-
摘要: 层析合成孔径雷达(TomoSAR)通过组合在不同高度上获取的多基线二维SAR数据,实现合成孔径雷达的三维成像。TomoSAR的求解本质是一维谱估计问题,基于压缩感知的方法可以在非均匀分布的少量基线观测下实现求解,逐渐成为了主流的成像方式。在经典的压缩感知算法流程中,需要将连续的高程向划分成固定的网格,并且假定目标正好位于所划分的网格上。然而该假设通常难以成立,从而引起“基失配”问题,目前该问题在TomoSAR中很少被讨论。该文首先讨论了目标不在网格(Off-grid)上的TomoSAR观测模型,提出了采用加性扰动项来修正目标偏离网格所带来影响的求解模型。在此基础之上,引入局部优化算法与
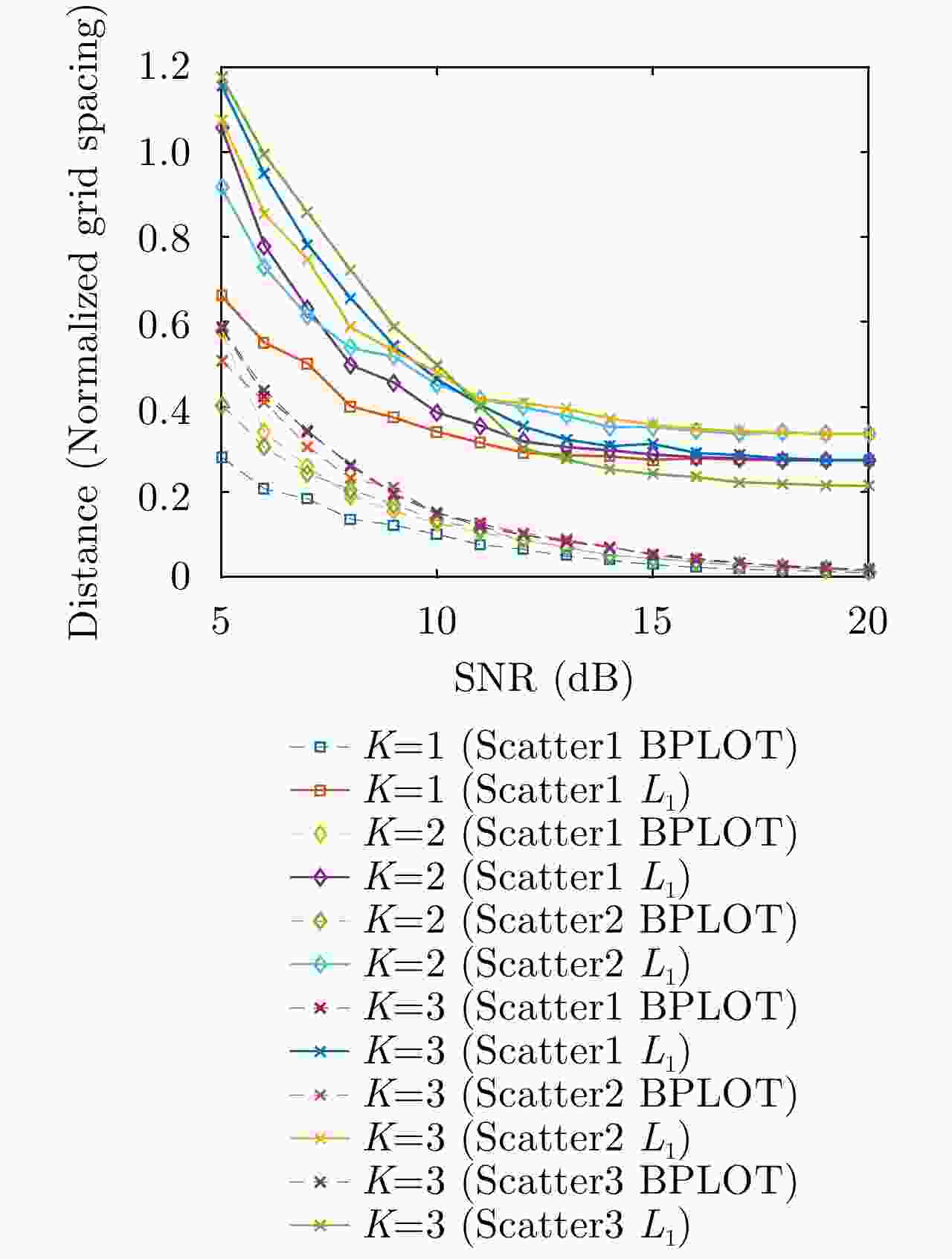
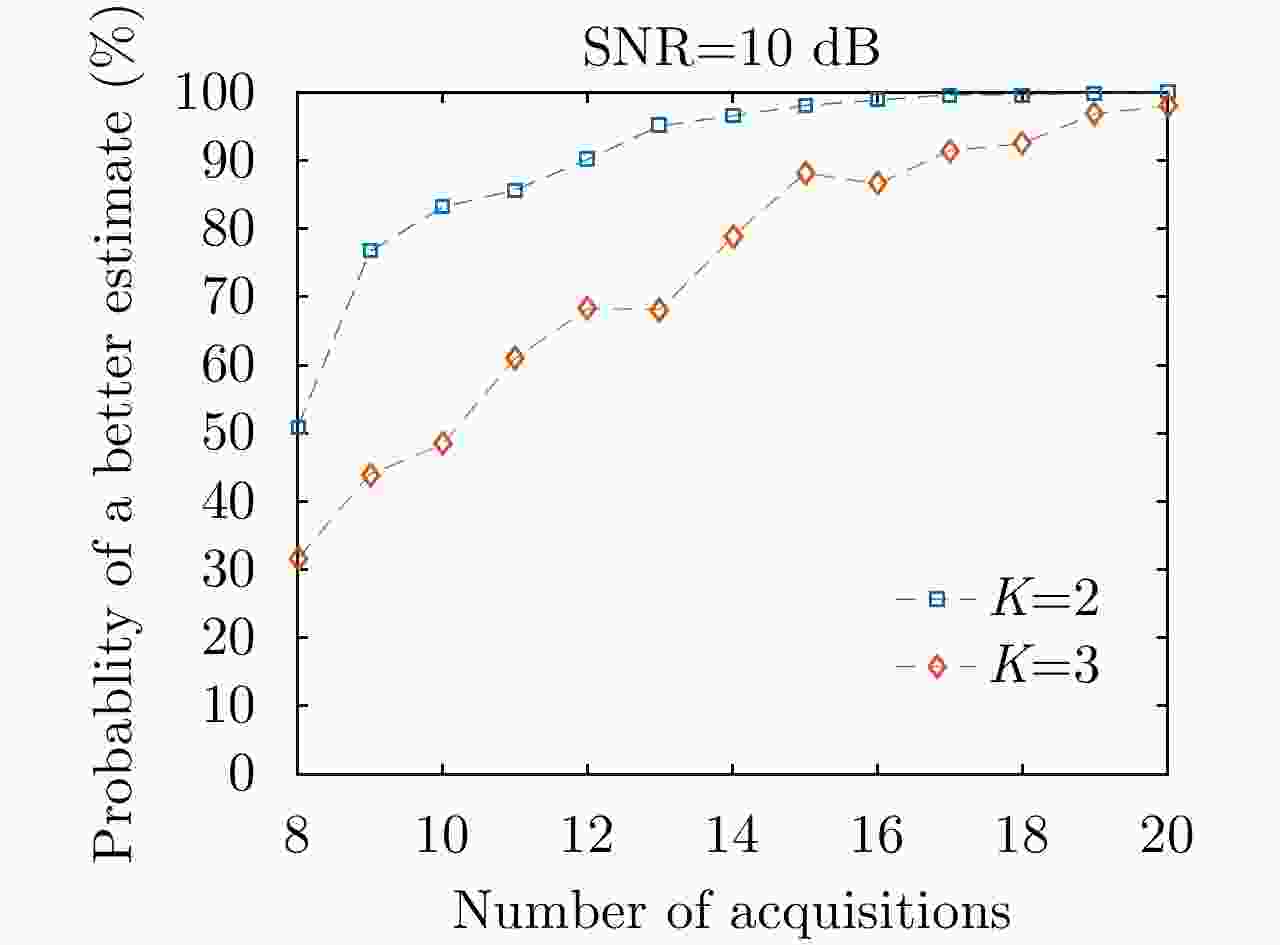
$ {L}_{1} $ 范数最小化结合的方法,求解所提出的Off-grid TomoSAR模型。最后,利用仿真数据和机载阵列干涉SAR实际飞行数据进行了验证,结果表明,对于Off-grid目标,该方法能够得到比基于$ {L}_{1} $ 范数最小化的经典方法更准确的位置、幅度和相位求解结果,证明了方法的优越性。Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Tomography (TomoSAR) is a novel technique that enables three-Dimensional (3-D) imaging using multi-baseline two-Dimensional (2-D) data. The essence of TomoSAR is actually to solve a one-dimensional spectral estimation problem. Compressed Sensing-based (CS) algorithm can retrieve solutions with only a few non-uniform acquisitions and has gradually become the main imaging method. In the conventional processing flow of CS algorithms, the continuous elevation direction is divided into a pre-set grid, and the targets are assumed to be exactly on the grid.$ {{L}}_{1} $ minimization has been proven to be effective in TomoSAR imaging. In the conventional processing flow, the continuous elevation axis is divided into fixed grids, and scatters are assumed to be exactly on the pre-set grid. However, this hypothesis is generally untenable, and will lead to a problem called “Basis Mismatch”, which is rarely discussed in TomoSAR. In this letter, we first discuss the model of Off-grid TomoSAR, and then propose an addictive perturbation model to compensate for the errors caused by the grid effect. We utilize the local optimization thresholding algorithm to solve the complex-valued$ {{L}}_{1} $ minimization problem of TomoSAR. We conducted experiments both on simulation data and actual airborne flight data. Our simulation results indicate that the proposed method can estimate a more accurate position of scatters, which leads to better original signal recovery. The reconstruction results of actual data verify that the impact of grid mismatch can be mostly eliminated. -
表 1 BPLOT的流程
Table 1. The process of BPLOT
算法 : BPLOT (1) 输入: $\boldsymbol{A},{\boldsymbol{A} }',\boldsymbol{g},\Delta s{\text{,}}\mathrm{稀}\mathrm{疏}\mathrm{度}K$
(2) $ {L}_{1} $范数求解:
$\mathrm{argmin} \left\{ {\left|\left|{ { {\boldsymbol{g} } } }-{{ {\boldsymbol{A} } } }_{\mathit{g} }{\boldsymbol\varGamma }\right|\right|}_{2}^{2}+\mu {\left|\left|{\boldsymbol\varGamma }\right|\right|}_{1}\right\}$
$\boldsymbol{\varGamma }={\left[\boldsymbol{\gamma }\;\;{\boldsymbol{\gamma } }'\right]}^{t},{\boldsymbol{A} }_{\mathit{g} }=\left[\begin{array}{cc}\boldsymbol{A}& {\boldsymbol{A} '} \end{array}\right]$
(3) For count t=1: K,
(4) $ {\alpha }_{t} $=${\mathrm{a}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{g}\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x} }_{p}\{\left|{\mathit{\gamma } }_{p}\right|+\left|{\mathit{\gamma } }_{p}\right|/|2\pi {\Delta }s\left|\right\}$, $ p\notin \left({S}^{t-1}\right) $
(5) $ {S}^{t}={S}^{t-1}\cup \left\{{\alpha }_{t}\right\} $
(6) 计算网格偏差 $\Delta k\Delta s=\mathfrak{R}e({{\boldsymbol{\gamma}} }'/({\rm{j} }2\pi {\boldsymbol{\gamma}} \left)\right)$
(7) 计算散射值
${\hat{\boldsymbol{A} } }_{f}={{\boldsymbol{A}}}(S+\Delta k\Delta s)$
${\hat{\gamma } }_{f}={\left({ {\hat{ \boldsymbol{A} } }_{f} }^{\rm{H} }{\hat{ \boldsymbol{A} } }_{f}\right)}^{-1}{ {\hat{ \boldsymbol{A} } }_{f} }^{\rm{H} }\boldsymbol{g}$
(8) 输出:${\hat{\gamma } }_{f},S,\Delta k$表 2 仿真参数
Table 2. Simulation parameters
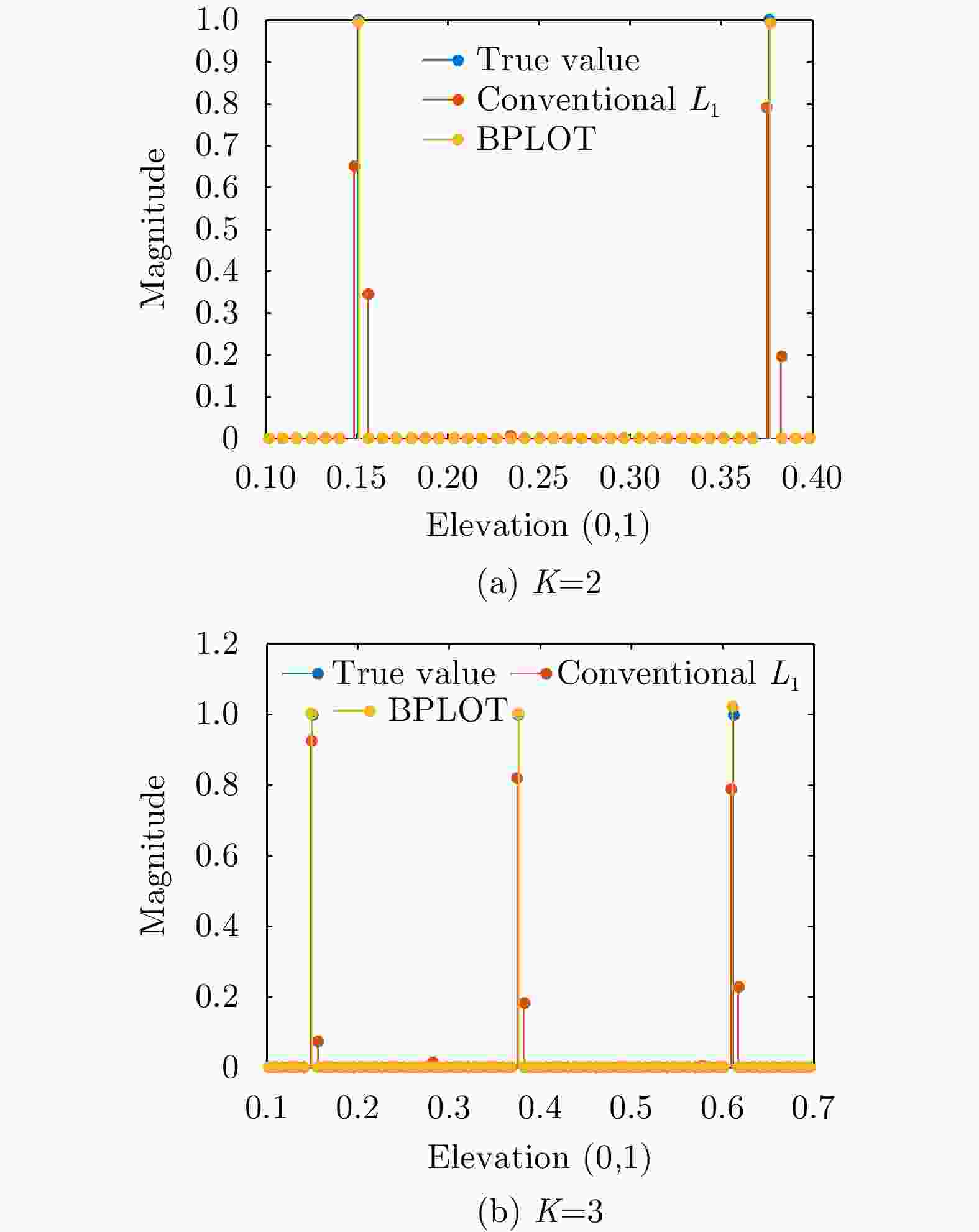
参数 参数值 载波频率(GHz) 14.5 信号带宽(MHz) 500 通道数N 8 基线宽度(m) 0.084 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 480 平台高度(m) 1200 平台速度(m/s) 70 下视角(°) 45 表 3 图3对应的位置计算结果
Table 3. Point calculation results corresponding to Fig. 3
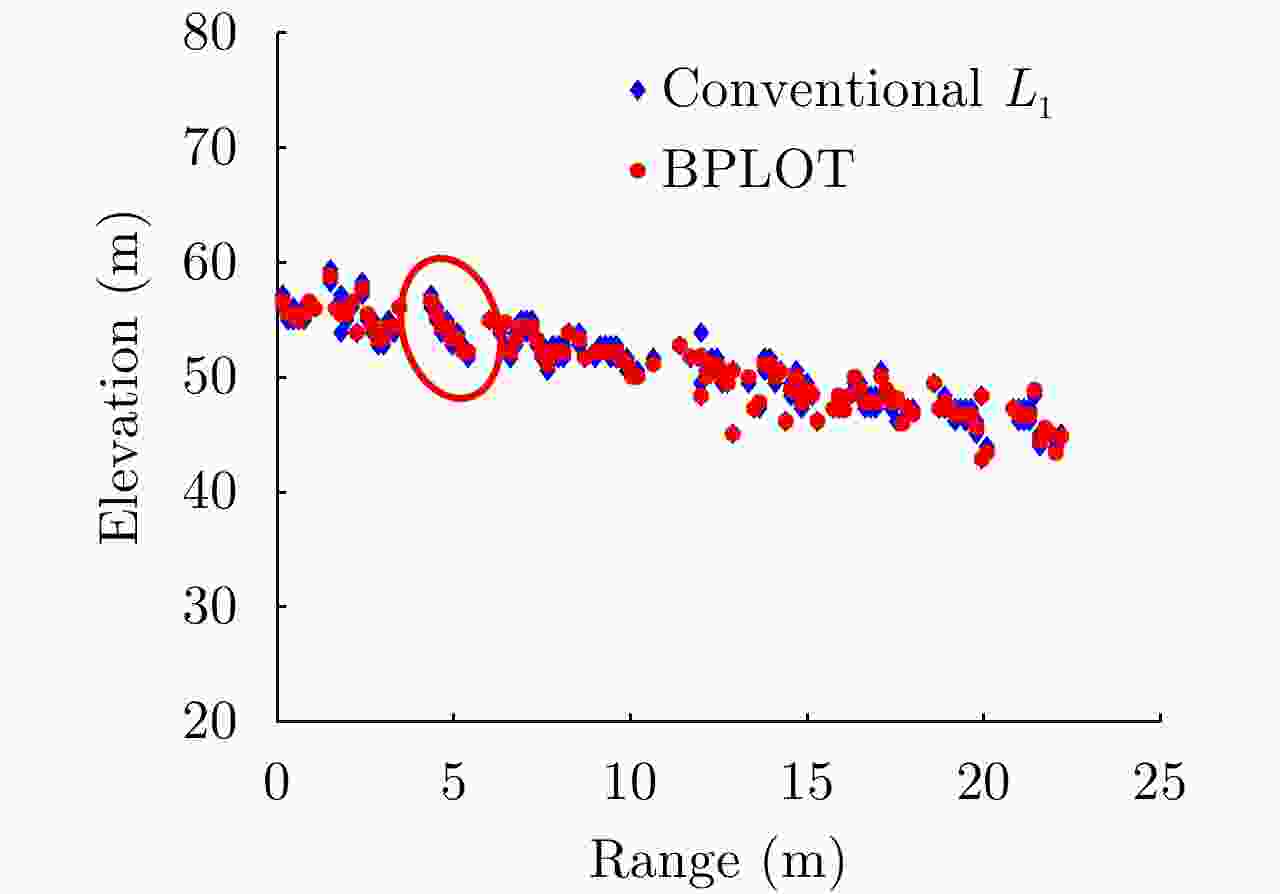
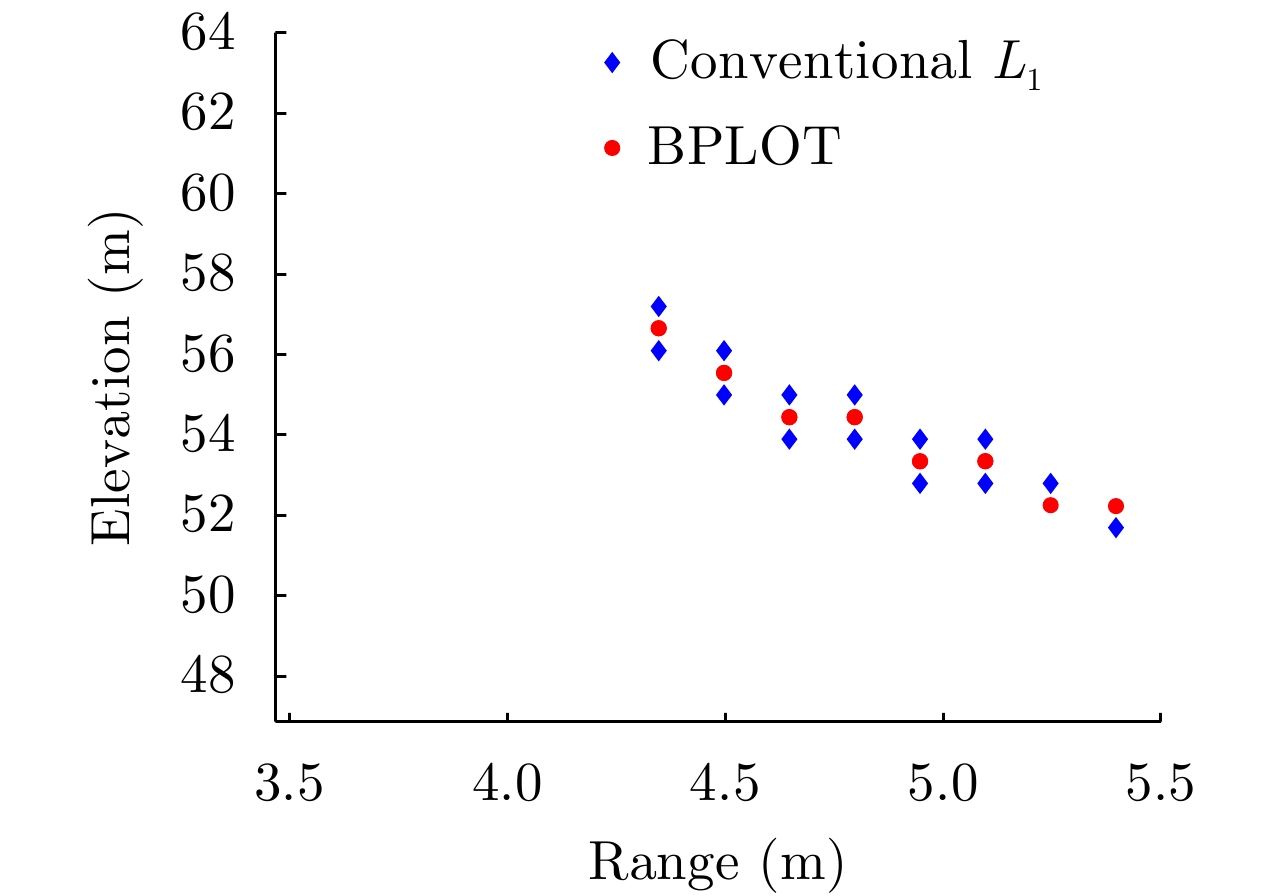
参数 真值 $ {L}_{1} $ BPLOT K=2 [0.1506, 0.3764] [0.1400, 0.3750] [0.1506, 0.3764] K=3 [0.1501, 0.3764, 0.6120] [0.1484, 0.3750, 0.6094] [0.1501 0.3765 0.6119] -
[1] FORNARO G, SERAFINO F, and SOLDOVIERI F. Three-dimensional focusing with multipass SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(3): 507–517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.809934 [2] REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873 [3] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4296–4308. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2050487 [4] FORNARO G, REALE D, and SERAFINO F. Four-dimensional SAR imaging for height estimation and monitoring of single and double scatterers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(1): 224–237. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2000837 [5] CHAI Huiming, LV Xiaolei, YAO Jingchuan, et al. Off-grid differential tomographic SAR and its application to railway monitoring[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(10): 3999–4013. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2940730 [6] AUSTIN C D, ERTIN E, and MOSES R L. Sparse signal methods for 3-D radar imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2011, 5(3): 408–423. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2010.2090128 [7] FERRARA M, JACKSON J A, and AUSTIN C. Enhancement of multi-pass 3D circular SAR images using sparse reconstruction techniques[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 7337, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVI, Orlando, United States, 2009. doi: 10.1117/12.820256. [8] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Super-resolution power and robustness of compressive sensing for spectral estimation with application to spaceborne tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(1): 247–258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160183 [9] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1-norm regularization—The compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(10): 3839–3846. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117 [10] 李杭, 梁兴东, 张福博, 等. 一种基于组稀疏的阵列干涉SAR三维重建方法[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2018, 48(8): 1051–1064. doi: 10.1360/N112017-00023LI Hang, LIANG Xingdong, ZHANG Fubo, et al. A novel 3-D reconstruction approach based on group sparsity of array InSAR[J]. Science in China Information, 2018, 48(8): 1051–1064. doi: 10.1360/N112017-00023 [11] JIAO Zekun, DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Urban 3D imaging using airborne TomoSAR: Contextual information-based approach in the statistical way[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 170: 127–141. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.10.013 [12] MA Peifeng, LIN Hui, LAN Hengxing, et al. On the performance of reweighted L1 minimization for tomographic SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 895–899. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2365613 [13] 廖明生, 魏恋欢, 汪紫芸, 等. 压缩感知在城区高分辨率SAR层析成像中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031LIAO Mingsheng, WEI Lianhuan, WANG Ziyun, et al. Compressive sensing in high-resolution 3D SAR tomography of urban scenarios[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031 [14] 王爱春, 向茂生. 基于块压缩感知的SAR层析成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(1): 57–64. doi: 10.12000/JR16006WANG Aichun and XIANG Maosheng. SAR tomography based on block compressive sensing[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(1): 57–64. doi: 10.12000/JR16006 [15] CHI Yuejie, SCHARF L L, PEZESHKI A, et al. Sensitivity to basis mismatch in compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(5): 2182–2195. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2112650 [16] HERMAN M A and NEEDELL D. Mixed operators in compressed sensing[C]. The 44th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Princeton, USA, 2010. doi: 10.1109/CISS.2010.5464909. [17] CANDÈS E and ROMBERG J. Sparsity and incoherence in compressive sampling[J]. Inverse Problems, 2007, 23(3): 969–985. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/23/3/008 [18] STOICA P and BABU P. Sparse estimation of spectral lines: Grid selection problems and their solutions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(2): 962–967. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2175222 [19] TANG Gongguo, BHASKAR B N, SHAH P, et al. Compressed sensing off the grid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2013, 59(11): 7465–7490. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2013.2277451 [20] YANG Zai and XIE Lihua. Enhancing sparsity and resolution via reweighted atomic norm minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(4): 995–1006. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2493987 [21] 陈栩杉, 张雄伟, 杨吉斌, 等. 如何解决基不匹配问题: 从原子范数到无网格压缩感知[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(3): 335–346. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150539CHEN Xushan, ZHANG Xiongwei, YANG Jibin, et al. How to overcome basis mismatch: from atomic norm to gridless compressive sensing[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(3): 335–346. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150539 [22] FANNJIANG A and LIAO Wenjing. Super-resolution by compressive sensing algorithms[C]. 2012 Conference Record of the Forty Sixth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR), Pacific Grove, USA, 2012. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2012.6489036. [23] HERMAN M A and STROHMER T. General deviants: An analysis of perturbations in compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2010, 4(2): 342–349. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2009.2039170 [24] YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and ZHANG Cishen. Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(1): 38–43. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2222378 [25] FANNJIANG A and TSENG H C. Compressive radar with off-grid targets: A perturbation approach[J]. Inverse Problems, 2013, 29(5): 054008. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/29/5/054008 [26] CHEN S S, DONOHO D L, and SAUNDERS M A. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit[J]. SIAM Review, 2001, 43(1): 129–159. doi: 10.1137/S003614450037906X [27] 仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 彭凌霄, 等. SARMV3D-1.0: SAR微波视觉三维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, PENG Lingxiao, et al. SARMV3D-1.0: Synthetic aperture radar microwave vision 3D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 485–498. doi: 10.12000/JR21112 [28] FANNJIANG A and LIAO Wenjing. Coherence pattern-guided compressive sensing with unresolved grids[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2012, 5(1): 179–202. doi: 10.1137/110838509 [29] SCHMITT M. Reconstruction of urban surface models from multi-aspect and multi-baseline interferometric SAR[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Technische Universität München, 2014. [30] ZHU Xiaoxiang. Spectral estimation for synthetic aperture radar tomography[D]. [Master dissertation], Technische Universität München, 2008. [31] 李杭. 阵列干涉SAR高精度三维成像算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学院大学, 2017.LI Hang. Research on high-precision 3-D imaging algorithm of array interferometric synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公


 下载:
下载: