Dense-repeated Jamming Suppression Algorithm Based on the Support Vector Machine for Frequency Agility Radar
-
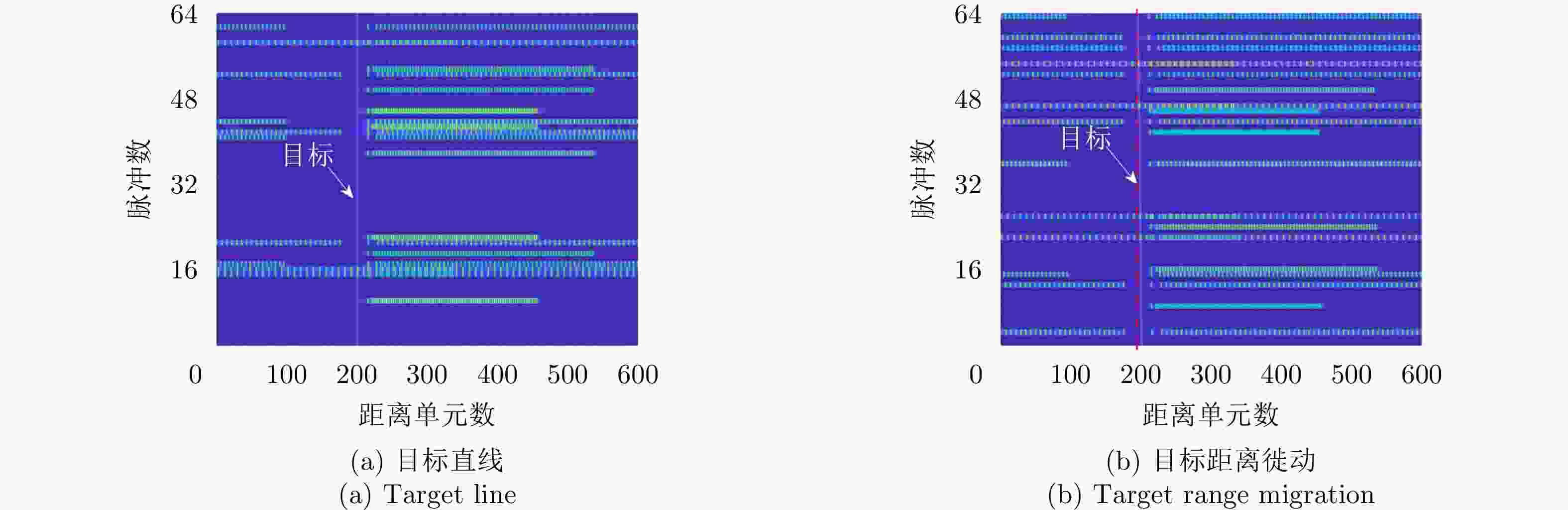
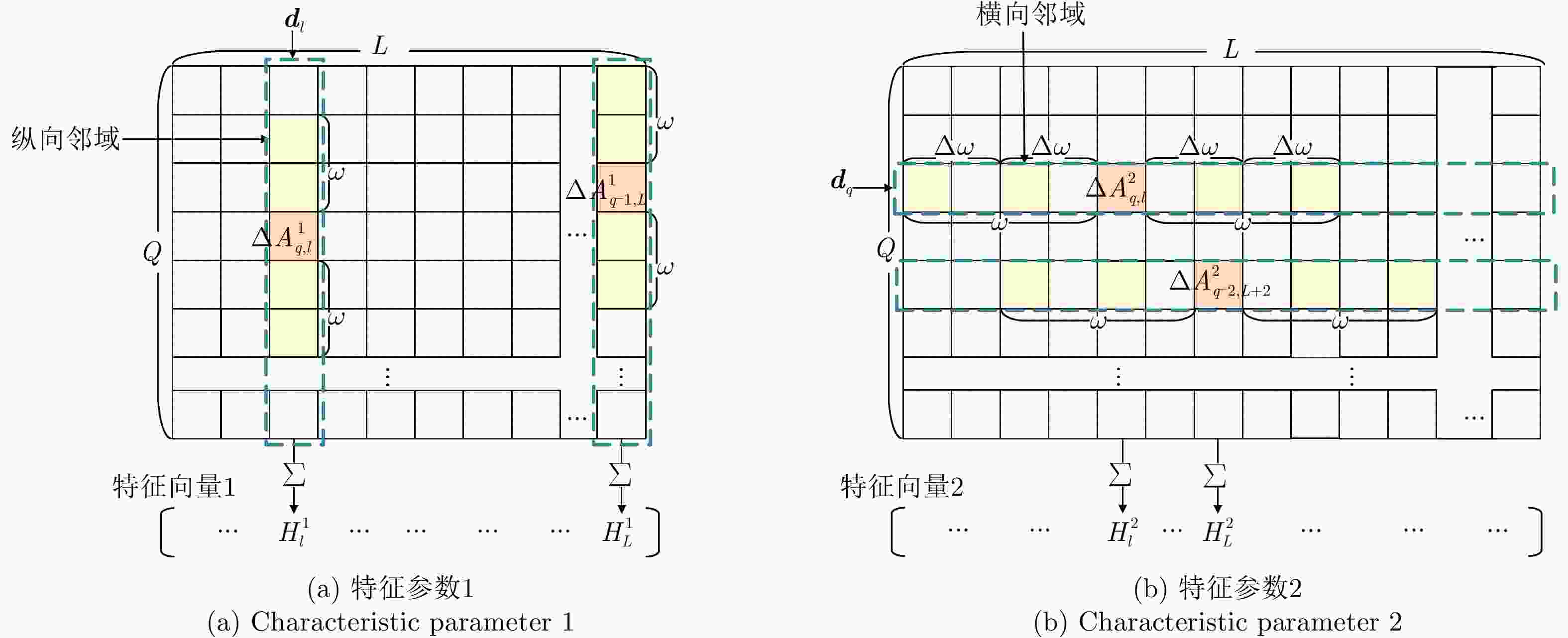
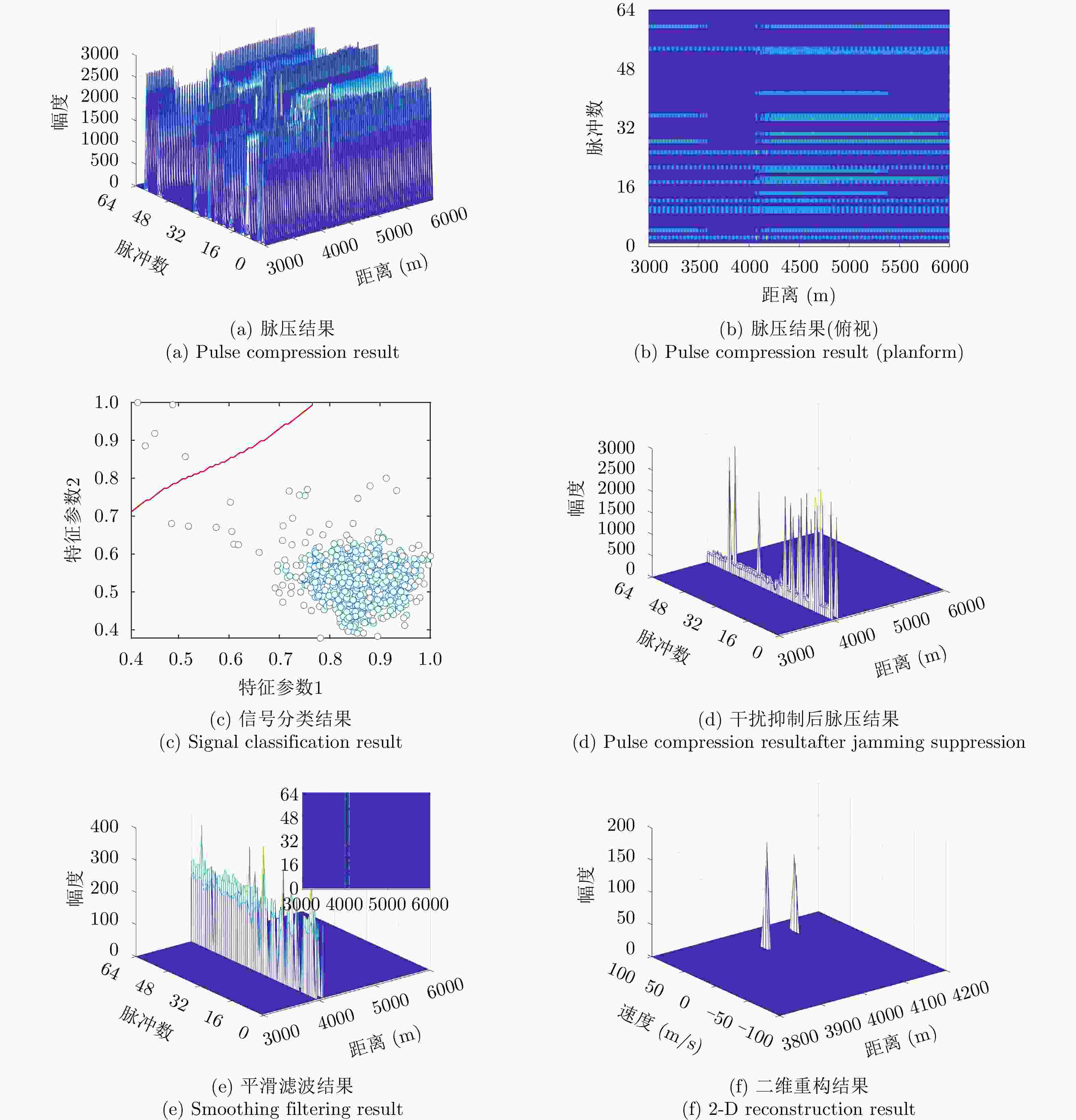
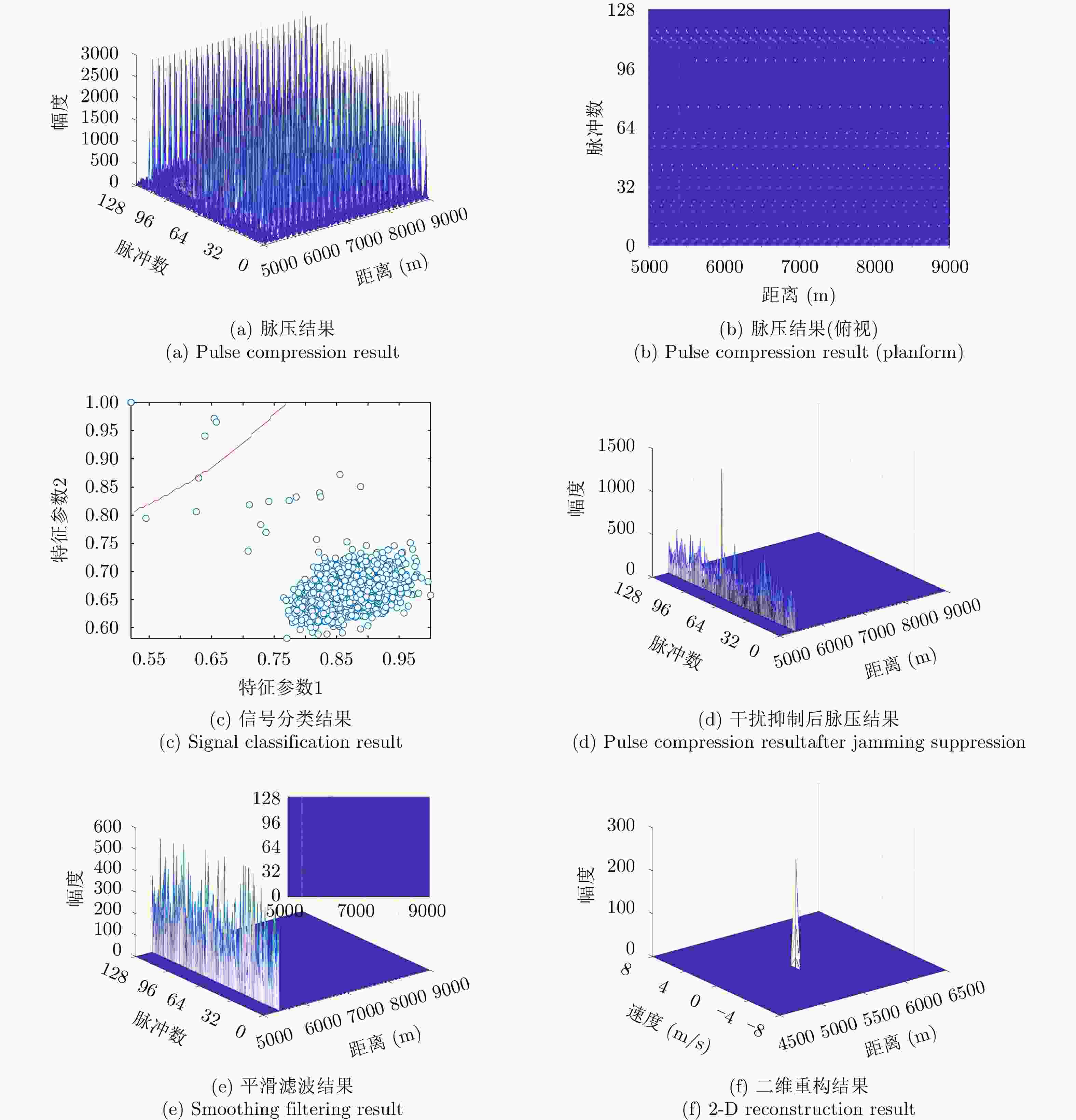
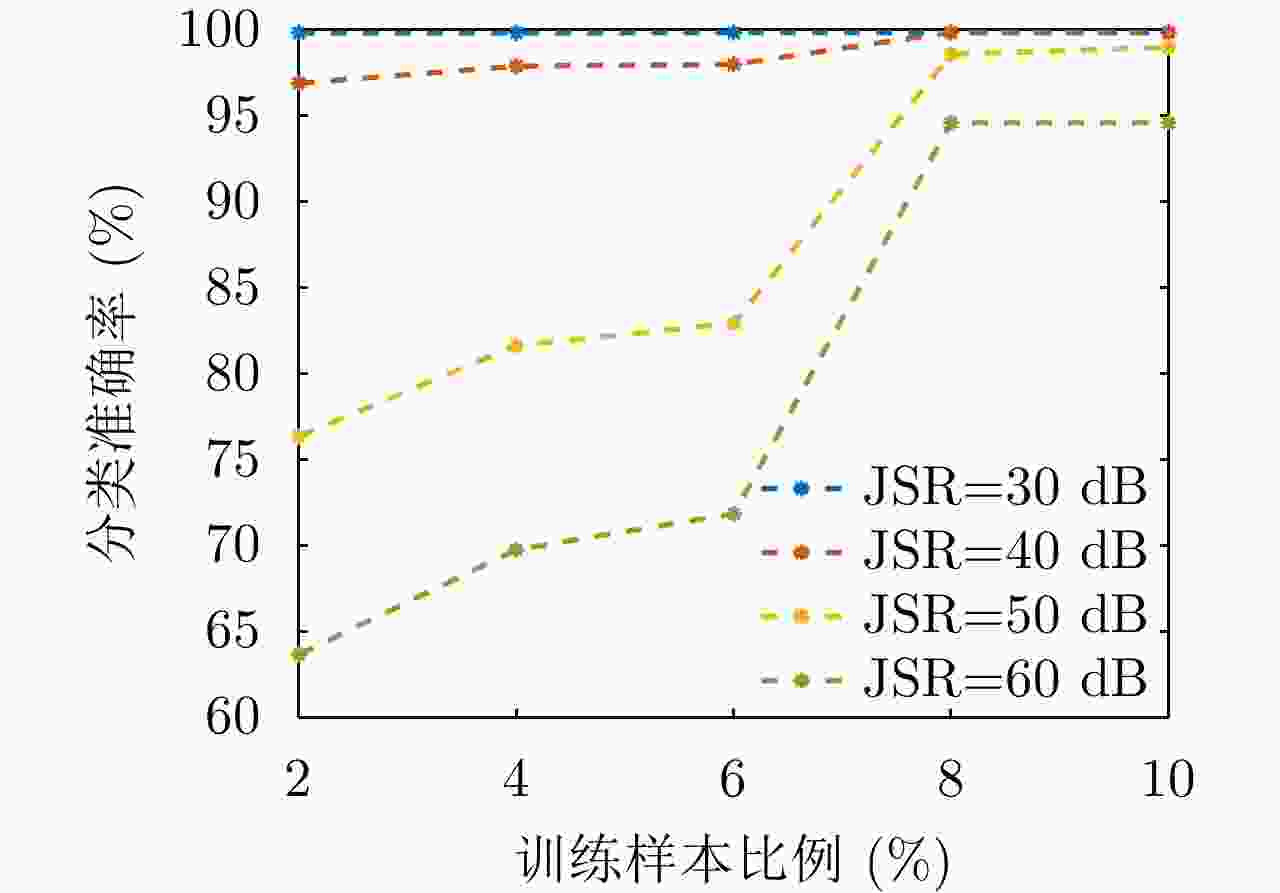
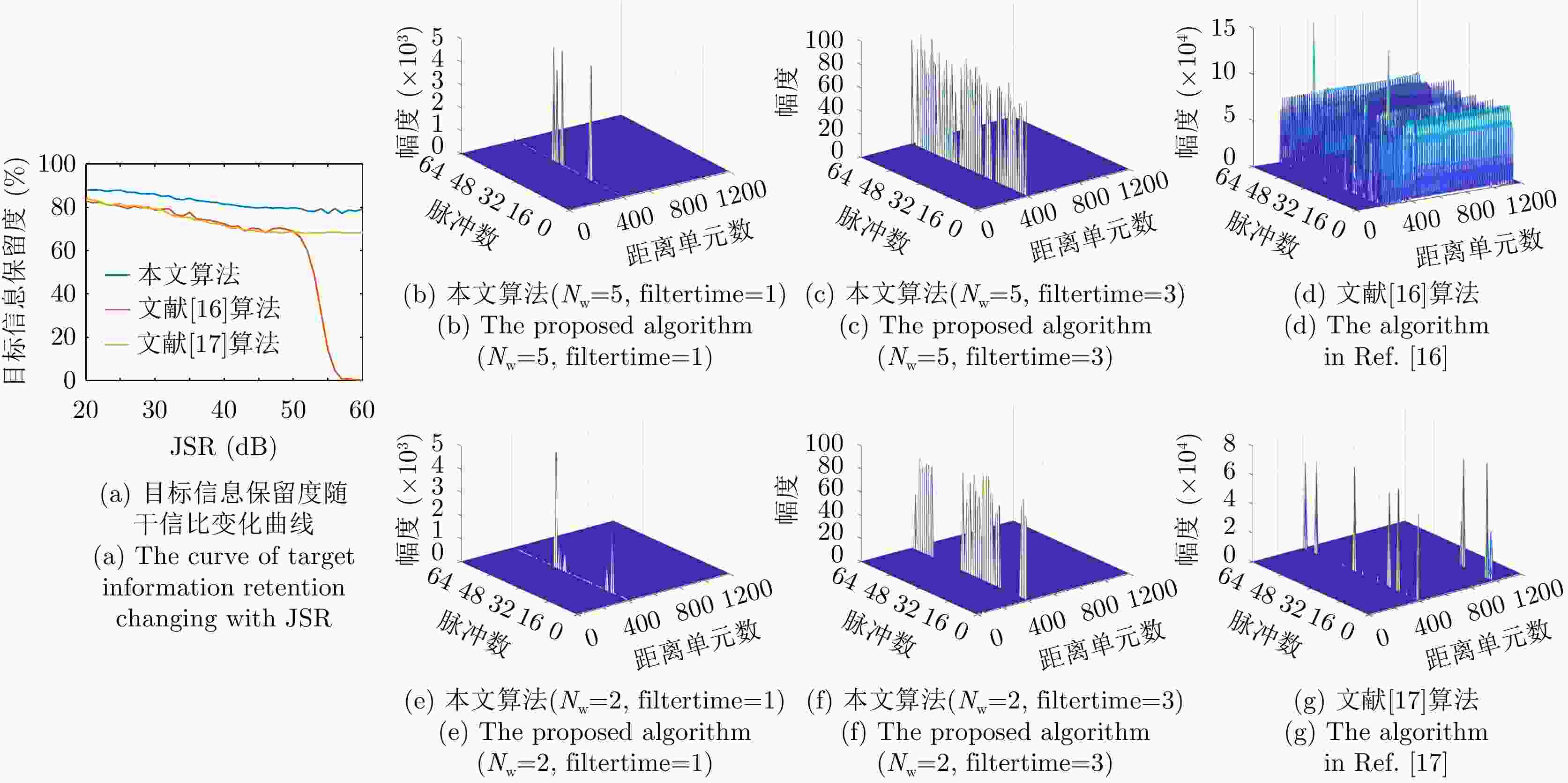
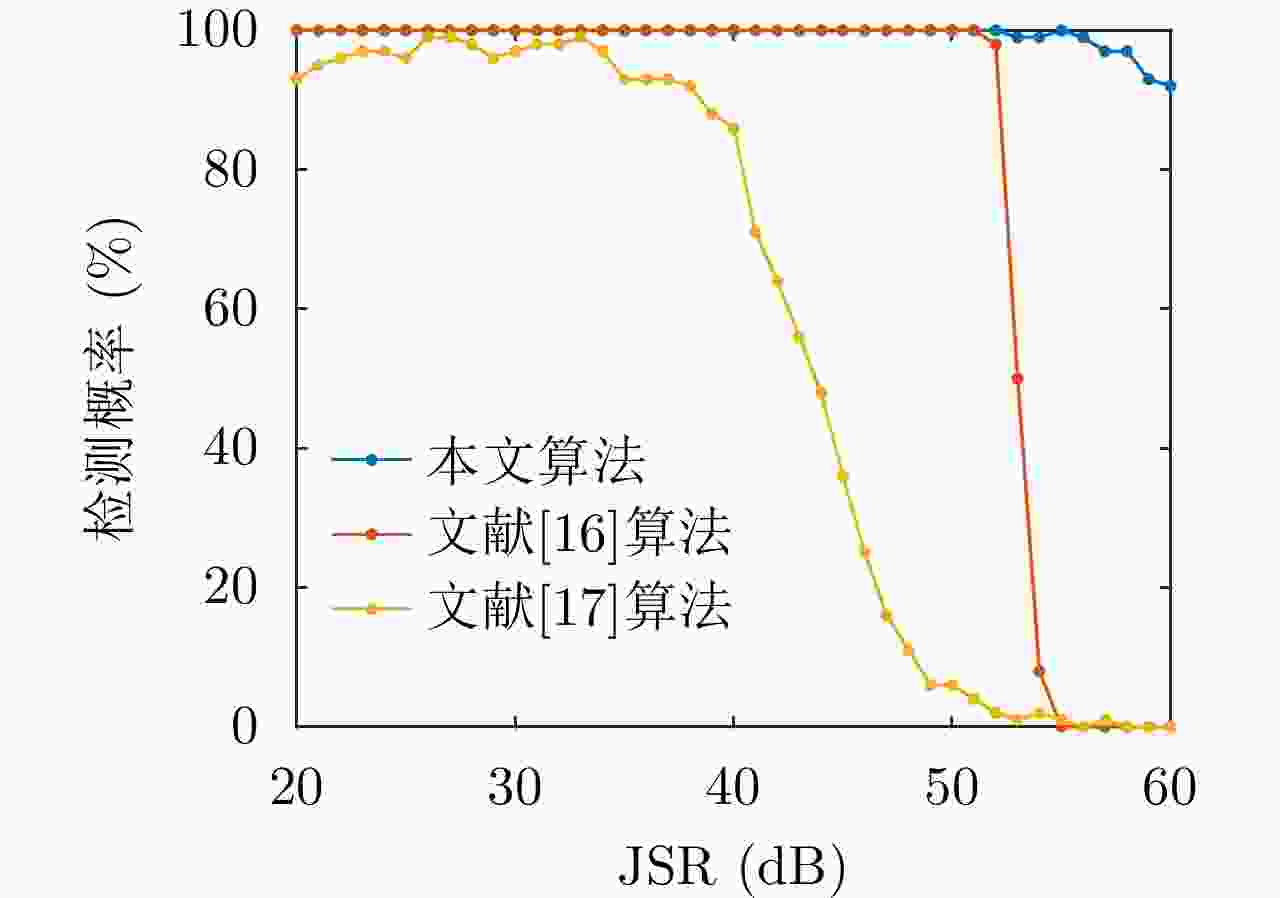
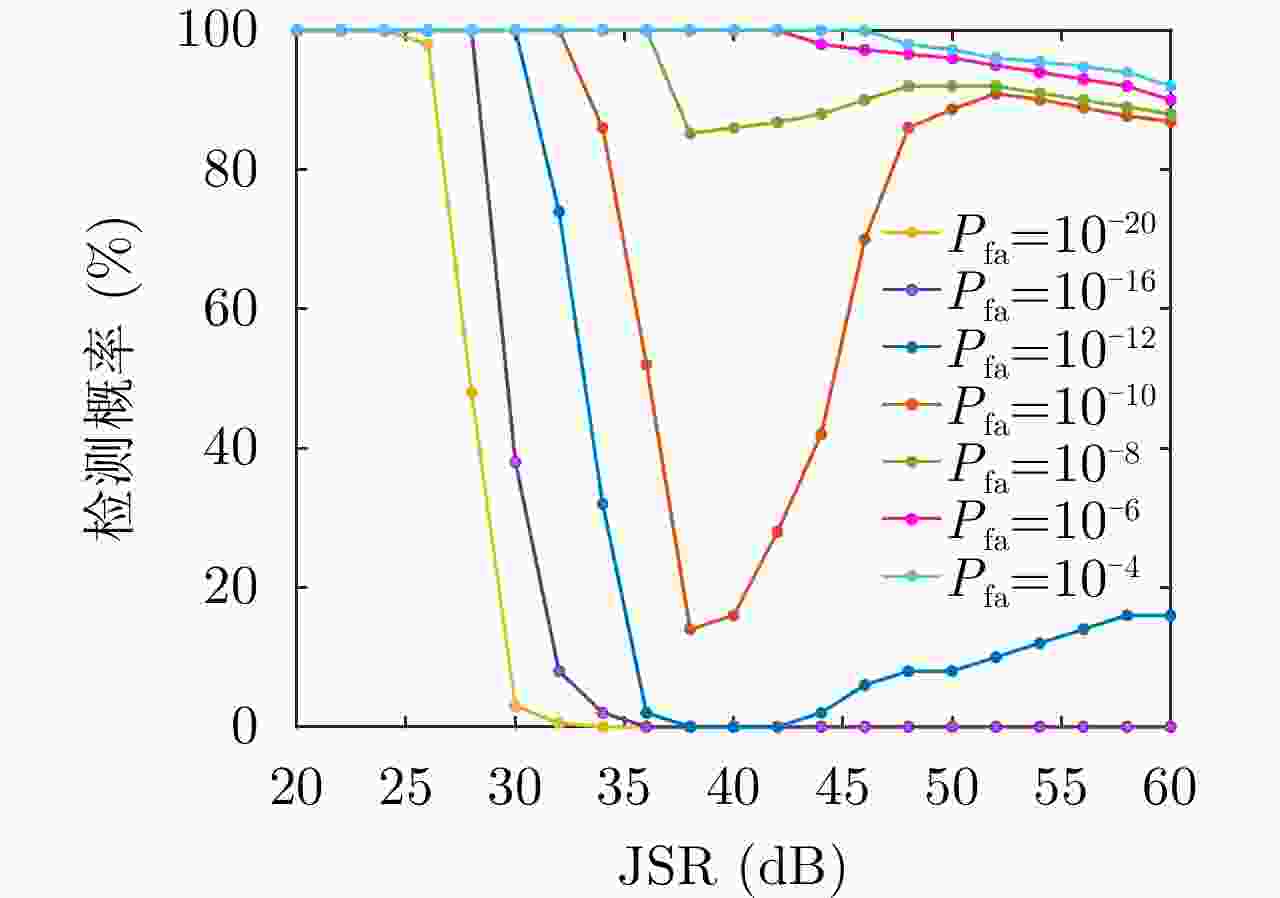
摘要: 密集转发干扰与雷达发射信号高度相关,兼具压制式和欺骗式干扰效果,使雷达系统难以检测到真实目标,严重威胁雷达作战能力。针对这一问题,该文提出一种基于支持向量机(SVM)的捷变频雷达密集转发干扰智能抑制方法。通过对随机样本集进行离线训练获得最优SVM模型,智能化识别并分类目标和干扰;然后,采用平滑滤波进一步抑制目标所在距离单元内的干扰信号;最后,基于压缩感知(CS)理论进行二维高分辨重构,估计出目标参数信息。仿真实验与实测数据处理结果表明,所提算法在不同场景下均能够有效抑制密集转发干扰,准确检测出真实目标。Abstract: Dense-repeated jamming is highly related to the radar-transmitted signal, and it has suppression and deception jamming effects, which makes detecting the real target difficult for a radar system and seriously threatens the operational capability of radar. To solve this problem, an intelligent suppression method based on the Support Vector Machine (SVM) is proposed in this paper. The optimal SVM model is obtained through offline training on a random sample set to intelligently identify and classify targets and interference. Then, the interference sidelobe in the target range unit is further suppressed by smoothing filtering. Finally, high-resolution two-dimensional reconstruction is performed based on Compress Sensing (CS) theory to estimate the target parameter information. Simulation experiments and measured data processing results reveal that the proposed algorithm can effectively suppress dense-repeated jamming and accurately detect real targets in different scenarios.
-
表 1 雷达参数
Table 1. Radar parameters
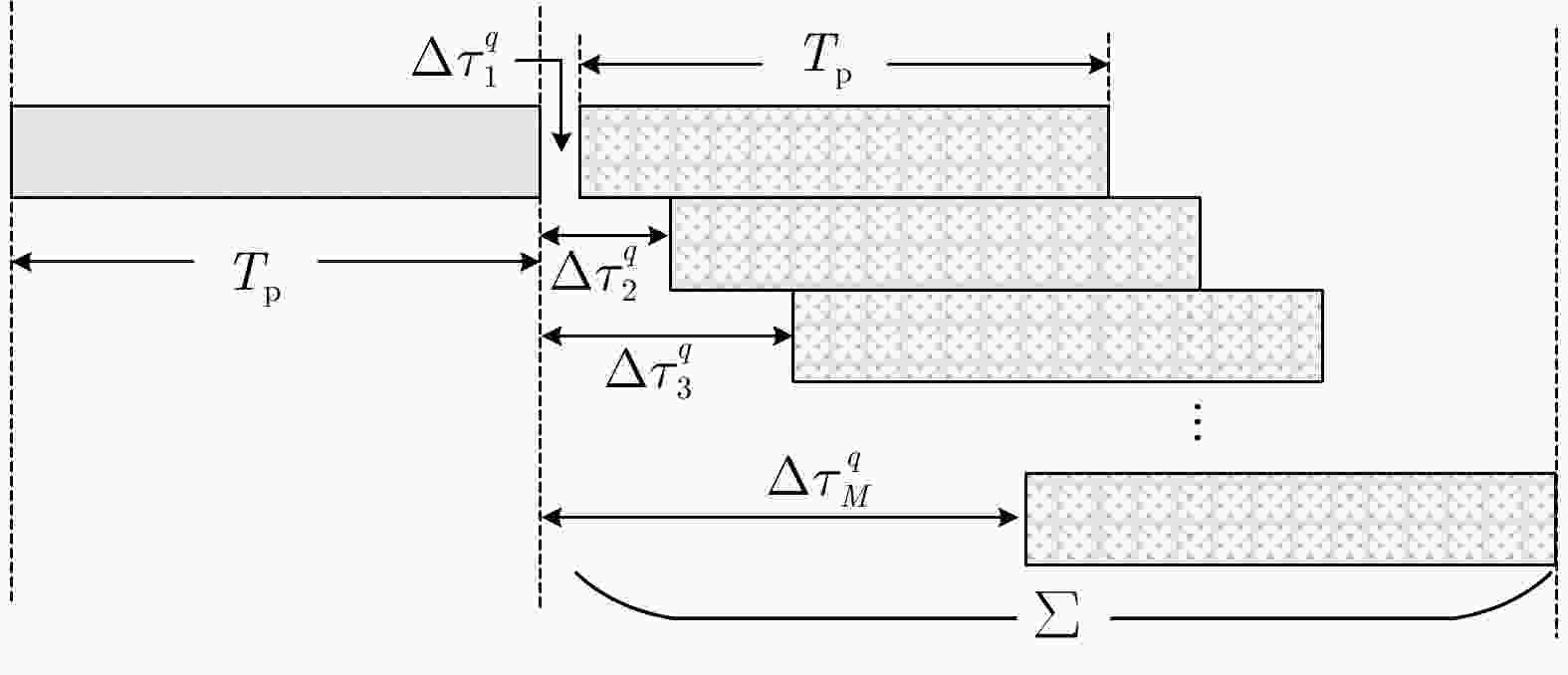
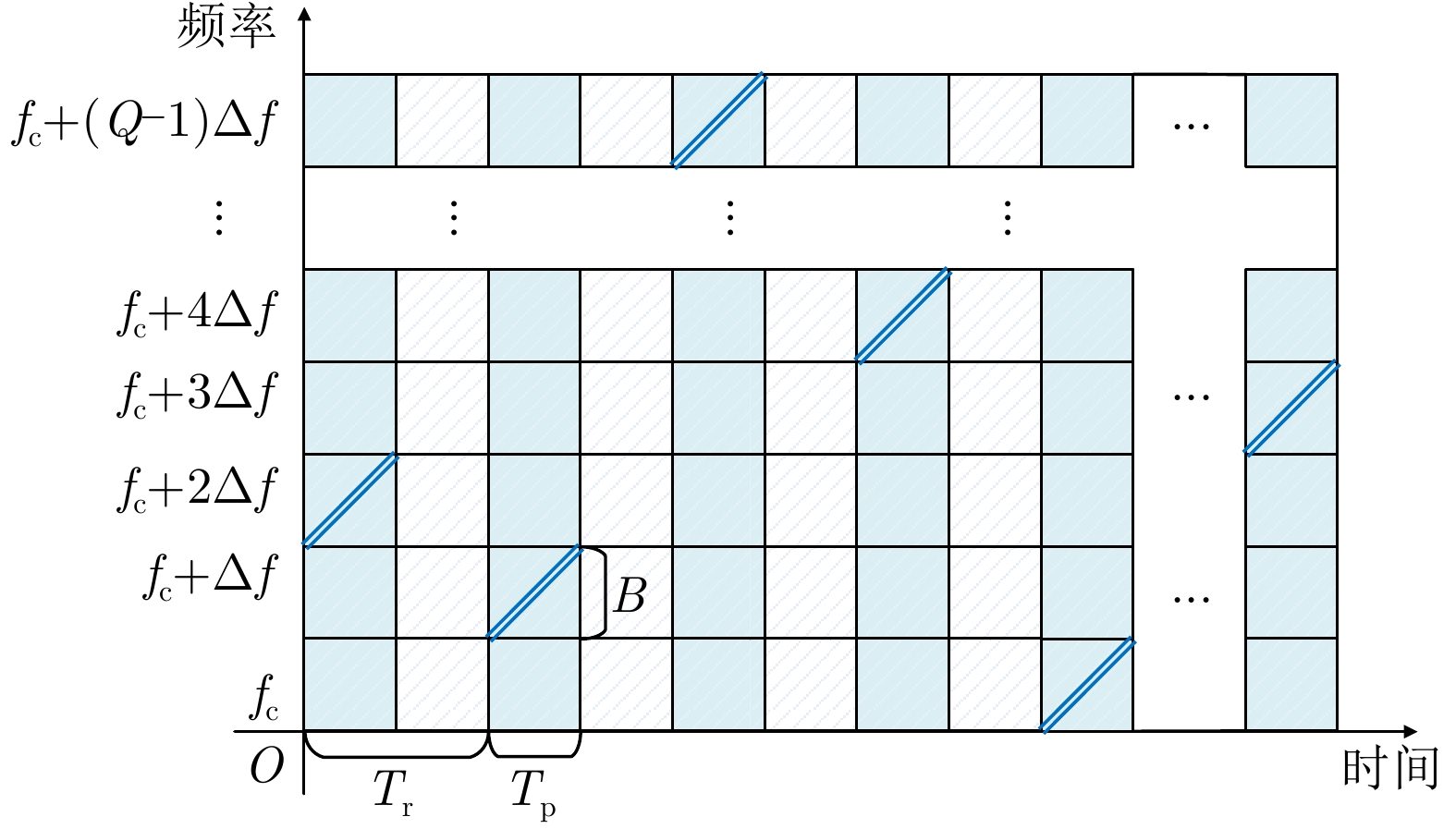
参数 数值 参数 数值 脉冲数Q 64 脉冲重复周期Tr 40 μs 信号脉宽Tp 4 μs 信号带宽B 20 MHz 初始载频fc 14 GHz 跳频间隔$ \Delta f$ 9 MHz 采样率fs 40 MHz 表 2 外场试验参数
Table 2. Outfield experiment parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 脉冲数Q 128 脉冲重复周期Tr 250 μs 信号脉宽Tp 4 μs 信号带宽B 20 MHz 跳频总数$Q' $ 256 载频跳变范围 33.2~34.2 GHz 采样率fs 60 MHz -
[1] FENG Dejun, XU Letao, PAN Xiaoyi, et al. Jamming wideband radar using interrupted-sampling repeater[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1341–1354. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2670958 [2] 周超, 刘泉华, 胡程. 间歇采样转发式干扰的时频域辨识与抑制[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 100–106. doi: 10.12000/JR18080ZHOU Chao, LIU Quanhua, and HU Cheng. Time-frequency analysis techniques for recognition and suppression of interrupted sampling repeater jamming[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 100–106. doi: 10.12000/JR18080 [3] 黎明也, 曹志华, 朱宝增. 对线性调频雷达的密集假目标干扰研究[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2014, 9(3): 272–276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2014.03.009LI Mingye, CAO Zhihua, and ZHU Baozeng. The study of dense false-farget jamming to LFM radar[J]. Journal of CAEIT, 2014, 9(3): 272–276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2014.03.009 [4] WEN Cai, PENG Jinye, ZHOU Yan, et al. Enhanced three-dimensional joint domain localized STAP for airborne FDA-MIMO radar under dense false-target jamming scenario[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(10): 4154–4166. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2820905 [5] 余康林, 匡华星, 王超宇. 基于多维特征的密集转发式干扰识别方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2021, 19(4): 448–454, 466. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.04.013YU Kanglin, KUANG Huaxing, and WANG Chaoyu. A recognition method of dense repeater jamming based on multiple features[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2021, 19(4): 448–454, 466. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2021.04.013 [6] XU Leilei, LIU Hongwei, ZHOU Shenghua, et al. Colocated MIMO radar waveform design against repeat radar jammers[C]. 2018 International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 1–5. [7] 刘智星, 杜思予, 吴耀君, 等. 脉间-脉内捷变频雷达抗间歇采样干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(2): 301–312. doi: 10.12000/JR22001LIU Zhixing, DU Siyu, WU Yaojun, et al. Anti-interrupted sampling repeater jamming method for interpulse and intrapulse frequency-agile radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(2): 301–312. doi: 10.12000/JR22001 [8] 卢刚, 唐斌, 罗双才. LFM雷达中DRFM假目标自适应对消方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2011, 33(8): 1760–1764. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.08.16LU Gang, TANG Bin, and LUO Shuangcai. Adaptive cancellation of DRFM false targets for LFM radar[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2011, 33(8): 1760–1764. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.08.16 [9] ZHOU Chao, LIU Quanhua, and CHEN Xinliang. Parameter estimation and suppression for DRFM-based interrupted sampling repeater jammer[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(1): 56–63. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0114 [10] 李培, 王峰. 基于域变换的雷达主瓣密集转发干扰抑制方法研究[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2021, 16(8): 797–804. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2021.08.008LI Pei and WANG Feng. Research on radar main lobe dense repeater jamming suppression method based on domain transform[J]. Journal of CAEIT, 2021, 16(8): 797–804. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2021.08.008 [11] 张亮, 王国宏, 张顺义, 等. 一种分数阶域的密集假目标干扰抑制算法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2020, 54(12): 79–87. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202012010ZHANG Liang, WANG Guohong, ZHANG Shunyi, et al. An algorithm for suppressing jamming of dense false targets in fractional Fourier transform domain[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2020, 54(12): 79–87. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202012010 [12] 孙殿星, 陈翔, 万建伟, 等. 基于多特征的密集假目标干扰融合识别与抑制[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(10): 2207–2215. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.10.08SUN Dianxing, CHEN Xiang, WAN Jianwei, et al. Fusion identification and suppression technique against concentrated false targets jamming based on multiple features[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(10): 2207–2215. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.10.08 [13] CHEN Fengbo, LI Rongfeng, DING Liming, et al. A method against DRFM dense false target jamming based on jamming recognization[C]. IET International Radar Conference 2015, Hangzhou, China, 2015: 1–4. [14] CAI Guang, SHAO Yinbo, LI Rongfeng, et al. A method for countering dense false target jamming based on correlation sample selection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Xiamen, China, 2017: 1–5. [15] LIU Kaiqiang, FU Xiongjun, GAO Zhiming, et al. Time-space two-dimensional dense false targets jamming and countermeasures[C]. 2018 13th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Wuhan, China, 2018: 1982–1987. [16] 方文, 全英汇, 沙明辉, 等. 捷变频联合波形熵的密集假目标干扰抑制算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(6): 1506–1514. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.06.07FANG Wen, QUAN Yinghui, SHA Minghui, et al. Dense false targets jamming suppression algorithm based on frequency agility and waveform entropy[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(6): 1506–1514. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.06.07 [17] 董淑仙, 全英汇, 陈侠达, 等. 基于捷变频联合数学形态学的干扰抑制算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(7): 1491–1498. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.07.09DONG Shuxian, QUAN Yinghui, CHEN Xiada, et al. Interference suppression algorithm based on frequency agility combined with mathematical morphology[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(7): 1491–1498. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.07.09 [18] LONG Xingwang, LI Kun, TIAN Jing, et al. Ambiguity function analysis of random frequency and PRI agile signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 382–396. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3016851 [19] AKHTAR J and OLSEN K E. Frequency agility radar with overlapping pulses and sparse reconstruction[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 0061–0066. [20] TAO Yanji, ZHANG Gong, TAO Tingbao, et al. Frequency-agile coherent radar target Sidelobe suppression based on sparse Bayesian learning[C]. 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Biomedical Conference (IMBioC), Nanjing, China, 2019: 1–4. [21] 张克舟, 李青山, 陆静, 等. LFM脉冲压缩雷达密集假目标干扰时序设计与分析[J]. 现代防御技术, 2015, 43(4): 132–137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2015.04.022ZHANG Kezhou, LI Qingshan, LU Jing, et al. Design and analysis of dense false target jamming time sequence of LFM pulse compression radar[J]. Modern Defense Technology, 2015, 43(4): 132–137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2015.04.022 [22] 何明浩, 韩俊. 现代雷达辐射源信号分选与识别[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 90–116.HE Minghao and HAN Jun. Modern Radar Emitter Signal Sorting and Recognition[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 90–116. [23] 滑文强, 王爽, 侯彪. 基于半监督学习的SVM-Wishart极化SAR图像分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(1): 93–98. doi: 10.12000/JR14138HUA Wenqiang, WANG Shuang, and HOU Biao. Semi-supervised learning for classification of polarimetric SAR images based on SVM-Wishart[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(1): 93–98. doi: 10.12000/JR14138 [24] 王福友, 罗钉, 刘宏伟. 低分辨机载雷达空地运动目标的分类识别算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(5): 497–504. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14092WANG Fuyou, LUO Ding, and LIU Hongwei. Low-resolution airborne radar air/ground moving target classification and recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(5): 497–504. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14092 [25] 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016: 121–140.ZHOU Zhihua. Machine Learning[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016: 121–140. [26] SZELISKI R. Computer Vision: Algorithms and Applications (Texts in Computer Science)[M]. London: Springer, 2010: 109–129. [27] EKSTROM M. Digital image processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1980, 28(4): 484–486. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1980.1163437 [28] GONZALEZ R C and WOODS R E. Digital Image Processing[M]. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, 2002: 144–156. [29] MARQUES E C, MACIEL N, NAVINER L, et al. A review of sparse recovery algorithms[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 1300–1322. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2886471 [30] QUAN Yinghui, LI Yachao, WU Yaojun, et al. Moving target detection for frequency agility radar by sparse reconstruction[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2016, 87(9): 094703. doi: 10.1063/1.4962700 [31] KNILL C, SCHWEIZER B, SPARRER S, et al. High range and doppler resolution by application of compressed sensing using low baseband bandwidth OFDM radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2018, 66(7): 3535–3546. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2018.2830389 [32] WEI Shaopeng, ZHANG Lei, and LIU Hongwei. Joint frequency and PRF agility waveform optimization for high-resolution ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5100723. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3051038 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: