-
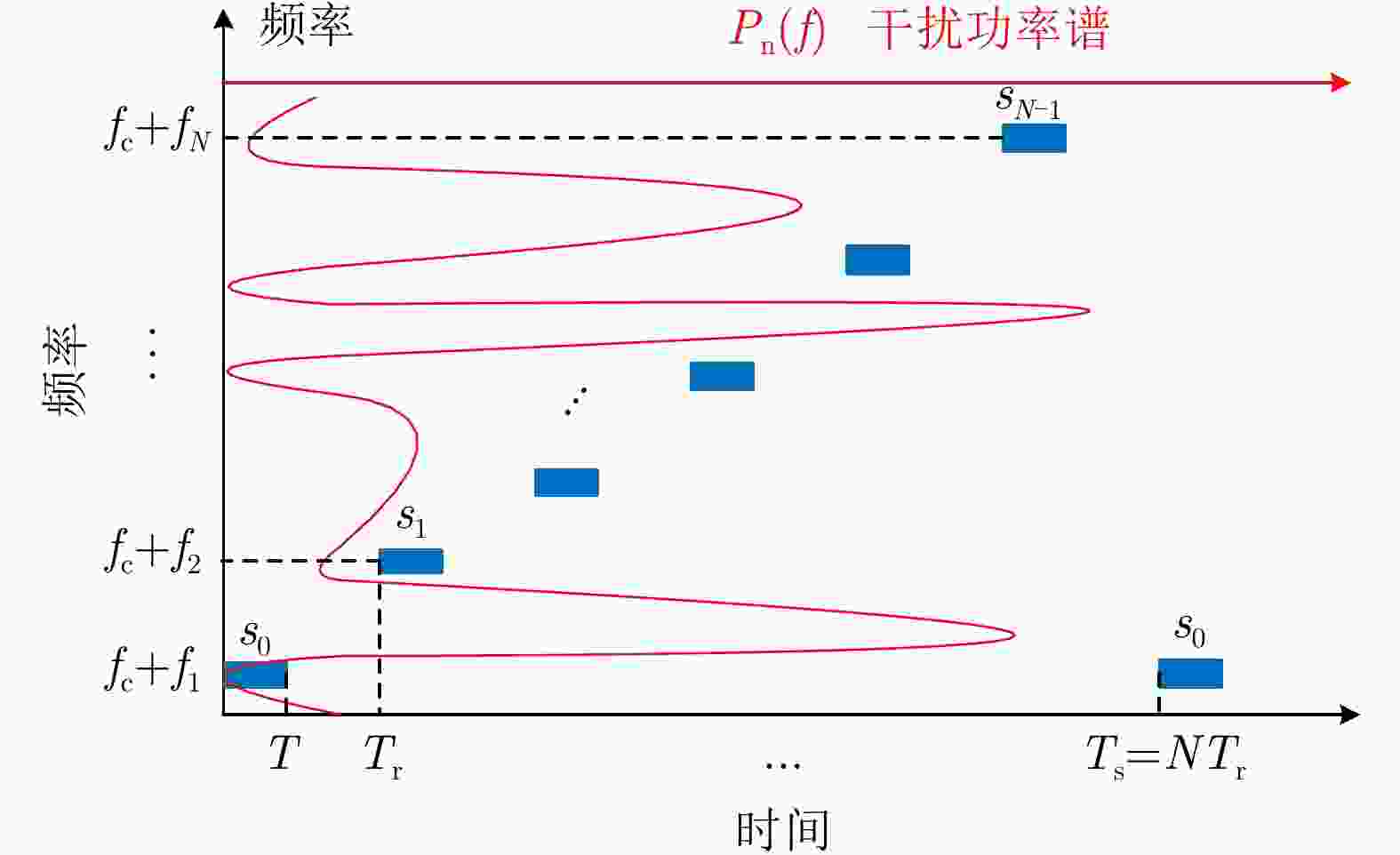
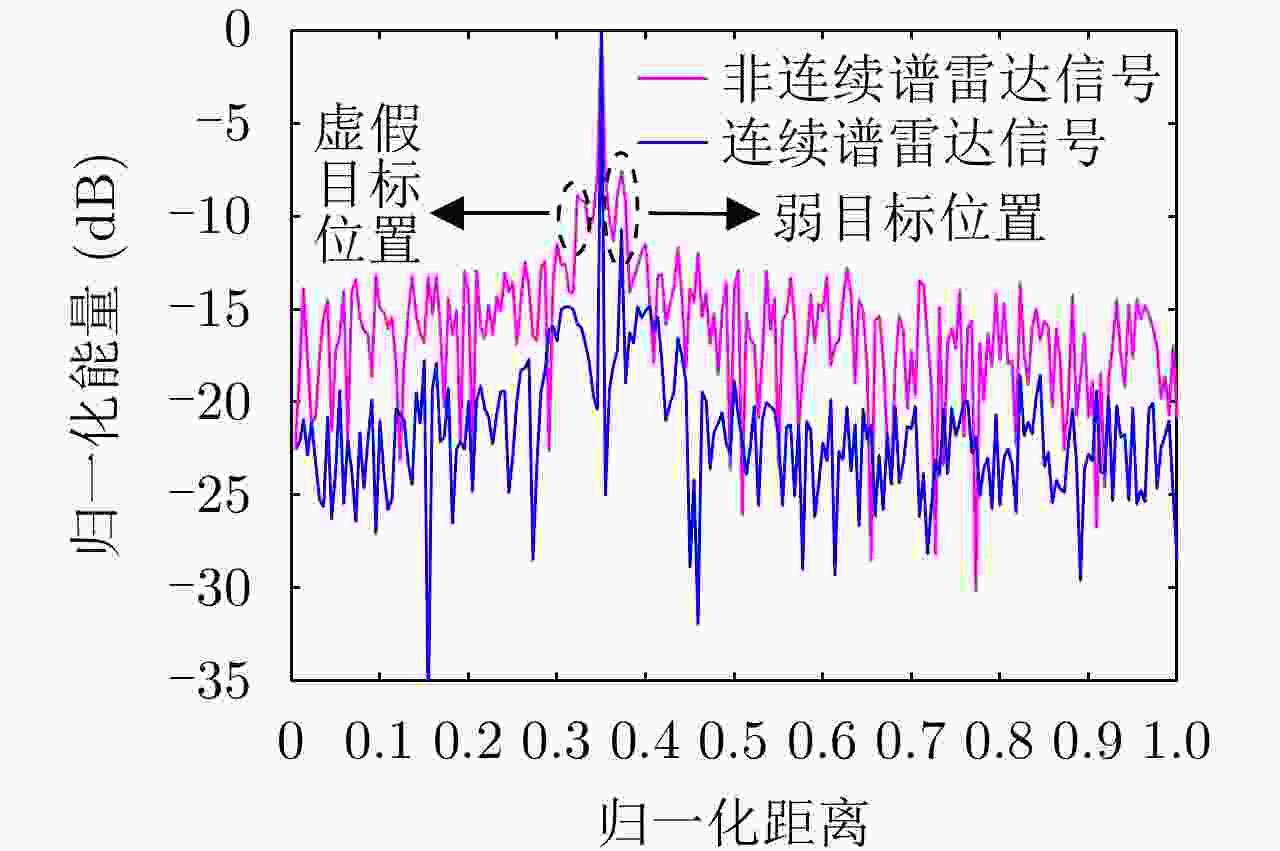
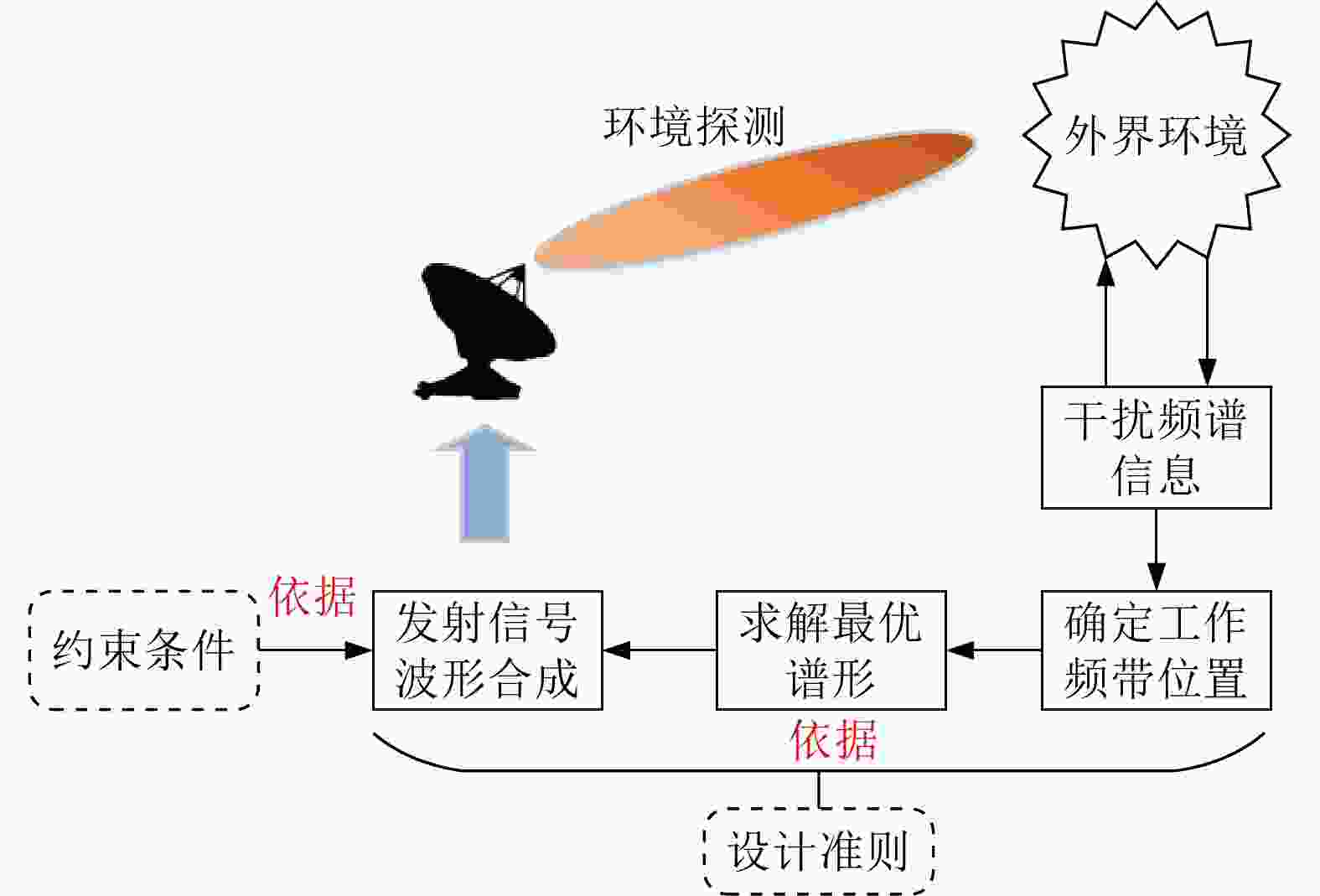
摘要: 非连续谱雷达信号是一种特殊的认知雷达信号,其频谱由多个离散的频带组成,且能够随着外界干扰的变化自适应地调整离散频带的分布结构。因此,这种信号适用于干扰密布、频谱拥堵的工作场景。非连续谱信号设计主要研究两个问题:一是如何根据干扰环境选取最优的非连续频谱结构以满足雷达抗干扰和分辨性能要求;二是如何根据最优的非连续频谱求解出时域发射信号。非连续谱雷达信号的一个典型应用是高频雷达的抗同频干扰,随着电子对抗的升级以及多电子设备共存引起的频谱拥堵问题,非连续谱信号在雷达抗干扰、电磁频谱兼容等方面日益受到重视。该文对非连续谱信号设计准则与约束、工作频带选取与塑形以及时域信号波形合成等3个方面的研究进行了归纳与总结,以促进非连续谱信号的研究与应用。Abstract: The discontinuous spectrum radar signal is a featured cognitive radar signal. Its spectrum is discontinuous and comprises multiple discrete frequency bands, and the distribution structure of the discrete frequency bands can be adapted to the change of external interference adequately. Therefore, this segmented signal is suitable for dense interference and congested spectrum based spectrum scenarios. The design of discontinuous spectrum signal is focused on two issues: (1) the optimal selection of the discontinuous spectrum structure in accordance with the interference environment to meet the requirements of radar anti-jamming and resolution performance, and (2) the solution of the time-domain emission based on the optimal discontinuous spectrum signal. A typical application of discontinuous spectrum radar signals is the anti-co-frequency interference derived of high-frequency radar. With the upgrade of electronic countermeasures and the spectrum congestion problem caused by the coexistence of multiple electronic devices, discontinuous spectrum signals are used in radar anti-jamming and electromagnetic spectrum compatibility. This paper discusses and summarizes the research on discontinuous signal design criteria and constraints, working frequency band selection and shaping, and time-domain signal waveform synthesis to promote the research and application of discontinuous spectrum signals.
-
表 1 非连续谱信号典型工作场景
Table 1. Typical work scene of discontinuous spectrum signals
工作频段 场景内典型雷达 场景内典型干扰辐射源 高频频段(3~30 MHz) 高频地波雷达 固定与移动通信、广播等无线电用户、干扰机 甚高频频段(30~300 MHz)
特高频频段(300~1000 MHz)叶簇穿透雷达 电视、移动通信、广播电台 L波段(1~2 GHz) 空中交通管制雷达 频分双工LTE蜂窝通信系统、全球卫星
导航系统、5G NRS波段(2~4 GHz)
C波段 (4~8 GHz)机载预警雷达、气象雷达、战场/地面监控雷达、
船舶交通服务雷达WLAN网络、3.5 GHz TDD-LTE、5G NR 极高频频段(30~300 GHz) 民用毫米波雷达 通信基站、车辆互联网络 表 2 工作场景类型
Table 2. Type of work scene
场景 干扰来源 干扰时变特性 第1类 敌方干扰机等 慢时变 第2类 敌方干扰机等 快时变 第3类 协同工作的电子设备 慢时变 第4类 协同工作的电子设备 快时变 表 3 非连续谱信号
Table 3. Typical application scenarios of discontinuous spectrum signals
分类方式 信号形式 典型信号 表达式 调制方式 相位编码 连续相位编码、离散相位编码 $ {\boldsymbol{s}} = {[s(1),s(2), \cdots ,s(N)]^{\text{T}}} = a\left( n \right){{\text{e}}^{{\text{j}}\varphi \left( n \right)}}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{j}}2\pi {f_{\text{c}}}t}} $
式中,a为信号幅度,$ \varphi $为编码相位,N为编码长度,$ {f_{\text{c}}} $为中心载频频率调制 线性调频、
非线性调频、多相编码调频${\boldsymbol{s}} = a\left( t \right){ {\text{e} }^{ {\text{j} }2\pi \left( { {f_{\text{c} } } + f\left( t \right)} \right)t} }$,式中,$ f\left( t \right) $为频率调制函数 频率编码 步进频率编码、分段步进频率编码、频率捷变编码 ${\boldsymbol{s}} = \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{m = 0}^{M - 1} s \left( {t - m{T_r} } \right){ {\text{e} }^{ {\text{j} }2\pi {f_m}\left( {t - m{T_r} } \right)} }$,
式中,$ {f_m} $为编码频率,M为编码长度复合调制 跳频脉内线性调频、脉间跳频脉内编码、多载频相位编码 ${\boldsymbol{s}} = \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{m = 0}^{M - 1} { {a_m}\left( t \right){ {\text{e} }^{ {\text{j} }\left( {2\pi \left( { {f_m} + {f_m}\left( t \right)} \right)t + \varphi \left( t \right)} \right)} } }$,式中,$ {f_m}\left( t \right) $为脉内频率调制函数,$ \varphi \left( t \right) $为脉内相位调制函数,$ {f_m} $为脉间编码频率 收发模式 单发单收 上述调制形式均可 – 多发多收 上述调制形式均可 ${\boldsymbol{s}} = {[{s_1},{s_2}, \cdots ,{s_l}, \cdots ,{s_L}]^{\text{T} } }$,式中,$ {s_l} $为第l 路发射信号,L为通道数 抗干扰维度 快时间域 相位编码、频率调制 – 慢时间域 频率编码、复合调制 空频联合域 单发单收、多发多收 表 4 常见信号性能评价准则
Table 4. Common signal performance evaluation criteria
性能准则 表达式 最大化SINR 信干噪比:${\text{SINR} } = \dfrac{ {\left| {w{\boldsymbol{s}}} \right|} }{ {E\left\{ {wn} \right\} } }$(任意滤波形式),w为雷达接收滤波器,n为干扰与噪声的和
信干噪比:${\text{SINR} } = \dfrac{ { { {\boldsymbol{s} }^{\text{H} } }{\boldsymbol{s} }{ {\boldsymbol{s} }^{\text{H} } }{\boldsymbol{s} } } }{ {E\left\{ { { {\boldsymbol{s} }^{\text{H} } }n{n^{\text{H} } }{\boldsymbol{s} } } \right\} } } = \dfrac{ { {E_{\rm{s} } } } }{ { { {\boldsymbol{s} }^{\text{H} } }{\boldsymbol{Ks} }} }$(匹配滤波形式),$E_{\rm{s}}$为信号能量,K为干扰与噪声联合相关矩阵最小化同频干扰 同频干扰:$\left|{p}_{\varOmega }\right|\le \mu ,\varOmega \in $阻带频率位置,p为发射信号功率谱,$ \mu $为阻带阈值 分辨性能 主瓣分辨性能 积分主瓣能量:${{\rm{IME}}} = \dfrac{1}{ {|\chi (0){|^2} } }\displaystyle\int_{ - {\tau _{ {\text{main} } } }}^{ {\tau _{ {\text{main} } } }} {|\chi (\tau ){|^2}{\text{d} }\tau }$,主瓣3 dB,宽度:$2\left| {{\tau _{3{\text{ dB}}}}} \right|$,${\tau _{{\rm{main}}}}$为自相关函数的第1零点,${\tau _{3{\text{ dB}}}}$为自相关函数的3 dB点 旁瓣分辨性能 积分旁瓣能量:${{\rm{ISE}}} = \dfrac{1}{ {|\chi (0){|^2} } }\left[ {\displaystyle\int_{ - T}^{ - {\tau _{ {\text{main} } } }} {|\chi (\tau ){|^2}{\text{d} }\tau } + \displaystyle\int_{ {\tau _{ {\text{main} } } }}^T {|\chi (\tau ){|^2}{\text{d} }\tau } } \right]$
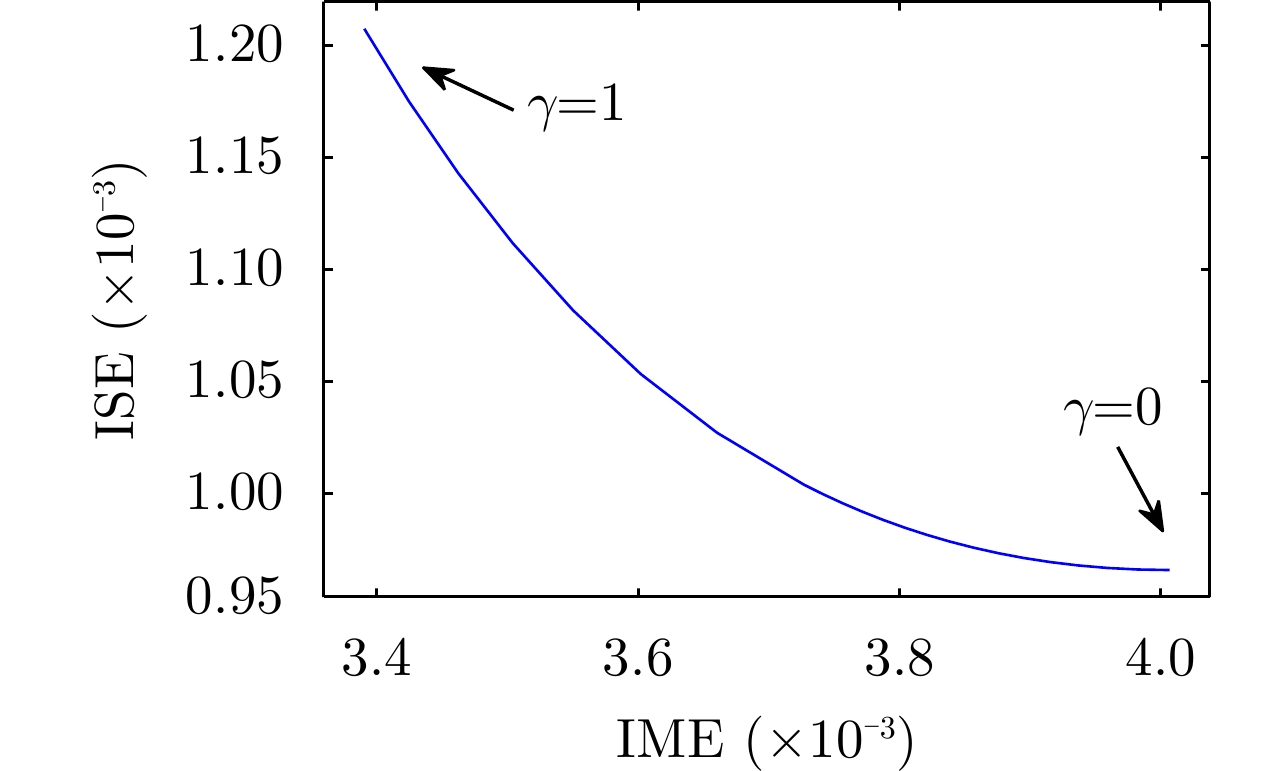
峰值旁瓣:$\mathrm{max}\left(|\chi (\tau ){|}^{2}\right),\tau \in \left[-T, -{\tau }_{\text{main} }\right]\cup \left[{\tau }_{\text{main} },T\right]$,加权积分旁瓣:${{\rm{WeIC}}}{ {{\rm{E}}}_\gamma } = \gamma \cdot {{\rm{IME}}} + {{\rm{ISE}}}$,$ \chi (\tau ) $为信号自相关函数表 5 常见信号约束条件
Table 5. Common signal performance evaluation criteria
约束条件 表达形式 能量约束 ${{\boldsymbol{s}}^{\text{H}}}{\boldsymbol{s}} \le E$ 峰均比约束 ${{\rm{PAPR}}} ({\boldsymbol{s} }) = \dfrac{ {\mathop {\max }\limits_k { {\left| { {s_k} } \right|}^2} } }{ {\dfrac{1}{N}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{k = 1}^N { { {\left| { {s_k} } \right|}^2} } } } = \dfrac{ {\mathop {\max }\limits_k { {\left| { {s_k} } \right|}^2} } }{ {E/N} } \le \mu$ 恒包络约束 $\Vert {\boldsymbol{s}}\Vert =1$ 相似性约束 ${\left\| {{\boldsymbol{s}} - {s_0} } \right\|^2} \le \varepsilon$
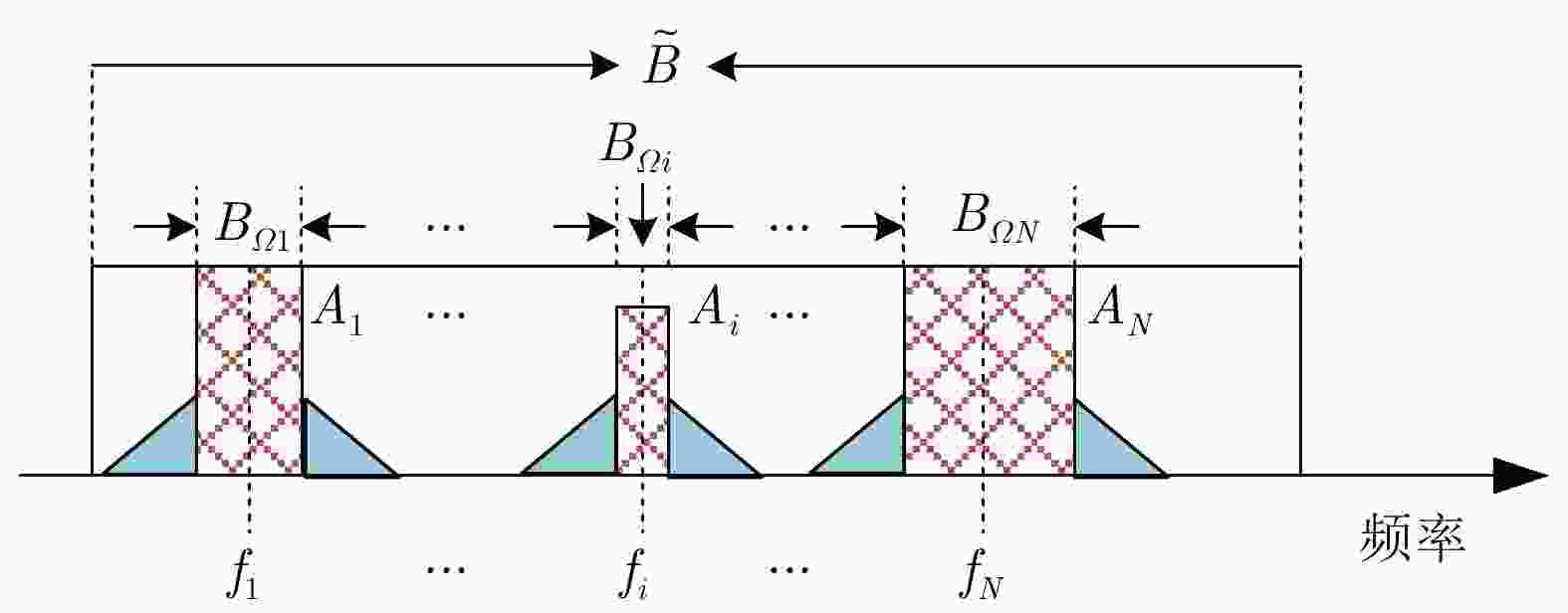
$ \varepsilon $是用来约束相似性程度,$ {s_0} $为参考的基准信号表 6 干扰功率谱描述参数
Table 6. Interference power spectrum description parameters
参数 含义 干扰频带
中心频率$\left[ { {f_1},{f_2}{\text{,} }\cdots{\text{,} }\,{f_N} } \right]$
矩形扩展模型阻带中心频率干扰源带宽 $\left[ { {B_{\varOmega 1} },{B_{\varOmega 2} }{\text{,} }\cdots{\text{,} }\,{B_{\varOmega N} } } \right]$, 每个干扰源占据的带宽 完整可用频带 $ \tilde B $ 可用比 $\rho = { {\left( {\tilde B - \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^N { {B_{\varOmega i} } } } \right)}/ {\tilde B} }$ 非连续比 $p = \left( {\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^N { {B_{\varOmega i} } } } \right)/\tilde B$ 表 7 优化问题形式
Table 7. Optimization problem form
问题形式 表达式 二次型优化问题 $\begin{gathered} \mathop { {\text{min} } }\limits_{\boldsymbol{s} } \displaystyle\sum\limits_{k = 1}^M { {\gamma _k}{ {\boldsymbol{s} }^{\text{H} } }{ {\boldsymbol{R} }_k}{\boldsymbol{s} } } {\text{ + } }\displaystyle\sum\limits_{l = 1}^N { {\gamma _l}\left| { { {\boldsymbol{s} }^{\text{H} } }{ {\boldsymbol{R} }_l}{\boldsymbol{s} } } \right|} \hfill \\ {\text{s} }{\text{.t} }{\text{. PAR} }\left( {\boldsymbol{s} } \right) \le \alpha /{\text{PAR} }\left( {\boldsymbol{s} } \right) = 1 \hfill \\ {\text{ } }{ {\text{l} }_\varOmega } \le \left| { { {\text{a} }^{\text{H} }_\varOmega }{\boldsymbol{s} } } \right| \le { {\text{u} }_\varOmega } \hfill \\ {\text{ } }\left| {{\boldsymbol{s}} - {{\boldsymbol{s}}_r} } \right| \le \varepsilon \hfill \\ \end{gathered}$ 四次型优化问题 $\begin{array}{l}\underset{ {\boldsymbol{s} } }{\mathrm{min} }\displaystyle\sum _{n=1}^{N}{\gamma }_{n}{\left({ {\boldsymbol{s} } }^{\text{H} }{\boldsymbol{R}}{\boldsymbol{s} }-{p}_{n}\right)}^{2}\\ \text{s}\text{.t}\text{. PAR}\left({\boldsymbol{s} }\right)\le \alpha /\text{PAR}\left({\boldsymbol{s} }\right)=1\\ {\text{ l} }_{\varOmega }\le \left|{\text{a} }_{\varOmega }^{\text{H} }{\boldsymbol{s} }\right|\le {\text{u} }_{\varOmega }\end{array}$ 极大极小型优化问题 $\begin{array}{l}\underset{ {\boldsymbol{s} } }{\text{min } }\text{max}\; {f} \left({\boldsymbol{s}}\right)\\ \text{s}\text{.t}\text{. PAR}\left({\boldsymbol{s} }\right)\le \alpha /\text{PAR}\left({\boldsymbol{s} }\right)=1\\ {\text{ l} }_{\varOmega }\le \left|{\text{a} }_{\varOmega }^{\text{H} }{\boldsymbol{s} }\right|\le {\text{u} }_{\varOmega }\\ \text{ }\left|{\boldsymbol{s} }-{ {\boldsymbol{s} } }_{r}\right|\le \varepsilon \end{array}$ 注:s为待合成信号,R为性能矩阵($ {{\boldsymbol{R}}_k} $为频域抗干扰性能矩阵、$ {{\boldsymbol{R}}_l} $为分辨性能矩阵),${f} \left( {\boldsymbol{s}} \right)$为信号性能函数,$ {p_n} $为频谱模板,$ \gamma $为准则加权系数,${\text{PAR} }\left( {\boldsymbol{s}} \right)$为信号的峰均功率水平($ 0 \le \alpha \le 1 $),当且仅当$ \alpha {\text{ = }}1 $时信号恒模,$\left| { {\text{a} }_\varOmega^{\text{H} }{\boldsymbol{s}}} \right|$是信号的离散频谱,$ {{\text{u}}_\varOmega } $和$ {{\text{l}}_\varOmega } $分别为频谱约束上、下限,$ \varOmega $为受限频率的集合,$\left| {{\boldsymbol{s}} - {{\boldsymbol{s}}_r} } \right| \le \varepsilon$为相似性约束,${{\boldsymbol{s}}_r}$为某些具有探测性能的信号(如LFM信号)。 -
[1] BLUNT S D and MOKOLE E L. Overview of radar waveform diversity[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2016, 31(11): 2–42. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2016.160071 [2] SALZMAN J, AKAMINE D, and LEFEVRE R. Optimal waveforms and processing for sparse frequency UWB operation[C]. 2001 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, USA, 2001: 105–110. [3] LEONG H W and DAWE B. Channel availability for east coast high frequency surface wave radar systems[R]. Defence Research Establishment Ottawa (Ontario), 2001. [4] GREEN S D and KINGSLEY S P. Investigation of wide bandwidth HF radar waveforms[C]. IEE Colloquium on Advanced Transmission Waveforms, London, UK, 1995. [5] KUTUZOV V M. Synthesis of non-regular multitone signals and algorithms of their processing[C]. Third International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 1996. [6] GREEN S D and KINGSLEY S P. Improving the range/time sidelobes of large bandwidth discontinuous spectra HF radar waveforms[C]. International Conference on Hf Radio Systems and Techniques, Nottingham, UK, 1997. [7] WEI Yinsheng and LIU Yongtan. New anti-jamming waveform designing and processing for HF radar[C]. 2001 CIE International Conference on Radar, Beijing, China, 2001. [8] WEI Yinsheng, LIU Yongtan, and XU Rongqing. A novel 2-D signal processing scheme for quasi-random step frequency signal[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2003, 14(3): 77–80. [9] ZHANG Dongpo and LIU Xingzhao. Signal processing technique for randomly discontinuous spectra HF radar waveforms[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2004, 15(4): 511–515. [10] ZHANG Dongpo and LIU Xingzhao. A sidelobes suppression technique for spectra discontinuous HF radar signal[C]. 7th International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 2004. [11] ZHANG Dongpo and LIU Xingzhao. A sidelobes suppression technique for spectra discontinuous HF radar signal based on spectra compensation algorithm[C]. 2004 Asia-Pacific Radio Science Conference, 2004, Qingdao, China, 2004: 242–245. [12] LINDENFELD M J. Sparse frequency transmit-and-receive waveform design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(3): 851–861. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1337459 [13] LIU Wenxian, LU Yilong, and LESTURGIE M. Optimal sparse waveform design for HFSWR system[C]. International Waveform Diversity and Design Conference, Pisa, Italy, 2007. [14] ZHAO Dehua, WEI Yinsheng, and LIU Yongtan. Hopped-frequency waveform design for range sidelobe suppression in spectral congestion[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(1): 87–94. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0232 [15] NUNN C and MOYER L R. Spectrally-compliant waveforms for wideband radar[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2012, 27(8): 11–15. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2012.6329156 [16] YU Xianxiang, CUI Guolong, GE Peng, et al. Constrained radar waveform design algorithm for spectral coexistence[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(8): 558–560. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.4524 [17] ZHAO Dehua, WEI Yinsheng, and LIU Yongtan. PCFM radar waveform design with spectral and correlation considerations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(6): 2885–2898. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2719359 [18] GERLACH K. Thinned spectrum ultrawideband waveforms using stepped-frequency polyphase codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1998, 34(4): 1356–1361. doi: 10.1109/7.722721 [19] FAUST H H, CONNOLLY B, FIRESTONE T M, et al. A spectrally clean transmitting system for solid-state phased-array radars[C]. 2004 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2004. [20] DE GRAAF J, FAUST H, ALATISHE J, et al. Generation of spectrally confined transmitted radar waveforms: Experimental results[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006. [21] PAN Mengguan, CHEN Baixiao, and YANG Minglei. A general range-velocity processing scheme for discontinuous spectrum FMCW signal in HFSWR applications[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 2016: 2609873. doi: 10.1155/2016/2609873 [22] ZHANG Dongpo and LIU Xingzhao. Range sidelobes suppression for wideband randomly discontinuous spectra OTH-HF radar signal[C]. 2004 IEEE Radar Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37509), Philadelphia, USA, 2004: 577–581. [23] MISHRA K V, MULLETI S, and ELDAR Y C. RaSSteR: Random sparse step-frequency radar[Z]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2004.05720, 2020. [24] ZHANG Jie. Study on wideband sparse spectrum waveform for anti-interception and anti-jamming countermeasure[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 2016: 1–5. [25] FAN Wen, LIANG Junli, SO H C, et al. Min-max metric for spectrally compatible waveform design via log-exponential smoothing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 1075–1090. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2969043 [26] YANG J, AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, et al. Multi-spectrally constrained transceiver design against signal-dependent interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022. [27] AUBRY A, DE MAIO A, PIEZZO M, et al. Radar waveform design in a spectrally crowded environment via nonconvex quadratic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1138–1152. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120731 [28] ALHUJAILI K, YU Xianxiang, CUI Guolong, et al. Spectrally compatible MIMO radar beampattern design under constant modulus constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(6): 4749–4766. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3003976 [29] 王璐璐, 王宏强, 王满喜. 雷达目标检测的最优波形设计综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 487–498. doi: 10.12000/JR16084WANG Lulu, WANG Hongqiang, and WANG Manxi. An overview of radar waveform optimization for target detection[J]. Journal of Radar, 2016, 5(5): 487–498. doi: 10.12000/JR16084 [30] PATTON L K and RIGLING B D. Autocorrelation constraints in radar waveform optimization for detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(2): 951–968. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6178041 [31] HAN S H and LEE J H. An overview of peak-to-average power ratio reduction techniques for multicarrier transmission[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2005, 12(2): 56–65. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2005.1421929 [32] LI Jian, GUERCI J R, and XU Luzhou. Signal waveform's optimal-under-restriction design for active sensing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2006, 13(9): 565–568. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2006.874465 [33] JONES A M, RIGLING B D, and RANGASWAMY M. Subspace approach to performance modelling of range-sidelobe suppressed waveforms[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(3): 466–473. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0283 [34] MARČENKO V A and PASTUR L A. Distribution of eigenvalues for some sets of random matrices[J]. Mathematics of the USSR-Sbornik, 1967, 1(4): 457–483. doi: 10.1070/SM1967v001n04ABEH001994 [35] GOODMAN N R. The distribution of the determinant of a complex wishart distributed matrix[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1963, 34(1): 178–180. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177704251 [36] FROST S W. Performance analysis of radar waveforms for congested spectrums[D]. [Master dissertation], Wright State University, 2011. [37] 毛智能. 非连续谱抗模糊波形设计研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.MAO Zhineng. Research on waveform design foramibgumty suppresson underdiscontinuous spectrum[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. doi: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2020.002047. [38] ZHAO Dehua, WEI Yinsheng, and LIU Yongtan. Correlation performance analysis for waveforms with spectral notches[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(11): 1644–1651. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0080 [39] WANG Guangtao and LU Yilong. Bounds on generalised integrated sidelobe level in waveforms with stopbands[J]. Electronics Letters, 2010, 46(23): 1561–1562. doi: 10.1049/el.2010.1876 [40] WANG Guohua, MAI Chaoyun, SUN Jinping, et al. Sparse frequency waveform analysis and design based on ambiguity function theory[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(4): 707–717. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0270 [41] 赵德华. 频谱拥堵环境下的自适应雷达波形设计研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.ZHAO Dehua. Research on waveform desgn for adaptmve radar in spectrum congested environment[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018. [42] ZHAO Dehua, WEI Yinsheng, and LIU Yongtan. Spectrum optimization via fft-based conjugate gradient method for unimodular sequence design[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 142: 354–365. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.07.035 [43] GERLACH K, FREY M R, STEINER M J, et al. Spectral nulling on transmit via nonlinear FM radar waveforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(2): 1507–1515. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5751276 [44] OECHSLIN R, WELLIG P, HINRICHSEN S, et al. Cognitive radar parameter optimization in a congested spectrum environment[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference, Oklahoma City, USA, 2018. [45] WEITZEL C E. RF power amplifiers for wireless communications[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2000, 1(1): 64. doi: 10.1109/MMW.2000.823830 [46] JAKABOSKY J, BLUNT S D, and HIGGINS T. Ultra-low sidelobe waveform design via spectral shaping and LINC transmit architecture[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon), Arlington, VA, USA, 2015. [47] KAY S M. Modern Spectral Estimation: Theory and Application[M]. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall, 1988. [48] JACKSON L, KAY S, and VANKAYALAPATI N. Iterative method for nonlinear FM synthesis of radar signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(2): 910–917. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5461666 [49] ZHUANG Shanna, HE Yapeng, and ZHU Xiaohua. Designing sparse frequency waveform with low range sidelobes for HFSWR[C]. 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011: 596–599. [50] HE Hao, LI Jian, and STOICA P. Waveform Design for Active Sensing Systems: A Computational Approach[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012. [51] BIŞKIN O T and AKAY O. A new algorithm for designing sequences using stopband and correlation constraints[C]. 2018 26th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Izmir, Turkey, 2018: 1–4. [52] AUBRY A, CAROTENUTO V, and MAIO A D. Forcing multiple spectral compatibility constraints in radar waveforms[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(4): 483–487. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2532739 [53] ALDAYEL O, MONGA V, and RANGASWAMY M. Successive QCQP refinement for MIMO radar waveform design under practical constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(14): 3760–3774. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2552501 [54] CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, FOGLIA G, et al. Quadratic optimization with similarity constraint for unimodular sequence synthesis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(18): 4756–4769. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2715010 [55] YU Xianxiang, CUI Guolong, YANG Jing, et al. Quadratic optimization for unimodular sequence design via an ADPM framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 3619–3634. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2998637 [56] GE Peng, CUI Guolong, KARBASI S M, et al. Cognitive radar sequence design under the spectral compatibility requirements[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(5): 759–767. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0239 [57] YANG Jing, CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, et al. Waveform design with spectral coexistence[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Boston, USA, 2019. [58] LIANG J, SO H C, LI J, et al. Unimodular sequence design based on alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(20): 5367–5381. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2597123 [59] ROWE W, STOICA P, and LI Jian. Spectrally constrained waveform design [sp Tips&Tricks][J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(3): 157–162. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2301792 [60] LIANG Junli, SO H C, LEUNG C S, et al. Waveform design with unit modulus and spectral shape constraints via Lagrange programming neural network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1377–1386. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2464178 [61] TANG Bo and LIANG Junli. Efficient algorithms for synthesizing probing waveforms with desired spectral shapes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(3): 1174–1189. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2876585 [62] MAO Zhineng and WEI Yinsheng. Waveform optimisation for unambiguous Doppler extension[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(2): 290–299. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5061 [63] GLADKOVA I. Analysis of stepped-frequency pulse train design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(4): 1251–1261. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5310296 [64] ZHAO Dehua, WEI Yinsheng, and LIU Yongtan. Design unimodular sequence train with low central and recurrent autocorrelation sidelobes via FFT-based cyclic algorithm[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(19): 1329–1331. doi: 10.1049/el.2017.2157 [65] AUBRY A, CAROTENUTO V, DE MAIO A, et al. Cognitive radar waveform design for spectral compatibility[C]. 2016 Sensor Signal Processing for Defence (SSPD), Edinburgh, UK, 2016: 1–5. [66] AUBRY A, MAIO A D, HUANG Yongwei, et al. A new radar waveform design algorithm with improved feasibility for spectral coexistence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(2): 1029–1038. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.140093 [67] TANG Bo, LI Jian, and LIANG Junli. Alternating direction method of multipliers for radar waveform design in spectrally crowded environments[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 142: 398–402. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.08.003 [68] CHENG Ziyang, LIAO Bin, HE Zishu, et al. Spectrally compatible waveform design for MIMO radar with transmit beampattern formation[C]. 2018 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), Shanghai, China, 2018. [69] Alaee-Kerahroodi M, RAEI E, KUMAR S, et al. Coexistence of communications and cognitive MIMO radar: Waveform design and prototype[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2103.11890, 2021. [70] MARTONE A and AMIN M. A view on radar and communication systems coexistence and dual functionality in the era of spectrum sensing[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2021, 119: 103135. [71] DENG M, CHENG Z, and HE Z. Spectrally compatible waveform design for large-scale MIMO radar beampattern synthesis with One-Bit DACs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022. [72] CHEN Ningkang, WEI Ping, GAO Lin, et al. Beampattern synthesis and spectral compatibility based MIMO radar waveform design[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2021, 118: 103211. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2021.103211. [73] YAO Yu, LIU Haitao, MIAO Pu, et al. MIMO radar design for extended target detection in a spectrally crowded environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021: 1–10. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3127727 [74] CHENG Ziyang, LIAO Bin, HE Zishu, et al. Spectrally compatible waveform design for MIMO radar in the presence of multiple targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(13): 3543–3555. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2833818 [75] SHI Shengnan, WANG Zhaoyi, HE Zishu, et al. Spectrally compatible waveform design for MIMO radar with ISL and PAPR constraints[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(5): 2368–2377. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2951740 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
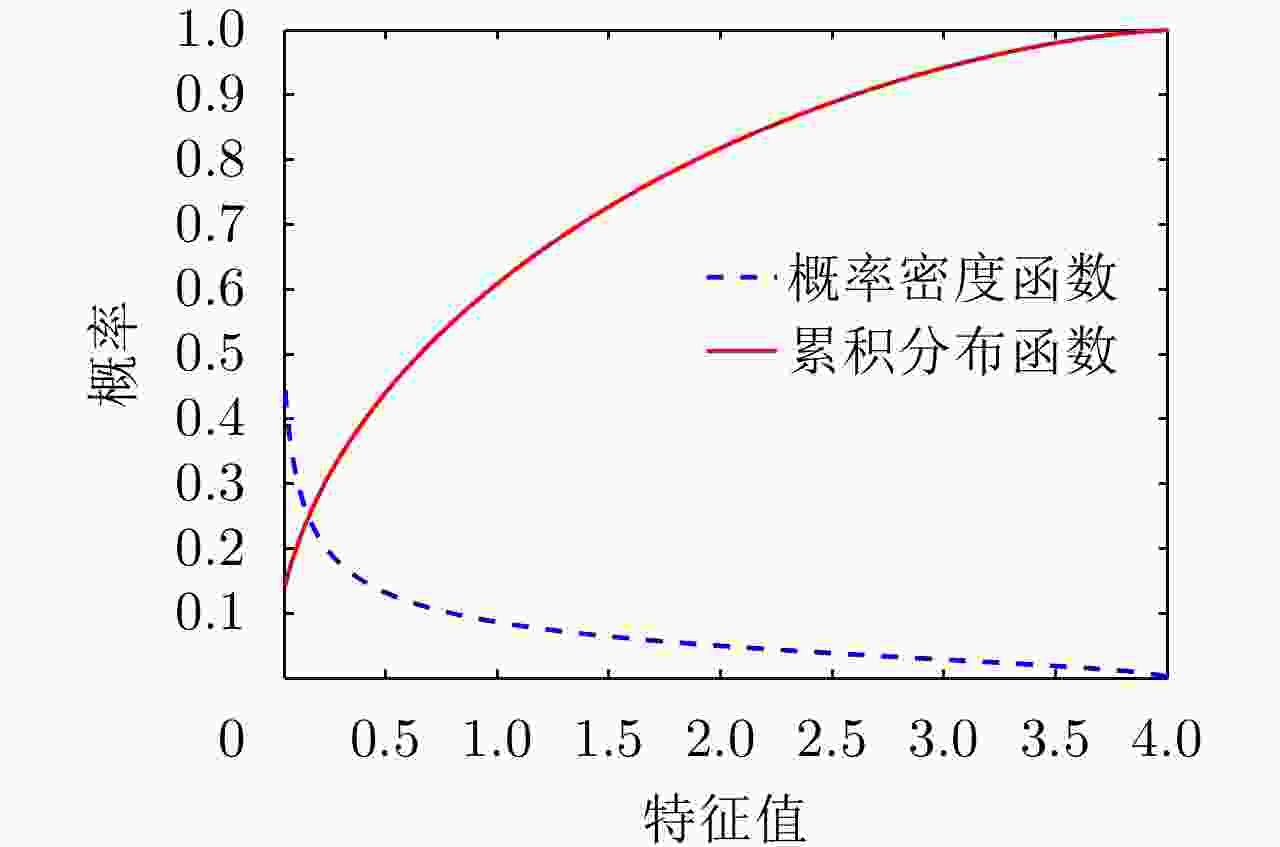
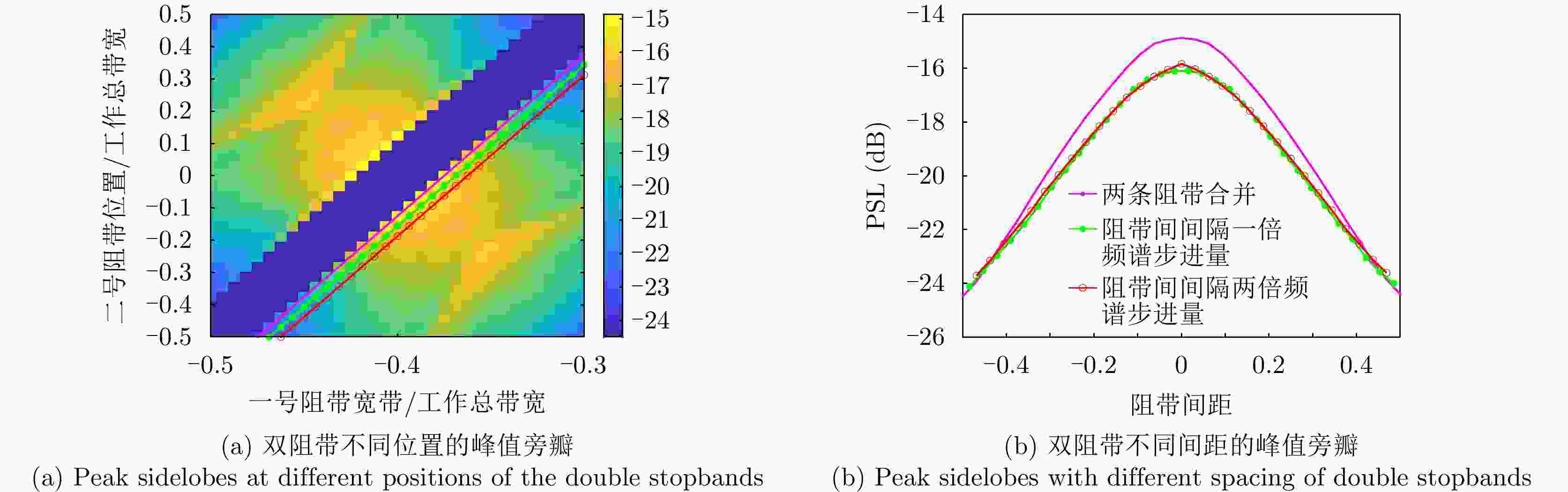
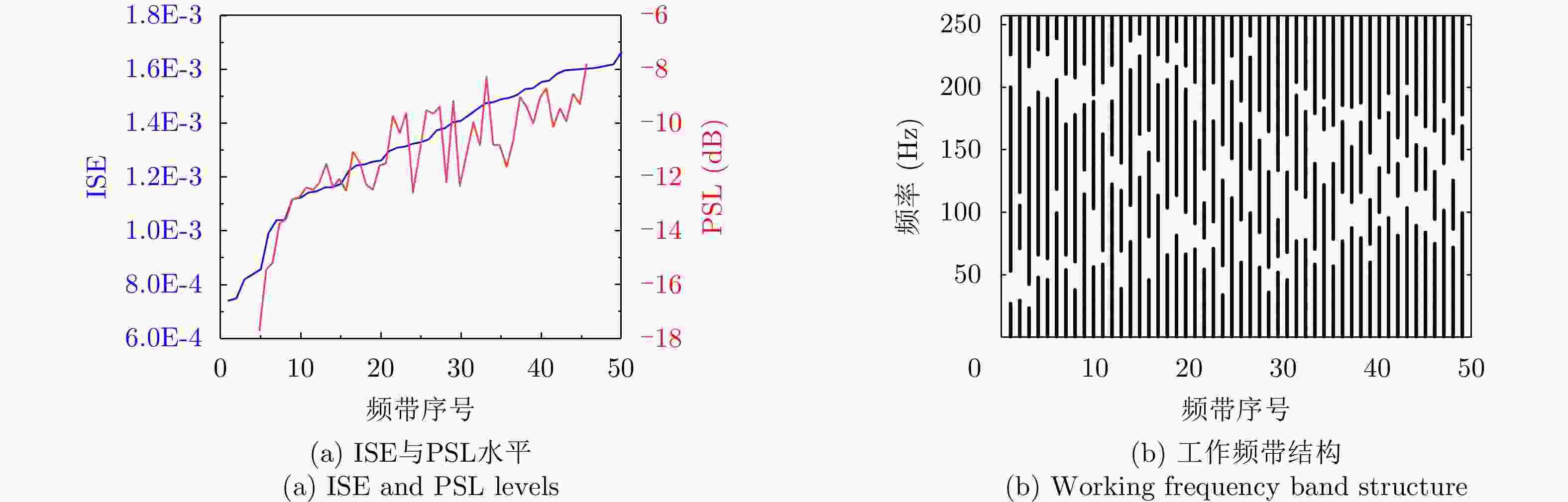
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
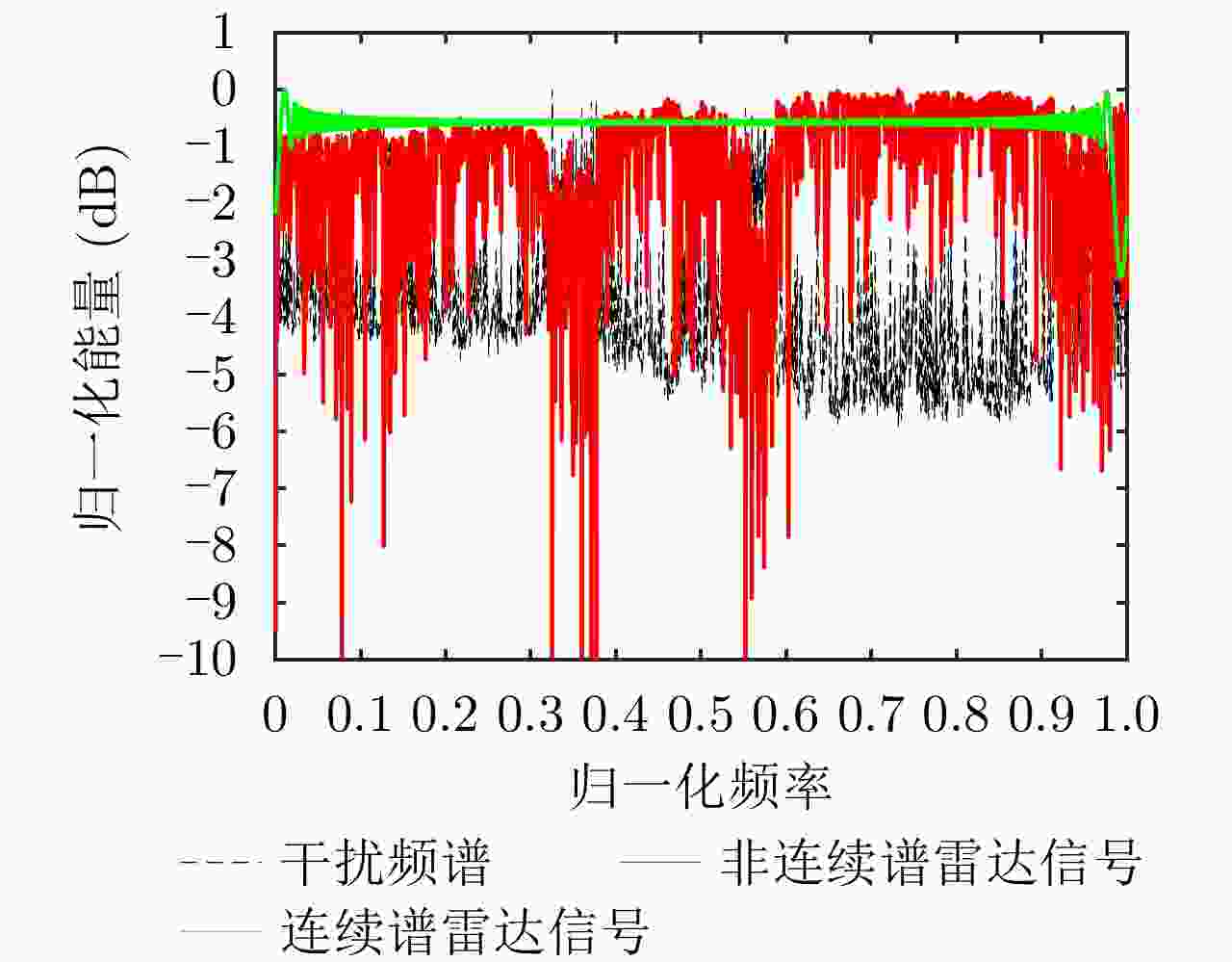
 下载:
下载: