-
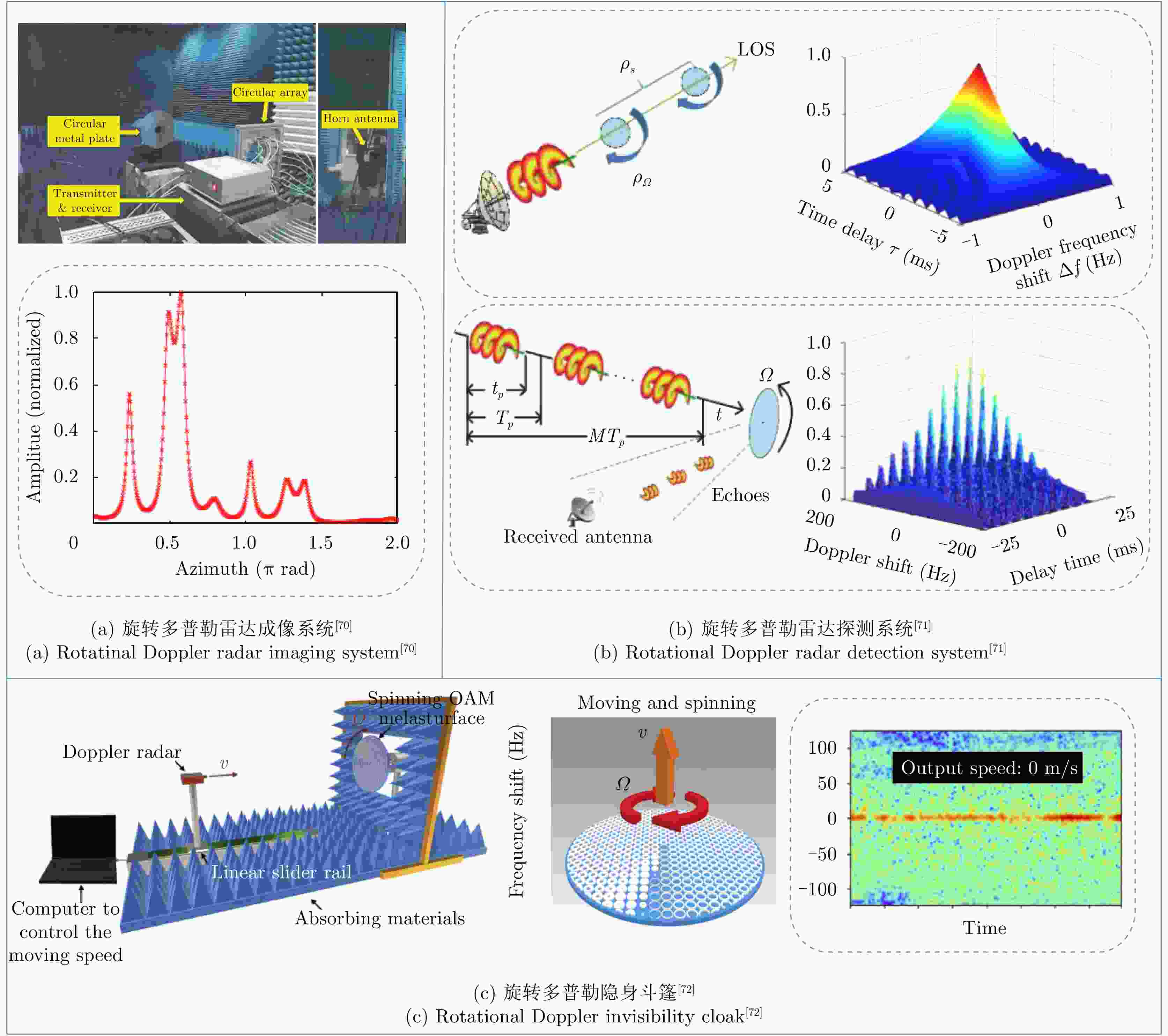
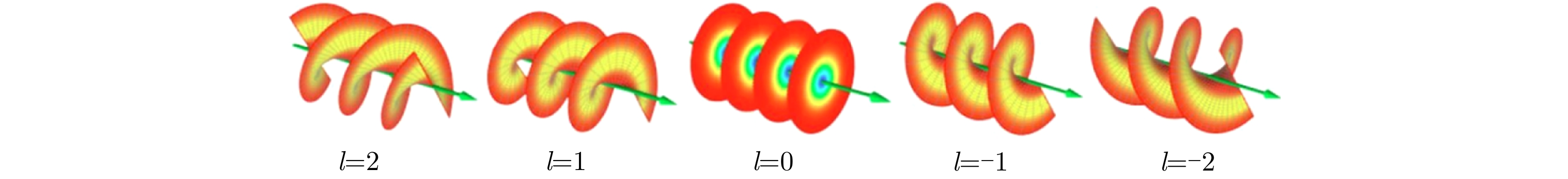
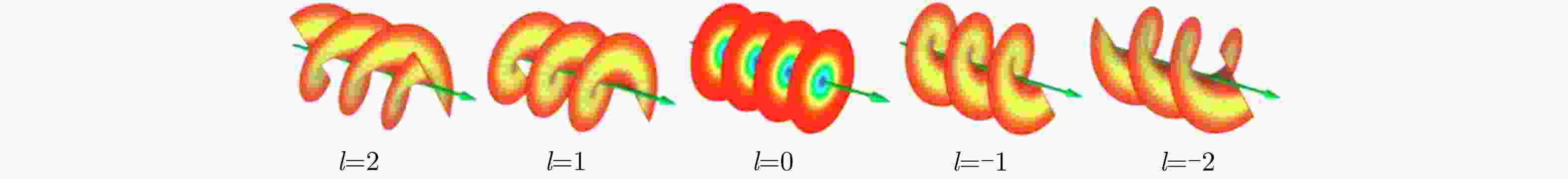
摘要: 依据多普勒效应,传统雷达可以实现对运动目标探测,但是在对旋转目标的角向运动趋势感知存在检测盲区。涡旋电磁波的旋转多普勒效应的发现,因有助于解决直视下的旋转目标的角向运动趋势感知问题,引起了国内外研究人员的广泛关注。该文主要介绍了近年来涡旋电磁波旋转多普勒效应的研究进展,特别是微波波段的相关研究成果,包括目标在准轴和非准轴状况下的旋转多普勒效应研究,复杂运动条件下的径向多普勒、微多普勒和旋转多普勒效应的解耦合研究,以及旋转多普勒效应在雷达成像和测速中的应用研究。同时,该文也对该领域亟待解决的问题进行了总结分析,并对未来的研究方向及相关应用进行了展望。Abstract: Traditional radars can detect moving targets using the Doppler effect. However, traditional radars have shadow areas in detecting the angular motion of the rotating targets. The discovery of the rotational Doppler effect based on vortex electromagnetic waves helps solve the problem of detecting the angular motion of the rotating targets under direct vision, which has attracted considerable attention from domestic and foreign scholars. In this study, we discussed the recent research progress on the rotational Doppler effect of vortex electromagnetic waves, particularly for related results in the microwave band, including the rotational Doppler effects on the target under on-axis and off-axis cases; decoupling linear Doppler, micro-Doppler and rotational Doppler effects under complex motion cases; and rotational Doppler effects on the applications of radar imaging and velocity measurement. We summarized and analyzed the existing problems demanding prompt solutions in this field, and proposed future research directions and relative applications.
-
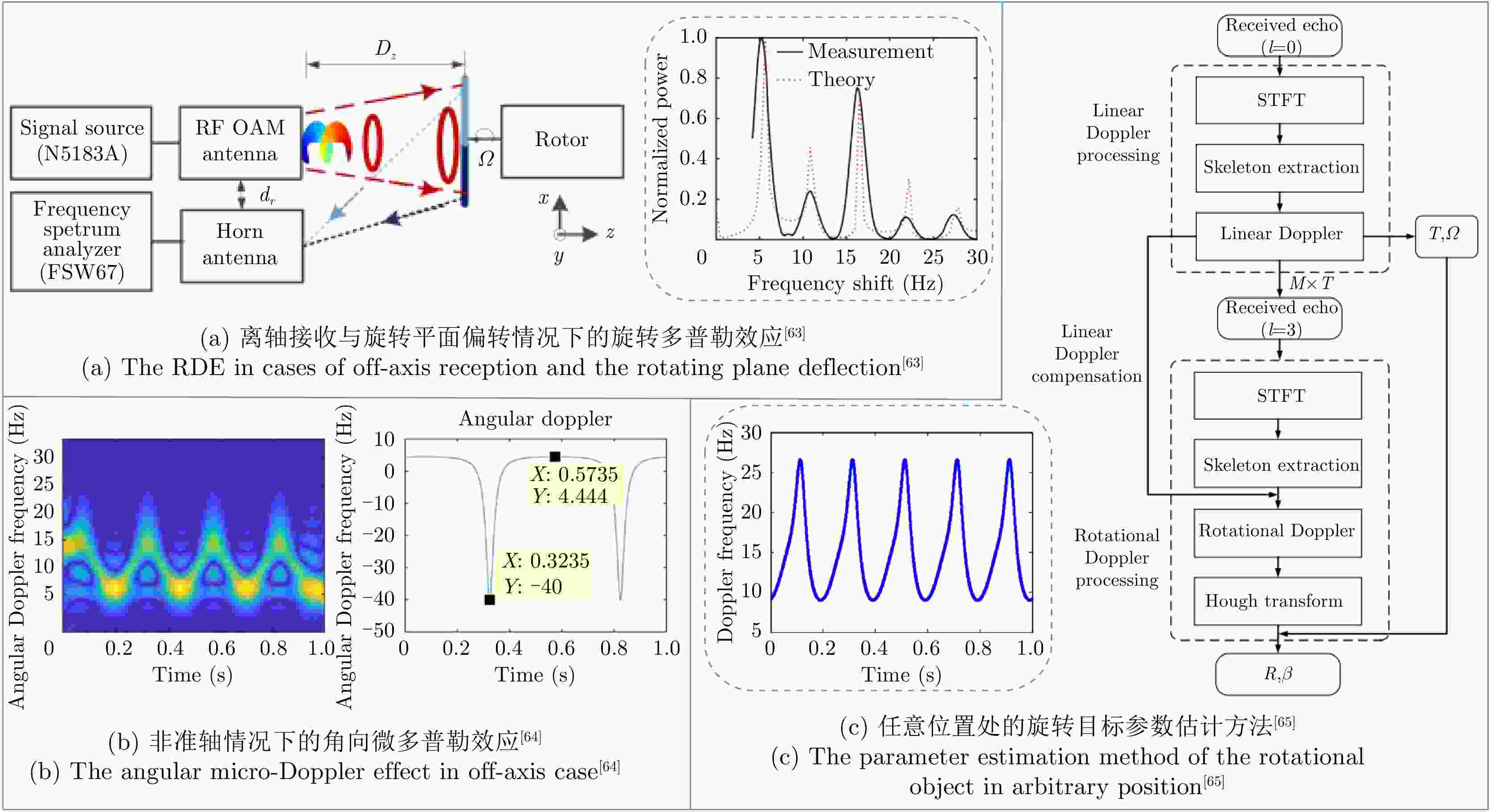
表 1 报道的准轴情况下的旋转多普勒效应检测性能
Table 1. Reported performances of detecting the rotational Doppler effect in on-axis case
表 2 报道的非准轴情况下的旋转多普勒效应检测性能
Table 2. Reported performances of detecting the rotational Doppler effect in off-axis case
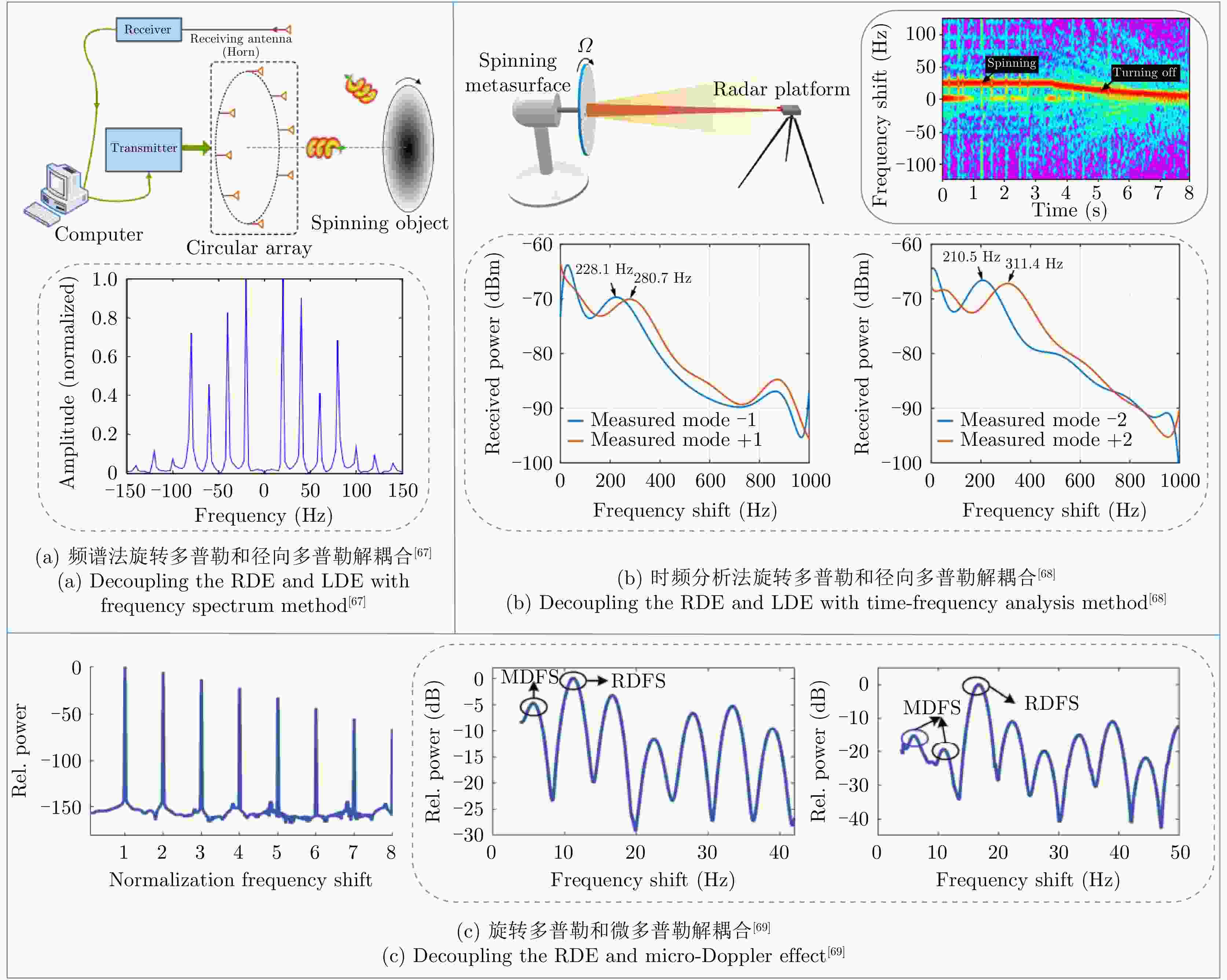
表 3 报道的多普勒效应解耦合方法
Table 3. Reported methods of decoupling the Doppler effect
-
[1] KRAJEWSKI W F and SMITH J A. Radar hydrology: Rainfall estimation[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2002, 25(8/12): 1387–1394. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00062-3 [2] 李晓峰, 张彪, 杨晓峰. 星载合成孔径雷达遥感海洋风场波浪场[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 425–443. doi: 10.12000/JR20079LI Xiaofeng, ZHANG Biao, and YANG Xiaofeng. Remote sensing of sea surface wind and wave from spaceborne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 425–443. doi: 10.12000/JR20079 [3] FIORANI L, COLAO F, and PALUCCI A. Environmental monitoring by laser radar[J]. Romanian Journal of Physics, 2011, 56(3/4): 448–459. [4] NEAL A. Ground-penetrating radar and its use in sedimentology: Principles, problems and progress[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2004, 66(3/4): 261–330. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.01.004 [5] KUSTAS W P, FRENCH A N, HATFIELD J L, et al. Remote sensing research in hydrometeorology[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2003, 69(6): 631–646. doi: 10.14358/PERS.69.6.631 [6] NIELSEN E and GREENWALD R A. Electron flow and visual aurora at the Harang discontinuity[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 1979, 84(A8): 4189–4200. doi: 10.1029/JA084iA08p04189 [7] 赵耀东, 吕晓德, 李纪传, 等. 无源雷达多普勒谱分析实现动目标检测的方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(2): 247–256. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20081ZHAO Yaodong, LÜ Xiaode, LI Jichuan, et al. Detection of moving targets based on Doppler spectrum analysis technique for passive coherent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 247–256. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20081 [8] 陈世超, 罗丰, 胡冲, 等. 基于多普勒谱非广延熵的海面目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 344–354. doi: 10.12000/JR19012CHEN Shichao, LUO Feng, HU Chong, et al. Small target detection in sea clutter background based on Tsallis entropy of Doppler spectrum[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 344–354. doi: 10.12000/JR19012 [9] ALLEN L, BEIJERSBERGEN M W, SPREEUW R J C, et al. Orbital angular momentum of light and the transformation of Laguerre-Gaussian laser modes[J]. Physical Review A, 1992, 45(11): 8185–8189. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.45.8185 [10] TAMBURINI F, MARI E, PARISI G, et al. Ripling the capacity of a point-to-point radio link by using electromagnetic vortices[J]. Radio Science, 2015, 50(6): 501–508. doi: 10.1002/2015RS005662 [11] PARK W, WANG Lei, BRÜNS H D, et al. Introducing a mixed-mode matrix for investigation of wireless communication related to orbital angular momentum[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(3): 1719–1728. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2889033 [12] ZHANG Yiming and LI Jialin. An orbital angular momentum-based array for in-band full-duplex communications[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2019, 18(3): 417–421. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2019.2893035 [13] LEI Yi, YANG Yang, WANG Yanzhe, et al. Throughput performance of wireless multiple-input multiple-output systems using OAM antennas[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(2): 261–265. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3027006 [14] 郭桂蓉, 胡卫东, 杜小勇. 基于电磁涡旋的雷达目标成像[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2013, 35(6): 71–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2013.06.013GUO Guirong, HU Weidong, and DU Xiaoyong. Electromagnetic vortex based radar target imaging[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2013, 35(6): 71–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2013.06.013 [15] YUAN Tiezhu, WANG Hongqiang, CHENG Yongqiang, et al. Electromagnetic vortex-based radar imaging using a single receiving antenna: Theory and experimental results[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 630. doi: 10.3390/s17030630 [16] LIU Kang, LI Xiang, GAO Yue, et al. High-resolution electromagnetic vortex imaging based on sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(21): 6918–6927. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2754554 [17] WANG Jianqiu, LIU Kang, CHENG Yongqiang, et al. Three-dimensional target imaging based on vortex stripmap SAR[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(4): 1338–1345. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2879814 [18] NGUYEN D K, PASCAL O, SOKOLOFF J, et al. Antenna gain and link budget for waves carrying orbital angular momentum[J]. Radio Science, 2015, 50(11): 1165–1175. doi: 10.1002/2015RS005772 [19] YAO Yu, LIANG Xianling, ZHU Weiren, et al. Experiments of orbital angular momentum phase properties for long-distance transmission[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 62689–62694. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2916029 [20] ZHANG Chao and ZHAO Yufei. Orbital angular momentum nondegenerate index mapping for long distance transmission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5027–5036. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2927672 [21] GARETZ B A and ARNOLD S. Variable frequency shifting of circularly polarized laser radiation via a rotating half-wave retardation plate[J]. Optics Communications, 1979, 31(1): 1–3. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(79)90230-X [22] NIENHUIS G. Doppler effect induced by rotating lenses[J]. Optics Communications, 1996, 132(1/2): 8–14. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(96)00295-7 [23] BIALYNICKI-BIRULA I and BIALYNICKA-BIRULA Z. Rotational frequency shift[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1997, 78(13): 2539–2542. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.2539 [24] COURTIAL J, DHOLAKIA K, ROBERTSON D A, et al. Measurement of the rotational frequency shift imparted to a rotating light beam possessing orbital angular momentum[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1998, 80(15): 3217–3219. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.3217 [25] LAVERY M P J, SPEIRITS F C, BARNETT S M, et al. Detection of a spinning object using light’s orbital angular momentum[J]. Science, 2013, 341(6145): 537–540. doi: 10.1126/science.1239936 [26] FANG Liang, PADGETT M J, and WANG Jian. Sharing a common origin between the rotational and linear Doppler effects[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2017, 11(6): 1700183. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201700183 [27] ZHOU Hailong, FU Dongzhi, DONG Jianji, et al. Theoretical analysis and experimental verification on optical rotational Doppler effect[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(9): 10050–10056. doi: 10.1364/OE.24.010050 [28] ZHAI Yanwang, FU Shiyao, YIN Ci, et al. Detection of angular acceleration based on optical rotational Doppler effect[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(11): 15518–15527. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.015518 [29] ZHAI Yanwang, FU Shiyao, ZHANG Jianqiang, et al. Remote detection of a rotator based on rotational Doppler effect[J]. Applied Physics Express, 2020, 13(2): 022012. doi: 10.35848/1882-0786/ab6e0c [30] FU Shiyao, WANG Tonglu, ZHANG Zheyuan, et al. Non-diffractive Bessel-Gauss beams for the detection of rotating object free of obstructions[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(17): 20098–20108. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.020098 [31] QIU Song, REN Yuan, LIU Tong, et al. Spinning object detection based on perfect optical vortex[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 124: 105842. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2019.105842 [32] QIU Song, LIU Tong, LI Zhimeng, et al. Influence of lateral misalignment on the optical rotational Doppler effect[J]. Applied Optics, 2019, 58(10): 2650–2655. doi: 10.1364/AO.58.002650 [33] ZHANG Zijing, CEN Longzhu, ZHANG Jiandong, et al. Rotation velocity detection with orbital angular momentum light spot completely deviated out of the rotation center[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(5): 6859–6867. doi: 10.1364/OE.380324 [34] QIU Song, LIU Tong, REN Yuan, et al. Detection of spinning objects at oblique light incidence using the optical rotational Doppler effect[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(17): 24781–24792. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.024781 [35] PADGETT M J, MIATTO F M, LAVERY M P J, et al. Divergence of an orbital-angular-momentum-carrying beam upon propagation[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2015, 17(2): 023011. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/17/2/023011 [36] LEACH J, PADGETT M J, BARNETT S M, et al. Measuring the orbital angular momentum of a single photon[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2002, 88(25): 257901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.257901 [37] TAMBURINI F, MARI E, SPONSELLI A, et al. Encoding many channels on the same frequency through radio vorticity: First experimental test[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2012, 14(3): 033001. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/14/3/033001 [38] TURNBULL G A, ROBERTSON D A, SMITH G M, et al. The generation of free-space Laguerre-Gaussian modes at millimetre-wave frequencies by use of a spiral phaseplate[J]. Optics Communications, 1996, 127(4/6): 183–188. doi: 10.1016/0030-4018(96)00070-3 [39] 郭忠义, 汪彦哲, 郑群, 等. 涡旋电磁波天线技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 631–655. doi: 10.12000/JR19091GUO Zhongyi, WANG Yanzhe, ZHENG Qun, et al. Advances of research on antenna technology of vortex electromagnetic waves[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 631–655. doi: 10.12000/JR19091 [40] XU Jianchun, ZHAO Mingyang, ZHANG Ru, et al. A wideband F-shaped microstrip antenna[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2017, 16: 829–832. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2606118 [41] SHEN Fei, MU Jiangnan, GUO Kai, et al. Generating circularly polarized vortex electromagnetic waves by the conical conformal patch antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(9): 5763–5771. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2922545 [42] ZHENG Shilie, HUI Xiaonan, JIN Xiaofeng, et al. Transmission characteristics of a twisted radio wave based on circular traveling-wave antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 63(4): 1530–1536. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2015.2393885 [43] WANG Lulu, CHEN Huiyong, GUO Kai, et al. An inner-and outer-fed dual-arm Archimedean spiral antenna for generating multiple orbital angular momentum modes[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(2): 251. doi: 10.3390/electronics8020251 [44] SHEN Fei, MU Jiangnan, GUO Kai, et al. Generation of continuously variable-mode vortex electromagnetic waves with three-dimensional helical antenna[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2019, 18(6): 1091–1095. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2019.2907931 [45] YANG Yang, GUO Kai, SHEN Fei, et al. Generating multiple OAM based on a nested dual-arm spiral antenna[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 138541–138547. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2942601 [46] YANG Yang, GONG Yubin, GUO Kai, et al. Broad-band multiple OAMs’ generation with eight-arm Archimedean spiral antenna (ASA)[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 53232–53239. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2980751 [47] THIDÉB, THEN H, SJÖHOLM J, et al. Utilization of photon orbital angular momentum in the low-frequency radio domain[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 99(8): 087701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.087701 [48] MOHAMMADI S M, DALDORFF L K S, BERGMAN J E S, et al. Orbital angular momentum in radio—A system study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(2): 565–572. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2009.2037701 [49] YU Nanfang, GENEVET P, KATS M A, et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: Generalized laws of reflection and refraction[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6054): 333–337. doi: 10.1126/science.1210713 [50] YIN Zhiping, ZHENG Qun, GUO Kai, et al. Tunable beam steering, focusing and generating of orbital angular momentum vortex beams using high-order patch array[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(15): 2949. doi: 10.3390/app9152949 [51] GUO Kai, ZHENG Qun, YIN Zhiping, et al. Generation of mode-reconfigurable and frequency-adjustable OAM beams using dynamic reflective metasurface[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 75523–75529. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988914 [52] CENSOR D. Theory of the Doppler effect: Fact, fiction and approximation[J]. Radio Science, 1984, 19(4): 1027–1040. doi: 10.1029/RS019i004p01027 [53] MO L Y L and COBBOLD R S C. "Speckle" in continuous wave Doppler ultrasound spectra: A simulation study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 1986, 33(6): 747–753. doi: 10.1109/T-UFFC.1986.26891 [54] BARLOW E J. Doppler radar[J]. Proceedings of the IRE, 1949, 37(4): 340–355. doi: 10.1109/JRPROC.1949.231638 [55] PADGETT M. Like a speeding watch[J]. Nature, 2006, 443(7114): 924–925. doi: 10.1038/443924a [56] LEACH J, KEEN S, PADGETT M J, et al. Direct measurement of the skew angle of the Poynting vector in a helically phased beam[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(25): 11919–11924. doi: 10.1364/OE.14.011919 [57] LAVERY M P J, BARNETT S M, SPEIRITS F C, et al. Observation of the rotational Doppler shift of a white-light, orbital-angular-momentum-carrying beam backscattered from a rotating body[J]. Optica, 2014, 1(1): 1–4. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.1.000001 [58] PHILLIPS D B, LEE M P, SPEIRITS F C, et al. Rotational Doppler velocimetry to probe the angular velocity of spinning microparticles[J]. Physical Review A, 2014, 90(1): 011801(R). doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.90.011801 [59] ANDERSON A Q, STRONG E F, HEFFERNAN B M, et al. Detection technique effect on rotational Doppler measurements[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(9): 2636–2639. doi: 10.1364/OL.390425 [60] ZHAO Mingyang, GAO Xinlu, XIE Mutong, et al. Measurement of the rotational Doppler frequency shift of a spinning object using a radio frequency orbital angular momentum beam[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(11): 2549–2552. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.002549 [61] BROUSSEAU C, MAHDJOUBI K, and EMILE O. Measurement of the rotational sense and velocity of an object using OAM wave in the radio-frequency band[J]. Electronics Letters, 2019, 55(12): 709–711. doi: 10.1049/el.2019.0942 [62] ZHOU Zhenglong, CHENG Yongqiang, LIU Kang, et al. Detection of uniformly accelerated spinning target based on OAM beams[C]. 2018 International conference On Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Chengdu, China, 2018: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/ICMMT.2018.8563538. [63] ZHENG Jiayu, ZHENG Shilie, SHAO Zhenlei, et al. Analysis of rotational Doppler effect based on radio waves carrying orbital angular momentum[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 124(16): 164907. doi: 10.1063/1.5050448 [64] LUO Ying, CHEN Yijun, ZHU Yongzhong, et al. Doppler effect and micro-Doppler effect of vortex-electromagnetic-wave-based radar[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(1): 2–9. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2019.0124 [65] WANG Yu, LIU Kang, LIU Hongyan, et al. Detection of rotational object in arbitrary position using vortex electromagnetic waves[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(4): 4989–4994. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3032665 [66] YANG Tao and WANG Gang. Rotational Doppler shift for electromagnetic waves carrying orbital angular momentum based on spectrum analysis[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2017, 1820(1): 090024. doi: 10.1063/1.4977408 [67] GONG Ting, CHENG Yongqiang, LI Xiang, et al. Micromotion detection of moving and spinning object based on rotational Doppler shift[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2018, 28(9): 843–845. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2018.2858552 [68] LIU Baiyang, CHU Hongchen, GIDDENS H, et al. Experimental observation of linear and rotational Doppler shifts from several designer surfaces[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 8971. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45516-1 [69] ZHENG Jiayu, ZHENG Shilie, SHAO Zhenlei, et al. Rotational Doppler effect based on the radio orbital angular momentum wave[C]. 2017 IEEE Asia Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2017: 1298–1301. doi: 10.1109/APMC.2017.8251700. [70] LIU Kang, LI Xiang, GAO Yue, et al. Microwave imaging of spinning object using orbital angular momentum[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 122(12): 124903. doi: 10.1063/1.4991655 [71] ZHOU Zhenglong, CHENG Yongqiang, LIU Kang, et al. Rotational Doppler resolution of spinning target detection based on OAM beams[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2019, 3(3): 5500404. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2019.2900227 [72] LIU Baiyang, GIDDENS H, LI Yin, et al. Design and experimental demonstration of Doppler cloak from spatiotemporally modulated metamaterials based on rotational Doppler effect[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(3): 3745–3755. doi: 10.1364/OE.382700 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: