Review of Noncontact Medical and Health Monitoring Technologies Based on FMCW Radar
-
摘要: 非接触式的医疗健康监测系统解决了用户依从性问题,避免了佩戴电极、传感设备进行监测带来的不舒适感,更有助于将健康监测融入日常生活。非接触式监测手段具有持续地监测用户健康状况的潜力,能够在突发急性医疗事件出现时及时示警,且能够满足新生儿、烧伤患者、传染病患者等特殊人群的监测需求。调频连续波(FMCW)雷达能够同时捕获雷达视场内目标的距离、速度信息,可用于非接触式地监测用户的心率、呼吸率等生理体征及跌倒等行为动作,且从技术上易于单片集成,成本可控,因此在医疗健康监测领域有着重要的应用价值。该文首先阐述了将FMCW雷达应用于非接触式医疗健康监测技术的理论基础,然后系统性地归纳了该领域中的典型前沿应用,最后总结了基于FMCW雷达的医疗健康应用这一领域的研究现状及局限性,并对其应用前景与潜在的研究方向进行了展望。Abstract: A contactless health monitoring system can contribute to health assessment in daily life by reducing appliance usage and avoiding discomfort from wearing electrodes or sensors. Such contactless approaches have the potential to continuously monitor the health status of users, alert patients and health personnel in time when acute medical emergencies occur, and meet the monitoring demands of special populations, such as newborns, burn patients, and patients with infectious diseases. The Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave (FMCW) radar can measure the range and velocity of sensing targets and be widely applied in heart and respiration rate monitoring and fall detection. Moreover, advances in FMCW radar have enabled low-cost radar-on-chip and antenna-on-chip systems. Thus, FMCW radar has vital application value in the medical and health monitoring fields. In this study, first, we introduce the basic knowledge of the application of FMCW radar in contactless health monitoring. Then, we systematically review the advanced applications and latest papers in this field. Finally, we summarize the present situations and limitations and provide a brief outlook for the application prospects and potential future research in the field.
-
Key words:
- FMCW radar /
- Contactless monitoring /
- Vital sign /
- Sleep monitoring /
- Falling detection
-
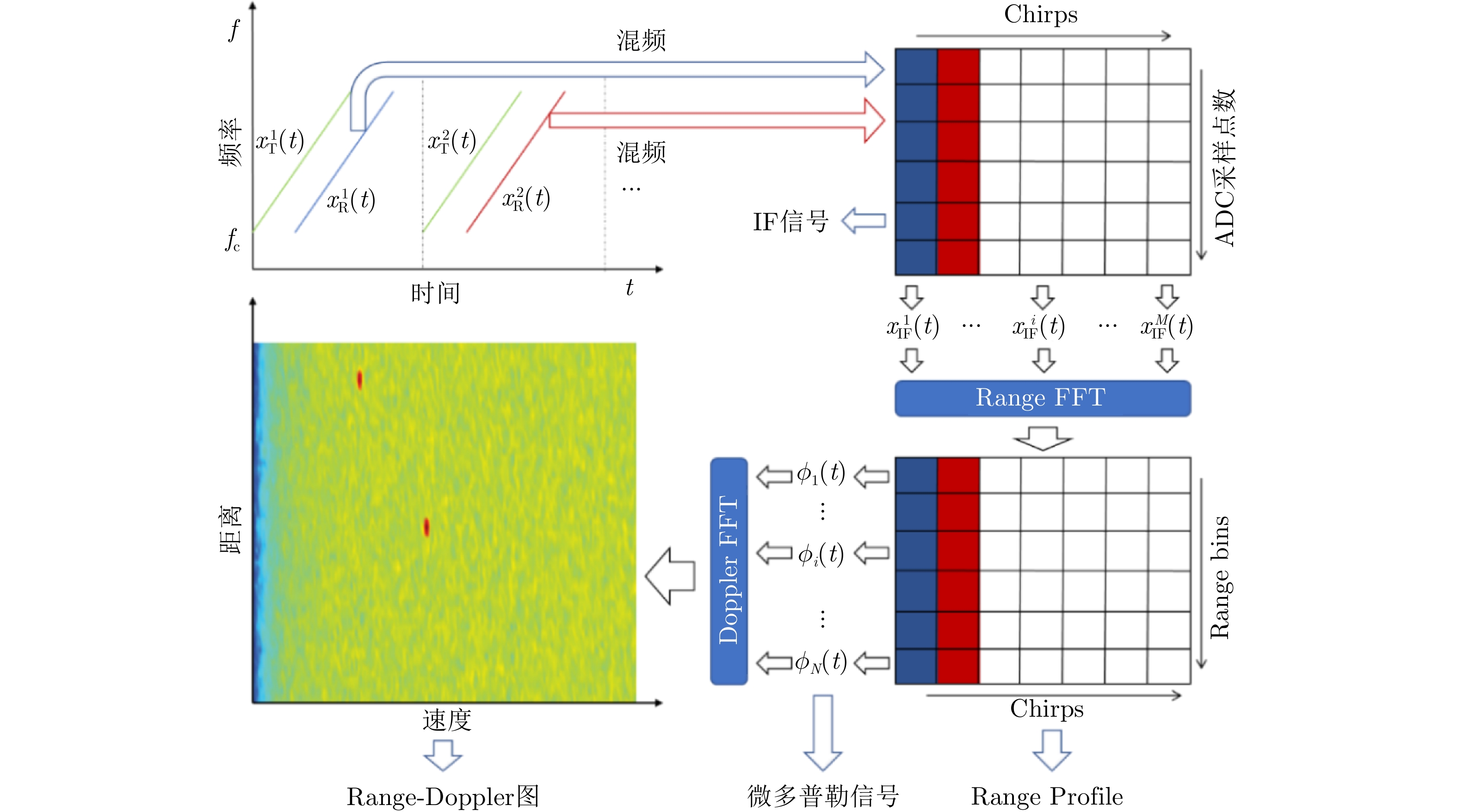
图 1 基于FMCW雷达的接收信号提取微多普勒信号与计算Range-Doppler图的信号处理流程。其中多个Chirp的IF信号经过FFT变换后得到的二维矩阵称为Range Profile
Figure 1. The signal processing flow of extracting micro-Doppler signal and calculating Range-Doppler map based on the received signal of FMCW radar. The two-dimensional matrix of multiple Chirp IF signals after FFT transform is called Range Profile
表 1 基于FMCW雷达的心率、呼吸率监测研究现状总结
Table 1. Summary of heart rate and respiratory rate monitoring based on FMCW radar
作者 信号获取方法 生理参数估计方法 实验设置 监测指标 Adib等人[21] 微多普勒信号提取 频谱分析 被试者保持静止,与雷达相距1 m RR准确率中位数为99.3%,HR准确率中位数为98.5% Mercuri等人[56] 微多普勒信号提取 频谱分析 2名被试者,静止,与雷达距离分别为2.6 m, 5.4 m 98.5%的RR估计误差小于3 次/
min, 95.5%的HR估计误差小于3 次/minWang等人[22] Beamforming,微多普勒信号提取 频谱分析 3名被试者,2名被试者与雷达距离1 m,AOA相差60°,1名被试者与雷达距离为1.5 m,保持静止 RR, HR平均准确率大于92.8% Chen等人[58] 相控阵技术,微多普勒信号提取 频谱分析 2名被试者,与雷达距离相同,约2 m,被试者间距离1 m,静止 97.8%的RR估计误差小于1.5 次/min, 93.6%的HR估计误差小于3 次/min Sun等人[59] EMD,微多普勒信号提取 频谱分析 被试者与雷达间距1.0~2.5 m,静止 HR估计误差RMSE为2.03~5.83 次/min Wang等人[45] VMD,微多普勒信号提取 峰值检测 被试者与雷达间距0.5~2.0 m,AOA为0~60°,静止 IBI RMSE为29.850~68.974 ms Toda等人[60] CNN,微多普勒信号提取 QRS波群检测 被试者静止,距离2.5 m IBI MAE为17.8 ms Ha等人[61] Beamforming,CNN,微多普勒信号提取 Unet[62] 被试者静止,面向雷达,距离25~50 cm 心脏收缩期、舒张期等心脏活动检测准确率90%,召回率为69.8% Zheng等人[63] CFAR,多变量VMD,微多普勒信号提取 频谱分析,峰值检测 被试者驾驶汽车,在不同路况下行驶 RR 误差中位数为 0.06 次/min, HR MAE误差中位数为 0.6 次/
min, IBI误差中位数约50 msChen等人[64] 深度对比学习算法,微多普勒信号提取 频谱分析,峰值检测 被试者存在步行,坐下/站起等大幅度肢体运动 RR HR的MAPE为2% ,3%;不同肢体运动下IBI误差中位数为20~40 ms 表 2 基于FMCW雷达的跌倒检测研究现状总结
Table 2. Summary of research status of falling detection based on FMCW radar
作者 雷达特征信息 算法概述 是否在新用户/
新环境下测试是否需要
采集跌倒样本非跌倒/跌倒
样本比例检测指标 Jokanovic等人[125] Range Profile,Range-Doppler图 Autoencoder+
Logistic回归否 是 43:17 Acc: 96% Tian等人[128] Range-Angle图 级联CNN分类器 是 是 450000:293 F1: 0.929 元志安等人[126] Range-Doppler图 CNN+LSTM 是 是 1:1 Acc: 96.67% Wang等人[127] IF信号 LKCNN 否 是 1:1 Acc: 95.24% Jin等人[46] 点云 VAE+RNN 否 否 4:1 Acc: 98% Li等人[40] Range-Doppler图 LSTM 是 是 5:1 Acc: 96% -
[1] LU Shan, WANG Anzhi, JING Shenqi, et al. A study on service-oriented smart medical systems combined with key algorithms in the IoT environment[J]. China Communications, 2019, 16(9): 235–249. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2019.09.018 [2] AL-MAHMUD O, KHAN K, ROY R, et al. Internet of things (IoT) based smart health care medical box for elderly people[C]. 2020 International Conference for Emerging Technology (INCET), Belgaum, India, 2020: 1–6. [3] VILLENEUVE E, HARWIN W, HOLDERBAUM W, et al. Reconstruction of angular kinematics from wrist-worn inertial sensor data for smart home healthcare[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 2351–2363. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2016.2640559 [4] MAHFOUZ M R, KUHN M J, and TO G. Wireless medical devices: A review of current research and commercial systems[C]. 2013 IEEE Topical Conference on Biomedical Wireless Technologies, Networks, and Sensing Systems, Austin, USA, 2013: 16–18. [5] PARK E, KIM J H, NAM H S, et al. Requirement analysis and implementation of smart emergency medical services[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 42022–42029. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2861711 [6] LIU Jian, CHEN Yingying, WANG Yan, et al. Monitoring vital signs and postures during sleep using WiFi signals[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(3): 2071–2084. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2822818 [7] WANG Hao, ZHANG Daqing, WANG Yasha, et al. RT-Fall: A real-time and contactless fall detection system with commodity WiFi devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2017, 16(2): 511–526. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2557795 [8] WANG Xuyu, YANG Chao, and MAO Shiwen. PhaseBeat: Exploiting CSI phase data for vital sign monitoring with commodity WiFi devices[C]. 2017 IEEE 37th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Atlanta, USA, 2017: 1230–1239. [9] LIN Feng, SONG Chen, ZHUANG Yan, et al. Cardiac scan: A non-contact and continuous heart-based user authentication system[C]. The 23rd Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Snowbird, USA, 2017: 315–328. [10] WILL C, SHI K, SCHELLENBERGER S, et al. Local pulse wave detection using continuous wave radar systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Electromagnetics, RF and Microwaves in Medicine and Biology, 2017, 1(2): 81–89. doi: 10.1109/JERM.2017.2766567 [11] RAHMAN T, ADAMS A T, RAVICHANDRAN R V, et al. DoppleSleep: A contactless unobtrusive sleep sensing system using short-range doppler radar[C]. The 2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Osaka, Japan, 2015: 39–50. [12] YANG Yang, HOU Chunping, LANG Yue, et al. Open-set human activity recognition based on micro-Doppler signatures[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 85: 60–69. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.07.030 [13] LARSON E C, GOEL M, BORIELLO G, et al. SpiroSmart: Using a microphone to measure lung function on a mobile phone[C]. The 2012 ACM Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Pittsburgh, USA, 2012: 280–289. [14] ZHANG Fusang, WANG Zhi, JIN Beihong, et al. Your smart speaker can “hear” your heartbeat![J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2020, 4(4): 161. doi: 10.1145/3432237 [15] 陆佳鑫. 基于深度神经网络的人体跌倒碰撞前行为检测研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2021.LU Jiaxin. A research of human pre-impact fall detection based on deep neural network[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021. [16] SADREAZAMI H, BOLIC M, and RAJAN S. Fall detection using standoff radar-based sensing and deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2020, 67(1): 197–201. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2019.2904498 [17] PENG Zhengyu and LI Changzhi. Portable microwave radar systems for short-range localization and life tracking: A review[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(5): 1136. doi: 10.3390/s19051136 [18] JARDAK S, ALOUINI M S, KIURU T, et al. Compact mmWave FMCW radar: Implementation and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2019, 34(2): 36–44. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2019.180130 [19] PATOLE S M, TORLAK M, WANG Dan, et al. Automotive radars: A review of signal processing techniques[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34(2): 22–35. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2016.2628914 [20] LI Changzhi, PENG Zhengyu, HUANG T Y, et al. A review on recent progress of portable short-range noncontact microwave radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2017, 65(5): 1692–1706. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2017.2650911 [21] ADIB F, MAO Hongzi, KABELAC Z, et al. Smart homes that monitor breathing and heart rate[C]. The 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2015: 837–846. [22] WANG Fengyu, ZHANG Feng, WU Chenshu, et al. ViMo: Multiperson vital sign monitoring using commodity millimeter-wave radio[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(3): 1294–1307. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3004046 [23] CHEN Baozhan, QIAO Siyuan, ZHAO Jie, et al. A security awareness and protection system for 5G smart healthcare based on zero-trust architecture[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(13): 10248–10263. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3041042 [24] 李健. 24GHz调频连续波雷达信号处理技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京理工大学, 2017.LI Jian. Research on signal processing technology of 24GHz FMCW radar[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2017. [25] 李艳莉. 毫米波通信技术的研究现状和进展[C]. 四川省通信学会2010年学术年会论文集, 成都, 2010: 46–49.LI Yanli. Research status and progress of millimeter wave communication technology[C]. Papers of the 2010 Annual Conference of Sichuan Communications Society, Chengdu, China, 2010: 46–49. [26] CHADWICK P E. Regulations and standards for wireless applications in eHealth[C]. 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 2007: 6170–6173. [27] YANG Xiaodong, FAN Dou, REN Aifeng, et al. Sleep apnea syndrome sensing at C-band[J]. IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine, 2018, 6: 2701008. doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2018.2879085 [28] OHAYON M, WICKWIRE E M, HIRSHKOWITZ M, et al. National sleep foundation’s sleep quality recommendations: First report[J]. Sleep Health, 2017, 3(1): 6–19. doi: 10.1016/j.sleh.2016.11.006 [29] 张群, 胡健, 罗迎, 等. 微动目标雷达特征提取、成像与识别研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049ZHANG Qun, HU Jian, LUO Ying, et al. Research progresses in radar feature extraction, imaging, and recognition of target with micro-motions[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049 [30] KEBE M, GADHAFI R, MOHAMMAD B, et al. Human vital signs detection methods and potential using radars: A review[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(5): 1454. doi: 10.3390/s20051454 [31] 龙腾, 毛二可, 何佩琨. 调频步进雷达信号分析与处理[J]. 电子学报, 1998, 26(12): 84–88. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1998.12.019LONG Teng, MAO Erke, and HE Peikun. Analysis and processing of modulated frequency stepped radar signal[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 1998, 26(12): 84–88. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.1998.12.019 [32] LV Hao, JIAO Teng, ZHANG Yang, et al. A novel method for breath detection via stepped-frequency continuous wave ultra-wideband (SFCW UWB) radars based on operational bandwidth segmentation[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(11): 3873. doi: 10.3390/s18113873 [33] 张杨, 焦腾, 荆西京, 等. 生物雷达技术的研究现状与新进展[J]. 信息化研究, 2010, 36(10): 6–10, 13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4888.2010.10.002ZHANG Yang, JIAO Teng, JING Xijing, et al. Current state and progress of the technology of bioradar[J]. Informatization Research, 2010, 36(10): 6–10, 13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4888.2010.10.002 [34] 黄文奎. 毫米波汽车防撞雷达的设计与实现[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院研究生院, 2006.HUANG Wenkui. Design and production of millimeter-wave automotive radar for collision avoidance application[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006. [35] 赵锴. 汽车防碰撞系统雷达设计与信号处理[D]. [硕士论文], 青岛理工大学, 2018.ZHAO Kai. Design and signal processing on automotive anti-collision radar system[D]. [Master dissertation], Qingdao University of Technology, 2018. [36] 胡程, 廖鑫, 向寅, 等. 一种生命探测雷达微多普勒测量灵敏度分析新方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 455–461. doi: 10.12000/JR16090HU Cheng, LIAO Xin, XIANG Yin, et al. Novel analytic method for determining micro-Doppler measurement sensitivity in life-detection radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 455–461. doi: 10.12000/JR16090 [37] DING Chuanwei, HONG Hong, ZOU Yu, et al. Continuous human motion recognition with a dynamic range-Doppler trajectory method based on FMCW radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6821–6831. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2908758 [38] 赵珍珍. 老年人跌倒检测算法的研究现状[J/OL]. 计算机工程与应用, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2127.tp.20211112.0903.002.html. 2021.ZHAO Zhenzhen. Research status of elderly fall detection algorithms[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2127.tp.20211112.0903.002.html. 2021. [39] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [40] LI Haobo, SHRESTHA A, HEIDARI H, et al. Bi-LSTM network for multimodal continuous human activity recognition and fall detection[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(3): 1191–1201. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2946095 [41] ALANAZI M A, ALHAZMI A K, YAKOPCIC C, et al. Machine learning models for human fall detection using millimeter wave sensor[C]. 2021 55th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Baltimore, USA, 2021: 1–5. [42] BHATTACHARYA A and VAUGHAN R. Deep learning radar design for breathing and fall detection[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(9): 5072–5085. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2967100 [43] 韩文婷, 娄昊, 樊阳, 等. 一种改进的 MIMO 生物雷达人体目标检测跟踪联合自适应算法[J]. 信号处理, 2021, 37(11): 2227–2234. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2021.11.025HAN Wenting, LOU Hao, FAN Yang, et al. An improved joint adaptive algorithm for MIMO bio-radar human target detection and tracking[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2021, 37(11): 2227–2234. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2021.11.025 [44] ADIB F, KABELAC Z, KATABI D, et al. 3D tracking via body radio reflections[C]. The 11th USENIX Conference on Networked Systems Design and Implementation, Seattle, USA, 2014: 317–329. [45] WANG Fengyu, ZENG Xiaolu, WU Chenshu, et al. MmHRV: Contactless heart rate variability monitoring using millimeter-wave radio[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(22): 16623–16636. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3075167 [46] JIN Feng, SENGUPTA A, and CAO Siyang. MmFall: Fall detection using 4-D mmWave radar and a hybrid variational RNN autoencoder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2020: 1–13. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2020.3042158 [47] GUPTA S, RAI P K, KUMAR A, et al. Target classification by mmWave FMCW radars using machine learning on range-angle images[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(18): 19993–20001. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3092583 [48] ZHANG Feng, WU Chenshu, WANG Beibei, et al. MmEye: Super-resolution millimeter wave imaging[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(8): 6995–7008. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3037836 [49] HSU C Y, HRISTOV R, LEE G H, et al. Enabling identification and behavioral sensing in homes using radio reflections[C]. The 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, UK, 2019: 548. [50] OUAKNINE A, NEWSON A, REBUT J, et al. CARRADA dataset: Camera and automotive radar with range-angle-Doppler annotations[C]. 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 2021: 5068–5075. [51] 陈功, 张业荣. 基于胶囊内窥镜的胃部肿瘤检测方法?[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(16): 194101. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.194101CHEN Gong and ZHANG Yerong. A method of detecting stomach tumour based on capsule endoscopy[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(16): 194101. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.194101 [52] REIMER T, SACRISTAN J, and PISTORIUS S. Improving the diagnostic capability of microwave radar imaging systems using machine learning[C]. 2019 13th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Krakow, Poland, 2019: 1–5. [53] OMER M, MOJABI P, KURRANT D, et al. Proof-of-concept of the incorporation of ultrasound-derived structural information into microwave radar imaging[J]. IEEE Journal on Multiscale and Multiphysics Computational Techniques, 2018, 3: 129–139. doi: 10.1109/JMMCT.2018.2865111 [54] INAN O T, MIGEOTTE P F, PARK K S, et al. Ballistocardiography and seismocardiography: A review of recent advances[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2015, 19(4): 1414–1427. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2014.2361732 [55] TAEBI A, SOLAR B E, BOMAR A J, et al. Recent advances in seismocardiography[J]. Vibration, 2019, 2(1): 64–86. doi: 10.3390/vibration2010005 [56] MERCURI M, LORATO I R, LIU Yaohong, et al. Vital-sign monitoring and spatial tracking of multiple people using a contactless radar-based sensor[J]. Nature Electronics, 2019, 2(6): 252–262. doi: 10.1038/s41928-019-0258-6 [57] MERCURI M, LU Yiting, POLITO S, et al. Enabling robust radar-based localization and vital signs monitoring in multipath propagation environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2021, 68(11): 3228–3240. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2021.3066876 [58] CHEN Feng, JIANG Xiaonan, JEONG M G, et al. Multitarget vital signs measurement with chest motion imaging based on MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(11): 4735–4747. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3076239 [59] SUN Li, HUANG Shuaiming, LI Yusheng, et al. Remote measurement of human vital signs based on joint-range adaptive EEMD[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 68514–68524. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2985286 [60] TODA D, ANZAI R, ICHIGE K, et al. ECG signal reconstruction using FMCW radar and convolutional neural network[C]. 2021 20th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), Tottori, Japan, 2021: 176–181. [61] HA U, ASSANA S, and ADIB F. Contactless seismocardiography via deep learning radars[C]. The 26th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, London, United Kingdom, 2020: 62. [62] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [63] ZHENG Tianyue, CHEN Zhe, CAI Chao, et al. V2iFi: In-vehicle vital sign monitoring via compact RF sensing[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2020, 4(2): 70. doi: 10.1145/3397321 [64] CHEN Zhe, ZHENG Tianyue, CAI Chao, et al. MoVi-Fi: Motion-robust vital signs waveform recovery via deep interpreted RF sensing[C]. The 27th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, New Orleans, USA, 2021: 392–405. [65] AHMAD A, ROH J C, WANG Dan, et al. Vital signs monitoring of multiple people using a FMCW millimeter-wave sensor[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 1450–1455. [66] MERCURI M, SACCO G, HORNUNG R, et al. 2-D localization, angular separation and vital signs monitoring using a SISO FMCW radar for smart long-term health monitoring environments[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(14): 11065–11077. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3051580 [67] 胡锡坤, 金添. 基于自适应小波尺度选择的生物雷达呼吸与心跳分离方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 462–469. doi: 10.12000/JR16103HU Xikun and JIN Tian. Adaptive wavelet scale selection-based method for separating respiration and heartbeat in bio-radars[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 462–469. doi: 10.12000/JR16103 [68] HE Mi, NIAN Yongjian, and GONG Yushun. Novel signal processing method for vital sign monitoring using FMCW radar[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2017, 33: 335–345. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2016.12.008 [69] DRAGOMIRETSKIY K and ZOSSO D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531–544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675 [70] RIBEIRO A H, RIBEIRO M H, PAIXÃO G M M, et al. Automatic diagnosis of the 12-lead ECG using a deep neural network[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1760. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15432-4 [71] ZHAO Mingmin, ADIB F, and KATABI D. Emotion recognition using wireless signals[C]. The 22nd Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, New York, USA, 2016: 95–108. [72] UR REHMAN N and AFTAB H. Multivariate variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(23): 6039–6052. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2951223 [73] CHEN Ting, KORNBLITH S, NOROUZI M, et al. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations[C]. The 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 2020: 1597–1607. [74] 祁富贵, 岳超, 梁福来, 等. SFCW生物雷达人体细粒度运动信号微多普勒特征增强方法研究[J]. 中国医疗设备, 2016, 31(2): 39–43, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1633.2016.02.009QI Fugui, YUE Chao, LIANG Fulai, et al. A study on the micro-Doppler signature enhanced technique for the finer-grained human activity signal acquired by the SFCW bio-radar[J]. China Medical Devices, 2016, 31(2): 39–43, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1633.2016.02.009 [75] 张杨, 吕昊, 于霄, 等. 基于超宽谱雷达多目标穿墙探测定位技术的研究[J]. 医疗卫生装备, 2016, 37(8): 10–13. doi: 10.7687/J.ISSN1003-8868.2016.08.010ZHANG Yang, LYU Hao, YU Xiao, et al. Research of through-wall detection and location technique for multihuman targets using ultra wideband radar[J]. Chinese Medical Equipment Journal, 2016, 37(8): 10–13. doi: 10.7687/J.ISSN1003-8868.2016.08.010 [76] MA Yangyang, WANG Pengfei, XUE Huijun, et al. Non-contact vital states identification of trapped living bodies using ultra-wideband bio-radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 9: 6550–6559. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3048381 [77] LIANG Fulai, LI Haonan, LIU Miao, et al. Autofocusing method for through-the-wall bioradar imagery of human vital signs[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(21): 7597–7600. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0540 [78] 李廉林, 崔铁军. 智能电磁感知的若干进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(2): 183–190. doi: 10.12000/JR21049LI Lianlin and CUI Tiejun. Recent progress in intelligent electromagnetic sensing[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(2): 183–190. doi: 10.12000/JR21049 [79] LI Lianlin, SHUANG Ya, MA Qian, et al. Intelligent metasurface imager and recognizer[J]. Light:Science & Applications, 2019, 8(1): 97. doi: 10.1038/s41377-019-0209-z [80] LIU Zhenyu, KONG Yongan, ZHANG Xin, et al. Vital sign extraction in the presence of radar mutual interference[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 1745–1749. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.3026942 [81] ZHANG Yang, QI Fugui, LV Hao, et al. Bioradar technology: Recent research and advancements[J]. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 2019, 20(8): 58–73. doi: 10.1109/MMM.2019.2915491 [82] HUANG Xinming, SUN Ling, TIAN Tian, et al. Real-time non-contact infant respiratory monitoring using UWB radar[C]. 2015 IEEE 16th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Hangzhou, China, 2015: 493–496. [83] LI Chuantao, CHEN Fuming, JIN Jingxi, et al. A method for remotely sensing vital signs of human subjects outdoors[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(7): 14830–14844. doi: 10.3390/s150714830 [84] 王健琪, 薛慧君, 吕昊, 等. 非接触生理信号检测技术[J]. 中国医疗设备, 2013, 28(11): 5–8, 80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1633.2013.11.002WANG Jianqi, XUE Huijun, LV Hao, et al. Non-contact detection technology for physiological signals[J]. Chinese Medical Devices, 2013, 28(11): 5–8, 80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1633.2013.11.002 [85] KUMAR S S, DASHTIPOUR K, ABBASI Q H, et al. A review on wearable and contactless sensing for COVID-19 with policy challenges[J]. Frontiers in Communications and Networks, 2021, 2: 636293. doi: 10.3389/frcmn.2021.636293 [86] 王健琪, 王海滨, 荆西京, 等. 呼吸、心率的雷达式非接触检测系统设计与研究[J]. 中国医疗器械杂志, 2001, 25(3): 132–135.WANG Jianqi, WANG Haibing, JING Xijing, et al. The study on non-contact detection of breathing and heartbeat based on radar principles[J] Chinese Journal of Medical Instrumentation, 2001, 25(3): 132–135. [87] SCHMIECH D, MULLER S, and DIEWALD A R. 4-channel I/Q-radar system for vital sign monitoring in a baby incubator[C]. 2018 19th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Bonn, Germany, 2018: 1–9. [88] SUN Guanghao, OKADA M, NAKAMURA R, et al. Twenty‐four‐hour continuous and remote monitoring of respiratory rate using a medical radar system for the early detection of pneumonia in symptomatic elderly bedridden hospitalized patients[J]. Clinical Case Reports, 2019, 7(1): 83–86. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.1922 [89] ADHIKARI A, HETHERINGTON A, and SUR S. MmFlow: Facilitating at-home spirometry with 5G smart devices[C]. 2021 18th Annual IEEE International Conference on Sensing, Communication, and Networking (SECON), Rome, Italy, 2021: 1–9. [90] JORGENSEN G, DOWNEY C, GOLDIN J, et al. An australasian commentary on the AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events[J]. Sleep and Biological Rhythms, 2020, 18(3): 163–185. doi: 10.1007/s41105-020-00259-9 [91] BONNET M H and ARAND D L. Heart rate variability: Sleep stage, time of night, and arousal influences[J]. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 1997, 102(5): 390–396. doi: 10.1016/S0921-884X(96)96070-1 [92] 彭小虎, 王国锋, 刘军, 等. 睡眠微观结构—CAP与睡眠质量评估[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2013, 21(6): 920–923. doi: 10.16128/J.CNKI.1005-3611.2013.06.030PENG Xiaohu, WANG Guofeng, LIU Jun, et al. Sleep microstructure—CAP and sleep quality assessment[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 2013, 21(6): 920–923. doi: 10.16128/J.CNKI.1005-3611.2013.06.030 [93] FONSECA P, DEN TEULING N, LONG Xi, et al. Cardiorespiratory sleep stage detection using conditional random fields[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2017, 21(4): 956–966. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2016.2550104 [94] SCHULZ S, ADOCHIEI F C, EDU I R, et al. Cardiovascular and cardiorespiratory coupling analyses: A review[J]. Philosophical Transactions. Series A, Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2013, 371(1997): 20120191. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2012.0191 [95] BARTSCH R P, LIU K K L, MA Q D Y, et al. Three independent forms of cardio-respiratory coupling: Transitions across sleep stages[C]. Computing in Cardiology 2014, Cambridge, USA, 2014: 781–784. [96] LONG Xi, FOUSSIER J, FONSECA P, et al. Analyzing respiratory effort amplitude for automated sleep stage classification[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2014, 14: 197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2014.08.001 [97] HSU C Y, AHUJA A, YUE Shichao, et al. Zero-Effort in-home sleep and insomnia monitoring using radio signals[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2017, 1(3): 1–18. doi: 10.1145/3130924 [98] ZHAO Mingmin, YUE Shichao, KATABI D, et al. Learning sleep stages from radio signals: A conditional adversarial architecture[C]. The 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 4100–4109. [99] TZENG E, HOFFMAN J, SAENKO K, et al. Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 7167–7176. [100] GOTTLIEB D J and PUNJABI N M. Diagnosis and management of obstructive sleep apnea: A review[J]. JAMA, 2020, 323(14): 1389–1400. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.3514 [101] THOMAS R J, MIETUS J E, PENG C K, et al. Differentiating obstructive from central and complex sleep apnea using an automated electrocardiogram-based method[J]. Sleep, 2007, 30(12): 1756–1769. doi: 10.1093/sleep/30.12.1756 [102] BABOLI M, SINGH A, SOLL B, et al. Wireless sleep apnea detection using continuous wave quadrature Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(1): 538–545. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2941198 [103] MENDONÇA F, MOSTAFA S S, RAVELO-GARCIA A G, et al. A review of obstructive sleep apnea detection approaches[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2019, 23(2): 825–837. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2823265 [104] NANDAKUMAR R, GOLLAKOTA S, and WATSON N. Contactless sleep apnea detection on smartphones[C]. The 13th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Florence, Italy, 2015: 45–57. [105] ISLAM S M M, RAHMAN A, YAVARI E, et al. Identity authentication of OSA patients using microwave doppler radar and machine learning classifiers[C]. 2020 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), San Antonio, USA, 2020: 251–254. [106] ARSALAN M, SANTRA A, and WILL C. Improved contactless heartbeat estimation in FMCW radar via Kalman filter tracking[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2020, 4(5): 1–4. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2020.2983706 [107] WANG Qisong, DONG Zhening, LIU Dan, et al. Frequency-modulated continuous wave radar respiratory pattern detection technology based on multifeature[J]. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2021, 2021: 9376662. doi: 10.1155/2021/9376662 [108] BAHAMMAM A S, TATE R, MANFREDA J, et al. Upper airway resistance syndrome: Effect of nasal dilation, sleep stage, and sleep position[J]. Sleep, 1999, 22(5): 592–598. doi: 10.1093/sleep/22.5.592 [109] GU Weixi, SHANGGUAN Longfei, YANG Zheng, et al. Sleep hunter: Towards fine grained sleep stage tracking with smartphones[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2016, 15(6): 1514–1527. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2015.2462812 [110] MENON A and KUMAR M. Influence of body position on severity of obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review[J]. International Scholarly Research Notices, 2013, 2013: 670381. doi: 10.1155/2013/670381 [111] UCHINO K, SHIRAISHI M, TANAKA K, et al. Impact of inability to turn in bed assessed by a wearable three-axis accelerometer on patients with Parkinson’s disease[J]. PLoS ONE, 2017, 12(11): e0187616. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187616 [112] LIEBENTHAL J A, WU Shasha, ROSE S, et al. Association of prone position with sudden unexpected death in epilepsy[J]. Neurology, 2015, 84(7): 703–709. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001260 [113] KLOSTER R and ENGELSKJØN T. Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP): A clinical perspective and a search for risk factors[J]. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 1999, 67(4): 439–444. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.67.4.439 [114] ZHOU Tao, XIA Zhaoyang, WANG Xiangfeng, et al. Human sleep posture recognition based on millimeter-wave radar[C]. 2021 Signal Processing Symposium (SPSympo), LODZ, Poland, 2021: 316–321. [115] ADIB F, HSU C Y, MAO Hongzi, et al. Capturing the human figure through a wall[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) , 2015, 34(6): 1–13. doi: 10.1145/2816795.2818072 [116] ZHAO Mingmin, LI Tianhong, ABU ALSHEIKH M, et al. Through-wall human pose estimation using radio signals[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7356–7365. [117] ZHAO Mingmin, TIAN Yonglong, ZHAO Hang, et al. RF-based 3D skeletons[C]. The 2018 Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, Budapest, Hungary, 2018: 267–281. [118] YUE Shichao, YANG Yezhe, WANG Hao, et al. BodyCompass: Monitoring sleep posture with wireless signals[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2020, 4(2): 1–25. doi: 10.1145/3397311 [119] RUBENSTEIN L Z. Falls in older people: Epidemiology, risk factors and strategies for prevention[J]. Age and Ageing, 2006, 35(S2): ii37–ii41. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afl084 [120] HOPKINS J. Falls Cost U. S. Hospitals $34 billion in direct medical costs[EB/OL]. https://www.johnshopkinssolutions.com/article/falls-cost-u-s-hospitals-30-billion-in-direct-medical-costs/, 2015. [121] KANNUS P, SIEVÄNEN H, PALVANEN M, et al. Prevention of falls and consequent injuries in elderly people[J]. The Lancet, 2005, 366(9500): 1885–1893. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67604-0 [122] FLEMING J and BRAYNE C. Inability to get up after falling, subsequent time on floor, and summoning help: Prospective cohort study in people over 90[J]. BMJ, 2008, 337: a2227. doi: 10.1136/bmj.a2227 [123] MUDRAZIJA S, ANGEL J L, CIPIN I, et al. Living alone in the United States and Europe: The impact of public support on the independence of older adults[J]. Research on Aging, 2020, 42(5/6): 150–162. doi: 10.1177/0164027520907332 [124] GURBUZ S Z and AMIN M G. Radar-based human-motion recognition with deep learning: Promising applications for indoor monitoring[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2019, 36(4): 16–28. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2018.2890128 [125] JOKANOVIĆ B and AMIN M. Fall detection using deep learning in range-Doppler radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 180–189. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2740098 [126] 元志安, 周笑宇, 刘心溥, 等. 基于RDSNet的毫米波雷达人体跌倒检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 656–664. doi: 10.12000/JR21015YUAN Zhian, ZHOU Xiaoyu, LIU Xinpu, et al. Human fall detection method using millimeter-wave radar based on RDSNet[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 656–664. doi: 10.12000/JR21015 [127] WANG Bo, GUO Liang, ZHANG Hao, et al. A millimetre-wave radar-based fall detection method using line kernel convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(22): 13364–13370. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3006918 [128] TIAN Yonglong, LEE G H, HE Hao, et al. RF-based fall monitoring using convolutional neural networks[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2018, 2(3): 137. doi: 10.1145/3264947 [129] DENG Muqing, WANG Cong, TANG Min, et al. Extracting cardiac dynamics within ECG signal for human identification and cardiovascular diseases classification[J]. Neural Networks, 2018, 100: 70–83. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2018.01.009 [130] OJAROUDI M and BILA S. Multiple time-variant targets detection using MIMO radar framework for cerebrovascular monitoring[C]. 2021 15th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Dusseldorf, Germany, 2021: 1–5. [131] HUANG Kewu, YANG Ting, XU Jianying, et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of asthma in China: A national cross-sectional study[J]. The Lancet, 2019, 394(10196): 407–418. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31147-X [132] WANG Chen, XU Jianying, YANG Lan, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health study): A national cross-sectional study[J]. The Lancet, 2018, 391(10131): 1706–1717. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30841-9 [133] VARON C, MORALES J, LÁZARO J, et al. A comparative study of ECG-derived respiration in ambulatory monitoring using the single-lead ECG[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 5704. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62624-5 [134] HA U, MADANI S, and ADIB F. WiStress: Contactless stress monitoring using wireless signals[J]. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2021, 5(3): 1–37. doi: 10.1145/3478121 [135] BAI Yang, GUAN Yu, and NG Wanfai. Fatigue assessment using ECG and actigraphy sensors[C]. The 2020 International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Virtual Event, Mexico, 2020: 12–16. [136] DE VRIES J, MICHIELSEN H, VAN HECK G L, et al. Measuring fatigue in sarcoidosis: The Fatigue Assessment Scale (FAS)[J]. British Journal of Health Psychology, 2004, 9(3): 279–291. doi: 10.1348/1359107041557048 [137] LIU Jie, ZHANG Kai, HE Wei, et al. Non-contact human fatigue assessment system based on millimeter wave radar[C]. 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics Technology (ICET), Chengdu, China, 2021: 173–177. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: