE 0.74 0.68 0.71 0.65 表 5 不同网络的定量比较
Table 5. Quantitative comparison of different networks
算法 Pair A Pair B Pair C Pair D RMSE NCM Time (s) RMSE NCM Time (s) RMSE NCM Time (s) RMSE NCM Time (s) FI+L2Net 1.13 51 34.35 0.81 22 30.38 1.56 18 3.63 0.84 41 28.17 FI+HardNet 0.85 55 32.50 0.77 42 29.41 0.79 29 3.99 0.76 68 28.42 FI+SOSNet 0.83 93 14.21 0.70 79 9.24 0.86 48 2.77 0.92 121 11.70 本文方法 0.74 209 18.10 0.68 594 7.95 0.71 51 3.60 0.65 306 24.70 -
[1] SUN Yili, LEI Lin, LI Xiao, et al. Structure consistency-based graph for unsupervised change detection with homogeneous and heterogeneous remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1–21. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3053571 [2] 苏娟, 李彬, 王延钊. 一种基于封闭均匀区域的SAR图像配准方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3282–3288. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160141SU Juan, LI Bin, and WANG Yanzhao. SAR image registration algorithm based on closed uniform regions[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3282–3288. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160141 [3] 张王菲, 陈尔学, 李增元, 等. 雷达遥感农业应用综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 444–461. doi: 10.12000/JR20051ZHANG Wangfei, CHEN Erxue, LI Zengyuan, et al. Review of applications of radar remote sensing in agriculture[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 444–461. doi: 10.12000/JR20051 [4] 周荣荣. 山地SAR影像配准方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 长安大学, 2019.ZHOU Rongrong. Research on registration method of mountainous SAR images[D]. [Master dissertation], Chang’an University, 2019. [5] SURI S and REINARTZ P. Mutual-information-based registration of TerraSAR-X and Ikonos imagery in urban areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 939–949. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2034842 [6] YOO J C and HAN T H. Fast normalized cross-correlation[J]. Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing, 2009, 28(6): 819–843. doi: 10.1007/s00034-009-9130-7 [7] SHI Wei, SU Fenzhen, WANG Ruirui, et al. A visual circle based image registration algorithm for optical and SAR imagery[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 2109–2112. [8] WANG Fei and VEMURI B C. Non-rigid multi-modal image registration using cross-cumulative residual entropy[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2007, 74(2): 201–215. doi: 10.1007/s11263-006-0011-2 [9] PAUL S and PATI U C. SAR image registration using an improved SAR-SIFT algorithm and Delaunay-triangulation-based local matching[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(8): 2958–2966. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2918211 [10] LOWE D G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features[C]. Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 1999: 1150–1157. [11] MIKOLAJCZYK K and SCHMID C. A performance evaluation of local descriptors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(10): 1615–1630. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.188 [12] MA Wenping, WEN Zelian, WU Yue, et al. Remote sensing image registration with modified SIFT and enhanced feature matching[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(1): 3–7. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2600858 [13] XIANG Yuming, WANG Feng, and YOU Hongjian. OS-SIFT: A robust SIFT-like algorithm for high-resolution optical-to-SAR image registration in suburban areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(6): 3078–3090. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2790483 [14] SCHWIND P, SURI S, REINARTZ P, et al. Applicability of the SIFT operator to geometric SAR image registration[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2010, 31(8): 1959–1980. doi: 10.1080/01431160902927622 [15] DELLINGER F, DELON J, GOUSSEAU Y, et al. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-like algorithm for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 453–466. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2323552 [16] WANG Shanhu, YOU Hongjian, and FU Kun. BFSIFT: A novel method to find feature matches for SAR image registration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(4): 649–653. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2177437 [17] FAN Jianwei, WU Yan, WANG Fan, et al. SAR image registration using phase congruency and nonlinear diffusion-based SIFT[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(3): 562–566. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2351396 [18] ELTANANY A S, AMEIN A S, and ELWAN M S. A modified corner detector for SAR images registration[J]. International Journal of Engineering Research in Africa, 2021, 53(106): 123–156. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/JERA.53.123 [19] YE Yuanxin, WANG Mengmeng, HAO Siyuan, et al. A novel keypoint detector combining corners and blobs for remote sensing image registration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(3): 451–455. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2980620 [20] ZHANG Han, NI Weiping, YAN Weidong, et al. Registration of multimodal remote sensing image based on deep fully convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(8): 3028–3042. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2916560 [21] GE Ynchen, XIONG Zhaolong, and LAI Zuomei. Image registration of SAR and optical based on salient image sub-patches[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2021, 1961(1): 12–17. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1961/1/012017 [22] ZHU Hao, JIAO Licheng, MA Wenping, et al. A novel neural network for remote sensing image matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(9): 2853–2865. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2888757 [23] MISHCHUK A, MISHKIN D, RADENOVIC F, et al. Working hard to know your neighbor’s margins: Local descriptor learning loss[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 4829–4840. [24] DU Wenliang, ZHOU Yong, and ZHAO Jiaqi, et al. Exploring the potential of unsupervised image synthesis for SAR-optical image matching[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 71022–71033. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3079327 [25] YE Famao, SU Yanfei, XIAO Hui, et al. Remote sensing image registration using convolutional neural network features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(2): 232–236. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2781741 [26] WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M, WU Y H, et al. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, USA, 2020: 1571–1580. [27] WANG Lina, SUN Mingchao, LIU Jinghong, et al. A robust algorithm based on phase congruency for optical and SAR image registration in suburban areas[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(20): 3339. doi: 10.3390/rs12203339 [28] XIANG Yuming, TAO Rongshu, WANG Feng, et al. Automatic registration of optical and SAR images VIA improved phase congruency[C]. IGARSS 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 931–934. [29] KOVESI P. Image features from phase congruency[J]. Videre:Journal of Computer Vision Research, 1999, 1(3): 1–26. doi: 10.1080/00268976.2015.1118568 [30] XIE Hua, PIERCE L E, and ULABY F T. Statistical properties of logarithmically transformed speckle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(3): 721–727. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.1000333 [31] HARRIS C and STEPHENS M. A combined corner and edge detector[C]. Alvey Vision Conference, Manchester, UK, 1988. [32] HAN Xufeng, LEUNG T, JIA Yangqing, et al. MatchNet: Unifying feature and metric learning for patch-based matching[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3279–3286. [33] DE TONE D, MALISIEWICZ T, and RABINOVICH A. Deep image homography estimation[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1606.03798, 2016. [34] MERKLE N, LUO Wenjie, AUER S, et al. Exploiting deep matching and SAR data for the geo-localization accuracy improvement of optical satellite images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(6): 586. doi: 10.3390/rs9060586 [35] BALNTAS V, RIBA E, PONSA D, et al. Learning local feature descriptors with triplets and shallow convolutional neural networks[C]. British Machine Vision Conference 2016, York, UK, 2016. [36] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2016: 2261–2269. [37] HERMANS A, BEYER L, and LEIBE B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1703.07737, 2017. [38] POURFARD M, HOSSEINIAN T, SAEIDI R, et al. KAZE-SAR: SAR image registration using KAZE detector and modified SURF descriptor for tackling speckle noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5207612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3084411 [39] TIAN Yurun, FAN Bin, and WU Fuchao. L2-Net: Deep learning of discriminative patch descriptor in euclidean space[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honnolulu, USA, 2017: 6128–6136. [40] TIAN Yurun, YU Xin, FAN Bin, et al. SOSNet: Second order similarity regularization for local descriptor learning[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 11008–11017. [41] TOUZI R. A review of speckle filtering in the context of estimation theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(11): 2392–2404. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803727 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: