Clutter Mitigation in Space-based Early Warning Radar Using a Convolutional Neural Network
-
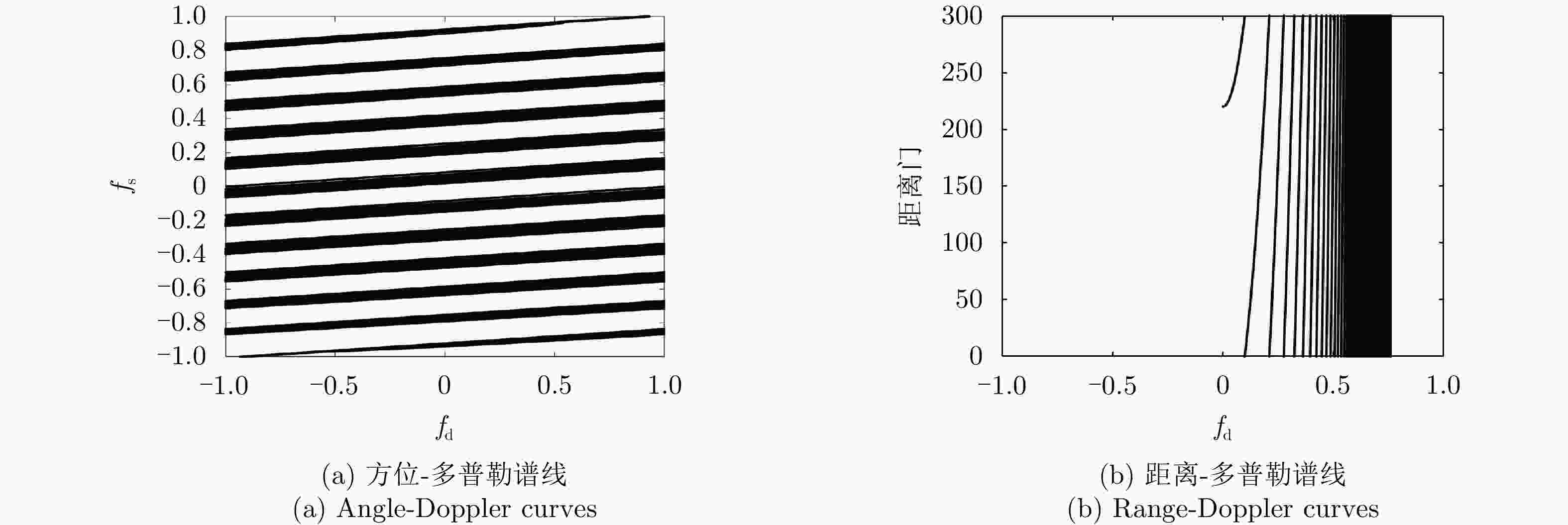
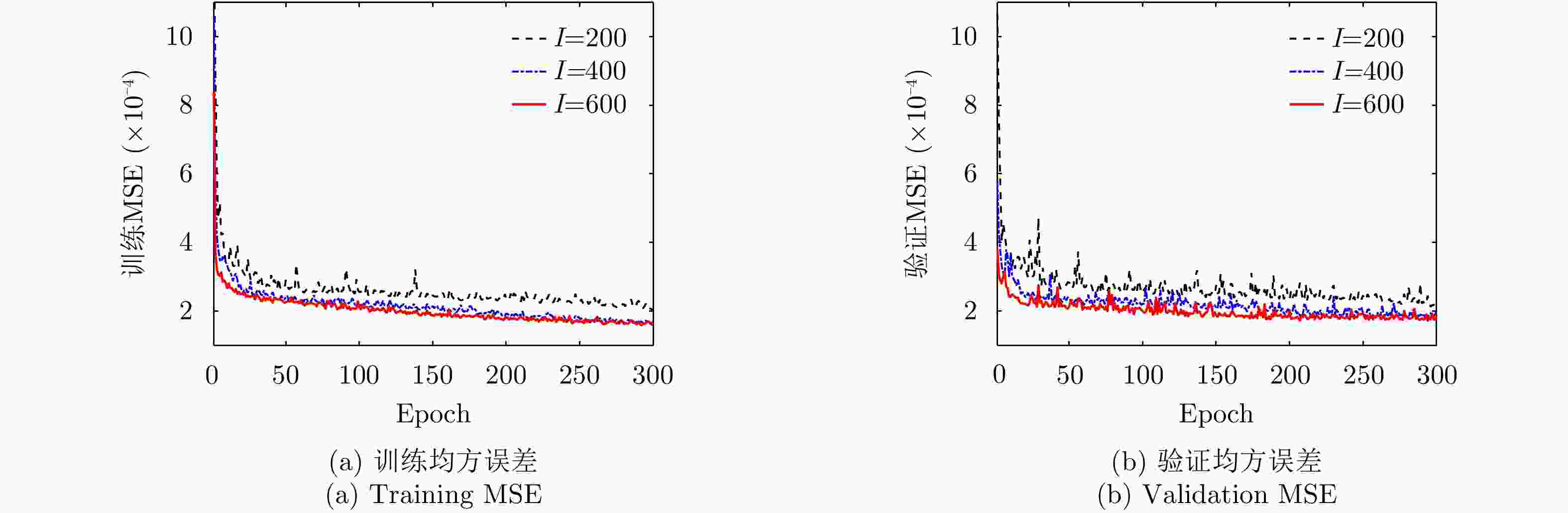
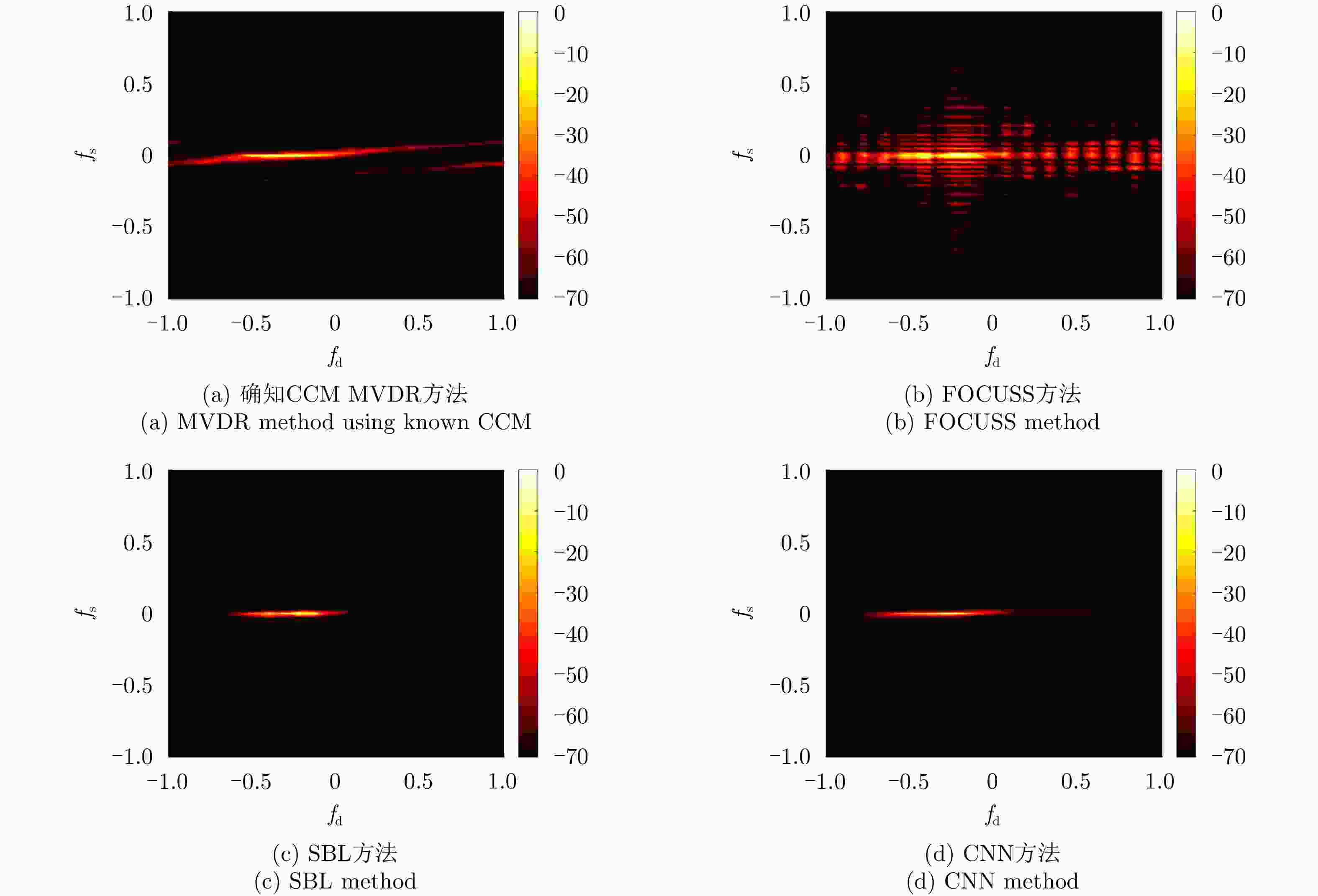
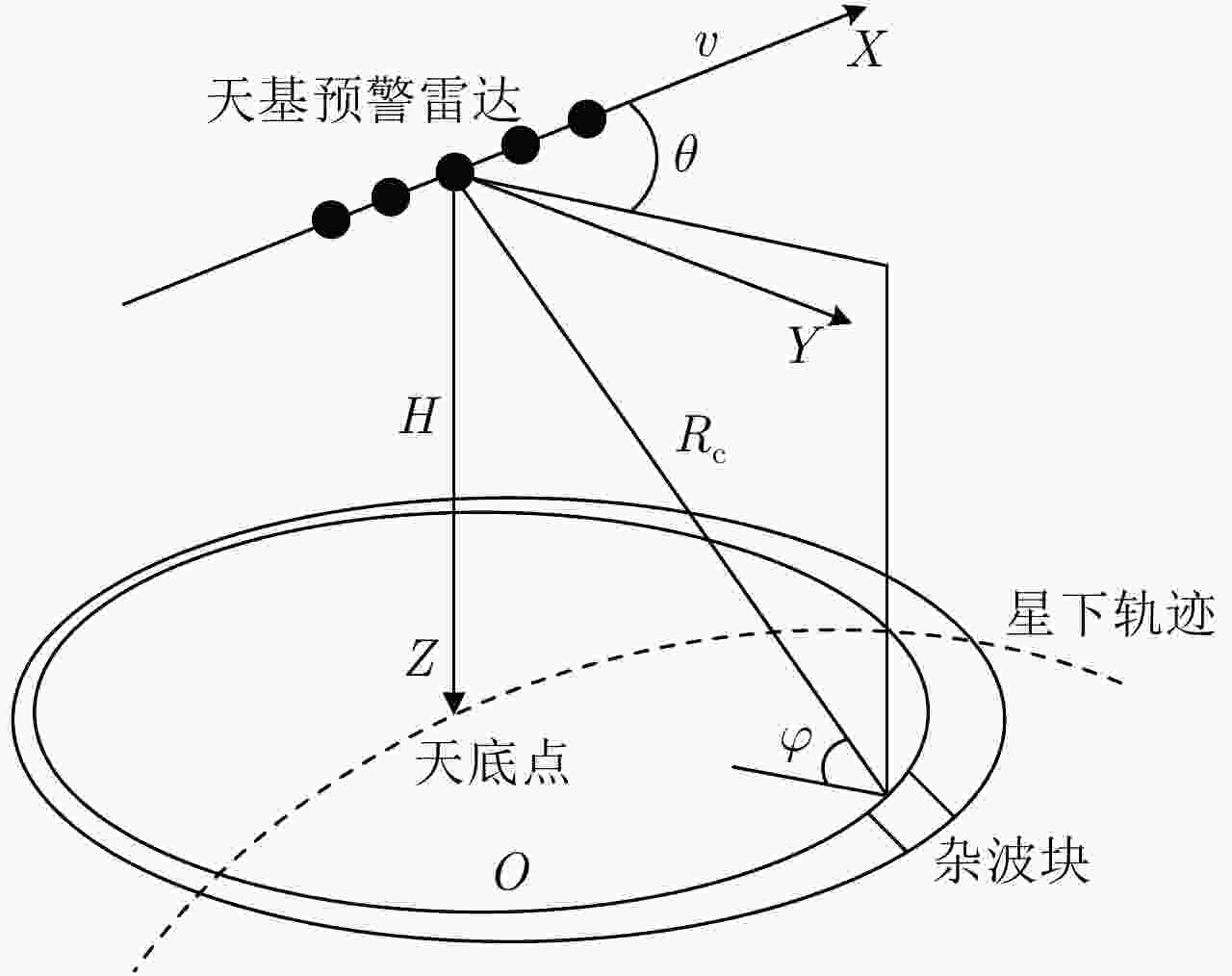
摘要: 利用天基预警雷达实现动目标指示具有重要的军事应用价值。对于天基预警雷达,其平台高速运动及受地球自转影响导致杂波复杂非平稳性,更大的波束照射区域带来更严重的杂波非均匀性,从而导致适用于机载预警雷达的传统空时自适应处理(STAP)方法无法直接应用。针对上述问题,该文分析了天基预警雷达杂波分布特性,并构建了基于卷积神经网络(CNN)超分辨谱估计的STAP处理框架。首先,利用雷达系统和卫星轨道参数,仿真随机生成不同纬度、距离门、阵元误差、杂波起伏和地貌散射系数的回波数据集;然后,设计并调优了含5个权重层的二维CNN,实现由小样本所估低分辨杂波谱到高分辨谱的非线性映射;最后,基于高分辨空时谱构造空时滤波器实现杂波抑制和目标检测。仿真实验验证所提方法在小样本条件下可实现次最优杂波抑制性能,同时所需在线运算量远低于现有稀疏超分辨类方法,因此适用于天基预警雷达实际应用。
-
关键词:
- 天基预警雷达 /
- 卷积神经网络(CNN) /
- 空时自适应处理(STAP) /
- 稀疏恢复 /
- 杂波抑制
Abstract: Moving target indication using space-based early warning radar is important in military applications. For the space-based early warning radar, complicated non-stationary clutter characteristics are induced due to the high-speed movement of the radar platform and Earth’s rotation, and more serious clutter non-homogeneity than the airborne radar scenario is caused by the large beam illumination region. Consequently, traditional Space-Time Adaptive Processing (STAP) methods, which have been widely used in airborne early warning radar, cannot be applied directly to the space-based early warning radar. In this study, we analyze the characteristic of clutter distribution and build a novel STAP framework, where high-resolution clutter spectra used to construct the adaptive weights is estimated via a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). First, clutter data sets were randomly simulated with different ranges of bin, latitude, spatial error, internal clutter motion, and coefficients of surface scattering, where the radar and satellite parameters were utilized as a priori knowledge. Then, we designed a two-dimensional CNN with five layers that converted a low-resolution clutter spectrum into a high-resolution spectrum. Finally, a space-time adaptive filter was calculated using the estimated high-resolution space-time spectrum and employed for clutter suppression and target detection. The simulation results show that the proposed CNN STAP can achieve sub-optimal performance under limited sample conditions, and a smaller computational load compared with a state-of-the-art sparse recovery STAP method. Therefore, this framework is suitable for practical application in space-based early warning radar. -
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Parameters of simulation
参数 数值 卫星轨道 506 km 卫星轨道倾角 70o 卫星速度 7610 m/s 天线尺寸 50 m×2 m 阵元数 384×12 合成通道数 32×1 工作频率 1250 MHz 带宽 3 MHz 主波束方位角 90o 主波束俯仰角 –30o 脉冲重复频率 10000 Hz 相参脉冲数 16 峰值辐射功率 25 kW 系统损耗 8 dB 表 2 稳定性分析
Table 2. Stability analysis
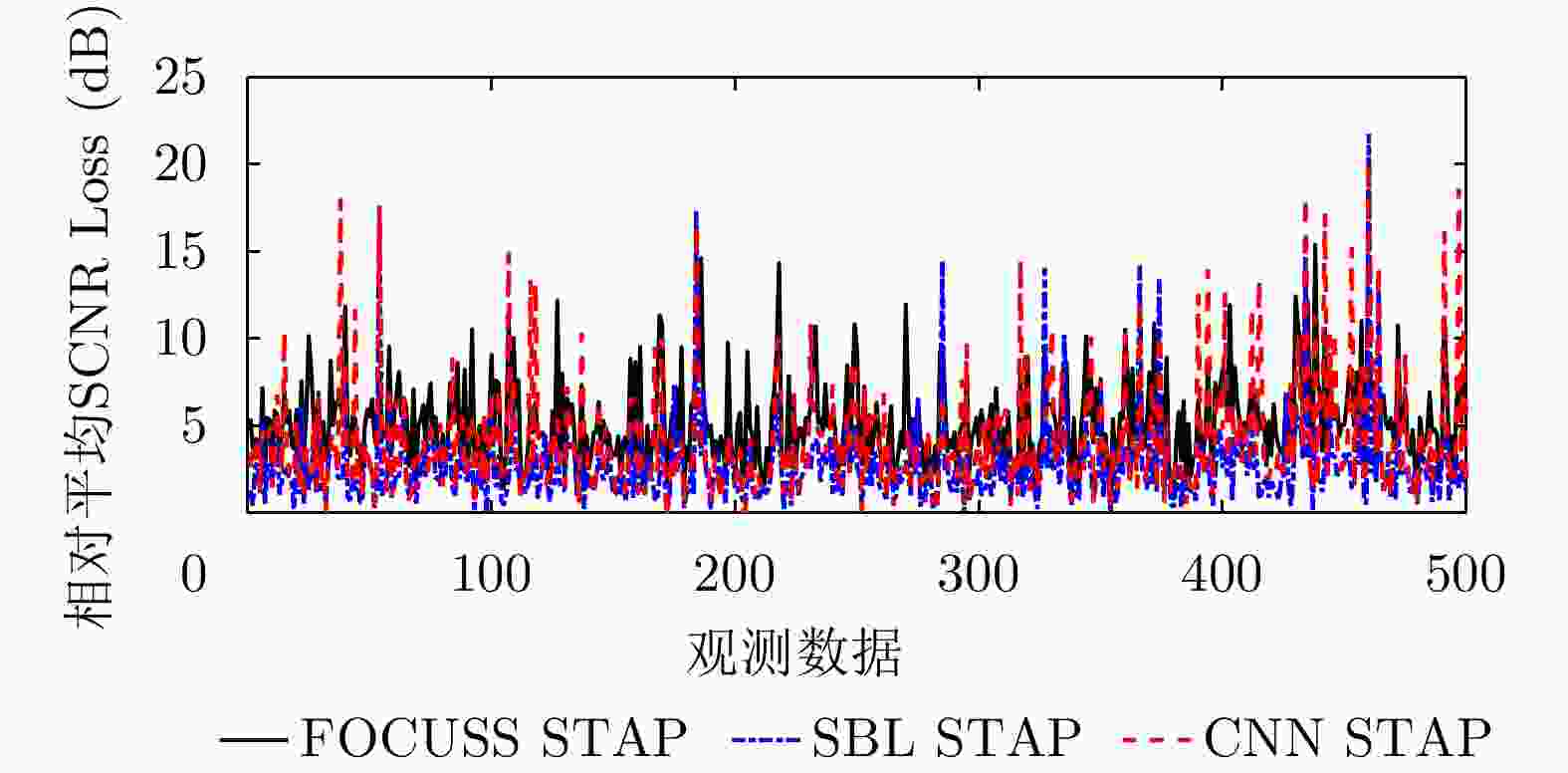
方法 ≤1 dB ≤3 dB ≤5 dB ≤7 dB ≤9 dB FOCUSS STAP 5.4% 35.0% 70.0% 87.0% 94.8% SBL STAP 44.0% 85.2% 90.0% 97.8% 98.0% CNN STAP 32.2% 73.6% 84.8% 92.0% 96.3% 表 3 运算复杂度分析
Table 3. Analysis of computational complexity
方法 运算复杂度 FOCUSS STAP $\begin{aligned} & {O}\left(\left(NM{N}_{\mathrm{s} }{N}_{\mathrm{d} }+{\left(NM\right)}^{3}+2{\left(NM\right)}^{2}{N}_{\mathrm{s} }{N}_{\mathrm{d} }\right.\right.\\& \left.\left.+NM{\left({N}_{\mathrm{s} }{N}_{\mathrm{d} }\right)}^{2}\right){k}_{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{C} }\right)\end{aligned}$ SBL STAP $\begin{aligned} & {O}\left(\left(NM{N}_{\mathrm{s} }{N}_{\mathrm{d} }+{\left(NM\right)}^{3}+3{\left(NM\right)}^{3}{N}_{\mathrm{s} }{N}_{\mathrm{d} }\right.\right.\\& \left.\left.+2NM{\left({N}_{\mathrm{s} }{N}_{\mathrm{d} }\right)}^{2}\right){k}_{\mathrm{S}\mathrm{B}\mathrm{L} }\right)\end{aligned}$ CNN STAP ${O}\left(28777{N}_{\mathrm{s} }{N}_{\mathrm{d} }\right)$ 表 4 运行时间比较
Table 4. Comparison of running time
方法 离线时间(s) 在线时间(s) FOCUSS STAP 0 30.84 SBL STAP 0 33.02 CNN STAP 5481 0.013 -
[1] 林幼权, 武楠. 天基预警雷达[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 1–2.LIN Youquan and WU Nan. Space Based Early Warning Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 1–2. [2] HOVANESSIAN S A, JOCIC L B, and LOPEZ J M. Spaceborne radar design equations and concepts[C]. 1997 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Snowmass, USA, 1997: 125–136. doi: 10.1109/AERO.1997.574402. [3] DAVIS M E. Technology challenges in affordable space based radar[C]. Record of the IEEE 2000 International Radar Conference, Alexandria, USA, 2000: 18–23. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2000.851798. [4] ROSEN P A and DAVIS M E. A joint space-borne radar technology demonstration mission for NASA and the air force[C]. 2003 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, Big Sky, USA, 2003: 1–444. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2003.1235073. [5] 左群声, 林幼权, 王友林. 天基预警雷达探测系统的发展[J]. 电子科学技术评论, 2004(3): 20–22, 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2004.03.004ZUO Qunsheng, LIN Youquan, and WANG Youlin. The development of space-based early warning radar system[J]. Review of Electronics Science and Technology, 2004(3): 20–22, 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2004.03.004 [6] 朱庆明, 金术玲, 孟祥玲. 国外天基预警雷达系统发展现状及关键技术[J]. 电讯技术, 2012, 52(6): 1054–1058. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2012.06.047ZHU Qingming, JIN Shuling, and MENG Xiangling. Current developments and key technologies of foreign space-based warning radars[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2012, 52(6): 1054–1058. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2012.06.047 [7] 陈荣. 美国天基预警雷达系统发展[J]. 国防科技, 2014, 35(2): 76–83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4547.2014.02.019CHEN Rong. Study of American space-based warning radar system development[J]. National Defense Science &Technology, 2014, 35(2): 76–83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4547.2014.02.019 [8] 李青, 林幼权, 武楠. 美国天基预警雷达发展历程及现状分析[J]. 现代雷达, 2018, 40(1): 7–10. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2018.01.002LI Qing, LIN Youquan, and WU Nan. Analysis of development history and status for American space-base early warning radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2018, 40(1): 7–10. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2018.01.002 [9] BRENNAN L E and REED L S. Theory of adaptive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1973, AES-9(2): 237–252. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1973.309792 [10] KOGON S M, RABIDEAU D J, and BARNES R M. Clutter mitigation techniques for space-based radar[C]. 1999 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Phoenix, USA, 1999: 2323–2326. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.1999.758403. [11] SCHUMAN H M, LI P G, SZCZEPANSKI W, et al. Space-time adaptive processing for space based radar[C]. 2004 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings, Big Sky, USA, 2004: 1904–1910. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2004.1367973. [12] PILLAI S, HIMED B, and LI Keyong. Effect of earth’s rotation and range foldover on space-based radar performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(3): 917–932. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.248188 [13] REED I D, MALLETT J D, and BRENNAN L E. Rapid convergence rate in adaptive arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1974, AES-10(6): 853–863. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1974.307893 [14] ZULCH P, DAVIS M, ADZIMA L, et al. The earth rotation effect on a LEO L-Band GMTI SBR and mitigation strategies[C]. 2004 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2004: 27–32. doi: 10.1109/NRC.2004.1316390. [15] LI Keyong, MANGIAT S, ZULCH P, et al. Clutter impacts on space based radar GMTI: A global perspective[C]. 2007 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2007: 1–15. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2007.353071. [16] ZULCH P A, HANCOCK R H, MORAN W, et al. Transmit waveform diversity for space based radar[C]. 2016 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2006: 10–16. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2006.1655932. [17] PAGE D A, HIMED B, and DAVIS M E. Improving STAP performance in bistatic space-based radar systems using an efficient expectation-maximization technique[C]. 2005 IEEE International Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2005: 109–114. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2005.1435803. [18] PAGE D A, HIMED B, and DAVIS M E. Higher order clutter mitigation in bistatic space-based radar systems using a knowledge-aided STAP approach[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006: 459–464. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2006.1631840. [19] 郁文贤, 张增辉, 胡卫东. 基于频率非均匀采样杂波谱配准的天基雷达STAP方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2009, 31(2): 358–362. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01244YU Wenxian, ZHANG Zenghui, and HU Weidong. STAP method for space based radar based on spectrum registration with non-uniformed frequency samples[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2009, 31(2): 358–362. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01244 [20] HALE T B, TEMPLE M A, and WICKS M C. Clutter suppression using elevation interferometry fused with space-time adaptive processing[J]. Electronics Letters, 2001, 37(12): 793–794. doi: 10.1049/el:20010494 [21] HALE T B, TEMPLE M A, RAQUET J F, et al. Localised three-dimensional adaptive spatial-temporal processing for airborne radar[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(1): 18–22. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030075 [22] MENG Xiangdong, WANG Tong, Wu Jianxin, et al. Short-range clutter suppression for airborne radar by utilizing prefiltering in elevation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(2): 268–272. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2012126 [23] SHEN M, MENG X, and ZHANG L. Efficient adaptive approach for airborne radar short-range clutter suppression[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(9): 900–904. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2011.0359 [24] Wu J X, WANG Tong, Meng X D, et al. Clutter suppression for airborne non-sidelooking radar using ERCB-STAP algorithm[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigatition, 2010, 4(4): 497–506. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2009.0121. [25] DUAN Keqing, XU Hong, YUAN Huadong, et al. Reduced-DOF three-dimensional STAP via subarray synthesis for nonsidelooking planar array airborne radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(4): 3311–3325. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2958174 [26] SARKAR T K, WANG Hong, PARK S, et al. A deterministic least-squares approach to space-time adaptive processing (STAP)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2001, 49(1): 91–103. doi: 10.1109/8.910535 [27] MELVIN W, WICKS M, ANTONIK P, et al. Knowledge-based space-time adaptive processing for airborne early warning radar[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 1998, 13(4): 37–42. doi: 10.1109/62.666835 [28] BERGIN J S, TEIXEIRA C M, TECHAU P M, et al. Improved clutter mitigation performance using knowledge-aided space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(3): 997–1009. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.248194 [29] WU Yong, TANG Jun, and PENG Yingning. On the essence of knowledge-aided clutter covariance estimate and its convergence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(1): 569–585. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5705692 [30] LI Jian, ZHU Xumin, STOICA P, et al. High resolution angle-Doppler imaging for MTI radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(3): 1544–1556. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5545209 [31] SUN Ke, MENG Huadong, WANG Yongliang, et al. Direct data domain STAP using sparse representation of clutter spectrum[J]. Signal Processing, 2011, 91(9): 2222–2236. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2011.04.006 [32] SEN S. OFDM radar space-time adaptive processing by exploiting spatio-temporal sparsity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(1): 118–130. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2222387 [33] YANG Xiaopeng, SUN Yuze, ZENG Tao, et al. Fast STAP method based on PAST with sparse constraint for airborne phased array radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(17): 4550–4561. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2569471 [34] YANG Zhaocheng, DE LAMARE R C, and LIU Weijian. Sparsity-based STAP using alternating direction method with gain/phase errors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(6): 2756–2768. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2714938 [35] DUAN Keqing, WANG Zetao, XIE Wenchong, et al. Sparsity-based STAP algorithm with multiple measurement vectors via sparse Bayesian learning strategy for airborne radar[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2017, 11(5): 544–553. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2016.0183 [36] HINTON G E and SALAKHUTDINOV R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science, 2016, 313(5786): 504–507. doi: 10.1126/science.1127647 [37] HINTON G E, OSINDERO S, and TEH Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets[J]. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7): 1527–1554. doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527 [38] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. doi: 10.5555/2999134.2999257. [39] DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]. The 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 184–199. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10593-2_13. [40] DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295–307. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281 [41] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28. [42] JIN K H, MCCANN M T, FROUSTEY E, et al. Deep convolutional neural network for inverse problems in imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(9): 4509–4522. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2713099 [43] MELVIN W L and SHOWMAN G A. An approach to knowledge-aided covariance estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(3): 1021–1042. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.248216 [44] 段克清, 袁华东, 许红, 等. 稀疏恢复空时自适应处理技术研究综述[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(3): 748–756. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.03.033DUAN Keqing, YUAN Huadong, XU Hong, et al. An overview on sparse recovery space-time adaptive processing technique[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(3): 748–756. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.03.033 [45] 陆军, 郦能敬, 曹晨, 等. 预警机系统导论[M]. 2版. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2011: 158–160.LU Jun, LI Nengjing, CAO Chen, et al. Introduction to Airborne Early Warning System[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2011: 158–160. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: