Orbital Angular Momentum Anti-interference Properties Analysis of Electromagnetic Vortex Wave
-
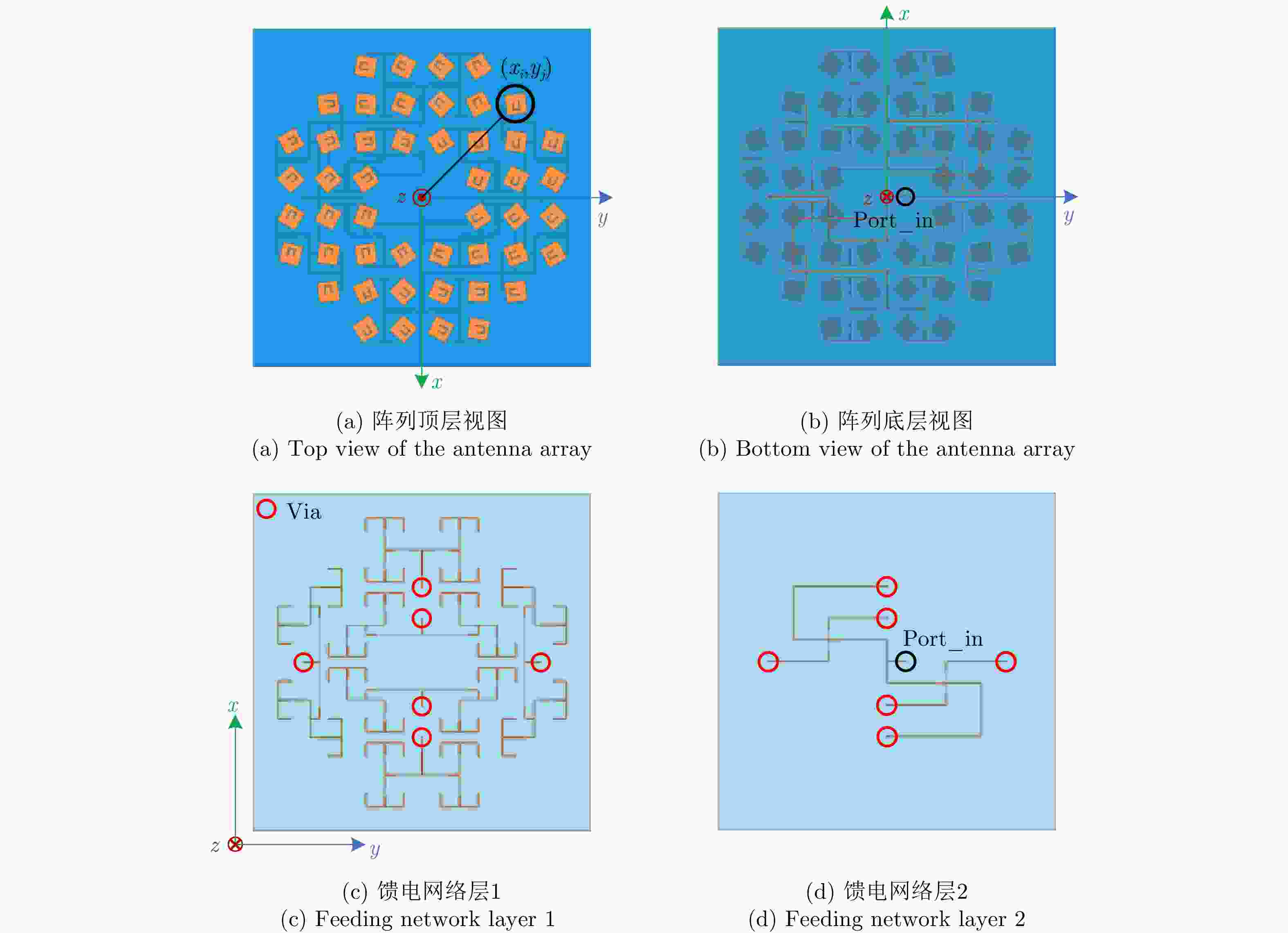
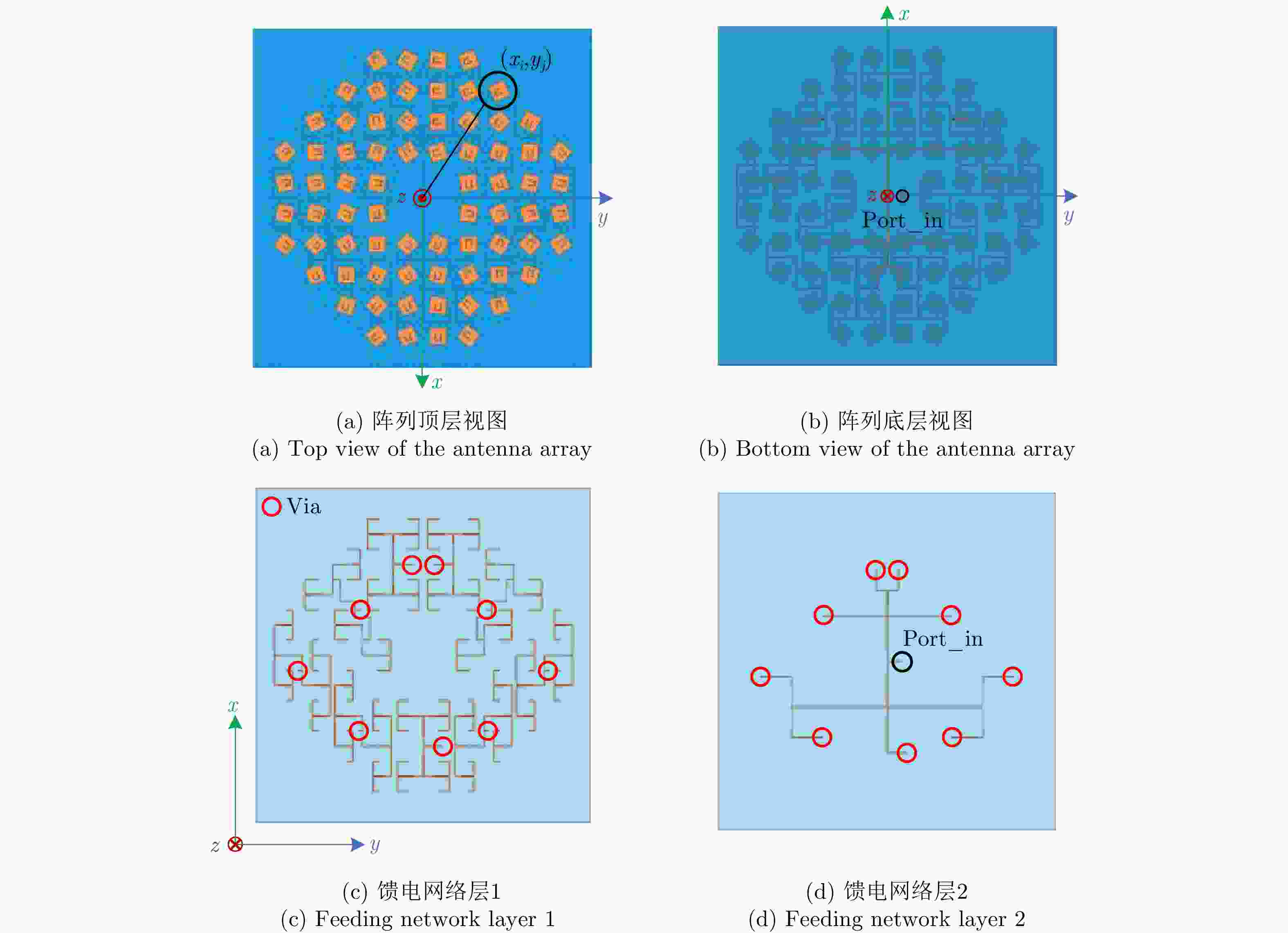
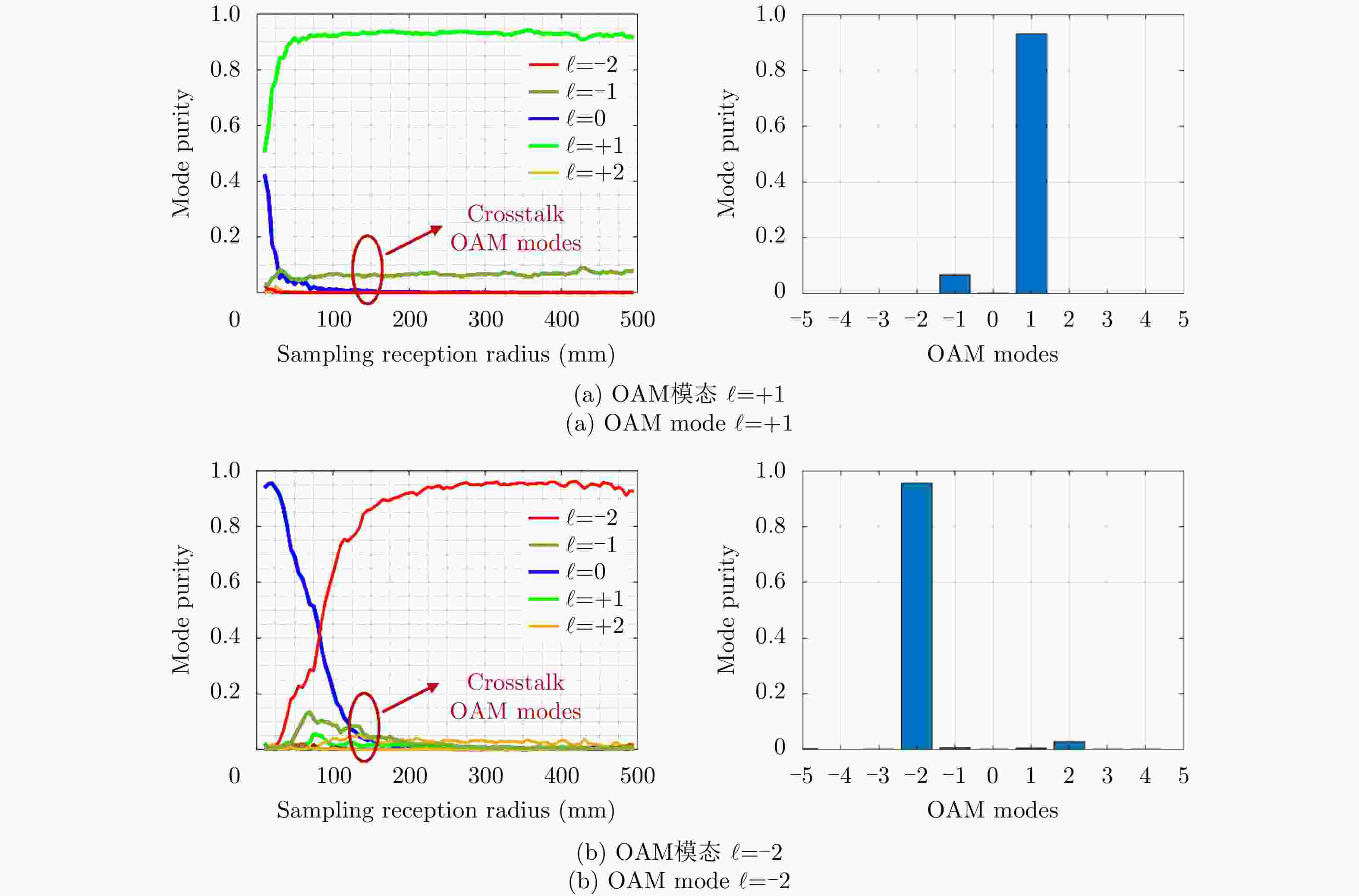
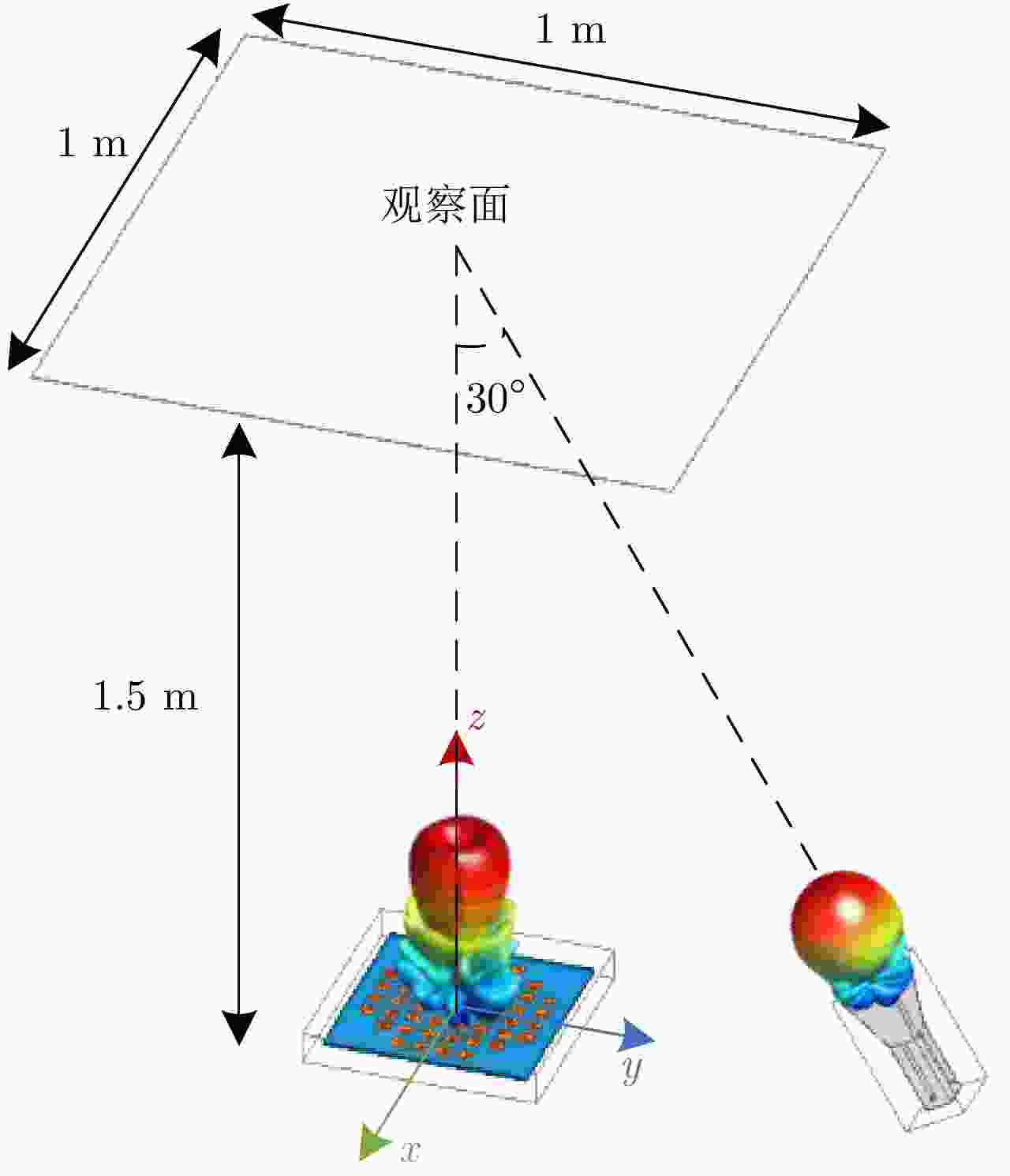
摘要: 鉴于涡旋电磁波所体现出的独特空间电磁场分布特征,以及其携带的轨道角动量(OAM)在理论上所具有的无穷维度模态正交特性,涡旋电磁波在无线通信领域和雷达探测与成像领域均表现出重要的研究价值和应用潜力。该文主要从涡旋电磁波空间电磁场分布的角度以及OAM模态正交性保持的角度,重点对涡旋电磁波射频收发链路中OAM模态的抗干扰性能进行分析。在C波段分别设计了不同的平面阵列天线用来产生和接收携带有OAM模态为
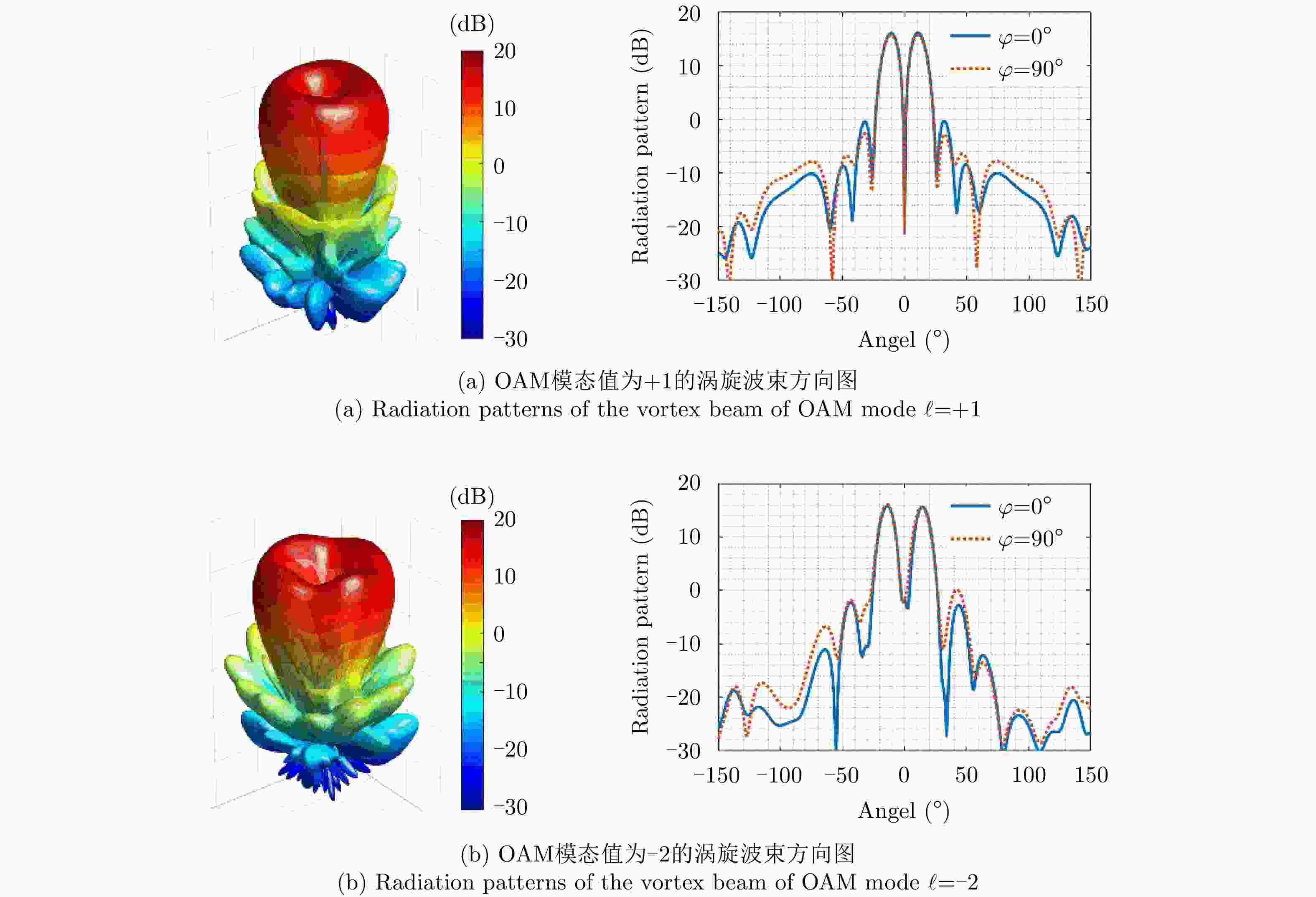
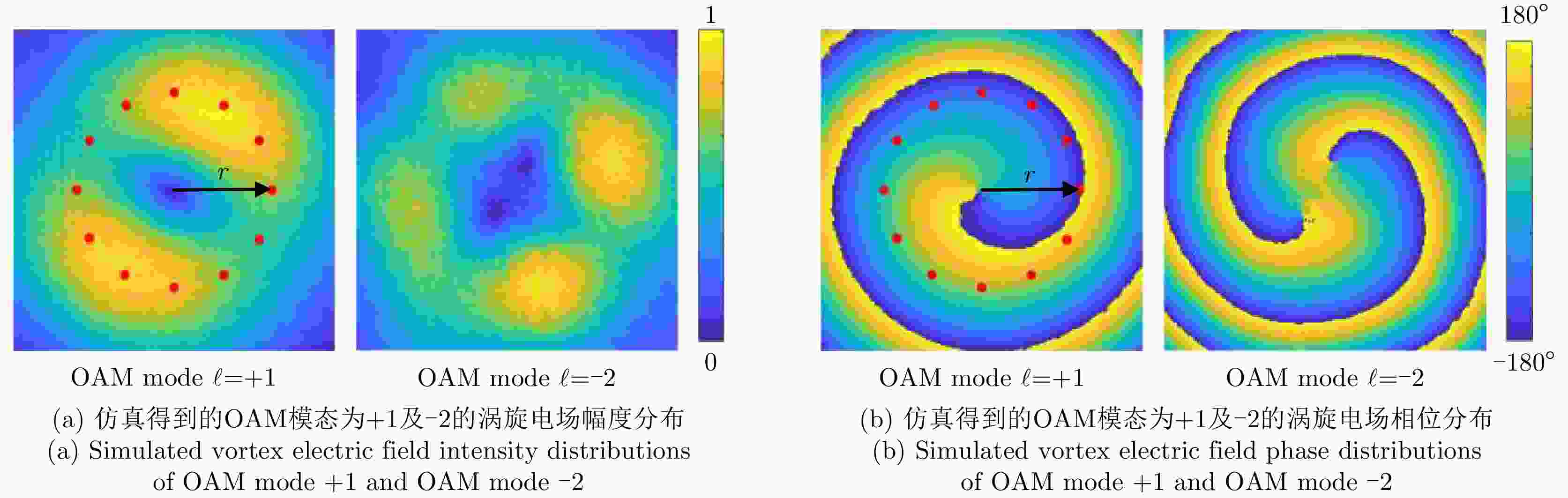
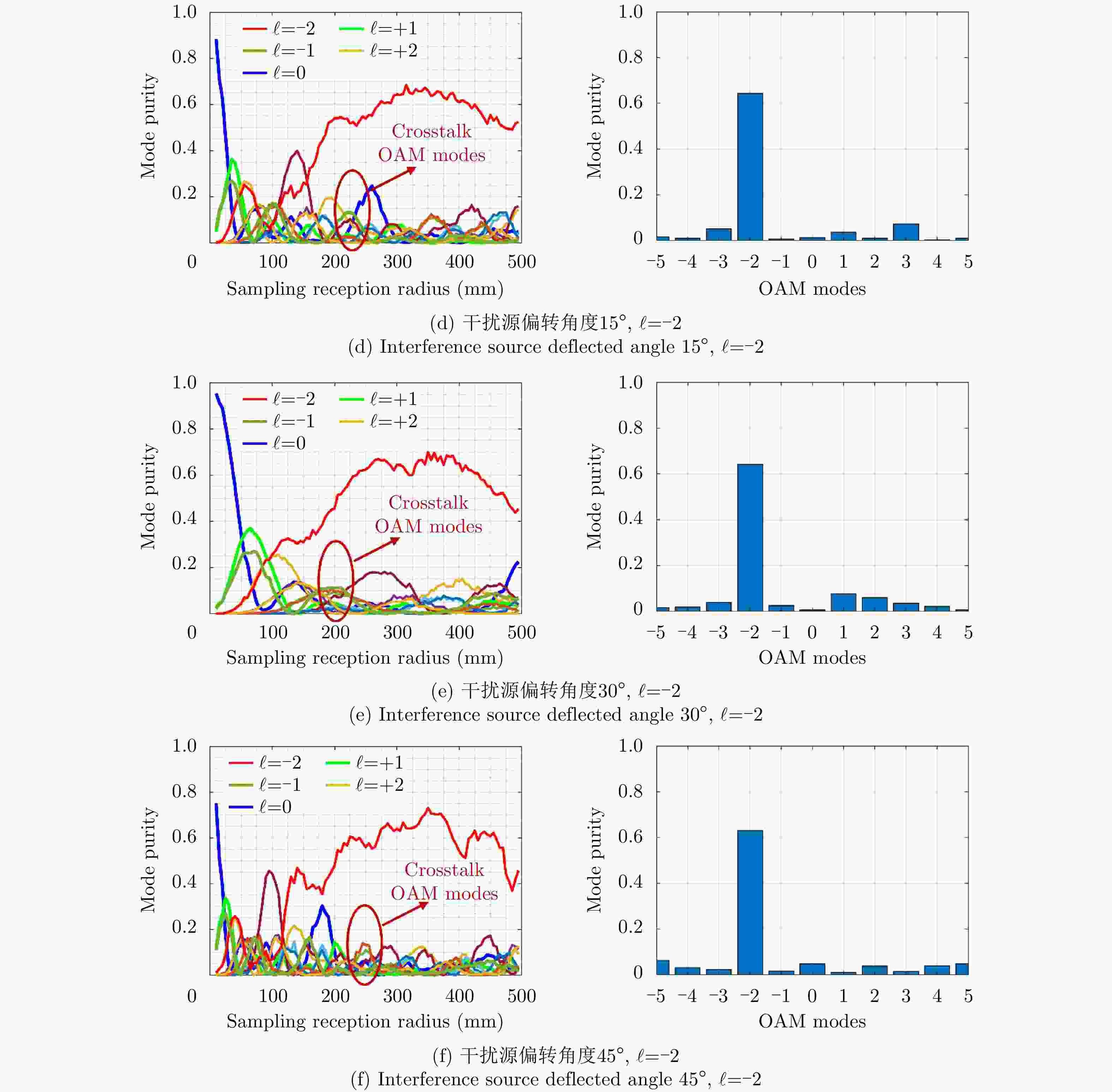
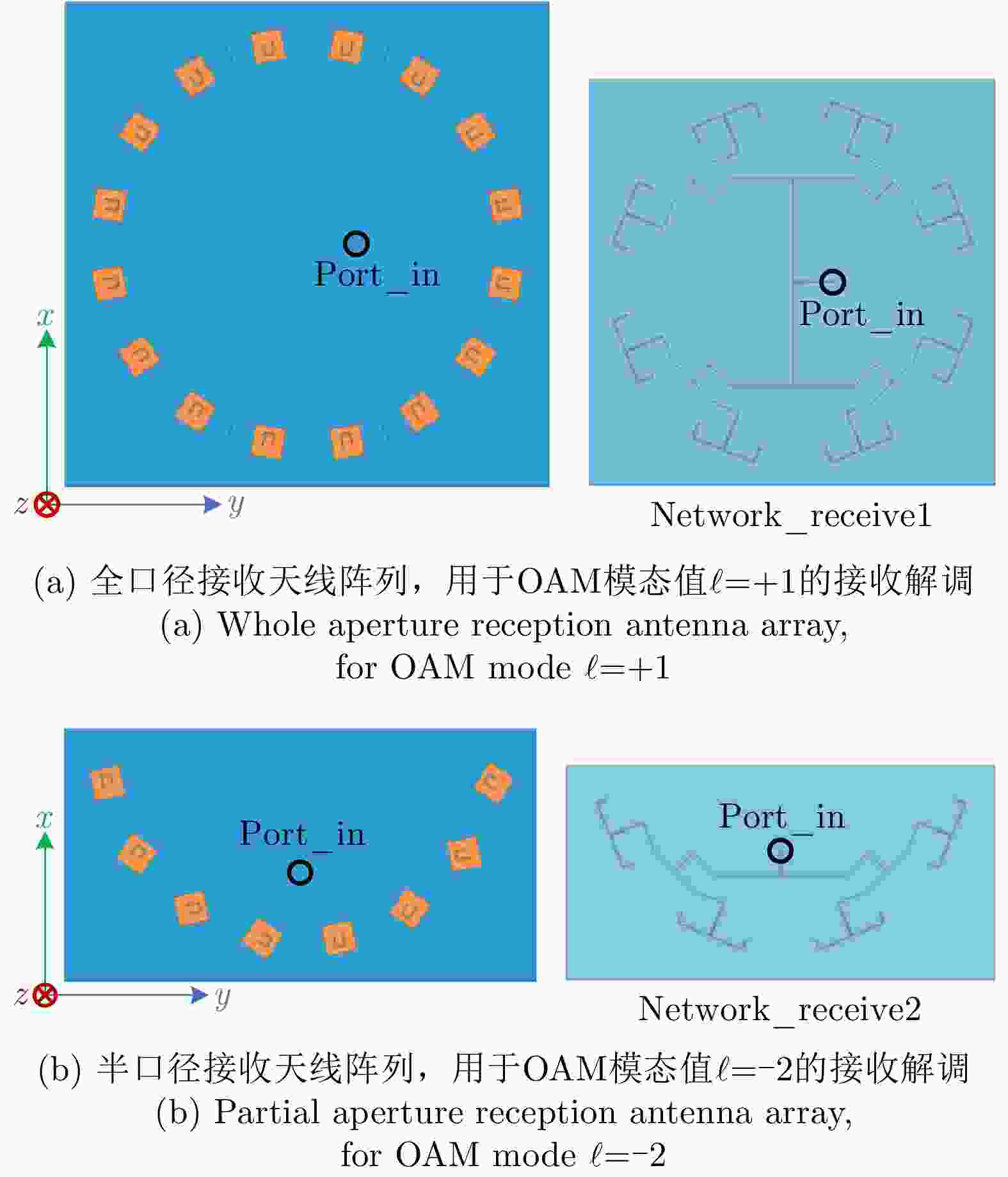
$\ell = + 1$ 和$\ell = - 2$ 的涡旋电磁波束,并建立起涡旋电磁波的射频收发链路。通过引入一个喇叭天线作为干扰源,以相应涡旋电磁波束的OAM模态谱分布以及OAM模态正交性作为主要的分析依据,在不同干扰场景下抗干扰性对涡旋电磁波的收发射频链路的OAM模态性能进行仿真和分析。该文对设计的天线模型进行加工和测试,对涡旋电磁波射频收发链路中OAM模态抗干扰性能的分析,可以为涡旋电磁波在无线通信及雷达探测与成像等有关研究领域提供一些前瞻性的探索和设计上的指导。Abstract: The electromagnetic vortex wave has demonstrated excellent research value with potential applications in the fields of wireless communication and radar detection and imaging due to its unusual electromagnetic field distribution and theoretically infinite orthogonal Orbital Angular Momentum (OAM) modes. This study analyzes the anti-interference performance of OAM modes in the electromagnetic vortex Radio Frequency (RF) transceiver link primarily from the perspective of the electromagnetic vortex field distributions in space and the OAM modes orthogonality. Planar antenna arrays are designed to generate the electromagnetic vortex beams with respective OAM modes of and in the C band, and the corresponding RF transceiver links are established. The OAM modes’ anti-interference properties under different interference situations are analyzed in the electromagnetic vortex RF transceiver link by using a horn antenna as the interference source. Meanwhile, the corresponding OAM mode spectrum and the OAM modes’ orthogonality are employed as the primary methods in our analysis. Finally, the designed antenna models are fabricated, and the electromagnetic vortex RF transceiver links are measured. The corresponding analyses and conclusions are presented in this study. The OAM modes’ anti-interference performance analysis in the vortex electromagnetic wave’s RF transceiver link can provide a reference for exploring and designing a vortex electromagnetic wave in wireless communication and radar detection and imaging research. -
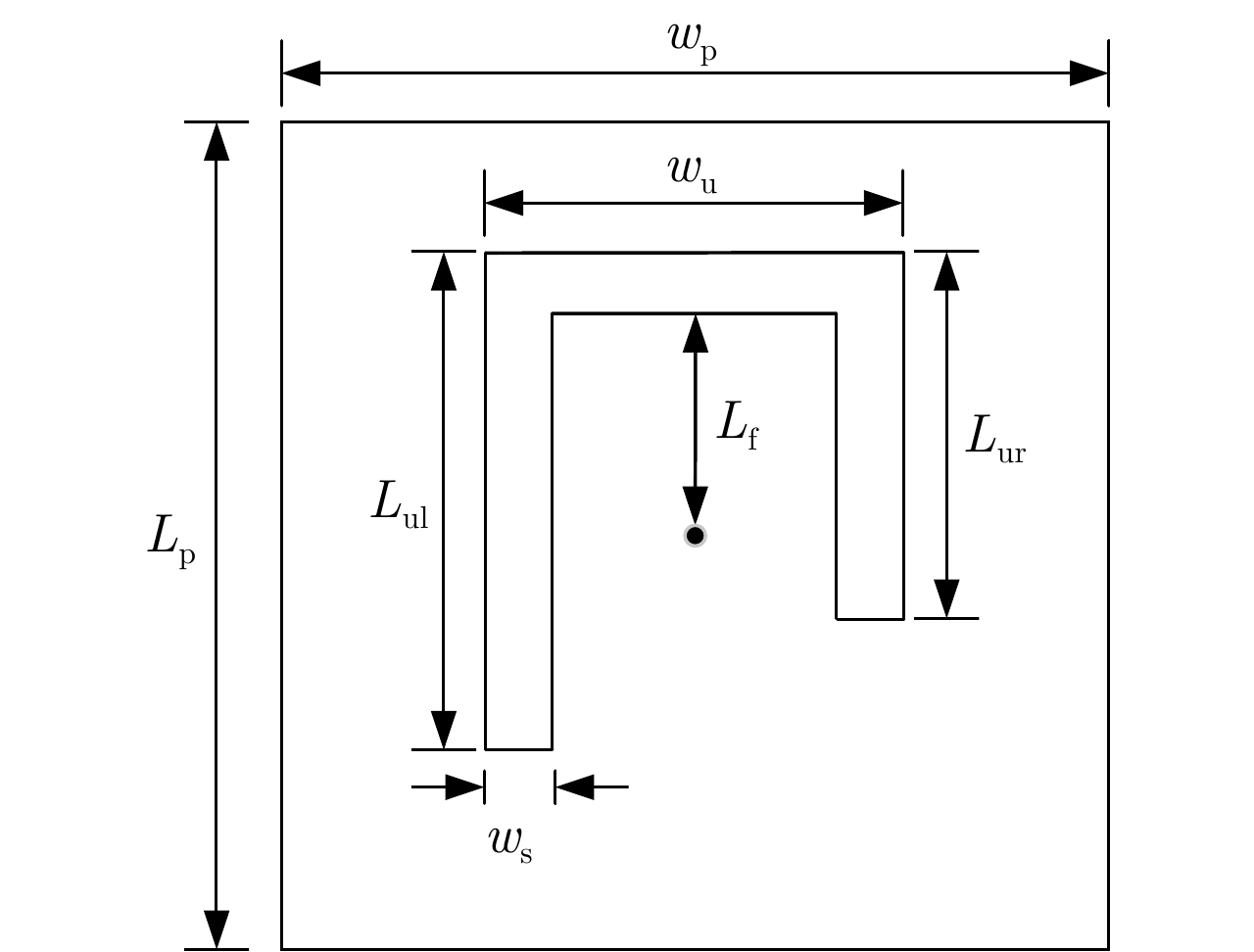
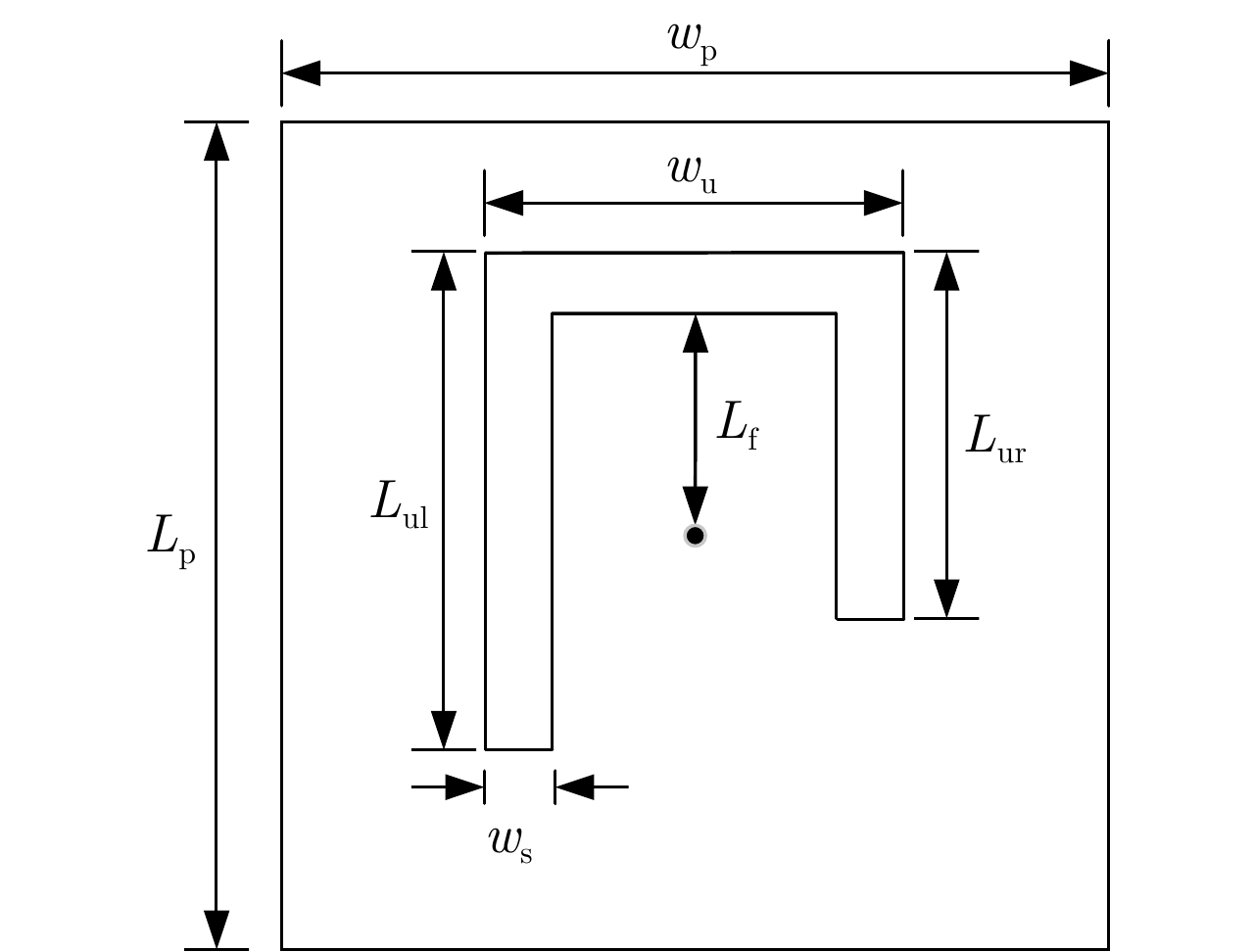
表 1 4.25 GHz右旋圆极化天线单元尺寸参数(单位:mm)
Table 1. Size parameters 4.25 GHz of the designed right-handed circularly polarized antenna unit (Unit: mm)
Parameter Value Parameter Value wp 18.2 Lur 7.2 Lp 18.2 Lf 4.7 wu 7 ws 1.1 Lul 9 表 2 不同OAM模态涡旋波束收发射频链路的传输系数仿真结果(单位:dB)
Table 2. Simulated transmission coefficients of vortex beams RF transceiver link under different OAM modes (Unit: dB)
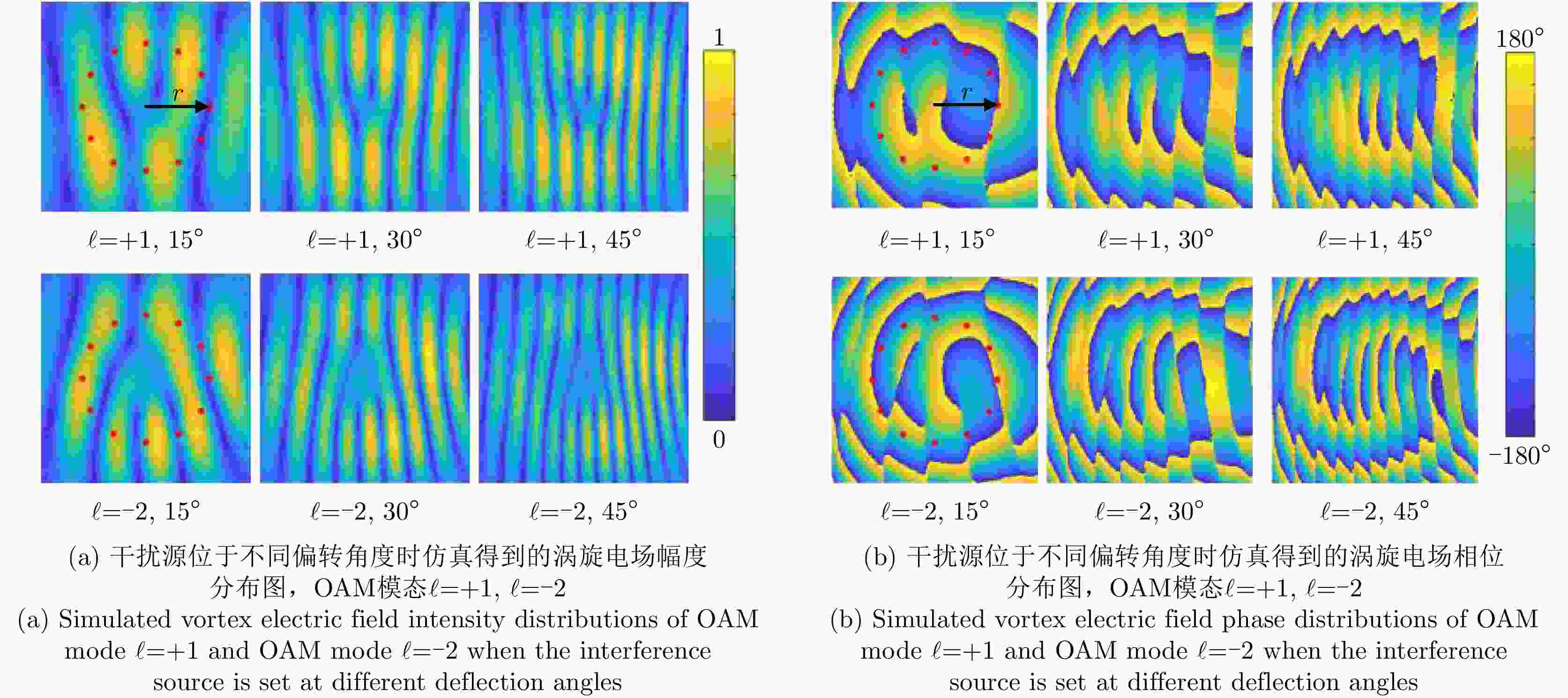
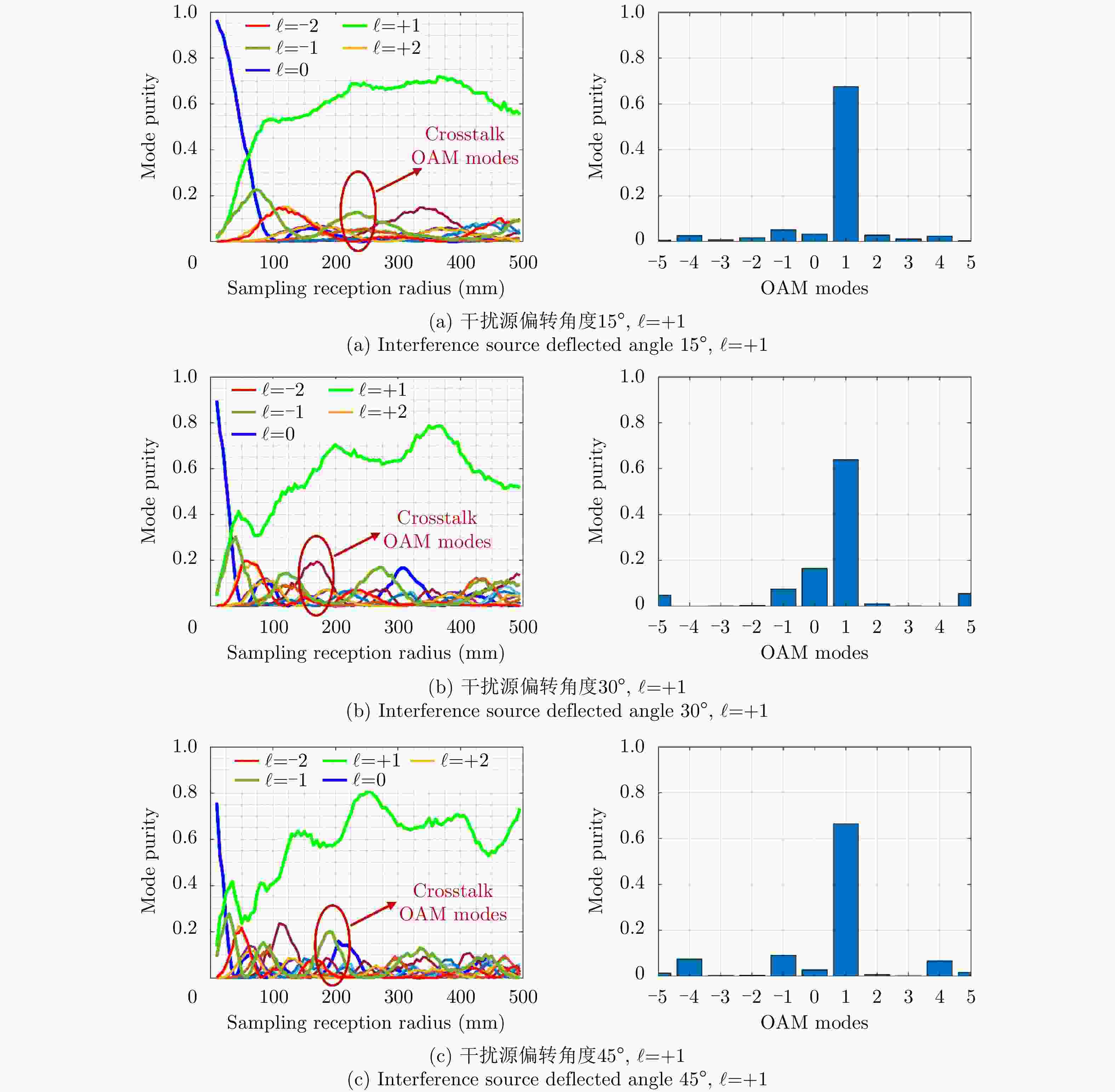
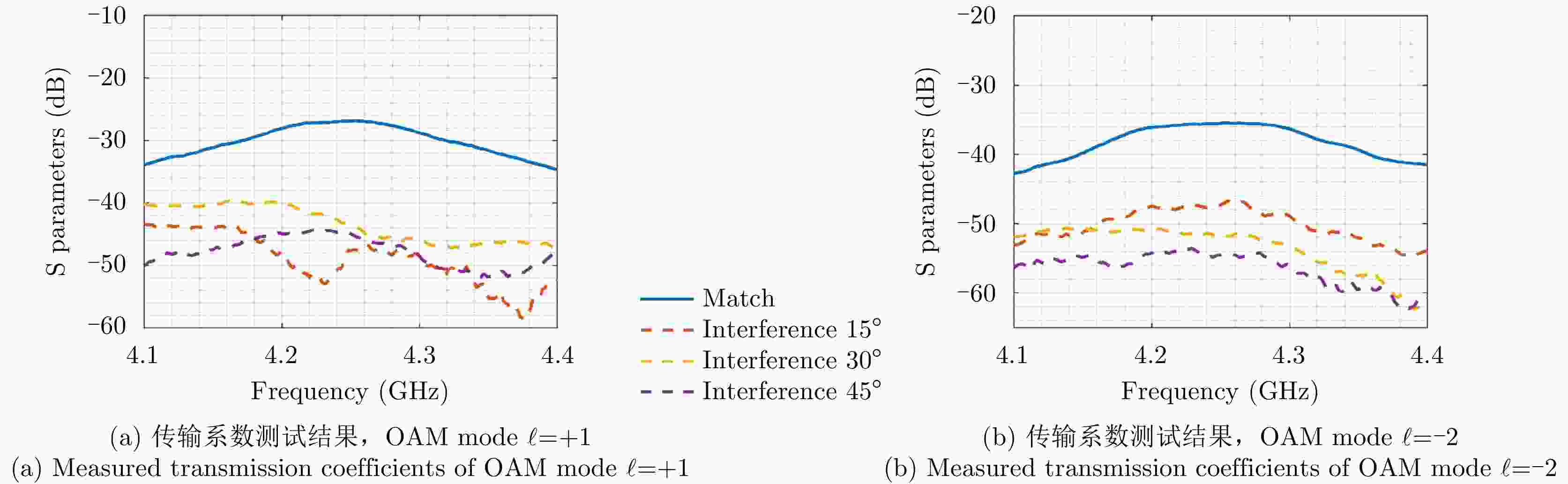
Tilted angle OAM mode $\ell $ = +1 OAM mode $\ell $ = –2 Match Interference Match Interference 15° –19.07 –29.4 –31.44 –45.25 30° –18.79 –31.7 –28.37 –48.32 45° –18.55 –36.4 –31.41 –42.69 -
[1] YAO A M and PADGETT M J. Orbital angular momentum: Origins, behavior and applications[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2011, 3(2): 161–204. doi: 10.1364/AOP.3.000161 [2] ALLEN L, BEIJERSBERGEN M W, SPREEUW R J C, et al. Orbital angular momentum of light and the transformation of Laguerre-Gaussian laser modes[J]. Physical Review A, 1992, 45(11): 8185–8189. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.45.8185 [3] WILLNER A E, WANG Jian, and HUANG Hao. A different angle on light communications[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6095): 655–656. doi: 10.1126/science.1225460 [4] YUE Yang, HUANG Hao, AHMED N, et al. Reconfigurable switching of orbital-angular-momentum-based free-space data channels[J]. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(23): 5118–5121. doi: 10.1364/OL.38.005118 [5] YAN Yan, XIE Guodong, LAVERY M P J, et al. High-capacity millimetre-wave communications with orbital angular momentum multiplexing[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4876. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5876 [6] REN Yongxiong, LI Long, XIE Guodong, et al. Line-of-sight millimeter-wave communications using orbital angular momentum multiplexing combined with conventional spatial multiplexing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(5): 3151–3161. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2675885 [7] WILLNER A E and LIU Cong. Perspective on using multiple orbital-angular-momentum beams for enhanced capacity in free-space optical communication links[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 10(1): 225–233. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2020-0435 [8] 郭桂蓉, 胡卫东, 杜小勇. 基于电磁涡旋的雷达目标成像[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2013, 35(6): 71–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2013.06.013GUO Guirong, HU Weidong, and DU Xiaoyong. Electromagnetic vortex based radar target imaging[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2013, 35(6): 71–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2013.06.013 [9] LIU Kang, CHENG Yongqiang, YANG Zhaocheng, et al. Orbital-angular-momentum-based electromagnetic vortex imaging[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2014, 14: 711–714. [10] LIU Kang, CHENG Yongqiang, LI Xiang, et al. Microwave-sensing technology using orbital angular momentum: Overview of its advantages[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2019, 14(2): 112–118. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2018.2890673 [11] JACKSON J D. Classical Electrodynamics[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1999. [12] THIDÉ B, TAMBURINI F, THEN H, et al. Angular momentum radio[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 8999, Complex Light and Optical Forces VIII, San Francisco, USA, 2014. doi: 10.1117/12.2041797. [13] ALLEN L. Orbital angular momentum: A personal memoir[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2017, 375(2087): 20160280. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2016.0280 [14] PADGETT M J. Orbital angular momentum 25 years on [Invited][J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(10): 11265–11274. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.011265 [15] FRANKE-ARNOLD S, ALLEN L, and PADGETT M. Advances in optical angular momentum[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2008, 2(4): 299–313. [16] THIDÉ B, THEN H, SJÖHOLM J, et al. Utilization of photon orbital angular momentum in the low-frequency radio domain[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 99(8): 087701. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.087701 [17] MOHAMMADI S M, DALDORFF L K S, BERGMAN J E S, et al. Orbital angular momentum in radio—A system study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2010, 58(2): 565–572. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2009.2037701 [18] TRICHILI A, PARK K H, ZGHAL M, et al. Communicating using spatial mode multiplexing: Potentials, challenges, and perspectives[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2019, 21(4): 3175–3203. [19] 郭忠义, 汪彦哲, 郑群, 等. 涡旋电磁波天线技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 631–655. doi: 10.12000/JR19091GUO Zhongyi, WANG Yanzhe, ZHENG Qun, et al. Advances of research on antenna technology of vortex electromagnetic waves[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 631–655. doi: 10.12000/JR19091 [20] ZHANG Kuang, WANG Yuxiang, YUAN Yueyi, et al. A review of orbital angular momentum vortex beams generation: From traditional methods to metasurfaces[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(3): 1015. doi: 10.3390/app10031015 [21] TAMBURINI F, MARI E, SPONSELLI A, et al. Encoding many channels on the same frequency through radio vorticity: First experimental test[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2012, 14(3): 033001. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/14/3/033001 [22] TAMBURINI F, THIDÉ B, BOAGA V, et al. Experimental demonstration of free-space information transfer using phase modulated orbital angular momentum radio[J/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1302.2990v2, 2013. [23] CHEN Rui, DU Hanyu, and LI Jiandong. Indoor communications with OAM array[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops, Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–5. [24] ZHOU Jiatong, CHENG Wenchi, and LIANG Liping. OAM transmission in sparse multipath environments with fading[C]. The ICC 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. [25] LEI Yi, YANG Yang, WANG Yanzhe, et al. Throughput performance of wireless multiple-input multiple-output systems using OAM antennas[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(2): 261–265. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3027006 [26] LIANG Liping, CHENG Wenchi, ZHANG Wei, et al. Joint OAM multiplexing and OFDM in sparse multipath environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(4): 3864–3878. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2966787 [27] SHU Jingyue, DENG Li, LI Shufang, et al. Use OFDM in OAM communication to redcuce multi-path effects[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Electronic Information and Communication Technology, Shenzhen, China, 2020: 54–56. [28] FENG Qiang, LIANG Jun, and LI Long. Variable scale aperture sampling reception method for multiple orbital angular momentum modes vortex wave[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 158847–158857. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2950112 [29] FENG Qiang, XUE Hao, LIU Yongjie, et al. Multiple orbital angular momentum vortex electromagnetic waves multiplex transmission and demultiplex reception analysis[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Computational Electromagnetics, Chengdu, China, 2018: 1–3. [30] KAN H K and WATERHOUSE R B. Low cross-polarised patch antenna with single feed[J]. Electronics Letters, 2007, 43(5): 261–262. doi: 10.1049/el:20070224 [31] TONG K F and WONG T P. Circularly polarized U-slot antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2007, 55(8): 2382–2385. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2007.901930 [32] LI Long and ZHOU Xiaoxiao. Mechanically reconfigurable single-arm spiral antenna array for generation of broadband circularly polarized orbital angular momentum vortex waves[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 5128. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23415-1 [33] LIANG Jun, JING Zhongliang, FENG Qiang, et al. Synthesis and measurement of a circular-polarized deflection OAM vortex beam with sidelobe suppression array[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 89143–89151. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2993877 [34] HU Yiping, ZHENG Shilie, ZHANG Zhuofan, et al. Simulation of orbital angular momentum radio communication systems based on partial aperture sampling receiving scheme[J]. IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, 2016, 10(10): 1043–1047. [35] ZHENG Shilie, HUI Xiaonan, ZHU Jiangbo, et al. Orbital angular momentum mode-demultiplexing scheme with partial angular receiving aperture[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(9): 12251–12257. doi: 10.1364/OE.23.012251 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公


 下载:
下载: