Fast Algorithm for Joint Waveform and Filter Design against Interrupted Sampling Repeater Jamming
-
摘要: 该文研究了一种快速的抗间歇采样转发干扰波形和滤波器联合设计方法。基于罚函数和帕累托最优化原理给出了联合设计模型的优化数学模型。推导优化波形和滤波器过程中矩阵迹的解析表达式,有效降低了算法的计算复杂度。提出了一种基于平方迭代加速方法,解决了主分量最小化方法目标函数近似造成的算法收敛速度降低问题,进一步加快了算法运行速度。仿真结果表明,该文所提出的算法比传统方法具有更快的运行速度。同时,当干扰目标和真实目标在距离上不可分时,该文方法仍能够有效抑制间歇采样转发干扰。Abstract: To suppress interrupted sampling jamming, a joint waveform and filter design method was proposed in this study. A fast algorithm was also suggested to design sequences with large code lengths. The joint design problem was formulated on the basis of the penalty function and Pareto optimization method. By deriving the theoretical solution of the trace of matrices in each iteration, the computation order of the proposed algorithm was decreased significantly compared to that of the conventional algorithm. Moreover, an accelerated scheme based on the squared iterative method, which further improves the running speed of the algorithm, was proposed. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm runs faster than traditional algorithms. Moreover, the designed waveform and filter can be applied to suppress interrupted sampling repeater jamming when the false targets are inseparable from the true targets in time-frequency domains.
-
表 1 快速抗间歇采样转发干扰波形和滤波器联合设计算法
Table 1. Fast algorithm for joint waveform and filter design against interrupted sampling repeater jamming
输入:波形和滤波器长度N 1:用随机相位编码序列初始化${{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( 0 \right)}}$ 和${{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( 0 \right)}}$; 2:重复 3: $ {{\boldsymbol{h}}_1} = F\left( {{{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( l \right)}},{{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( l \right)}}} \right) $ 4: $ {{\boldsymbol{h}}_2} = F\left( {{{\boldsymbol{h}}_1},{{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( l \right)}}} \right) $ 5: ${{\boldsymbol{r}}_1} = {{\boldsymbol{h}}_1} - {{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( l \right)}}$ 6: ${{\boldsymbol{v}}_1} = {{\boldsymbol{h}}_2} - {{\boldsymbol{h}}_1} - {{\boldsymbol{r}}_1}$ 7: $ {\alpha _1} = - {{{{\left\| {{{\boldsymbol{r}}_1}} \right\|}_2}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{{\left\| {{{\boldsymbol{r}}_1}} \right\|}_2}} {{{\left\| {{{\boldsymbol{v}}_1}} \right\|}_2}}}} \right. } {{{\left\| {{{\boldsymbol{v}}_1}} \right\|}_2}}} $ 8: $ {{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( {l + 1} \right)}} = F\left( {{{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( l \right)}} - 2{\alpha _1}{{\boldsymbol{r}}_1} + \alpha _1^2{{\boldsymbol{v}}_1},{{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( l \right)}}} \right) $ 9: 若$ f\left( {{{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( l \right)}},{{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( {l + 1} \right)}}} \right) > f\left( {{{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( l \right)}},{{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( l \right)}}} \right) $,循环 10: $ {\alpha _1} \leftarrow {{\left( {{\alpha _1} - 1} \right)} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\left( {{\alpha _1} - 1} \right)} 2}} \right. } 2} $ 11: $ {{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( {l + 1} \right)}} = F\left( {{{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( l \right)}} - 2\alpha {{\boldsymbol{r}}_1} + {\alpha ^2}{{\boldsymbol{v}}_1},{{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( l \right)}}} \right) $ 12: 结束 13: $ {{\boldsymbol{x}}_1} = G\left( {{{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( {l + 1} \right)}},{{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( l \right)}}} \right) $ 14: $ {{\boldsymbol{x}}_2} = G\left( {{{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( {l + 1} \right)}},{{\boldsymbol{x}}_1}} \right) $ 15: ${{\boldsymbol{r}}_2} = {{\boldsymbol{x}}_1} - {{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( l \right)}}$ 16: ${{\boldsymbol{v}}_2} = {{\boldsymbol{x}}_2} - {{\boldsymbol{x}}_1} - {{\boldsymbol{r}}_1}$ 17: $ {\alpha _2} = - {{{{\left\| {{{\boldsymbol{r}}_2}} \right\|}_2}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{{\left\| {{{\boldsymbol{r}}_2}} \right\|}_2}} {{{\left\| {{{\boldsymbol{v}}_2}} \right\|}_2}}}} \right. } {{{\left\| {{{\boldsymbol{v}}_2}} \right\|}_2}}} $ 18: $ {{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( {l + 1} \right)}} = G\left( {{{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( {l + 1} \right)}},{{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( l \right)}} - 2{\alpha _2}{{\boldsymbol{r}}_2} + \alpha _2^2{{\boldsymbol{v}}_2}} \right) $ 19: 若$ f\left( {{{{\boldsymbol{\tilde x}}}^{\left( l \right)}},{{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( {l + 1} \right)}}} \right) > f\left( {{{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( l \right)}},{{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( {l + 1} \right)}}} \right) $,循环 20: $ {\alpha _2} \leftarrow {{\left( {{\alpha _2} - 1} \right)} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\left( {{\alpha _2} - 1} \right)} 2}} \right. } 2} $ 21: $ {{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( {l + 1} \right)}} = G\left( {{{\boldsymbol{h}}^{\left( {l + 1} \right)}},{{\boldsymbol{x}}^{\left( l \right)}} - 2{\alpha _2}{{\boldsymbol{r}}_2} + \alpha _2^2{{\boldsymbol{v}}_2}} \right) $ 22: 结束 23: $l \leftarrow l + 1$ 24: 直至收敛 输出:波形和滤波器。 表 2 算法性能对比
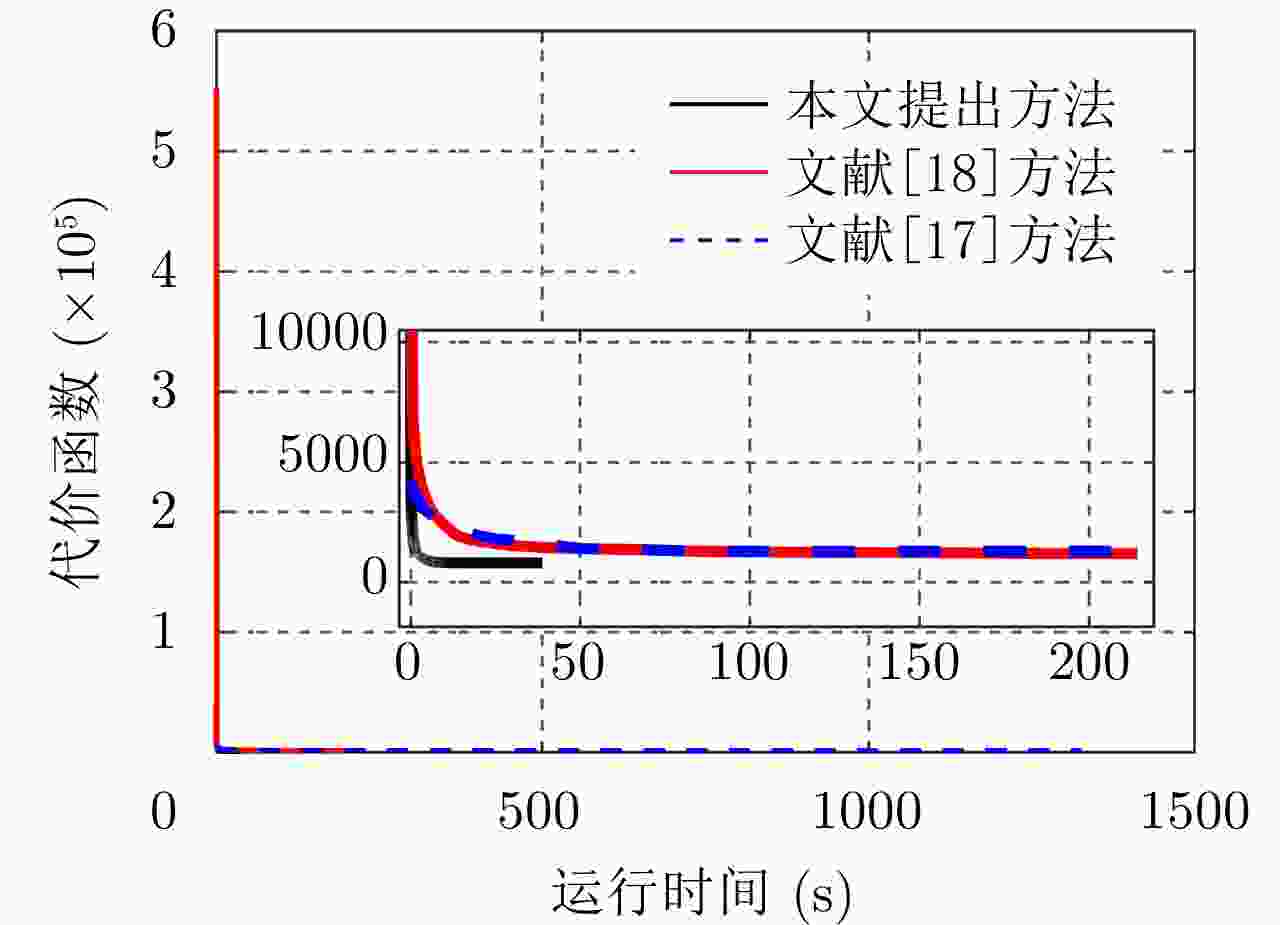
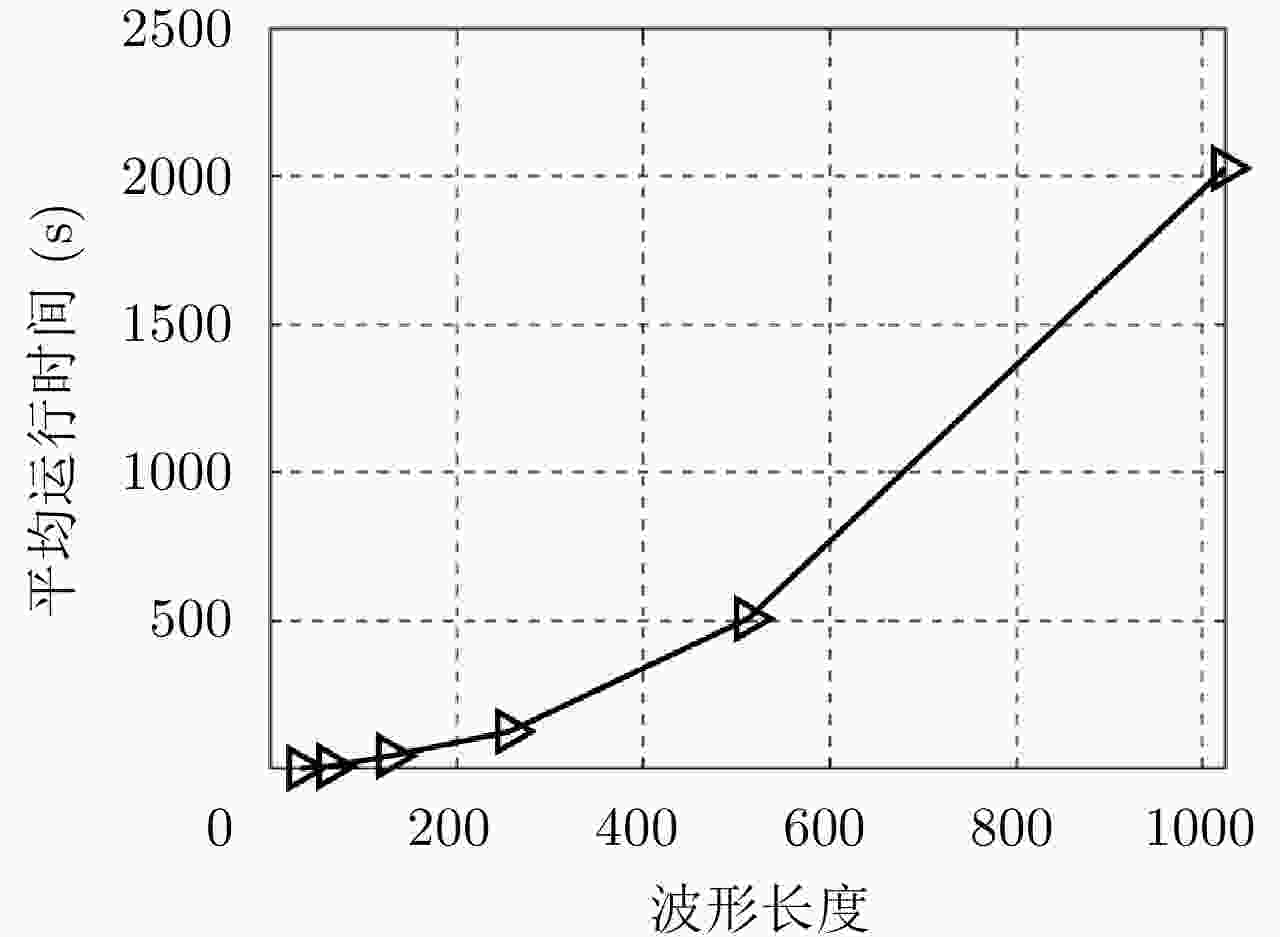
Table 2. Performance comparison of tested algorithms
表 3 仿真参数
Table 3. Simulation parameters
参数 数值 时宽(μs) 40 带宽(MHz) 20 采样重复周期(μs) 10 采样信号时宽(μs) 2.5 雷达位置(m) (0,0,0) 干扰机位置(m) (0,2000,0) 目标位置(m) (0,3000,0) 干扰机时延(μs) 2 表 4 两组波形和非匹配滤波器性能对比
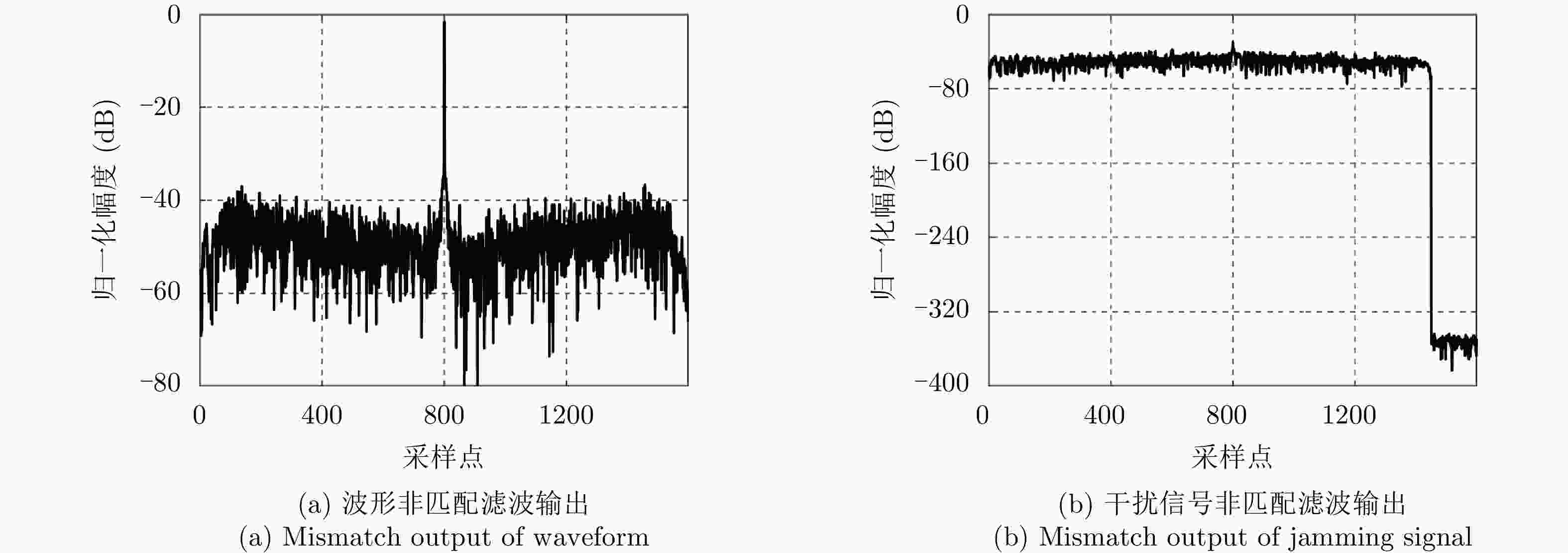
Table 4. The mismatch output performance of designed waveform via tested algorithms
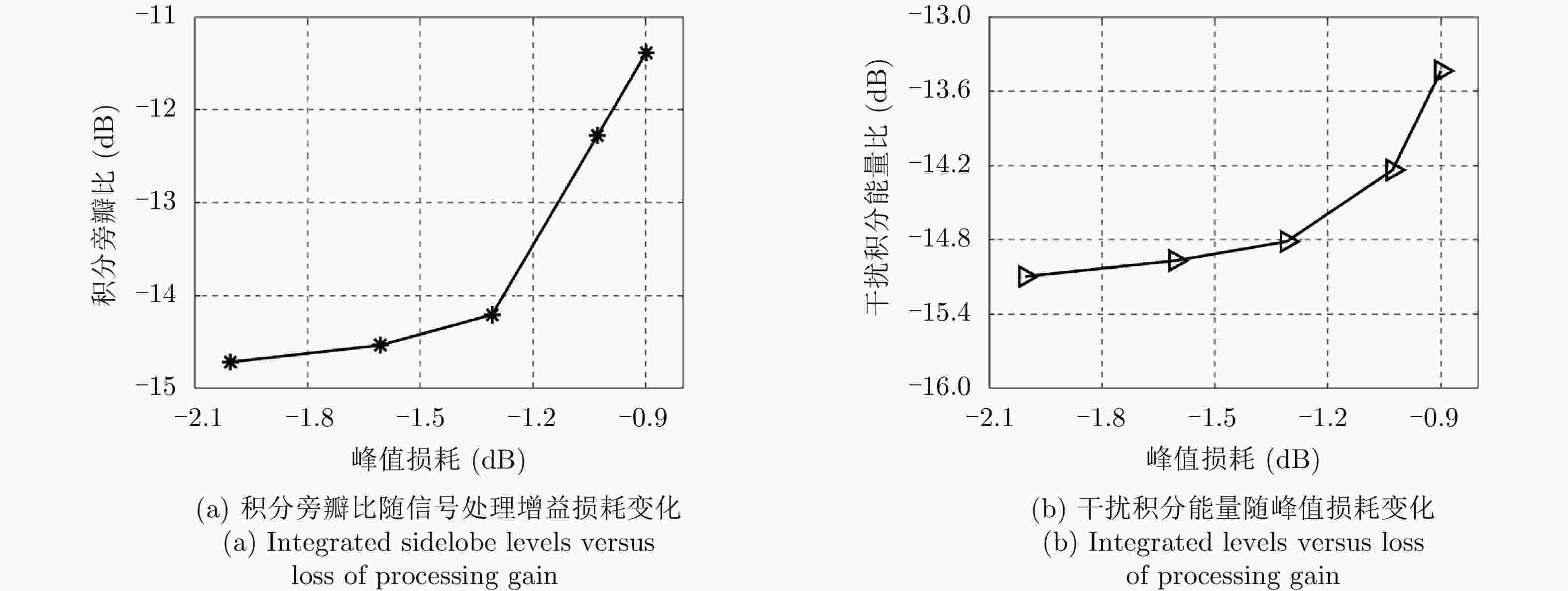
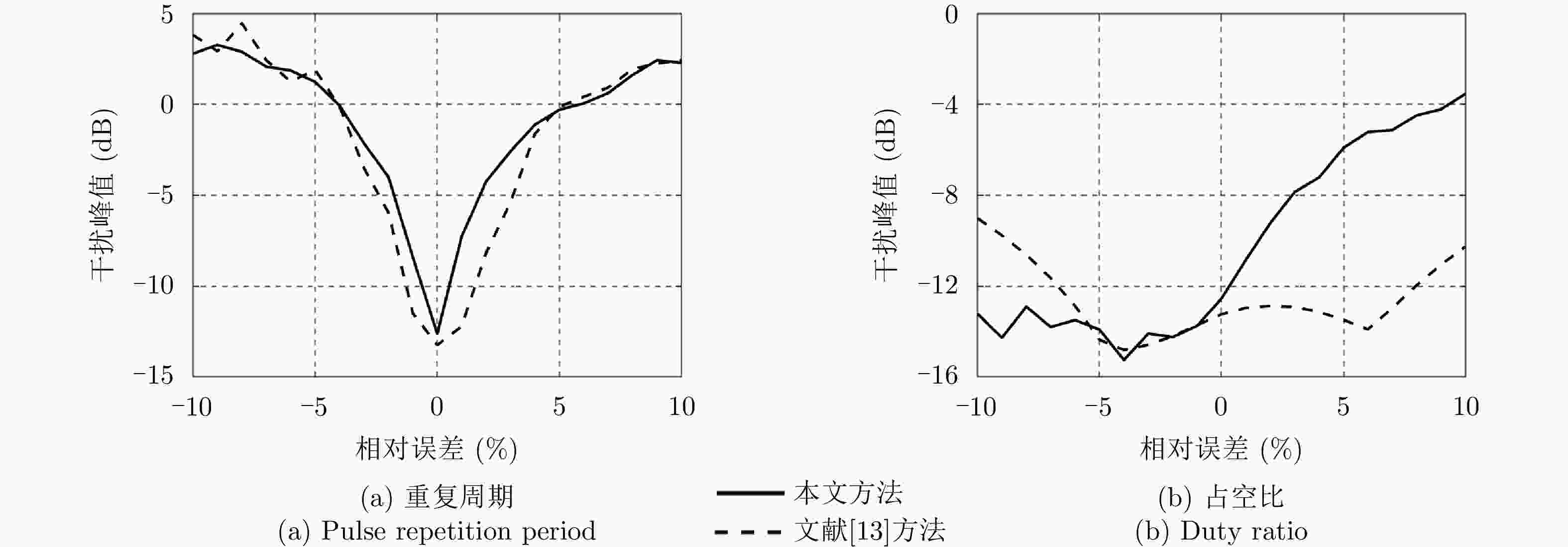
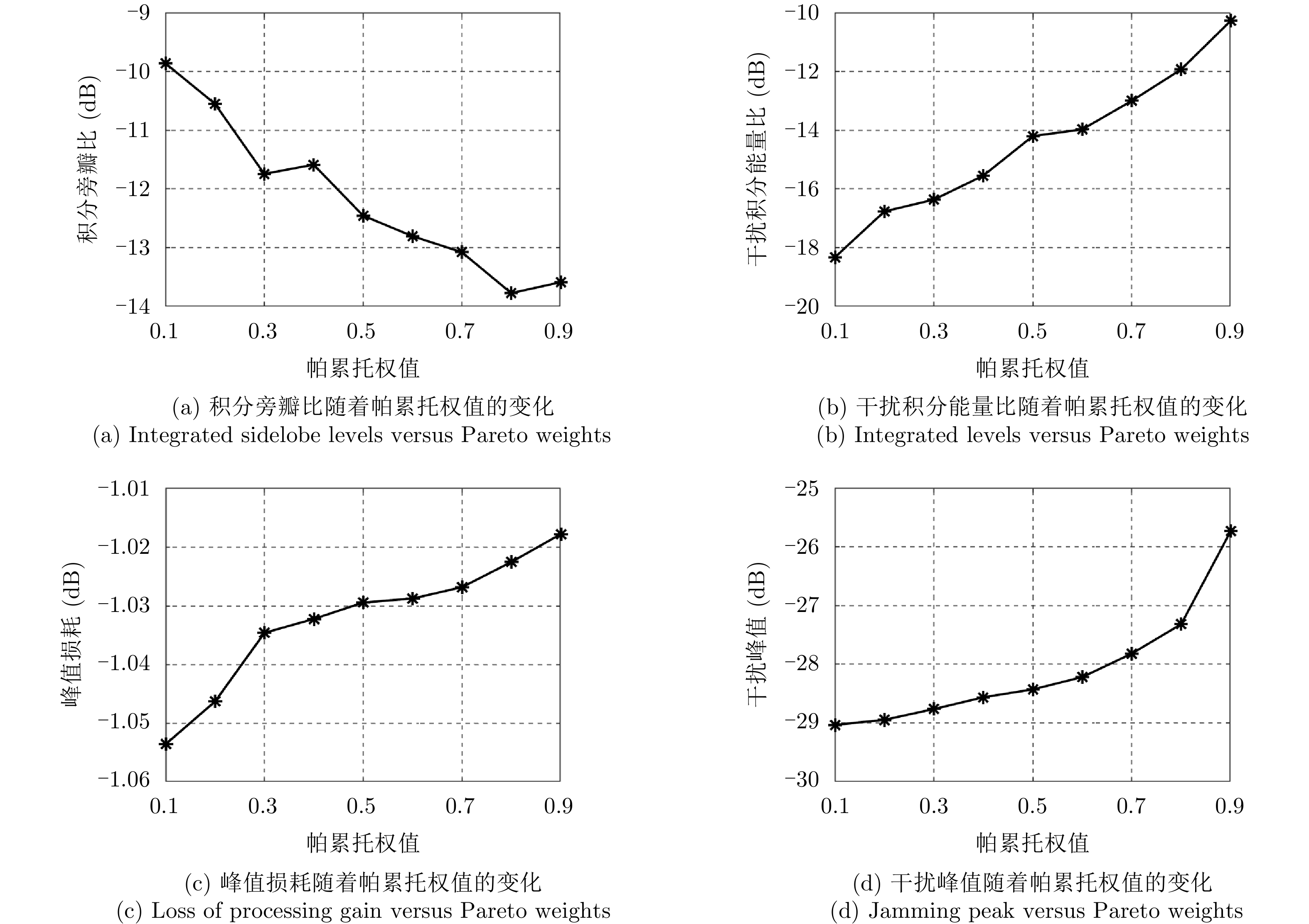
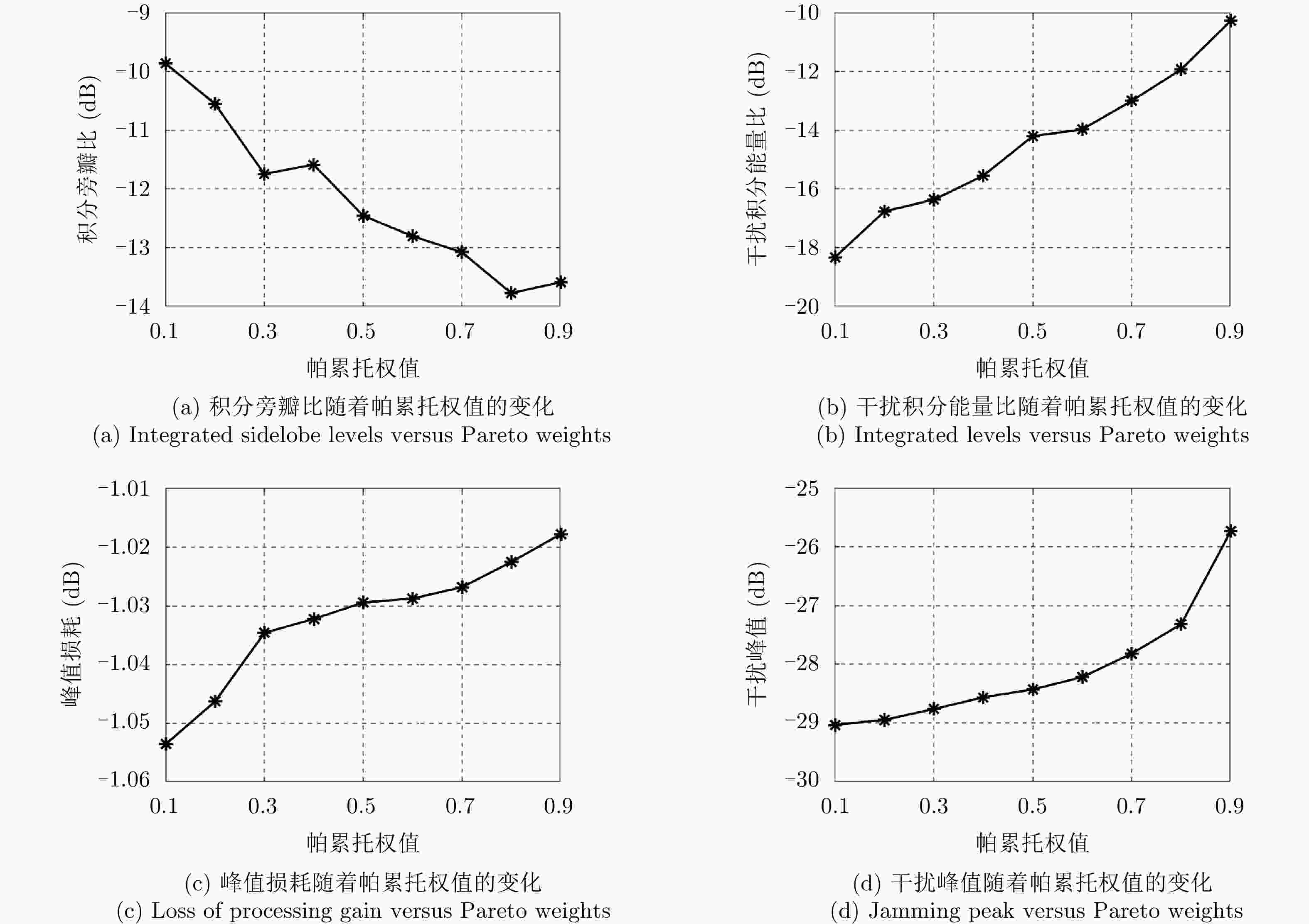
方法 LPG (dB) ISLR (dB) ILs (dB) Peak interference (dB) 文献[17] –1.61 –11.73 –14.29 –30.00 本文方法 –1.61 –12.60 –14.52 –29.99 -
[1] HEAGNEY C P. Digital radio frequency memory synthetic instrument enhancing US navy automated test equipment mission[J]. IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine, 2018, 21(4): 41–63. doi: 10.1109/MIM.2018.8423745 [2] SOUMEKH M. SAR-ECCM using phase-perturbed LFM chirp signals and DRFM repeat jammer penalization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 191–205. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603414 [3] 李永祯, 黄大通, 邢世其, 等. 合成孔径雷达干扰技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 753–764. doi: 10.12000/JR20087LI Yongzhen, HUANG Datong, XING Shiqi, et al. A review of synthetic aperture radar jamming technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 753–764. doi: 10.12000/JR20087 [4] TIAN Tian, ZHOU Feng, BAI Xueru, et al. A partitioned deceptive jamming method against TOPSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(2): 1538–1552. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2933958 [5] WANG Xuesong, LIU Jiancheng, ZHANG Wenming, et al. Mathematic principles of interrupted-sampling repeater jamming (ISRJ)[J]. Science in China Series F:Information Sciences, 2007, 50(1): 113–123. doi: 10.1007/s11432-007-2017-y [6] FENG Dejun, XU Letao, PAN Xiaoyi, et al. Jamming wideband radar using interrupted-sampling repeater[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1341–1354. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2670958 [7] 吴晓芳, 王雪松, 卢焕章. 对SAR的间歇采样转发干扰研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2009, 30(5): 2043–2048, 2072. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2009.05.050WU Xiaofang, WANG Xuesong, and LU Huanzhang. Study of intermittent sampling repeater jamming to SAR[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2009, 30(5): 2043–2048, 2072. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2009.05.050 [8] 杨伟宏, 陈永光, 王涛. 对波形捷变SAR的间歇采样快/慢时间调制干扰[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2012, 34(12): 2456–2462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506x.2012.12.09YANG Weihong, CHEN Yongguang, and WANG Tao. Intermittent sampling jamming against waveform agile SAR modulated in fast or slow time[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 34(12): 2456–2462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506x.2012.12.09 [9] WU Qihua, ZHAO Feng, AI Xiaofeng, et al. Two-dimensional blanket jamming against ISAR using nonperiodic ISRJ[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(11): 4031–4038. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2897363 [10] 周超, 刘泉华, 胡程. 间歇采样转发式干扰的时频域辨识与抑制[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 100–106. doi: 10.12000/JR18080ZHOU Chao, LIU Quanhua, and HU Cheng. Time-frequency analysis techniques for recognition and suppression of interrupted sampling repeater jamming[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 100–106. doi: 10.12000/JR18080 [11] WU Wenzhen, ZOU Jiangwei, CHEN Jian, et al. False-target recognition against interrupted-sampling repeater jamming based on integration decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(5): 2979–2991. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3068443 [12] CHEN Jian, WU Wenzhen, XU Shiyou, et al. Band pass filter design against interrupted-sampling repeater jamming based on time-frequency analysis[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(10): 1646–1654. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5658 [13] ZHOU Chao, LIU Quanhua, and CHEN Xinliang. Parameter estimation and suppression for DRFM-based interrupted sampling repeater jammer[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(1): 56–63. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0114 [14] 周畅, 汤子跃, 朱振波, 等. 抗间歇采样转发干扰的波形设计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(9): 2198–2205. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171236ZHOU Chang, TANG Ziyue, ZHU Zhenbo, et al. Anti-interrupted sampling repeater jamming waveform design method[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(9): 2198–2205. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171236 [15] 周畅, 汤子跃, 余方利, 等. 基于脉内正交的抗间歇采样转发干扰方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2017, 39(2): 269–276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.02.06ZHOU Chang, TANG Ziyue, YU Fangli, et al. Anti intermittent sampling repeater jamming method based on intrapulse orthogonality[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(2): 269–276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.02.06 [16] 张建中, 穆贺强, 文树梁, 等. 基于脉内步进LFM波形的抗间歇采样转发干扰方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(5): 1013–1020. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.05.12ZHANG Jianzhong, MU Heqiang, WEN Shuliang, et al. Anti interrupted-sampling repeater jamming method based on stepped LFM waveform[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(5): 1013–1020. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.05.12 [17] ZHOU Kai, LI Dexin, SU Yi, et al. Joint design of transmit waveform and mismatch filter in the presence of interrupted sampling repeater jamming[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 1610–1614. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.3021667 [18] ZHOU Kai, LI Dexin, QUAN Sinong, et al. SAR waveform and mismatched filter design for countering interrupted-sampling repeater jamming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5214514. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3107328 [19] 周凯, 李德鑫, 粟毅, 等. 基于雷达发射波形和非匹配滤波联合设计的间歇采样转发干扰抑制方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(7): 1939–1946. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200299ZHOU Kai, LI Dexin, SU Yi, et al. Joint transmitted waveform and mismatched filter design against interrupted-sampling repeater jamming[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(7): 1939–1946. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200299 [20] ZHOU Kai, QUAN Sinong, LI Dexin, et al. Waveform and filter joint design method for pulse compression sidelobe reduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5107615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3131590 [21] SONG Junxiao, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Optimization methods for designing sequences with low autocorrelation sidelobes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(15): 3998–4009. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2425808 [22] SONG Junxiao, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Sequence set design with good correlation properties via majorization-minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(11): 2866–2879. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2535312 [23] SUN Ying, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Majorization-minimization algorithms in signal processing, communications, and machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(3): 794–816. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2601299 [24] LIANG Junli, SO H C, LI Jian, et al. Unimodular sequence design based on alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(20): 5367–5381. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2597123 [25] CHANG Huibin, ENFEDAQUE P, MARCHESINI S, et al. Blind ptychographic phase retrieval via convergent alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2019, 12(1): 153–185. doi: 10.1137/18M1188446 [26] BOLTE J, SABACH S, and TEBOULLE M. Proximal alternating linearized minimization for nonconvex and nonsmooth problems[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2014, 146(1/2): 459–494. doi: 10.1007/s10107-013-0701-9 [27] GEIPING J and MOELLER M. Composite optimization by nonconvex majorization-minimization[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2018, 11(4): 2494–2528. doi: 10.1137/18M1171989 [28] VARADHAN R and ROLAND C. Simple and globally convergent methods for accelerating the convergence of any EM algorithm[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 2008, 35(2): 335–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9469.2007.00585.x [29] ZHAO Licheng, SONG Junxiao, BABU P, et al. A unified framework for low autocorrelation sequence design via majorization-minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(2): 438–453. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2620113 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: