-
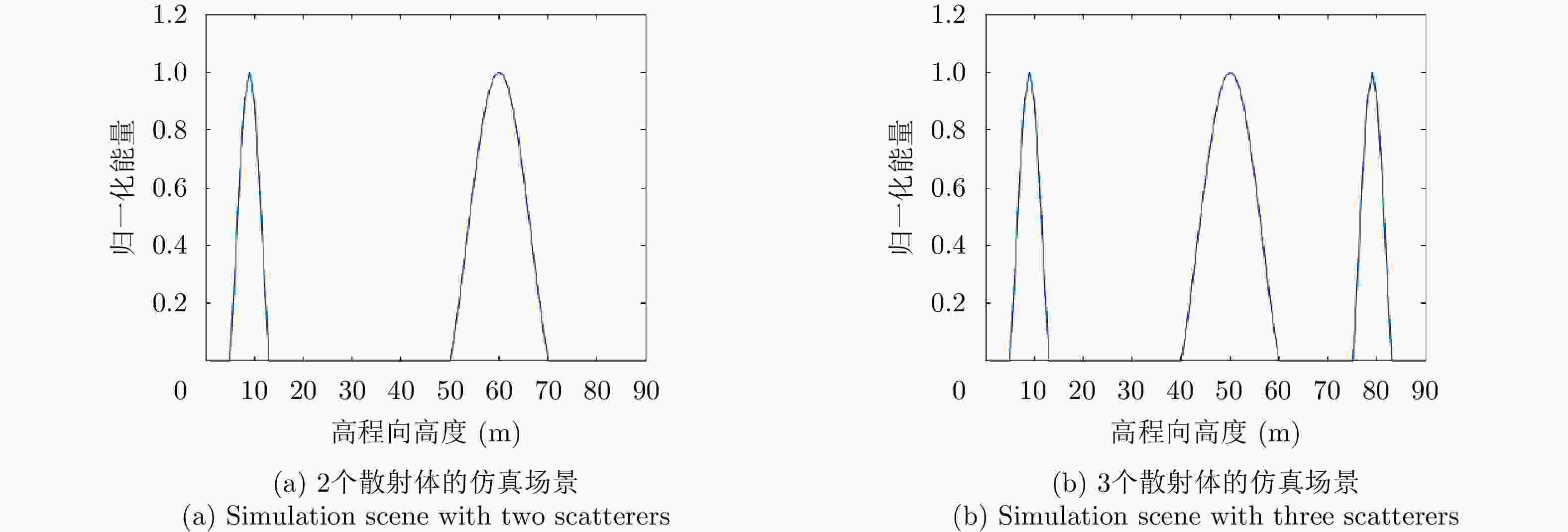
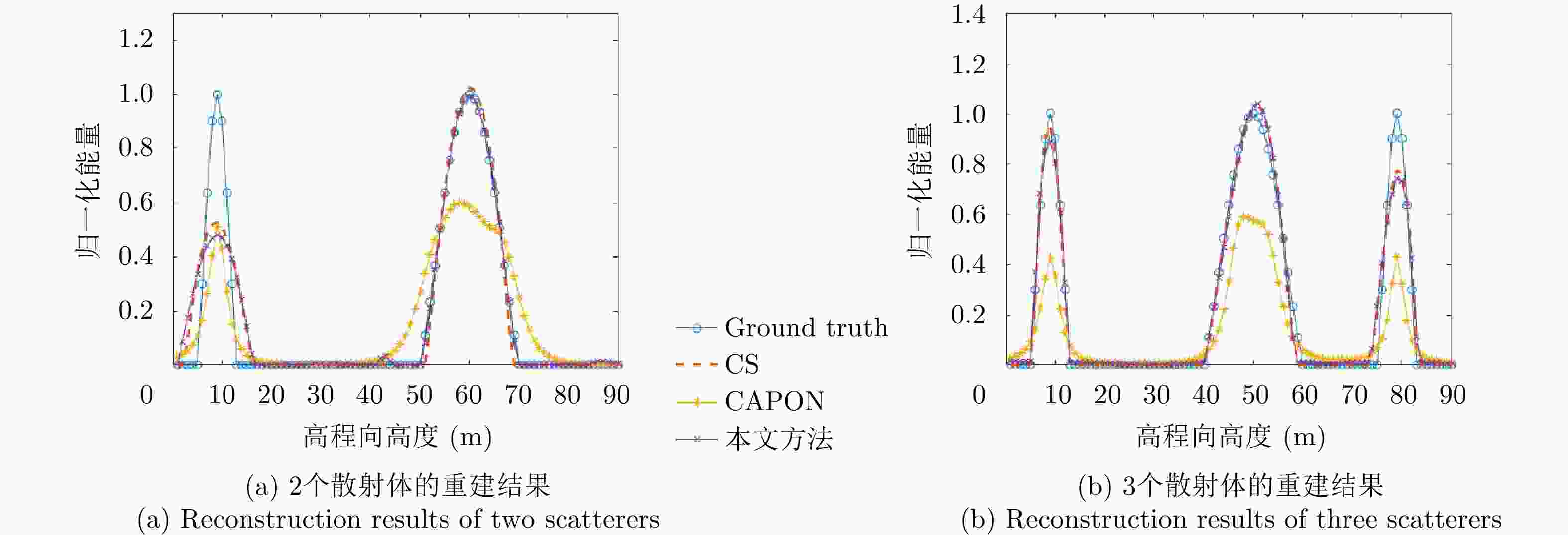
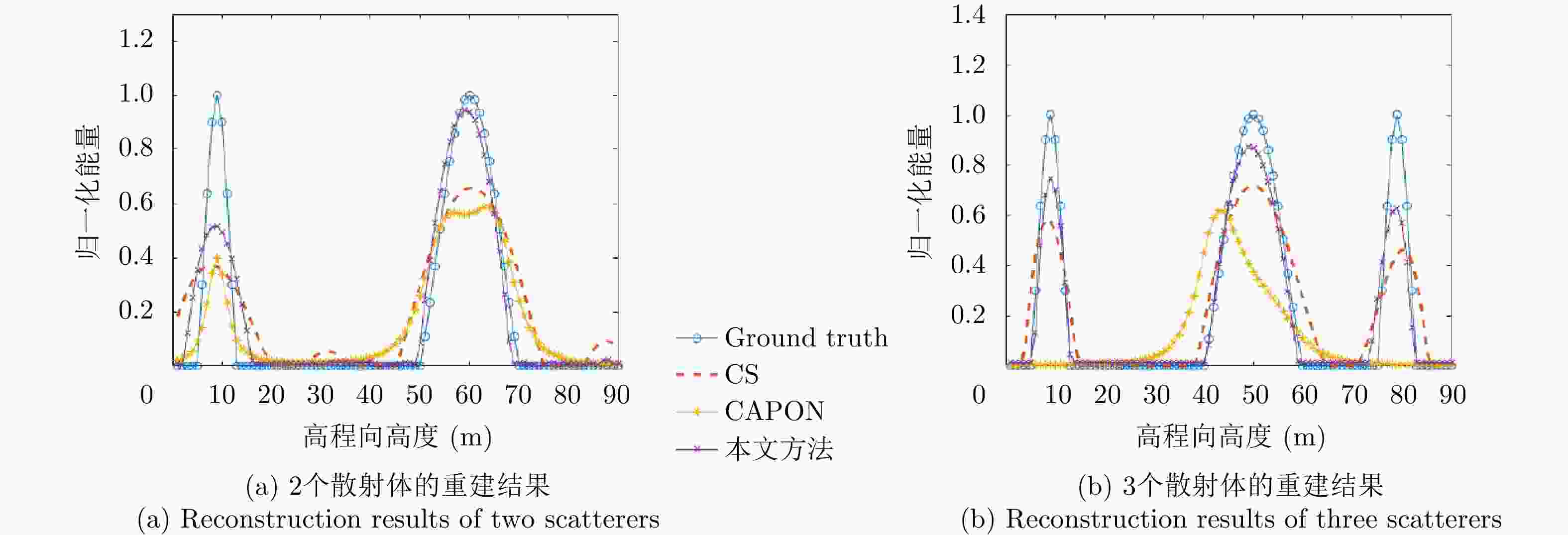
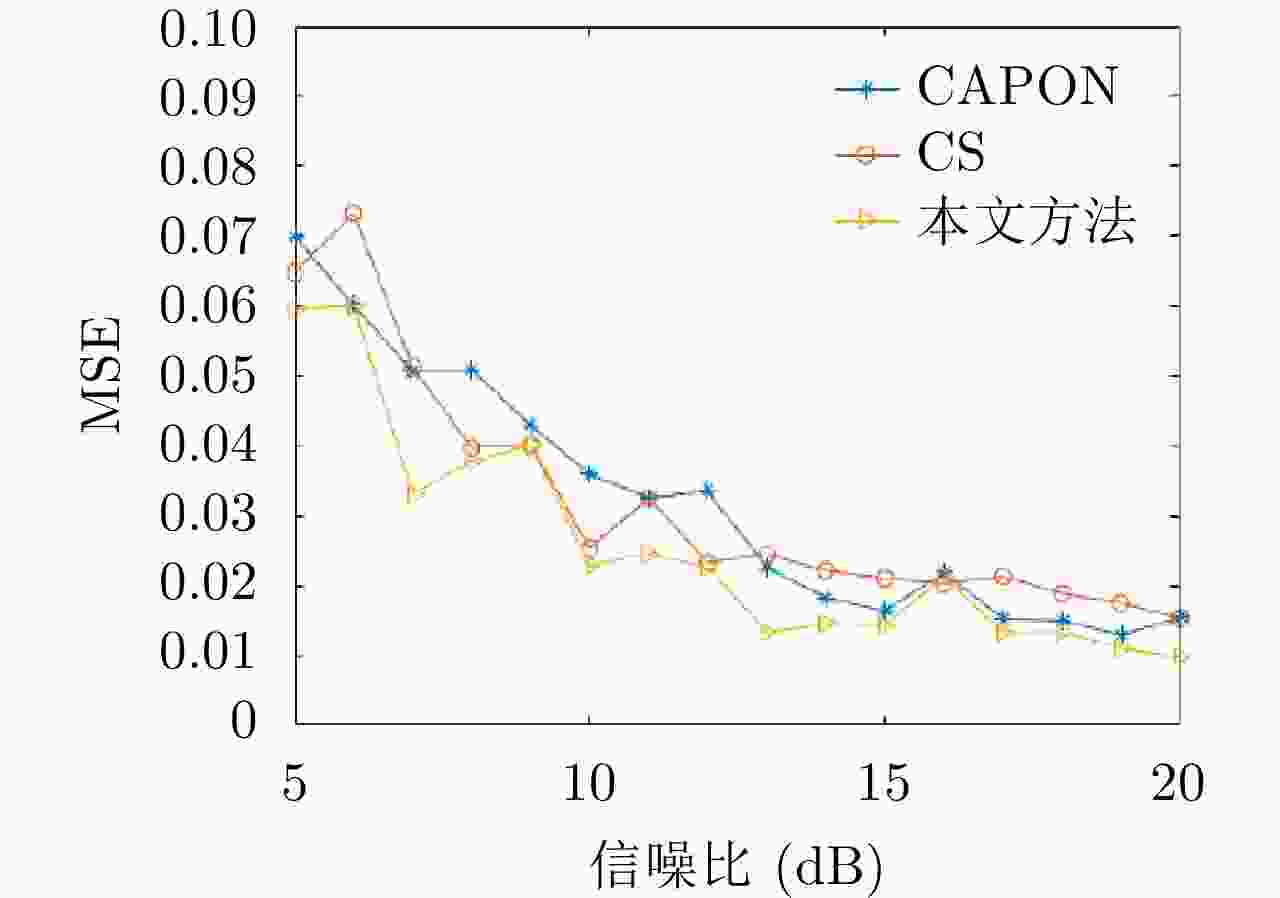
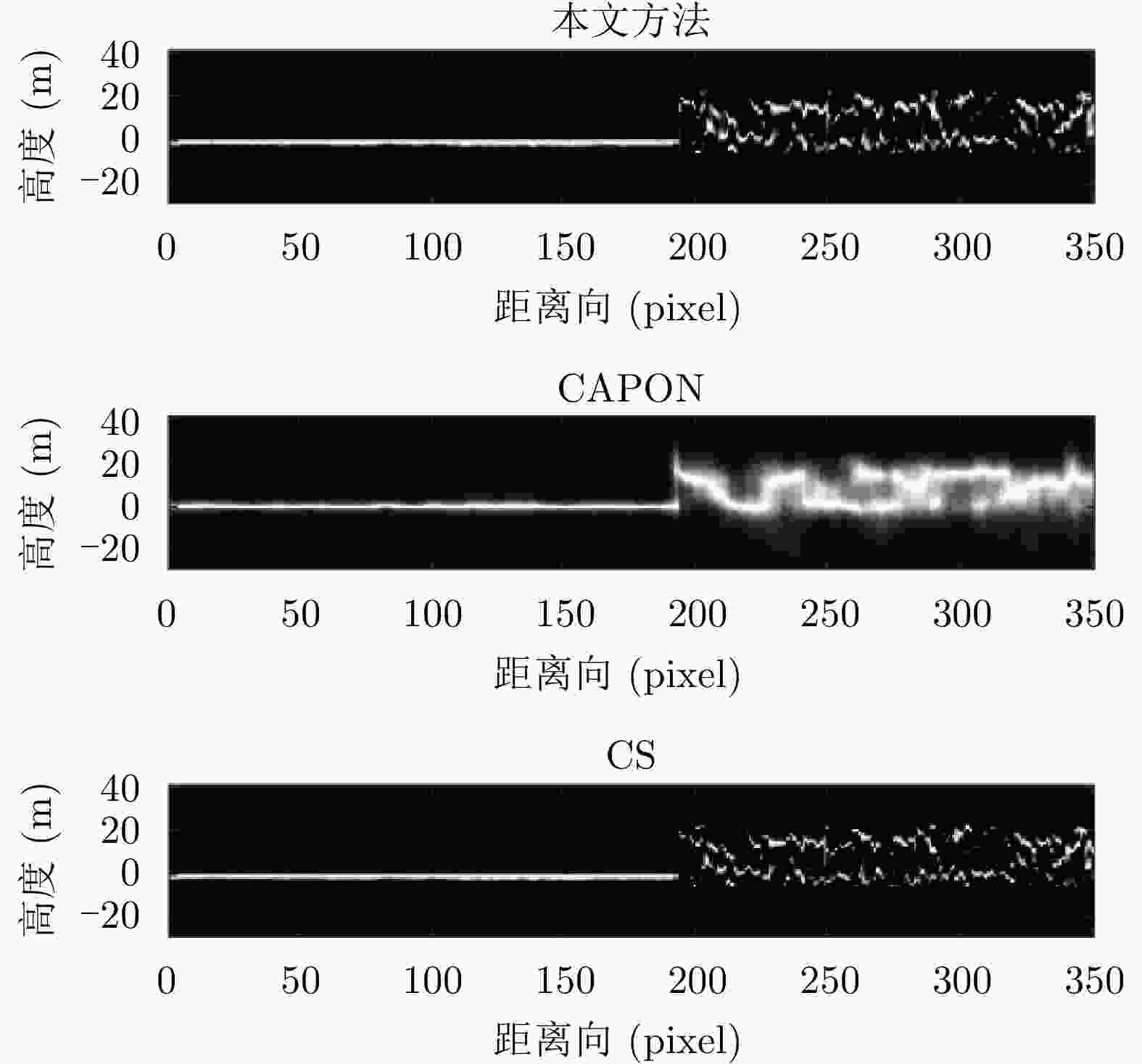
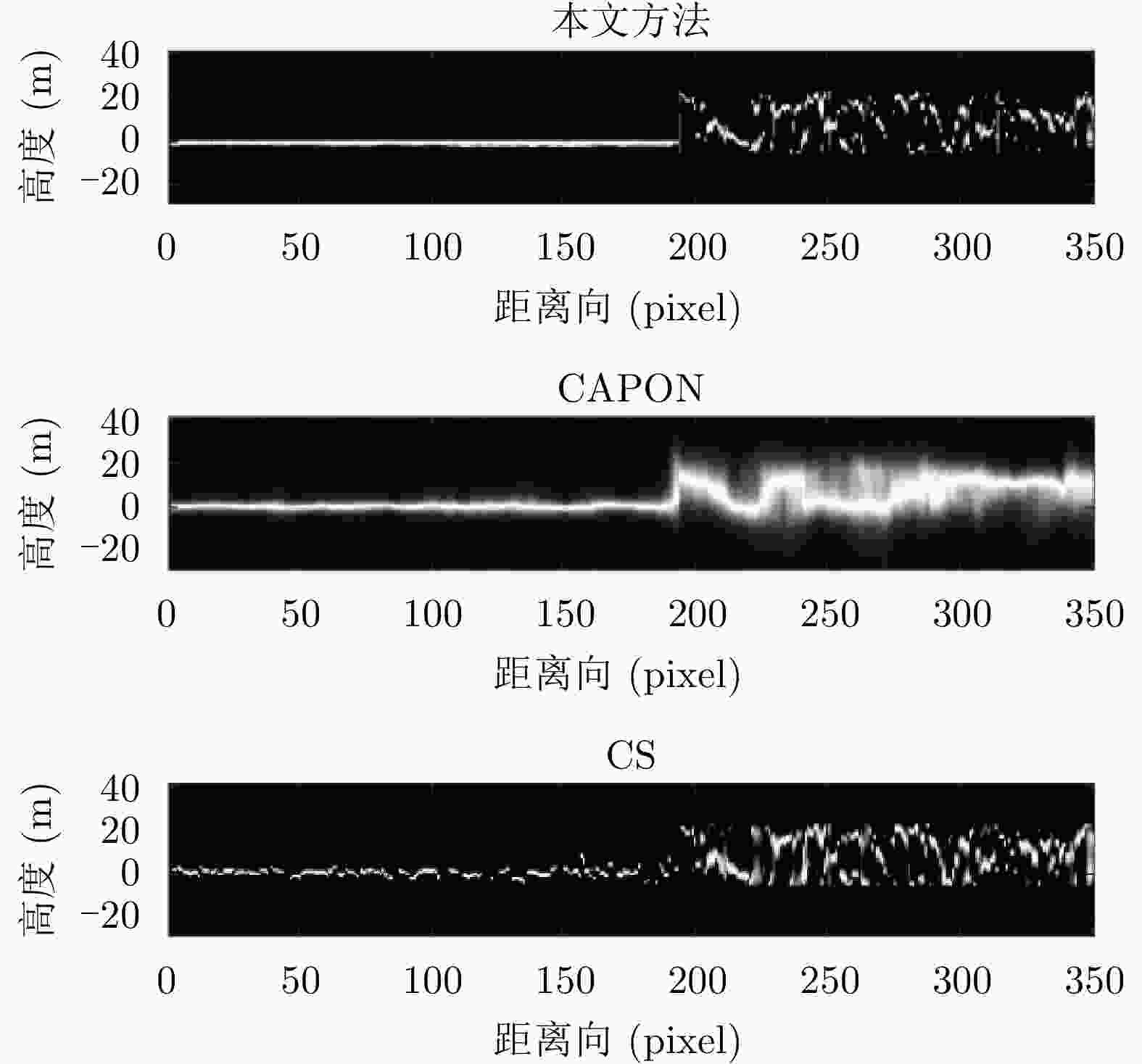
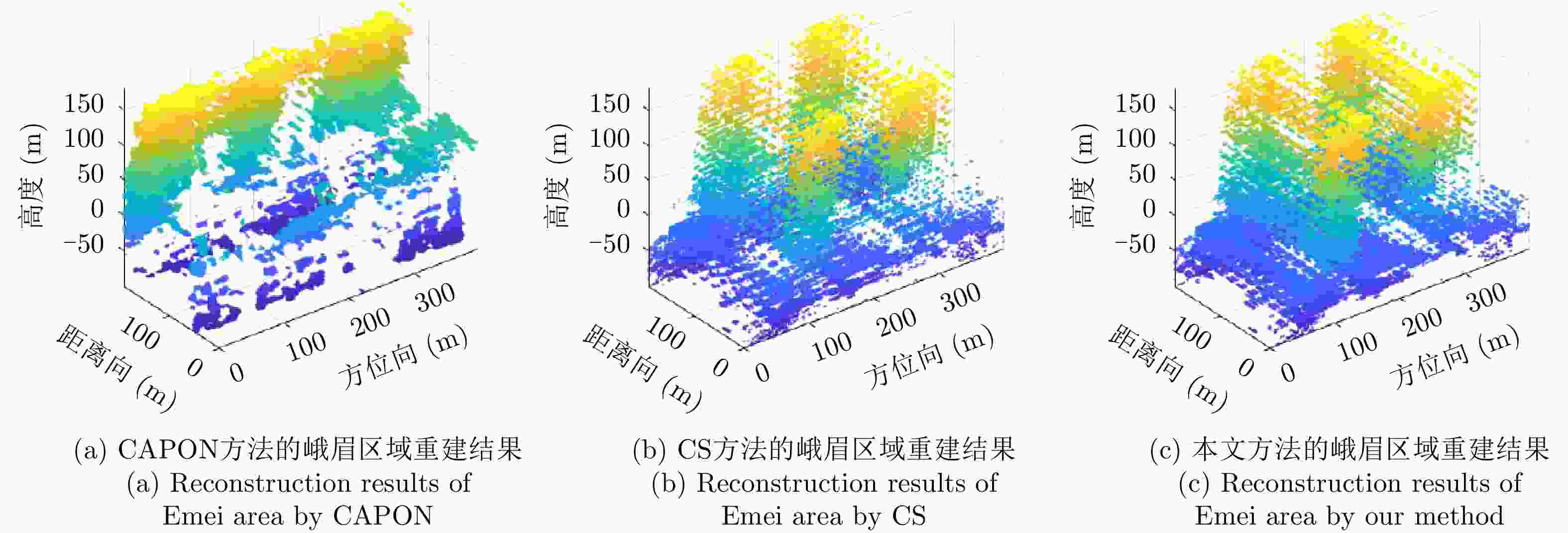
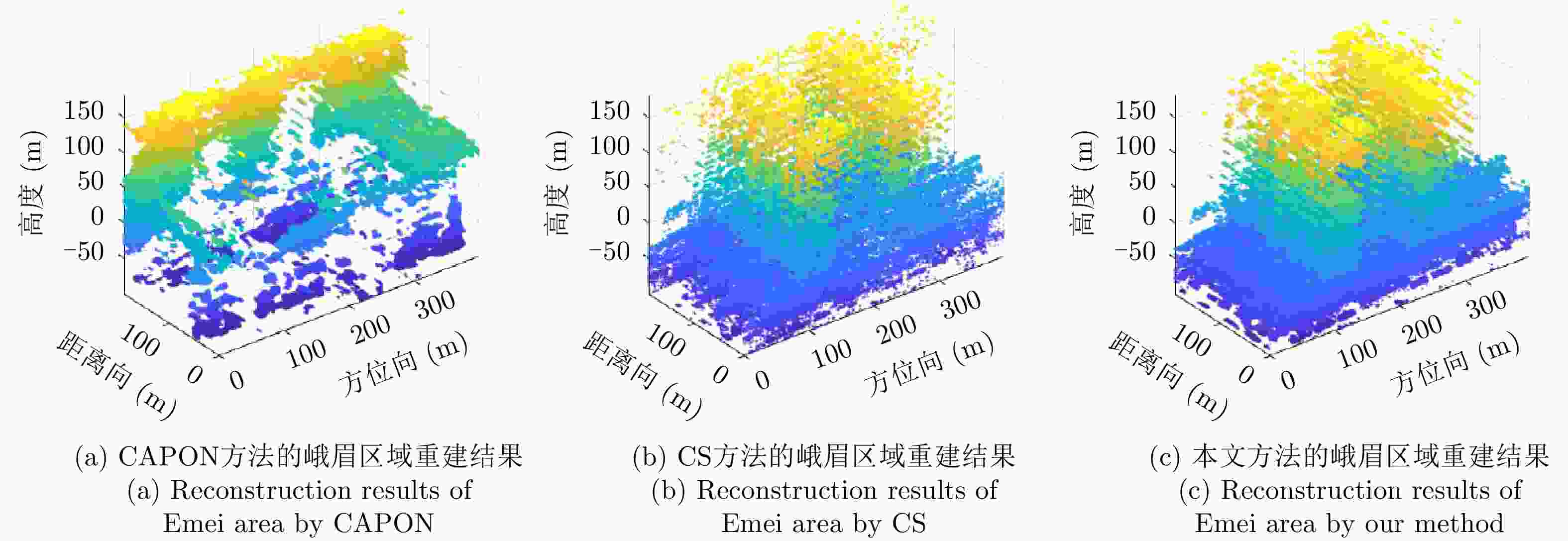
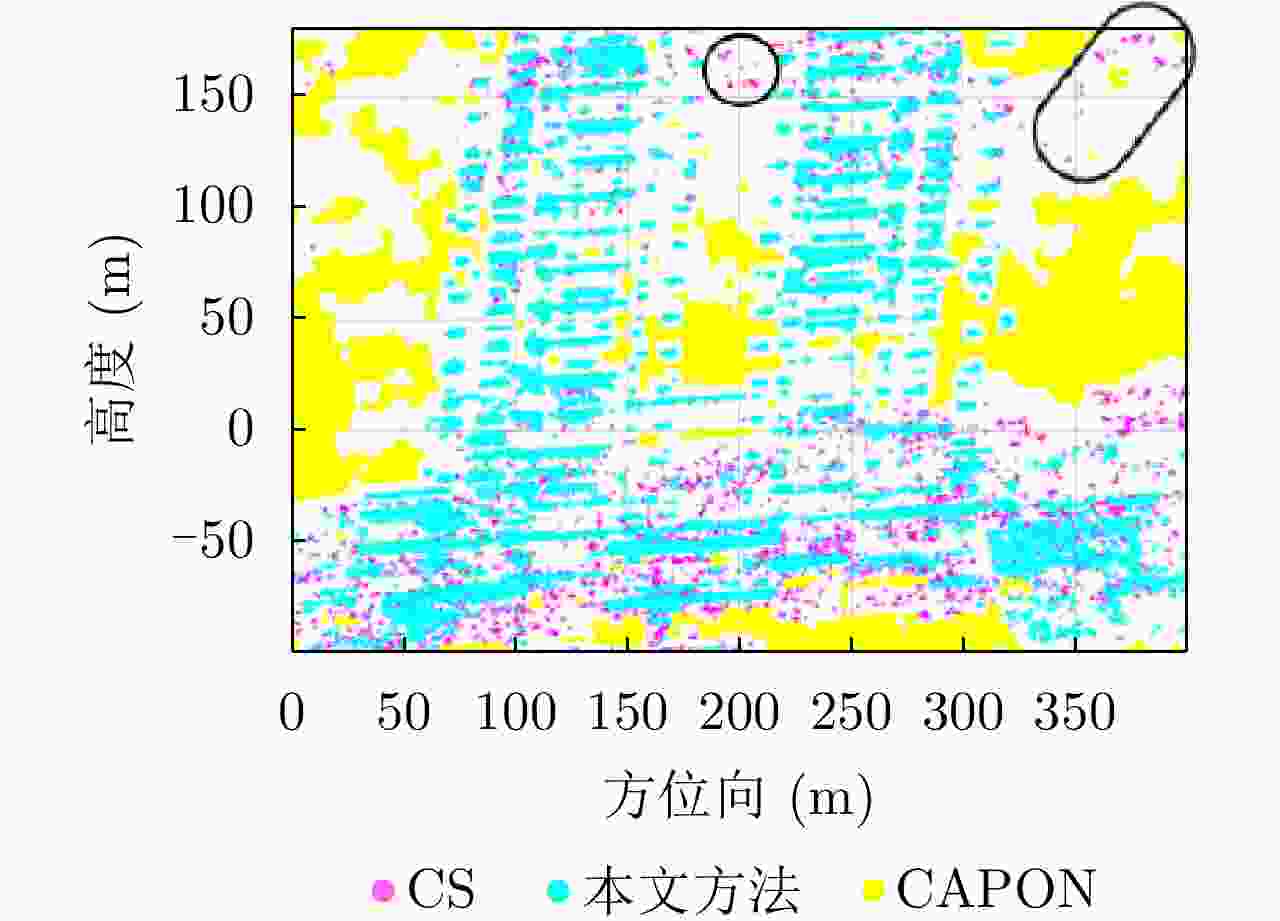
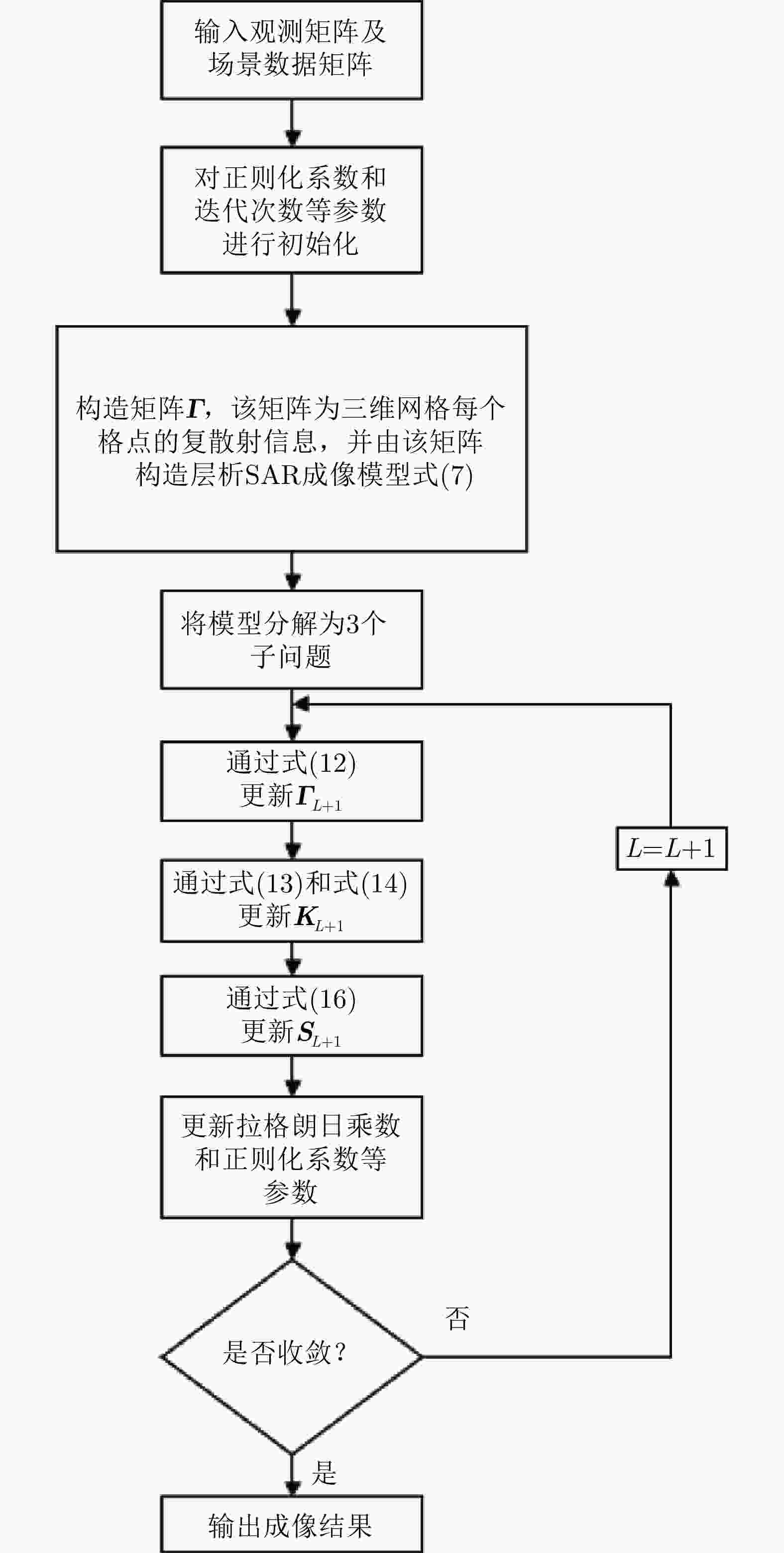
摘要: 该文提出了一种基于稀疏和低秩结构的层析SAR三维成像方法。传统基于压缩感知的层析SAR成像方法仅仅对给定方位-距离单元的高程向进行稀疏表征和重建。考虑城市和森林等区域中各自的布局分布较为类似,目标在相邻方位-距离单元的高程向分布具有较强相关性。该方法通过引入Karhunen Loeve变换来表征相邻方位-距离单元的高程向的低秩结构特性,构建稀疏和低秩结构相结合的目标区域层析SAR成像模型,采用ADMM算法对层析SAR成像模型进行求解,将复杂的原优化问题分解为若干相对简单的子问题,通过优化变量交替投影的方式进行算法求解,得到层析SAR成像结果。该方法提高了低航过数或低通道数情况下的重建精度,拥有更好的成像性能。仿真和实测数据实验表明,该重建方法能够有效分离散射体并保证重建能量的精度,且在降低航过数或通道数的情况下保持良好的成像效果,有效抑制伪影现象。
-
关键词:
- 三维成像 /
- 层析SAR成像 /
- 稀疏特性 /
- 低秩结构 /
- Karhunen Loeve变换
Abstract: This paper proposes a three-dimensional tomographic SAR imaging method based on a combined sparse and low-rank structures. The traditional Compressed Sensing (CS) based tomographic SAR imaging methods only utilize the sparse representation and reconstruct along the elevation axis of a given azimuth-distance unit. Considering that the target distributions in cities, forests, and other cases are relatively similar, the elevation backscattering patterns of adjacent azimuth-range cells (pixels) are expected to be highly correlated. The proposed method introduces the Karhunen-Loeve transform to characterize the low-rank structures of the elevation of the target areas and constructs a tomographic SAR imaging model that combines sparse and low-rank structures. The ADMM algorithm is applied to solve the tomographic SAR imaging model, the complex original optimization problem is decomposed into several relatively simple sub-problems, and the tomographic SAR imaging results are obtained by the alternate projection of optimization variables. This method improves the reconstruction accuracy in the case of a few interferograms or channels and has better imaging performance. Simulations and real data experiments show that the reconstruction method can effectively separate the scatterers and ensure the accuracy of the reconstruction energy, maintain a good imaging performance under the condition of reducing the number of interferograms or channels, and effectively suppress the artifacts.-
Key words:
- Three-Dimensional (3-D) imaging /
- SAR tomography /
- Sparse /
- Low-rank /
- Karhunen Loeve transform
-
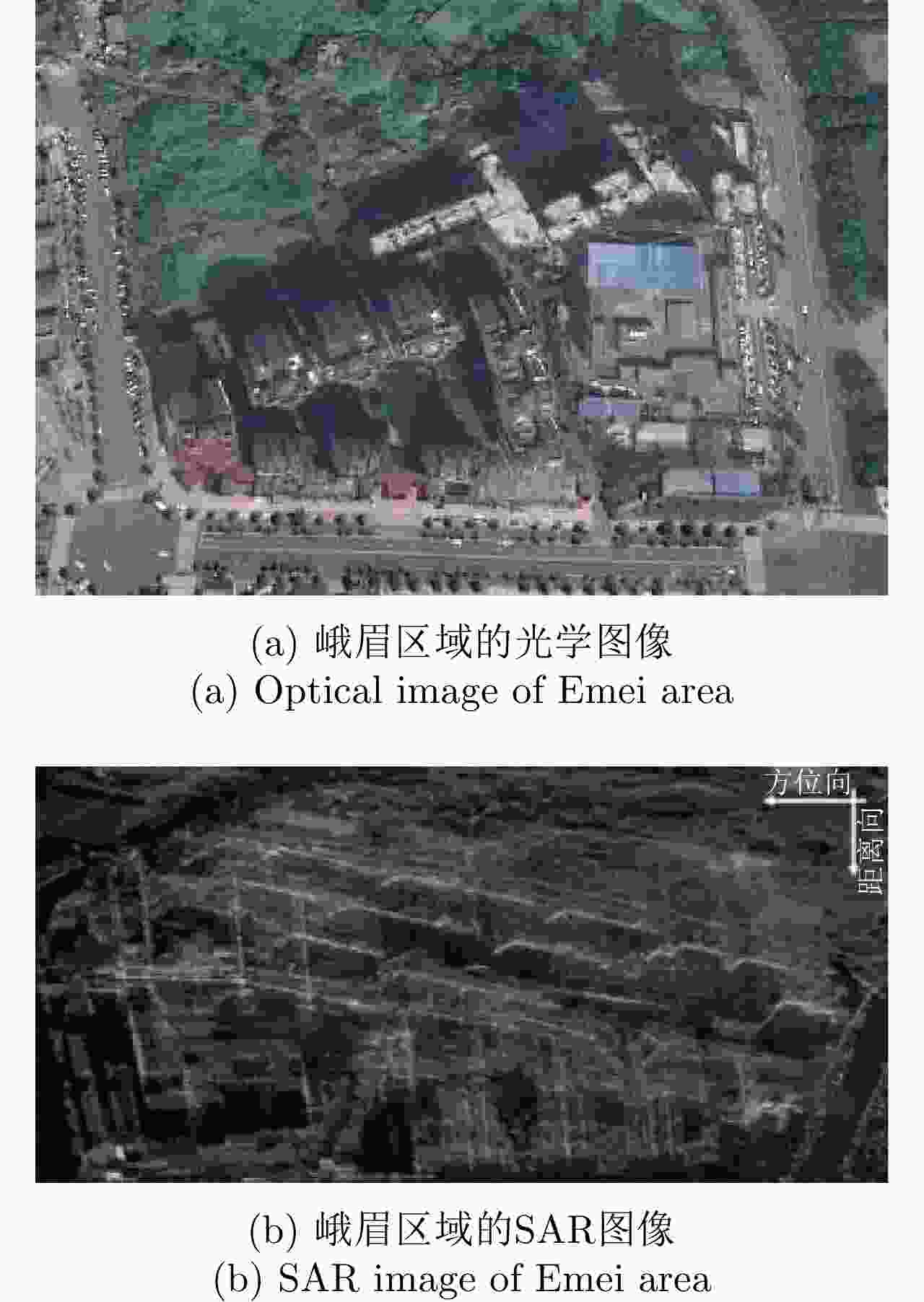
表 1 Ku波段雷达系统参数
Table 1. Ku-band radar system parameters
参数 数值 载波频率(GHz)
通道数N
成像场景海拔(m)
图像最近斜距(m)
航线海拔(m)
距离向像素尺寸(m)
方位向像素尺寸(m)
基线长度(m)14.5
12420
1861
2157
0.1362
0.1051
2表 2 各方法耗时对比
Table 2. Time comparison of each method
方法 耗时(s) CAPON 61.844378 CS 43386.651744 本文方法 72769.757387 -
[1] 李震, 张平, 乔海伟, 等. 层析SAR地表参数信息提取研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 116–130. doi: 10.12000/JR20095LI Zhen, ZHANG Ping, QIAO Haiwei, et al. Advances in information extraction of surface Parameters using Tomographic SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 116–130. doi: 10.12000/JR20095 [2] SCHMITT M and ZHU Xiaoxiang. Demonstration of single-pass millimeterwave SAR tomography for forest volumes[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(2): 202–206. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2506150 [3] 张斌, 韦立登, 胡庆荣, 等. 基于四阶累积量的机载多基线SAR谱估计解叠掩方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 740–749. doi: 10.12000/JR18087ZHANG Bin, WEI Lideng, HU Qingrong, et al. Solution to layover problemin airborne multi-baseline SAR based on spectrum estimation with fourth-order cumulant[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 740–749. doi: 10.12000/JR18087 [4] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像—从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090 [5] 张冰尘, 王万影, 毕辉, 等. 基于压缩多信号分类算法的森林区域极化SAR层析成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(3): 625–630. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140584ZHANG Bingchen, WANG Wanying, BI Hui, et al. Polarimetric SAR tomography for forested areas based on compressive multiple signal classification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(3): 625–630. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140584 [6] SHI Yilei, BAMLER R, WANG Yuanyuan, et al. SAR tomography at the limit: Building height reconstruction using only 3–5 TanDEM-X bistatic interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(11): 8026–8037. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2986052 [7] CAPON J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8): 1408–1418. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1969.7278 [8] LOMBARDINI F and REIGBER A. Adaptive spectral estimation for multibaseline SAR tomography with airborne L-band data[C]. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS’03, Toulouse, France, 2003: 2014–2016. [9] SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830 [10] 庞礴, 代大海, 邢世其, 等. SAR层析成像技术的发展和展望[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(7): 1421–1429. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.07.12PANG Bo, DAI Dahai, XING Shiqi, et al. Development and perspective of tomographic SAR imaging technique[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(7): 1421–1429. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.07.12 [11] 解金卫, 李真芳, 王帆, 等. 基于幅相不一致准则的建筑物SAR层析成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 154–165. doi: 10.12000/JR19062XIE Jinwei, LI Zhenfang, WANG Fan, et al. SAR tomography imaging for buildings using an inconsistency criterion for amplitude and phase[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 154–165. doi: 10.12000/JR19062 [12] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183 [13] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1-Norm regularization—The compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(10): 3839–3846. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117 [14] 廖明生, 魏恋欢, 汪紫芸, 等. 压缩感知在城区高分辨率SAR层析成像中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031LIAO Mingsheng, WEI Lianhuan, WANG Ziyun, et al. Compressive sensing in high-resolution 3D SAR tomography of urban scenarios[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031 [15] AGUILERA E, NANNINI M, and REIGBER A. Wavelet-based compressed sensing for SAR tomography of forested areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(12): 5283–5295. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2231081 [16] LINGALA S G, HU Yue, DIBELLA E, et al. Accelerated dynamic MRI exploiting sparsity and low-rank structure: K-T SLR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2011, 30(5): 1042–1054. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2010.2100850 [17] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Sparse reconstrcution techniques for SAR tomography[C]. 17th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), Corfu, Greece, 2011: 1–8. [18] LEE K and BRESLER Y. ADMiRA: Atomic decomposition for minimum rank approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2010, 56(9): 4402–4416. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2010.2054251 [19] RECHT B, FAZEL M, and PARRILO P A. Guaranteed minimum-rank solutions of linear matrix equations via nuclear norm minimization[J]. SIAM Review, 2010, 52(3): 471–501. doi: 10.1137/070697835 [20] TRUCKENBRODT J. EO-College tomography tutorial[EB/OL]. https://github.com/EO-College/tomography_tutorial, 2018. [21] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 彭凌霄, 等. SARMV3D-1.0: SAR微波视觉三维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, PENG Lingxiao, et al. SARMV3D-1.0: Synthetic aperture radar microwave vision 3D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: