-
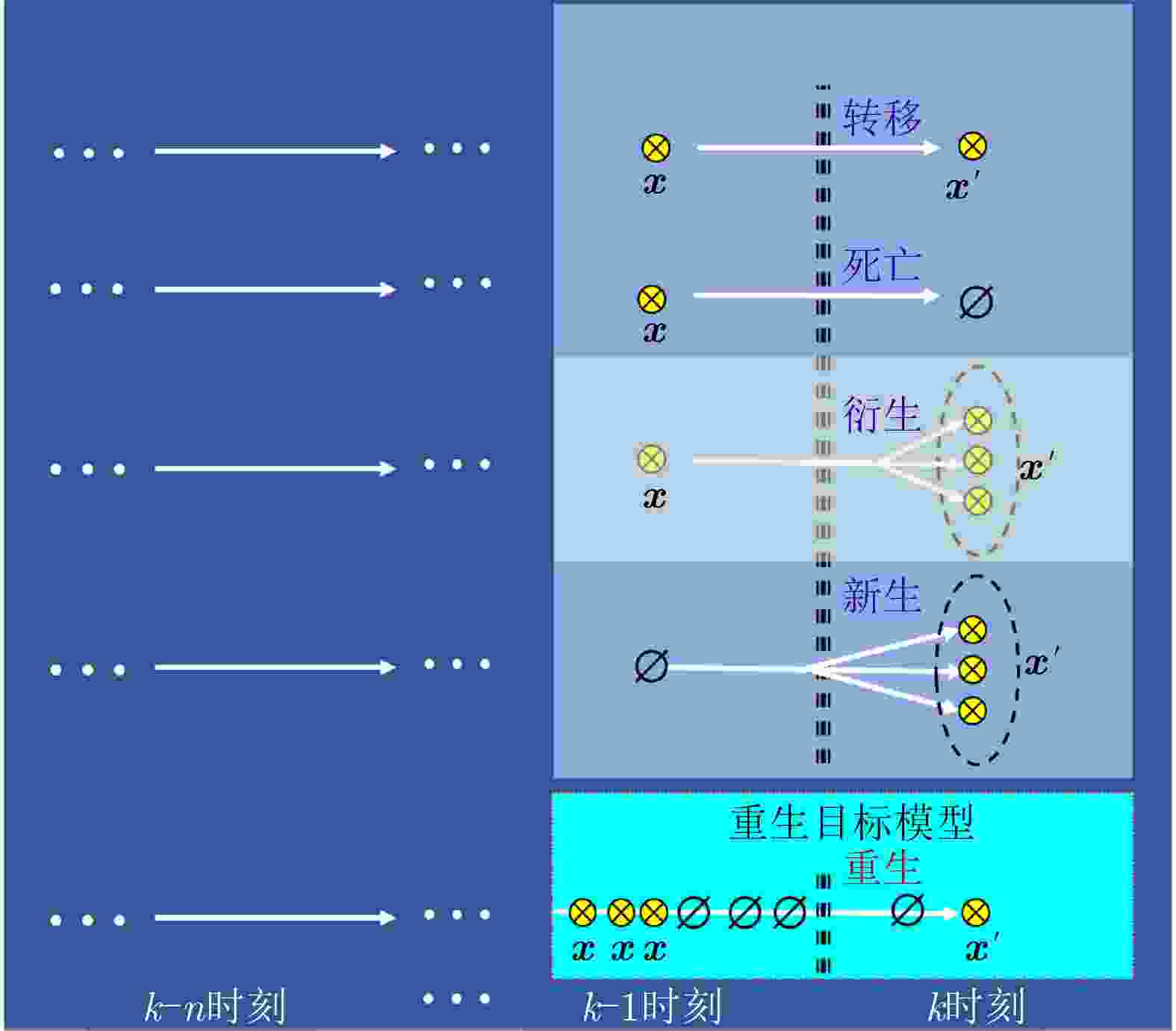
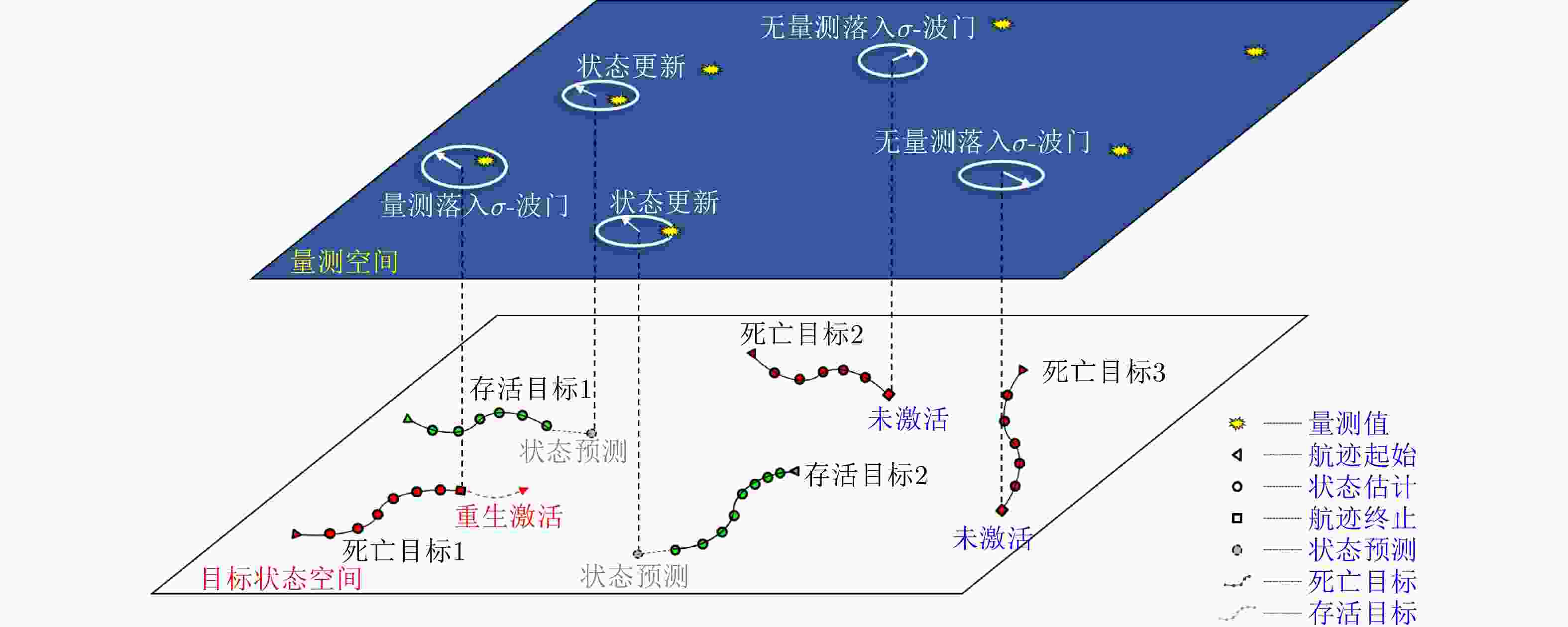
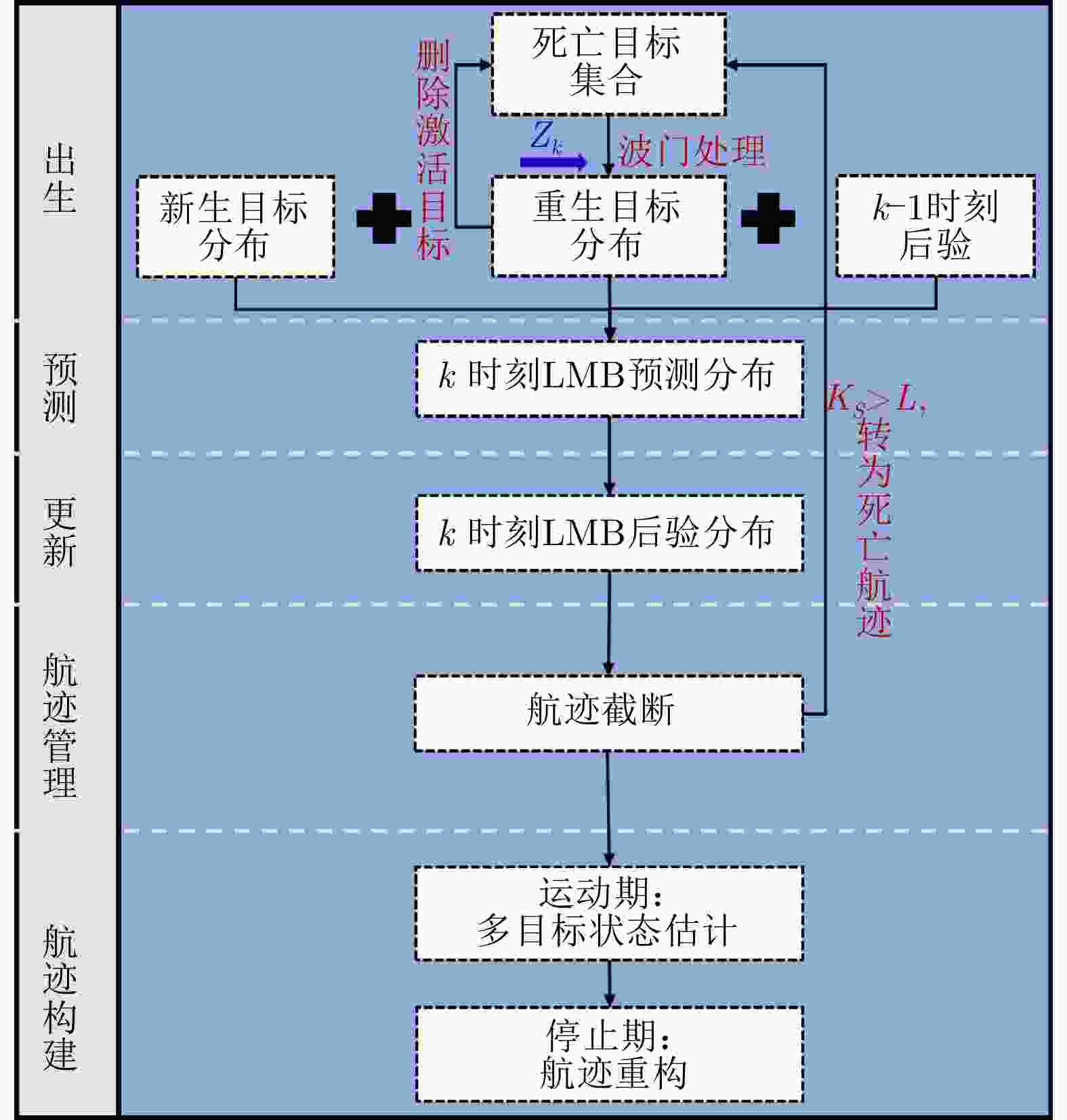
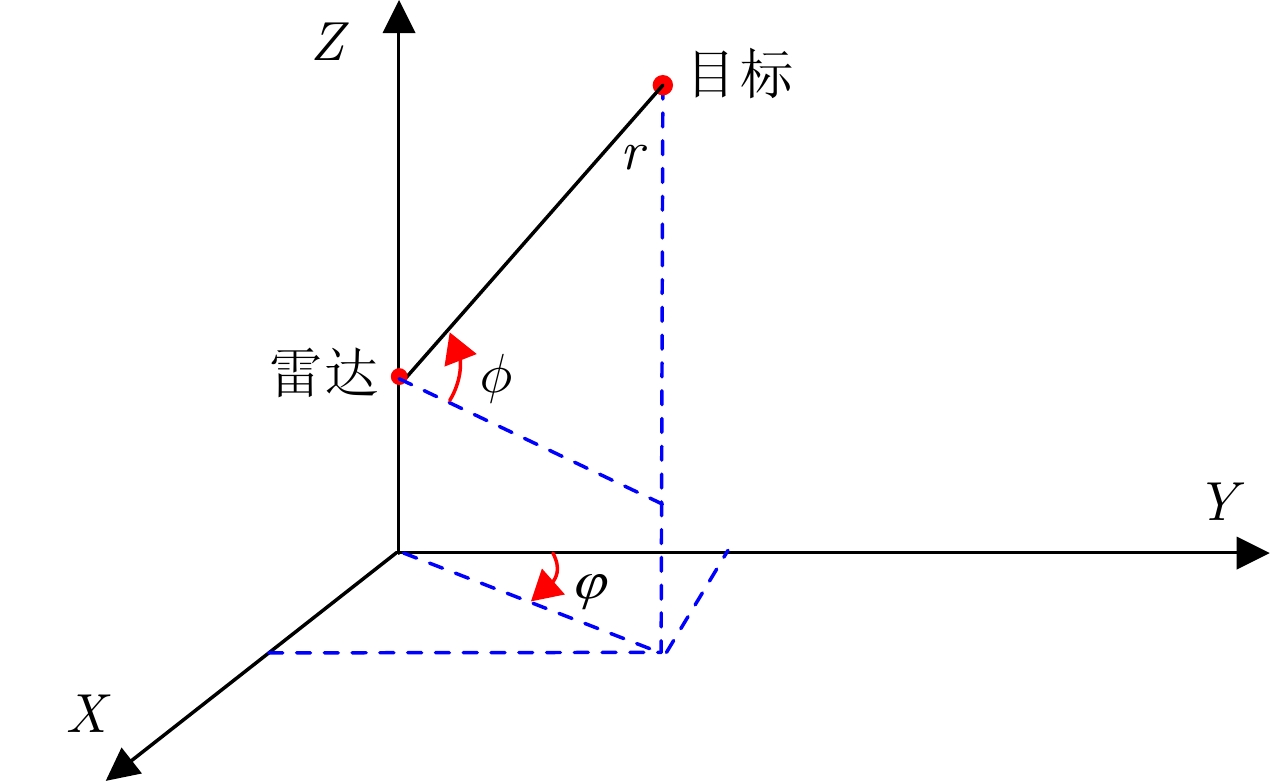
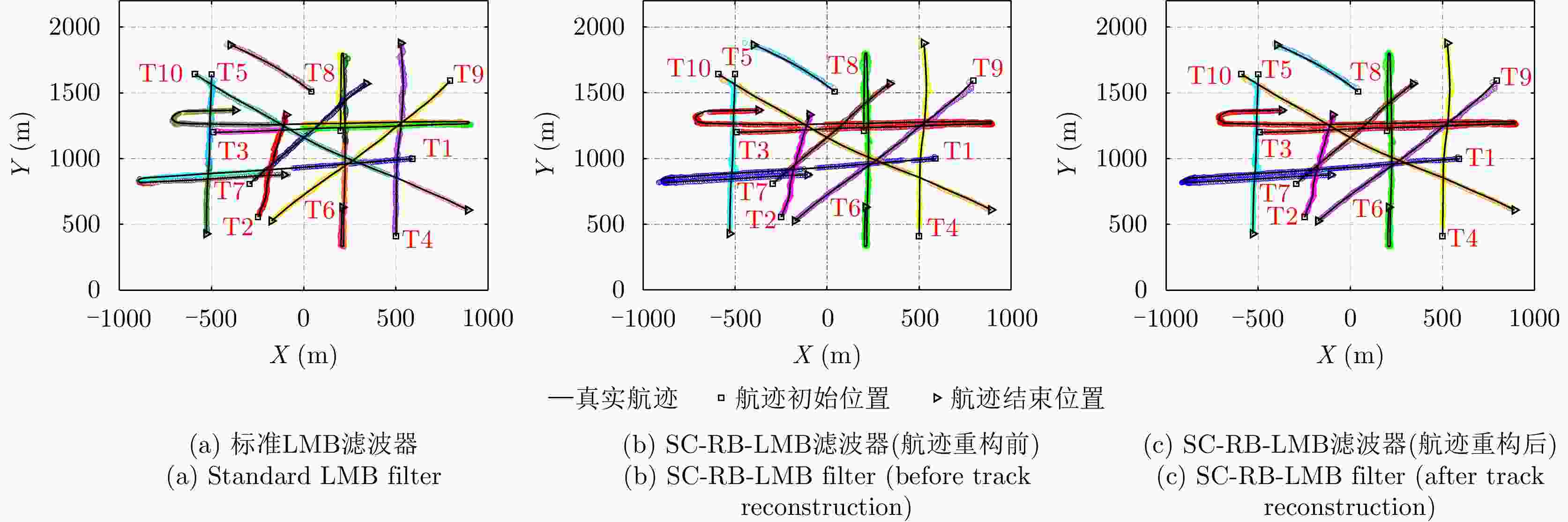
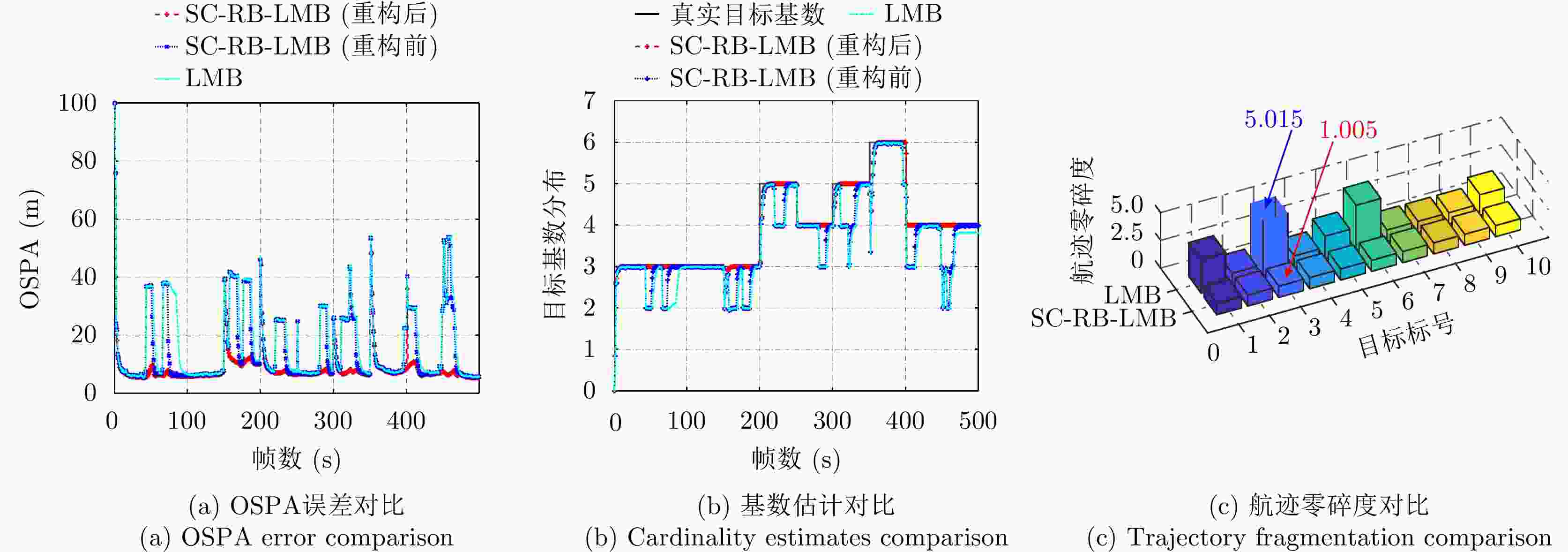
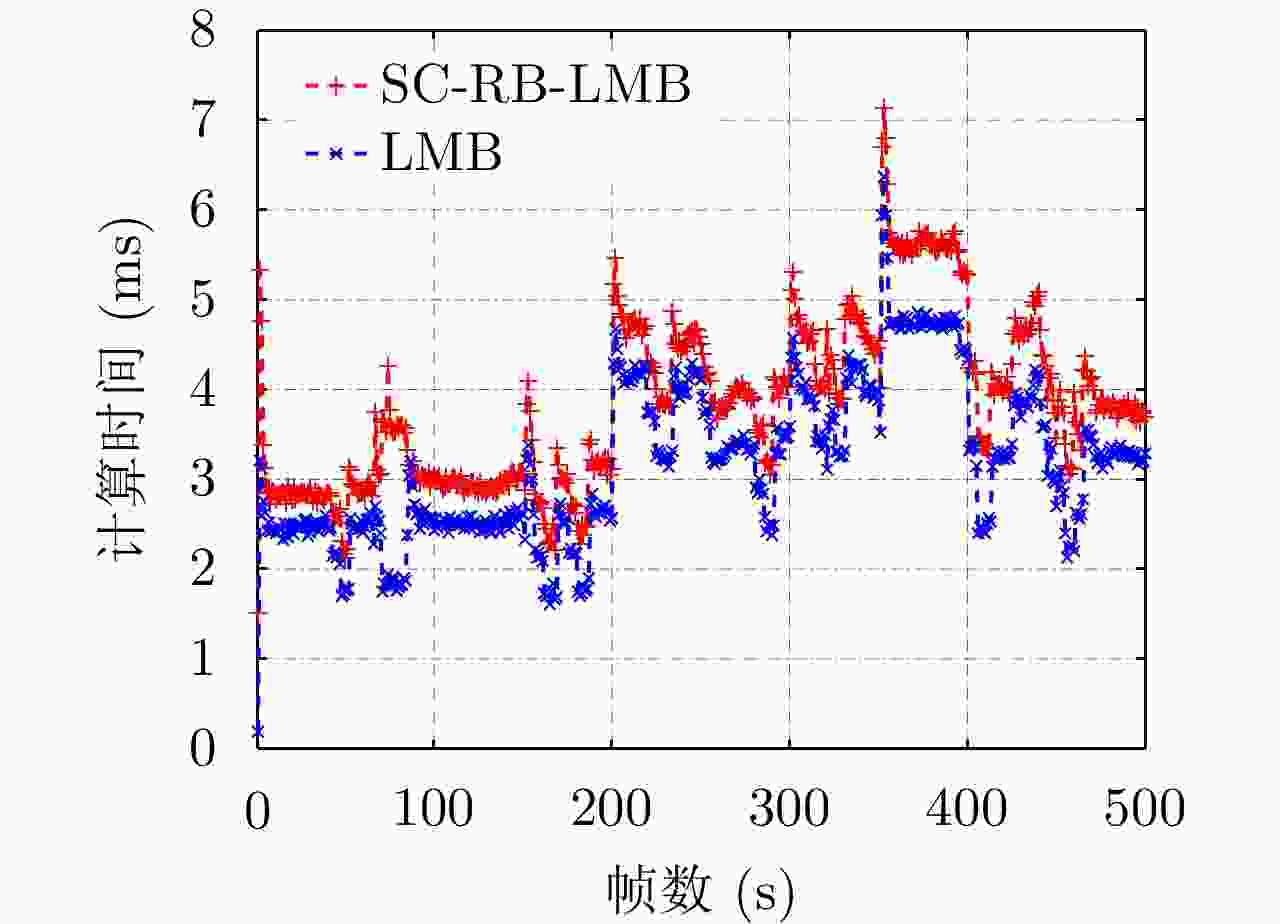
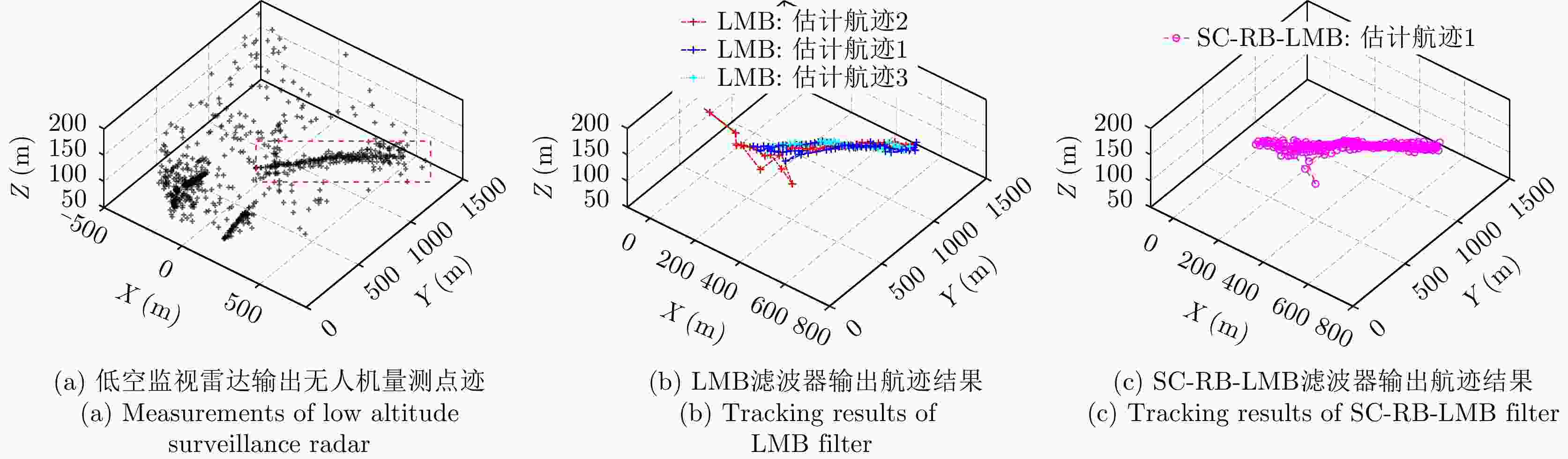
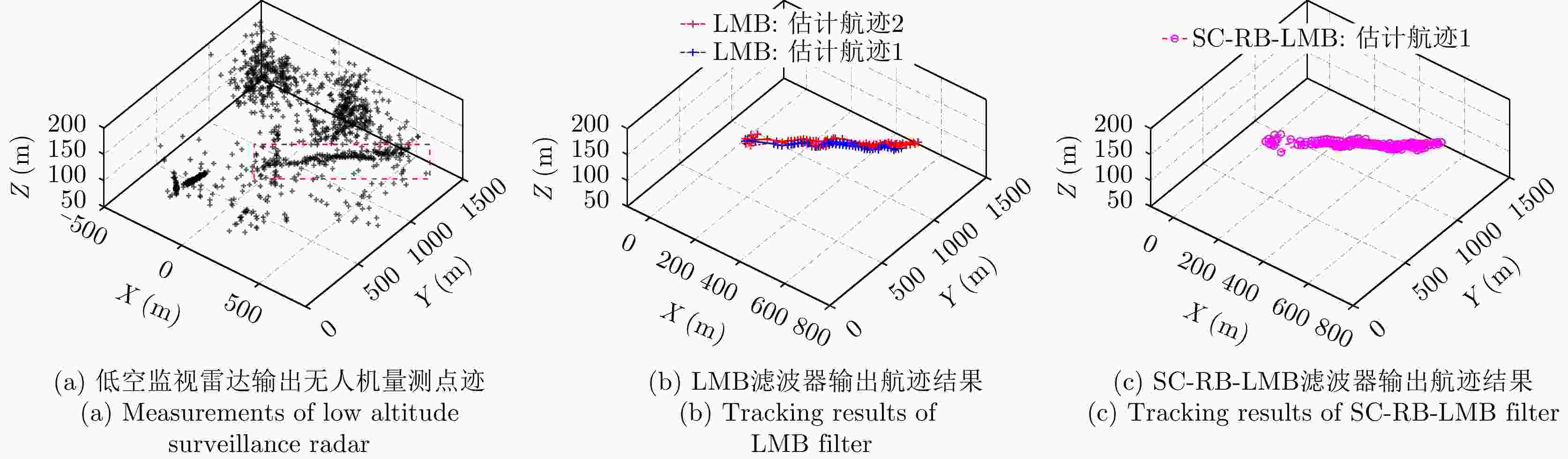
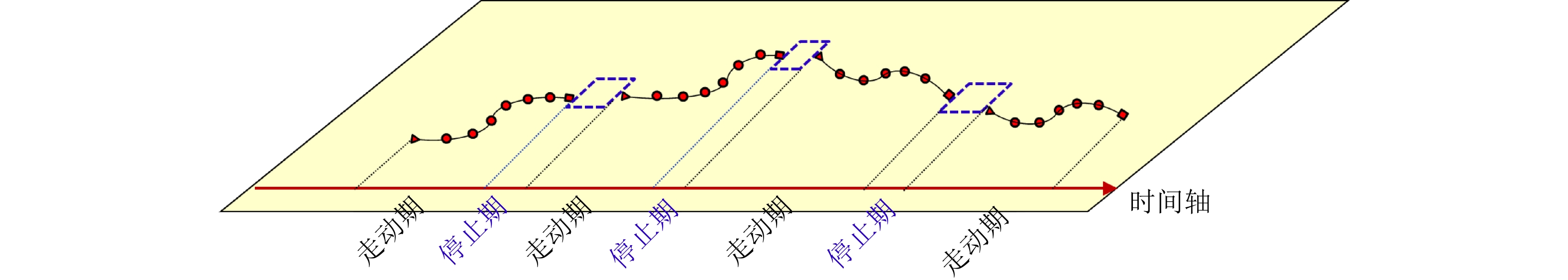
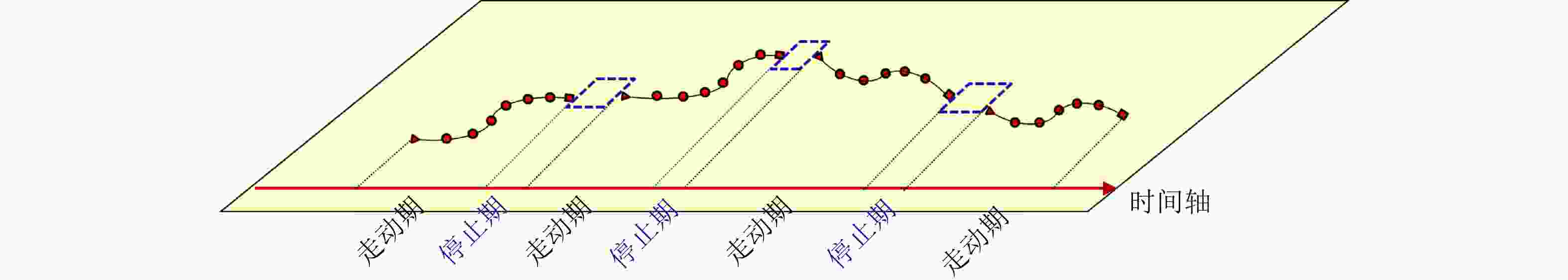
摘要: 以旋翼无人机为代表的低空小目标常采用低速“走-停”策略或利用障碍物遮挡,躲避雷达追踪,对重要信息装备和战略要地进行点穴式打击或干扰。这类目标可多次消失-重返于雷达视域,称之“走-停-走”目标。若采用传统目标跟踪模型和算法处理这类目标,易导致目标身份不连续、航迹碎片化。该文在随机集理论框架下,基于标签多伯努利(LMB)滤波器,研究低空监视雷达“走-停-走”目标连续跟踪问题。为描述“走-停-走”目标多次往返于雷达视域的演化特性,首次引入第3类出生目标模型,即重生(RB)过程模型。首先,利用目标重返雷达视域前-后目标状态的空间位置和动力学参数关系,提出一种基于空域相关(SC)的RB过程;然后,基于SC-RB过程,在贝叶斯滤波框架下,设计了SC-RB-LMB滤波器算法,可实现多“走-停-走”目标连续稳健跟踪,维持航迹标签的连续性;最后,在典型低空监视场景下,通过仿真和实测数据验证了提出模型和算法的有效性和性能优势。
-
关键词:
- 低空监视雷达 /
- “走-停-走”目标跟踪 /
- 随机集理论 /
- 重生过程模型 /
- 标签多伯努利滤波器
Abstract: Low-altitude small targets, represented by rotor unmanned aerial vehicles, always adopt slow move-and-stop strategy or employ an obstacle blocking strategy to avoid radar detection and conduct point-and-point strikes or interference on important information equipment and strategic bases. This type of target can appear and disappear from the radar Field of View (FoV) multiple times, thus, it is referred to as move-stop-move targets. Dealing with this type of target using traditional tracking models and algorithms can lead to discontinuities in target identity and track fragmentation. To this end, this study investigates the tracking problem of move-stop-move targets with the Labeled Multi-Bernoulli (LMB) filter based on random finite set statistics. To describe the evolution characteristics of multiple entries to the radar FoV, first, we introduce the third type of birth procedure, that is, the Re-Birth (RB) procedure. Specifically, based on the spatial and kinematic relationships between target states before and after returning to the radar FoV, a Spatial Correlation-based RB (SC-RB) procedure is proposed. Then, in the framework of Bayesian filtering, we derive the SC-RB-LMB filter with the proposed SC-RB model, which is capable of tracking move-stop-move targets continuously with its identity unchanged. In typical low-altitude surveillance scenarios, the effectiveness of the proposed model and algorithm is highlighted. -
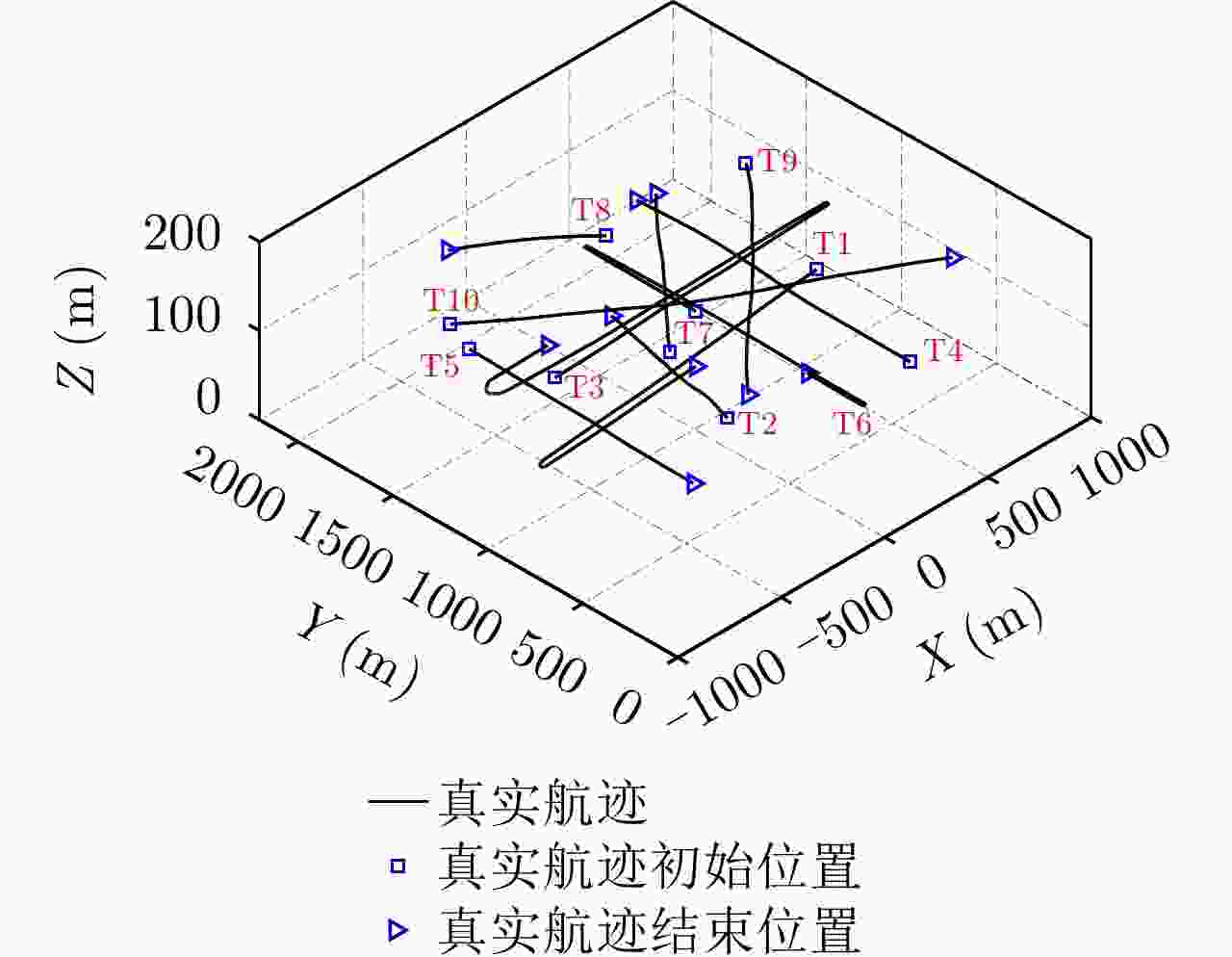
表 1 不同目标的出生时刻和死亡时刻
Table 1. Time of births and deaths for different targets
目标 出生帧数 死亡帧数 起始位置(m) 结束位置(m) 平均速度(m/s) T1 1 250 (590,1000) (–106,877) (–20,–2) T2 1 150 (–250,560) (–95,1333) (3.5,12) T3 1 500 (–500,1200) (–372,1368) (18,0.5) T4 200 350 (500,410) (525,1878) (0.2,18) T5 151 500 (–500,1650) (–530,430) (–0.2,–18) T6 200 350 (200,1210) (208,630) (0,20) T7 151 500 (–300,800) (340,1570) (12,15) T8 300 400 (42,1510) (–400,1865) (–17,18) T9 351 500 (800,1600) (–175,527) (–12,–16) T10 351 500 (–600,1650) (890,610) (18,–16) 表 2 “走-停-走”目标停止期
Table 2. Stopping period of move-stop-move targets
目标 停止帧数 T1 66~73, 157~168 T3 43~51, 168~176, 310~322, 396~412, 448~450 T5 82~91 T6 70~83, 171~180, 300~309 T10 106~114 -
[1] 丁凯. 低空监视雷达信号处理方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2017: 1–93.DING Kai. Research on radar signal processing method of low altitude surveillance[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017: 1–93. [2] 张浩. 低空目标探测雷达高速目标检测与跟踪技术研究与实现[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2016: 1–91.ZHANG Hao. Research on algorithm and implementation of low-altitude and high-speed targets detection and tracking[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2016: 1–91. [3] KIRUBARAJAN T and BAR-SHALOM Y. Tracking evasive move-stop-move targets with a GMTI radar using a VS-IMM estimator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 1098–1103. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238762 [4] LIN L, BAR-SHALOM Y, and KIRUBARAJAN T. New assignment-based data association for tracking move-stop-move targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(2): 714–725. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1310016 [5] ZHANG Shuo and BAR-SHALOM Y. Tracking move-stop-move targets with state-dependent mode transition probabilities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(3): 2037–2054. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5937281 [6] HERNANDEZ M, BENAVOLI A, GRAZIANO A, et al. Performance measures and MHT for tracking move-stop-move targets with MTI sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(2): 996–1025. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5751239 [7] LIU Shuo, LI Hongbo, ZHANG Yun, et al. Multiple hypothesis method for tracking move-stop-move target[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(19): 6155–6159. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0182 [8] CORALUPPI S P, CARTHEL C A, and WILLSKY A S. Multi-sensor tracking of move-stop-move targets[C]. Proceedings of 2017 Sensor Data Fusion: Trends, Solutions, Applications, Bonn, Germany, 2017: 1–6. [9] MAHLER R P S. Statistical Multisource-Multitarget Information Fusion[M]. Boston, USA: Artech House, 2007: 1–888. [10] MAHLER R P S. Multitarget Bayes filtering via first-order multitarget moments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(4): 1152–1178. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1261119 [11] VO B T, VO B N, and CANTONI A. Analytic implementations of the cardinalized probability hypothesis density filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(7): 3553–3567. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.894241 [12] VO B T, VO B N, and CANTONI A. The cardinality balanced multi-target multi-Bernoulli filter and its implementations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(2): 409–423. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2007924 [13] 王佰录, 易伟, 李溯琪, 等. 分布式多目标伯努利滤波器的网络共识技术[J]. 信号处理, 2018, 34(1): 1–12. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.01.001WANG Bailu, YI Wei, LI Suqi, et al. Consensus for distributed multi-Bernoulli filter[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2018, 34(1): 1–12. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.01.001 [14] VO B T and VO B N. Labeled random finite sets and multi-object conjugate priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(13): 3460–3475. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2259822 [15] VO B N, VO B T, and PHUNG D. Labeled random finite sets and the Bayes multi-target tracking filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(24): 6554–6567. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2364014 [16] REUTER S, VO B T, VO B N, et al. The labeled multi-Bernoulli filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(12): 3246–3260. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2323064 [17] LI Suqi, YI Wei, HOSEINNEZHAD R, et al. Multi-object tracking for generic observation model using labeled random finite sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(2): 368–383. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2764864 [18] XIE Xin, SUN Hemin, WU Weihua, et al. MM-GM-PHD filter-based maneuvering target tracking in the presence of Doppler blind zone[C]. The IEEE 3rd Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Chengdu, China, 2019: 1352–1357. [19] WU Weihua, SUN Hemin, CAI Yichao, et al. Tracking multiple maneuvering targets hidden in the DBZ based on the MM-GLMB filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 2912–2924. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2988635 [20] LI Suqi, BATTISTELLI G, CHISCI L, et al. Computationally efficient multi-agent multi-object tracking with labeled random finite sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(1): 260–275. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2880704 [21] LI Suqi, YI Wei, HOSEINNEZHAD R, et al. Robust distributed fusion with labeled random finite sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(2): 278–293. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2760286 [22] 李溯琪. 基于标号随机集的传感器网络分布式融合技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2018: 1–142.LI Suqi. Labeled random finite set based distributed fusion over sensor network[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018: 1–142. [23] SCHUHMACHER D, VO B T, and VO B N. A consistent metric for performance evaluation of multi-object filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(8): 3447–3457. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.920469 [24] 邹伟, 刘兵, 孙倩. 多源信息融合能力评估关键技术综述[J]. 计算机与数学工程, 2010, 38(3): 1–5, 70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2010.03.001ZOU Wei, LIU Bing, and SUN Qian. Survey of key technologies on efficiency evaluation of information fusion system with multiple sources[J]. Computer and Digital Engineering, 2010, 38(3): 1–5, 70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2010.03.001 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: