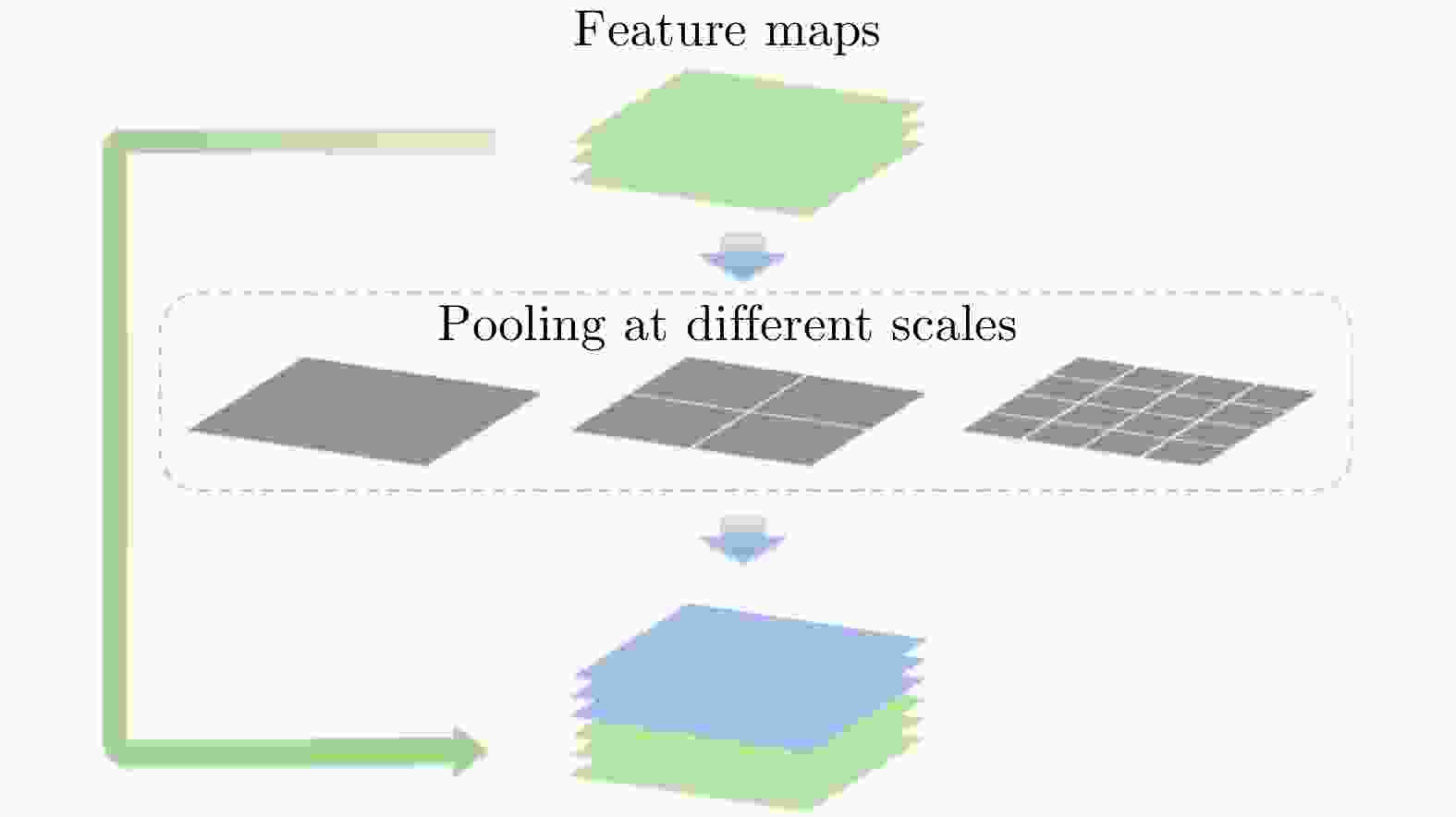
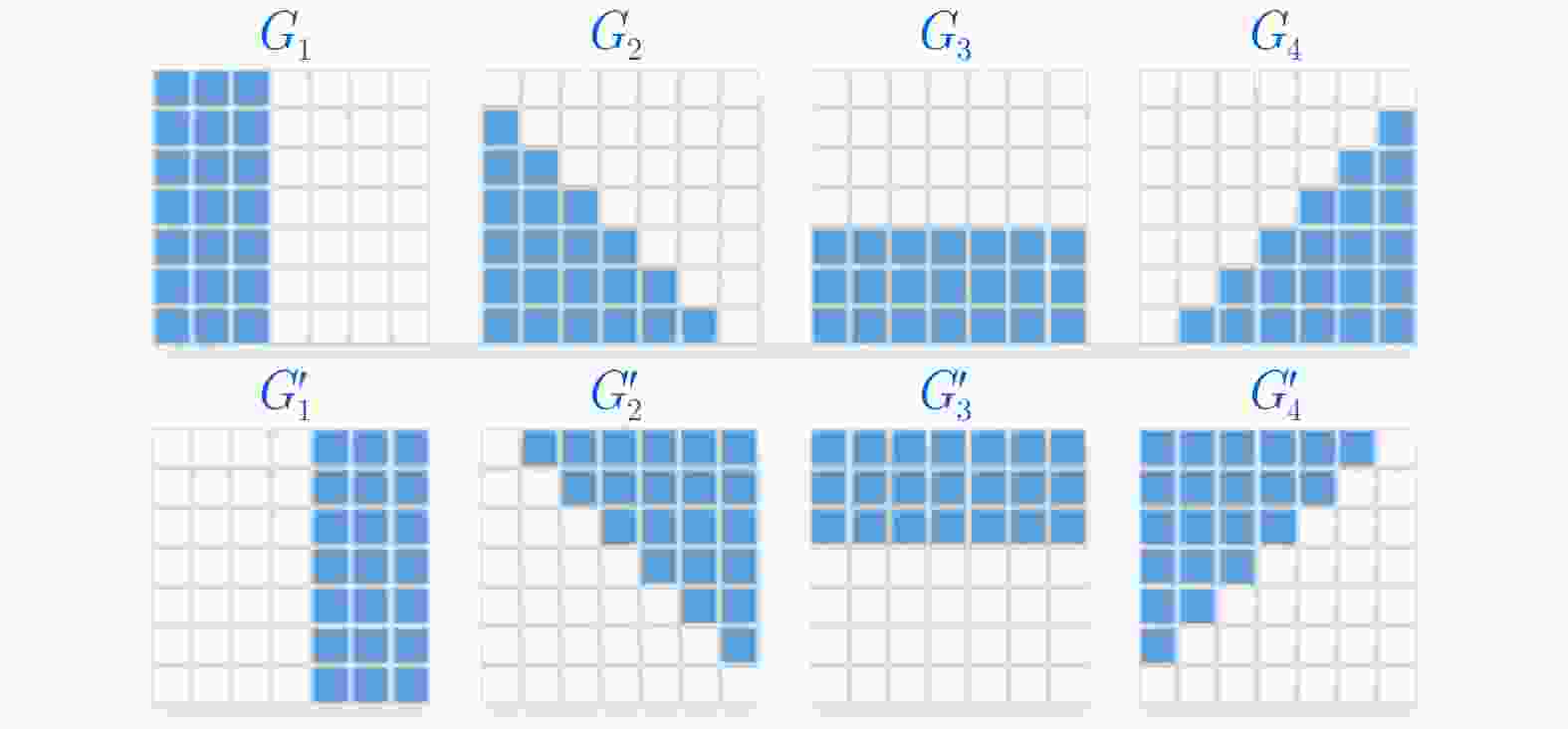
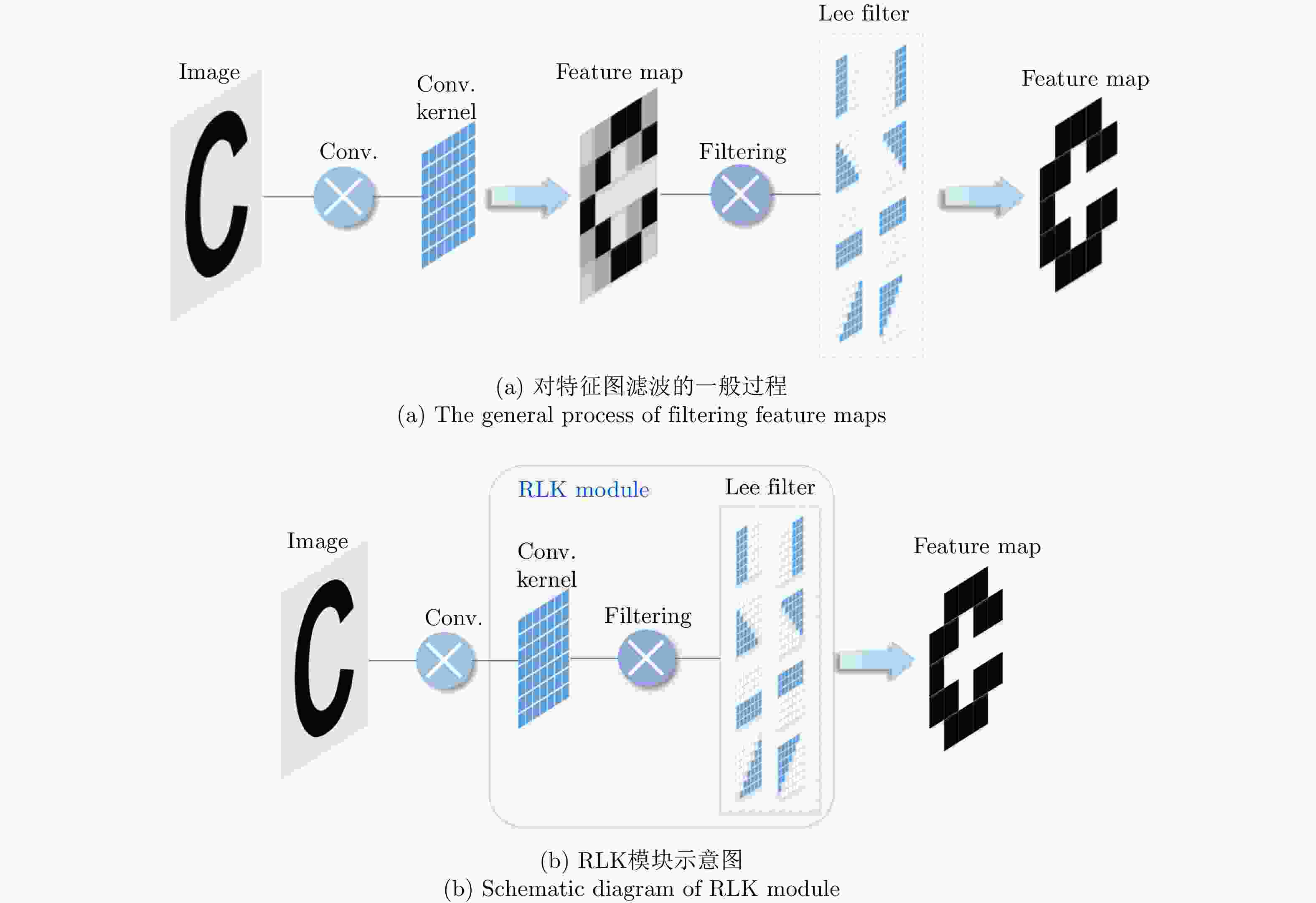
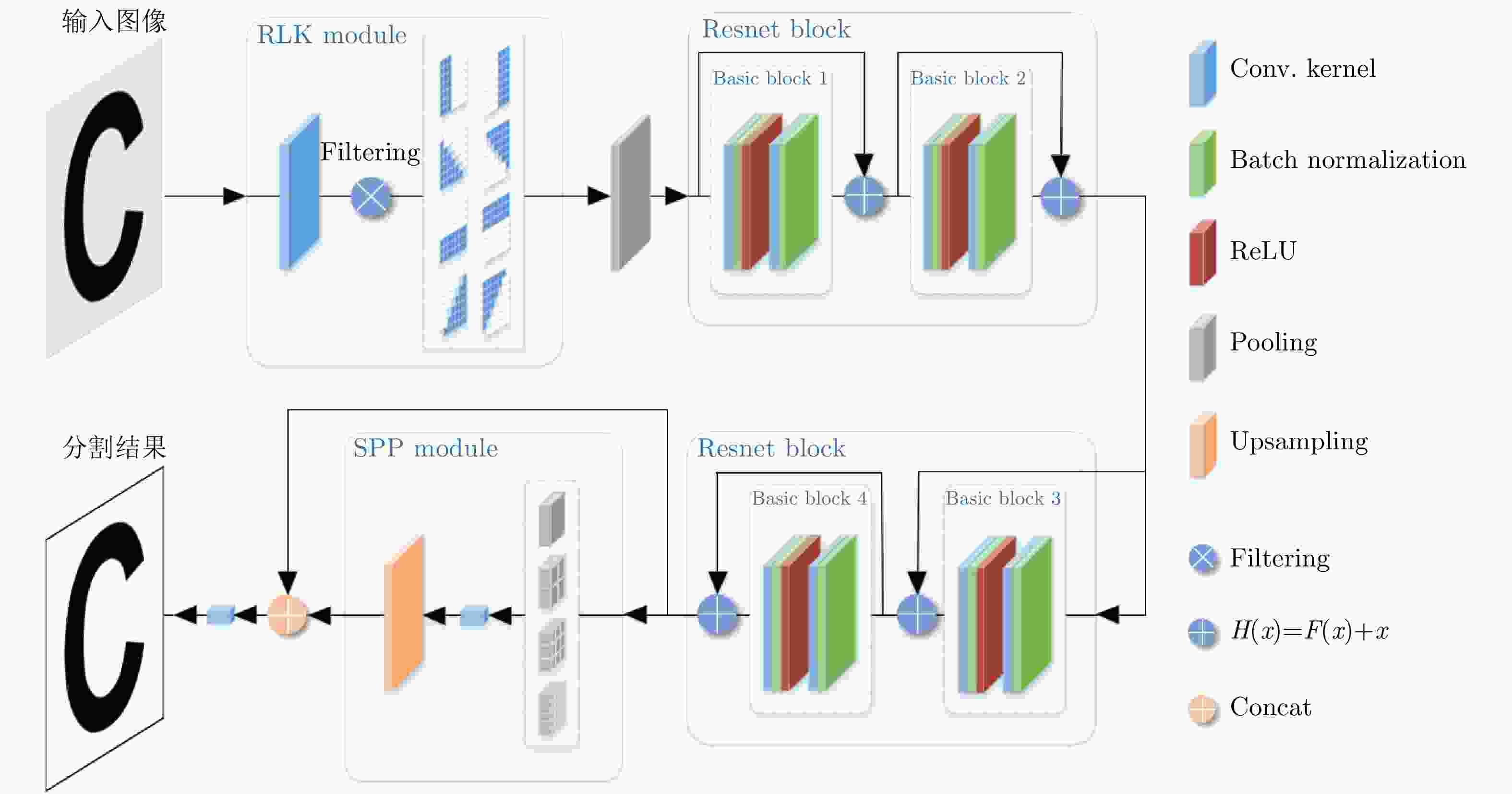
River-Net: A Novel Neural Network Model for Extracting River Channel Based on Refined-Lee Kernel
-
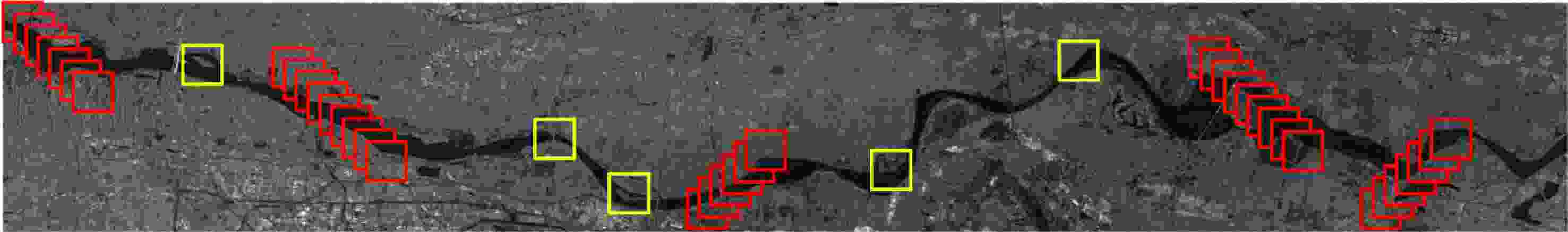
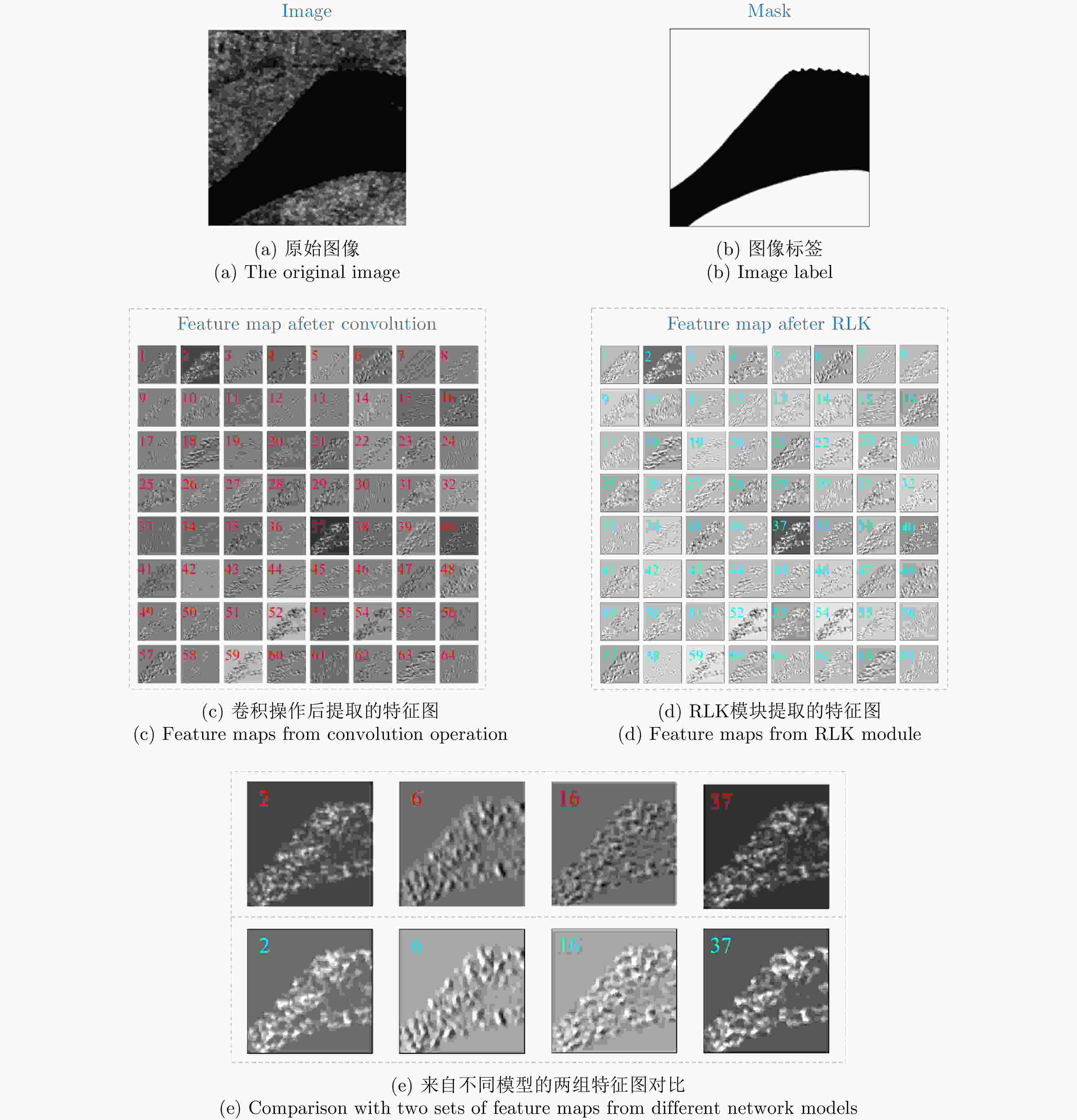
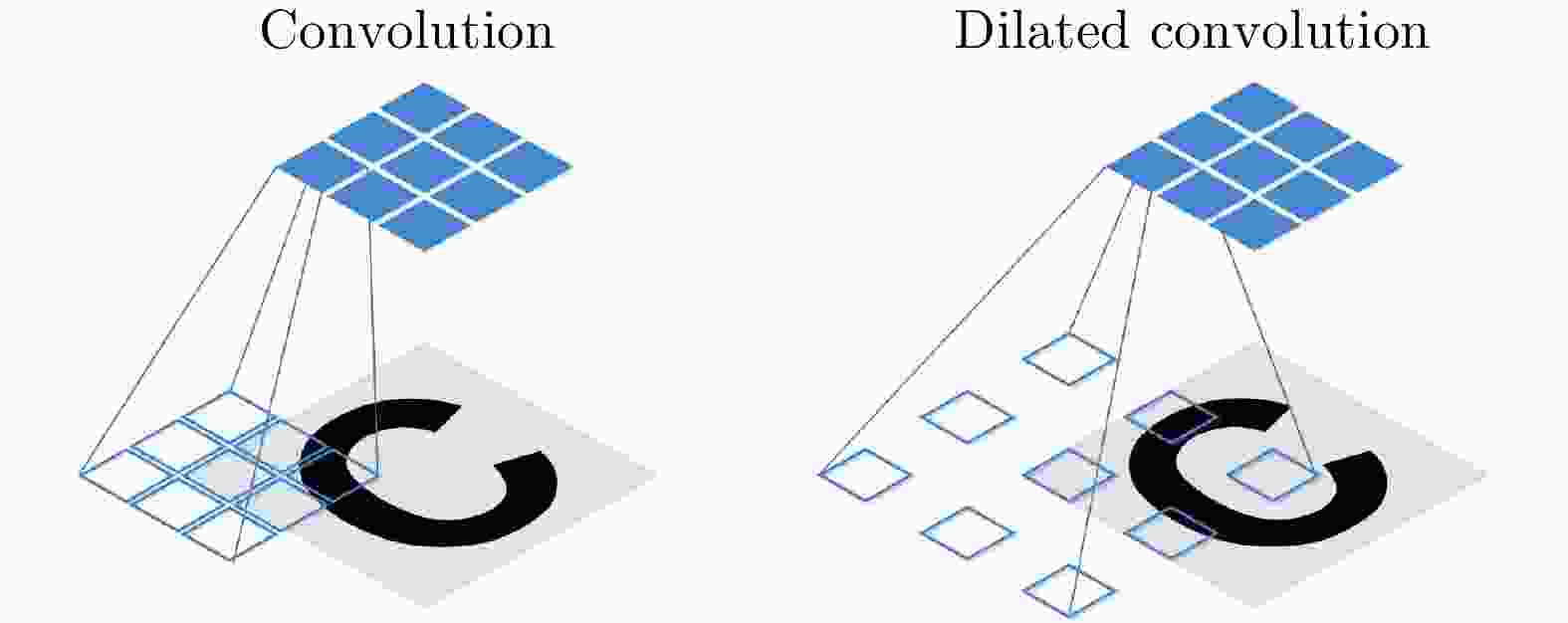
摘要: 高精度提取合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像中的河流边界,对河流水势监测具有重要意义。以检测郑州7·20暴雨后黄河的健康状况为实施例,该文融合精致Lee滤波思想与卷积操作的滤波特性,提出了基于河道几何特性的优化内部权值卷积核Refined-Lee Kernel,进而提出了一种新型河道提取深度神经网络模型,即River-Net。为验证所提模型的有效性,该文获取了郑州7·20暴雨前后两景欧空局Sentinel-1卫星20 m分辨率干涉宽幅(IW)影像数据,利用暴雨前的影像对模型进行训练,用于提取暴雨后的黄河河道,分析黄河在暴雨后的涨势情况。实验结果表明,相比主流语义分割模型,所提模型能够更精确地在SAR图像中提取河道,对洪水灾害的检测与评估有重要应用价值。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR) /
- Refined-Lee Kernel /
- 精致Lee滤波 /
- 神经网络 /
- 河道提取
Abstract: High-precision extraction of river boundaries in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images is of great significance in monitoring rivers. In this paper, the detection of the health of the Yellow River after the rainstorm in 20 July, 2021 in Zhengzhou is the focus of this paper. The refined-Lee filtering concept and the filtering characteristics of the convolution operation are combined, and an optimized internal weight convolution kernel Refined-Lee Kernel is proposed according to the geometric characteristics of the river channel. A novel river extraction deep neural network model, the River-Net, is also proposed. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed model, this article utilized 20 m resolution Interferometric Wideswath (IW) image data obtained from the European Space Agency Sentinel-1 satellite before and after the 20 July rainstorm in Zhengzhou, employing the images before the rainstorm to train the model. The model, after training, was used to extract the Yellow River channel and analyze the rise of the river after the rainstorm. Experimental results show that the proposed model can extract river channels from SAR images more accurately than trendy semantic segmentation models. The model has important application value for flood disaster detection and evaluation. -
表 1 混淆矩阵
Table 1. Confusion matrix
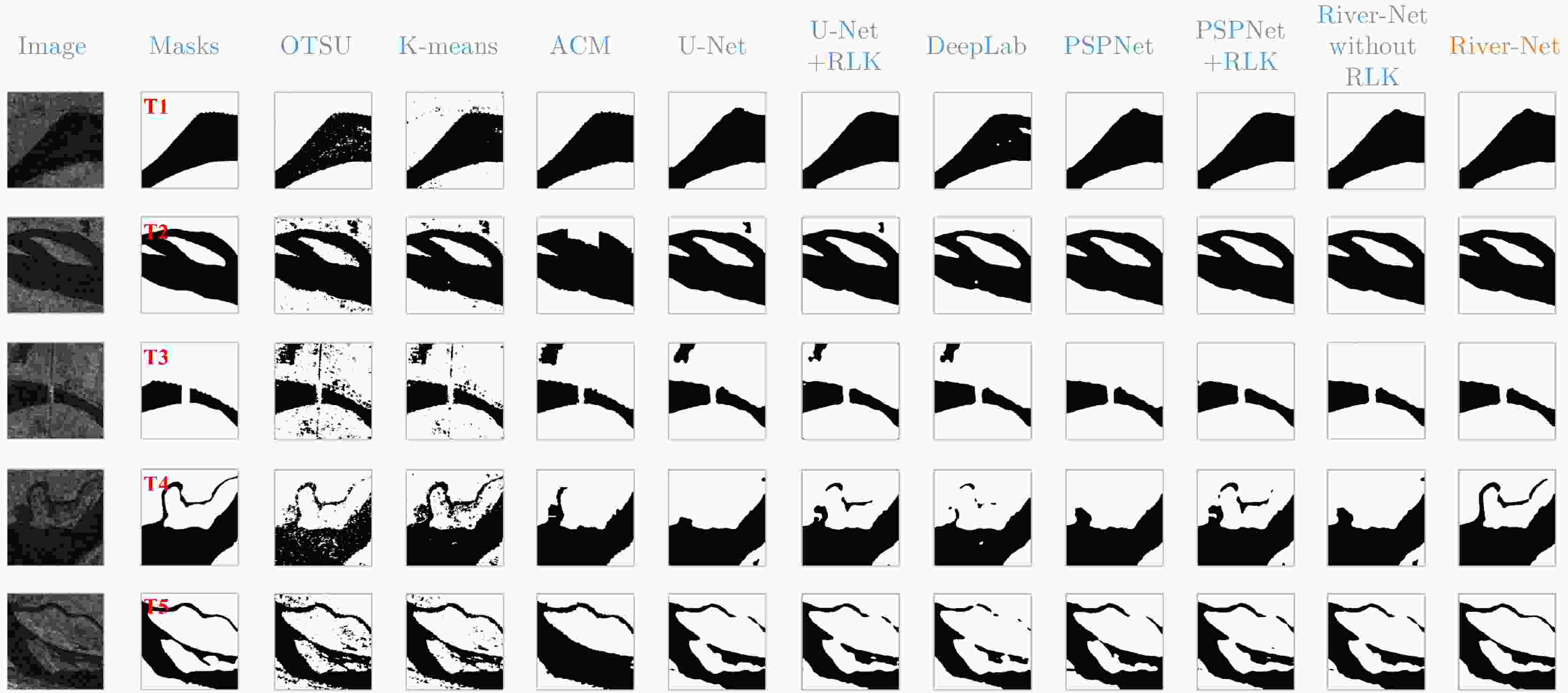
混淆矩阵 真实值 河道 背景 预测值 河道 TP FP 背景 FN TN 表 2 分割结果评价
Table 2. Evaluation of segmentation results
Algorithms/Models Precision (%) Recall (%) IoU (%) F1-score (%) 传统方法 OTSU 93.05 84.74 81.99 88.70 K-means 95.10 87.18 86.67 90.97 ACM 92.08 84.08 81.99 87.90 深度学习 U-Net 95.70 91.03 88.00 93.30 U-Net+RLK 96.22 93.18 91.92 94.68 DeepLab 95.42 91.13 89.40 93.23 PSPNet 96.06 92.73 90.04 94.36 PSPNet+RLK 97.17 93.24 93.36 95.16 River-Net without RLK 96.33 93.36 91.03 94.82 River-Net 97.32 94.40 92.93 95.84 -
[1] LI Ning, WANG R, DENG Yunkai, et al. Waterline mapping and change detection of tangjiashan dammed lake after wenchuan earthquake from multitemporal high-resolution airborne SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(8): 3200–3209. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2345417 [2] 冷英, 李宁. 一种改进的变化检测方法及其在洪水监测中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 204–212. doi: 10.12000/JR16139LENG Ying and LI Ning. Improved change detection method for flood monitoring[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 204–212. doi: 10.12000/JR16139 [3] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [4] 李宁, 牛世林. 基于局部超分辨重建的高精度SAR图像水域分割方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 174–184. doi: 10.12000/JR19096LI Ning and NIU Shilin. High-precision water segmentation from synthetic aperture radar images based on local super-resolution restoration technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 174–184. doi: 10.12000/JR19096 [5] 程江华, 高贵, 库锡树, 等. 高分辨率SAR图像道路交叉口检测与识别新方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 100–108. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20024CHENG Jianghua, GAO Gui, KU Xishu, et al. A novel method for detecting and identifying road junctions from high resolution SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 100–108. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20024 [6] LIU Tao, YANG Ziyuan, MARINO A, et al. PolSAR ship detection based on neighborhood polarimetric covariance matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(6): 4874–4887. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3022181 [7] LIU Zhongling, LI Fei, LI Ning, et al. A novel region-merging approach for coastline extraction from sentinel-1A IW Mode SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(3): 324–328. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2510745 [8] LI Wenyu and GONG Peng. Continuous monitoring of coastline dynamics in western Florida with a 30-year time series of Landsat imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 179: 196–209. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.03.031 [9] LI Ning, NIU Shilin, GUO Zhengwei, et al. Dynamic waterline mapping of inland great lakes using time-series SAR data from GF-3 and S-1A satellites: A case study of DJK reservoir, China[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(11): 4297–4314. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2952902 [10] JIANG Liguang, NIELSEN K, DINARDO S, et al. Evaluation of Sentinel-3 SRAL SAR altimetry over Chinese rivers[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2020, 237: 111546. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111546.0 [11] 安成锦, 牛照东, 李志军, 等. 典型Otsu算法阈值比较及其SAR图像水域分割性能分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(9): 2215–2219. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01426AN Chengjin, NIU Zhaodong, LI Zhijun, et al. Otsu threshold comparison and SAR water segmentation result analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(9): 2215–2219. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01426 [12] BAO Linan, LV Xiaolei, and YAO Jingchuan. Water extraction in SAR Images using features analysis and dual-threshold graph cut model[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(17): 3465. doi: 10.3390/rs13173465 [13] 冷英, 刘忠玲, 张衡, 等. 一种改进的ACM算法及其在鄱阳湖水域监测中的应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(5): 1064–1070. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160870LENG Ying, LIU Zhongling, ZHANG Heng, et al. Improved ACM algorithm for poyang lake monitoring[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(5): 1064–1070. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160870 [14] LI Ning, WANG R, LIU Yabo, et al. Robust river boundaries extraction of dammed lakes in mountain areas after Wenchuan Earthquake from high resolution SAR images combining local connectivity and ACM[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 94: 91–101. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.04.020 [15] JIA Lu, LI Ming, ZHANG Peng, et al. SAR image change detection based on multiple kernel k-means clustering with local-neighborhood information[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(6): 856–860. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2550666 [16] SUN Xian, WANG Bing, WANG Zhirui, et al. Research progress on few-shot learning for remote sensing image interpretation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 2387–2402. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3052869 [17] LIU Wenjie, ZHANG Wenkai, SUN Xian, et al. HECR-Net: Height-embedding context reassembly network for semantic segmentation in aerial images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 9117–9131. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3109439 [18] LATINI D, DEL FRATE F, PALAZZO F, et al. Coastline extraction from SAR COSMO-SkyMed data using a new neural network algorithm[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 5975–5977. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6352247. [19] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3431–3440. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298965. [20] PAI M M M, MEHROTRA V, AIYAR S, et al. Automatic segmentation of river and land in SAR images: A deep learning approach[C]. 2019 IEEE Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Knowledge Engineering, Sardinia, Italy, 2019: 15–20. doi: 10.1109/AIKE.2019.00011. [21] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28. [22] PAI M M M, MEHROTRA V, VERMA U, et al. Improved semantic segmentation of water bodies and land in SAR images using generative adversarial networks[J]. International Journal of Semantic Computing, 2020, 14(1): 55–69. doi: 10.1142/S1793351X20400036 [23] VERMA U, CHAUHAN A, PAI M M M, et al. DeepRivWidth: Deep learning based semantic segmentation approach for river identification and width measurement in SAR images of Coastal Karnataka[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2021, 154: 104805. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2021.104805. [24] 张金松, 邢孟道, 孙光才. 一种基于密集深度分离卷积的SAR图像水域分割算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 400–412. doi: 10.12000/JR19008ZHANG Jinsong, XING Mengdao, and SUN Guangcai. A water segmentation algorithm for SAR image based on dense depthwise separable convolution[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 400–412. doi: 10.12000/JR19008 [25] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834–848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [26] ZHAO Hengshuang, SHI Jianping, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6230–6239. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.660. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: