Key Technology and Preliminary Progress of Microwave Vision 3D SAR Experimental System
-
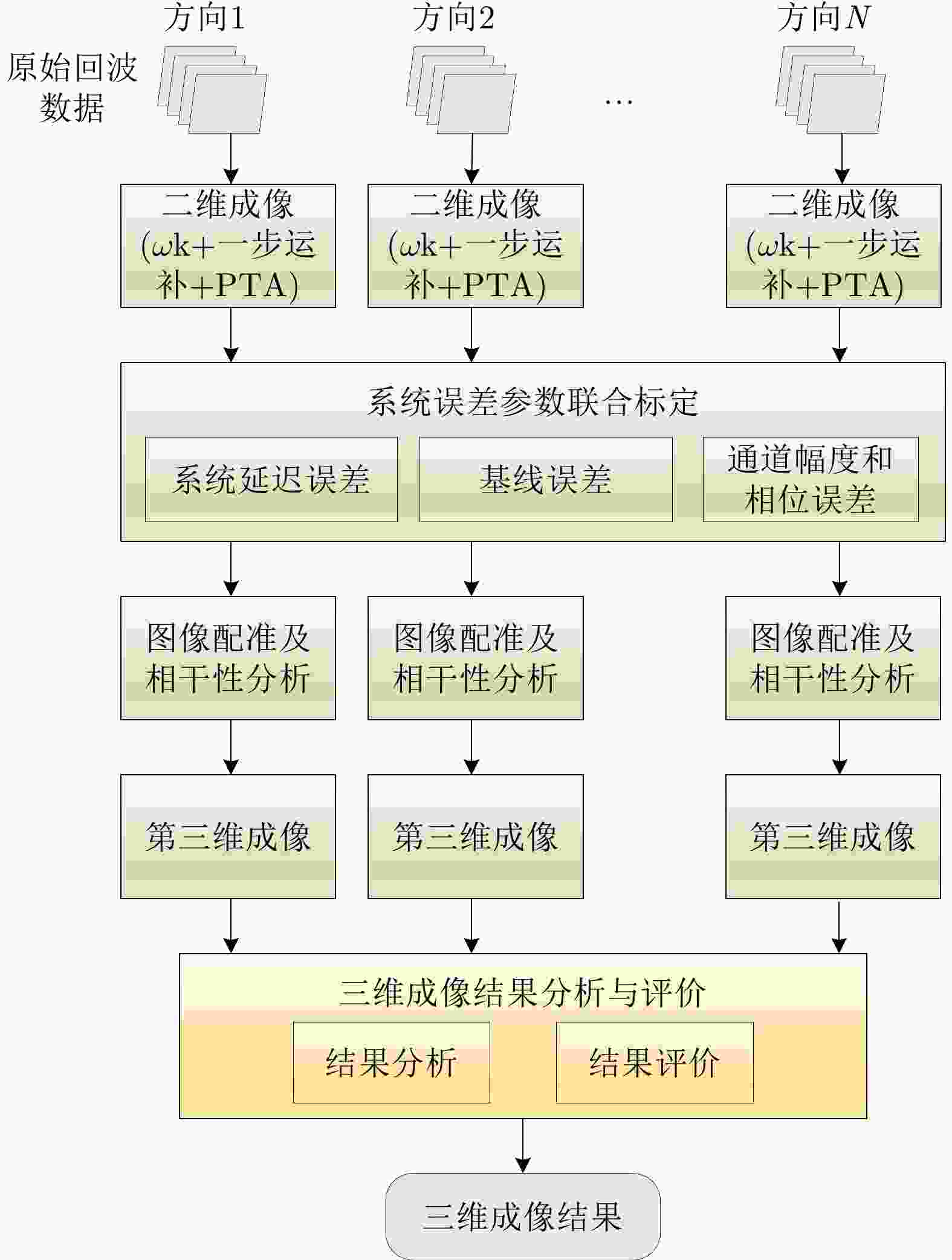
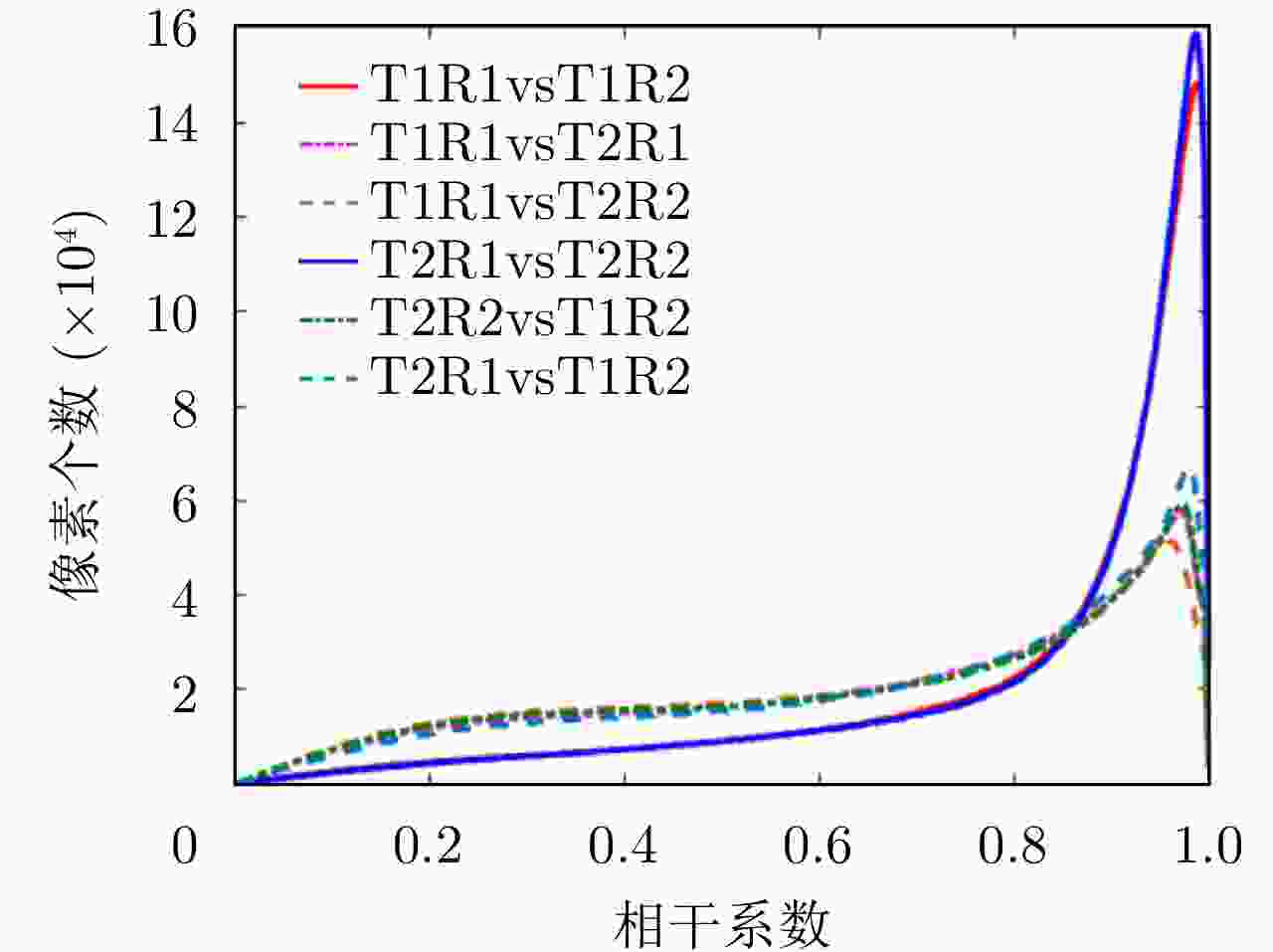
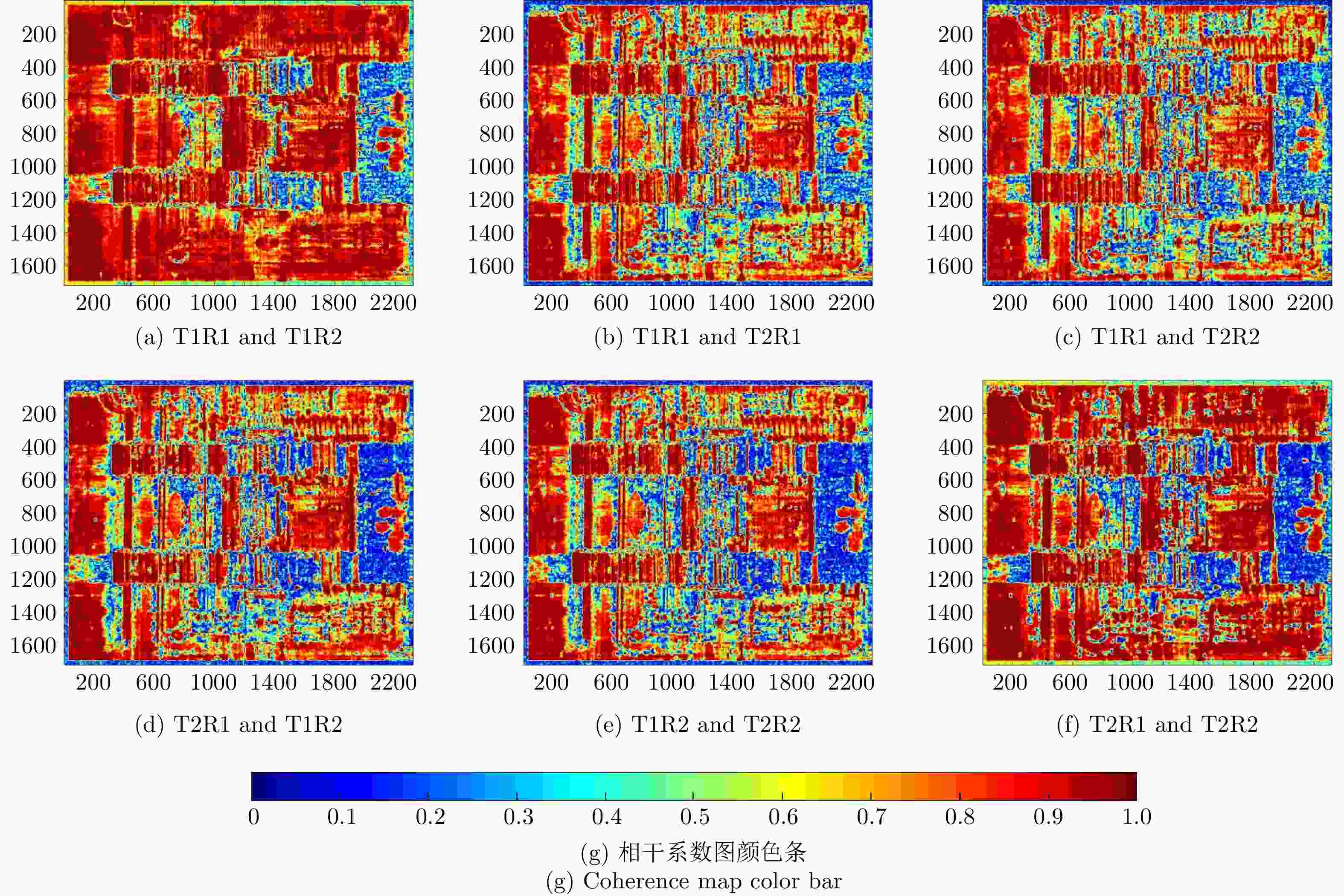
摘要: 合成孔径雷达(SAR)三维成像在复杂地形测绘、复杂环境下目标发现与识别等方面具有重要应用潜力,是当前SAR领域的重要发展方向之一。为推动SAR三维成像技术的发展和应用,中国科学院空天信息创新研究院牵头设计并研制了一套无人机载微波视觉三维SAR实验系统(MV3DSAR),为相关技术研究和验证提供实验平台。目前该系统的单极化版本已研制完成,并在天津开展了首次校飞实验。该文介绍了该系统的基本构成、主要性能以及系统和数据处理的关键技术,给出了首次校飞实验的实施情况以及初步的数据处理结果,验证了系统的基本性能指标和三维成像能力。该系统为后续SAR三维成像数据集构建和处理方法研究提供了良好的实验验证平台。Abstract: Three-Dimensional (3D) Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging has considerable application potential in steep-terrain mapping and target recognition in complex environments and is an important development direction in the current SAR field. To promote the development and application of the 3D SAR imaging technology, the Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences designed and developed an unmanned aerial vehicle-borne Microwave-Vision 3D SAR (MV3DSAR) experimental system, which provides an experimental platform for the research and verification of related technologies. Currently, the single-polarization version of the system has been developed, and the first flight experiment has been conducted in Tianjin. This study introduces the structure, performance, key technologies, and data processing of the system. This study also presents the implementation and preliminary data processing results of the first experiment, verifying the basic performance and 3D imaging capability of the system. The MV3DSAR provides a good experimental and verification platform for analyzing 3D SAR imaging algorithms and constructing 3D SAR imaging datasets.
-
Key words:
- SAR 3D imaging /
- Microwave vision /
- UAV borne SAR /
- InSAR calibration /
- Motion compensation
-
表 1 MV3DSAR系统总体构成
Table 1. The overall composition of the MV3DSAR system
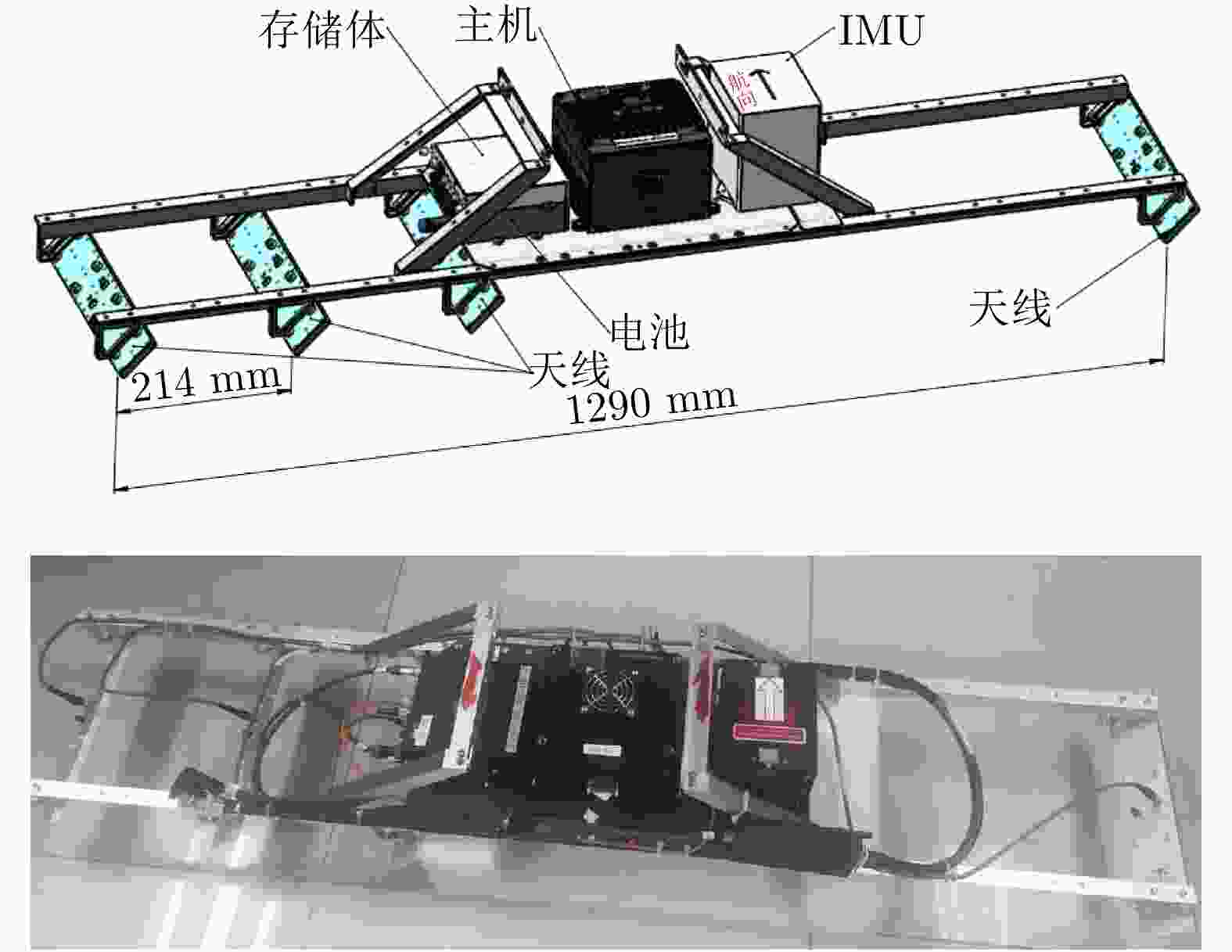
序号 名称 说明 1 微小型
Ku-SARKu-波段SAR系统由雷达主机、天线及天线支架、开关组合、数据存储模块等组成 2 无人机平台 采用KWT-X6L-15六旋翼无人机,最大作业载荷15 kg、最大翼展尺寸2.53 m,最大飞行速度15 m/s 3 导航系统 由GPS模块和微型惯性测量单元(MIMU)模块组成;航迹测量精度0.05 m,姿态测量精度0.02° 表 2 Ku-SAR载荷参数
Table 2. Parameters of Ku-SAR payload
序号 参数名称 参数值 1 中心频率 15.2 GHz 2 信号形式 调频连续波(FMCW) 3 极化方式 HH(后续将扩展全极化) 4 信号带宽 1200 MHz 5 天线尺寸(单通道) 0.05 m(俯仰)×0.32 m(方位) 6 每个极化的阵列通道数 4 7 分辨率 优于0.2 m×0.2 m 8 通道相位不平衡稳定度 ±5° (10 min内) 9 通道幅度不平衡稳定度 ±0.2 dB (10 min内) 10 中心视角 45° 11 NESZ 不大于–30 dB
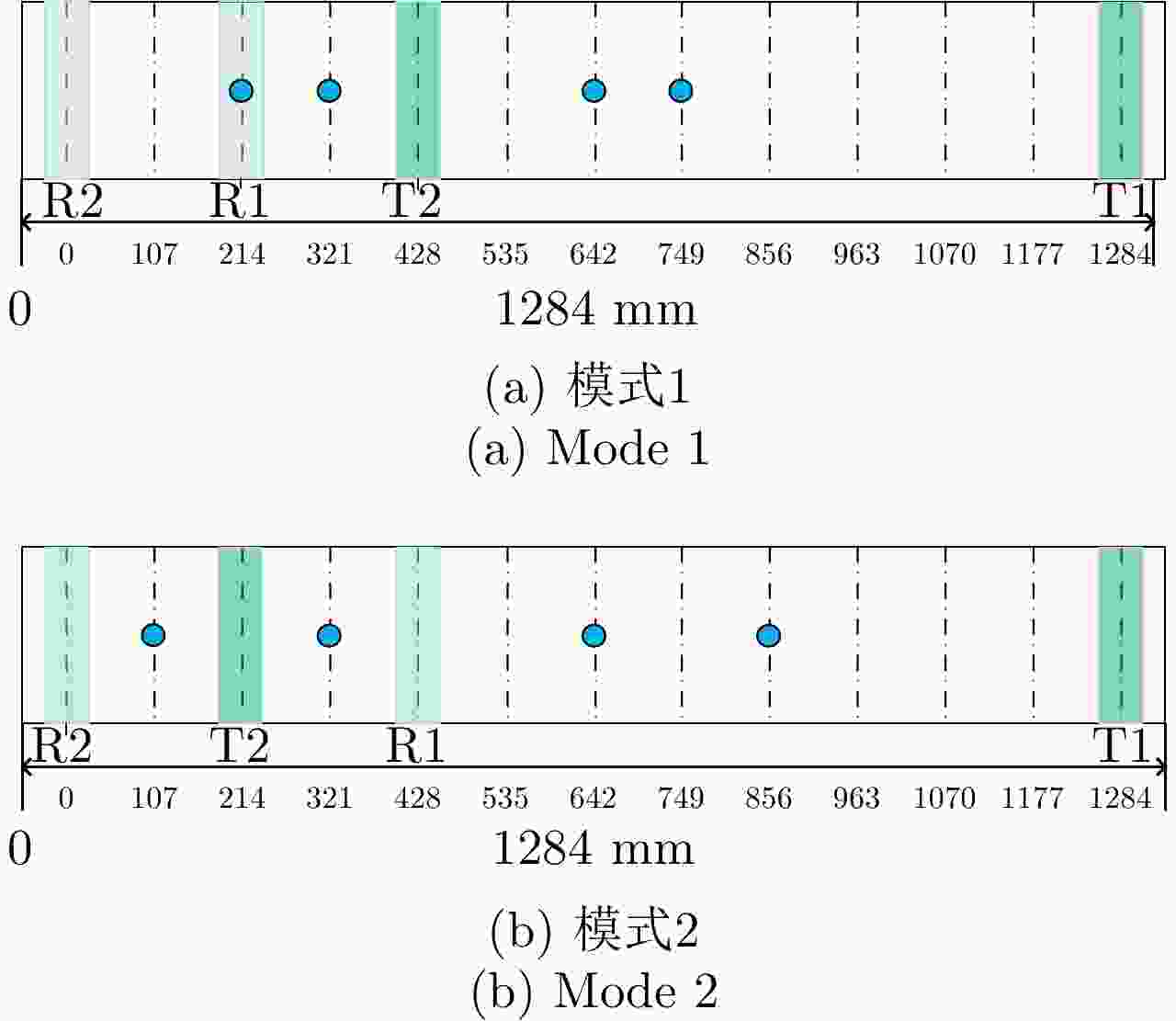
(最远作用距离3.6 km)12 天线最小间隔 0.107 m 13 天线最大间隔 1.284 m 14 Ku-SAR重量 主机、存储、电池、天线、结构等一共7.07 kg 表 3 MV3DSAR校飞实验基线长度
Table 3. Baseline length of MV3DSAR flight experiment
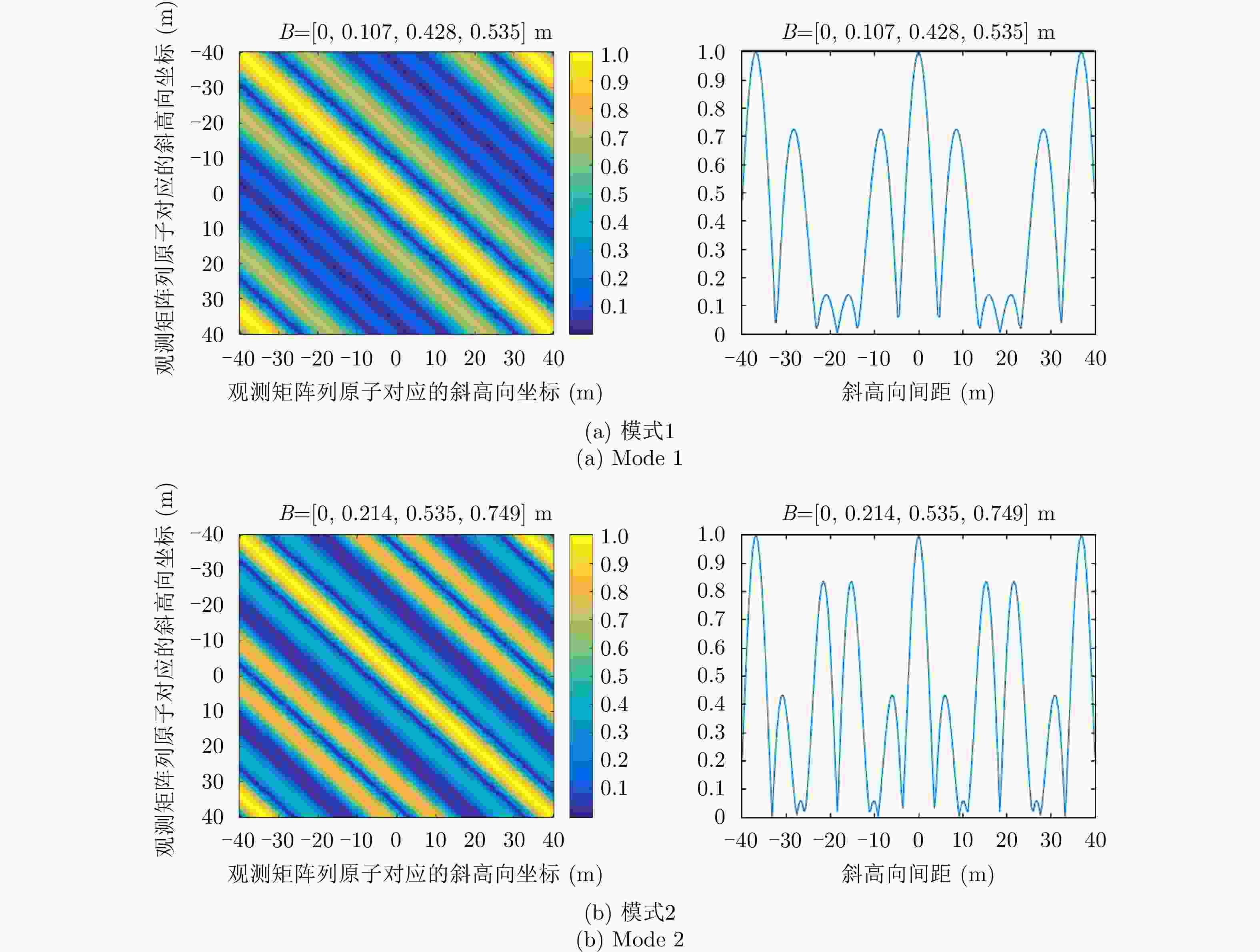
模式 等效天线相位中心 说明 模式1 [0, 0.107, 0.428, 0.535] m 不均匀,最短基线小,
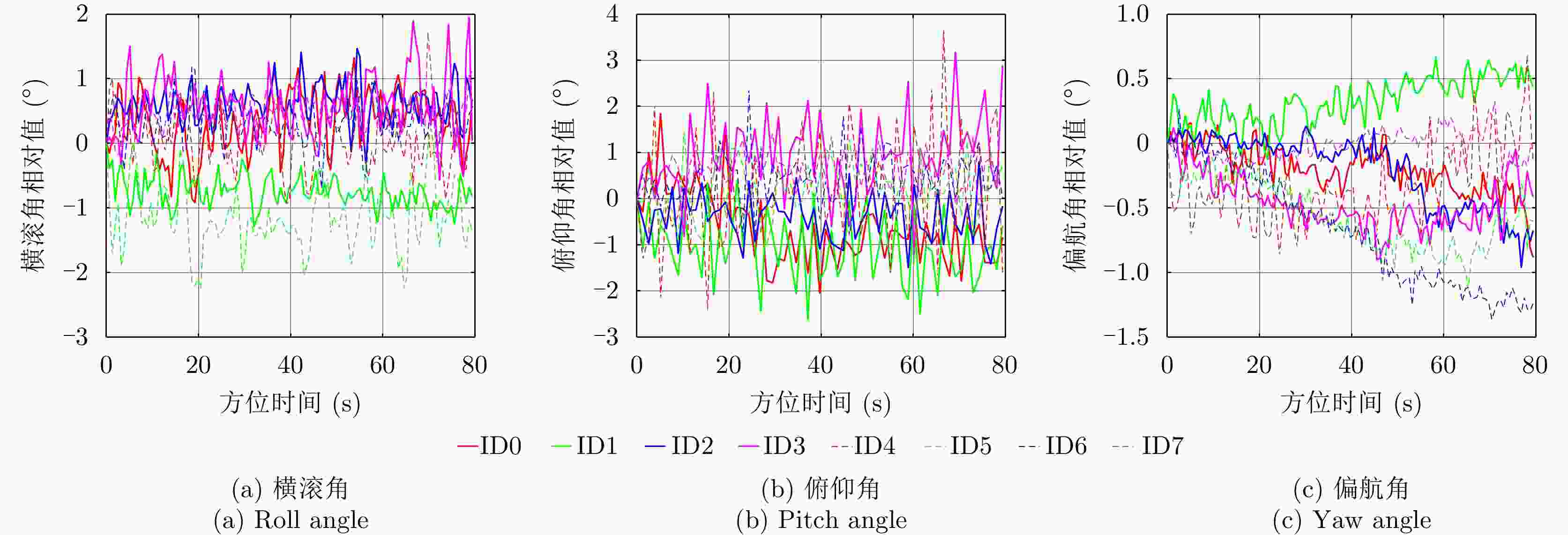
总基线较短模式2 [0, 0.214, 0.535, 0.749] m 较均匀,最短基线较大,
总基线较长表 4 天线相位中心相对位置
Table 4. Relative position of antenna phase center
模式1 T R2 R1 T2 T1 X (mm) 0 –818.14 –603.95 –389.86 465.86 Y (mm) 0 27.95 24.27 20.04 3.92 Z (mm) 0 –109.18 –109.53 –110.0 –110.40 表 5 定标器分辨率
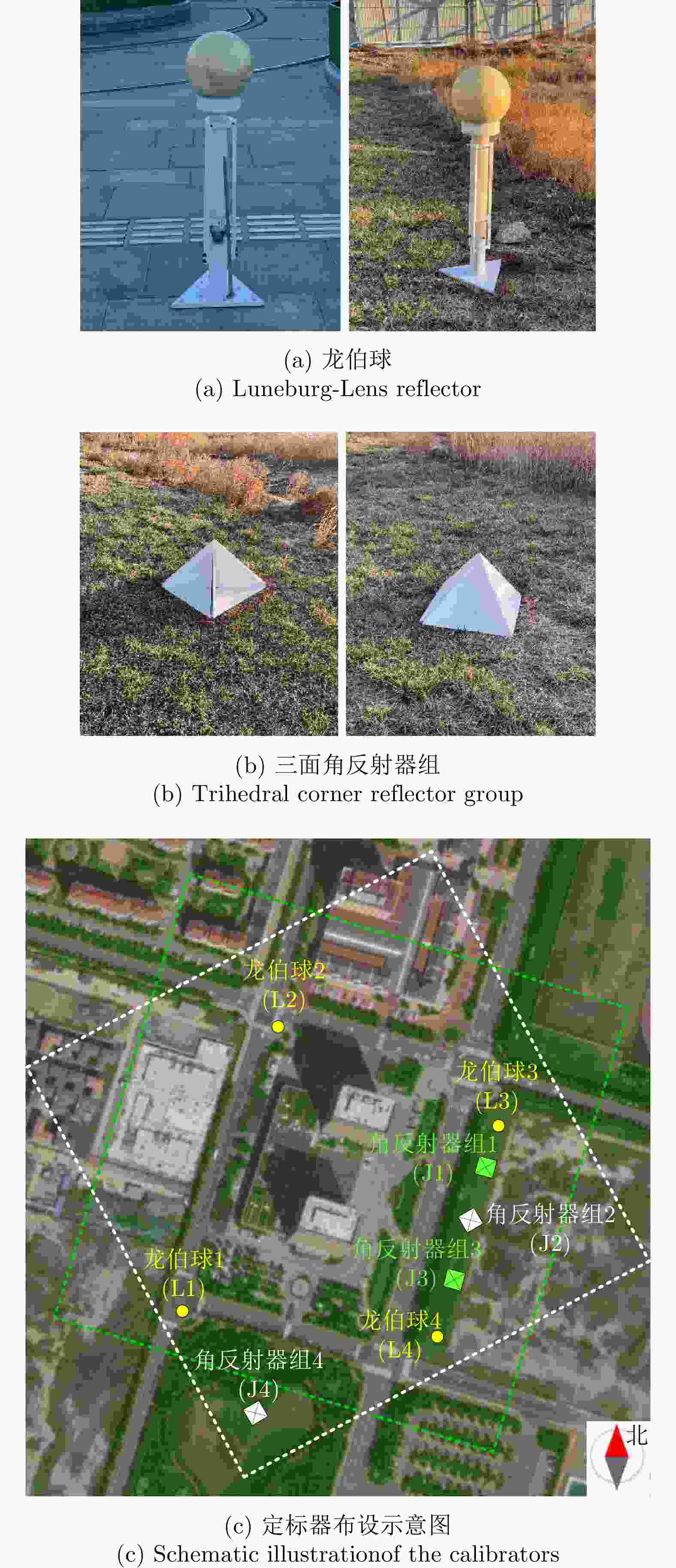
Table 5. Resolution of the calibrators
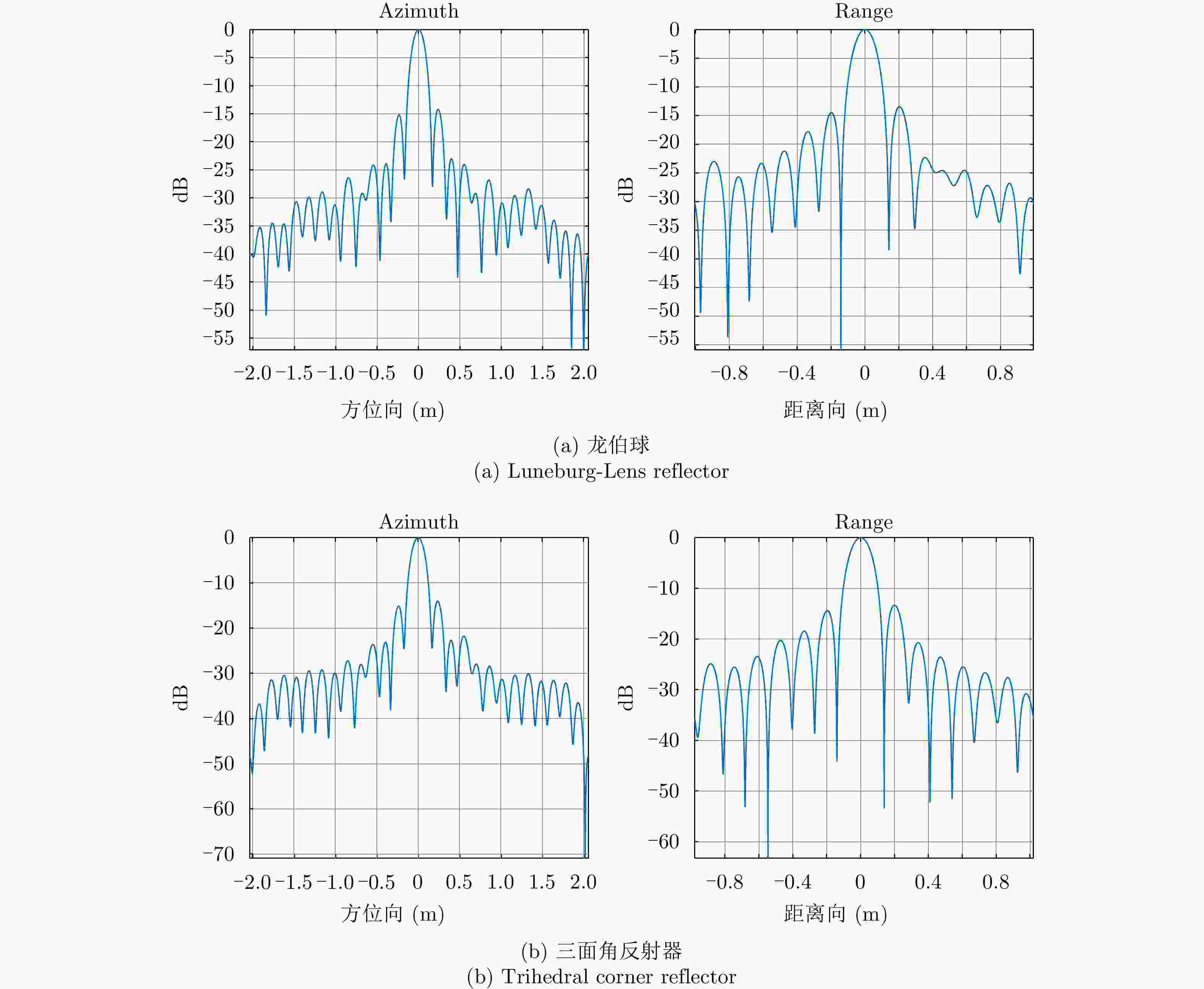
指标 龙伯球 角反射器 理论值 方位向 分辨率(m) 0.1471 0.1478 0.1362 峰值旁瓣比(dB) –14.19 –14.04 –13.26 积分旁瓣比(dB) –12.45 –12.16 –10.02 距离向 斜距分辨率(m) 0.1241 0.1231 0.1227 地距分辨率(m) 0.1756 0.1740 0.1735 峰值旁瓣比(dB) –13.45 –13.31 –13.26 积分旁瓣比(dB) –11.12 –11.21 –10.02 表 6 斜距误差标定结果
Table 6. Calibration result of slope distance error
方法 $ \Delta {R_0} $(m) $ \Delta {R_1} $(m/距离门) 有控 1.765427 0.000492772 无控 1.868205 0.000475285 表 7 两种方法的三维位置偏差(厘米)
Table 7. 3D position deviation of the two methods (cm)
方法 J1 J2 J3 J4 中误差 有控 1.7 8.0 3.2 3.5 4.7 无控 11.8 12.2 8.9 8.9 10.6 表 8 基线与基线角(T2R2为参考通道)
Table 8. Baseline and baseline angle (T2R2 channel for reference)
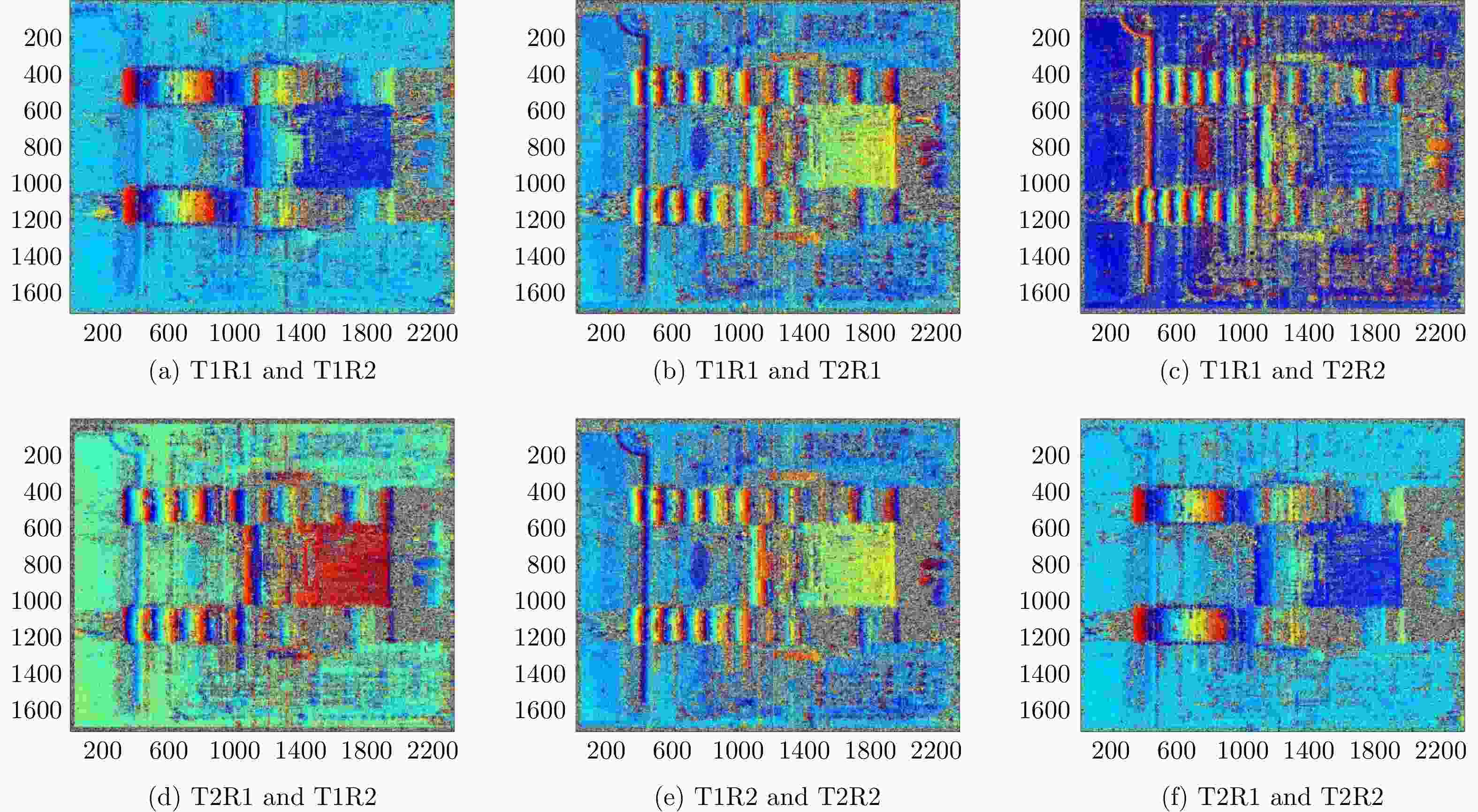
参数 T2R2 T2R1 T1R2 T1R1 基线长度(mm) – 107.10 427.88 534.97 基线角(°) – –3.9976 –3.9238 –3.9386 表 9 通道幅度误差标定结果(T2R2为参考通道)
Table 9. Calibration result of channel amplitude error (T2R2 channel for reference)
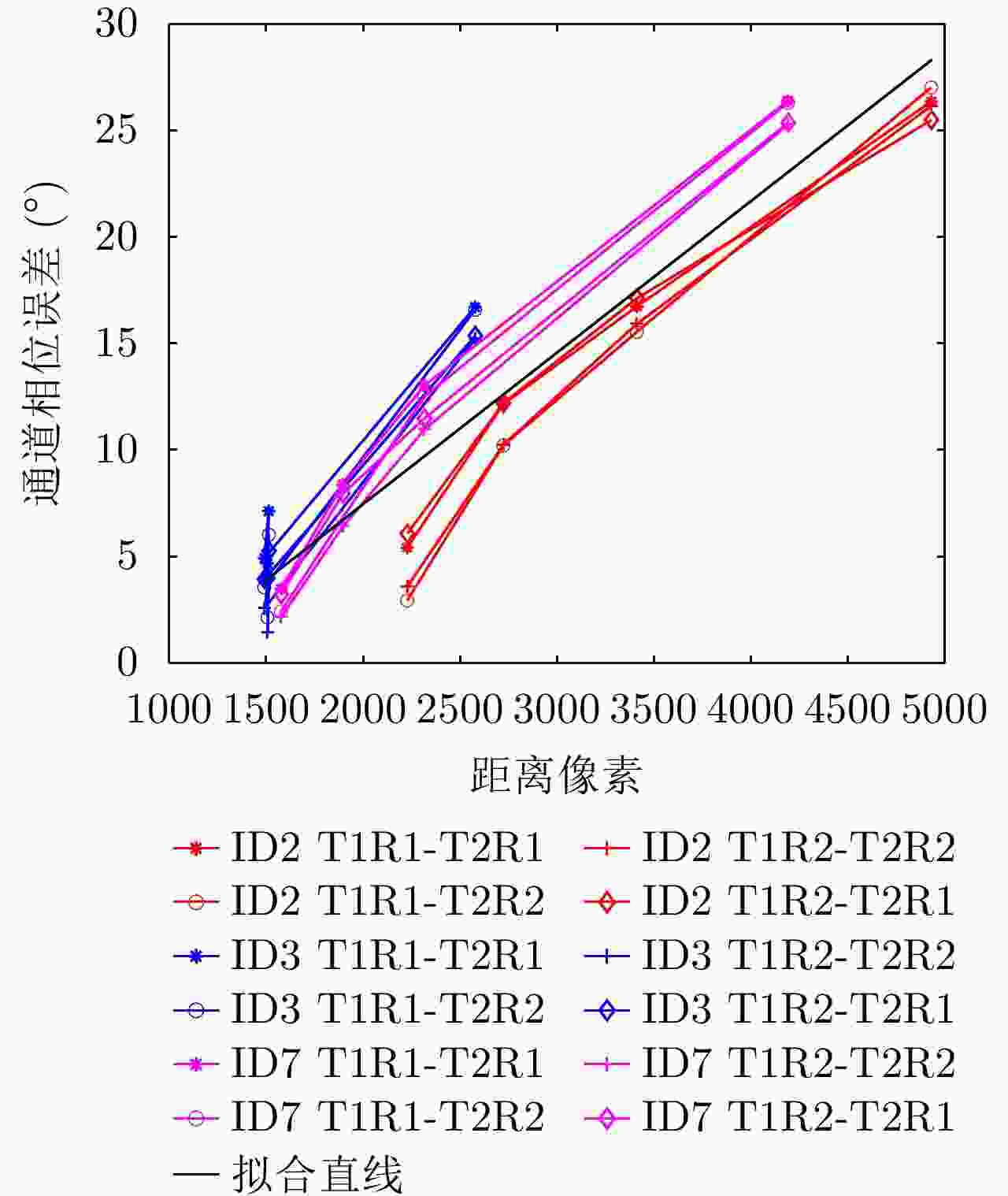
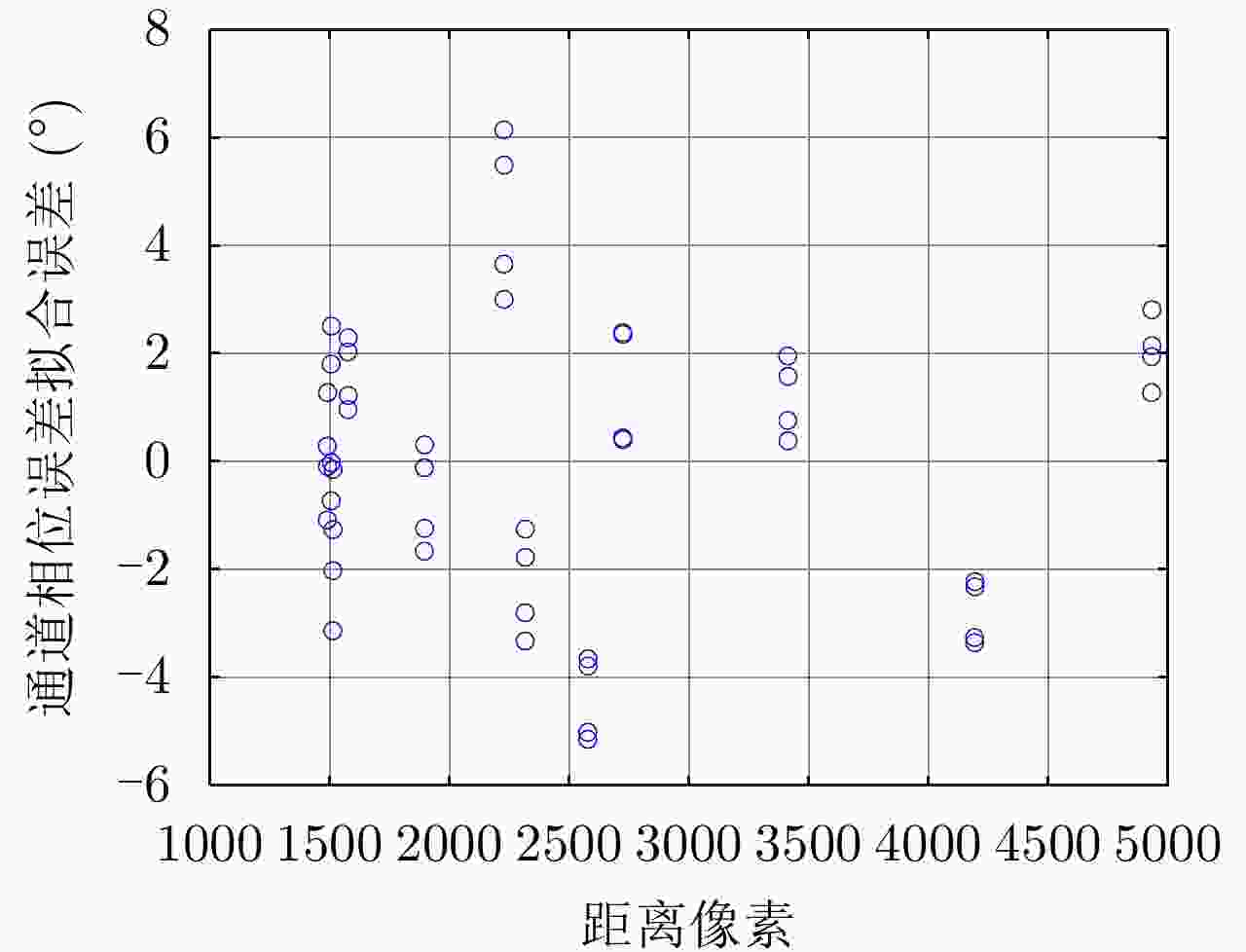
参数 T2R2 T2R1 T1R2 T1R1 幅度误差均值(dB) – 0.0398 0.1238 0.1712 幅度误差峰峰值(dB) – ±0.049 ±0.081 ±0.132 表 10 通道相位误差标定结果
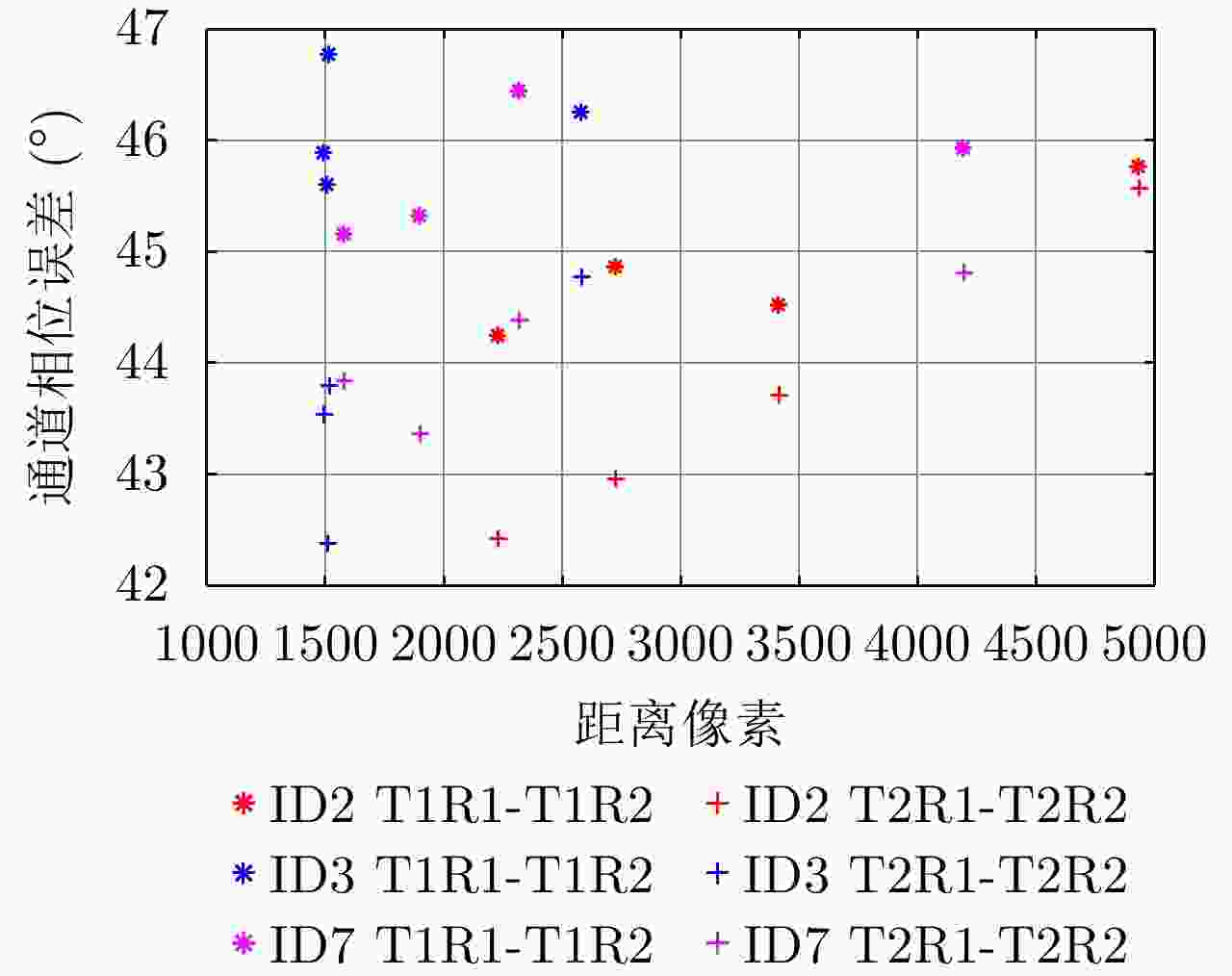
Table 10. Channel phase error calibration results
常数项(°) 线性项(°/距离门) 接收通道间相位误差(R1-R2) 44.6805 0 发射通道间相位误差(T1-T2) –6.7496 0.0071068539 表 11 三维点云的精度及完整性
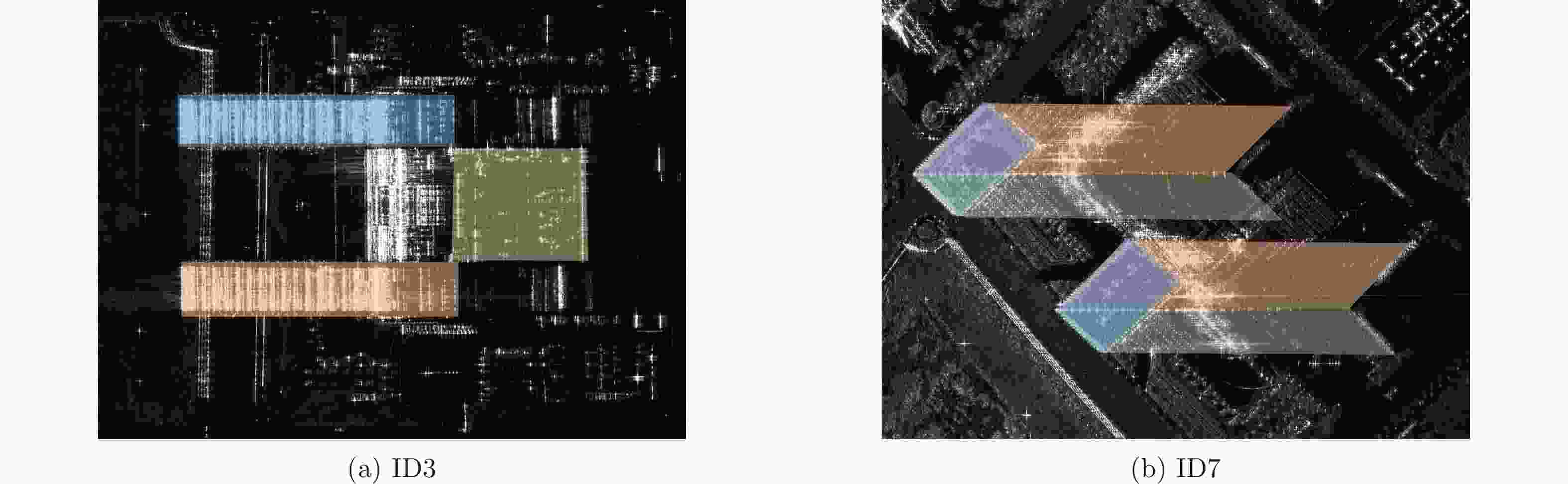
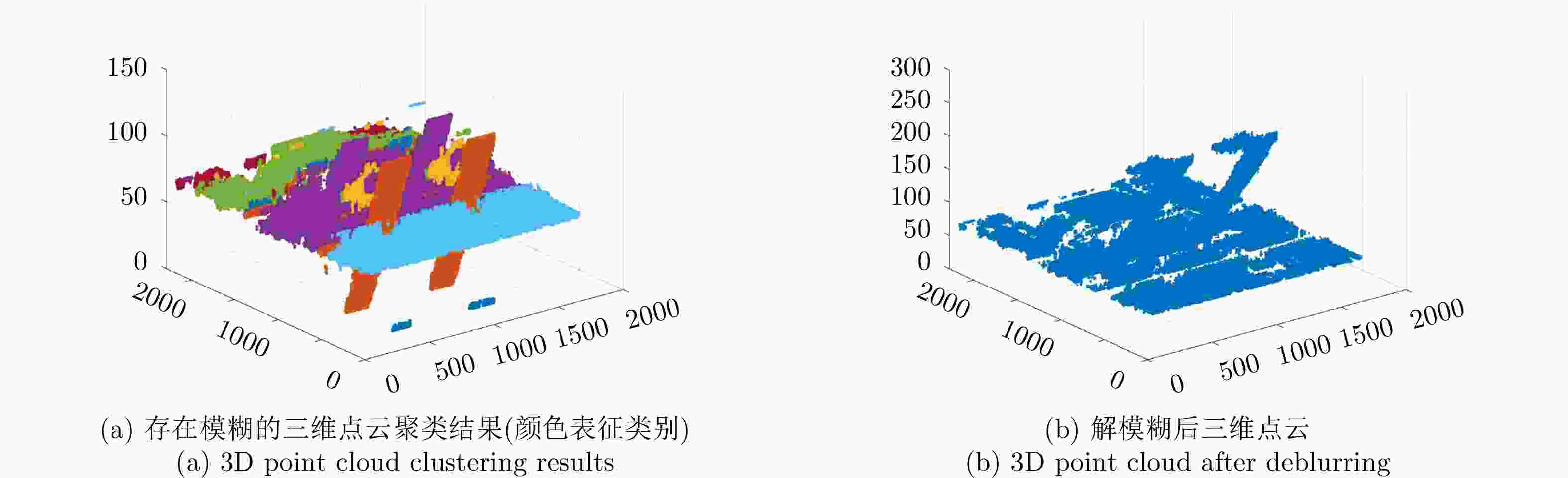
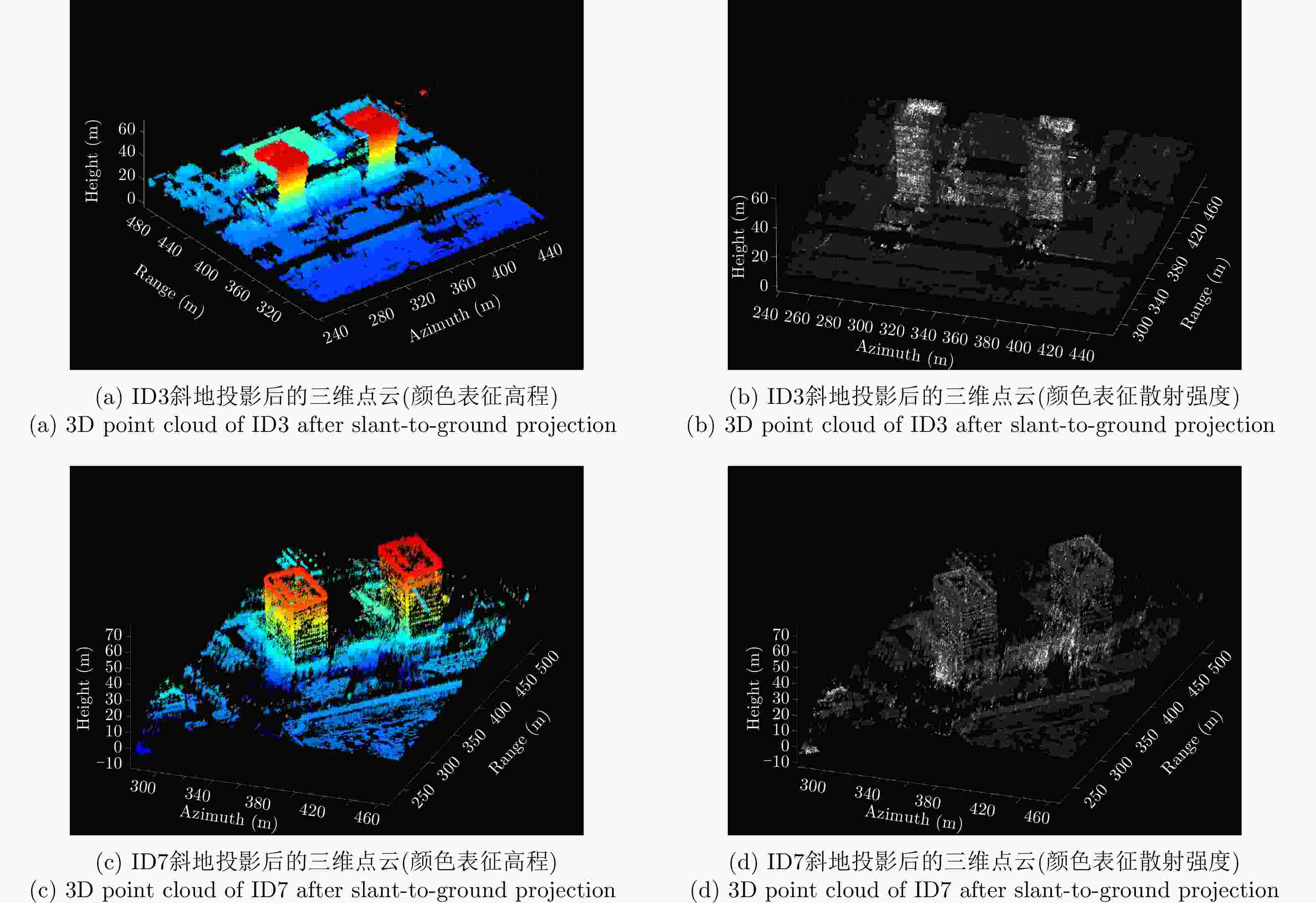
Table 11. Accuracy and completeness of 3D clouds
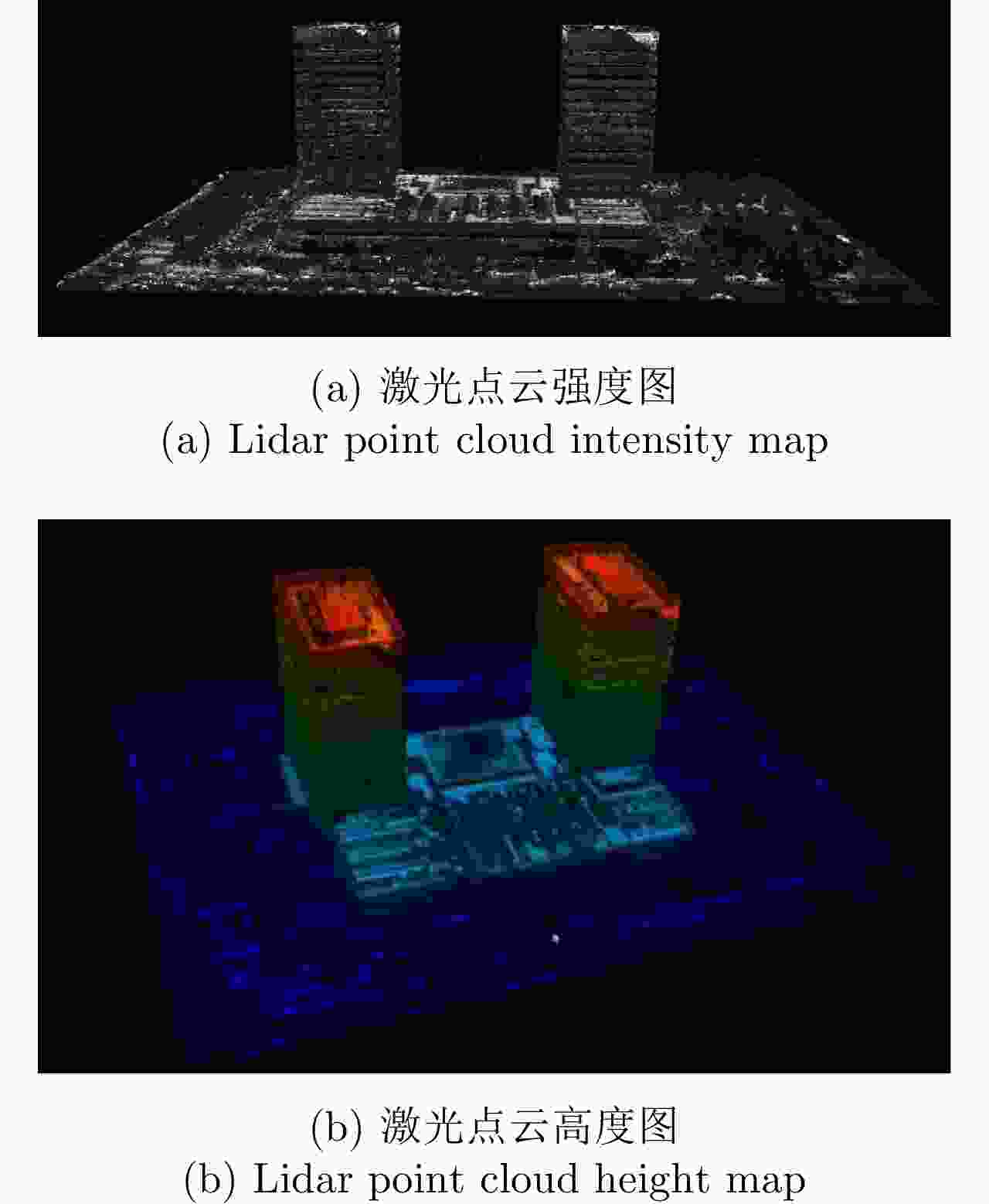
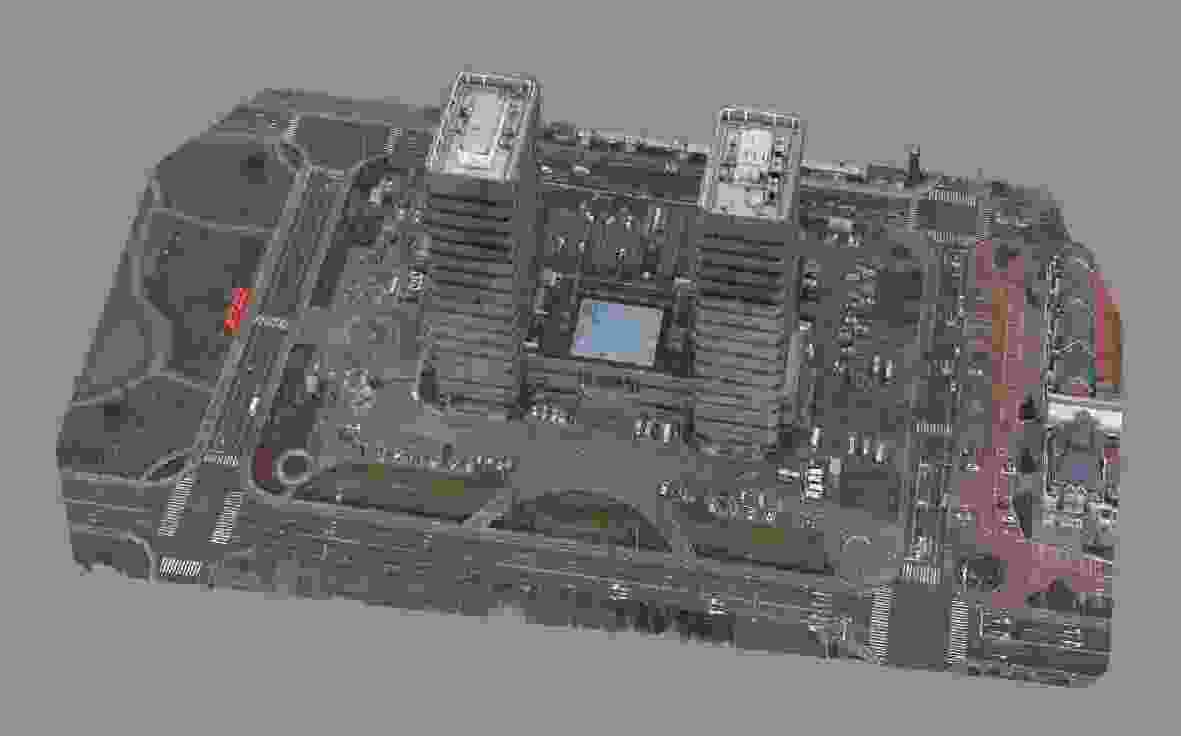
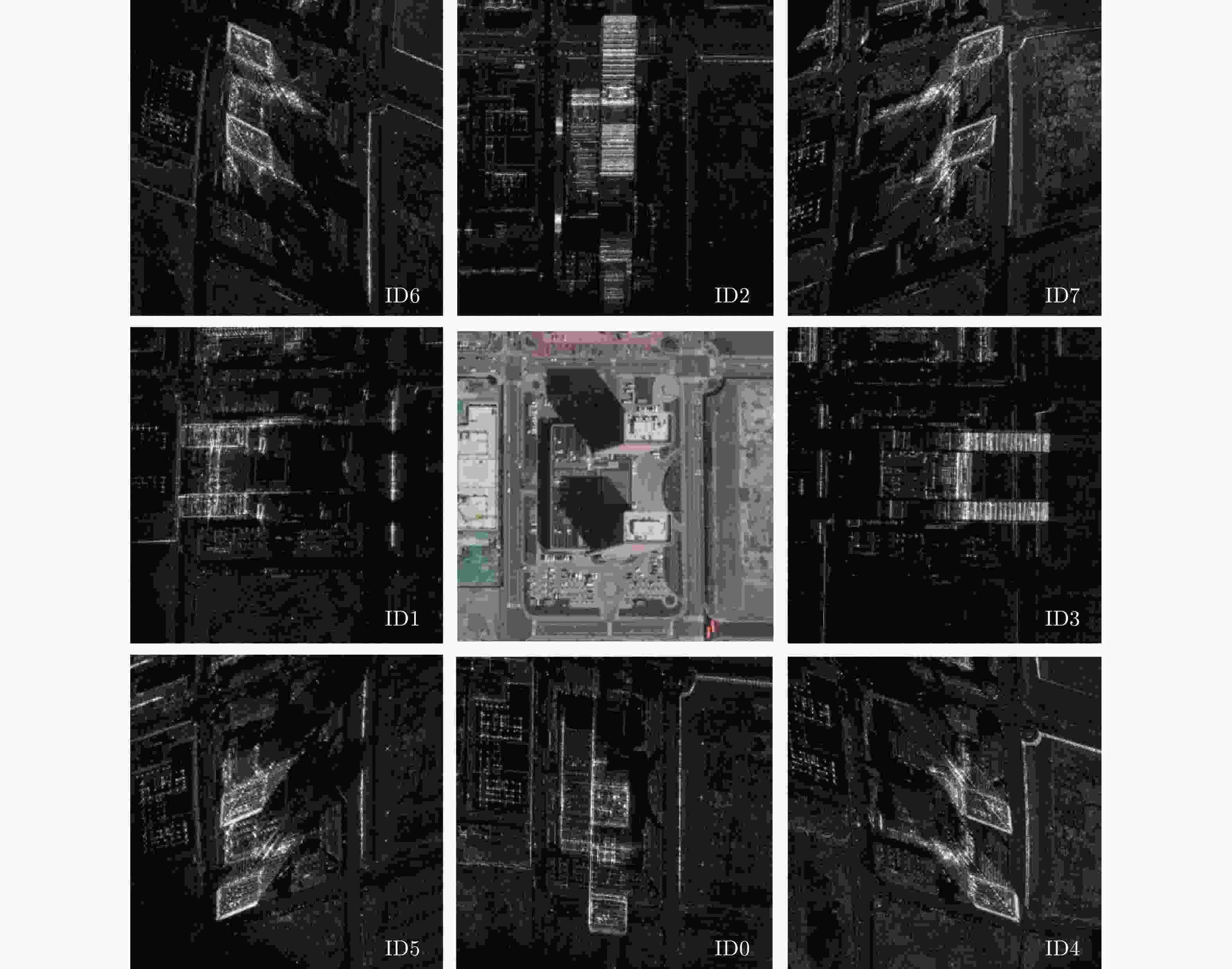
重建精度(m) 重建完整性(m) ID3重建结果 2.3090 4.9050 ID7重建结果 1.9982 3.9695 两角度融合结果 1.9349 2.7328 -
[1] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像—从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090 [2] 张福博. 阵列干涉SAR三维重建信号处理技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2015.ZHANG Fubo. Research on signal processing of 3-D reconstruction in linear array synthetic aperture radar interferometry[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. [3] KLARE J, WEISS M, PETERS O, et al. ARTINO: A new high resolution 3D imaging radar system on an autonomous airborne platform[C]. 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, USA, 2006. [4] WEISS M, PETERS O, and ENDER J. First flight trials with ARTINO[C]. The 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008. [5] WEISS M and GILLES M. Initial ARTINO radar experiments[C]. The 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010: 1–4. [6] LI Hang, LIANG Xingdong, ZHANG Fubo, et al. A novel 3-D reconstruction approach based on group sparsity of array InSAR[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2018, 48(8): 1051–1064. doi: 10.1360/N112017-00023 [7] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 彭凌霄, 等. SARMV3D-1.0: SAR微波视觉三维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, PENG Lingxiao, et al. SARMV3D-1.0: Synthetic aperture radar microwave vision 3D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112 [8] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183 [9] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 吴一戎. 全息合成孔径雷达的概念、体制和方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 399–408. doi: 10.12000/JR20063DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, and WU Yirong. Concept, system, and method of holographic synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 399–408. doi: 10.12000/JR20063 [10] NANNINI M, SCHEIBER R, and MOREIRA A. Estimation of the minimum number of tracks for SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(2): 531–543. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2007846 [11] 任烨仙, 徐丰. 若干层析SAR成像方法在解叠掩性能上的对比分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 71–82. doi: 10.12000/JR21139REN Yexian and XU Feng. Comparative experiments on separation performance of overlapping scatterers with several tomography imaging methods[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 71–82. doi: 10.12000/JR21139 [12] 董勇伟, 梁兴东, 丁赤飚. 调频连续波SAR非线性处理方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(5): 1034–1039. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00582DONG Yongwei, LIANG Xingdong, and DING Chibiao. Non-linear signal processing for FMCW SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(5): 1034–1039. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00582 [13] FU Xikai, XIANG Maosheng, WANG Bingnan, et al. A robust yaw and pitch estimation method for mini-InSAR system[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(11): 2157–2161. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2756101 [14] 董勇伟, 李焱磊, 梁兴东, 等. 基于局部线性误差模型的调频连续波SAR运动补偿方法[P]. 中国, 201711370093.7, 2017.DONG Yongwei, LI Yanlei, LIANG Xingdong, et al. Local linear error model-based frequency modulation continuous wave SAR motion compensation method[P]. CN, 201711370093.7, 2017. [15] 董勇伟. 基于调频连续波体制的SAR系统及其处理方法[P]. 中国, 201810978000.7, 2018.DONG Yongwei. SAR system based on frequency modulated continuous wave system as well as processing method thereof[P]. CN, 201810978000.7, 2018. [16] DENG Huazeng, FARQUHARSON G, BALABAN M, et al. System error analysis of an airborne along-track interferometric fmcw SAR for surface velocity estimate[C]. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 1677–1680. [17] 董勇伟, 李焱磊, 丁满来, 等. 一种高分辨率W波段SAR系统[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(5): 1266–1270. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170461DONG Yongwei, LI Yanlei, DING Manlai, et al. High resolution W-band SAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(5): 1266–1270. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170461 [18] 刘季超. LTCC微波元件的结构模型研究与设计[J]. 电子测试, 2020(5): 19–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8519.2020.05.005LIU Jichao. Research and design of LTCC microwave element structure model[J]. Electronic Test, 2020(5): 19–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8519.2020.05.005 [19] JIAO Zekun, DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Urban 3D imaging using airborne TomoSAR: Contextual information-based approach in the statistical way[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 170: 127–141. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.10.013 [20] 李芳芳, 仇晓兰, 孟大地, 等. 机载双天线InSAR运动补偿误差的影响分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(3): 559–567. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00850LI Fangfang, QIU Xiaolan, MENG Dadi, et al. Effects of motion compensation errors on performance of airborne dual-antenna InSAR[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2013, 35(3): 559–567. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00850 [21] FU Xikai, XIANG Maosheng, JIANG Shuai, et al. Motion compensation scheme for LFM-CW miniature InSAR system mounted on small aircrafts[C]. The 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2018: 1–3. [22] 孟大地. 机载合成孔径雷达运动补偿算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院电子学研究所, 2006.MENG Dadi. Research on motion compensation algorithm for airborne SAR[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Institute of Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006. [23] LUO Yitong, QIU Xiaolan, DONG Qian, et al. A robust stereo positioning solution for multiview spaceborne SAR images based on the range-Doppler model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 19: 4008705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3048731 [24] LV Zexin, LI Fangfang, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Effects of motion compensation residual error and polarization distortion on UAV-borne PolInSAR[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(4): 618. doi: 10.3390/rs13040618 [25] 卜运成. 阵列干涉SAR定标技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2018: 71–95.BU Yuncheng. Research on calibration technology of array synthetic aperture radar interferometry[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018: 71–95. [26] 卜运成, 王宇, 张福博, 等. 基于子空间正交的阵列干涉SAR系统相位中心位置定标方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(3): 335–345. doi: 10.12000/JR18007BU Yuncheng, WANG Yu, ZHANG Fubo, et al. Antenna phase center calibration for array InSAR system based on orthogonal subspace[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(3): 335–345. doi: 10.12000/JR18007 [27] 冯珂. InSAR复图像配准方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 长沙理工大学, 2013.FENG Ke. InSAR image registration method[D]. [Master dissertation], Changsha University of Science & Technology, 2013. [28] FANG Dongsheng, LV Xiaolei, YUN Ye, et al. An InSAR fine registration algorithm using uniform tie points based on voronoi diagram[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(8): 1403–1407. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2715189 [29] CHEN Jiankun, QIU Xiaolan, DING Chibiao, et al. CVCMFF Net: Complex-valued convolutional and multifeature fusion network for building semantic segmentation of InSAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5205714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3068124 [30] 王伟, 许华荣, 魏含玉, 等. 面向阵列InSAR点云规则化的渐近式建筑立面检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 144–156. doi: 10.12000/JR21177WANG Wei, XU Huarong, WEI Hanyu, et al. Progressive building facade detection for regularizing array InSAR point clouds[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 144–156. doi: 10.12000/JR21177 [31] 胡占义. 合成孔径雷达三维成像中的视觉语义浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 11(1): 20–26. doi: 10.12000/JR21149HU Zhanyi. A note on visual semantics in SAR 3D imaging[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 11(1): 20–26. doi: 10.12000/JR21149 [32] LI Xiaowan, ZHANG Fubo, LI Yanlei, et al. An elevation ambiguity resolution method based on segmentation and reorganization of TomoSAR point cloud in 3D mountain reconstruction[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(24): 5118. doi: 10.3390/rs13245118 [33] ZHANG Fubo, LIANG Xingdong, CHENG Ruichang, et al. Building corner reflection in MIMO SAR tomography and compressive sensing-based corner reflection suppression[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(3): 446–450. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2926301 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: