Supervised Contrastive Learning Regularized High-resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar Building Footprint Generation
-
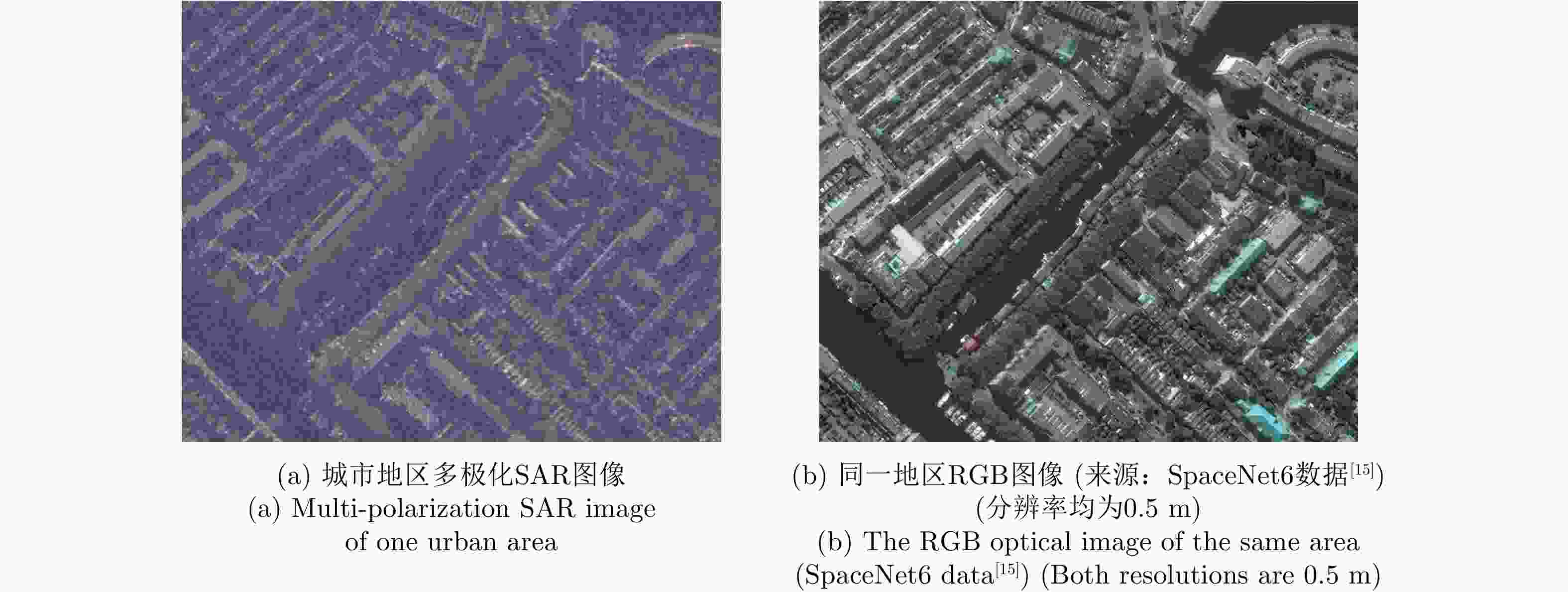
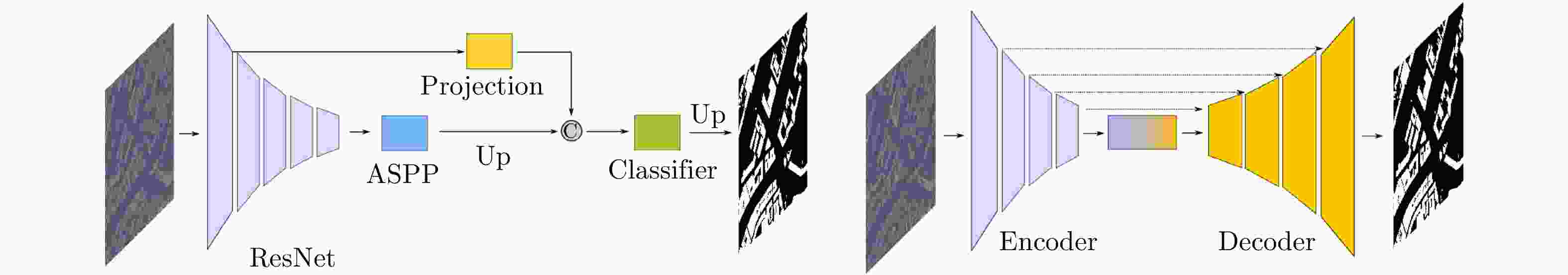
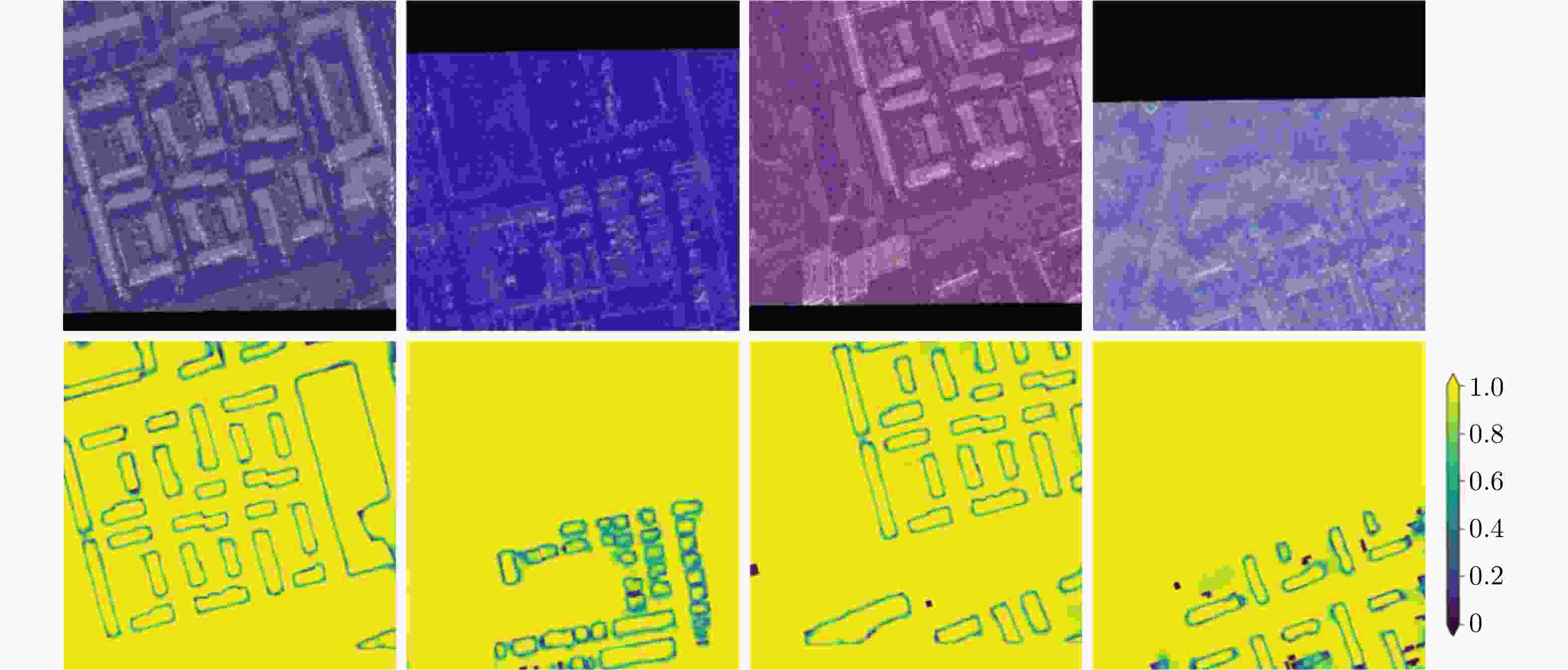
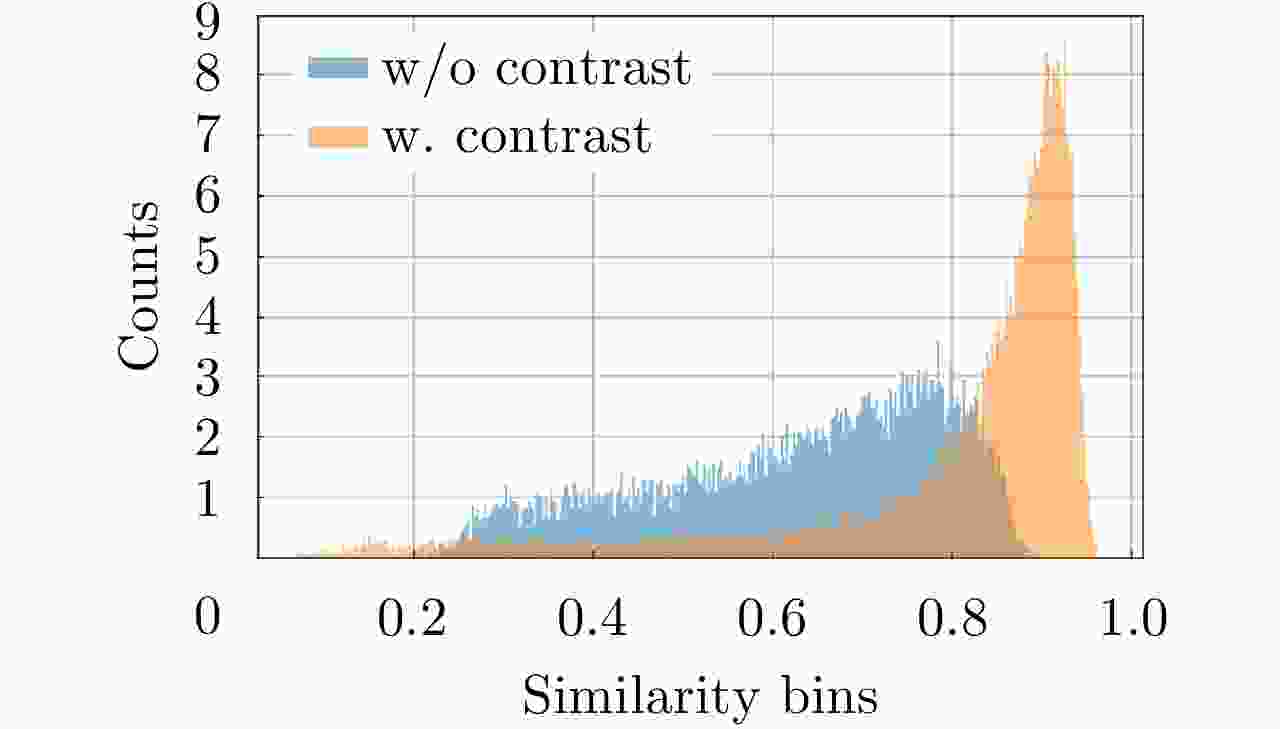
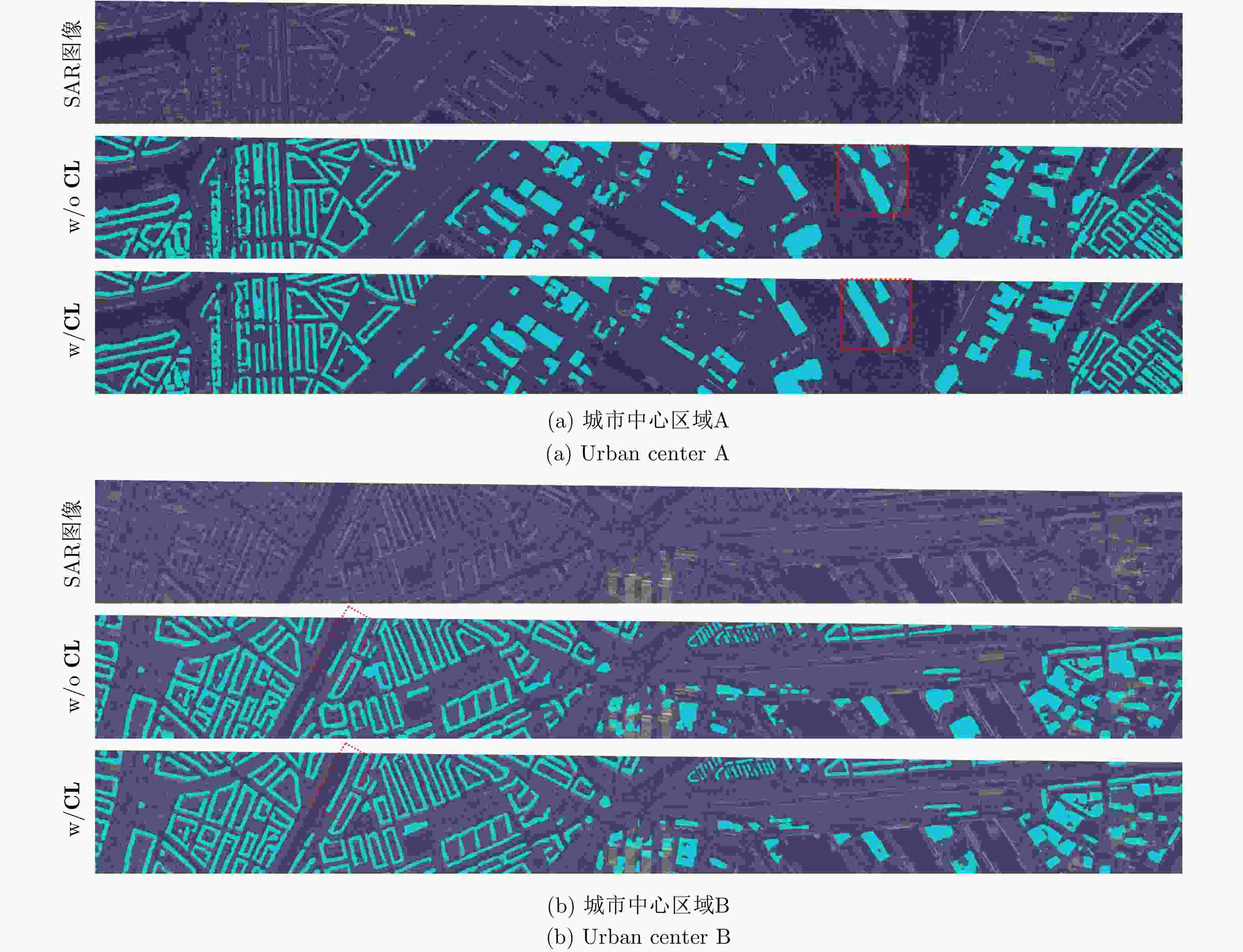
摘要: 近年来,高分辨合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像的智能解译技术在城市规划、变化监测等方面得到了广泛应用。不同于光学图像,SAR图像的获取方式、图像中目标的几何结构等因素制约了现有深度学习方法对SAR图像地物目标的解译效果。该文针对高分辨SAR图像城市区域建筑物提取,提出了基于监督对比学习的正则化方法,其主要思想是增强同一类别像素在特征空间中的相似性以及不同类别像素之间的差异性,使得深度学习模型能更加关注SAR图像中建筑物与非建筑物区域在特征空间中的区别,从而提升建筑物识别精度。利用公开的大场景SpaceNet6数据集,通过对比实验,提出的正则化方法,其建筑物提取精度相比于常用的分割方法在不同网络结构下至少提升1%,分割结果证明了该文方法在实际数据上的有效性,可以对复杂场景下的城市建筑物区域进行有效分割。此外,该方法也可以拓展应用于其他SAR图像像素级别的地物分割任务中。Abstract: Over the recent years, high-resolution Synthetic-Aperture Radar (SAR) images have been widely applied for intelligent interpretation of urban mapping, change detection, etc. Different from optical images, the acquisition approach and object geometry of SAR images have limited the interpretation performances of the existing deep-learning methods. This paper proposes a novel building footprint generation method for high-resolution SAR images. This method is based on supervised contrastive learning regularization, which aims to increase the similarities between intra-class pixels and diversities of interclass pixels. This increase will make the deep learning models focus on distinguishing building and nonbuilding pixels in latent space, and improve the classification accuracy. Based on public SpaceNet6 data, the proposed method can improve the segmentation performance by 1% compared to the other state-of-the-art methods. This improvement validates the effectiveness of the proposed method on real data. This method can be used for building segmentation in urban areas with complex scene background. Moreover, the proposed method can be extended for other types of land-cover segmentation using SAR images.
-
表 1 训练过程采用的数据增强方法
Table 1. Adopted data augmentation methods for training
数据增强 数值 随机裁剪 512×512 水平翻转 0.5 归一化 均值:128 方差:32 表 2 训练过程中的参数设定
Table 2. Other parameters for training
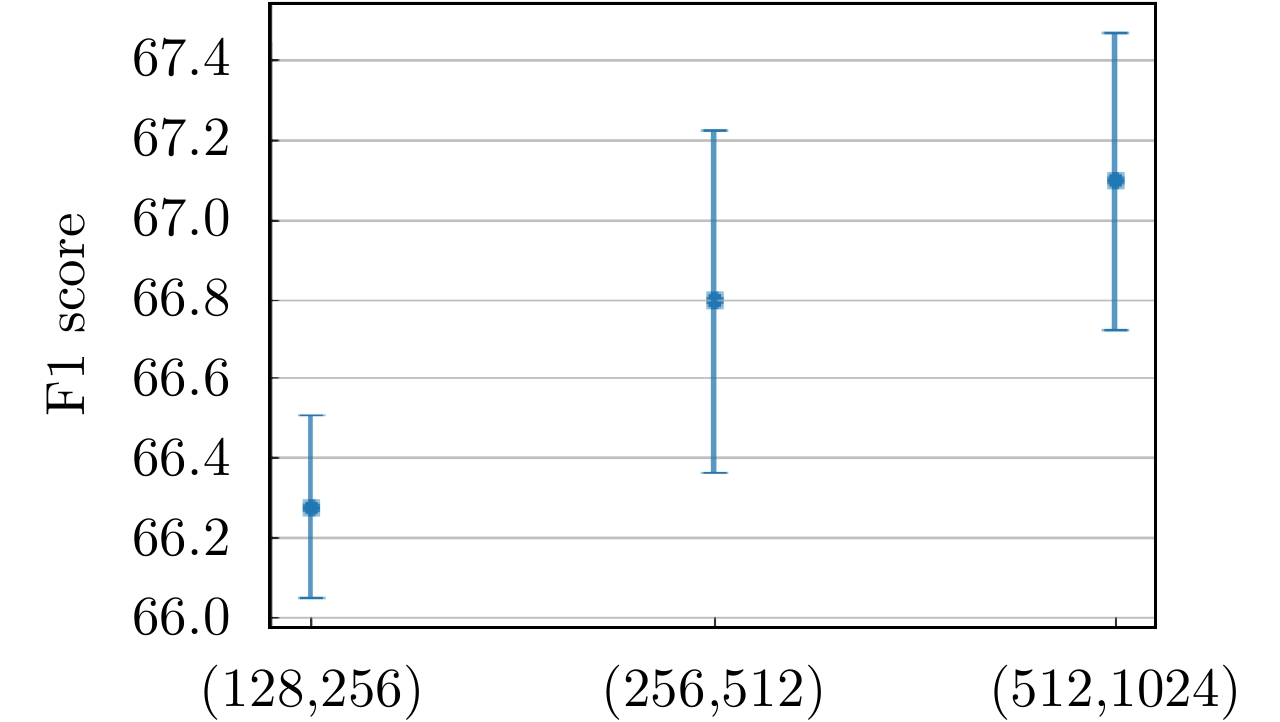
参数 数值 Mq 256 Mk 512 $ \tau $ 0.1 D 128 $ \delta $ 0.97 Learning rate 1×10–3 Batch size 16 Epoch 200 表 3 不同网络模型及损失函数下的建筑物提取性能比较(单位:%)
Table 3. Performance comparison of the building segmentation based on different methods (Unit: %)
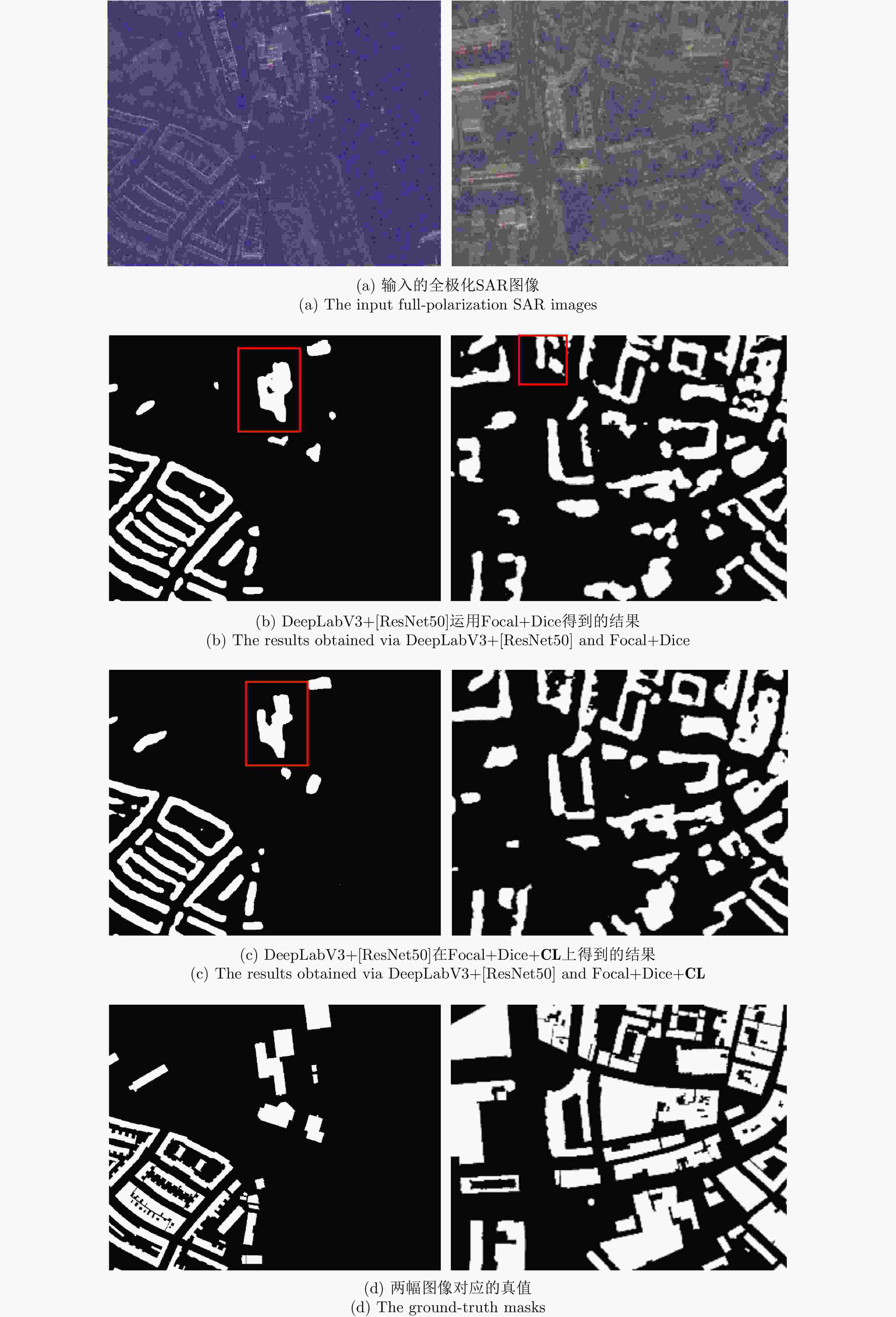
网络模型 损失函数 IoU Dice Precision Recall U-Net[15] Focal+Dice 34.98[1.48] 51.81[1.61] 62.30[1.50] 44.42[2.38] DeepLabV3+[ResNet34] Focal+Dice 48.40[0.14] 65.23[0.13] 76.95[0.37] 56.61[0.03] DeepLabV3+[ResNet34] Focal+Dice+CL 49.81[0.31] 66.50[0.28] 78.32[0.48] 57.78[0.68] DeepLabV3+[ResNet50]
DeepLabV3+[ResNet50]Focal+Dice
Focal+Dice+CL48.72[0.48]
50.15[0.62]65.51[0.43]
66.79[0.54]76.55[0.31]
78.30[0.48]57.26[0.49]
58.25[0.87]U-Net[ResNet34] Focal+Dice 49.09[0.12] 65.85[0.11] 77.36[0.13] 57.33[0.20] U-Net[ResNet34] Focal+Dice+CL 50.62[0.58] 67.21[0.52] 76.32[0.25] 60.05[0.97] U-Net[ResNet50] Focal+Dice 49.24[0.30] 65.99[0.27] 77.37[0.23] 57.53[0.34] U-Net[ResNet50] Focal+Dice+CL 50.99[1.18] 67.53[1.03] 78.21[1.32] 59.50[2.36] -
[1] 徐丰, 王海鹏, 金亚秋. 深度学习在SAR目标识别与地物分类中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130XU Feng, WANG Haipeng, and JIN Yaqiu. Deep learning as applied in SAR target recognition and terrain classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 136–148. doi: 10.12000/JR16130 [2] 王雪松, 陈思伟. 合成孔径雷达极化成像解译识别技术的进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109WANG Xuesong and CHEN Siwei. Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interpretation and recognition: Advances and perspectives[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109 [3] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像——从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090 [4] 李宁, 牛世林. 基于局部超分辨重建的高精度SAR图像水域分割方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 174–184. doi: 10.12000/JR19096LI Ning and NIU Shilin. High-precision water segmentation from synthetic aperture radar images based on local super-resolution restoration technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 174–184. doi: 10.12000/JR19096 [5] ZHAO Lingjun, ZHOU Xiaoguang, and KUANG Gangyao. Building detection from urban SAR image using building characteristics and contextual information[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2013, 2013: 56. doi: 10.1186/1687-6180-2013-56 [6] TUPIN F and ROUX M. Detection of building outlines based on the fusion of SAR and optical features[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2003, 58(1/2): 71–82. [7] XU Feng and JIN Yaqin. Automatic reconstruction of building objects from multiaspect meter-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(7): 2336–2353. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.896614 [8] MICHAELSEN E, SOERGEL U, and THOENNESSEN U. Perceptual grouping for automatic detection of man-made structures in high-resolution SAR data[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2006, 27(4): 218–225. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2005.08.002 [9] FERRO A, BRUNNER D, and BRUZZONE L. Automatic detection and reconstruction of building radar footprints from single VHR SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 51(2): 935–952. [10] ZHANG Fengli, SHAO Yun, ZHANG Xiao, et al. Building L-shape footprint extraction from high resolution SAR image[C]. 2011 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Munich, Germany, 2011: 273–276. [11] WANG Yinghua, TUPIN F, HAN Chongzhao, et al. Building detection from high resolution PolSAR data by combining region and edge information[C]. IGARSS 2008-2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 2009: IV–153. [12] GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, and COURVILLE A. Deep Learning[M]. Cambridge: MIT press, 2016: 1–800. [13] WANG Xiaying, CAVIGELLI L, EGGIMANN M, et al. Hr-SAR-NET: A deep neural network for urban scene segmentation from high-resolution SAR data[C]. 2020 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2020: 1–6. [14] 杜康宁, 邓云凯, 王宇, 等. 基于多层神经网络的中分辨SAR图像时间序列建筑区域提取[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(4): 410–418. doi: 10.12000/JR16060DU Kangning, DENG Yunkai, WANG Yu, et al. Medium resolution SAR image time-series built-up area extraction based on multilayer neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(4): 410–418. doi: 10.12000/JR16060 [15] SHERMEYER J, HOGAN D, BROWN J, et al. SpaceNet 6: Multi-sensor all weather mapping dataset[C]. The 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2020: 768–777. [16] SHAHZAD M, MAURER M, FRAUNDORFER F, et al. Buildings detection in VHR SAR images using fully convolution neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(2): 1100–1116. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2864716 [17] JING Hao, SUN Xian, WANG Zhirui, et al. Fine building segmentation in high-resolution SAR images via selective pyramid dilated network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 6608–6623. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3076085 [18] CHEN Jiankun, QIU Xiaolan, DING Chibiao, et al. CVCMFF Net: Complex-valued convolutional and multifeature fusion network for building semantic segmentation of InSAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, in press. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3068124 [19] SUN Yao, HUA Yuansheng, MOU Lichao, et al. CG-Net: Conditional GIS-Aware network for individual building segmentation in VHR SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, in press. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3043089 [20] CHEN L, ZHU Yukun, PAPANDREOU G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]. The European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 833–851. [21] CHEN Ting, KORNBLITH S, NOROUZI M, et al. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations[C]. The 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual Event, 2020: 1597–1607. [22] HE Kaiming, FAN Haoqi, WU Yuxin, et al. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning[C]. The 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 9726–9735. [23] KHOSLA P, TETERWAK P, WANG Chen, et al. Supervised contrastive learning[C]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Virtual, 2020: 18661–18673. [24] LIU Shikun, ZHI Shuaifeng, JOHNS E, et al. Bootstrapping semantic segmentation with regional contrast[J]. arXiv: 2104.04465, 2021. [25] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999–3007. [26] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [27] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Caesars Palace, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: