A Radio Frequency Interference Mitigation Method for Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radars
-
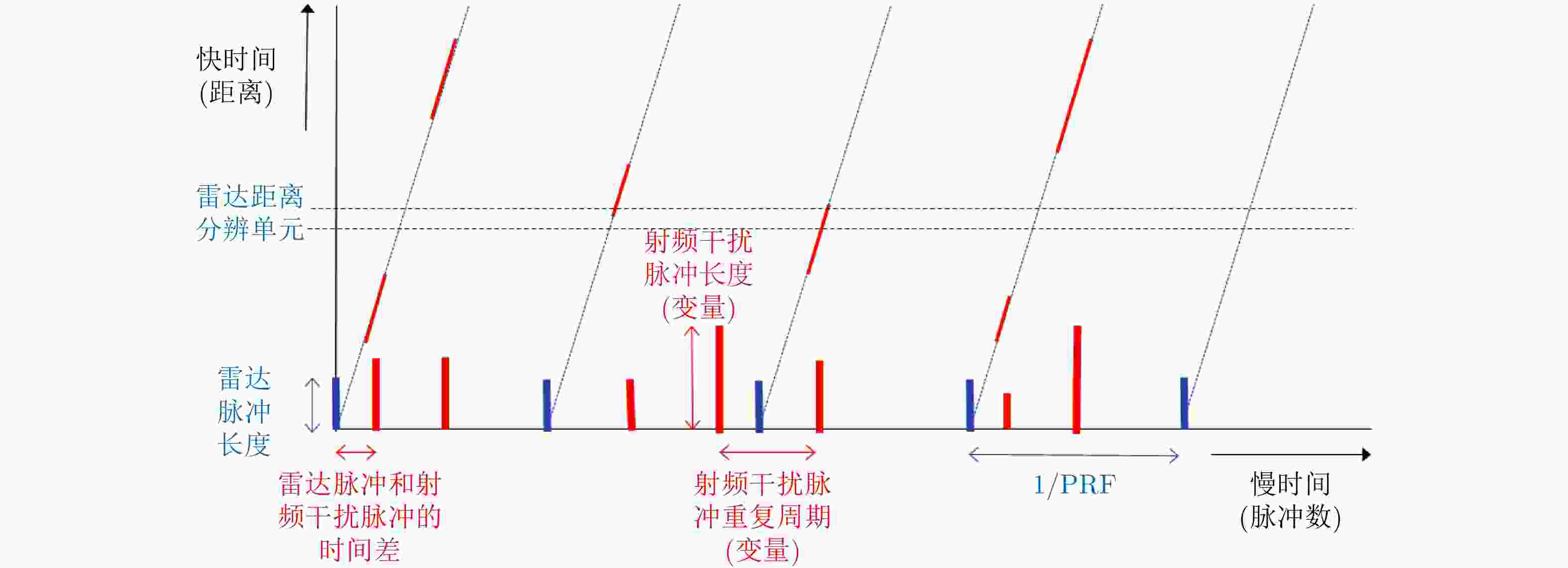
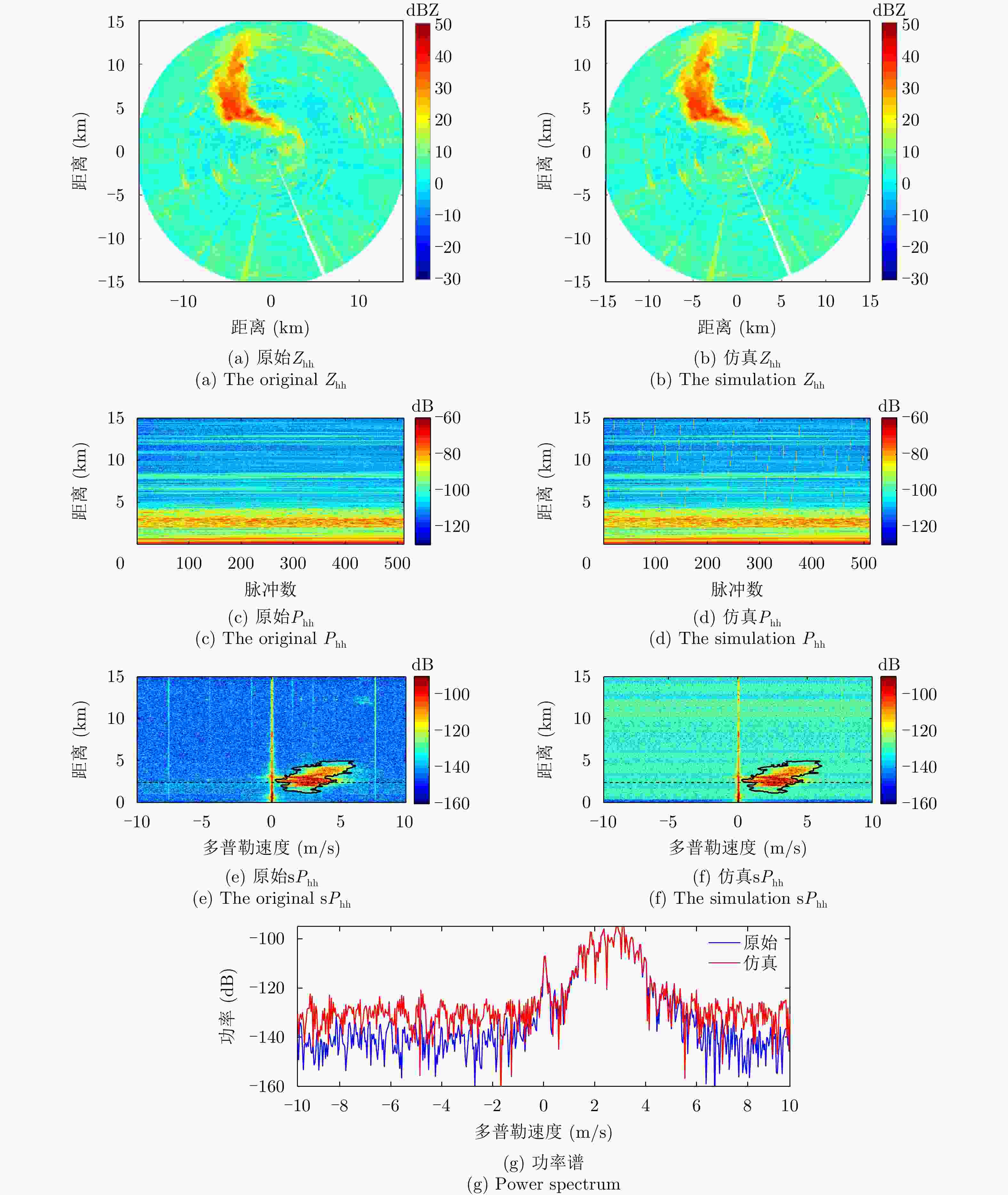
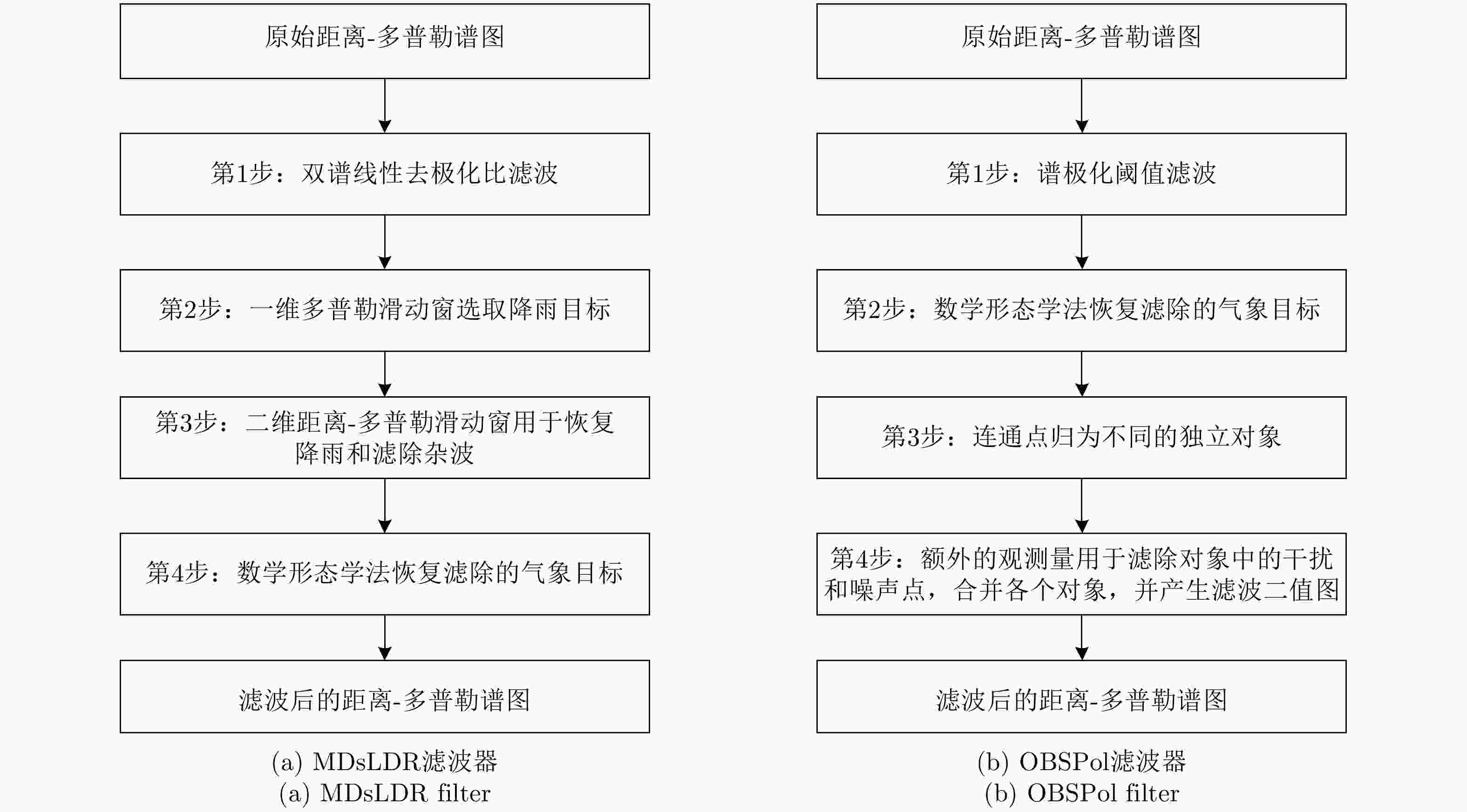
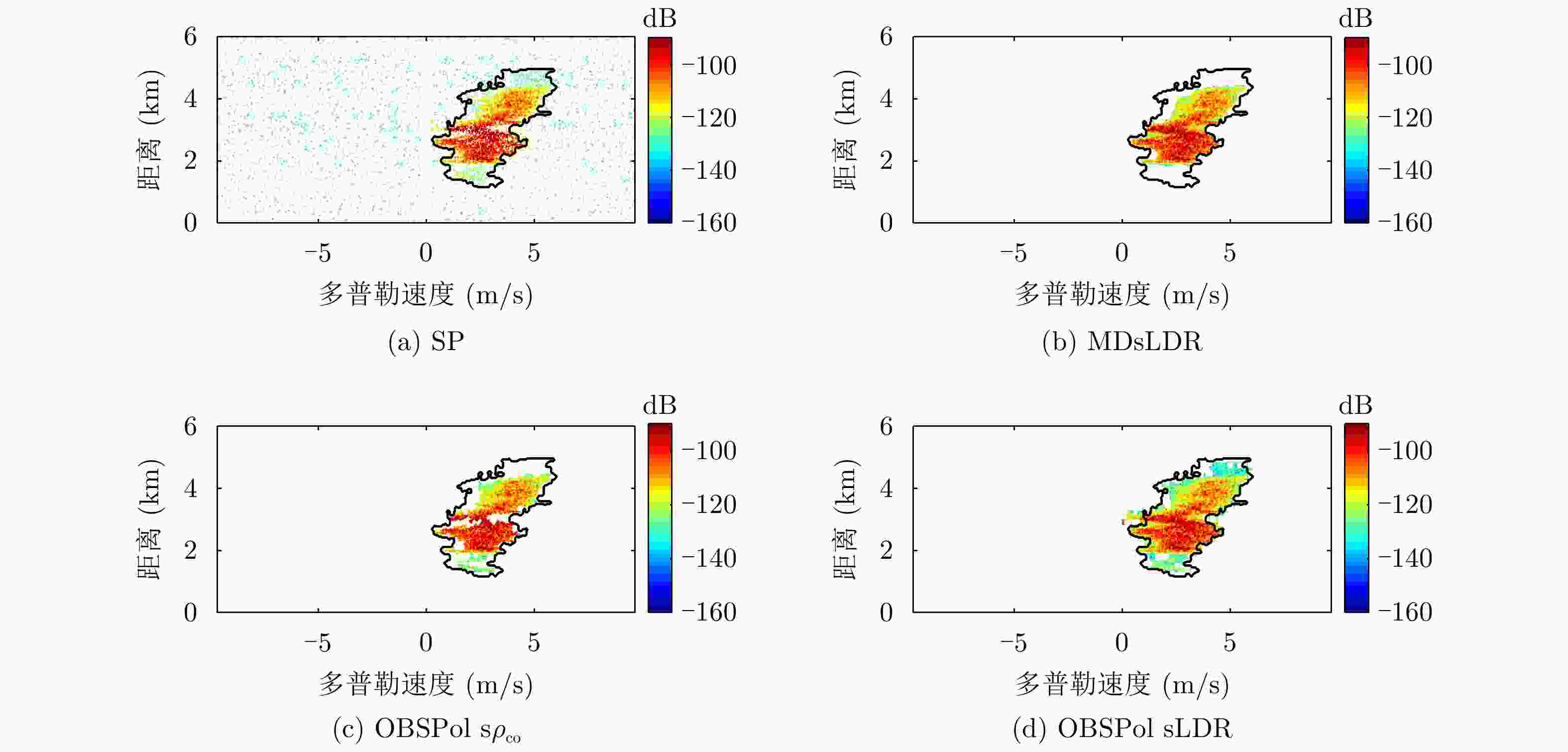
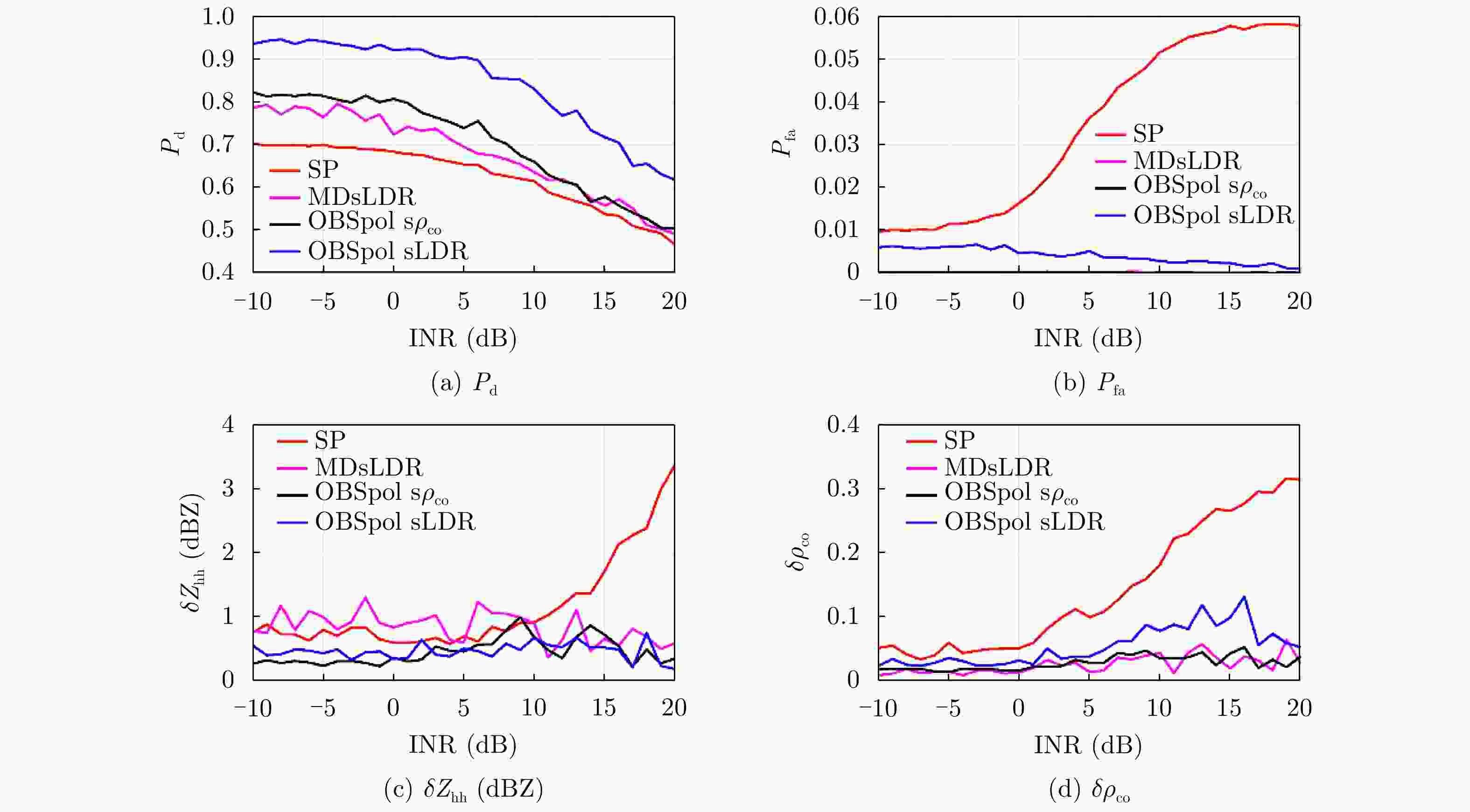
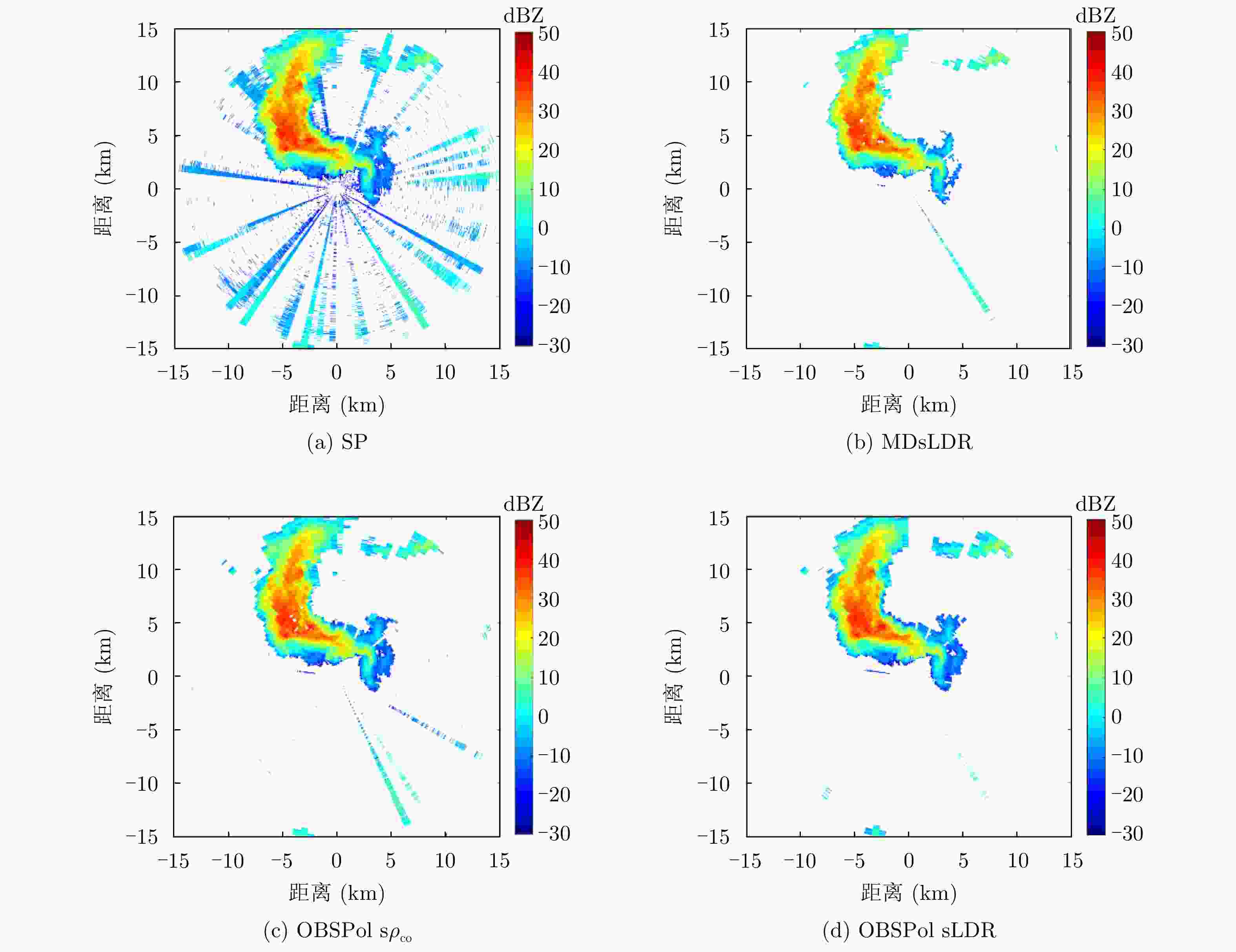
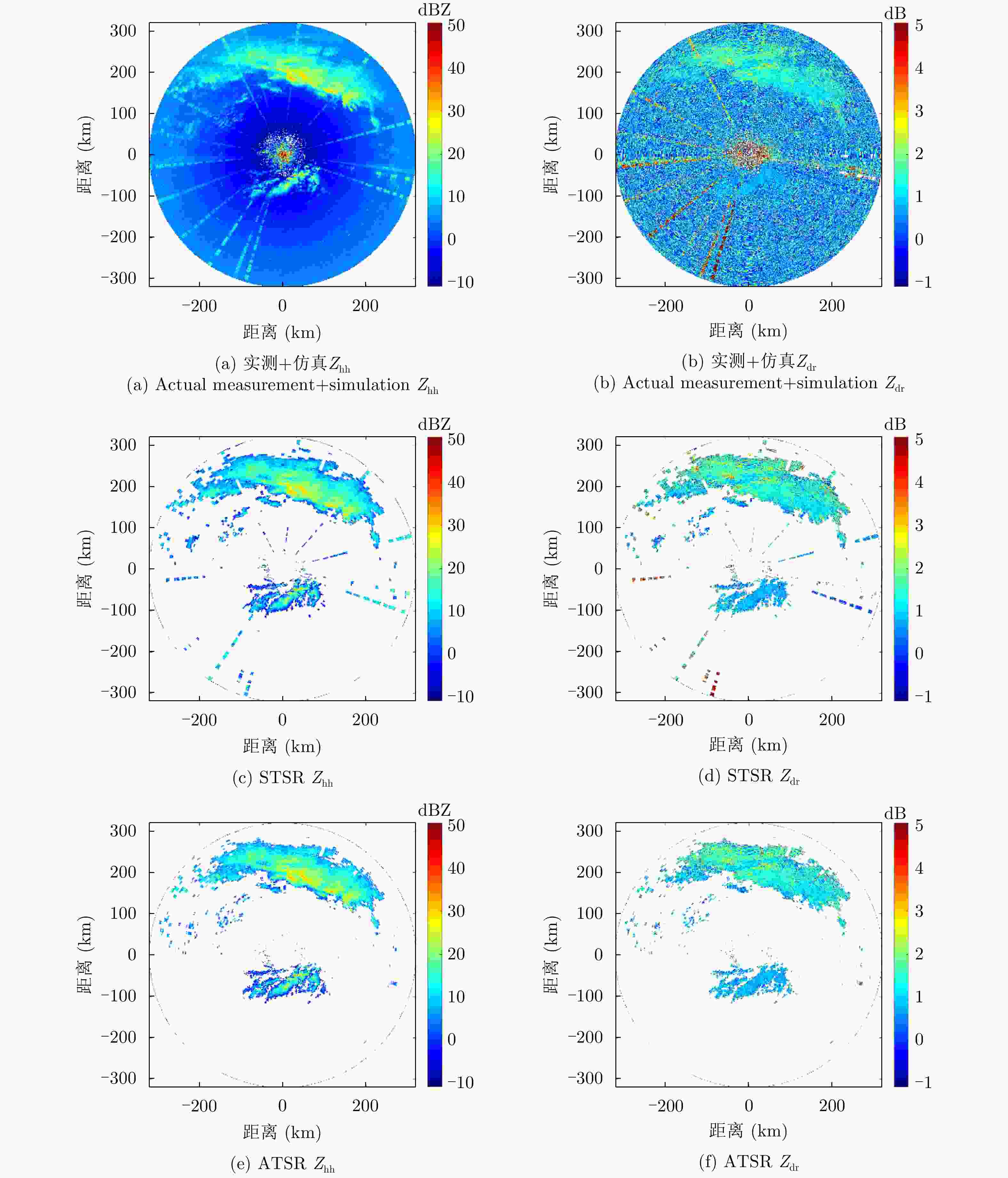
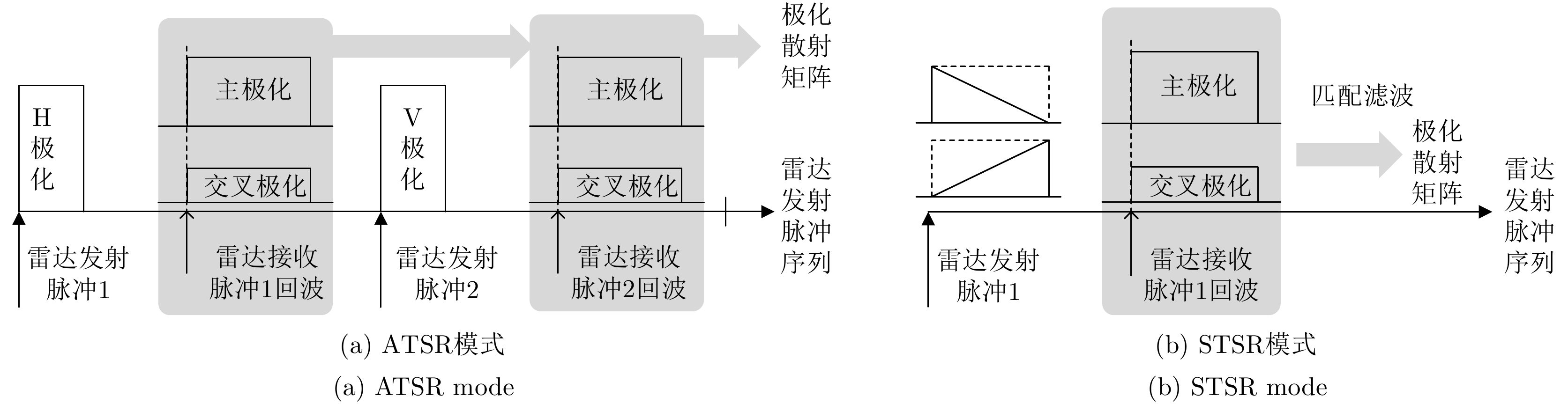
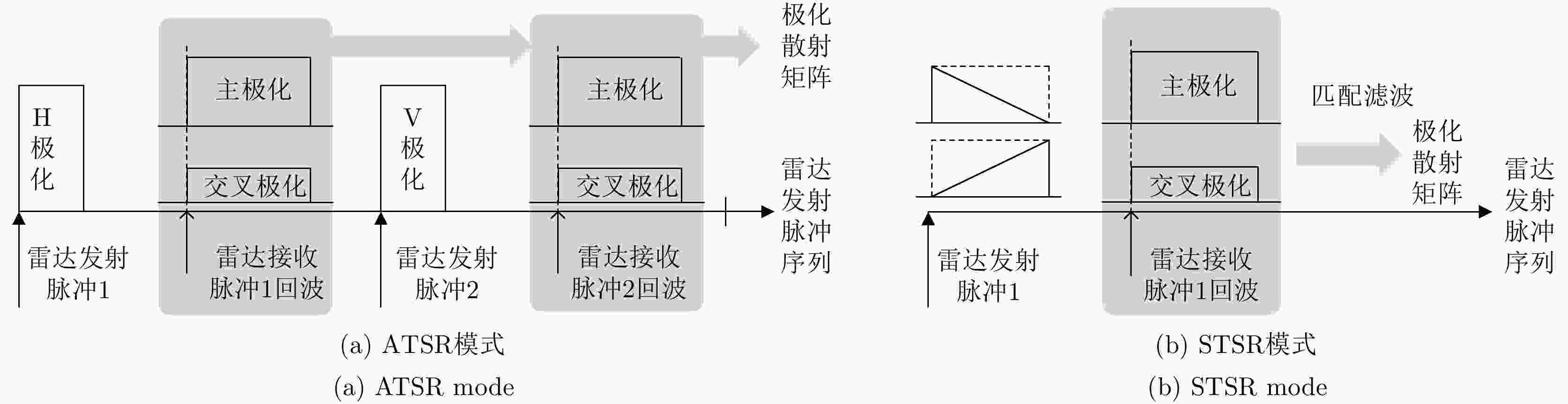
摘要: 为了滤除极化-多普勒气象雷达中的射频干扰,该文提出利用谱极化滤波器,适用于同时发射同时接收(STSR)和分时发射同时接收(ATSR)体制的极化气象雷达。首先利用C波段STSR气象雷达的实测数据研究射频干扰的时域、频域和极化域特性,建立射频干扰信号模型。然后,在X波段ATSR雷达的数据中仿真加入射频干扰,验证谱极化滤波器的有效性。总体看来,在ATSR雷达中利用谱极化滤波器可以有效保留降雨目标并且滤除射频干扰。最后,针对STSR雷达提出利用数据分集的方法,STSR雷达的实测数据可以模拟ATSR雷达数据,再利用谱极化滤波器实现射频干扰滤除,同样可以取得较好的滤波效果。
-
关键词:
- 极化-多普勒气象雷达 /
- 射频干扰 /
- 谱极化滤波器 /
- 数据分集
Abstract: To mitigate Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) for polarimetric Doppler weather radars, this paper proposes to use spectral polarimetric filters. Polarimetric weather radars can be divided into two basic categories: Simultaneously Transmitting and Simultaneously Receiving (STSR) and Alternately Transmitting and Simultaneously Receiving (ATSR). First, the real RFI measurements from an operational C-band STSR weather radar help characterize the temporal, spectral and polarimetric features of RFI. Then, RFI is simulated in an X-band ATSR radar to quantify the performances of spectral polarimetric filters. Overall, spectral polarimetric filters can keep the precipitation and remove RFI in an ATSR radar. Finally, the data division method is put forward for STSR radars by mimicking the ATSR measurements. Good performance in RFI mitigation is also verified by using the same spectral polarimetric filters. -
表 1 KNMI雷达手册
Table 1. KNMI radar specifications
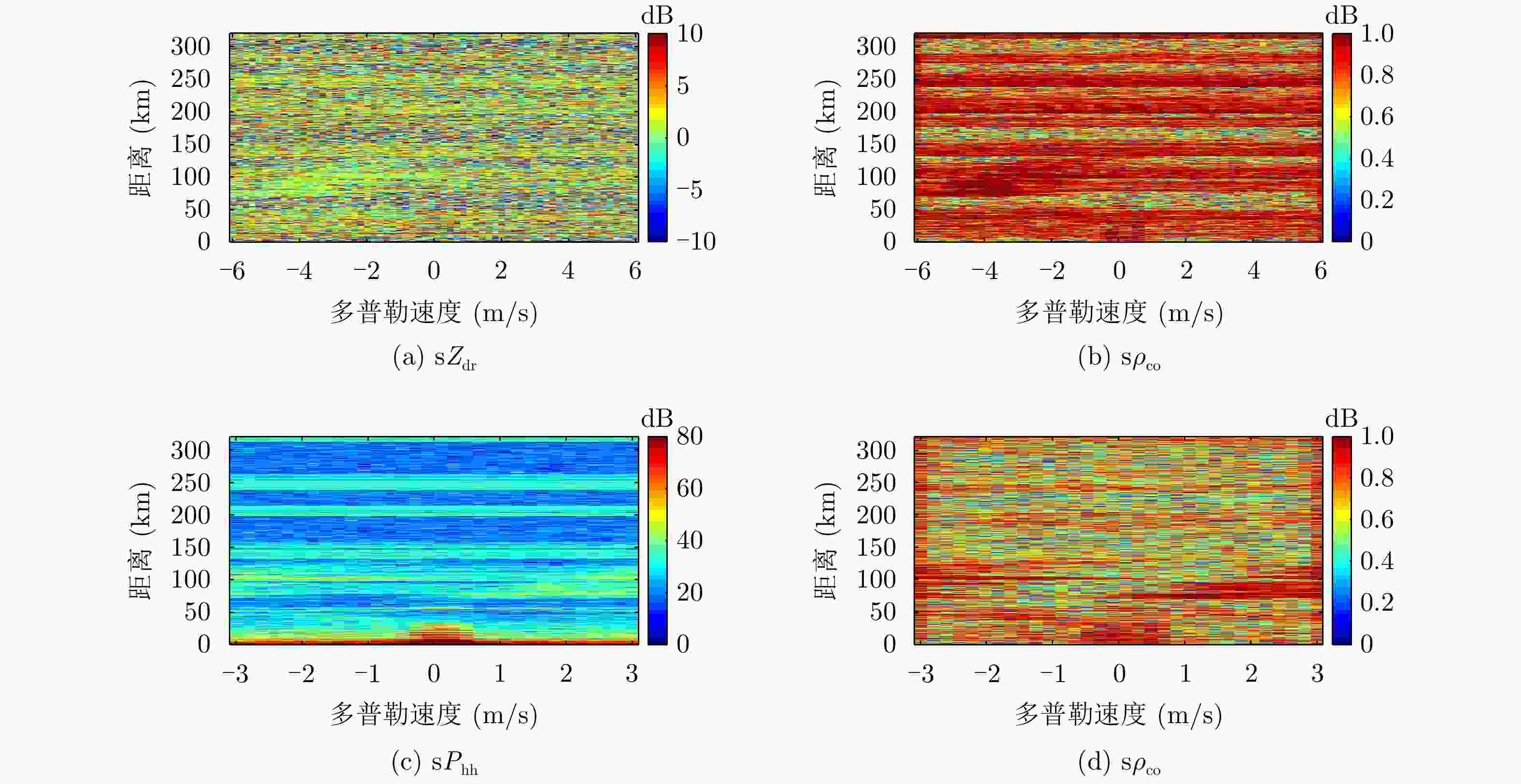
雷达类型 脉冲多普勒 发射机类型 磁控管 极化类型 STSR模式 中心频率 5.63 GHz 发射功率 500 kW 脉冲宽度 0.5~3.5 μs 脉冲重复频率 175~2400 Hz 天线宽度 1° 扫描角 方位–2°~90°,俯仰0°~360° 扫描周期 16扫描模式/5 min 表 2 射频干扰极化参量与不同极化的辐射源的关系
Table 2. The relationship between polarization variables and RF source with different polarization
RF极化 参量 H极化 45°线极化 V极化 ${Z_{{\rm{dr}}} }$ (dB) 无限大 0 无限小 STSR的$ {\rho _{{\text{co}}}} $ 小 大 小 ATSR的$ {\rho _{{\text{co}}}} $ 小 小 小 表 3 IDRA雷达参数
Table 3. IDRA radar specifications
雷达类型 线性FMCW 发射机类型 固态 极化类型 ATSR模式 中心频率 9.475 GHz 发射功率 20 W 扫描时间 409.6 μs 带宽 5 MHz 天线宽度 1.8° 扫描角 俯仰 0.5°,方位0°~360° 扫描周期 1圈/min -
[1] DOVIAK R J and ZRNIĆ D S. Doppler Radar and Weather Observations[M]. Mineola: Dover Publications, 2006. [2] BRINGI V N and CHANDRASEKAR V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar: Principles and Applications[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001. [3] YIN Jiapeng. Advanced techniques in clutter mitigation and calibration for weather radars[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Delft University of Technology, 2019. [4] PALMER R, WHELAN D, BODINE D, et al. The need for spectrum and the impact on weather observations[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2021, 102(7): E1402–E1407. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-21-0009.1 [5] SALTIKOFF E, CHO J Y N, TRISTANT P, et al. The threat to weather radars by wireless technology[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2016, 97(7): 1159–1167. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-15-00048.1 [6] CHO J Y N. A new radio frequency interference filter for weather radars[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2017, 34(7): 1393–1406. doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-17-0028.1 [7] CARROLL J E, SANDERS F H, SOLE R L, et al. Case study: Investigation of interference into 5 GHz weather radars from unlicensed national information infrastructure devices[R]. NTIA Technical Report TR-11-473, 2010. [8] VACCARONO M, CHANDRASEKAR C V, BECHINI R, et al. Survey on electromagnetic interference in weather radars in northwestern Italy[J]. Environments, 2019, 6(12): 126. doi: 10.3390/environments6120126 [9] LAKE J L, YEARY M, and CURTIS C D. Adaptive radio frequency interference mitigation techniques at the national weather radar testbed: First results[C]. 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, USA, 2014: 840–845. [10] ROJAS L C, MOISSEEV D N, CHANDRASEKAR V, et al. Dual-polarization spectral filter for radio frequency interference suppression[C]. The 7th European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology, Toulouse, France, 2012. [11] YANOVSKY F J, RUSSCHENBERG H W J, and UNAL C M H. Retrieval of information about turbulence in rain by using Doppler-polarimetric Radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2005, 53(2): 444–450. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2004.840772 [12] YIN Jiapeng, UNAL C M H, and RUSSCHENBERG H W J. Narrow-band clutter mitigation in spectral polarimetric weather radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(8): 4655–4667. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2696263 [13] YIN Jiapeng, UNAL C, and RUSSCHENBERG H. Object-orientated filter design in spectral domain for polarimetric weather radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(5): 2725–2740. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2876632 [14] MELNIKOV V M and ZRNIĆ D S. On the alternate transmission mode for polarimetric phased array weather radar[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2015, 32(2): 220–233. doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-13-00176.1 [15] HURTADO M and NEHORAI A. Polarimetric detection of targets in heavy inhomogeneous clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(4): 1349–1361. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.909046 [16] FIGUERAS I VENTURA J. Design of a high resolution X-band Doppler polarimetric weather radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Delft University of Technology, 2009. [17] FULTON C, HERD J, KARIMKASHI S, et al. Dual-polarization challenges in weather radar requirements for multifunction phased array radar[C]. 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Phased Array Systems and Technology, Waltham, USA, 2013: 494–501. [18] ZRNIĆ D S, ZHANG Guifu, and DOVIAK R J. Bias correction and Doppler measurement for polarimetric phased-array radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(2): 843–853. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2057436 [19] IVIĆ I R, CURTIS C, and TORRES S M. Radial-based noise power estimation for weather radars[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2013, 30(12): 2737–2753. doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-13-00008.1 [20] BACHMANN S and ZRNIĆ D. Spectral density of polarimetric variables separating biological scatterers in the VAD display[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2007, 24(7): 1186–1198. doi: 10.1175/JTECH2043.1 [21] MOISSEEV D N and CHANDRASEKAR V. Polarimetric spectral filter for adaptive clutter and noise suppression[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2009, 26(2): 215–228. doi: 10.1175/2008JTECHA1119.1 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: