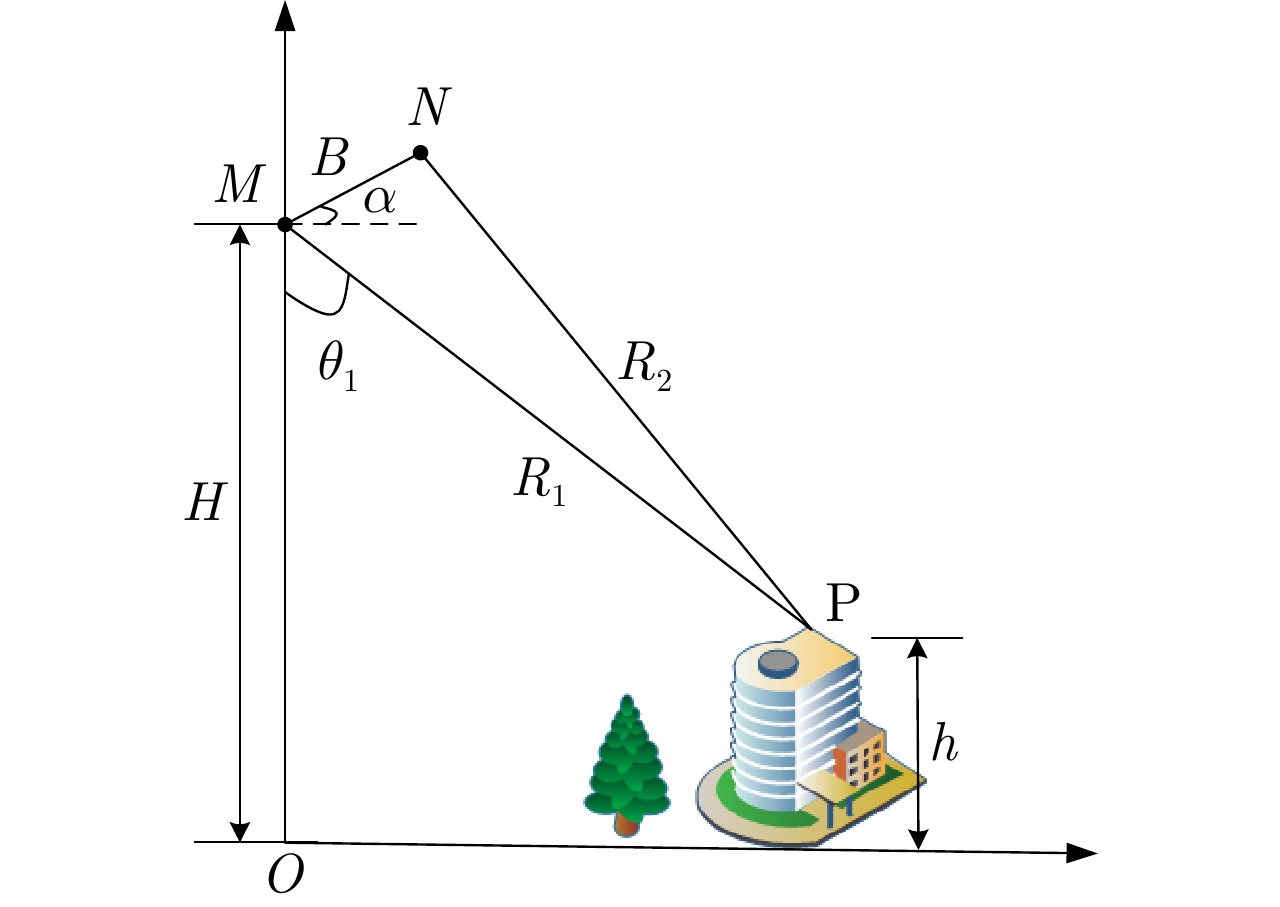
Error Analysis of Polarimetric Interferometric SAR under Different Processing Modes in Urban Areas
-
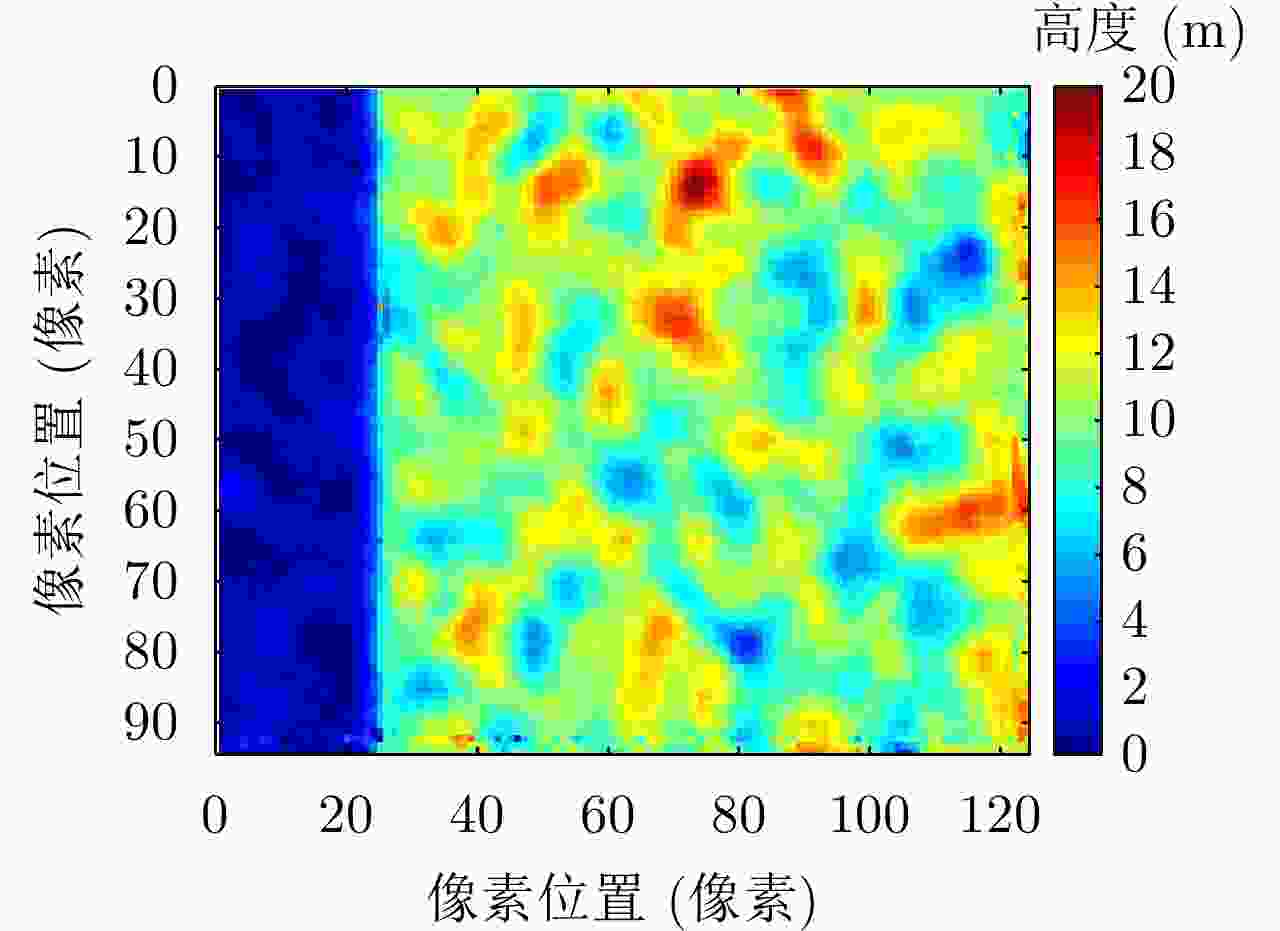
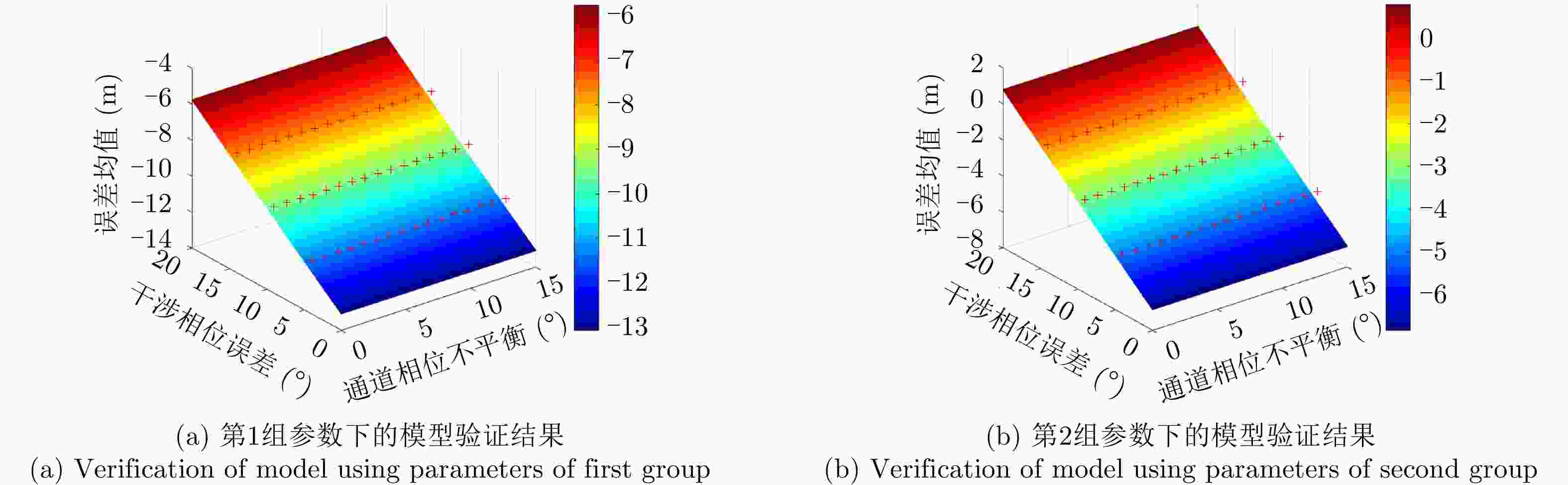
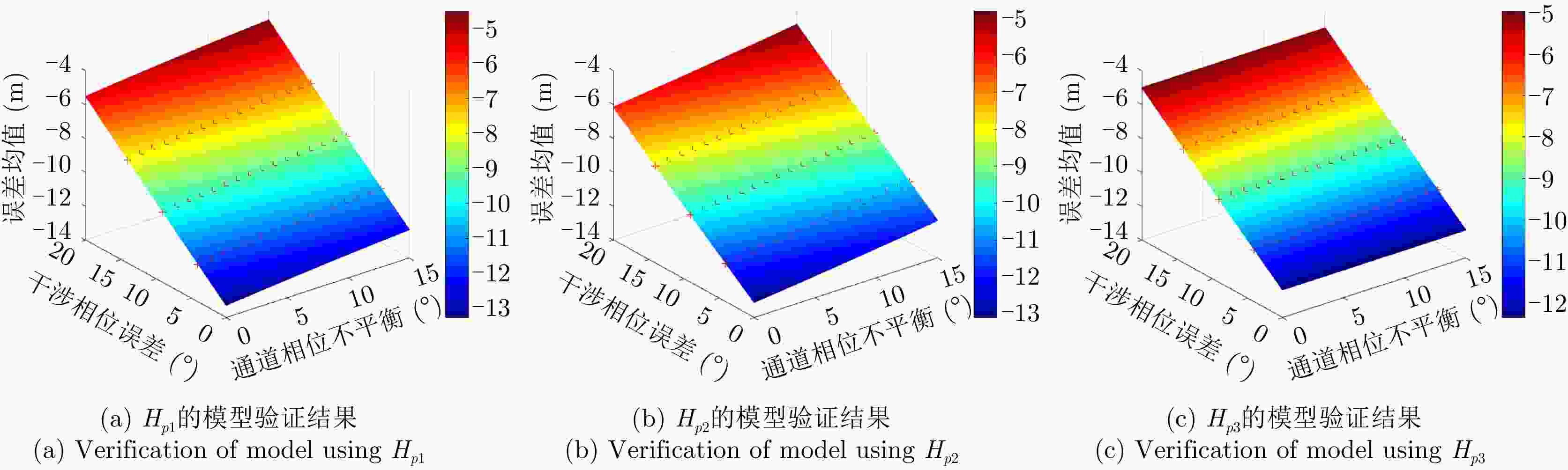
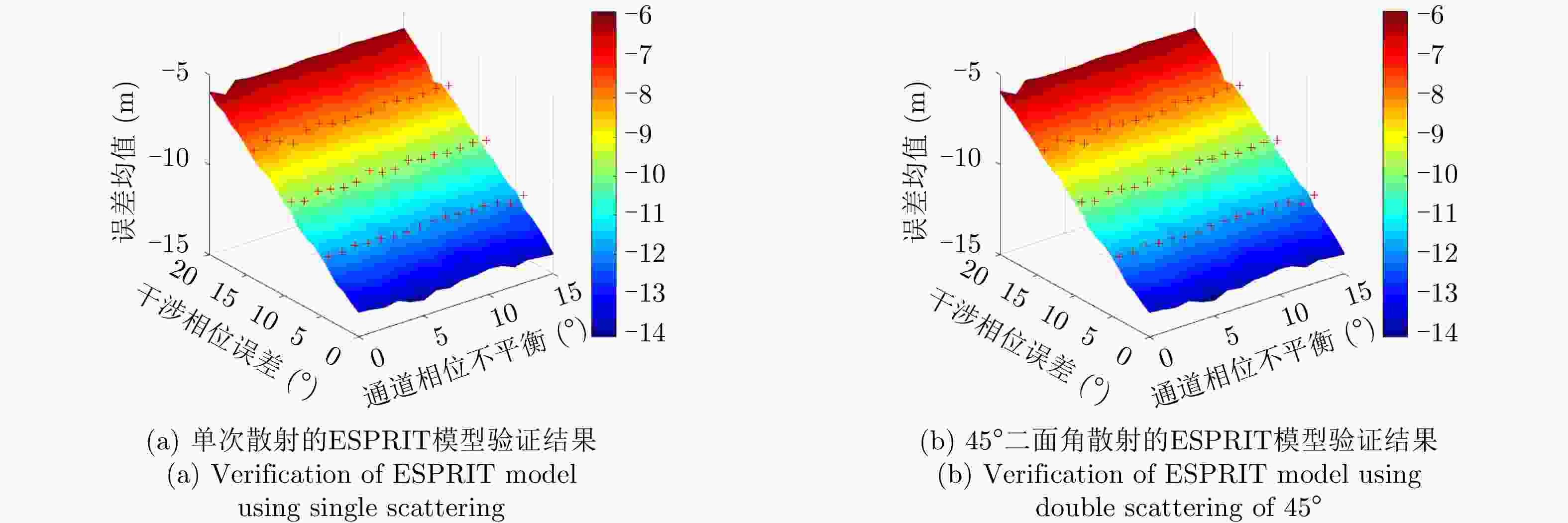
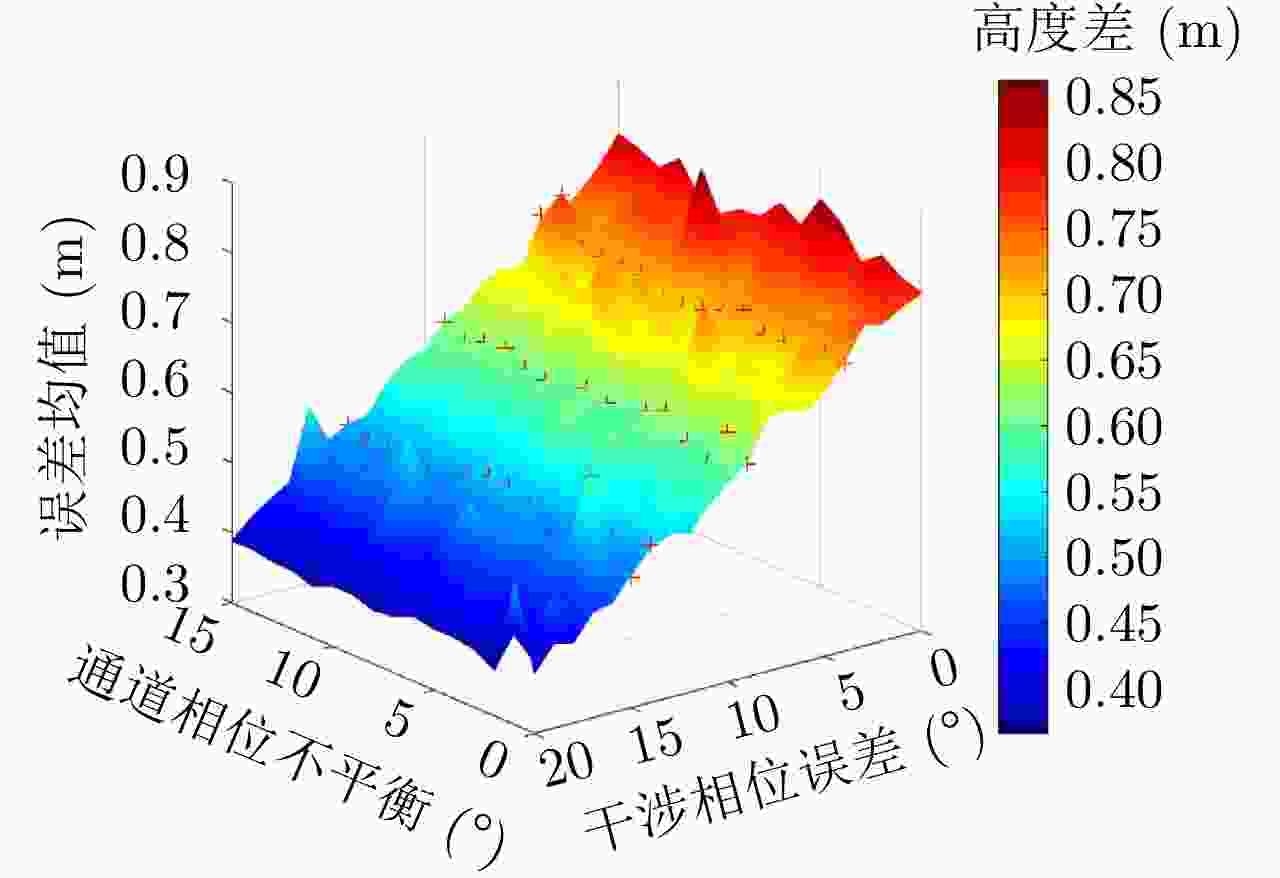
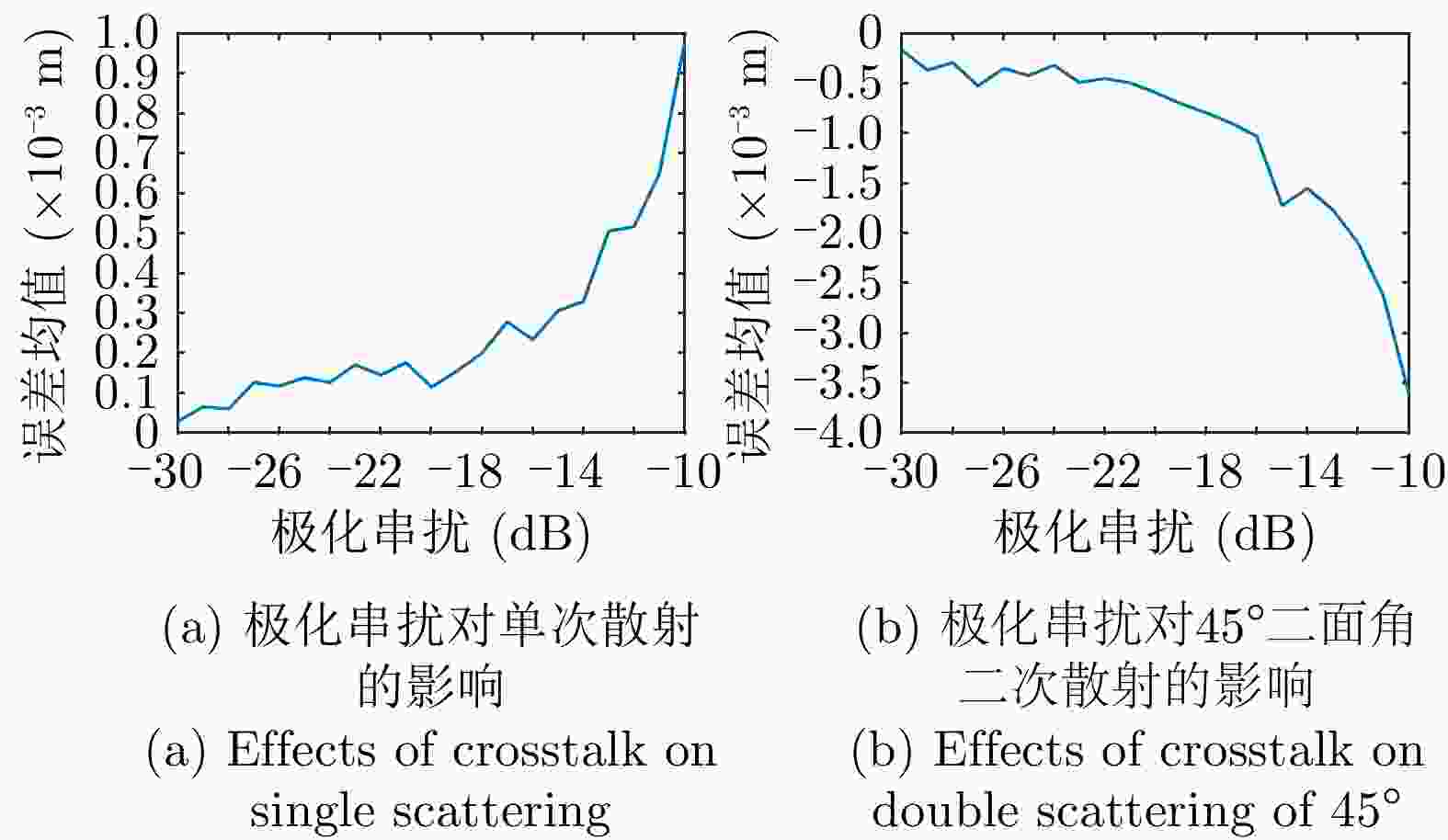
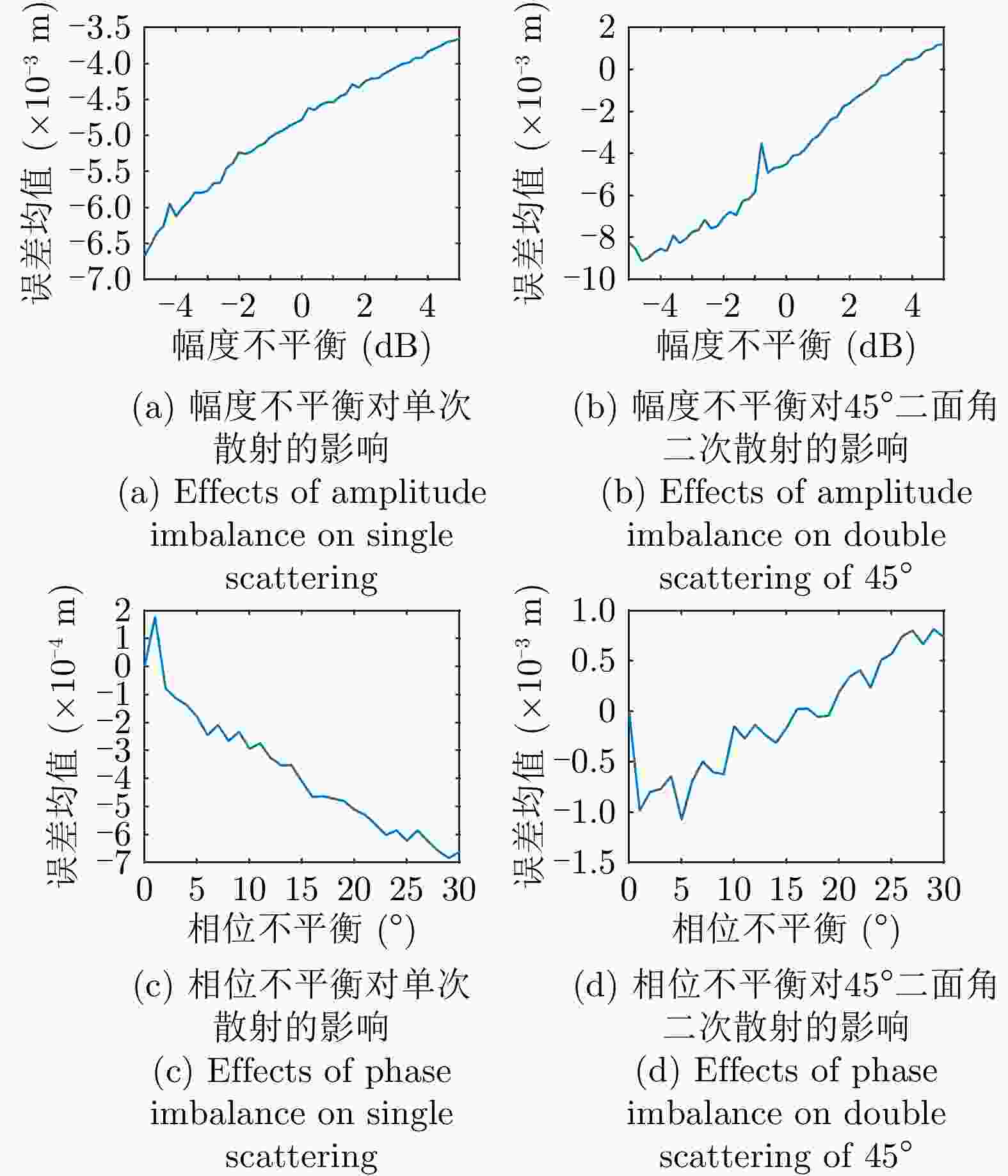
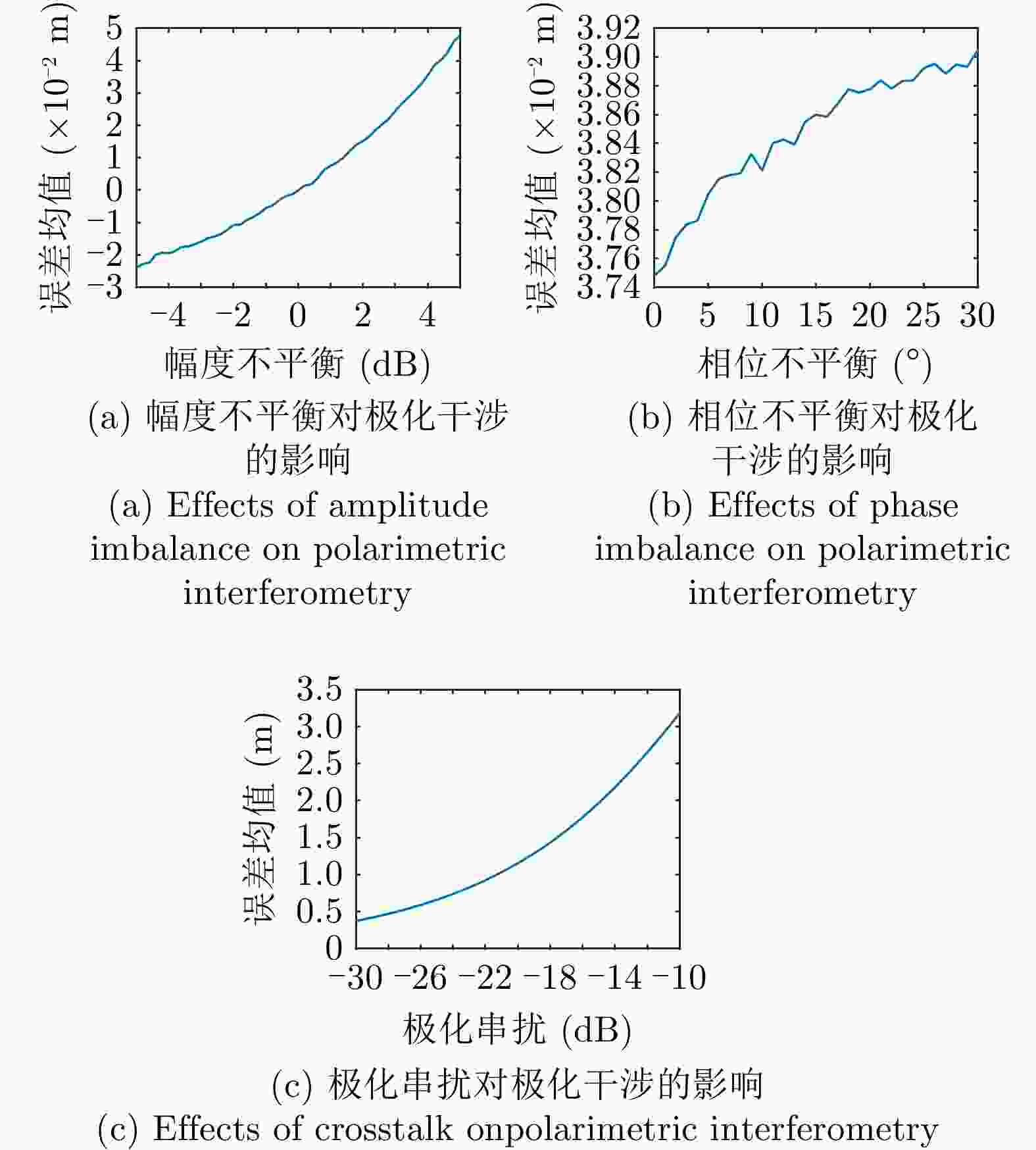
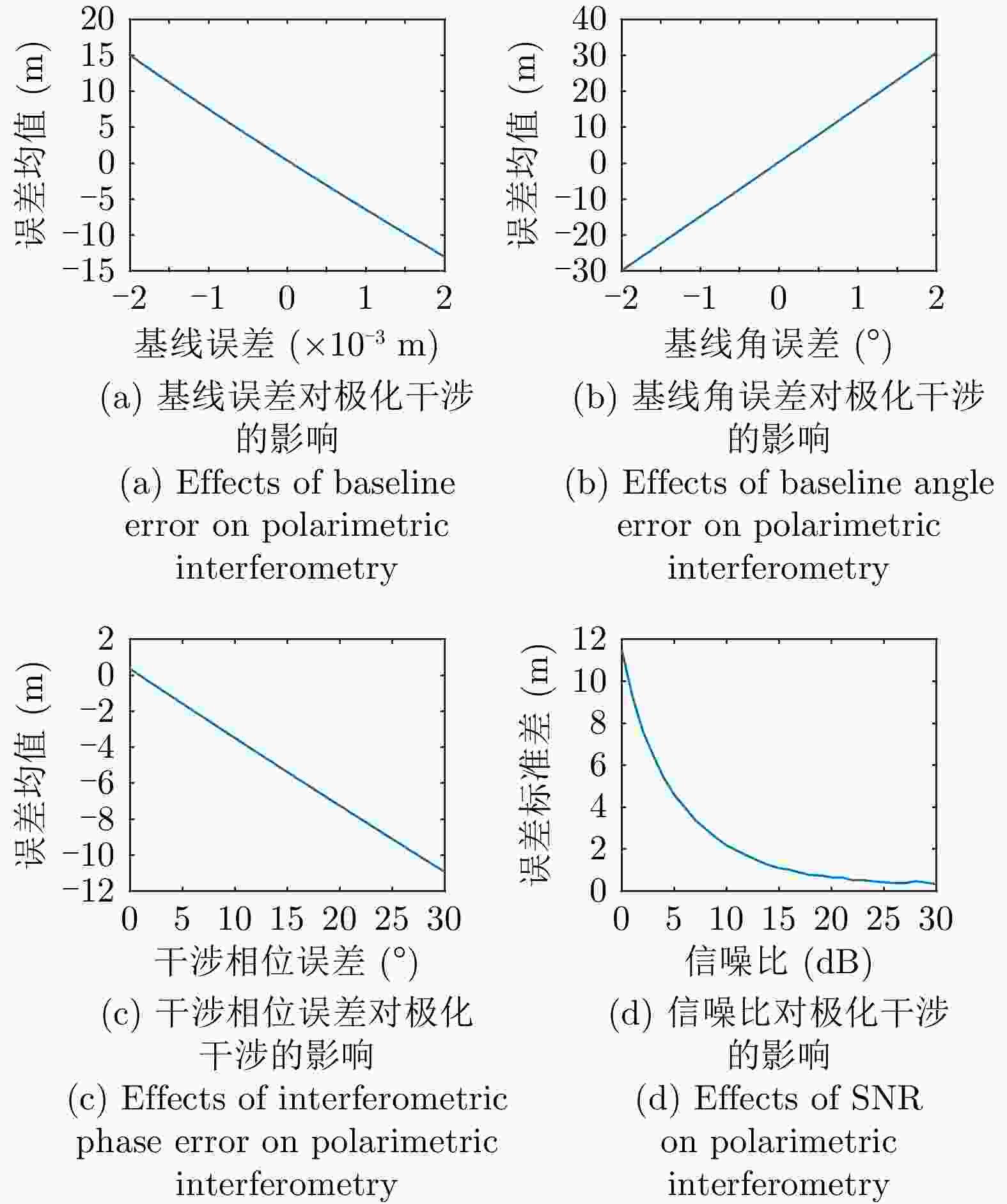
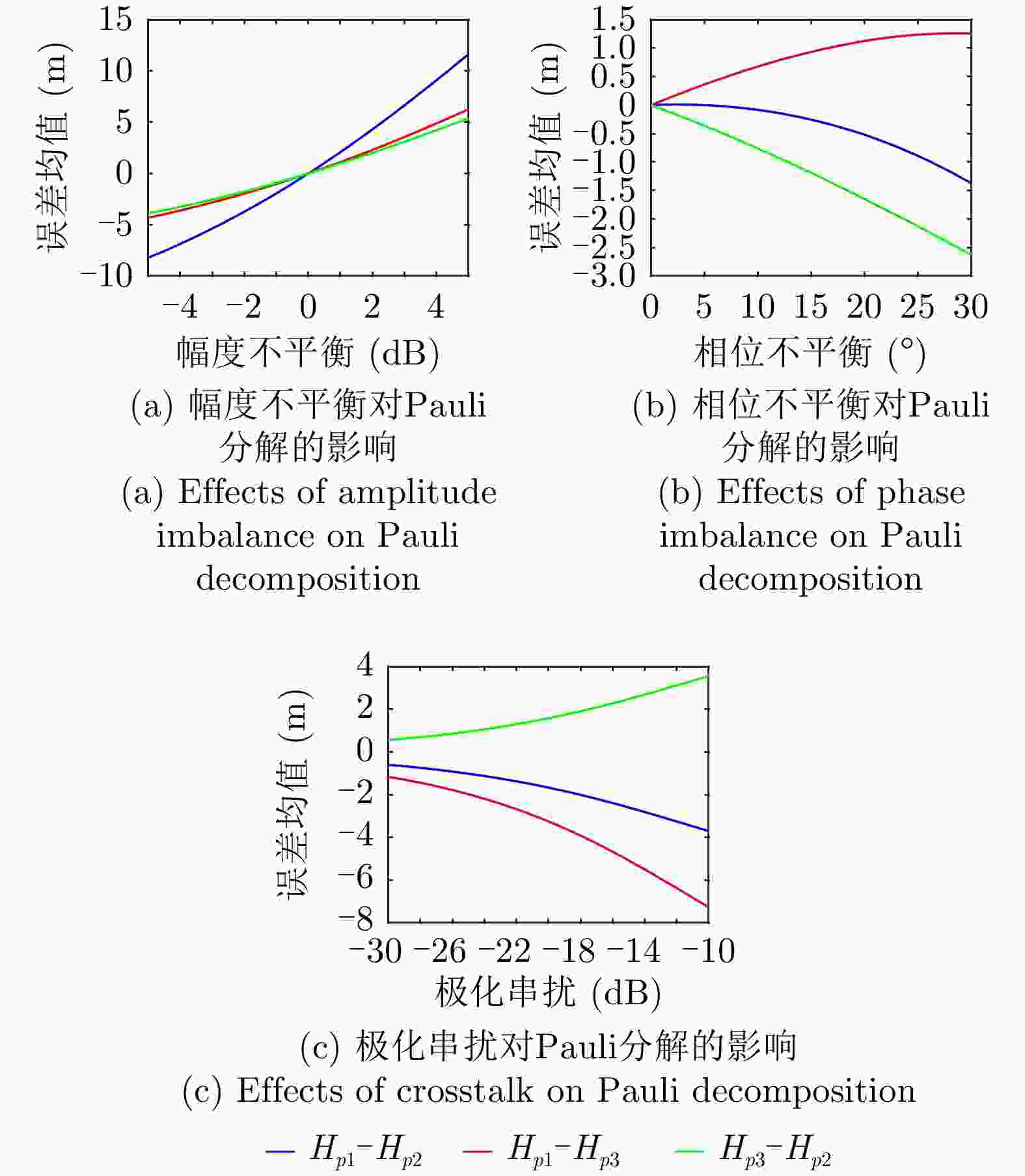
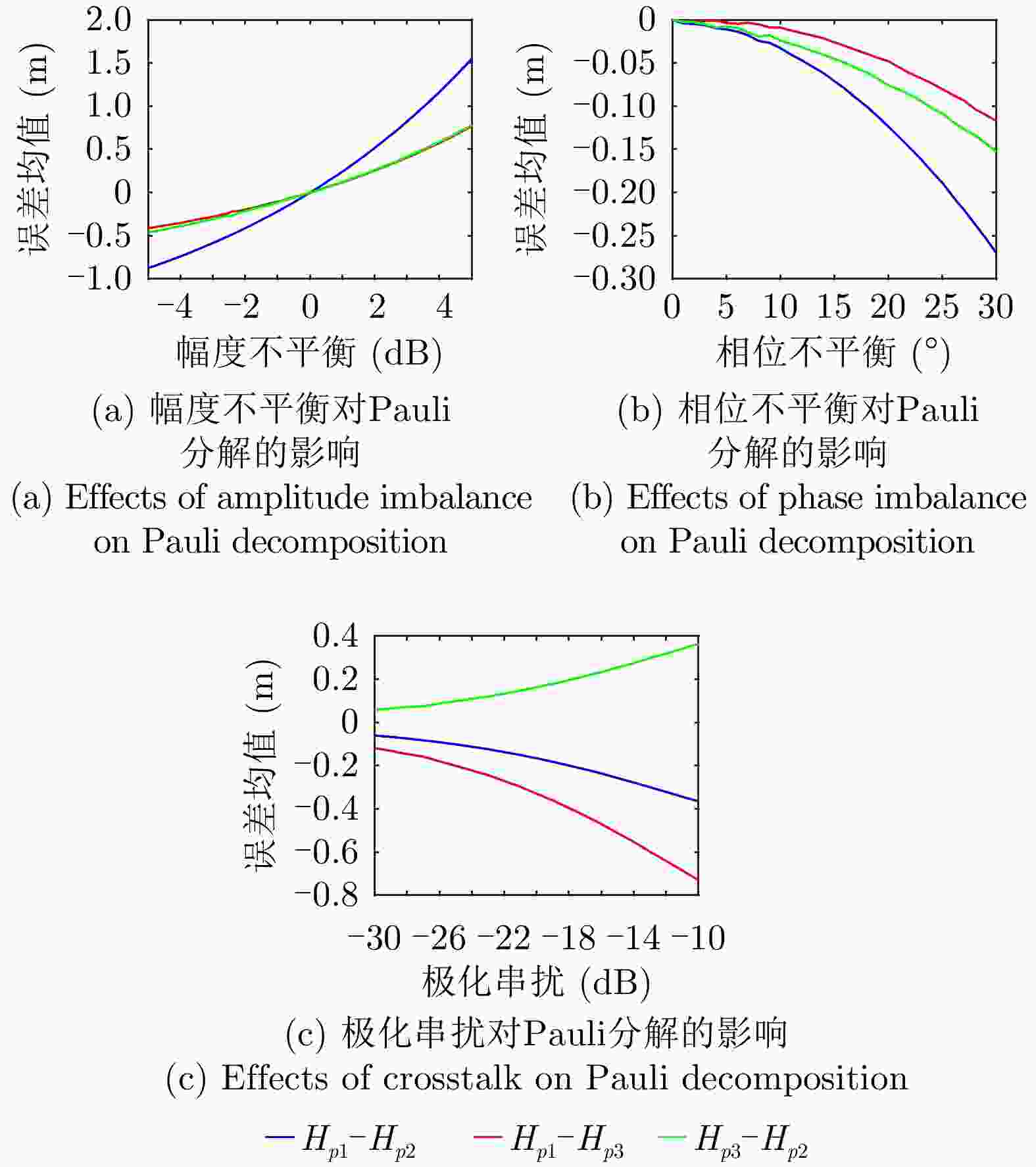
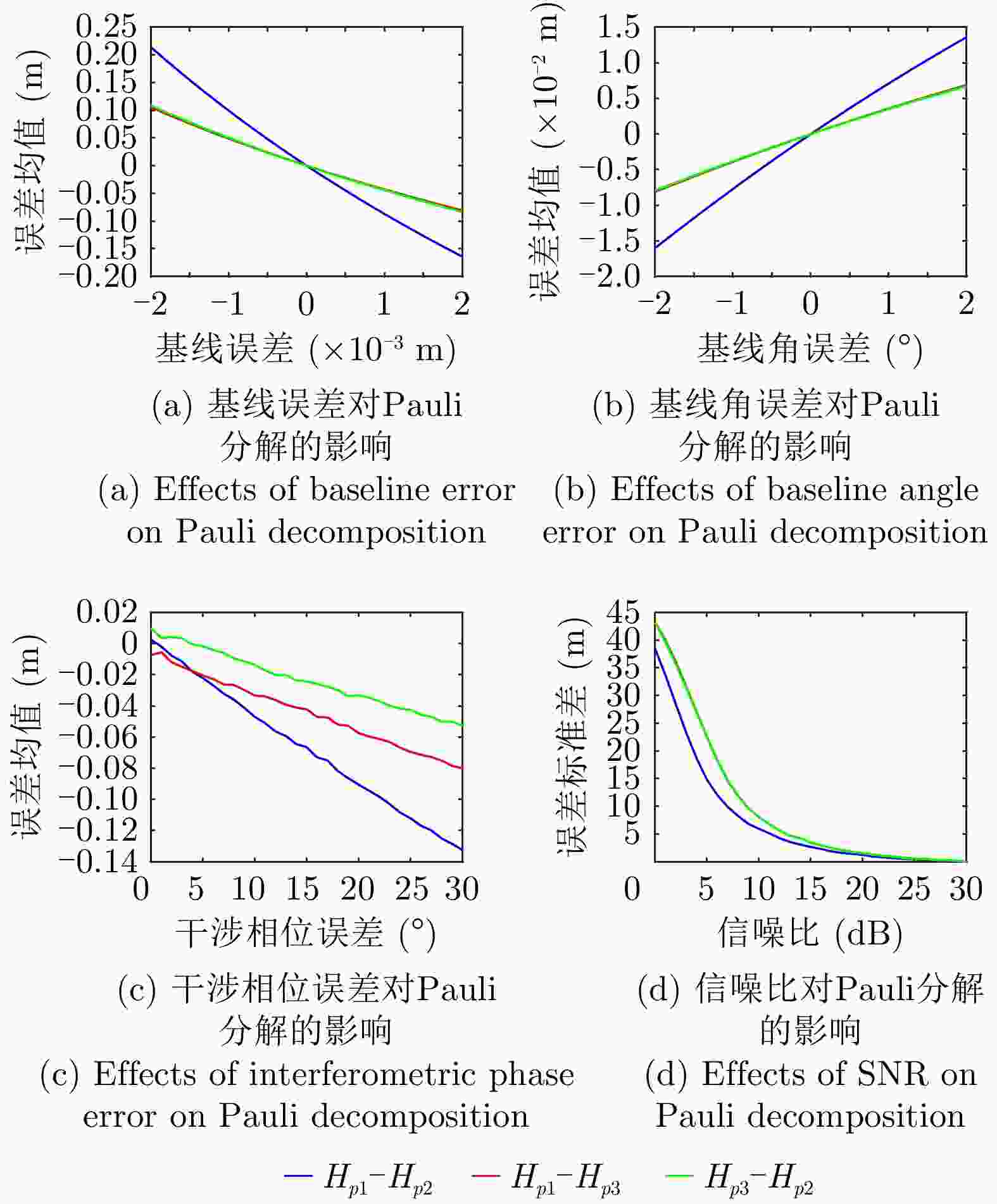
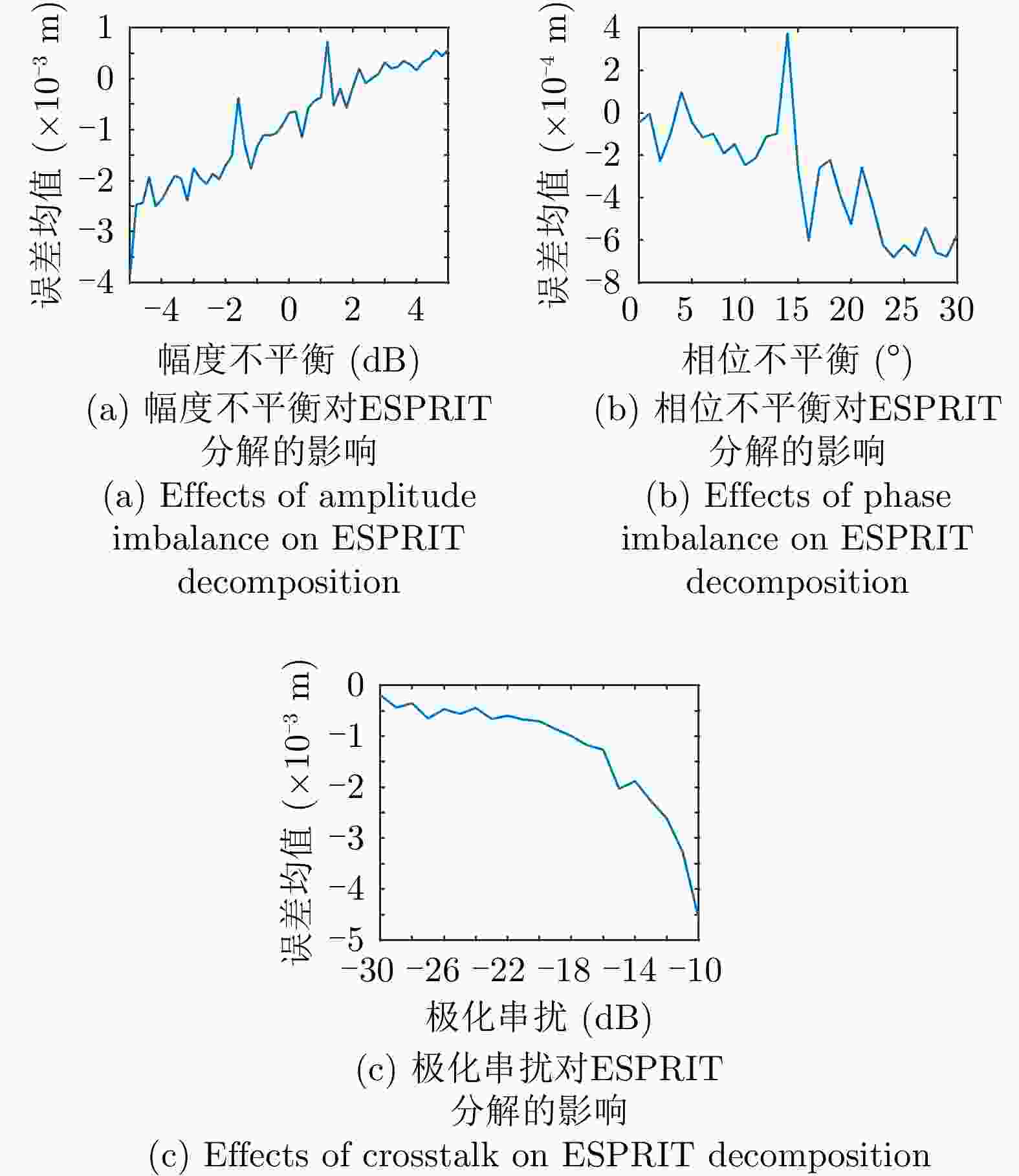
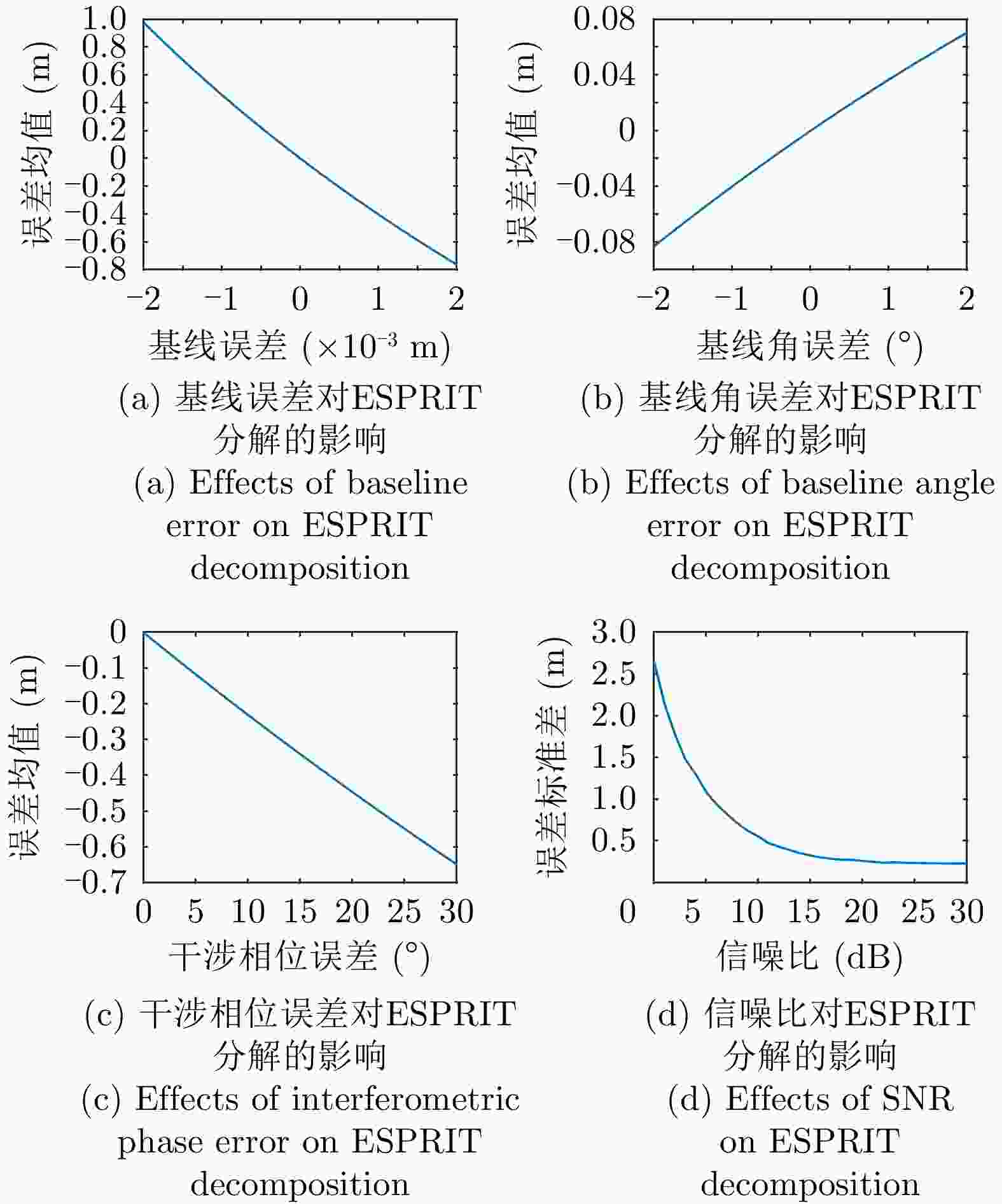
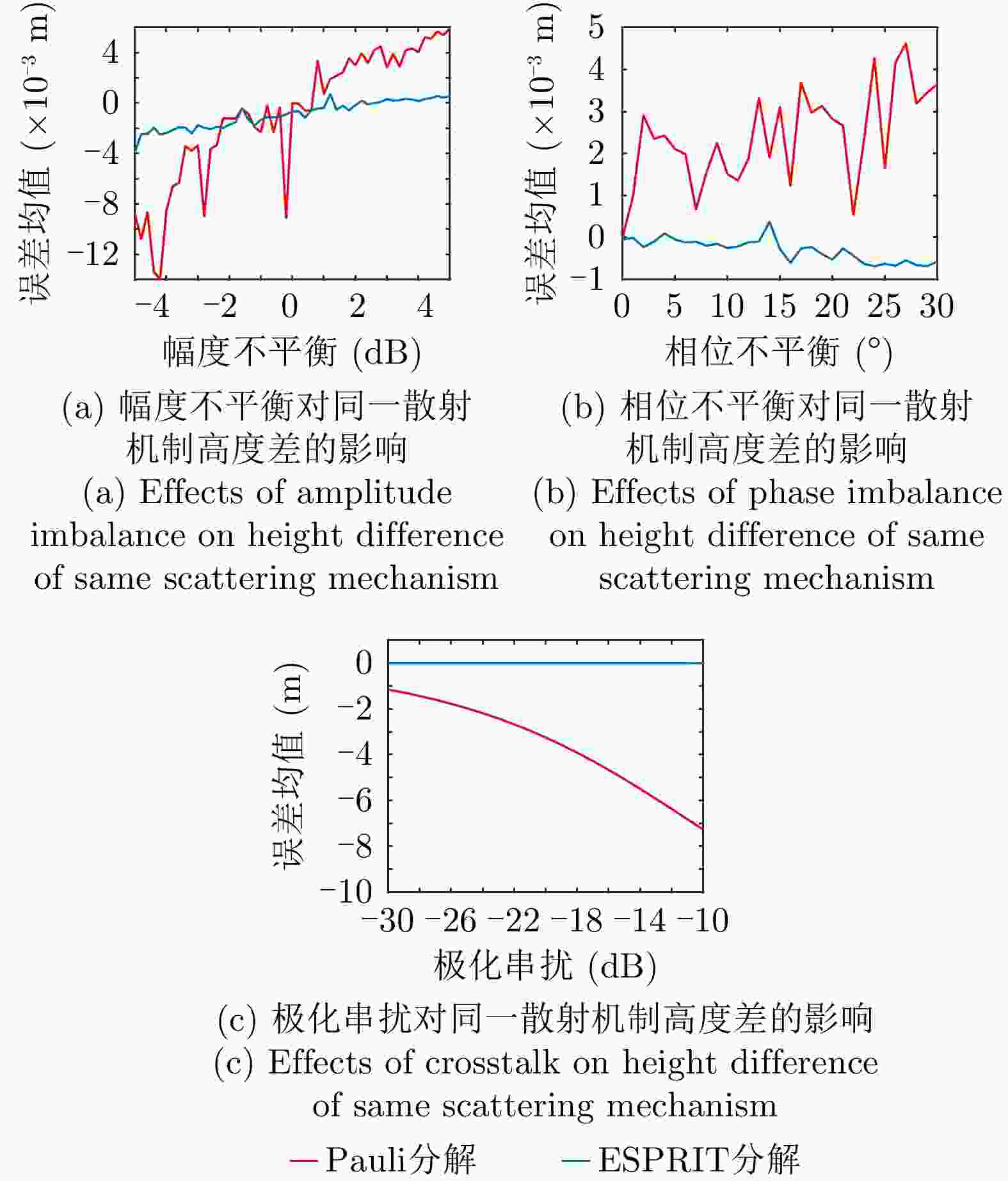
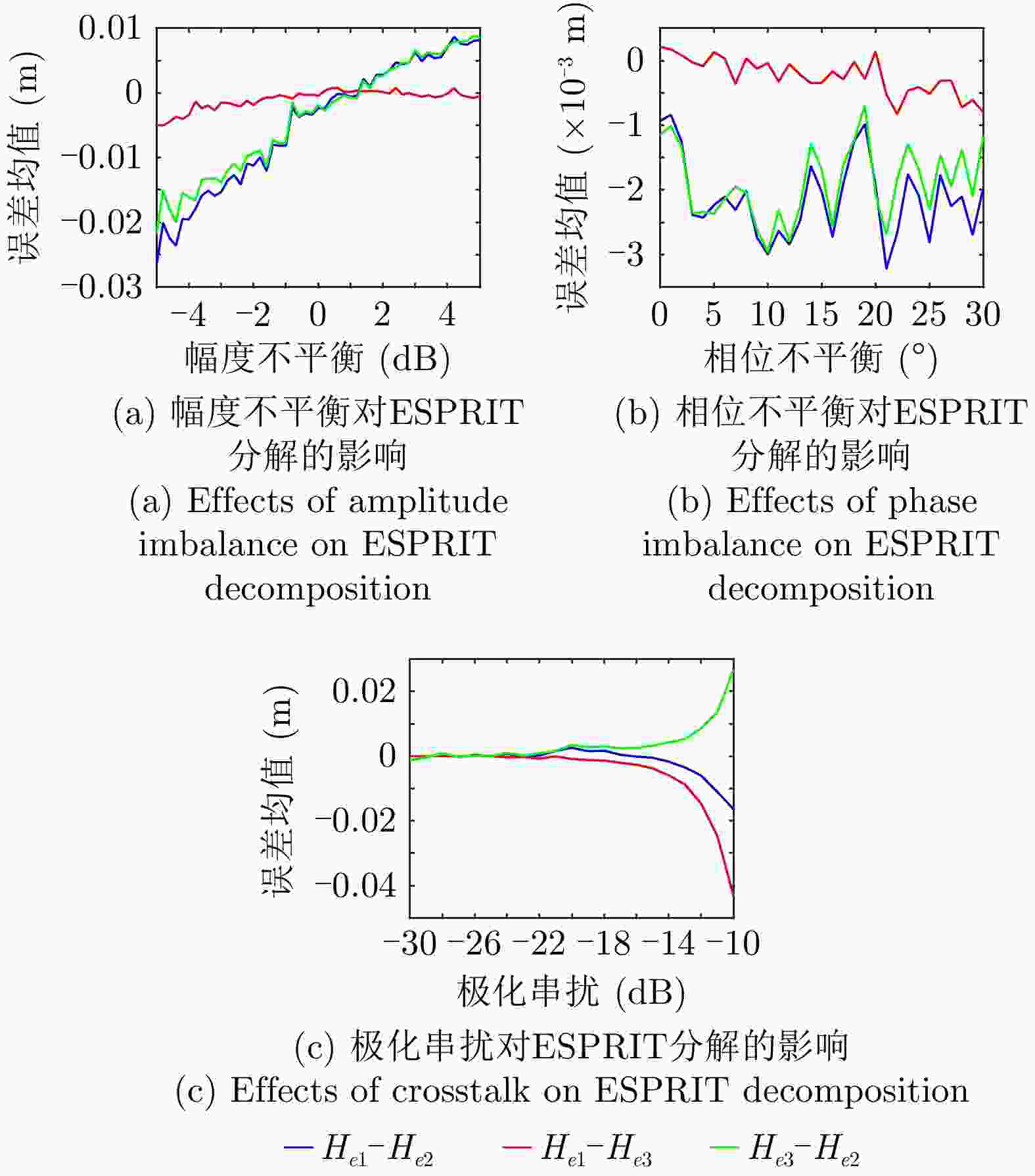
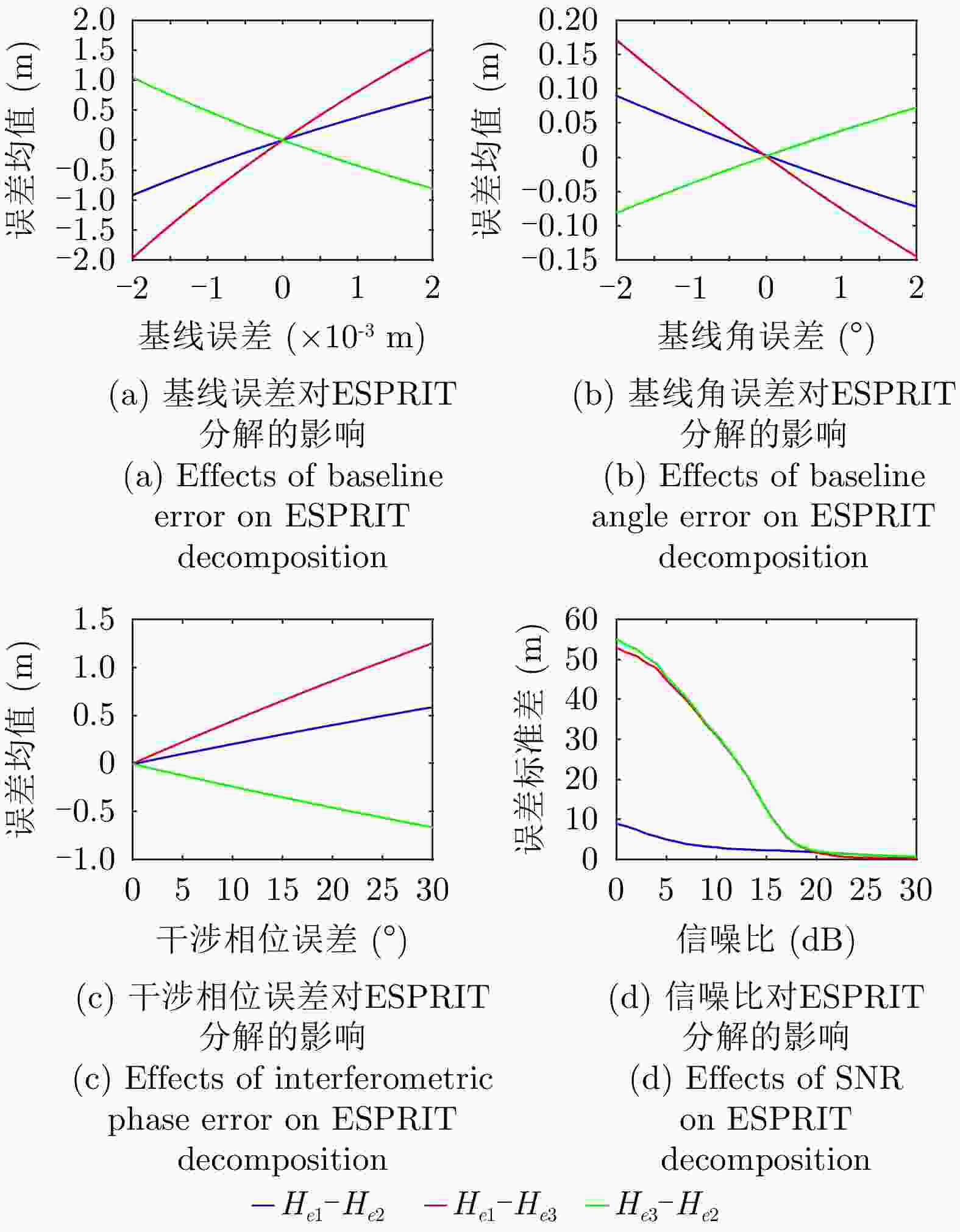
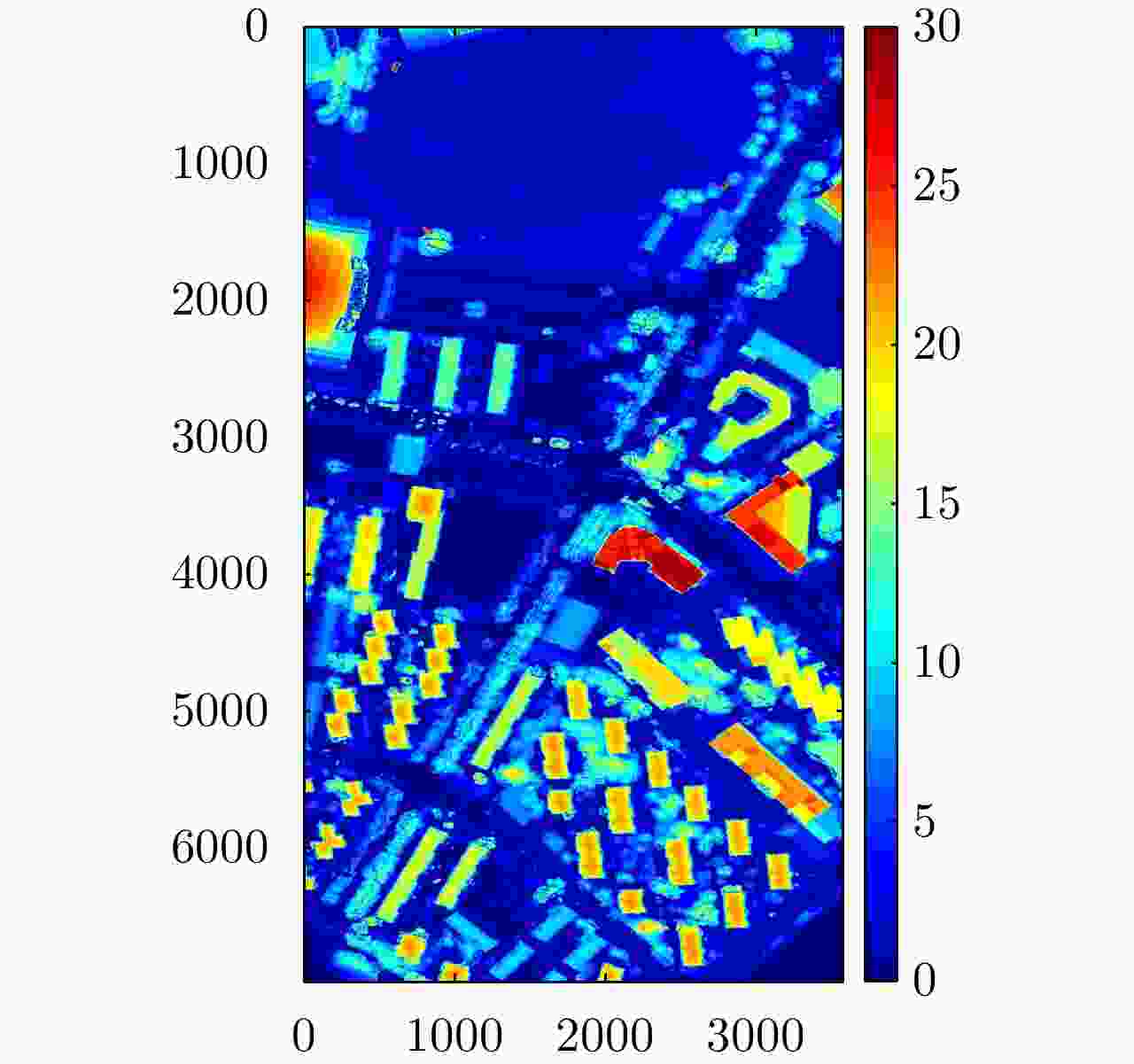
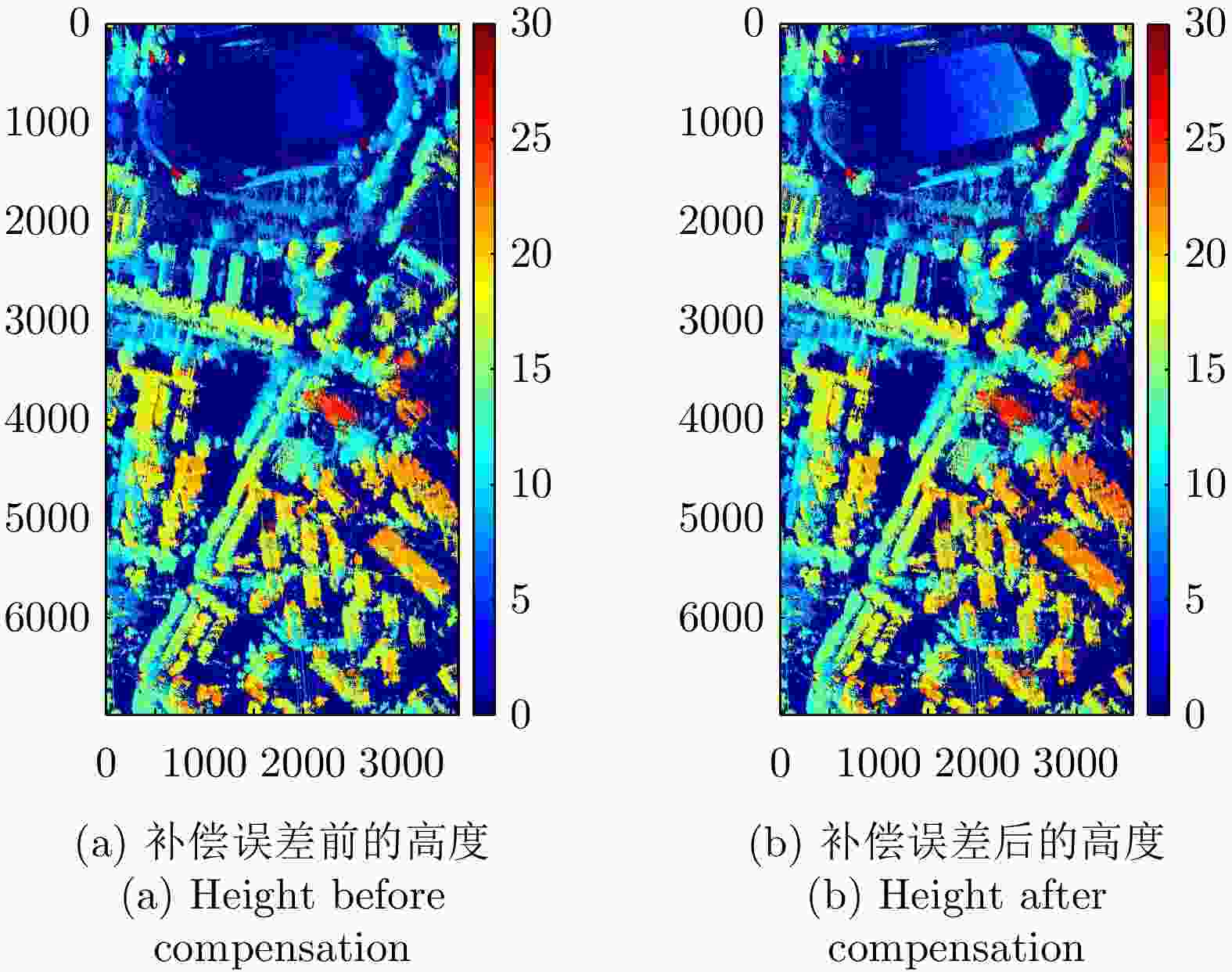
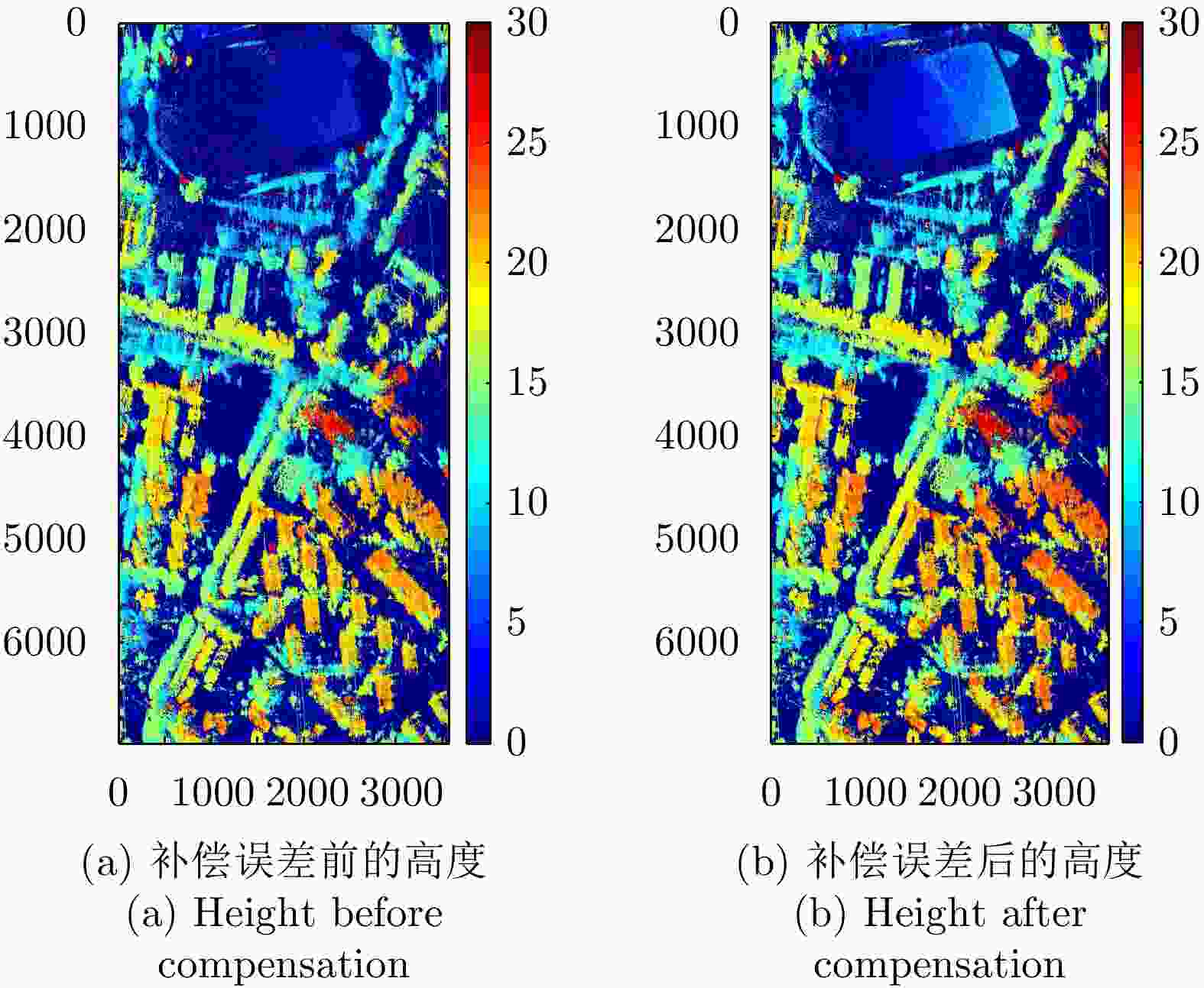
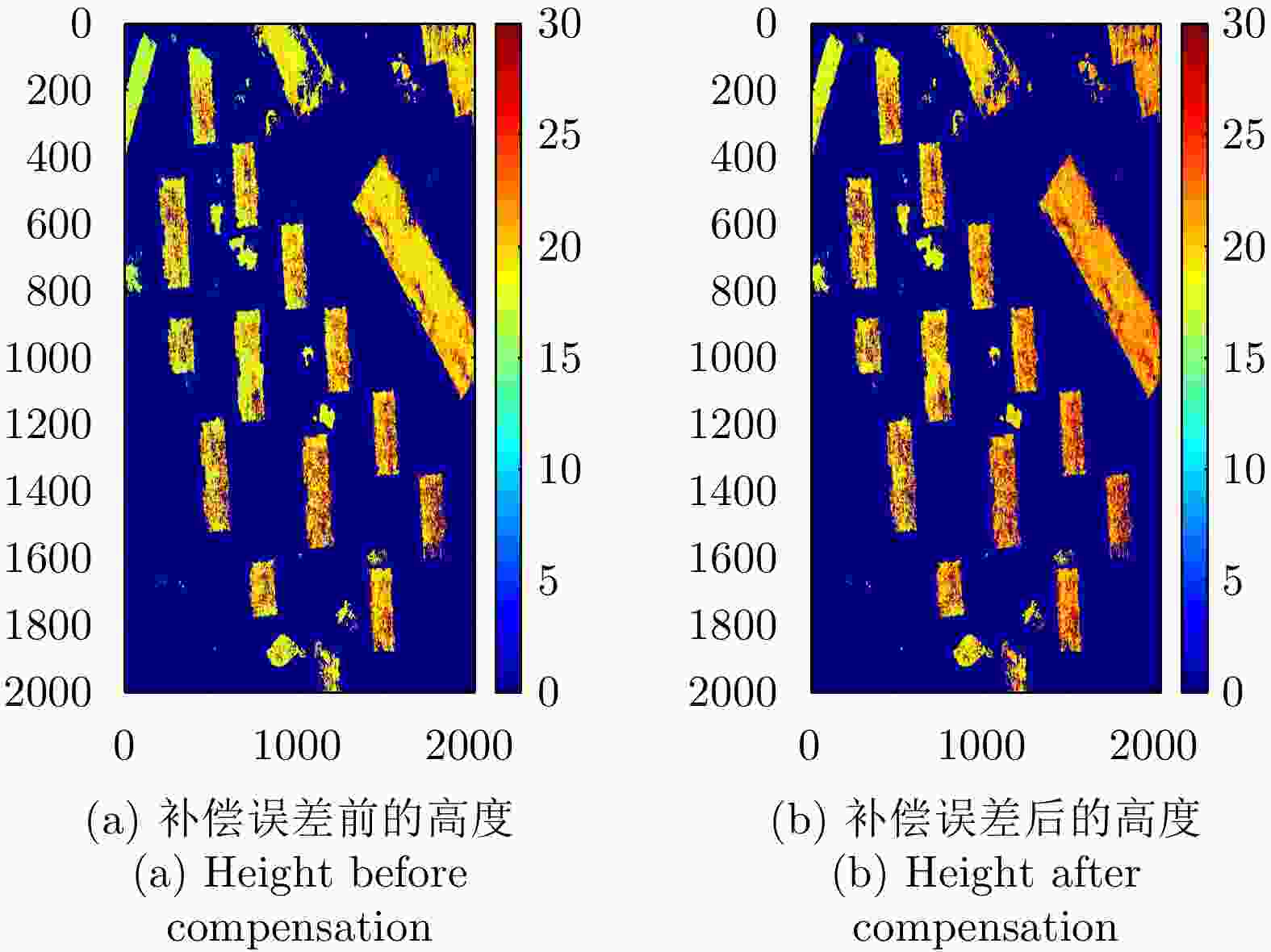
摘要: 极化干涉合成孔径雷达(PolInSAR)在城区等复杂场景下的应用受到了越来越多的关注。面向城区的极化干涉SAR处理主要包括基于极化最优相干的干涉测高、基于极化分解的干涉测高、联立极化干涉观测方程直接求解不同散射机制高度这3种模式。现有研究对各类误差在极化干涉SAR不同处理模式下的综合影响分析尚很欠缺。该文在构建极化干涉SAR误差模型的基础上,提出了联立极化观测方程下散射机制的求解方法,推导了极化失真和干涉误差在极化干涉SAR不同处理模式下的综合影响模型,并通过仿真验证了模型的正确性,同时给出了3种处理模式补偿误差后的高度反演结果,补偿误差后通过极化最优相干得到建筑区域高度的均方根误差(RMSE)为2.77 m。在此基础上,通过仿真给出了极化干涉SAR不同处理模型下的误差影响曲线,比较了不同处理模型受误差影响的程度,并给出了合理解释,研究结果为极化干涉SAR系统设计、处理方法选择及数据应用提供了参考。
-
关键词:
- 极化干涉合成孔径雷达 /
- 误差分析 /
- 极化最优相干 /
- Pauli分解 /
- ESPRIT分解
Abstract: Polarimetric Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolInSAR) simultaneously has interferometric height measurement and full-polarized detection capabilities, which can better reflect the structural properties of feature targets. Therefore, its potential for application in complex scenarios, such as urban areas, has attracted increasing attention. In urban areas, the processing mainly includes three modes: using interferometry to extract height based on polarimetric optimal coherence, using interferometry based on polarized decomposition, and associating polarimetric interferometric observation equations to retrieve the heights of different scattering mechanisms. The analysis of error factors and effects on Interferometric SAR (InSAR) and polarized SAR is almost complete, but the analysis of error effects under different processing modes of PolInSAR is insufficient. Based on the PolInSAR error model, our paper proposes a method for solving the scattering mechanism under the simultaneous polarization observation equation. Moreover, we derive the model including each error under different processing modes in PolInSAR from the aspect of polarized errors, interferometric errors, and the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR). Furthermore, the model is verified through simulations, and we provide height inversion results through three processing modes after compensating for polarized errors and interferometric errors. After the error compensation, we obtain a Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) in building areas of 2.77 m through polarimetric optimal coherence. Finally, the simulations provide the error impact curves under different processing modes of PolInSAR and compare the degree of different processing methods affected by errors, which provides a reasonable explanation for the design of the PolInSAR system, selection of processing methods, and data application. -
表 1 系统仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters of system
参数 数值 中心频率 15.2 GHz 飞行高度 205 m 斜距 889 m 基线 0.6 m 基线角 –1° 表 2 ESPRIT方法得到散射机制的结果
Table 2. Scattering mechanisms obtained by ESPRIT
极化方式 主图像 辅图像 含串扰的
主图像含串扰的
辅图像单次散射 –0.89
+0.11i–0.85
–0.25–0.54
+0.03i–0.45
–0.33i0°二次散射 0.02
–0.01i0.02
–0.01i0.02
+0.01i0.02
+0.01i45°二次散射 1 1 1 1 表 3 ESPRIT方法得到的干涉相位
Table 3. Interferometric phase obtained by ESPRIT
极化方式 理想(°) 含串扰(°) 单次散射 58.90 58.41 45°二次散射 84.87 84.24 表 4 Pauli分解得到散射机制的结果
Table 4. Scattering mechanisms obtained by Pauli decomposition
极化方式 主图像 辅图像 含串扰的主图像 含串扰的辅图像 单次散射 0.10 0.29 0.09+0.04i 0.28+0.04i 0°二次散射 0.002 0.001i –0.001i 0.003 45°二次散射 1 1 1 1 表 5 –20 dB串扰误差下两种分解的干涉相位误差
Table 5. Interferometric phase error of two decompositions under –20 dB crosstalk
极化方式 ESPRIT (°) Pauli (°) 单次散射 0.49 15.69 45°二次散射 0.63 –0.45 -
[1] CLOUDE S R and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(5): 1551–1565. doi: 10.1109/36.718859 [2] TREUHAFT R N and CLOUDE S R. The structure of oriented vegetation from polarimetric interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2620–2624. doi: 10.1109/36.789657 [3] CLOUDE S R and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. Three-stage inversion process for Polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(3): 125–134. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030449 [4] PAPATHANASSIOU K P and CLOUDE S R. Single-baseline Polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(11): 2352–2363. doi: 10.1109/36.964971 [5] GARESTIER F, DUBOIS-FERNANDEZ P, DUPUIS X, et al. PolInSAR analysis of X-band data over vegetated and urban areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(2): 356–364. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.862525 [6] 王萍, 汪长城, 彭星, 等. 基于PolInSAR三分量分解的建筑物高度向信息提取方法[J]. 测绘工程, 2014, 23(6): 16–20, 26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7949.2014.06.004WANG Ping, WANG Changcheng, PENG Xing, et al. Building height information extraction method based on three-component decomposition for PolInSAR data[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2014, 23(6): 16–20, 26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7949.2014.06.004 [7] GUILLASO S, FERRO-FAMIL L, REIGBER A, et al. Analysis of built-up areas from Polarimetric interferometric SAR images[C]. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 1727–1729. [8] COLIN E, TITIN-SCHNAIDER C, and TABBARA W. An interferometric coherence optimization method in radar polarimetry for high-resolution imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(1): 167–175. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.859357 [9] COLIN-KOENIGUER E and TROUVÉ N. Performance of building height estimation using high-resolution PolInSAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(9): 5870–5879. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2293605 [10] CLOUDE S R. Calibration requirements for forest parameter estimation using POLinSAR[C]. CEOS Working Group on Calibration/Validation SAR Workshop, London, UK, 2002: 151–158. [11] 张林涛, 洪峻, 明峰. PolInSAR极化误差对最优相干相位的影响研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(2): 412–417. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00331ZHANG Lintao, HONG Jun, and MING Feng. Study on the impact of Polarimetric error on optimal coherence phase of PolInSAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(2): 412–417. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00331 [12] 许丽颖. 极化干涉合成孔径雷达系统与信息处理技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2014: 127–136.XU Liying. Study on system and information processing of Polarimetric SAR interferometry[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014: 127–136. [13] 孙翔. 极化干涉合成孔径雷达地物参数估计与系统设计方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2018: 110–113.SUN Xiang. On approach of estimating ground feature parameters and system design of Polarimetric SAR interferometry[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018: 110–113. [14] SUN Zhongchang, GUO Huadong, LI Xinwu, et al. Error analysis of DEM derived from airborne single-pass interferometric SAR data[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 3405–3408. [15] ZHAO Shuyuan, GU Defeng, YI Bin, et al. Error analysis for the baseline estimation and calibration of distributed InSAR satellites[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 4179–4182. [16] 生强强. InSAR DEM精度分析与定量评估方法[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2018.SHENG Qiangqiang. InSAR DEM accuracy analysis and quantitative evaluation[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2018. [17] 方东生, 吕孝雷, 李缘廷, 等. 运动补偿对机载SAR重轨干涉成像的影响分析[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2016, 14(4): 355–363. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2016.04.003FANG Dongsheng, LV Xiaolei, LI Yuanting, et al. Effect of motion compensation on airborne repeat pass InSAR imaging[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2016, 14(4): 355–363. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2016.04.003 [18] WANG Huiqiang, ZHU Jianjun, FU Haiqiang, et al. Modeling and robust estimation for the residual motion error in airborne SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(1): 65–69. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2867868 [19] 孙晗伟, 曾涛, 杨健, 等. SAR残余相位误差对森林高度反演影响的全链路模拟与分析[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2015, 40(2): 153–158. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20130052SUN Hanwei, ZENG Tao, YANG Jian, et al. Simulation and analysis of SAR residual phase error on forest height inversion[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2015, 40(2): 153–158. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20130052 [20] LV Zexin, LI Fangfang, QIU xiaolan, et al. Effects of motion compensation residual error and polarization distortion on UAV-borne PolInSAR[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(4): 618. doi: 10.3390/rs13040618 [21] ROY R and KAILATH T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(7): 984–995. doi: 10.1109/29.32276 [22] LV Zexin, QIU Xiaolan, CHENG Yao, et al. Multi-rotor UAV-borne PolInSAR data processing and preliminary analysis of height inversion in urban area[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(9): 2161. doi: 10.3390/rs14092161 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: