Comparative Experiments on Separation Performance of Overlapping Scatterers with Several Tomography Imaging Methods
-
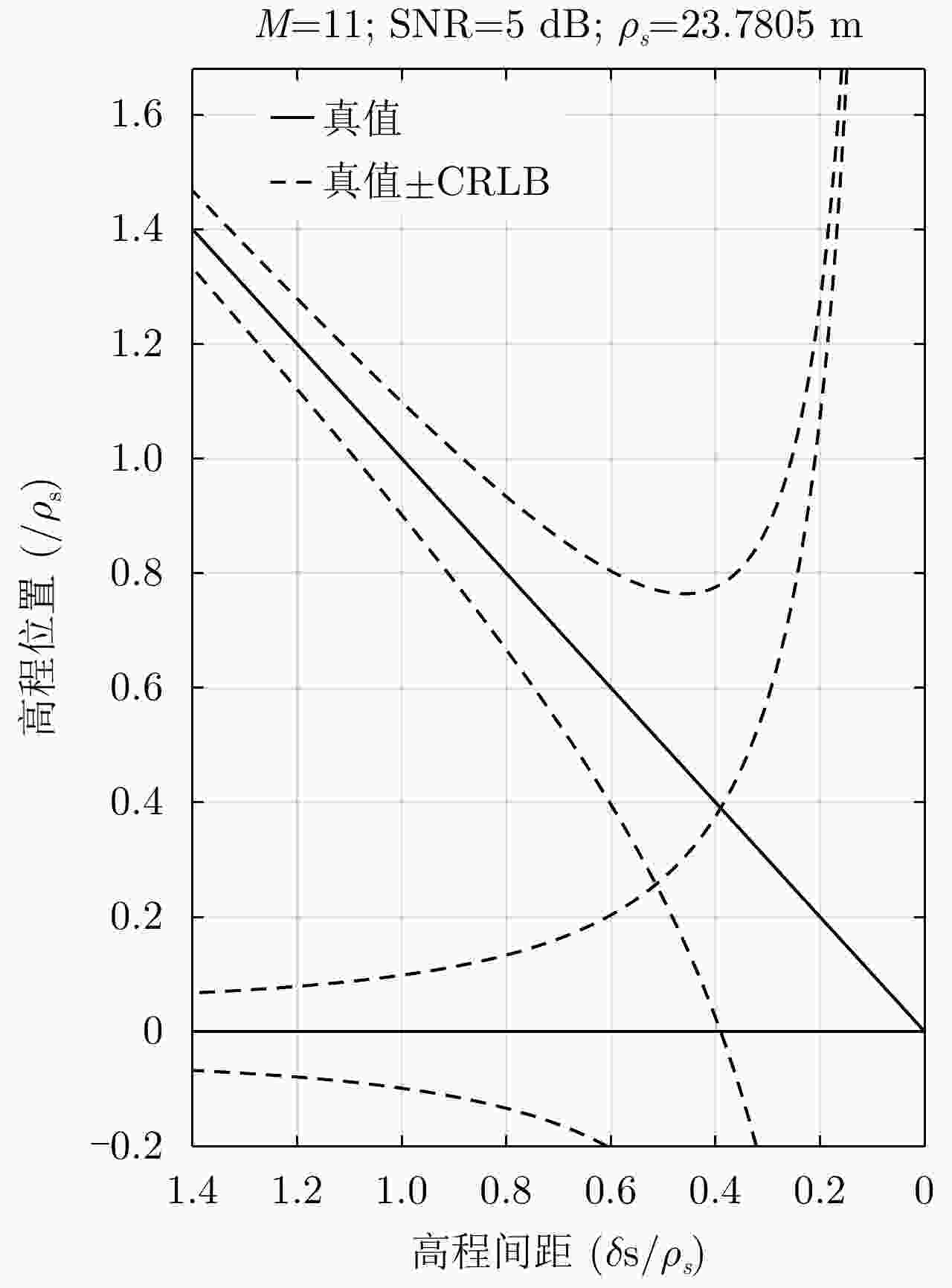
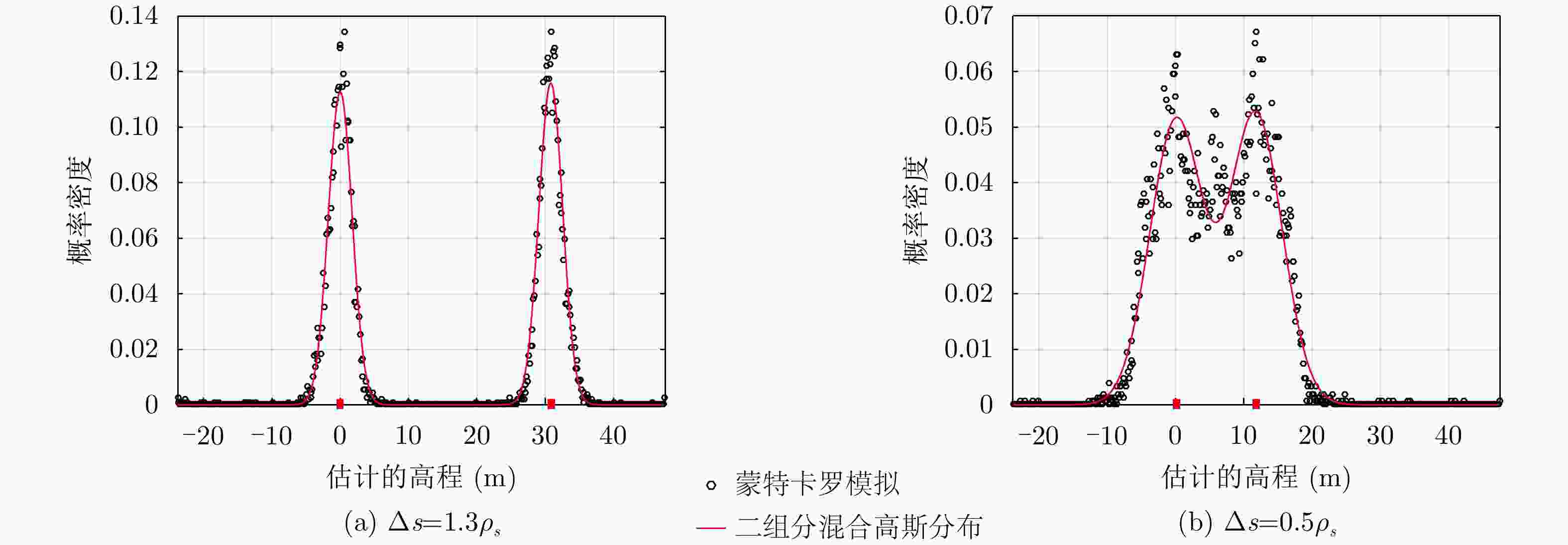
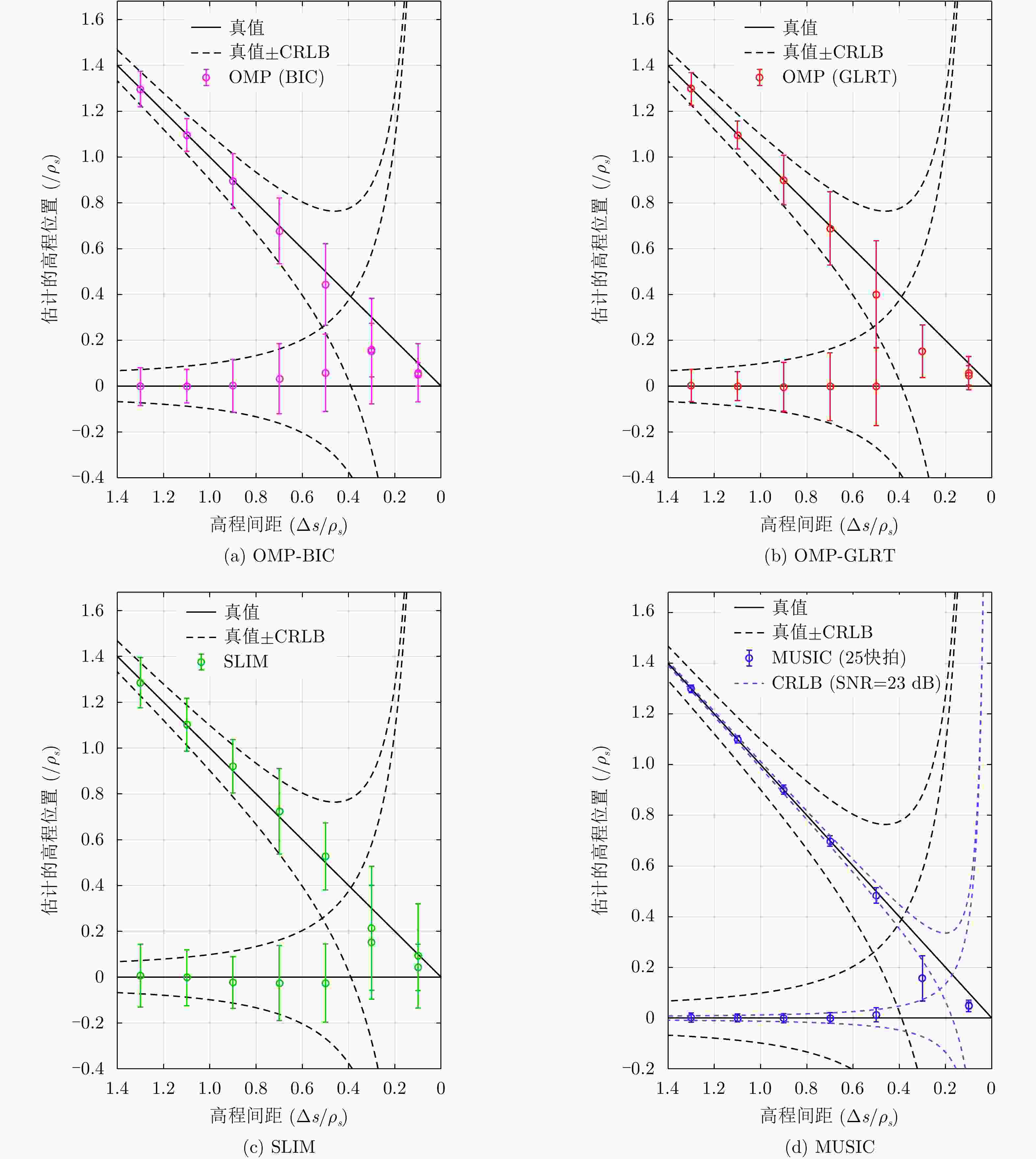
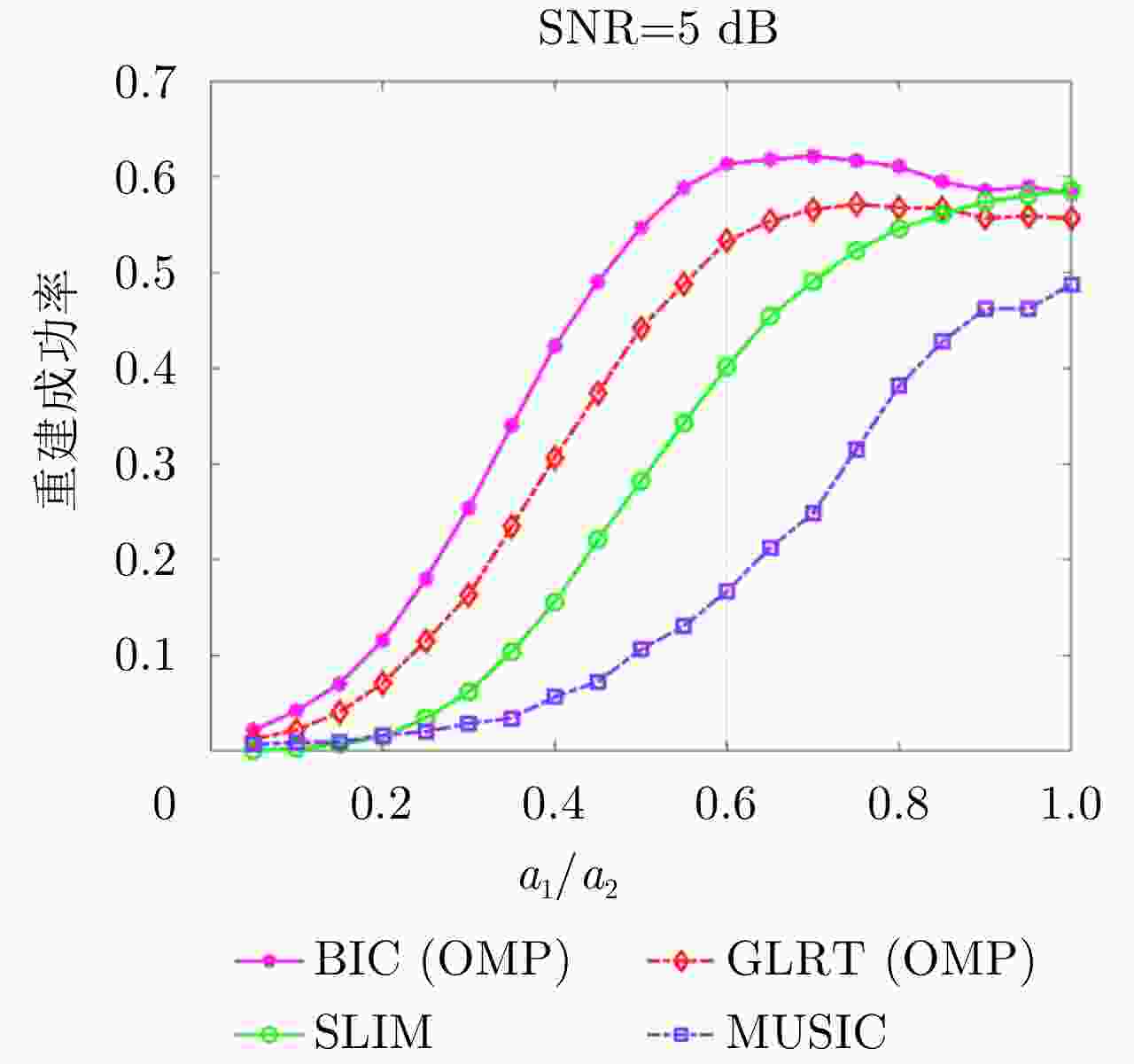
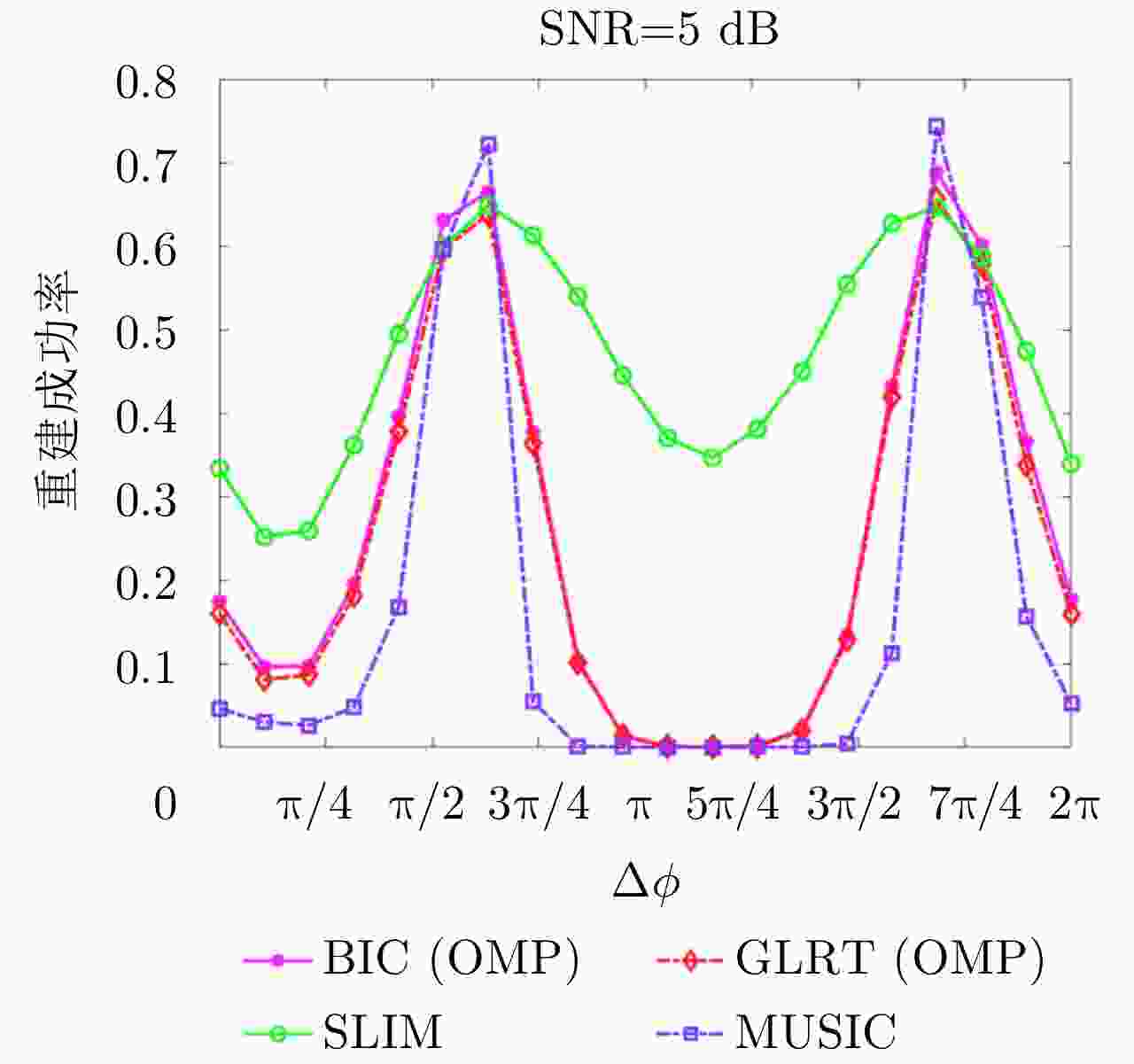
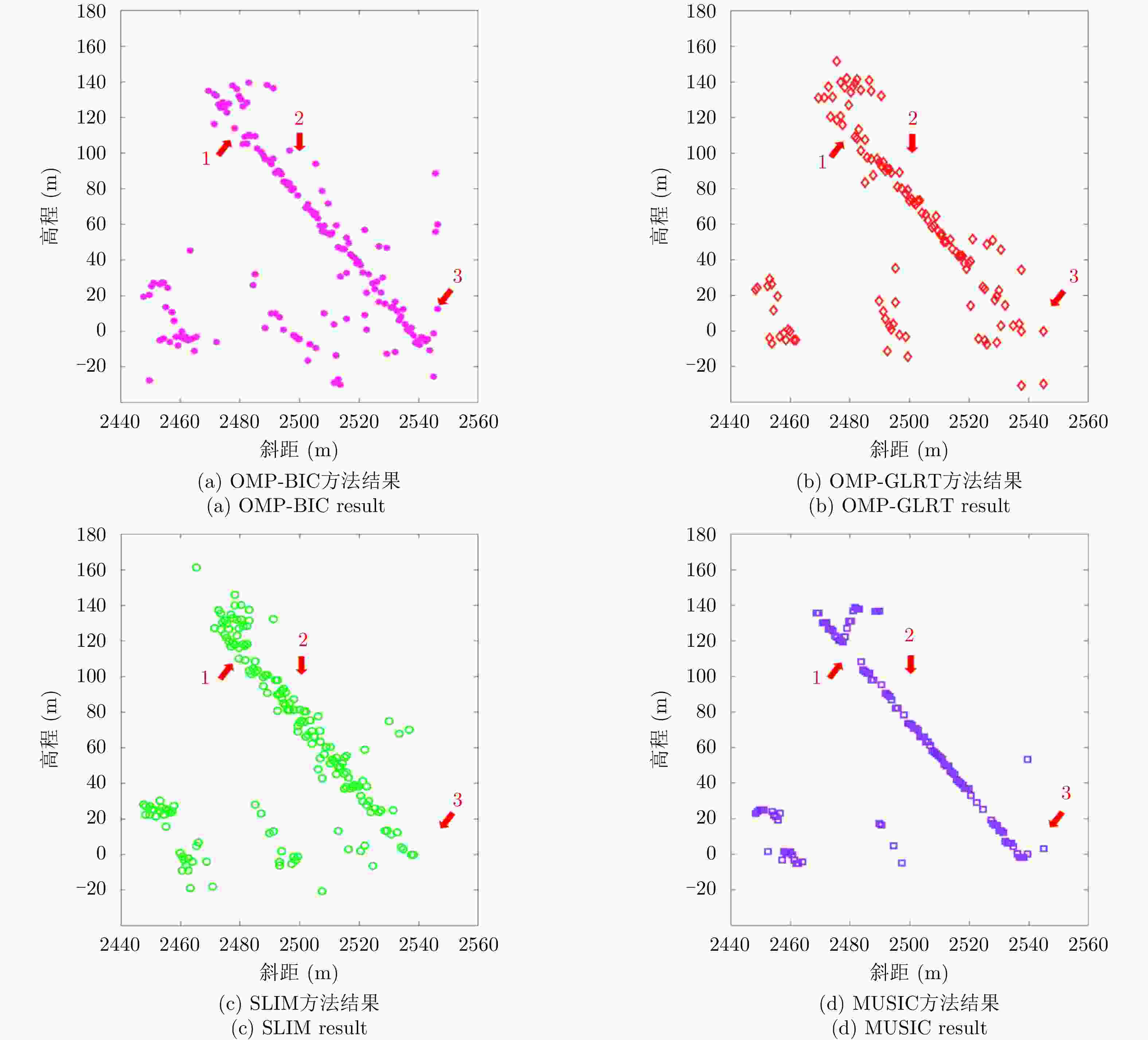
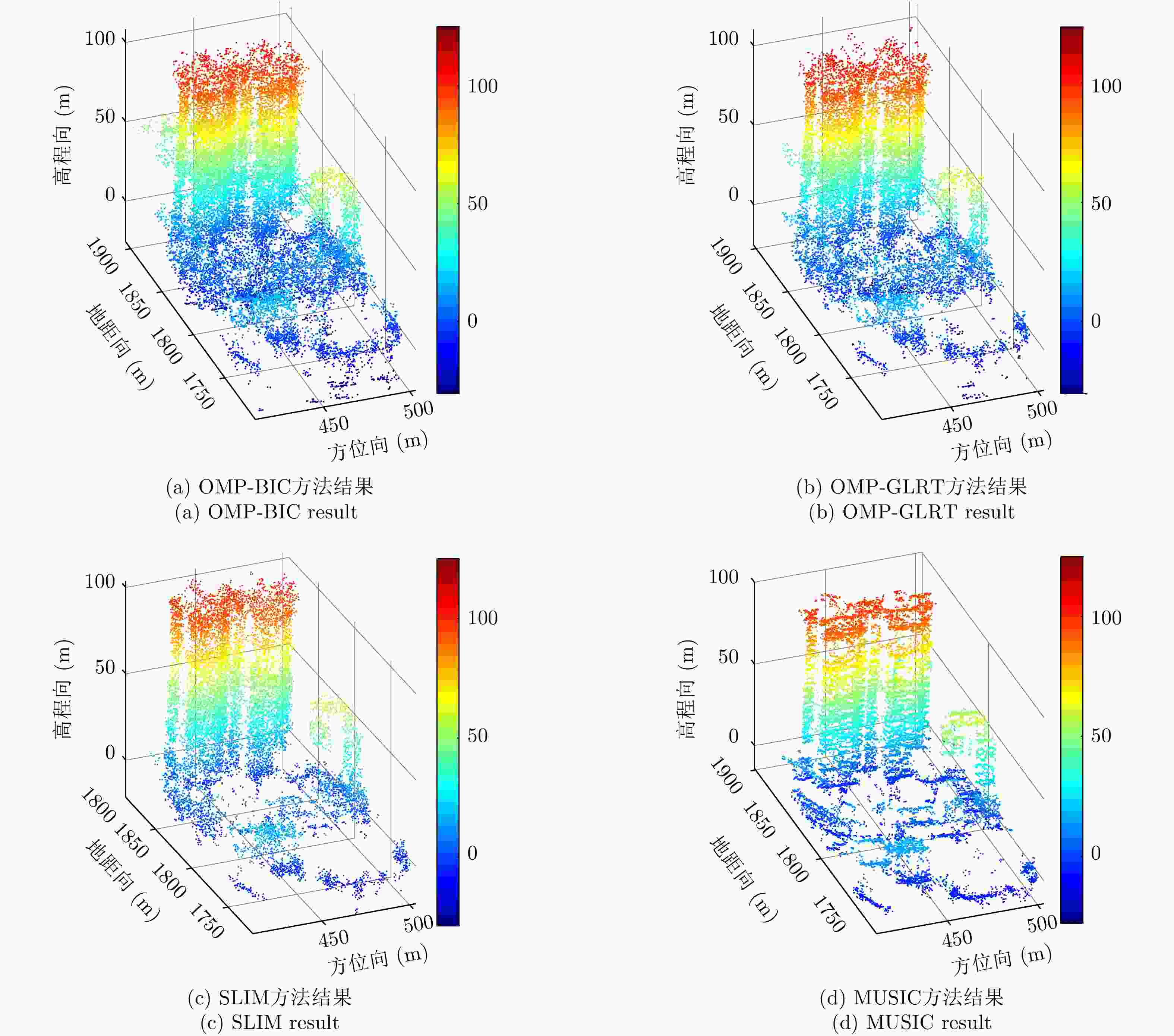
摘要: 层析技术因具有解译城区SAR影像上复杂叠掩场景的能力而备受关注。层析成像包含两个部分:估计散射体在高程向的分布和确定散射体在混叠像元内的真实数目。该文以中科院空天院峨眉数据的机载阵列干涉系统参数为基础,选取了若干代表性的方法,包括OMP, SLIM和MUSIC等层析谱估计方法以及BIC和GLRT等模型定阶方法,进行了模拟叠掩目标的层析反演实验,使用了克拉默-拉奥界和重建成功率来评估实验结果。实验表明:在机载阵列数很有限的条件下,(1)使用2阶统计量反演的高程估计量的方差比单个观测矢量反演结果的方差更小;(2)叠掩散射体间的幅度比、相位差和散射间距会影响层析算法解叠掩的成功率;(3)叠掩散射体间的相位差会使层析算法的高程估计发生偏差。Abstract: The tomographic technique has attracted much attention because of its ability to separate overlapping scatterers in urban Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images. The general method of SAR Tomography (TomSAR) imaging combines the following two aspects: estimating the distribution of the scatterers in the elevation direction and determining the number of strong scatterers in an overlapped pixel. This study applied several sophisticated spectrum estimations (e.g., Orthogonal Matching Pursuit, Sparse Learning via Iterative Minimization and Multiple Signal Classification) and model order selection approaches (e.g., Bayesian information criterion and generalized likelihood ratio test) with highly technical potential to recover the simulated overlapping scatterers. This simulation experiment is based on the parameters of the AIRCAS X-band TomoSAR data from Emei, Sichuan, China. The Cramér-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB) and recovery probability are used to evaluate the performances of different methods for the separation of overlapped scatterers. The experimental results revealed the following: (1) the standard deviation of estimation using second-order statistics is smaller than that of a single observation vector, especially when the number of acquisitions is very limited; (2) the amplitude ratio, phase difference, and elevation spacing between overlapping scatterers will have a significant impact on the different kinds of algorithms; and (3) the phase difference between overlapping scatterers will make the phase center estimation of greedy algorithm or spectrum estimation algorithm biased.
-
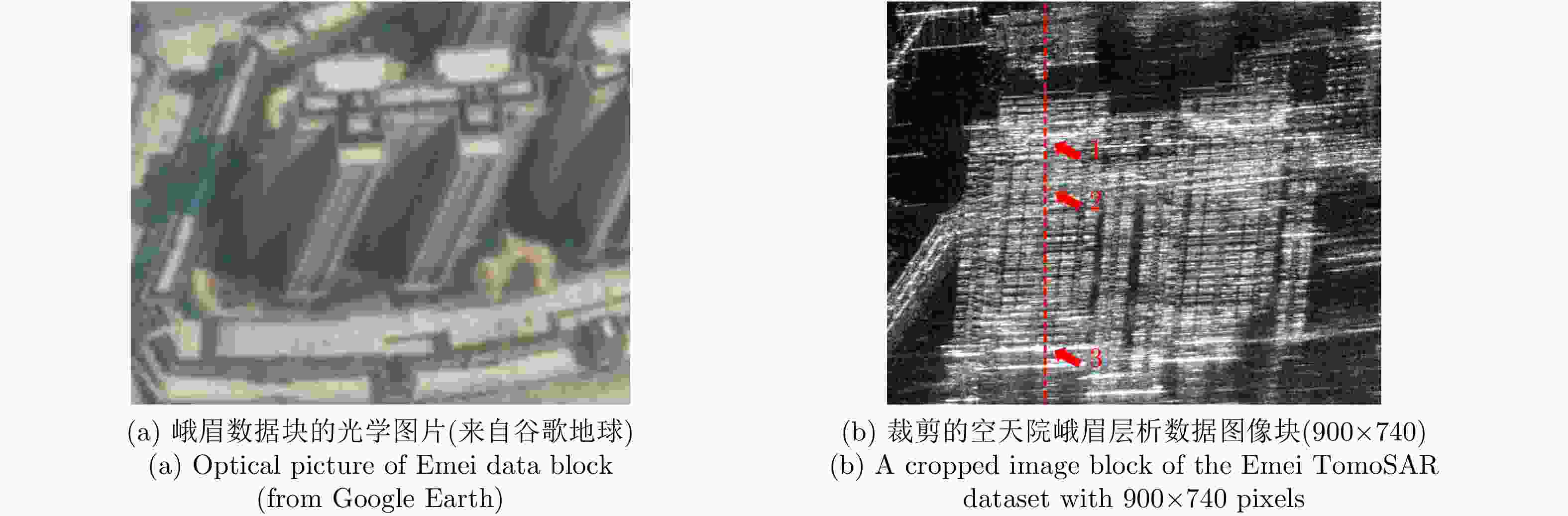
表 1 峨眉数据的参数
Table 1. Parameters of Emei data
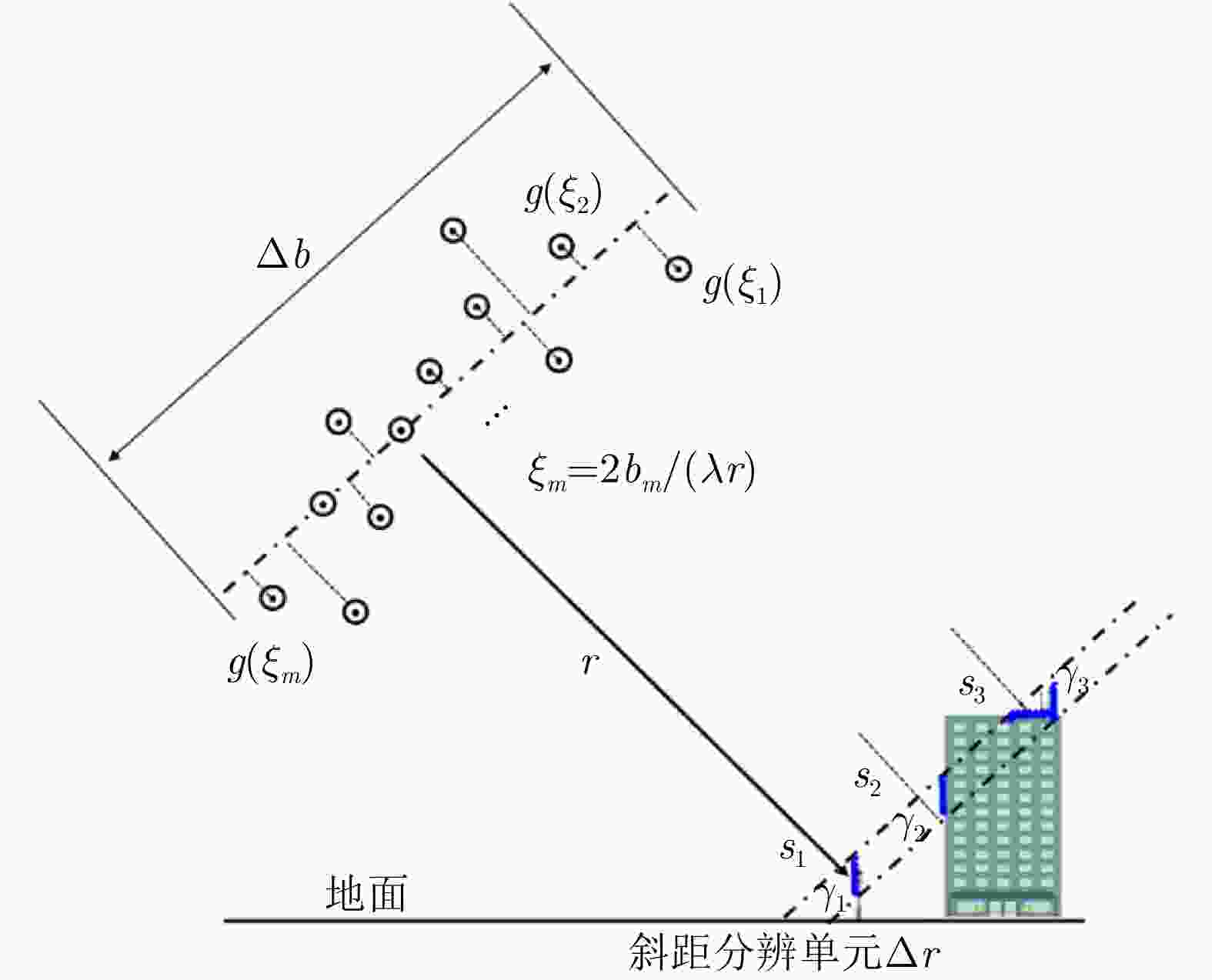
参数 数值 波长 $\lambda $ 0.031 m 斜距 r 1629 m 入射角 $ \theta $ $ {47}^{\circ } $ 基线 b 0.2$ \times $11 m 瑞利分辨率 ${\rho _s}$ 23.78 m -
[1] KNAELL K K and CARDILLO G P. Radar tomography for the generation of three-dimensional images[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1995, 142(2): 54–60. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19951791 [2] 廖明生, 魏恋欢, 汪紫芸, 等. 压缩感知在城区高分辨率SAR层析成像中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031LIAO Mingsheng, WEI Lianhuan, WANG Ziyun, et al. Compressive sensing in high-resolution 3D SAR tomography of urban scenarios[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031 [3] REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873 [4] FORNARO G, SERAFINO F, and SOLDOVIERI F. Three-dimensional focusing with multipass SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(3): 507–517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.809934 [5] BUDILLON A, EVANGELISTA A, and SCHIRINZI G. SAR tomography from sparse samples[C]. 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009: 865–868. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2009.5417514. [6] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183 [7] VRIEZE S I. Model selection and psychological theory: A discussion of the differences between the Akaike information criterion (AIC) and the Bayesian information criterion (BIC)[J]. Psychological Methods, 2012, 17(2): 228–243. doi: 10.1037/a0027127 [8] BUDILLON A and SCHIRINZI G. GLRT based on support estimation for multiple scatterers detection in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1086–1094. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2494376 [9] ZHU Xiaoxiang, GE Nan, and SHAHZAD M. Joint sparsity in SAR tomography for urban mapping[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1498–1509. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2469646 [10] FERRO-FAMIL L, HUANG Yue, and TEBALDINI S. Polarimetric characterization of 3-D scenes using high-resolution and Full-Rank Polarimetric tomographic SAR focusing[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 5694–5697. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730487. [11] TEBALDINI S, ROCCA F, D’ALESSANDRO M M, et al. Phase calibration of airborne tomographic SAR data via phase center double localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(3): 1775–1792. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2488358 [12] NANNINI M, SCHEIBER R, HORN R, et al. First 3-D reconstructions of targets hidden beneath foliage by means of polarimetric SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(1): 60–64. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2160329 [13] 柳祥乐. 多基线层析成像合成孔径雷达研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院研究生院(电子学研究所), 2007.LIU Xiangle. Study on multibaseline tomography synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Chinese Acedamy of Sciences, 2007. [14] 王金峰. SAR层析三维成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2010.WANG Jinfeng. Study of three-dimentional synthetic aperture radar tomography imaging technology[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2010. [15] WANG Xiao, XU Feng, and JIN Yaqiu. Numerical simulation of tomographic-SAR imaging and object reconstruction using compressive sensing with L1/2-norm regularization[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(33): 4600–4607. doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0554-5 [16] 刘康. 基于高分辨率SAR影像提取建筑物高度的研究[D]. [博士论文], 武汉大学, 2012.LIU Kang. Advanced methods for building height extraction from high resolution SAR images[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Wuhan University, 2012. [17] SUN Xilong, YU Anxi, DONG Zhen, et al. Three-dimensional SAR focusing via compressive sensing: The case study of angel stadium[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(4): 759–763. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2181321 [18] 李震, 张平, 乔海伟, 等. 层析SAR地表参数信息提取研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 116–130. doi: 10.12000/JR20095LI Zhen, ZHANG Ping, QIAO Haiwei, et al. Advances in information extraction of surface parameters using tomographic SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 116–130. doi: 10.12000/JR20095 [19] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 彭凌霄, 等. SARMV3D-1.0: SAR微波视觉三维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, PENG Lingxiao, et al. SARMV3D-1.0: Synthetic aperture radar microwave vision 3D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112 [20] JIAO Zekun, DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Urban 3D imaging using airborne TomoSAR: Contextual information-based approach in the statistical way[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 170: 127–141. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.10.013 [21] ZHANG Fubo, LIANG Xingdong, CHENG Ruichang, et al. Building corner reflection in MIMO SAR tomography and compressive sensing-based corner reflection suppression[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(3): 446–450. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2926301 [22] 李杭, 梁兴东, 张福博, 等. 基于高斯混合聚类的阵列干涉SAR三维成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 630–639. doi: 10.12000/JR17020LI Hang, LIANG Xingdong, ZHANG Fubo, et al. 3D imaging for array InSAR based on Gaussian mixture model clustering[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 630–639. doi: 10.12000/JR17020 [23] KAY S M, 罗鹏飞, 张文明, 刘忠, 等译. 统计信号处理基础: 估计与检测理论[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2011: 451–453.KAY S M, LUO Pengfei, ZHANG Wenming, LIU Zhong, et al. translation. Fundamentals of Statistical Signal Processing Volume I: Estimation Theory[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2011: 451–453. [24] BAMLER R, EINEDER M, ADAM N, et al. Interferometric potential of high resolution spaceborne SAR[J]. Photogrammetrie - Fernerkundung - Geoinformation, 2009, 5: 407–419. doi: 10.1127/1432-8364/2009/0029 [25] CHEN S, BILLINGS S A, and LUO W. Orthogonal least squares methods and their application to non-linear system identification[J]. International Journal of Control, 1989, 50(5): 1873–1896. doi: 10.1080/00207178908953472 [26] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [27] MA Peifeng, LIN Hui, LAN Hengxing, et al. On the performance of reweighted L1 minimization for tomographic SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 895–899. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2365613 [28] TAN Xing, ROBERTS W, LI Jian, et al. Sparse learning via iterative minimization with application to MIMO radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(3): 1088–1101. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2096218 [29] SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830 [30] MOON T K. The expectation-maximization algorithm[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 1996, 13(6): 47–60. doi: 10.1109/79.543975 [31] KRIEGER G, ROMMEL T, and MOREIRA A. MIMO-SAR tomography[C]. The 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, Germany, 2016. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: