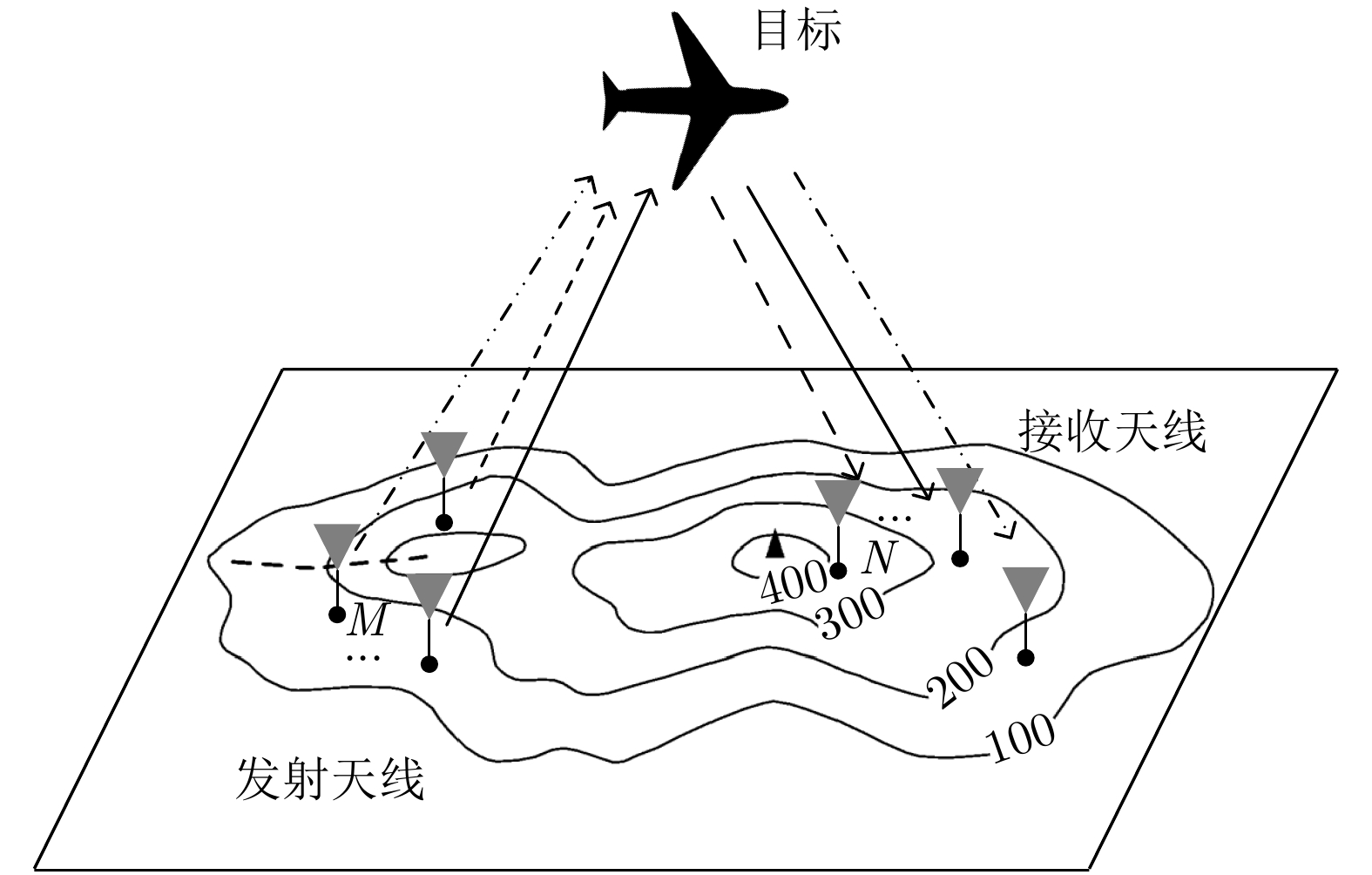
-
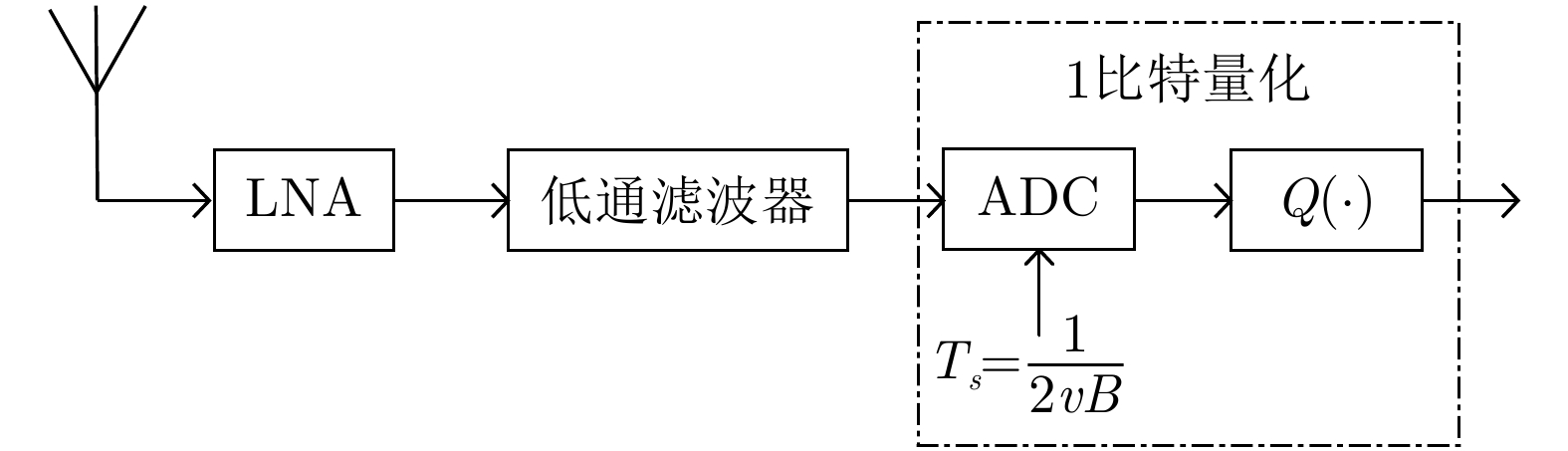
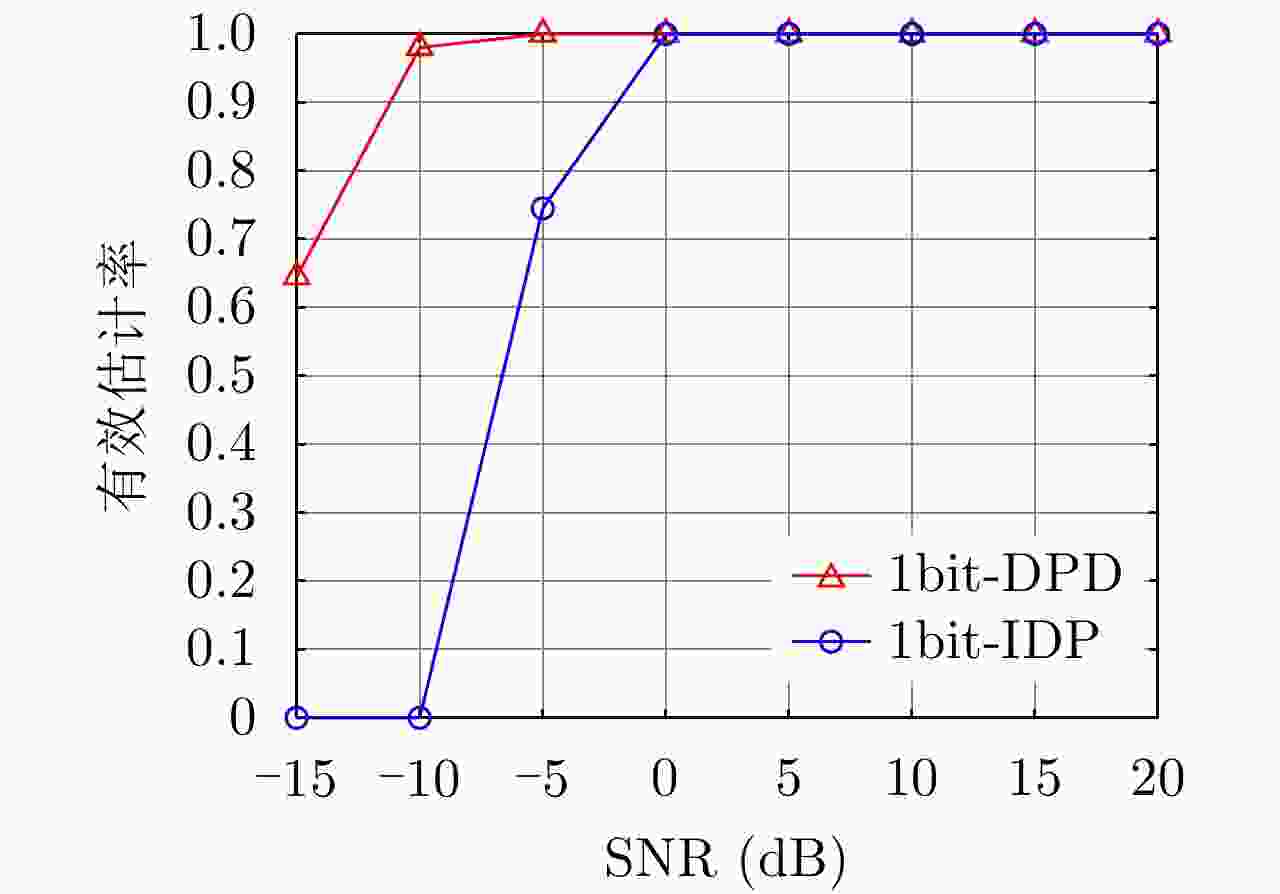
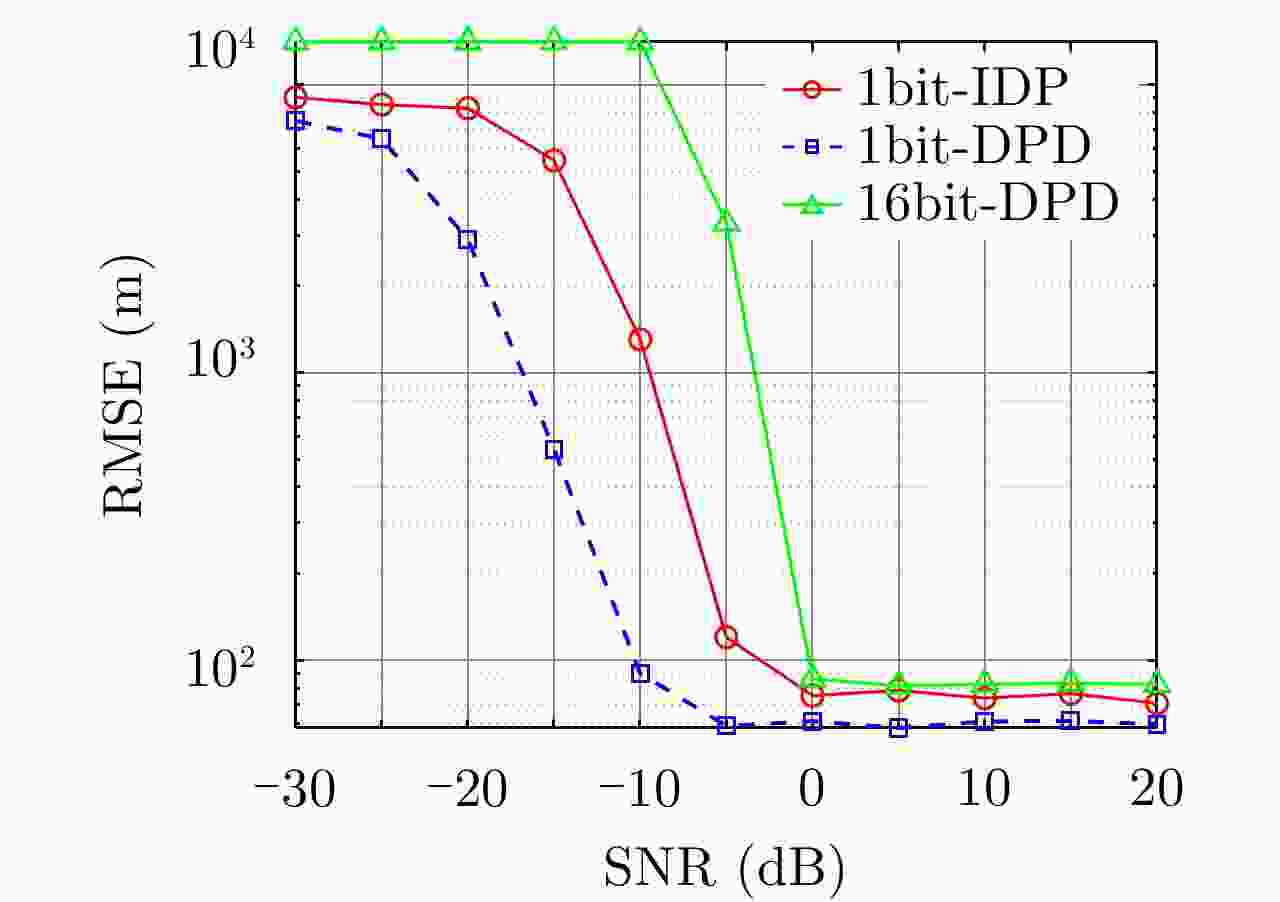
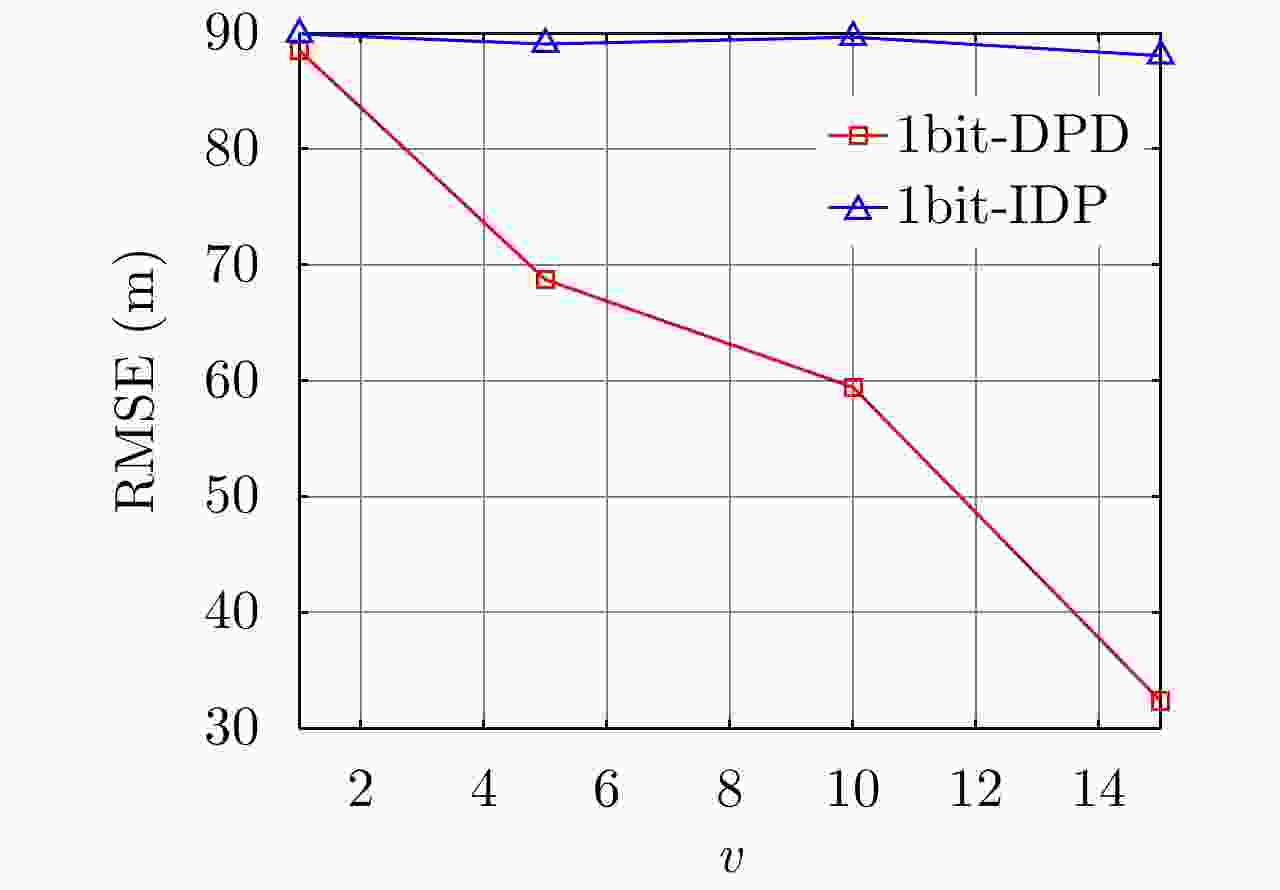
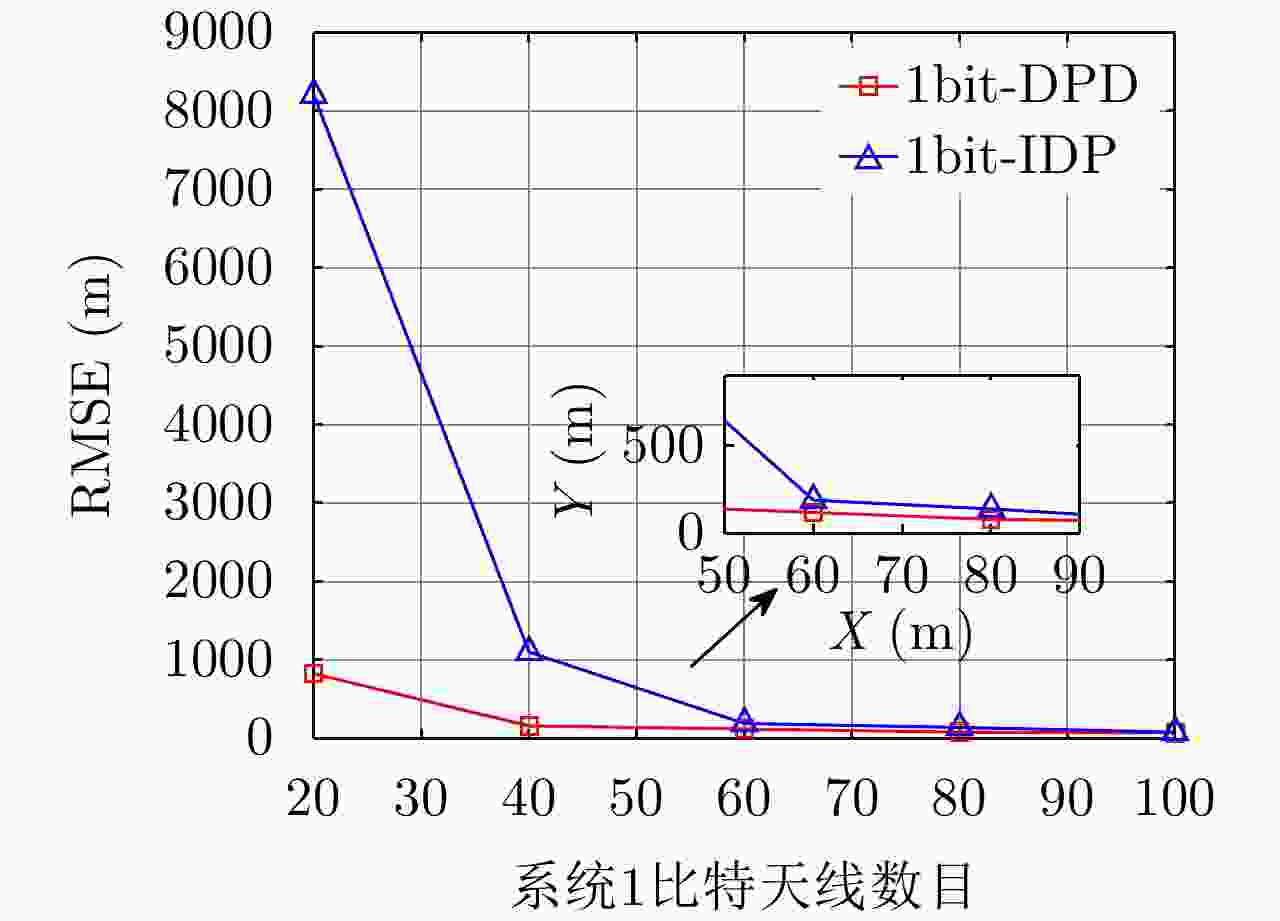
摘要: 1比特量化技术在大规模MIMO雷达系统中的应用使得系统成本、功耗及传输带宽显著降低。但这同时也对如何从1比特量化后的数据中提取目标高精度信息提出了严峻挑战。针对基于1比特量化的二次定位算法在低信噪比下定位精度低、鲁棒性差的问题,该文提出了一种基于1比特量化的大规模MIMO雷达系统目标直接定位算法。首先,通过将接收信号进行1比特量化,并推导基于1比特信号的概率分布,建立了关于目标位置的代价函数;其次,通过证明代价函数的凸性,利用梯度下降算法求解了回波中未知的信号参数;最后,根据最大似然估计实现了目标直接定位。仿真实验分析了所提算法的定位性能,结果表明,所提算法仅需传输相较于高精度采样(16比特为例)直接定位算法6.25%的通信带宽,同时其功耗仅为前者的0.1%。此外,与基于1比特量化的二次定位算法相比,所提算法在低信噪比下便可实现对目标位置的有效估计,并且其定位性能在低信噪比和低MIMO天线数量下均明显优于前者。同时,其性能会随着过采样技术的应用进一步提升。Abstract: The application of one-bit quantization technology in a massive MIMO radar system significantly reduced the system cost, power consumption, and transmission bandwidth. However, it also poses a severe challenge to extract high-precision target information from one-bit quantized data. To address the problem of low positioning accuracy and poor robustness of secondary positioning based on one-bit quantization under low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), this paper proposes a multi-station radar target direct position determination algorithm based on one-bit quantization. First, by quantizing the received signal with one bit, and deriving the probability distribution based on the one-bit signal, the cost function about the target position is established. Second, by proving the convexity of the cost function, the maximum likelihood estimation and gradient descent algorithm are used to solve the unknown signal parameters in the echo. Finally, the direct positioning of the target is achieved according to the maximum likelihood estimation. Simulation experiments were performed to analyze the positioning performance of the proposed algorithm, and the results showed that the proposed algorithm only needed to transmit 6.25% of the communication bandwidth compared with the high-bit sampling (e.g., 16 bits) direct position determination algorithm, and its power consumption is only 0.1% of the former. In addition, compared with the secondary positioning algorithm based on one-bit quantization, the proposed algorithm can achieve an effective estimation of the target position under a low SNR. In addition, its localization performance is significantly better than the former under low SNR and a low number of MIMO antennas. Simultaneously, its performance will be further improved with the application of oversampling technology.
-
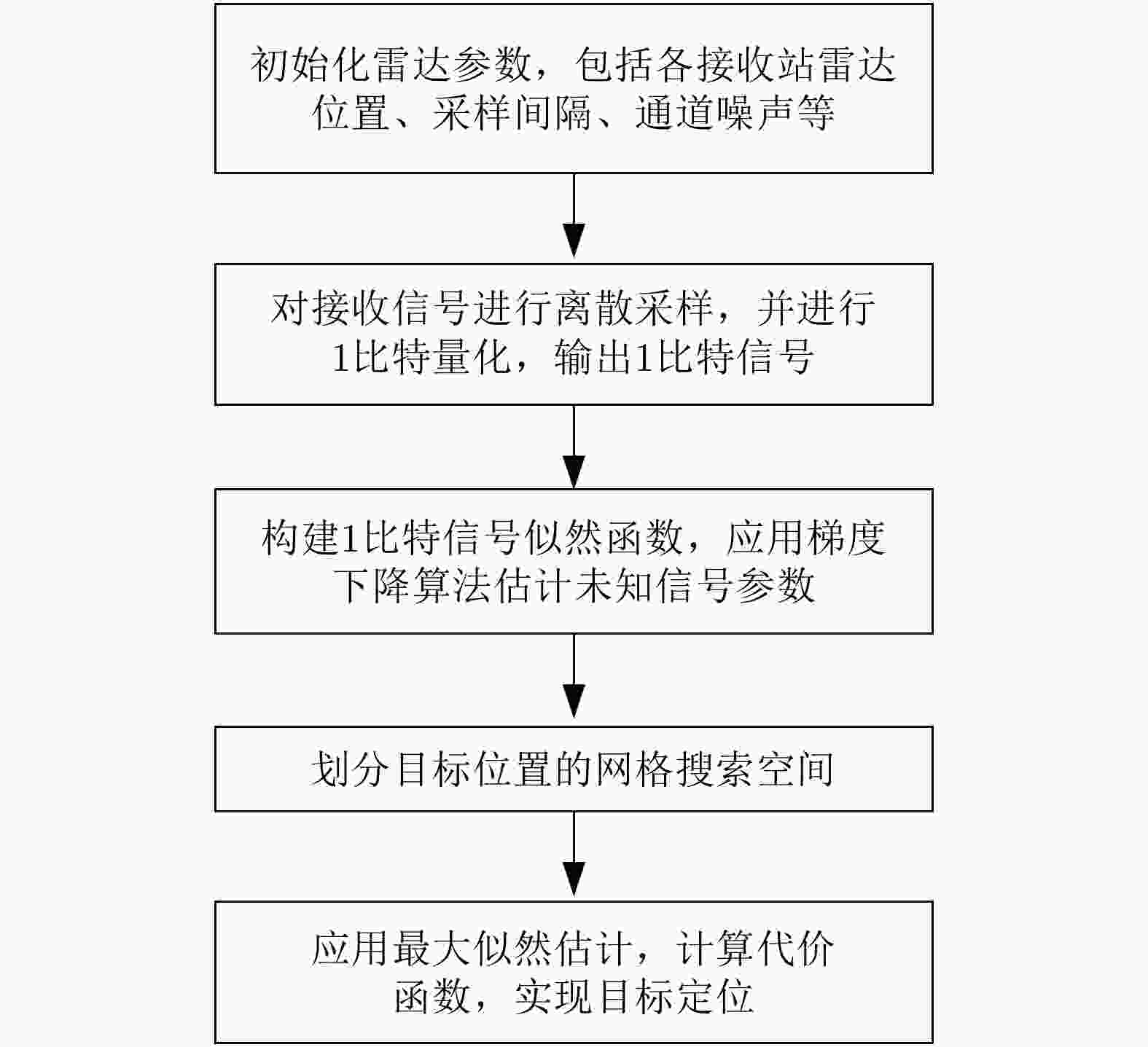
表 1 式(25)的梯度下降求解步骤
Table 1. The gradient descent solution for Eq. (25)
初始化:$\tilde \alpha _{ {\rm{mn} } }^0$, $0 < \xi \le 1$, $0 < \zeta \le 1$ 迭代:对于$l = 0 \to {l_{\max }}$ 1:计算代价函数$\Xi \left( {\tilde \alpha _{{\rm{mn}}}^l} \right)$和$\nabla \left( {\Xi \left( {\tilde \alpha _{{\rm{mn}}}^l} \right)} \right)$; 2:初始化步长${u^l} = {u_{{\rm{init}}} }$,更新
$\tilde \alpha _{{\rm{mn}}}^{l + 1} = \tilde \alpha _{{\rm{mn}}}^l - {u^l}\nabla \left( {\Xi \left( {{{\tilde \alpha }_{{\rm{mn}}}}} \right)} \right)$;3:当$\Xi \left( {\tilde \alpha _{{\rm{mn}}}^{l + 1}} \right) > \Xi \left( {\tilde \alpha _{{\rm{mn}}}^l} \right) - \xi {u^l}\left\| {\nabla \left( {\Xi \left( {\tilde \alpha _{{\rm{mn}}}^l} \right)} \right)} \right\|_2^2$,令
${u^l} = \zeta {u_{{\rm{init}}} }$更新$\tilde \alpha _{{\rm{mn}}}^{l + 1} = \tilde \alpha _{{\rm{mn}}}^l - {u^l}\nabla \left( {\Xi \left( {{{\tilde \alpha }_{{\rm{mn}}}}} \right)} \right)$; 4:满足停止条件,退出 表 2 数据量及功耗对比
Table 2. Comparison of data volume and power consumption
算法 单个采样点数据量 功耗 16bit-DPD 2 Byte(实部/虚部) 约为几瓦 1bit-DPD 1 bit(实部/虚部) 约几毫瓦 -
[1] LESTURGIE M. T06 — MIMO radar[C]. 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, USA, 2014: 33. [2] NORRDINE A, CETINKAYA H, and HERSCHEL R. Radar wave based positioning of spatially distributed MIMO radar antenna systems for near-field nondestructive testing[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2020, 4(5): 5500804. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2020.2989546 [3] KHAMIDULLINA L, PODKURKOV I, and HAARDT M. Conditional and unconditional Cramér-Rao bounds for near-field localization in bistatic MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 3220–3234. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3082469 [4] SONG Haibo, WEN Gongjian, LIANG Yuanyuan, et al. Target localization and clock refinement in distributed MIMO radar systems with time synchronization errors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 3088–3103. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3081038 [5] DONTAMSETTI S G and KUMAR R V R. A distributed MIMO radar with joint optimal transmit and receive signal combining[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 623–635. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3027103 [6] LA MANNA M and FUHRMANN D R. Cramér-Rao lower bounds comparison for 2D hybrid-MIMO and MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(2): 404–413. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2016.2627187 [7] HACK D E, PATTON L K, HIMED B, et al. Detection in passive MIMO radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(11): 2999–3012. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2319776 [8] ZHENG Yang, SHENG Min, LIU Junyu, et al. Exploiting AoA estimation accuracy for indoor localization: A weighted AoA-based approach[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(1): 65–68. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2853745 [9] SHAO Huajie, ZHANG Xiaoping, and WANG Zhi. Efficient closed-form algorithms for AOA based self-localization of sensor nodes using auxiliary variables[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(10): 2580–2594. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2314064 [10] 刘振, 苏晓龙, 刘天鹏, 等. 基于矩阵差分的远场和近场混合源定位方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 432–442. doi: 10.12000/JR20145LIU Zhen, SU Xiaolong, LIU Tianpeng, et al. Matrix differencing method for mixed far-field and near-field source localization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 432–442. doi: 10.12000/JR20145 [11] ZHANG Fengrui, GAO Lin, SUN Yimao, et al. Time-delay-based target localization in wireless sensor network with unknown noise covariance[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2021, 5(1): 7000104. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2020.3048417 [12] JIA Tianyi, HO K C, WANG Haiyan, et al. Effect of sensor motion on time delay and Doppler shift localization: Analysis and solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(22): 5881–5895. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2946025 [13] WEN Fei, LIU Peilin, WEI Haichao, et al. Joint azimuth, elevation, and delay estimation for 3-D indoor localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(5): 4248–4261. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2794322 [14] 赵勇胜, 赵拥军, 赵闯. 联合角度和时差的单站无源相干定位加权最小二乘算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 302–311. doi: 10.12000/JR15133ZHAO Yongsheng, ZHAO Yongjun, and ZHAO Chuang. Weighted least squares algorithm for single-observer passive coherent location using DOA and TDOA measurements[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 302–311. doi: 10.12000/JR15133 [15] AMAR A and WEISS A J. Localization of narrowband radio emitters based on Doppler frequency shifts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(11): 5500–5508. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.929655 [16] BIANCHI V, CIAMPOLINI P, and DE MUNARI I. RSSI-based indoor localization and identification for ZigBee wireless sensor networks in smart homes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2019, 68(2): 566–575. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2018.2851675 [17] HOANG M T, YUEN B, DONG Xiaodai, et al. Recurrent neural networks for accurate RSSI indoor localization[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 10639–10651. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2940368 [18] TIRER T and WEISS A J. High resolution direct position determination of radio frequency sources[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(2): 192–196. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2503921 [19] TIRER T and WEISS A J. Performance analysis of a high-resolution direct position determination method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(3): 544–554. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2621729 [20] MA Fuhe, LIU Zhangmeng, and GUO Fucheng. Distributed direct position determination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(11): 14007–14012. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3025386 [21] XIA Wei, LIU Wei, and ZHU Lingfeng. Distributed adaptive direct position determination based on diffusion framework[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 27(1): 28–38. [22] WEISS A J. Direct position determination of narrowband radio frequency transmitters[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2004, 11(5): 513–516. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2004.826501 [23] PICARD J S and WEISS A J. Direct position determination sensitivity to NLOS propagation effects on Doppler-shift[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(14): 3870–3881. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2923152 [24] 吴癸周, 郭福成, 张敏. 信号直接定位技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(6): 998–1013. doi: 10.12000/JR20040WU Guizhou, GUO Fucheng, and ZHANG Min. Direct position determination: An overview[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(6): 998–1013. doi: 10.12000/JR20040 [25] 陈芳香, 易伟, 周涛, 等. 基于分数阶傅里叶变换的多辐射源被动直接定位算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 523–530. doi: 10.12000/JR18027CHEN Fangxiang, YI Wei, ZHOU Tao, et al. Passive direct location determination for multiple sources based on FRFT[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 523–530. doi: 10.12000/JR18027 [26] LI Bin, WANG Shusen, FENG Zhiyong, et al. Fast pseudo-spectrum estimation for automotive massive MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, in press. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3052512 [27] AHMED A M, AHMAD A A, FORTUNATI S, et al. A reinforcement learning based approach for multi-target detection in massive MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, in press. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3061809 [28] LI Bin, WANG Shusen, ZHANG Jun, et al. Fast randomized-MUSIC for Mm-wave massive MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(2): 1952–1956. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3051266 [29] FORTUNATI S, SANGUINETTI L, GINI F, et al. Massive MIMO radar for target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 859–871. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2967181 [30] LARSSON E G, EDFORS O, TUFVESSON F, et al. Massive MIMO for next generation wireless systems[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(2): 186–195. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.6736761 [31] GOKCEOGLU A, BJÖRNSON E, LARSSON E G, et al. Spatio-temporal waveform design for multiuser massive MIMO downlink with 1-bit receivers[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(2): 347–362. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2016.2628347 [32] CIUONZO D, JAVADI S H, MOHAMMADI A, et al. Bandwidth-constrained decentralized detection of an unknown vector signal via multisensor fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 2020, 6: 744–758. doi: 10.1109/TSIPN.2020.3037832 [33] WANG Xueqian, LI Gang, and VARSHNEY P K. Detection of sparse stochastic signals with quantized measurements in sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(8): 2210–2220. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2903034 [34] 陈莹, 钟菲, 郭树旭. 非合作跳频信号参数的盲压缩感知估计[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(5): 531–537. doi: 10.12000/JR15106CHEN Ying, ZHONG Fei, and GUO Shuxu. Blind compressed sensing parameter estimation of non-cooperative frequency hopping signal[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(5): 531–537. doi: 10.12000/JR15106 [35] KILIÇ B, GÜNGÖR A, KALFA M, et al. Sensing matrix design for compressive sensing based direction of arrival estimation[C]. 2020 28th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Gaziantep, Turkey, 2020: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/SIU49456.2020.9302073. [36] DING Wenbo, YANG Fang, PAN Changyong, et al. Compressive sensing based channel estimation for OFDM systems under long delay channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2014, 60(2): 313–321. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2014.2315913 [37] REN Jiaying and LI Jian. One-bit digital radar[C]. 2017 51st Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2017: 1142–1146. doi: 10.1109/ACSSC.2017.8335529. [38] LI Yongzhi, TAO Cheng, SECO-GRANADOS G, et al. Channel estimation and performance analysis of one-bit massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(15): 4075–4089. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2706179 [39] DABEER O and KARNIK A. Signal parameter estimation using 1-bit dithered quantization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(12): 5389–5405. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.885461 [40] DABEER O and MASRY E. Multivariate signal parameter estimation under dependent noise from 1-bit dithered quantized data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2008, 54(4): 1637–1654. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2008.917637 [41] FANG Jun, LIU Yumeng, LI Hongbin, et al. One-bit quantizer design for multisensor GLRT fusion[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(3): 257–260. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2243144 [42] LI Xiaoying, FANG Jun, LIU Yumeng, et al. One-bit quantization for multi-sensor GLRT detection of unknown deterministic signals[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, Canada, 2013: 4251–4255. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2013.6638461. [43] BAR-SHALOM O and WEISS A J. DOA estimation using one-bit quantized measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(3): 868–884. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2002.1039405 [44] XI Feng, XIANG Yijian, ZHANG Zhen, et al. Joint angle and Doppler frequency estimation for MIMO radar with one-bit sampling: A maximum likelihood-based method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(6): 4734–4748. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3000841 [45] ZHU Si, SUN Fei, and CHEN Xiaohui. Joint UWB TOA and AOA estimation under 1-bit quantization resolution[C]. 2013 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Xi’an, China, 2013: 321–326. doi: 10.1109/ICCChina.2013.6671136. [46] YI Wei, ZHOU Tao, AI Yue, et al. Suboptimal low complexity joint multi-target detection and localization for non-coherent MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 901–916. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2968282 [47] HAIMOVICH A M, BLUM R S, and CIMINI L J. MIMO radar with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(1): 116–129. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2008.4408448 [48] HE Qian, BLUM R S, and HAIMOVICH A M. Noncoherent MIMO radar for location and velocity estimation: More antennas means better performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(7): 3661–3680. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2044613 [49] RIBEIRO A and GIANNAKIS G B. Bandwidth-constrained distributed estimation for wireless sensor networks-part I: Gaussian case[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(3): 1131–1143. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.863009 [50] WANG Wei and LI Hongbin. Distributed maximum likelihood estimation for bandwidth-constrained wireless sensor networks[C]. 2006 IEEE 12th Digital Signal Processing Workshop & 4th IEEE Signal Processing Education Workshop, Teton National Park, USA, 2006: 506–510. doi: 10.1109/DSPWS.2006.265475. [51] BOYD S P and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2004. [52] HAN Xiaodong, SHU Ting, HE Jin, et al. Joint angle-frequency estimation using nested sampling with one-bit quantization[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2020, 39(8): 4187–4197. doi: 10.1007/s00034-020-01351-8 [53] OPPENHEIM A V and SCHAFER R W. Discrete-Time Signal Processing[M]. 3rd ed. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, 2009: 140–214. [54] ZAMIR R. A proof of the Fisher information inequality via a data processing argument[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1998, 44(3): 1246–1250. doi: 10.1109/18.669301 [55] SAMPFORD M R. Some inequalities on mill’s ratio and related functions[J]. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1953, 24(1): 130–132. doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177729093 [56] PINELIS I. Exact bounds on the inverse mills ratio and its derivatives[J]. Complex Analysis and Operator Theory, 2019, 13(4): 1643–1651. doi: 10.1007/s11785-018-0765-x -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
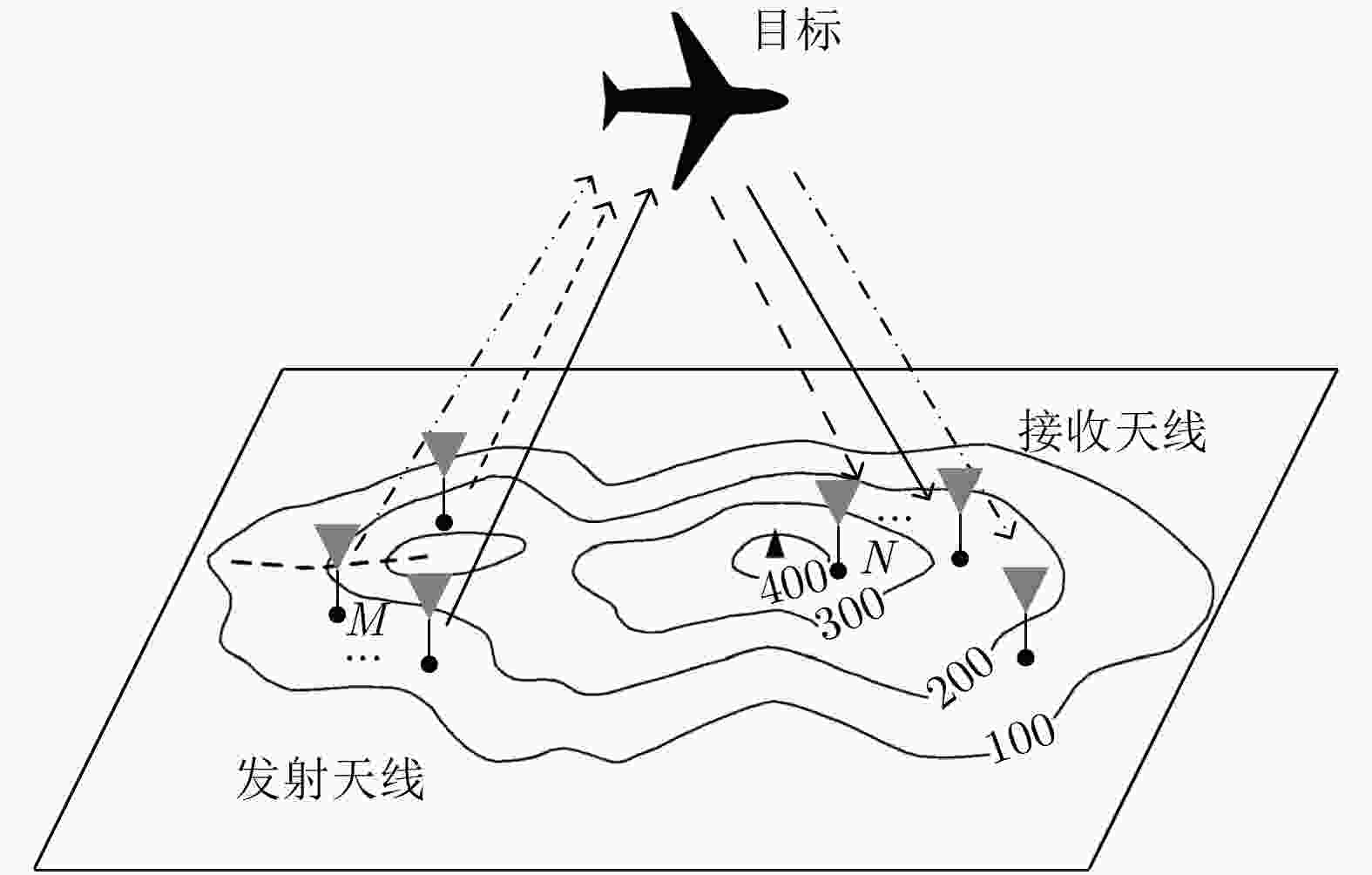
 下载:
下载: