-
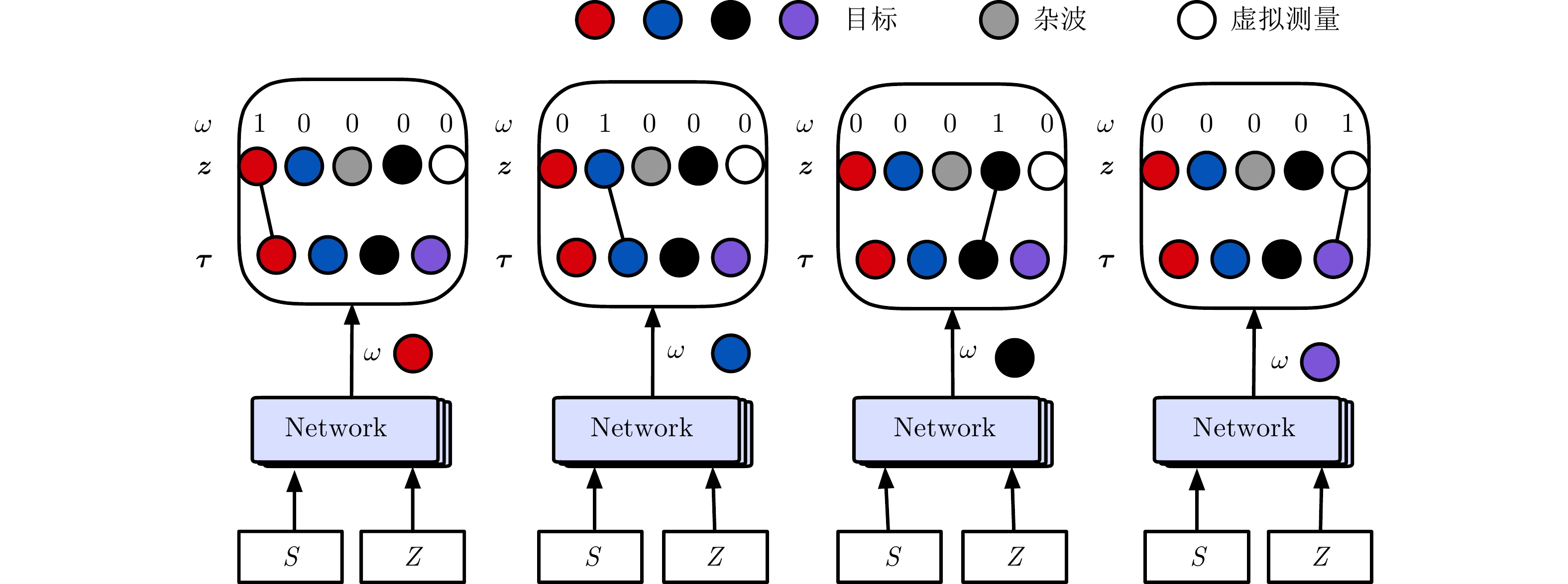
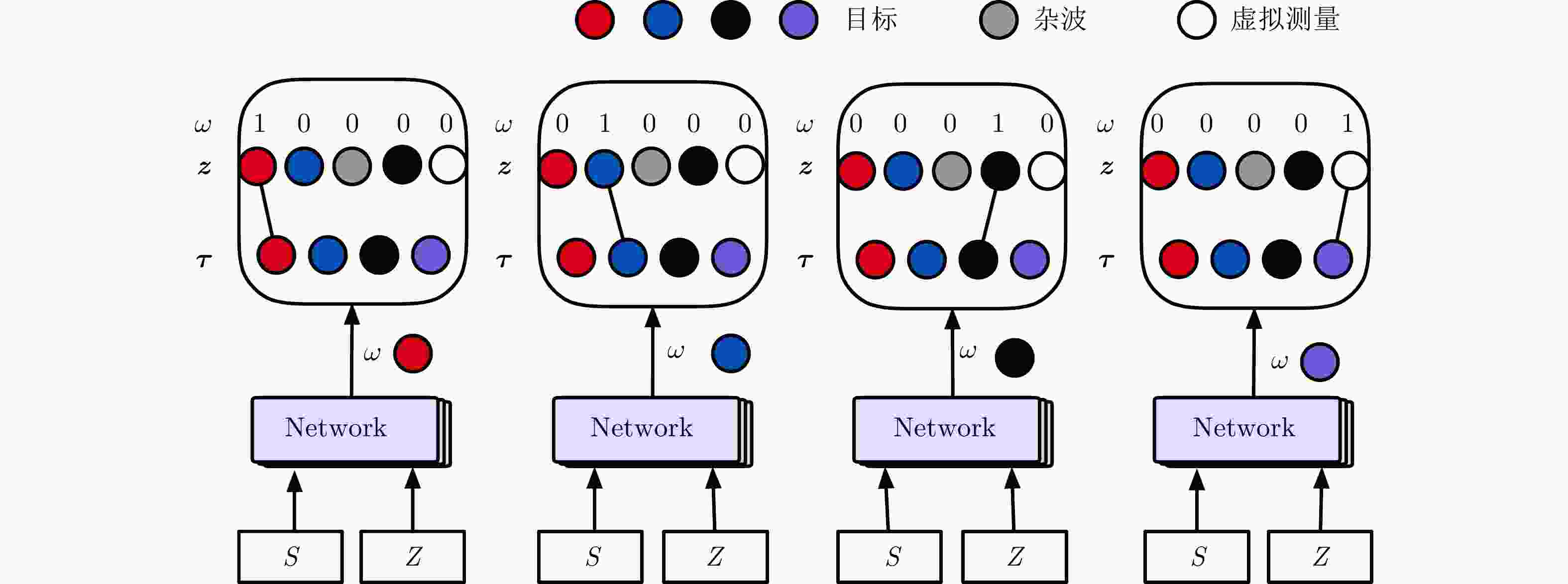
摘要: 传统的多目标跟踪数据关联算法需要提前知晓目标运动模型和杂波密度等先验信息,然而这些先验信息在跟踪之前无法及时准确地获取。针对这个问题,提出一种基于Transformer网络的多目标跟踪数据关联算法。首先,考虑到传感器会存在漏检的情况,引入虚拟量测来重新建立数据关联模型。在此基础上,提出基于Transformer网络的数据关联方法来解决多目标与多量测的匹配问题。同时,设计了一种掩蔽交叉熵损失与重叠度损失相结合的损失函数(MCD)用于优化网络参数。仿真和实测数据结果表明:在不同检测概率条件下,所提算法性能均优于经典的数据关联算法和基于双向长短时记忆网络的算法。
-
关键词:
- 机载雷达 /
- 多目标跟踪 /
- 数据关联 /
- Transformer网络 /
- 注意力机制
Abstract: Conventional multitarget-tracking data association algorithms must have prior information, such as the target motion model and clutter density. However, such prior information cannot be obtained timely and accurately before tracking. To address this issue, a data association algorithm for multitarget tracking based on a transformer network is proposed. First, considering that the radar may not perform accurate detected the target, virtual measurements are performed to re-establish the data association model. Thus, a data association method based on the transformer network is proposed to solve the matching problem of multitargets and multimeasurements. Moreover, a loss function combining Masked Cross entropy loss and Dice (MCD) loss is designed to optimize the network parameters. Simulation data and real measurement data results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms classic data association algorithms and algorithms based on bidirectional long short-term memory network under varying detection probability conditions.-
Key words:
- Airborne radar /
- Multitarget-tracking /
- Data association /
- Transformer network /
- Attention mechanism
-
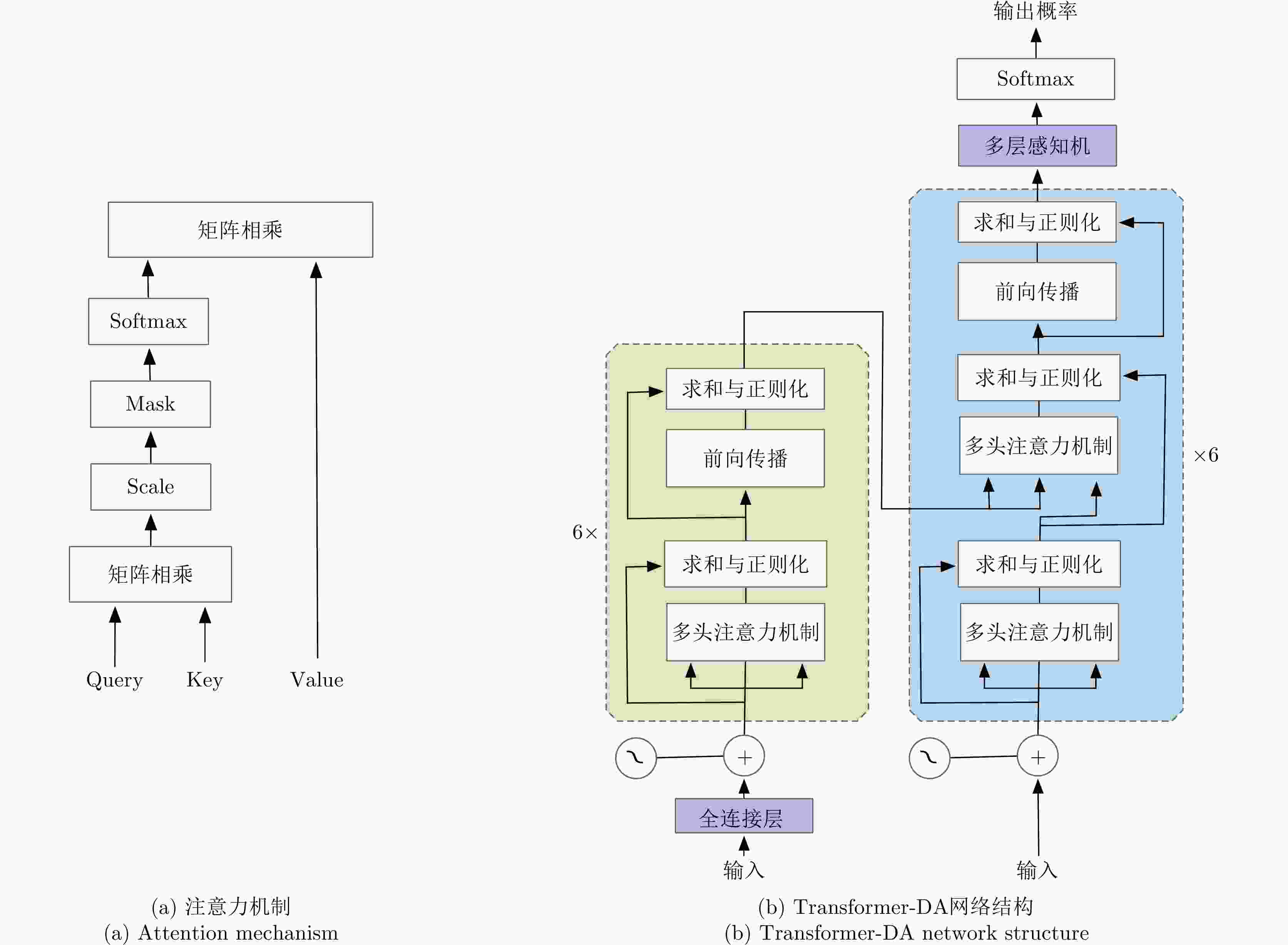
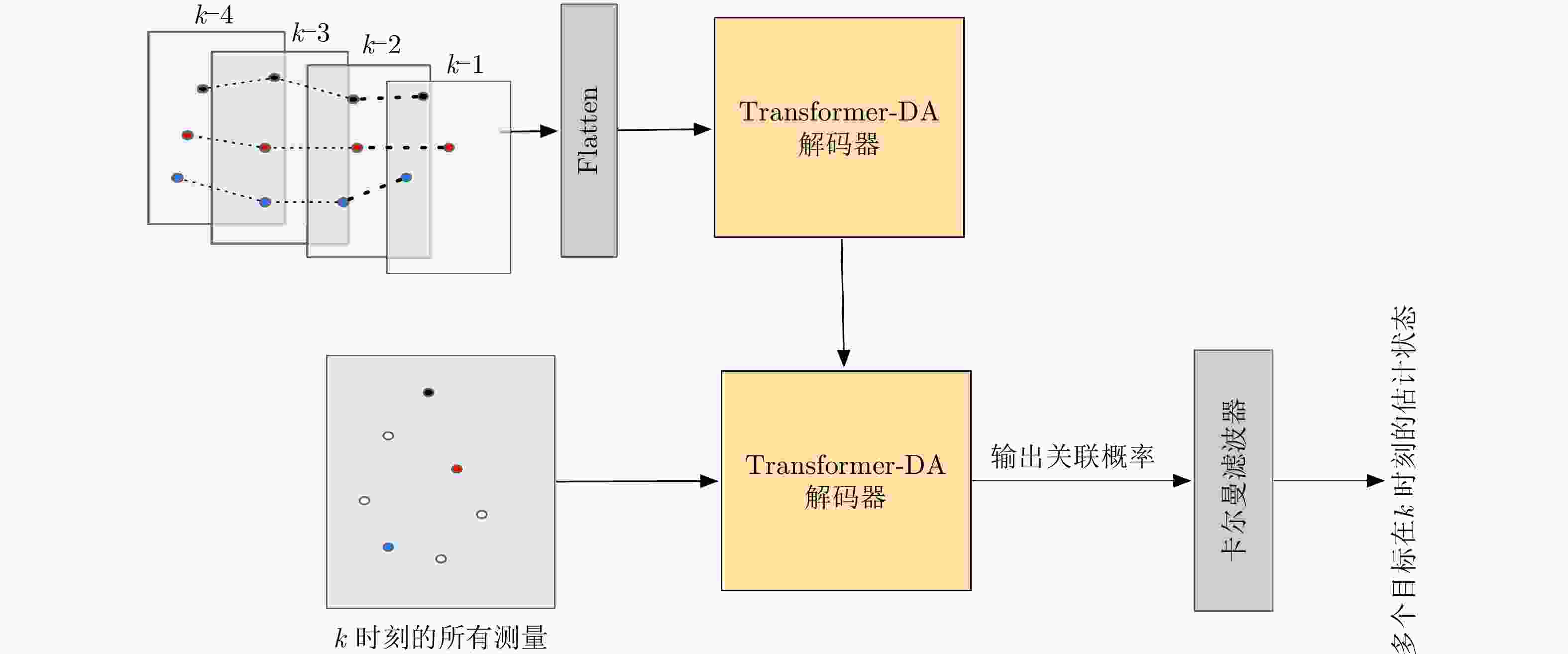
表 1 Transformer-DA网络参数
Table 1. Transformer-DA network parameters
参数 数值 编码器输入数据维度 5$ \times $20 解码器输入数据维度 100$ \times $4 输出数据维度 100$ \times $6 多头注意力的头数 8 编码器输入最大序列长度 5 解码器输入最大序列长度 100 解码器数目 6 编码器数目 6 前向传播网络大小 512 隐藏层大小 512 Dropout率 0.1 表 2 使用仿真数据时算法在不同检测概率下的OSPA对比
Table 2. OSPA comparison of the algorithm under different detection probabilities when using simulation data
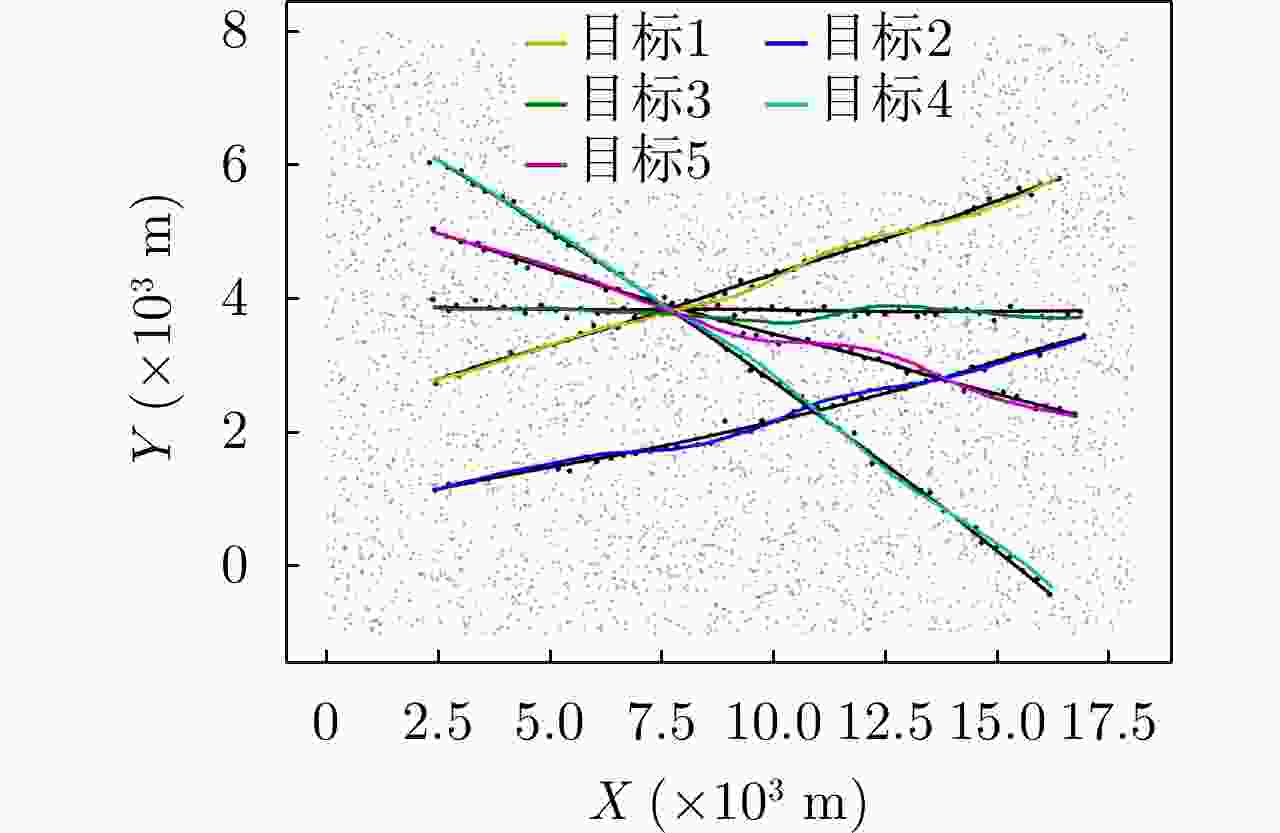
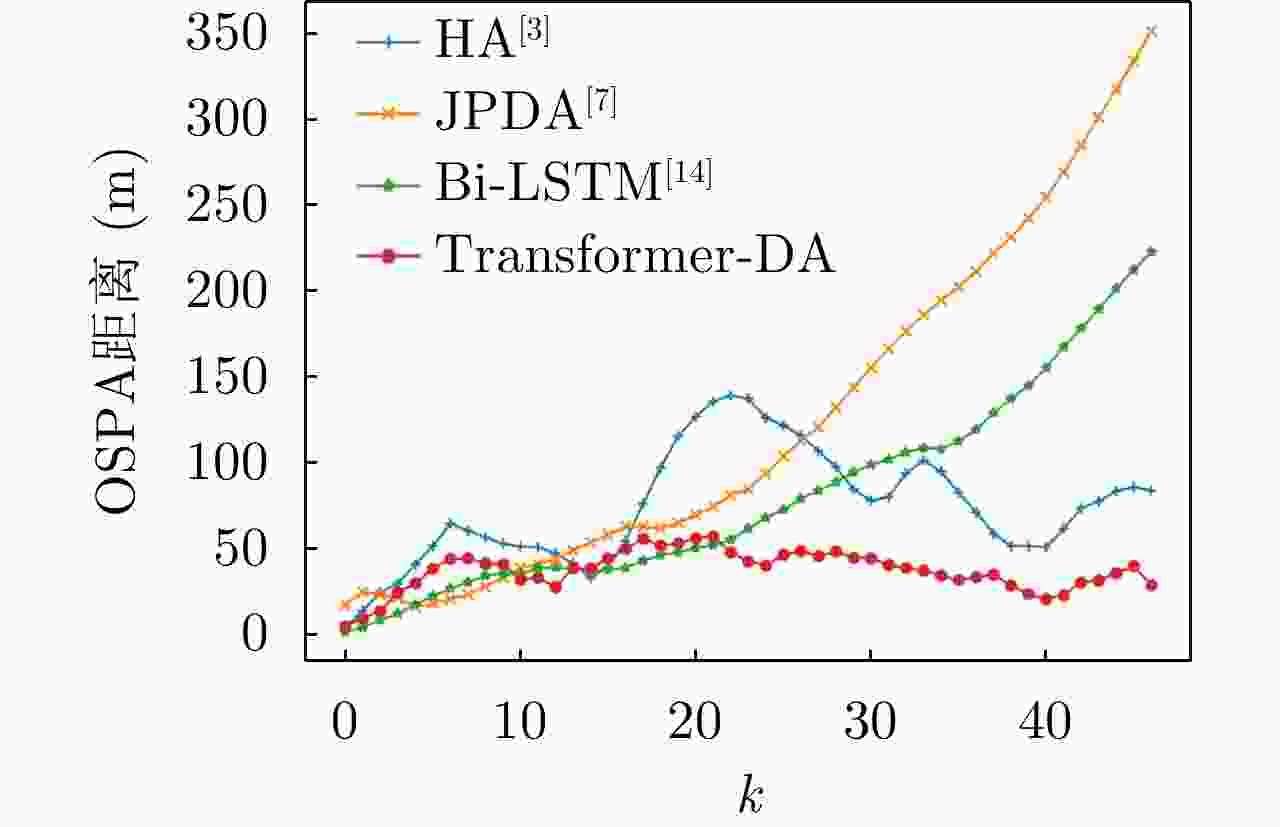
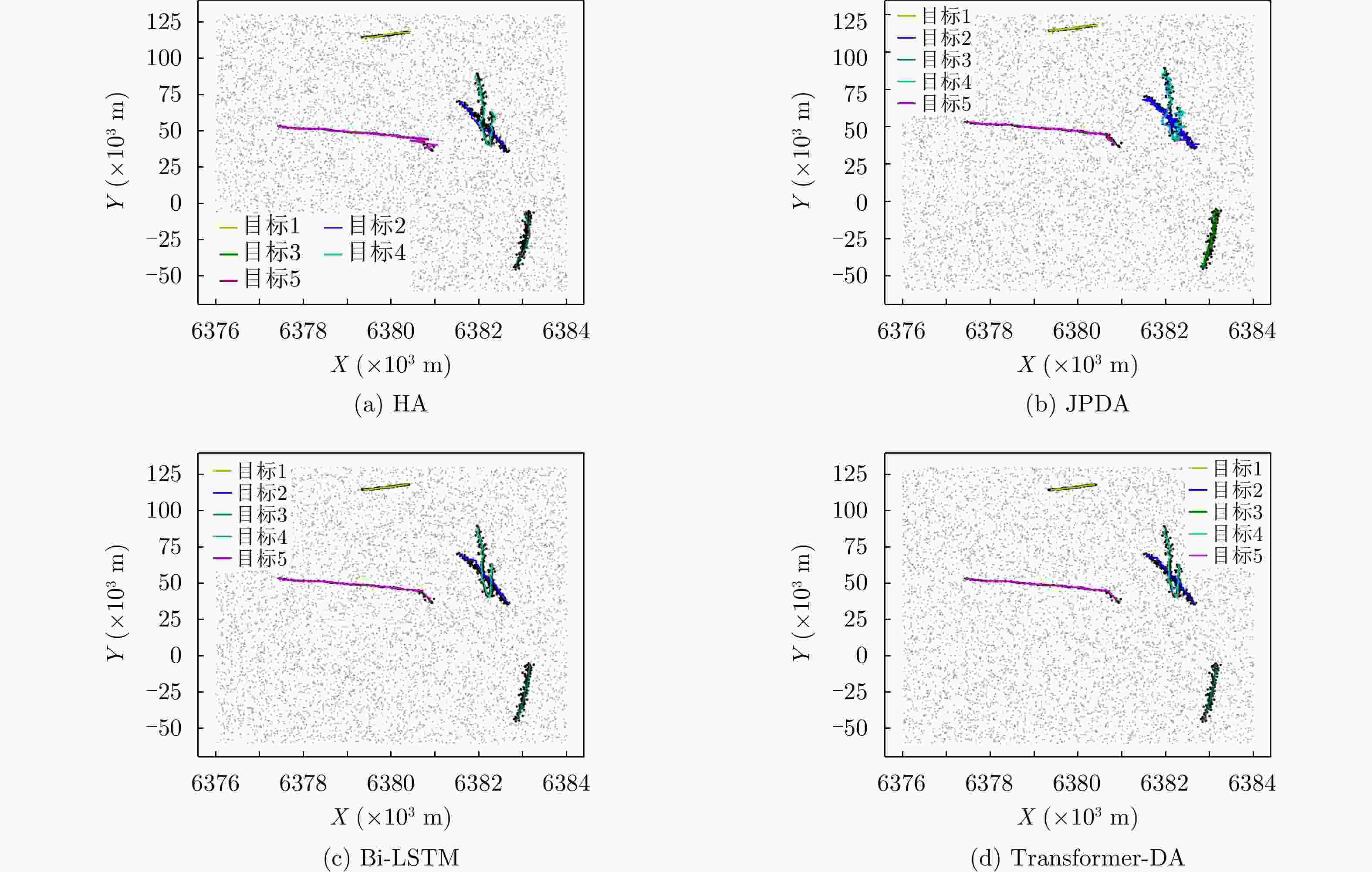
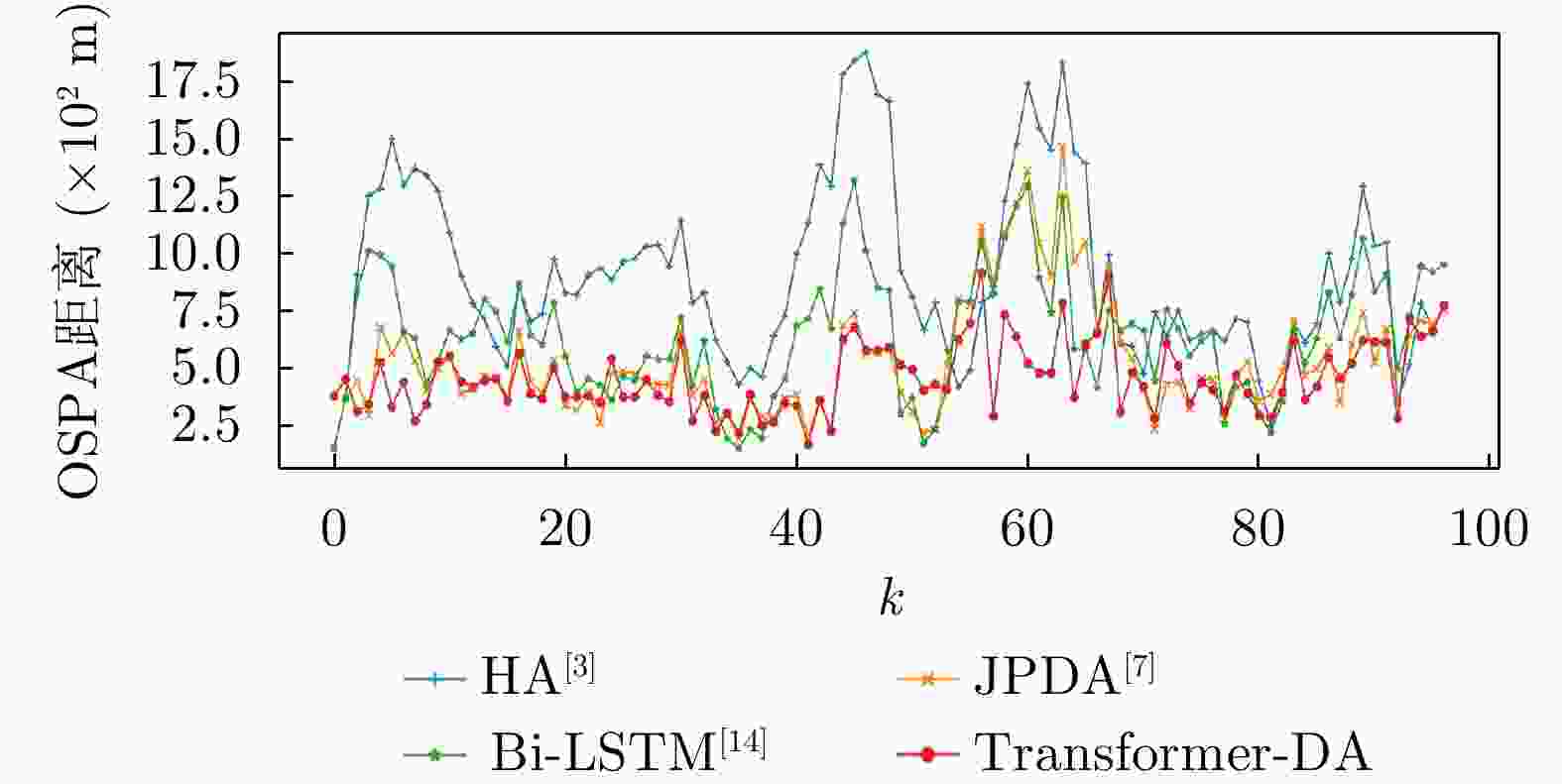
算法 ${p_d} = 0.99$ ${p_d} = 0.90$ ${p_d} = 0.60$ HA 81.39 145.88 573.64 JPDA 159.38 217.10 487.70 Bi-LSTM 99.95 120.43 257.19 Transformer-DA 39.47 51.28 134.65 表 3 使用实际数据时算法在不同检测概率下的OSPA对比
Table 3. OSPA comparison of the algorithm under different detection probabilities when using actual data
算法 ${p_d} = 0.99$ ${p_d} = 0.90$ ${p_d} = 0.60$ HA 1000.76 1347.90 1859.65 JPDA 590.68 793.12 1319.21 Bi-LSTM 695.75 810.34 1256.33 Transformer-DA 481.91 587.63 923.10 表 4 不同检测概率下所提算法识别漏检目标的准确率(%)
Table 4. The accuracy of the proposed algorithm to identify missed targets under different detection probabilities (%)
实验类型 ${p_d} = 0.90$ ${p_d} = 0.60$ 仿真数据实验 95.83 93.75 真实轨迹数据实验 95.91 89.90 -
[1] BERTSIMAS D, SAUNDERS Z, and SHTERN S. Multitarget tracking via mixed integer optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(11): 3627–3642. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2832468 [2] EMAMI P, PARDALOS P M, ELEFTERIADOU L, et al. Machine learning methods for solving assignment problem in multi-object tracking[J]. arXiv: 1802.06897, 2018. [3] WANG Jianguo, HE Peikun, and CAO Wei. Study on the Hungarian algorithm for the maximum likelihood data association problem[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2007, 18(1): 27–32. doi: 10.1016/S1004-4132(07)60045-0 [4] ZHENG Le and WANG Xiaodong. Improved multiple hypothesis tracker for joint multiple target tracking and feature extraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 3080–3089. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2897035 [5] ZHANG Guangnan and LIU Penghui. Probabilistic data association algorithm based on modified input estimation[C]. 2011 7th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Wuhan, China, 2011: 1–4. [6] NI Longqiang, GAO Shesheng, and XUE Li. Improved probabilistic data association and its application for target tracking in clutter[C]. 2011 International Conference on Electronics, Communications and Control (ICECC), Ningbo, China, 2011: 293–296. [7] WANG Yuhuan, WANG Jinkuan, and WANG Bin. A modified multi-target tracking algorithm based on joint probability data association and Gaussian particle filter[C]. The 11th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Shenyang, China, 2014: 2500–2504. [8] HE Shaoming, SHIN H S, and TSOURDOS A. Joint probabilistic data association filter with unknown detection probability and clutter rate[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI), Daegu, Korea, 2017: 559–564. [9] AINSLEIGH P L, LUGINBUHL T E, and WILLETT P K. A sequential target existence statistic for joint probabilistic data association[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 371–381. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3018899 [10] HOPFIELD J J and TANK D W. “Neural” computation of decisions in optimization problems[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1985, 52(3): 141–152. doi: 10.1007/bf00339943 [11] LEE M, XIONG Yuanhao, YU Guanding, et al. Deep neural networks for linear sum assignment problems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(6): 962–965. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2843359 [12] MILAN A, REZATOFIGHI S H, GARG R, et al. Data-driven approximations to NP-hard problems[C]. The Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 1453–1459. [13] LIU Huajun, ZHANG Hui, and MERTZ C. DeepDA: LSTM-based deep data association network for multi-targets tracking in clutter[C]. 2019 22th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Ottawa, Canada, 2019: 1–8. [14] VERMA R, RAJESH R, and EASWARAN M S. Modular multi target tracking using LSTM networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.09839, 2020. [15] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, USA, 2017. [16] CHEN Yonghui and LI Huiying. DAM: Transformer-based relation detection for question answering over knowledge Base[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 201/202: 106077. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106077 [17] PILAULT J, LI R, SUBRAMANIAN S, et al. On extractive and abstractive neural document summarization with transformer language models[C]. The 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2020: 9308–9319. [18] ZHANG Qian, LU Han, SAK H, et al. Transformer transducer: A streamable speech recognition model with transformer encoders and RNN-T loss[C]. ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 7829–7833. [19] XU Yihong, BAN Yutong, DELORME G, et al. TransCenter: Transformers with dense queries for multiple-object tracking[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15145v1, 2021. [20] SUN Peize, CAO Jinkun, JIANG Yi, et al. TransTrack: Multiple object tracking with Transformer[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.15460, 2021. [21] MEINHARDT T, KIRILLOV A, LEAL-TAIXE L, et al. Trackformer: Multi-object tracking with transformers[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.02702, 2021. [22] STORMS P P A and SPIEKSMA F C R. An LP-based algorithm for the data association problem in multitarget tracking[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2003, 30(7): 1067–1085. doi: 10.1016/S0305-0548(02)00057-6 [23] RISTIC B, VO B N, CLARK D, et al. A metric for performance evaluation of multi-target tracking algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(7): 3452–3457. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2140111 [24] 马天力. 复杂环境下机载雷达多机动目标跟踪关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 西北工业大学, 2018.MA Tianli. Research on the key technology of multiple maneuvering targets tracking for airborne radar under complex environment[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2018. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: