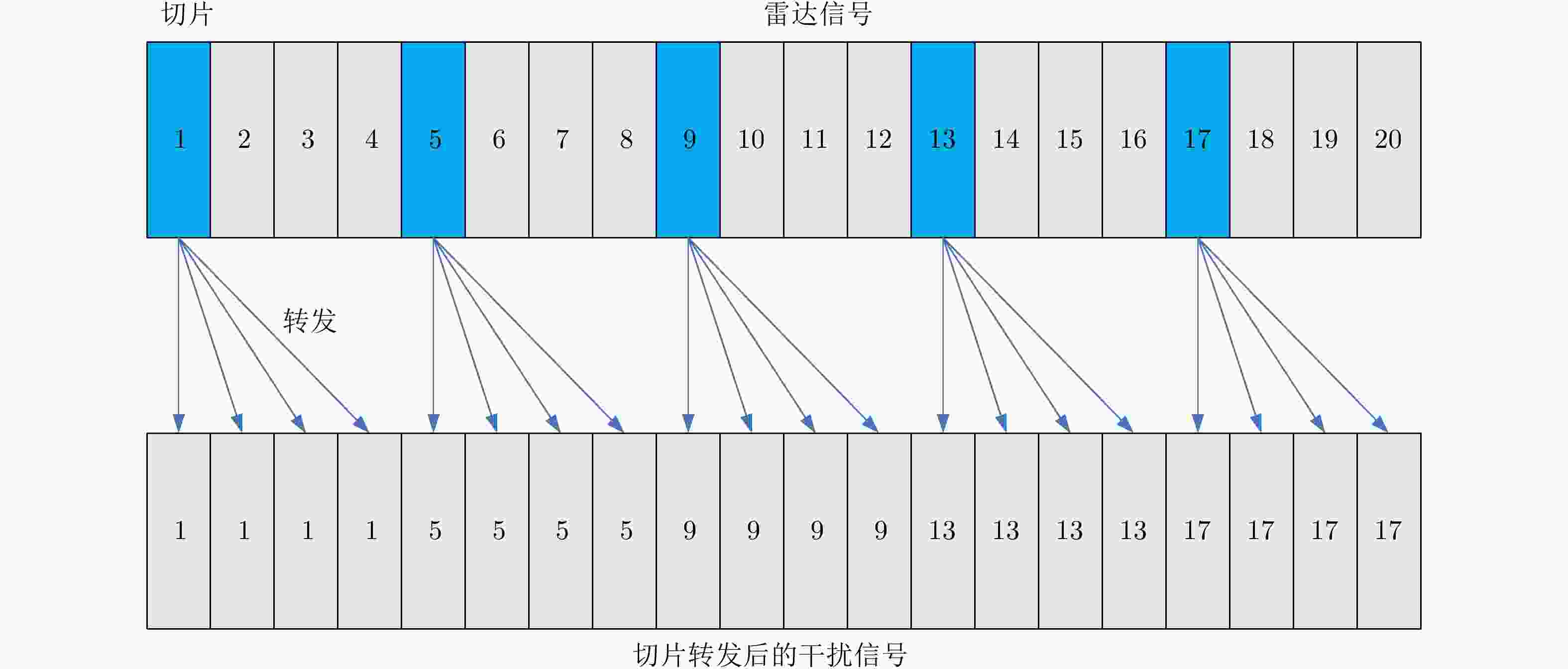
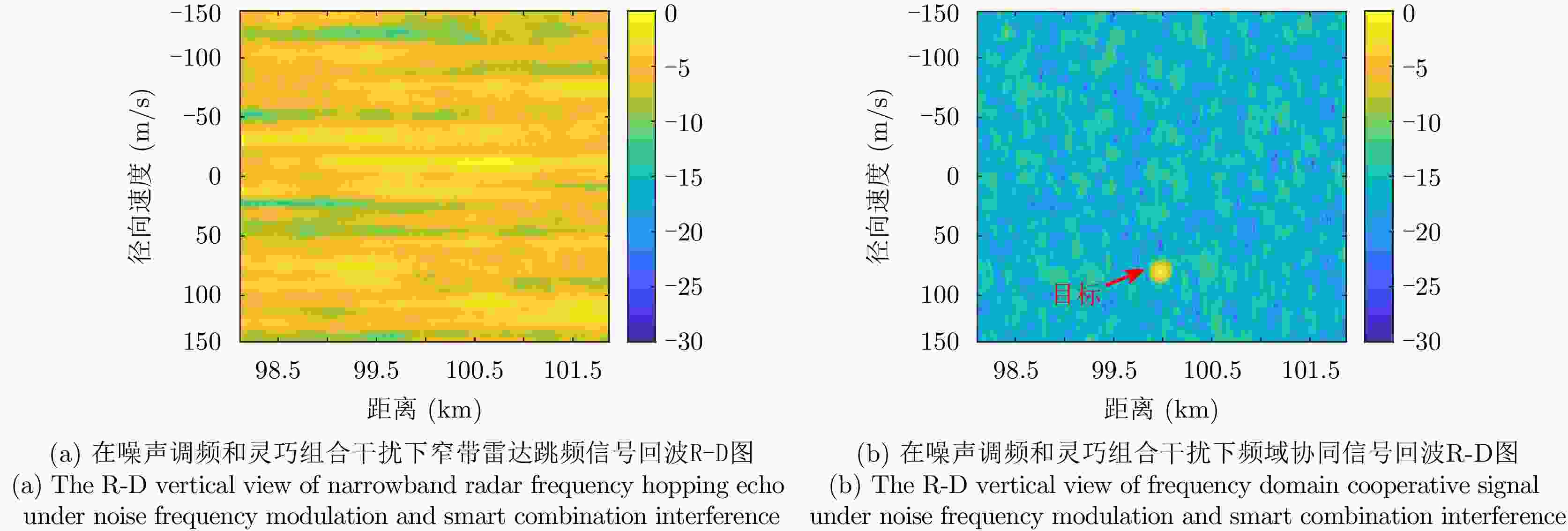
-
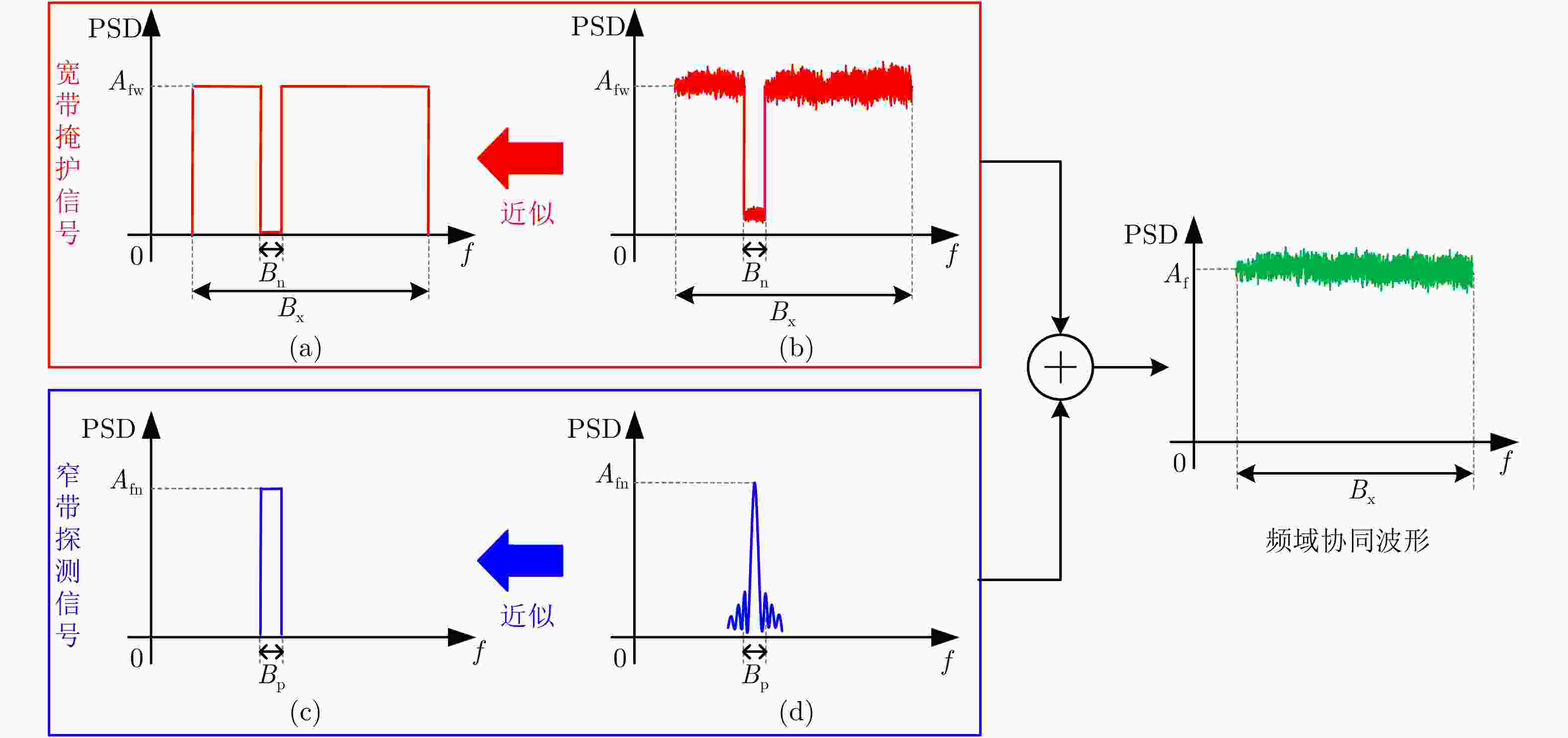
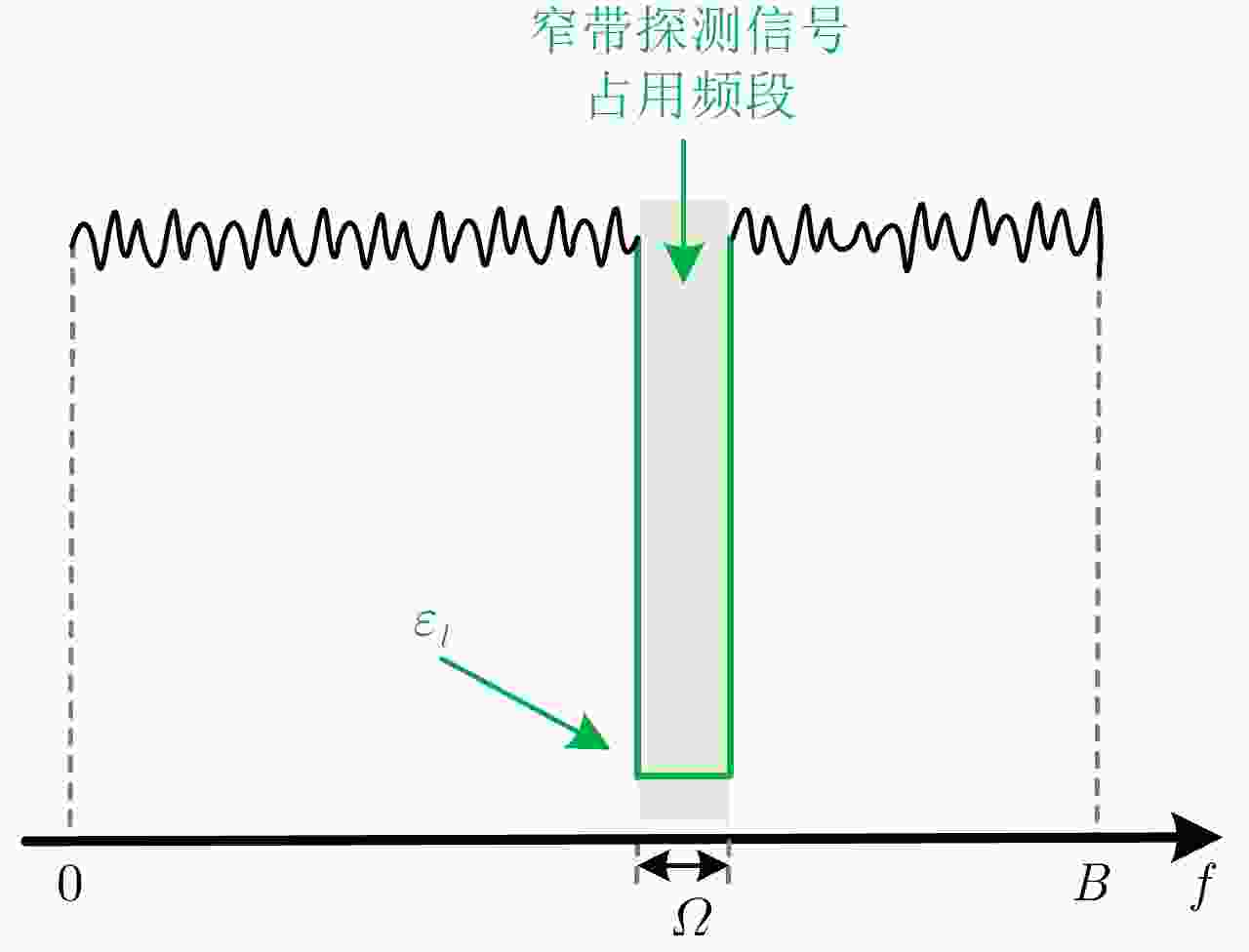
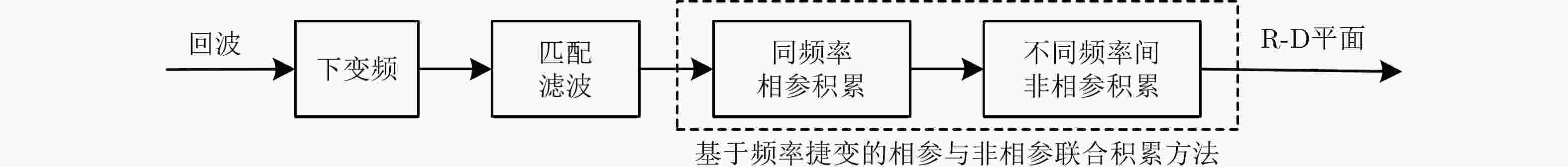
摘要: 多节点收发分置系统通过波形在空时频能等多域进行协同工作,能够提供相比单雷达更多的抗干扰自由度。该文针对抗多主瓣干扰问题,提出一种基于两部短基线收发分置系统的频域协同波形设计方法。首先,利用基于MM原理的近端乘子法(MM-PMM)算法,优化设计具有局部良好自相关电平的窄带探测信号;接着,依据窄带探测信号脉间频率跳变特点,优化对应的宽带频谱置零信号,作为窄带信号的掩护信号;然后,利用两个发射节点分别将窄带与宽带信号进行协同发射;最后,利用基于频率捷变的相参和非相参联合积累的信号处理方法实现对频域协同波形回波的处理。数值仿真实验验证了频域协同波形设计方法算法收敛性、频域掩护原理以及抗多主瓣干扰的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 短基线 /
- 频域协同波形 /
- 抗干扰 /
- 低截获概率 /
- 相参与非相参联合积累
Abstract: Multinode transceiver division systems can cooperate across multiple domains, including space, time, frequency, and energy, through waveforms. Moreover, it can provide greater anti-interference degrees of freedom than that from a single radar. Through this paper, we propose a frequency domain cooperative waveform design method based on two short baseline transceiver separation systems to resist multi-mainlobe interference. First, a narrowband detection signal with a locally good autocorrelation level was optimized using the Majorization-Minimization-based Proximal Method of Multipliers (MM-PMM) algorithm. Then, according to the characteristics of the frequency hopping of the narrowband detection signal, the corresponding wideband signal with a null spectrum was optimized as the cover signal of a narrowband signal. Further, two transmitting nodes were used to transmit the narrowband and wideband signals. Finally, a signal processing method based on phase-coherent and nonphase-coherent joint accumulation, with known frequency agility was used to process the cooperative waveform in the frequency domain. Numerical simulation results demonstrated the convergence of the MM-PMM algorithm, principle of frequency domain cover, and effectiveness of the frequency domain cooperative waveform design method against multi-mainlobe interference. -
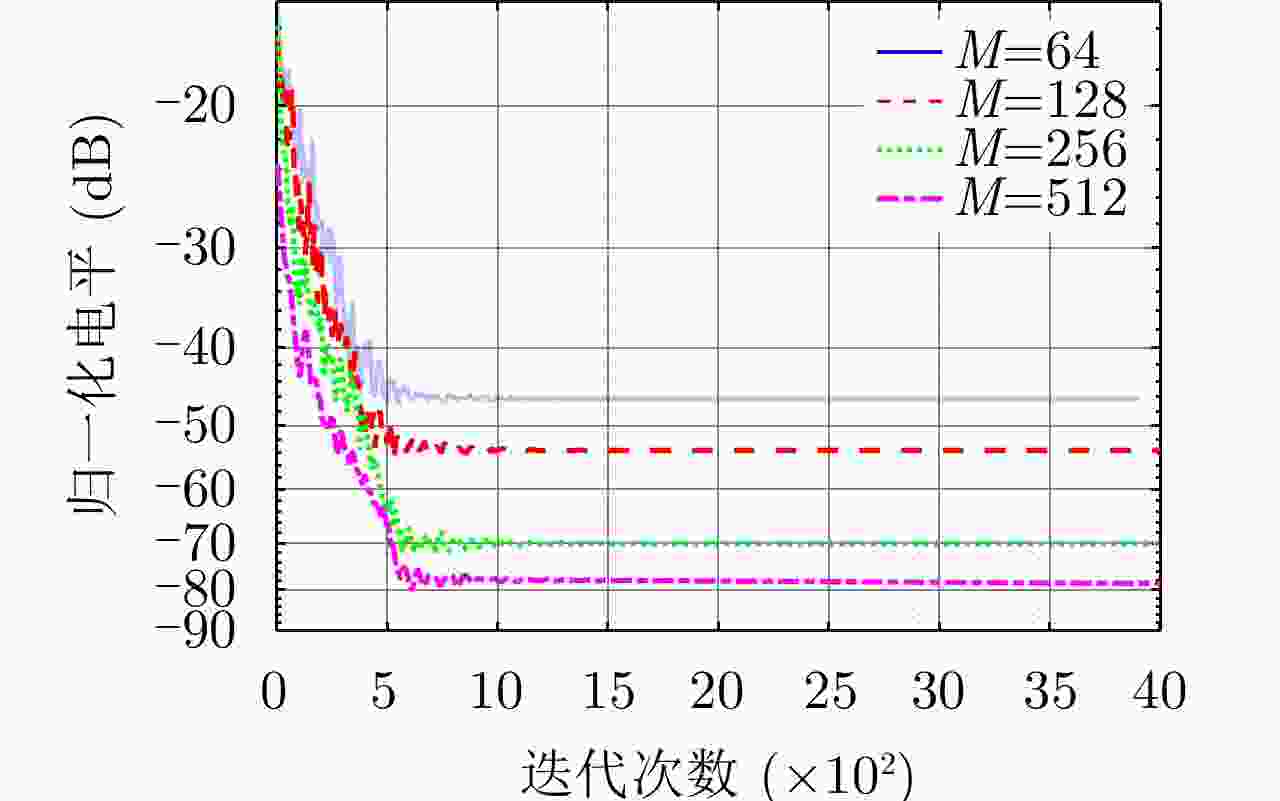
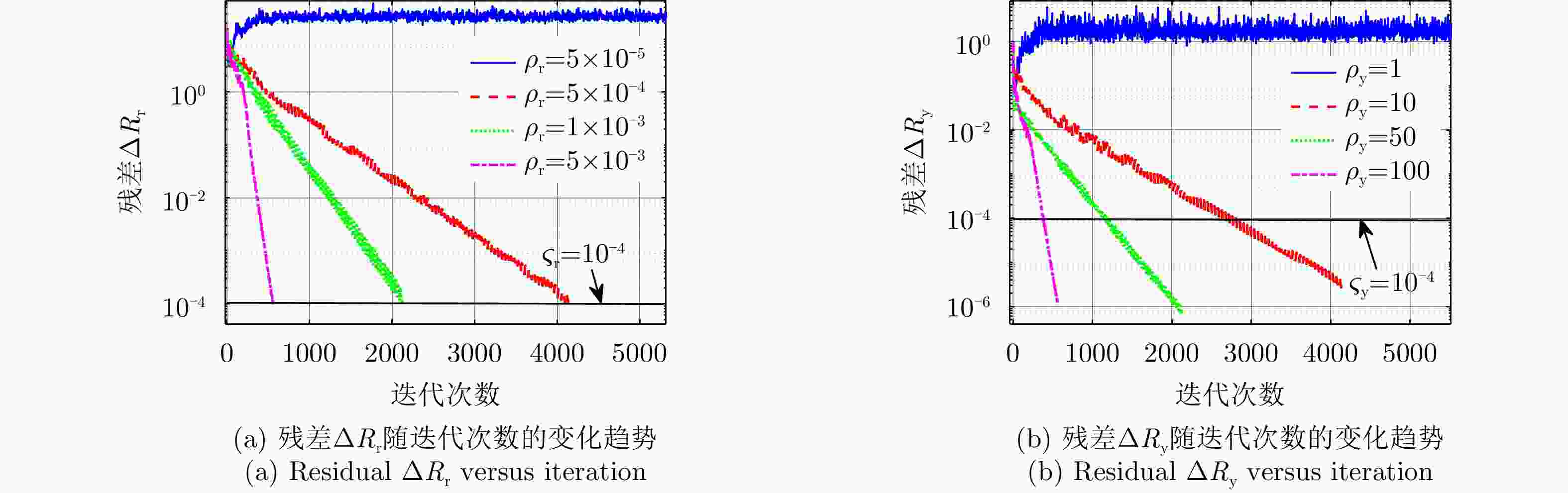
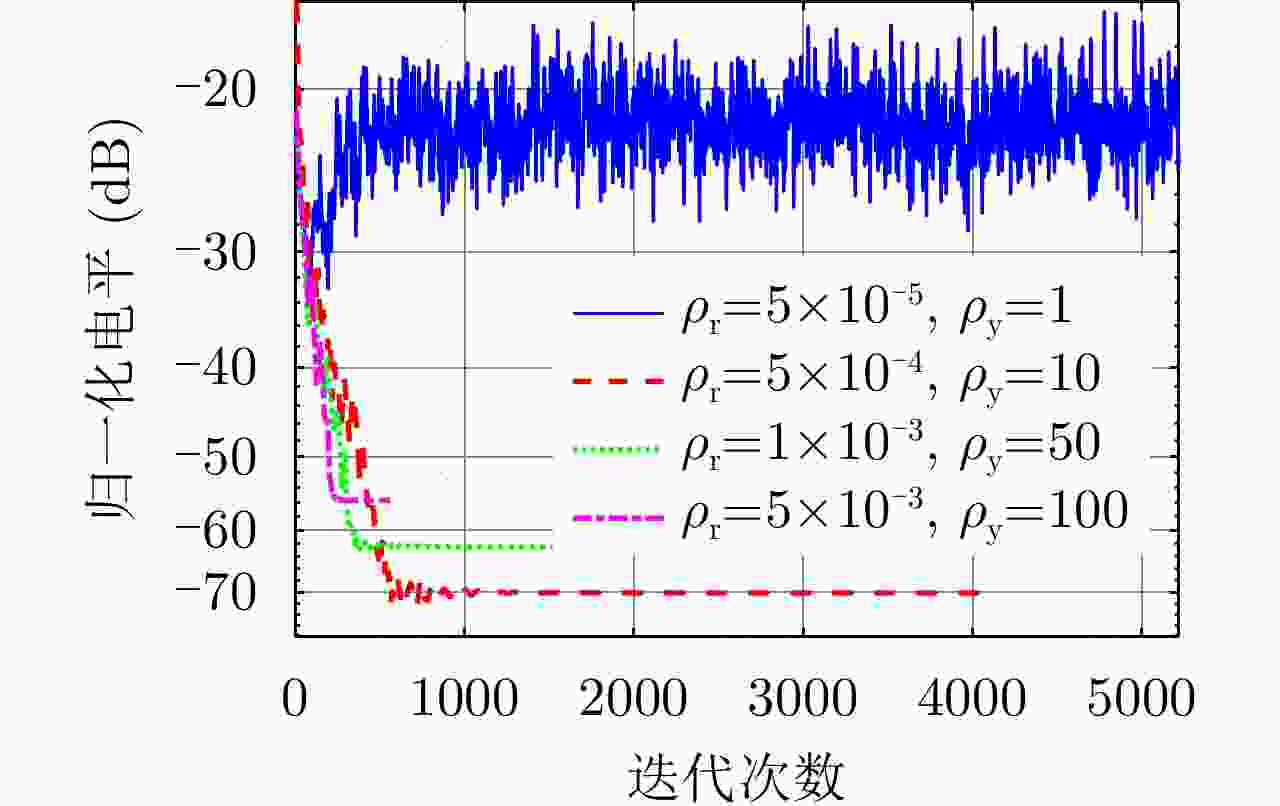
表 1 惩罚参数设置
Table 1. Simulation parameters of penalty parameters
情况 惩罚参数${\rho _{\text{r}}}$ 惩罚参数${\rho _{\text{y}}}$ 情况1 $5 \times {10^{ - 5} }$ $1$ 情况2 $5 \times {10^{ - 4} }$ $10$ 情况3 $1 \times {10^{ - 3} }$ $50$ 情况4 $5 \times {10^{ - 3} }$ $100$ 表 2 频域协同波形仿真参数
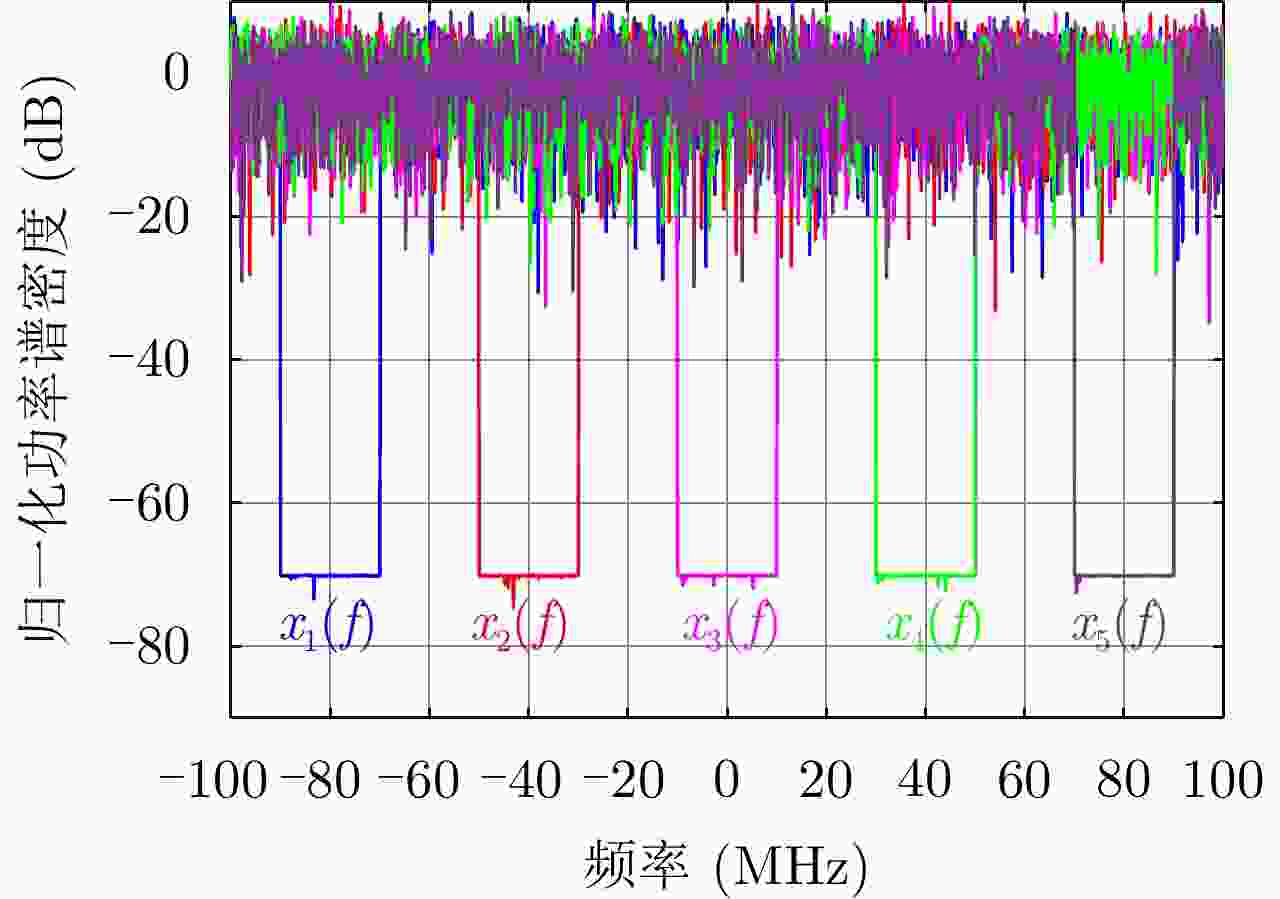
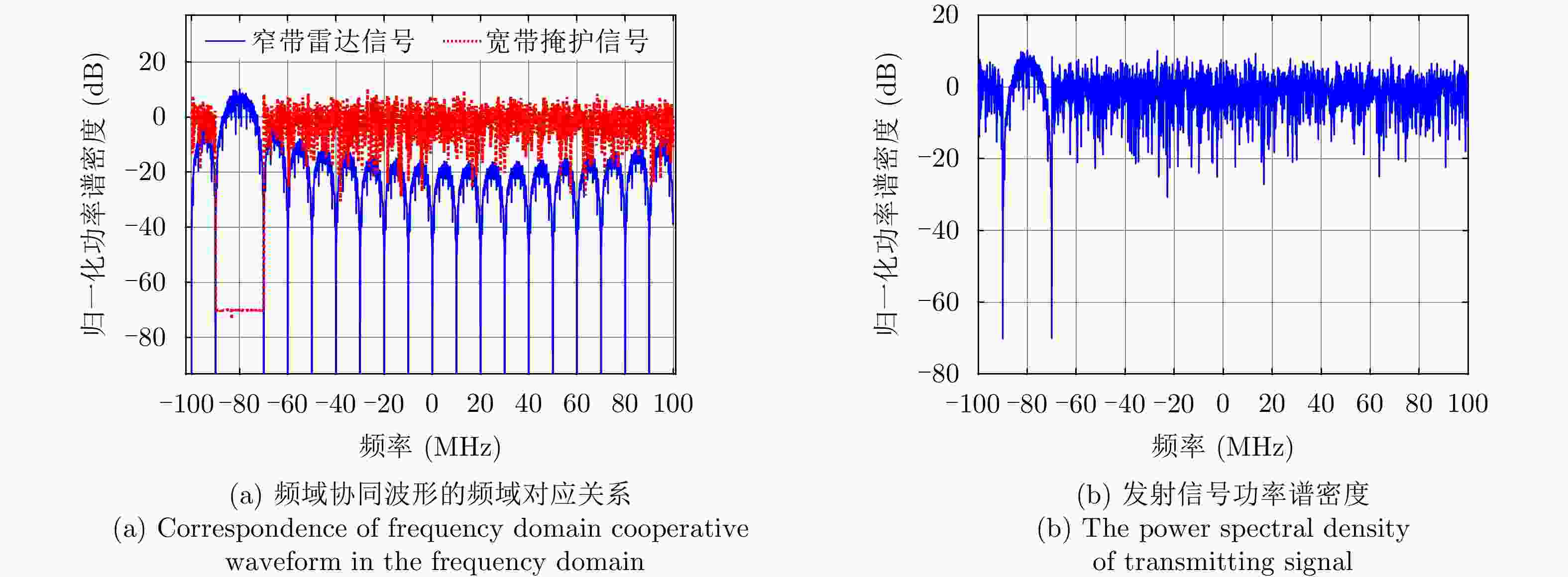
Table 2. Simulation parameters of frequency domain cooperative waveform
参数 数值 载频${f_{\text{c}}}$ 1 GHz 时宽T 10 μs 脉冲重复间隔${T_{\text{r}}}$ 100 μs 采样率${F_{\text{s}}}$ 200 MHz 脉冲个数$N$ 200 宽带信号带宽${B_{\text{x}}}$ 200 MHz 宽带信号的幅度${A_{\text{x}}}$ 1 窄带信号带宽${B_{\text{p}}}$ 10 MHz 窄带信号幅度${A_{\text{p}}}$ 0.5 跳频频点${f_z}$ [–80 –40 0 40 80] MHz 表 3 抗干扰场景参数
Table 3. Simulation parameters of anti-interference scenes
参数 数值 目标距离$R$ [99 101] km 目标速度$v$ [90 80] m/s 窄带探测信号信噪比SNR [15 10] dB 干噪比JNR 30 dB 表 4 抗干扰场景参数
Table 4. Simulation parameters of anti-interference scenes
参数 数值 目标距离$R$ 100 km 目标速度$v$ 80 m/s 窄带雷达信号信噪比SNR 15 dB 灵巧干扰假目标距离 [98 99] km 灵巧干扰假目标速度 [1 1] m/s 灵巧干扰干噪比JNR [35 30] dB 灵巧干扰切片时长$m$ [1 5] μs 灵巧干扰转发次数$n$ [5 3] 灵巧干扰中噪声信号等效带宽$\Delta B$ 10 MHz 噪声调频干扰干噪比JNR 30 dB -
[1] 谢绍斌. 载波调制混沌雷达信号理论研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2012.XIE Shaobin. Research on signal theory for carrier modulation chaotic radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2012. [2] 张锡熊, 陈方林. 雷达抗干扰原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1981.ZHANG Xixiong and CHEN Fanglin. Principle of Radar Anti-Interference[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1981. [3] 杨娟. 雷达射频掩护的认知抗干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2018.YANG Juan. Research on the cognitive anti-jamming technology of radar radio frequency-screen[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2018. [4] 胡祺勇, 谢军伟, 张浩为, 等. 掩护信号抗转发干扰技术研究[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2017, 37(4): 168–172. doi: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2017.04.039HU Qiyong, XIE Junwei, ZHANG Haowei, et al. Study on anti repeat jamming technology of screen signal[J]. Journal of Projectiles,Rockets,Missiles and Guidance, 2017, 37(4): 168–172. doi: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2017.04.039 [5] 金珊珊, 王春阳, 邱程, 等. 对抗应答式干扰的射频掩护脉冲设计[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2014, 9(4): 377–381. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2014.04.010JIN Shanshan, WANG Chunyang, QIU Cheng, et al. Design of RF protecting signal for transponder jamming suppression[J]. Journal of CAEIT, 2014, 9(4): 377–381. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2014.04.010 [6] 张昭建, 谢军伟, 杨春晓, 等. 掩护脉冲信号抗转发式欺骗干扰性能分析[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2016, 36(4): 149–152, 156. doi: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2016.04.039ZHANG Zhaojian, XIE Junwei, YANG Chunxiao, et al. Performance analysis of screening pulse signal confronts to deception jamming[J]. Journal of Projectiles,Rockets,Missiles and Guidance, 2016, 36(4): 149–152, 156. doi: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2016.04.039 [7] 周伟江, 王培强, 张进, 等. 雷达射频掩护信号分析及对抗方法研究[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2013, 29(5): 47–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2013.05.014ZHOU Weijiang, WANG Peiqiang, ZHANG Jin, et al. Analysis and countermeasures of radar radio frequency-screen signal[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2013, 29(5): 47–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2013.05.014 [8] 蒋铁珍, 廖同庆. 分布式雷达抗主瓣干扰方法研究[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2015, 10(4): 389–394. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2015.04.011JIANG Tiezhen and LIAO Tongqing. Research on anti-mainlobe jamming method of distributed radar based on LMS algorithm[J]. Journal of CAEIT, 2015, 10(4): 389–394. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2015.04.011 [9] 付姣姣. 双站协同抗干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京理工大学, 2019.FU Jiaojiao. Research on cooperative interference interference technology of two stations[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2019. [10] 杨超, 蒋卫锋. 雷达有源诱饵设计考虑因素[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2016, 36(5): 81–82, 95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2016.05.021YANG Chao and JIANG Weifeng. Considerations for radar active decoy design[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2016, 36(5): 81–82, 95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2016.05.021 [11] CUI Guolong, YANG Jing, LU Shuping, et al. Dual-use unimodular sequence design via frequency nulling modulation[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 62470–62481. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2876644 [12] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 杨婧, 等. 认知雷达波形优化设计方法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 537–557. doi: 10.12000/JR19072CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, YANG Jing, et al. An overview of waveform optimization methods for cognitive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 537–557. doi: 10.12000/JR19072 [13] BOHRA P and UNSER M. Continuous-domain signal reconstruction using L p-norm regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 4543–4554. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3013781 [14] SONG Junxiao, BABU P, and PALOMAR D P. Sequence design to minimize the weighted integrated and peak sidelobe levels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(8): 2051–2064. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2510982 [15] FAN Wen, LIANG Junli, YU Guoyang, et al. MIMO radar waveform design for quasi-equiripple transmit beampattern synthesis via weighted L p-minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(13): 3397–3411. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2917871 [16] FAN Wen, LIANG Junli, YU Guoyang, et al. Minimum local peak sidelobe level waveform design with correlation and/or spectral constraints[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 171: 107450. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.107450 [17] DHINGRA N K, KHONG S Z, and JOVANOVIĆ M R. The proximal augmented lagrangian method for nonsmooth composite optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(7): 2861–2868. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2867589 [18] BU Yi, YU Xianxiang, YANG Jing, et al. A new approach for design of constant modulus discrete phase radar waveform with low WISL[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 187: 108145. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108145 [19] TANG Bo and LIANG Junli. Efficient algorithms for synthesizing probing waveforms with desired spectral shapes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(3): 1174–1189. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2876585 [20] PATTON L K and RIGLING B D. Phase retrieval for radar waveform optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(4): 3287–3302. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6324705 [21] ROWE W, STOICA P, and LI Jian. Spectrally constrained waveform design [sp Tips&Tricks][J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(3): 157–162. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2301792 [22] 张洋. 弹载环境下雷达抗干扰波形设计研究[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.ZHANG Yang. Research on anti-jamming waveform design of missile-borne radar[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. [23] 孟祥东, 夏德平. 脉冲间跳频波形的相参积累目标检测方法[J]. 现代雷达, 2022, 44(3): 70–75. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.03.012MENG Xiangdong and XIA Deping. Coherent integration methods for detecting targets in inter-pulse frequency hopping waveform[J]. Modern Radar, 2022, 44(3): 70–75. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.03.012 [24] LU Qinghui, CUI Guolong, LIU Ruitao, et al. Wideband beampattern synthesis using single digital beamformer with integer time delay flters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, in press. [25] 彭德强. 线性调频信号和噪声调频信号性能对比分析[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2021, 44(1): 22–26. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2021.01.005PENG Deqiang. Analysis of the performance comparison between LFM signal and noise FM signal[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2021, 44(1): 22–26. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2021.01.005 [26] 金珊珊, 王春阳, 李欣. 灵巧干扰及其对抗技术综述[J]. 现代防御技术, 2014, 42(4): 131–135, 142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2014.04.022JIN Shanshan, WANG Chunyang, and LI Xin. Overview on smart noise jamming and countermeasures[J]. Modern Defense Technology, 2014, 42(4): 131–135, 142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2014.04.022 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
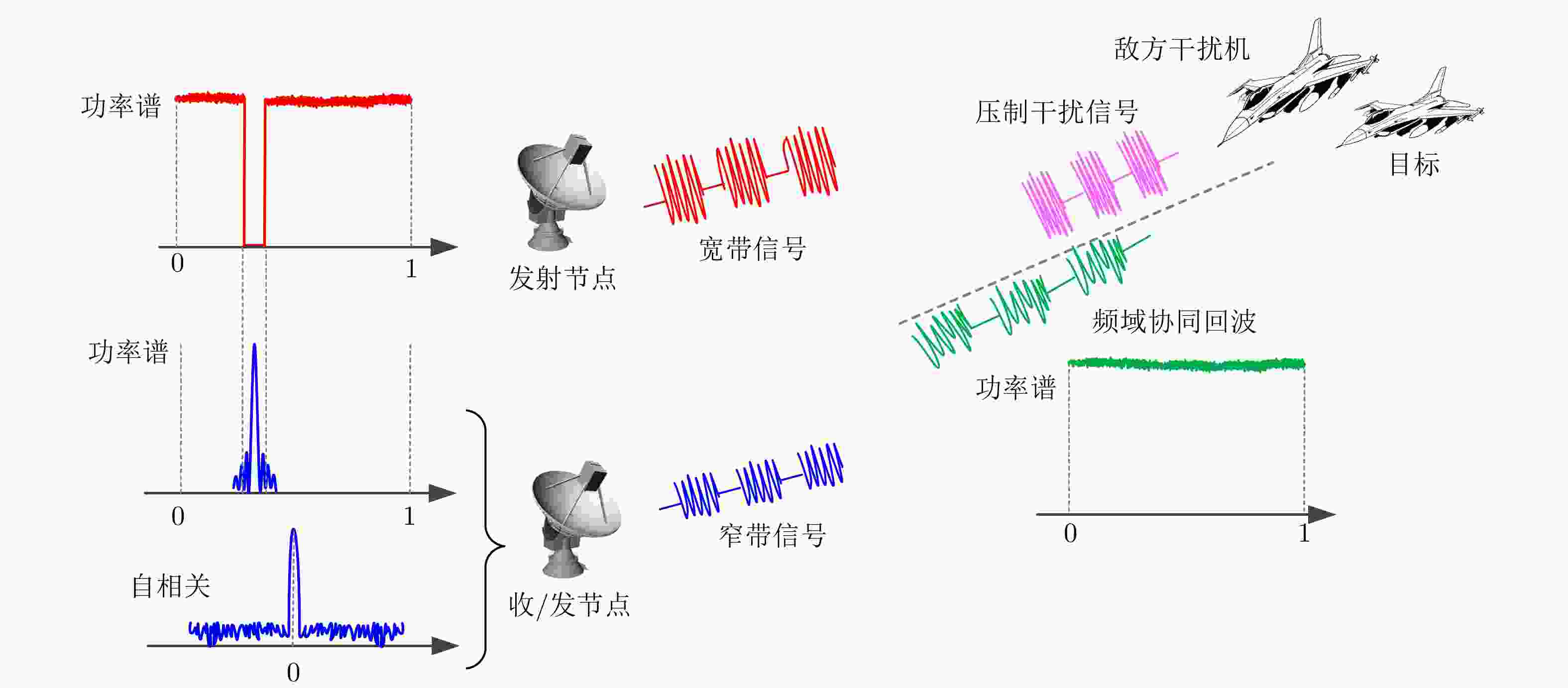
 下载:
下载: