Scattering Information and Meta-learning Based SAR Images Interpretation for Aircraft Target Recognition
-
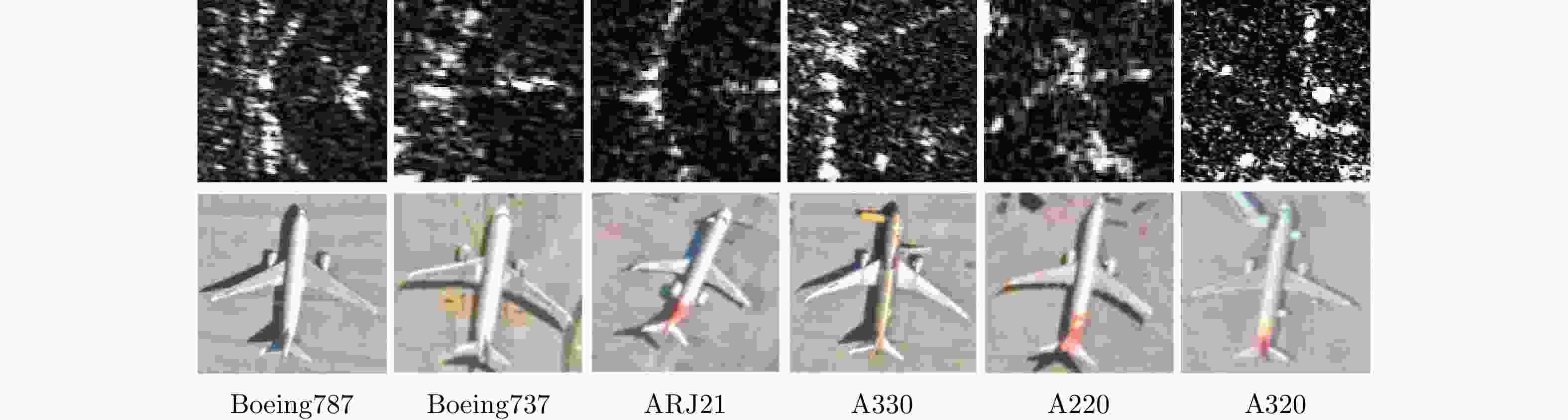
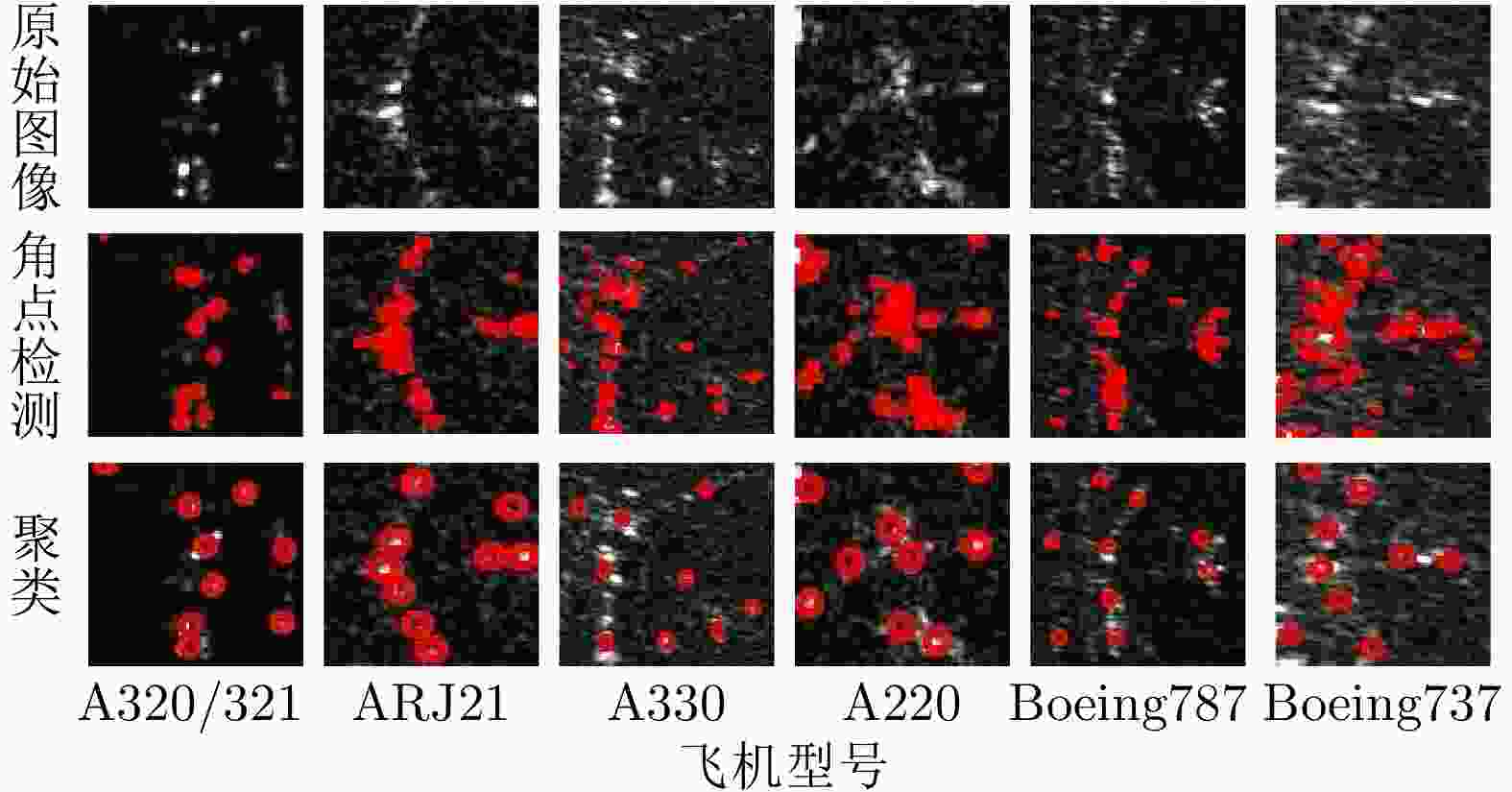
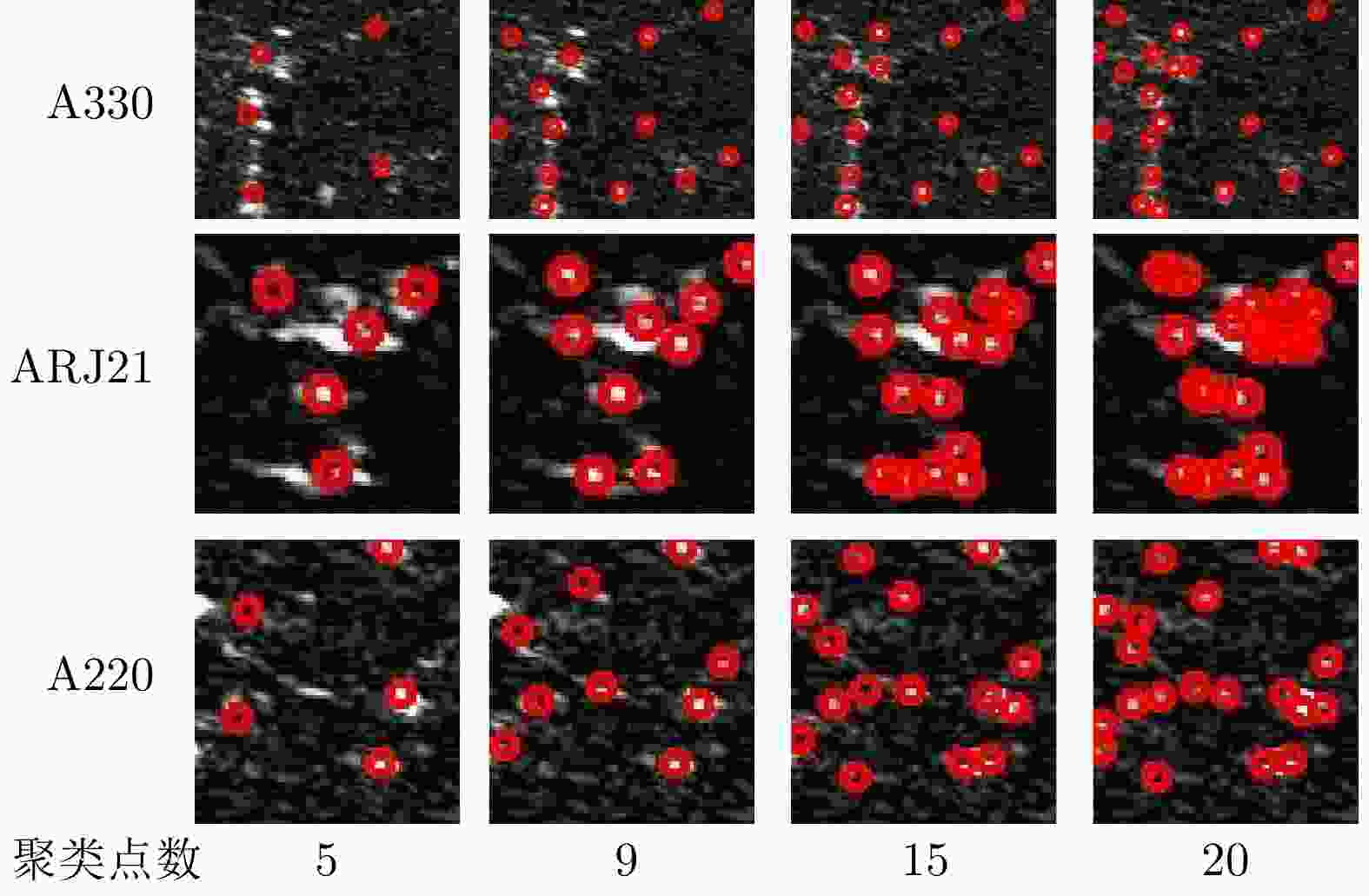
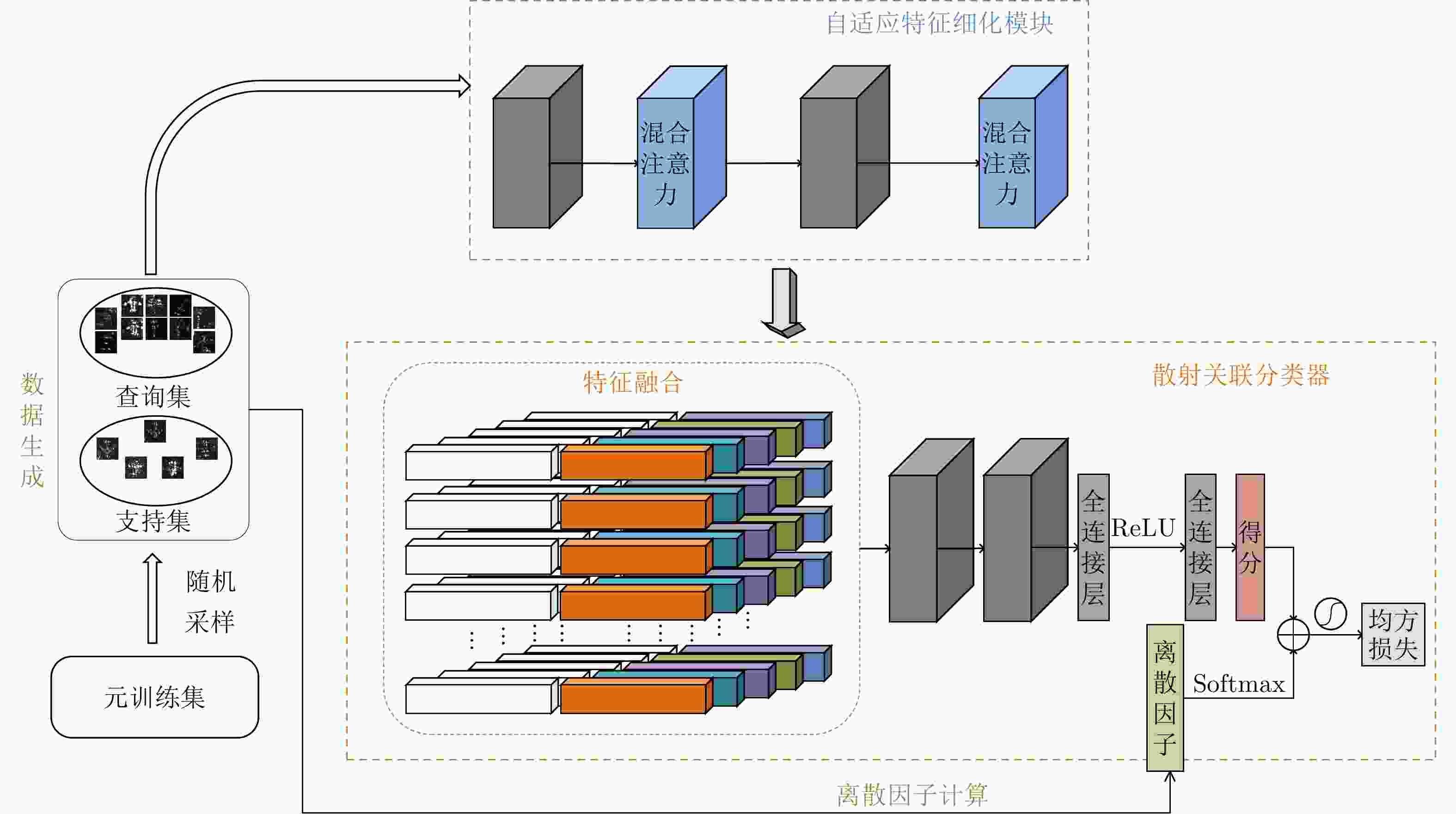
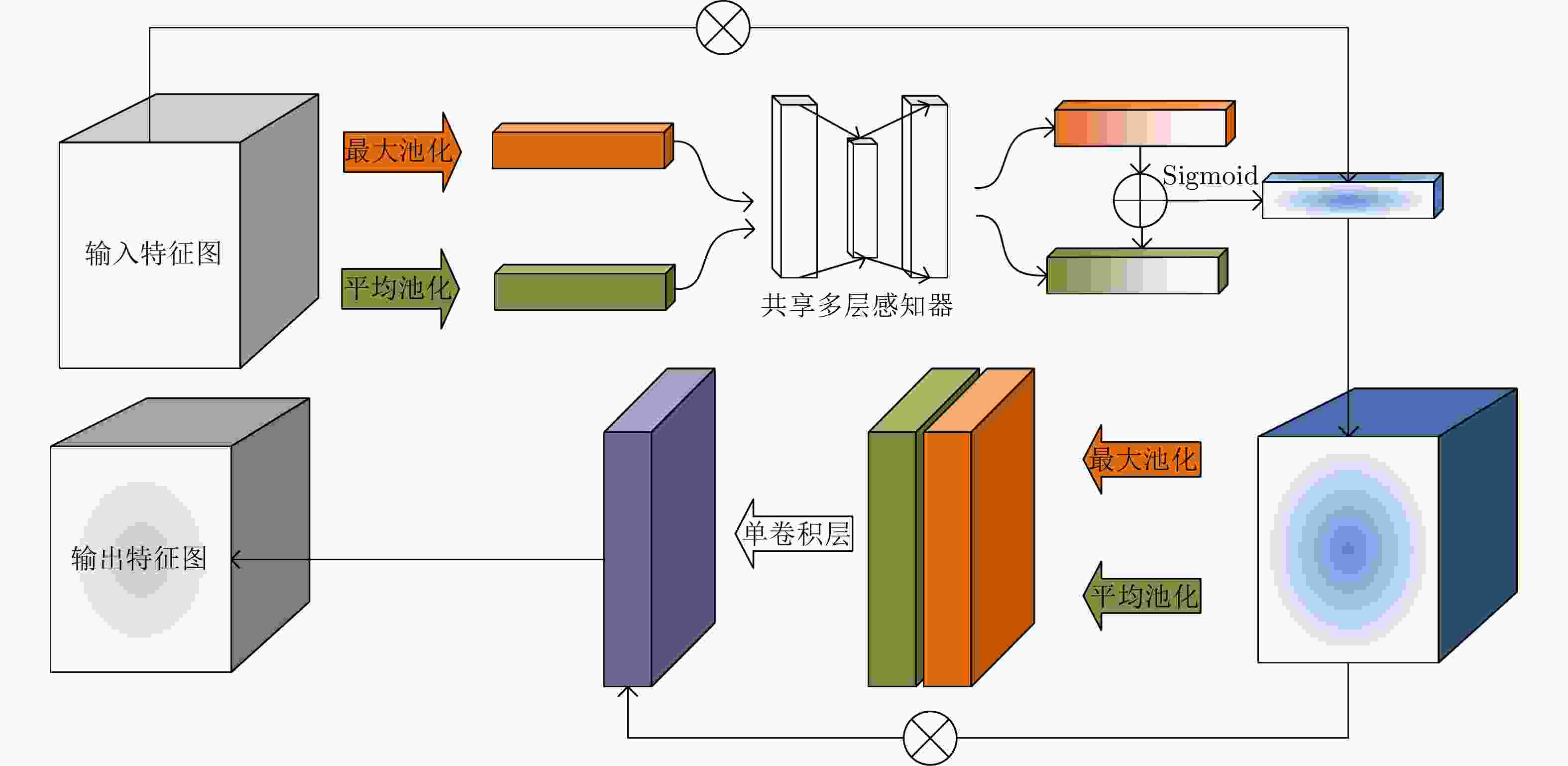
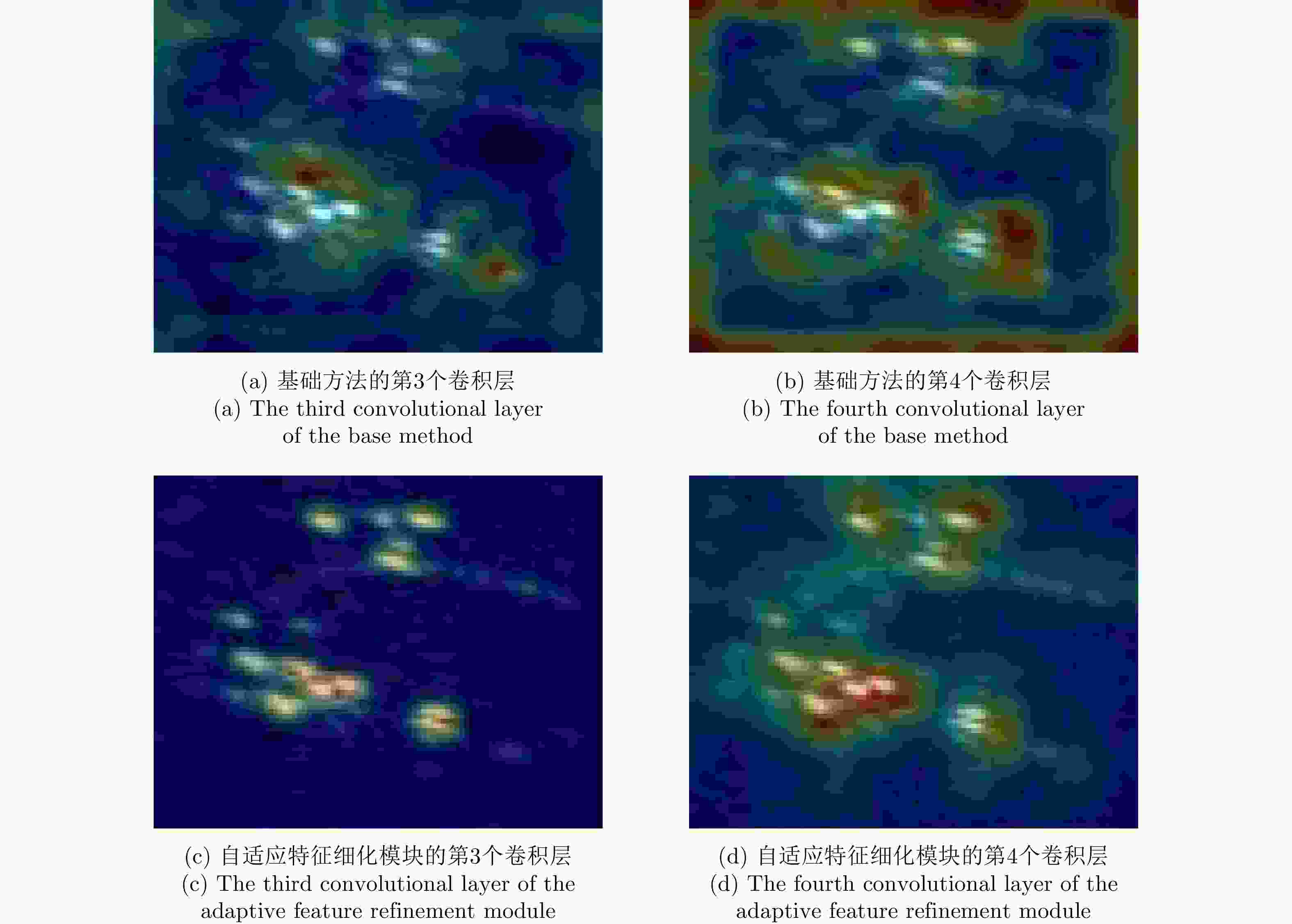
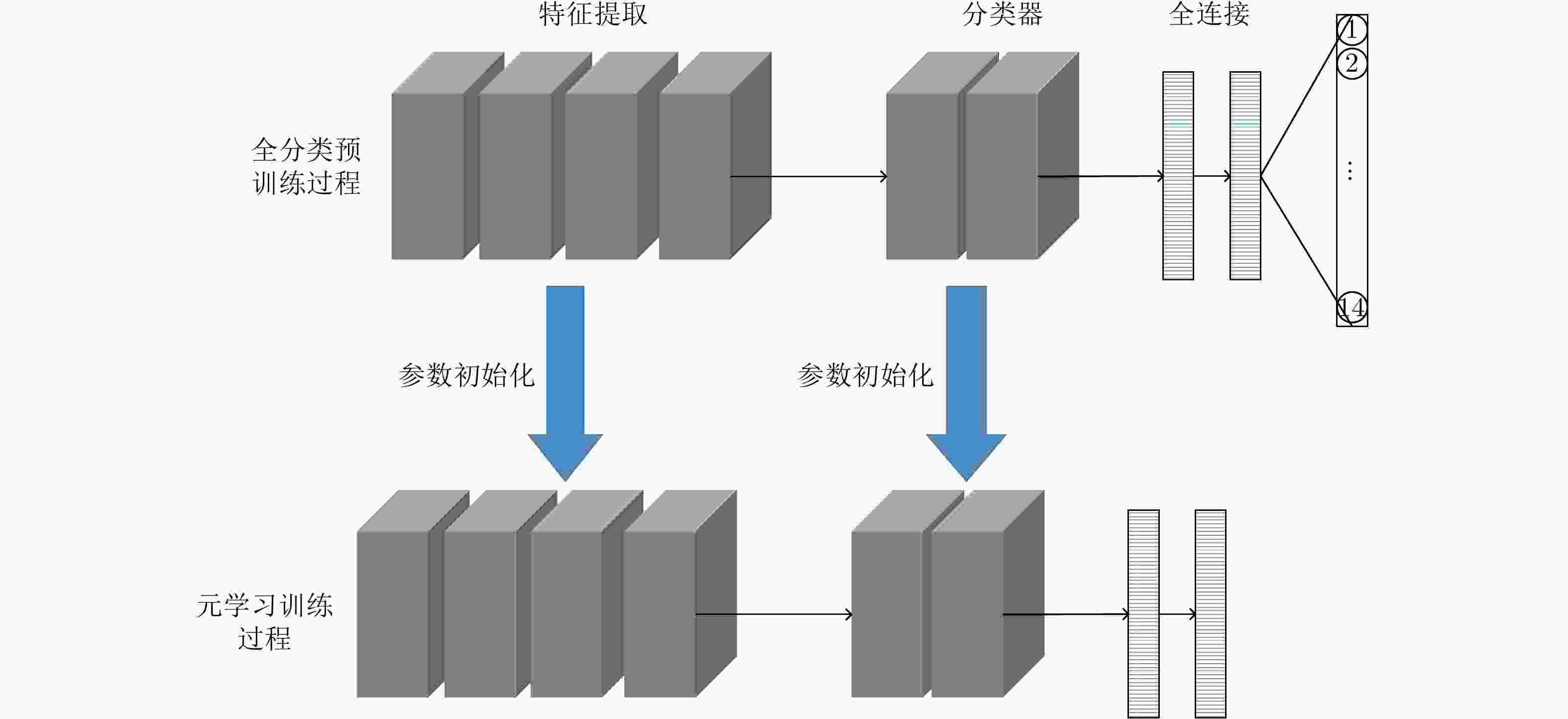
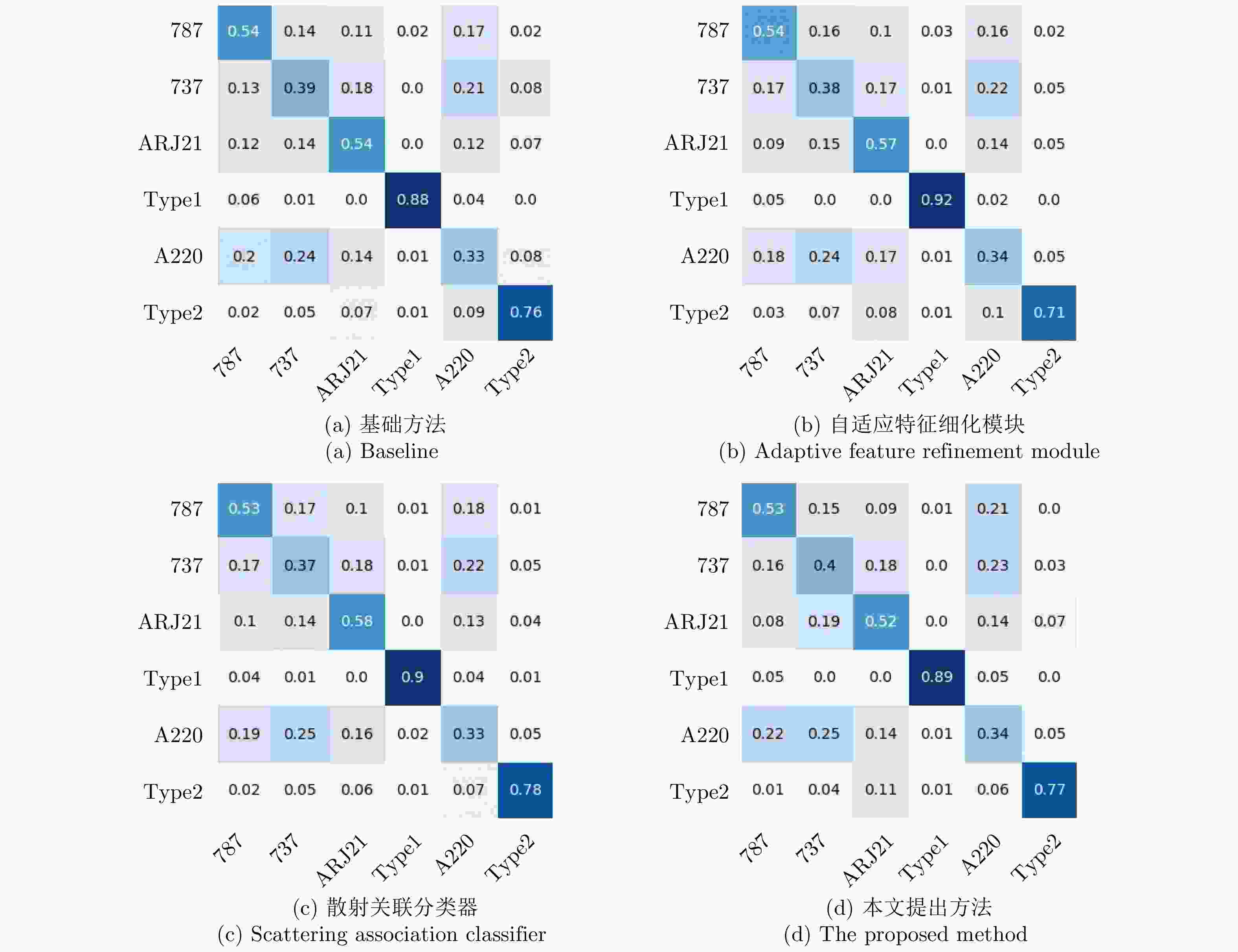
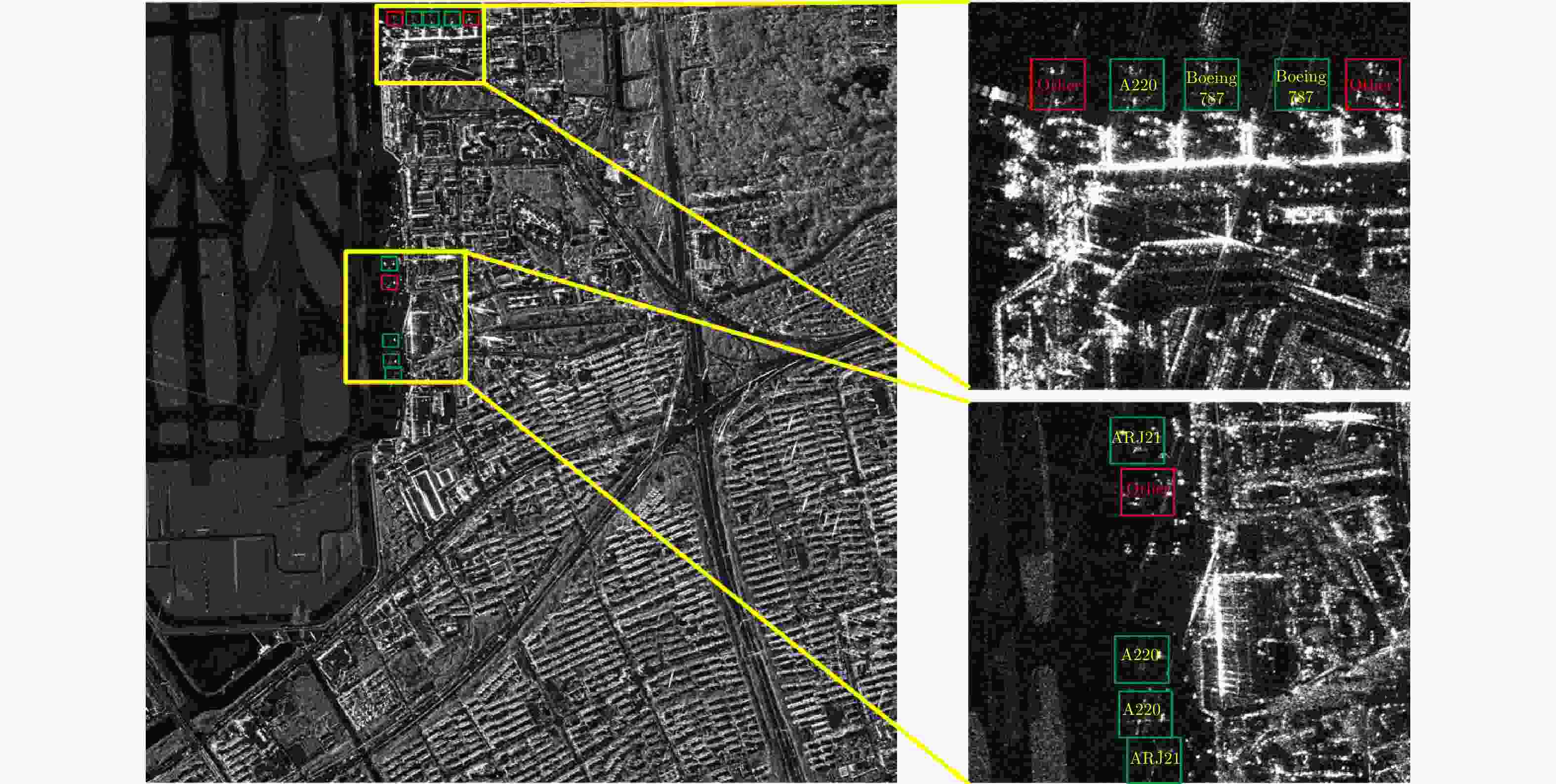
摘要: SAR图像由于数据获取难度大,样本标注难,目标覆盖率不足,导致包含地理空间目标的影像数量稀少。为了解决这些问题,该文开展了基于散射信息和元学习的SAR图像飞机目标识别方法研究。针对SAR图像中不同型号飞机空间结构离散分布差异较大的情况,设计散射关联分类器,对飞机目标的离散程度量化建模,通过不同目标离散分布的差异来动态调整样本对的权重,指导网络学习更具有区分性的类间特征表示。考虑到SAR目标成像易受背景噪声的影响,设计了自适应特征细化模块,促使网络更加关注飞机的关键部件区域,减少背景噪声干扰。该文方法有效地将目标散射分布特性与网络的自动学习过程相结合。实验结果表明,在5-way 1-shot的极少样本新类别识别任务上,该方法识别精度为59.90%,相比于基础方法提升了3.85%。减少一半训练数据量后,该方法在新类别的极少样本识别任务上仍然表现优异。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR) /
- 飞机目标识别 /
- 元学习 /
- 散射信息
Abstract: The sample scarcity issue is still challenged for SAR images interpretation. The number of geospatial targets related images is constrained of the SAR images interpretation ability of data acquisition, sample labeling, and the lack of target coverage. Our SAR-ATR method is demonstrated based on scattering information and meta-learning. First, the discrete distribution of the spatial structure of different types of aircraft is quite different in SAR images. An associated scattering classifier is designed to guide the network to learn more discriminative intra-class and inter-class feature descriptions. Our proposed classifier facilitates the modeling of discrete degree of the aircraft target quantitatively and balance the weights of sample pairs dynamically through the differentiated analysis of different target discrete distributions. In addition, an adaptive feature refinement module is designed to optimize the network cohesion for the key parts of the aircraft and reduce the interference of background noise. The proposed method integrates the target scattering distribution properties to the network learning process. On 5-way 1-shot emerging categorized recognition task involved only few samples, our experimental results demonstrate that the recognition accuracy of this method is 59.90%, which is 3.85% higher than the benchmark. After reducing the amount of training data by half, the proposed method is still competitive on the new category of few-shot recognition tasks. -
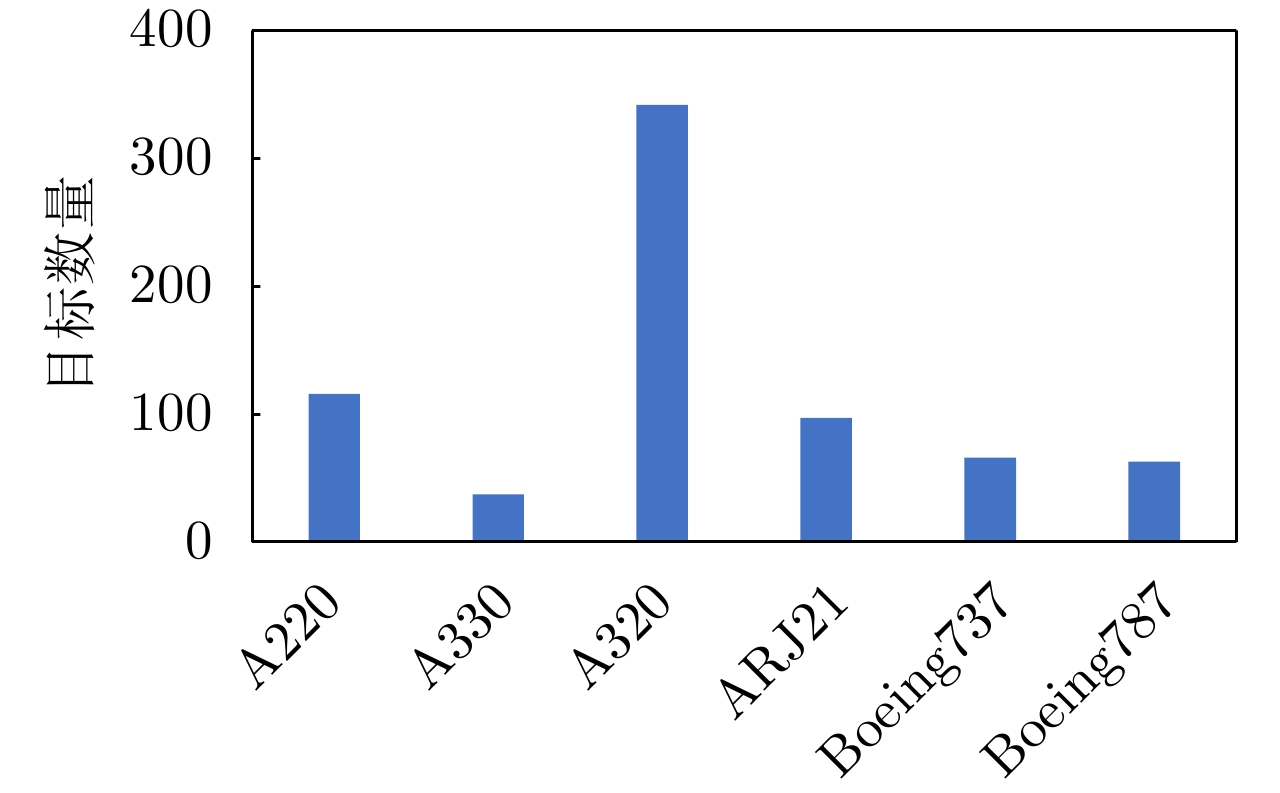
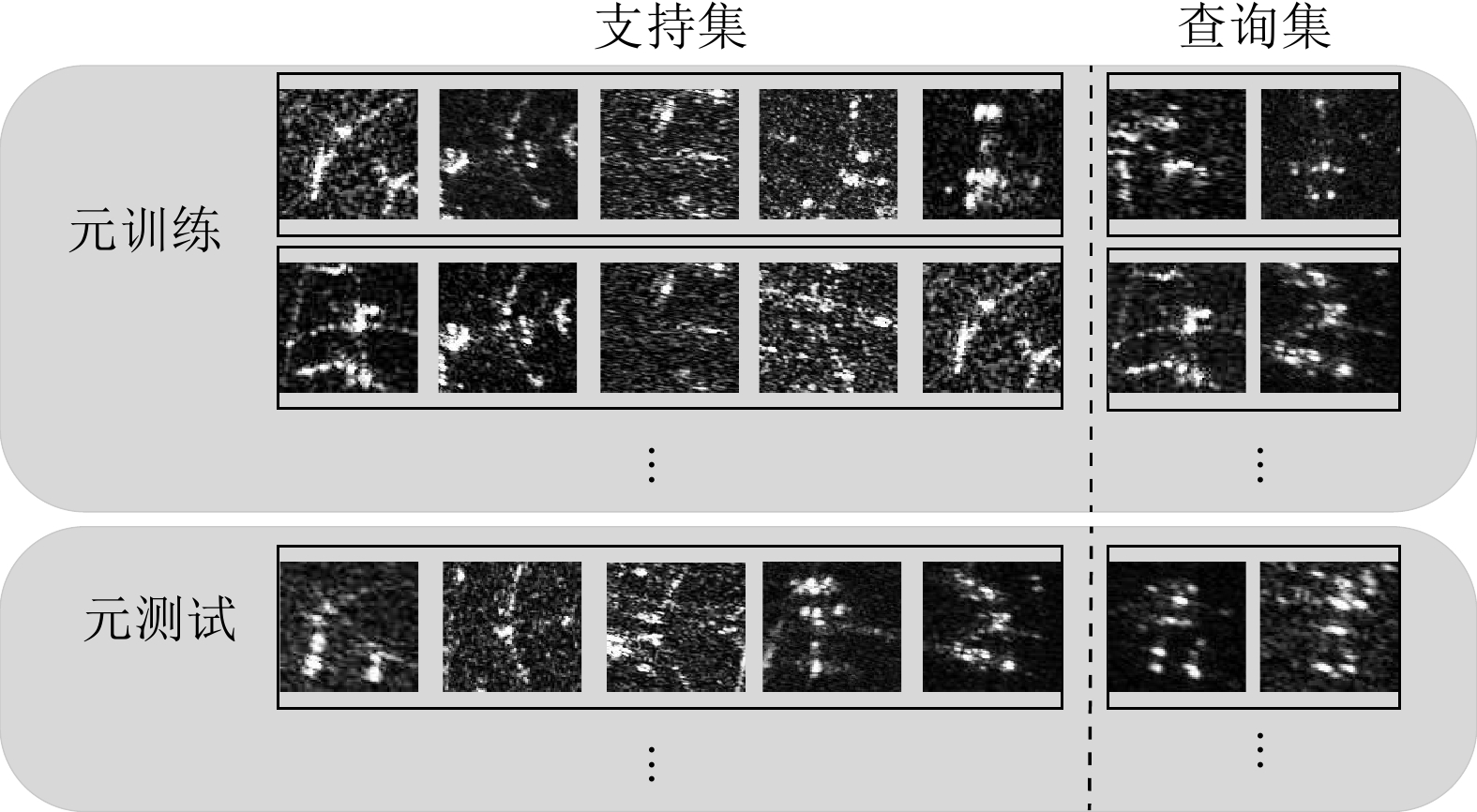
表 1 实验中训练和测试期间数据设置
Table 1. Data setup during training and testing
设置 5-way 5-shot 5-way 1-shot 支持集 查询集 支持集 查询集 元训练 5 15 1 15 元测试 5 15 1 15 表 2 自适应特征细化模块和散射关联分类器的消融实验
Table 2. Ablation study on adaptive feature refinement module and scattering association module
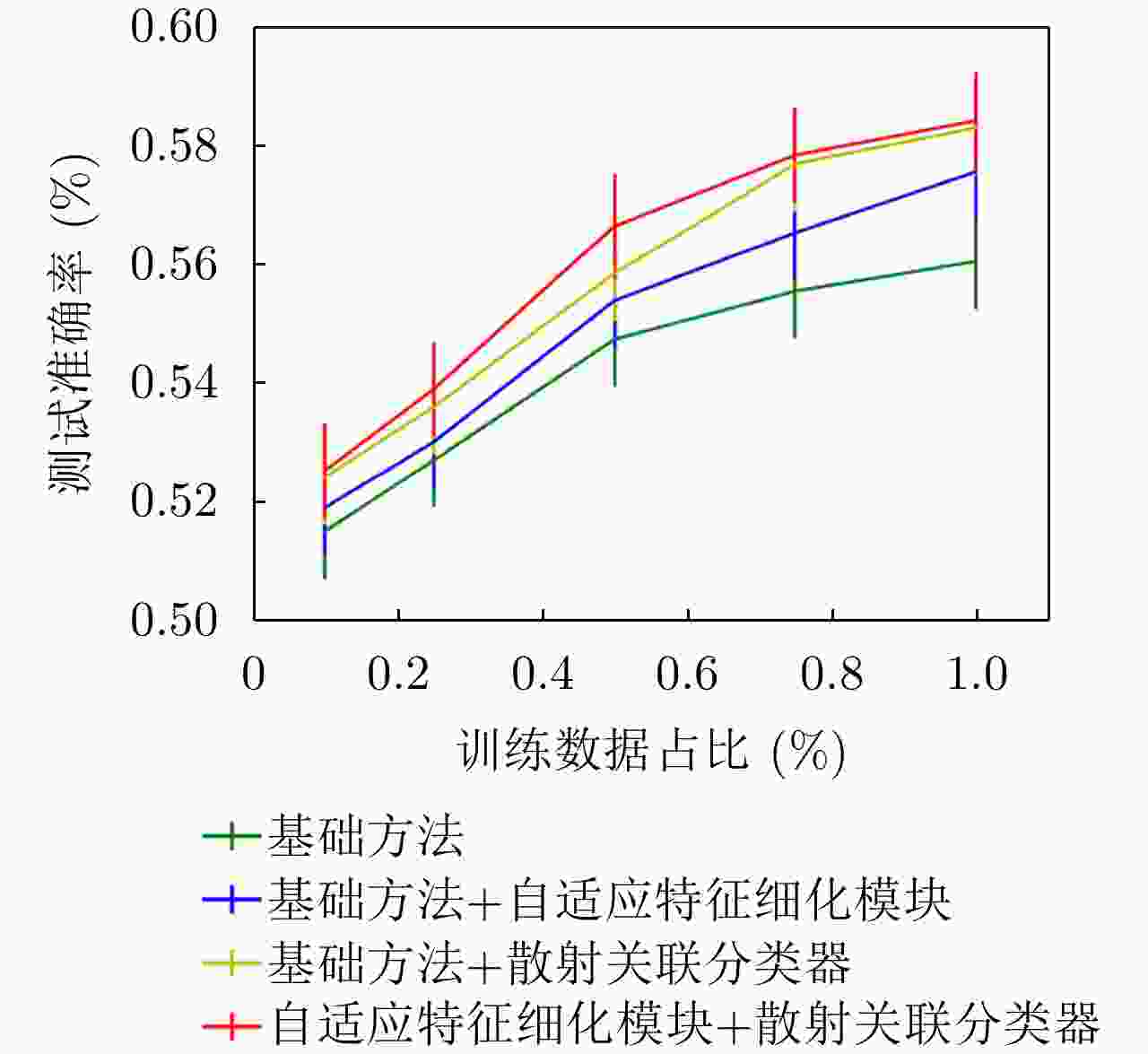
散射关联分类器 自适应特征细化模块 5-way 1-shot (%) 5-way 5-shot (%) × × 56.05 ± 0.8 66.71 ± 0.7 × √ 57.57 ± 0.9 67.80 ± 0.7 √ × 58.31 ± 0.9 68.20 ± 0.7 √ √ 58.43 ± 0.8 68.52 ± 0.7 表 3 结合预训练过程的消融实验
Table 3. Ablation study combined with the pre-training process
散射关联分类器 自适应特征细化模块 5-way 1-shot (%) 5-way 5-shot (%) × × 57.33 ± 0.9 67.60 ± 0.7 × √ 58.86 ± 0.8 68.72 ± 0.7 √ × 59.60 ± 0.9 68.85 ± 0.7 √ √ 59.90 ± 0.9 70.13 ± 0.7 -
[1] DONG Ganggang and KUANG Gangyao. Classification on the monogenic scale space: Application to target recognition in SAR image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(8): 2527–2539. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2421440 [2] NOVAK L M, OWIRKA G L, and BROWER W S. Performance of 10-and 20-target MSE classifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2000, 36(4): 1279–1289. doi: 10.1109/7.892675 [3] WAGNER S A. SAR ATR by a combination of convolutional neural network and support vector machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(6): 2861–2872. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.160061 [4] 康健, 王智睿, 祝若鑫, 等. 基于监督对比学习正则化的高分辨率SAR图像建筑物提取方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 157–167. doi: 10.12000/JR21124KANG Jian, WANG Zhirui, ZHU Ruoxin, et al. Supervised contrastive learning regularized high-resolution synthetic aperture radar building footprint generation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 157–167. doi: 10.12000/JR21124 [5] HE Chu, TU Mingxia, XIONG Dehui, et al. Adaptive component selection-based discriminative model for object detection in high-resolution SAR imagery[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2018, 7(2): 72. doi: 10.3390/ijgi7020072 [6] KANG Yuzhuo, WANG Zhirui, FU Jiamei, et al. SFR-Net: Scattering feature relation network for aircraft detection in complex SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5218317. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3130899 [7] 赵鹏菲, 黄丽佳. 一种基于EfficientNet与BiGRU的多角度SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 895–904. doi: 10.12000/JR20133ZHAO Pengfei and HUANG Lijia. Target recognition method for multi-aspect synthetic aperture radar images based on EfficientNet and BiGRU[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 895–904. doi: 10.12000/JR20133 [8] ZHANG Jinsong, XING Mengdao, and XIE Yiyuan. FEC: A feature fusion framework for SAR target recognition based on electromagnetic scattering features and deep CNN features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(3): 2174–2187. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3003264 [9] HUANG Zhongling, DATCU M, PAN Zongxu, et al. Deep SAR-Net: Learning objects from signals[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 161: 179–193. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.01.016 [10] YANG Yue, ZHANG Zhuo, MAO Wei, et al. Radar target recognition based on few-shot learning[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2021: 3. doi: 10.1007/s00530-021-00832-3 [11] CAO Changjie, CUI Zongyong, CAO Zongjie, et al. An integrated counterfactual sample generation and filtering approach for SAR automatic target recognition with a small sample set[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(19): 3864. doi: 10.3390/rs13193864 [12] GUO Jiayi, LEI Bin, DING Chibiao, et al. Synthetic aperture radar image synthesis by using generative adversarial nets[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(7): 1111–1115. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2699196 [13] RADFORD A, METZ L, and CHINTALA S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1511. 06434v1, 2015. [14] CUI Zongyong, ZHANG Mingrui, CAO Zongjie, et al. Image data augmentation for SAR sensor via generative adversarial nets[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 42255–42268. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2907728 [15] KUSK A, ABULAITIJIANG A, and DALL J. Synthetic SAR image generation using sensor, Terrain and target models[C]. EUSAR 2016: 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 1–5. [16] LIN Zhao, JI Kefeng, KANG Miao, et al. Deep convolutional highway unit network for SAR target classification with limited labeled training data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(7): 1091–1095. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2698213 [17] 喻玲娟, 王亚东, 谢晓春, 等. 基于FCNN和ICAE的SAR图像目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR18066YU Lingjuan, WANG Yadong, XIE Xiaochun, et al. SAR ATR based on FCNN and ICAE[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 622–631. doi: 10.12000/JR18066 [18] PAN Zongxu, BAO Xianjie, ZHANG Yueting, et al. Siamese network based metric learning for SAR target classification[C]. IGARSS 2019–2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 1342–1345. [19] MA Yu, LIANG Yan, ZHANG Wanying, et al. SAR target recognition based on transfer learning and data augmentation with LSGANs[C]. 2019 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Hangzhou, China, 2019: 2334–2337. [20] WANG Ke, ZHANG Gong, and LEUNG H. SAR target recognition based on cross-domain and cross-task transfer learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 153391–153399. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2948618 [21] ZHANG Wei, ZHU Yongfeng, and FU Qiang. Semi-supervised deep transfer learning-based on adversarial feature learning for label limited SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 152412–152420. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2948404 [22] KANG Chenyao and HE Chu. SAR image classification based on the multi-layer network and transfer learning of mid-level representations[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 2016: 1146–1149. [23] HUANG Zhongling, PAN Zongxu, and LEI Bin. What, where, and how to transfer in SAR target recognition based on deep CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2324–2336. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2947634 [24] DU Lan, CAO Lanying, and LIU Hongwei. Few-shot learning neural network for SAR target recognition[C]. 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–4. [25] WANG Ke, ZHANG Gong, XU Yanbing, et al. SAR target recognition based on probabilistic meta-learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(4): 682–686. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2983988 [26] FU Kun, ZHANG Tengfei, ZHANG Yue, et al. Few-shot SAR target classification via metalearning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 2000314. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3058249 [27] DIEMUNSCH J R and WISSINGER J. Moving and stationary target acquisition and recognition (MSTAR) model-based automatic target recognition: Search technology for a robust ATR[C]. The SPIE 3370, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery V, Orlando, FL, USA, 1998: 481–492. [28] FU Kun, FU Jiamei, WANG Zhirui, et al. Scattering-Keypoint-Guided network for oriented ship detection in high-resolution and large-scale SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 11162–11178. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3109469 [29] GUO Qian, WANG Haipeng, and XU Feng. Scattering enhanced attention pyramid network for aircraft detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(9): 7570–7587. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3027762 [30] HOU Xiyue, AO Wei, SONG Qian, et al. FUSAR-Ship: building a high-resolution SAR-AIS matchup dataset of Gaofen-3 for ship detection and recognition[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(4): 140303. doi: 10.1007/s11432-019-2772-5 [31] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [32] FINN C, ABBEEL P, and LEVINE S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[C]. 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1126–1135. [33] VINYALS O, BLUNDELL C, LILLICRAP T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processiing Systems, Red Hook, USA, 2016: 3637–3645. [34] SNELL J, SWERSKY K, and ZEMEL R S. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]. 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Red Hook, USA, 2017: 4080–4090. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: