Feature-transferable Pyramid Network for Cross-scale Object Detection in SAR Images
-
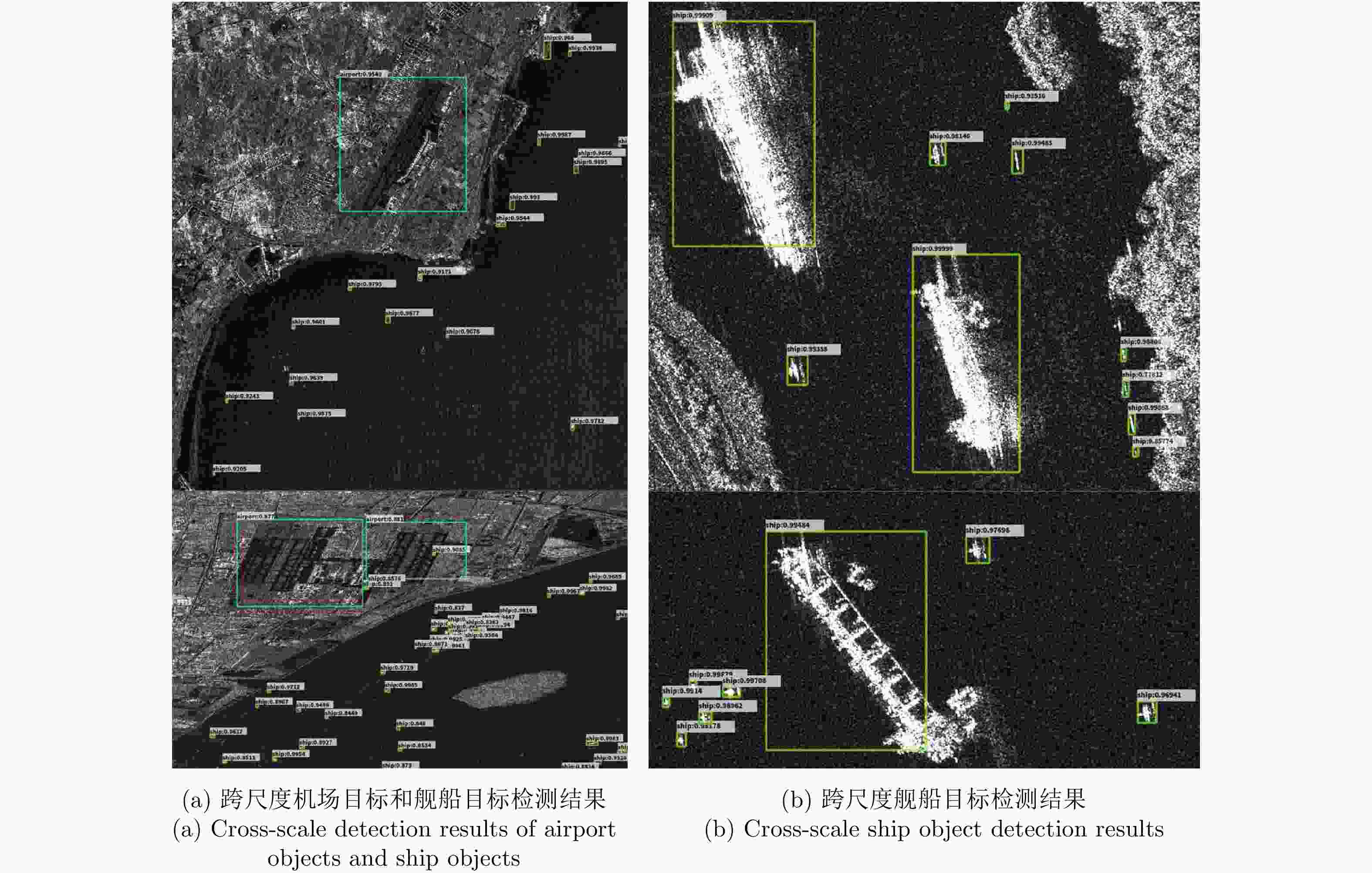
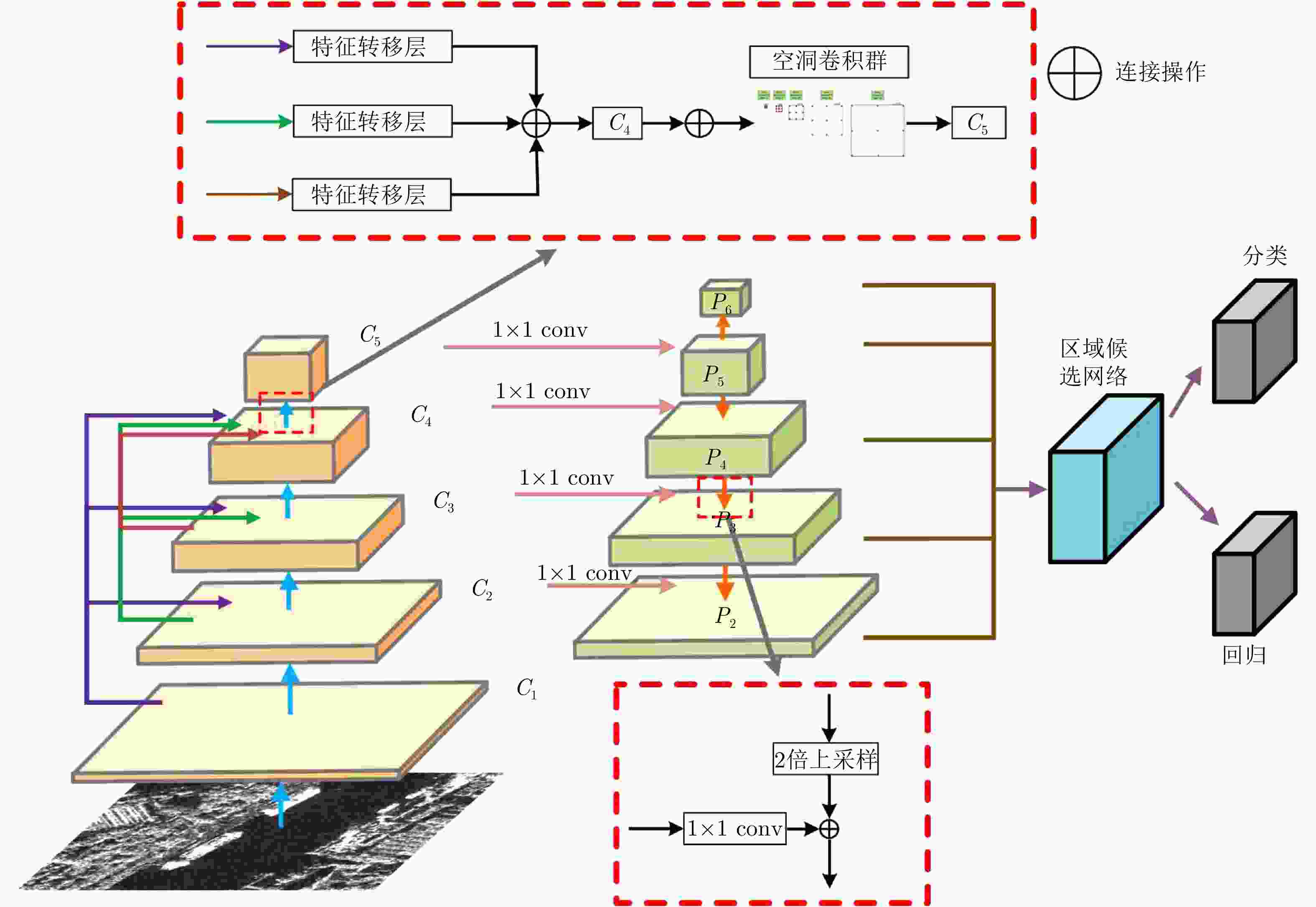
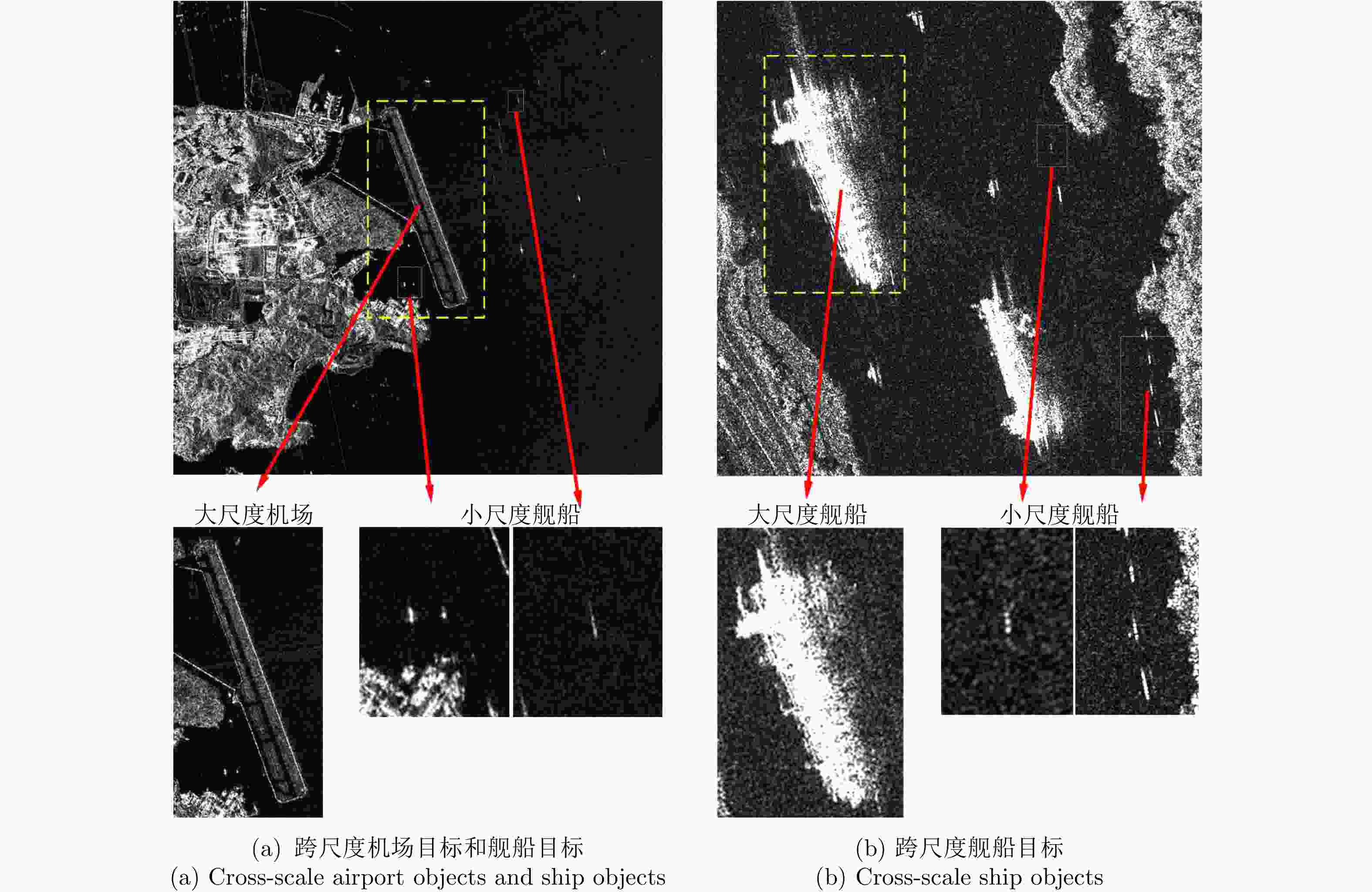
摘要: SAR图像多尺度目标检测能够实现大场景SAR图像中关键目标的定位与识别,是SAR图像解译的关键技术之一。然而针对尺寸相差较大的SAR目标的同时检测,即跨尺度目标检测问题,现有目标检测方法难以实现。该文提出一种基于特征转移金字塔网络(FTPN)的SAR图像跨尺度目标检测方法。在特征提取阶段采用特征转移方法,实现各层特征图的有效连接,实现不同尺度特征图的提取;同时采用空洞卷积群方法,增大特征提取的感受野,促使网络提取到大尺度目标特征。上述环节能够有效保留不同尺寸目标特征,从而实现SAR图像中跨尺度目标的同时检测。基于高分三号SAR数据、SSDD数据集及高分辨率SAR舰船检测数据集-2.0等数据集的试验表明,该文方法能够实现SAR图像中机场、舰船等跨尺度目标的检测,在已有数据集上mAP达96.5%,较特征金字塔网络算法提升8.1%,并且整体性能优于现阶段最新的YOLOv4等目标检测算法。Abstract: Multiscale object detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images can locate and recognize key objects in large-scene SAR images, and it is one of the key technologies in SAR image interpretation. However, for the simultaneous detection of SAR objects with large size differences, that is, cross-scale object detection, existing object detection methods are difficult to extract the features of cross-scale objects, and also difficult to realize cross-scale object simultaneous detection. In this study, we propose a multiscale object detection method based on the Feature-Transferable Pyramid Network (FTPN) for SAR images. In the feature extraction stage, the feature migration method is used to obtain an effective mosaic of the feature images of each layer and extract feature images with different scales. Simultaneously, the void convolution method is used to increase the receptive field of feature extraction and aid the network in extracting large object features. These steps can effectively preserve the features of objects of different sizes, to realize the simultaneous detection of cross-scale objects in SAR images. The experiments based on the GaoFen-3 SAR dataset, SAR Ship Detection Dataset (SSDD), and high-resolution SSDD-2.0 show that the proposed method can detect cross-scale objects, such as airports and ships in SAR images, and the mean Average Precision (mAP) can reach 96.5% on the existing dataset, which is 8.1% higher than that of the characteristic pyramid network algorithm. Moreover, the overall performance of the proposed method is better than that of the latest YOLOv4 and other object detection algorithms.
-
Key words:
- SAR object detection /
- Feature pyramid /
- Feature-transfer /
- Dilated convolution group /
- Cross-scale
-
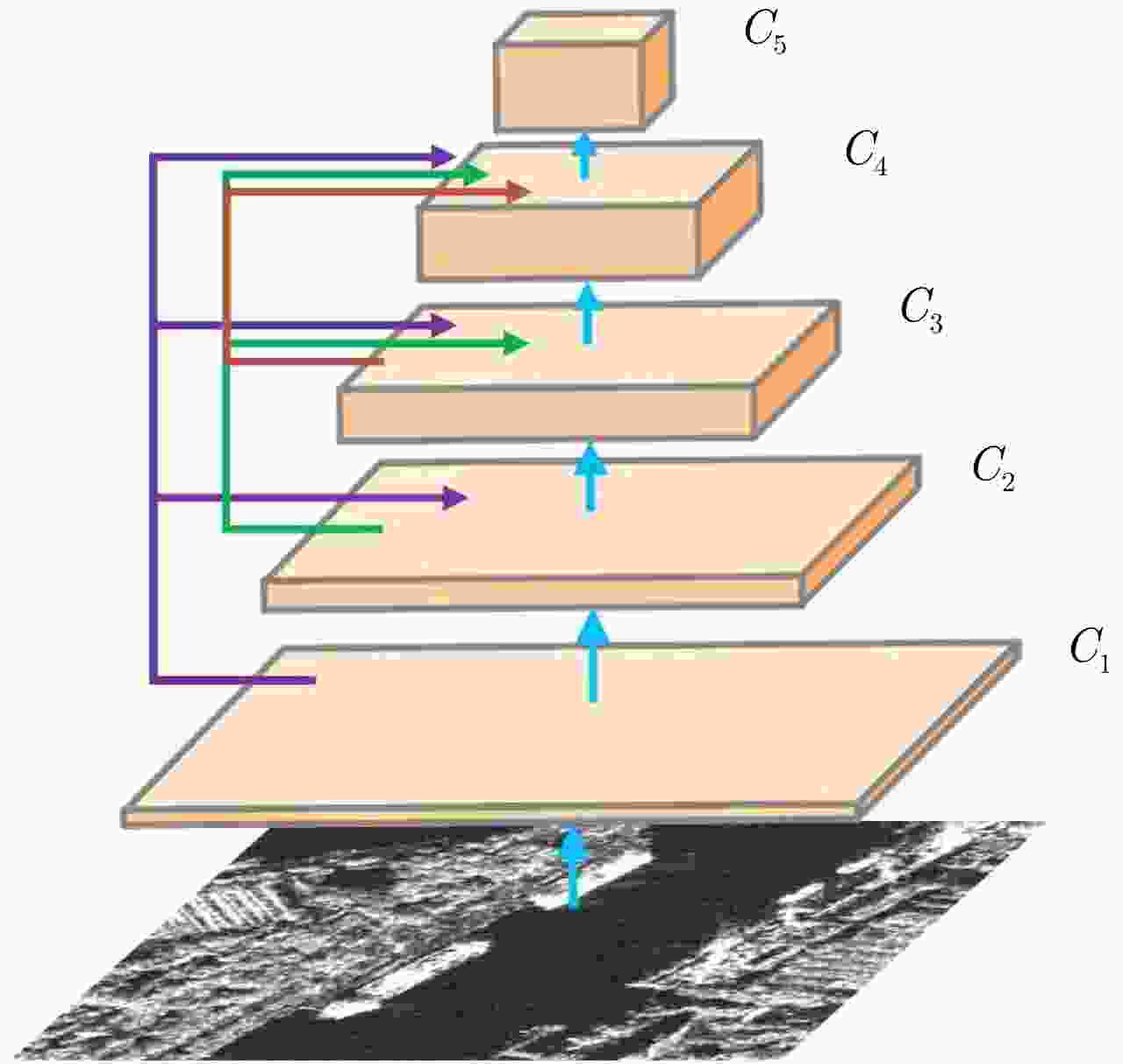
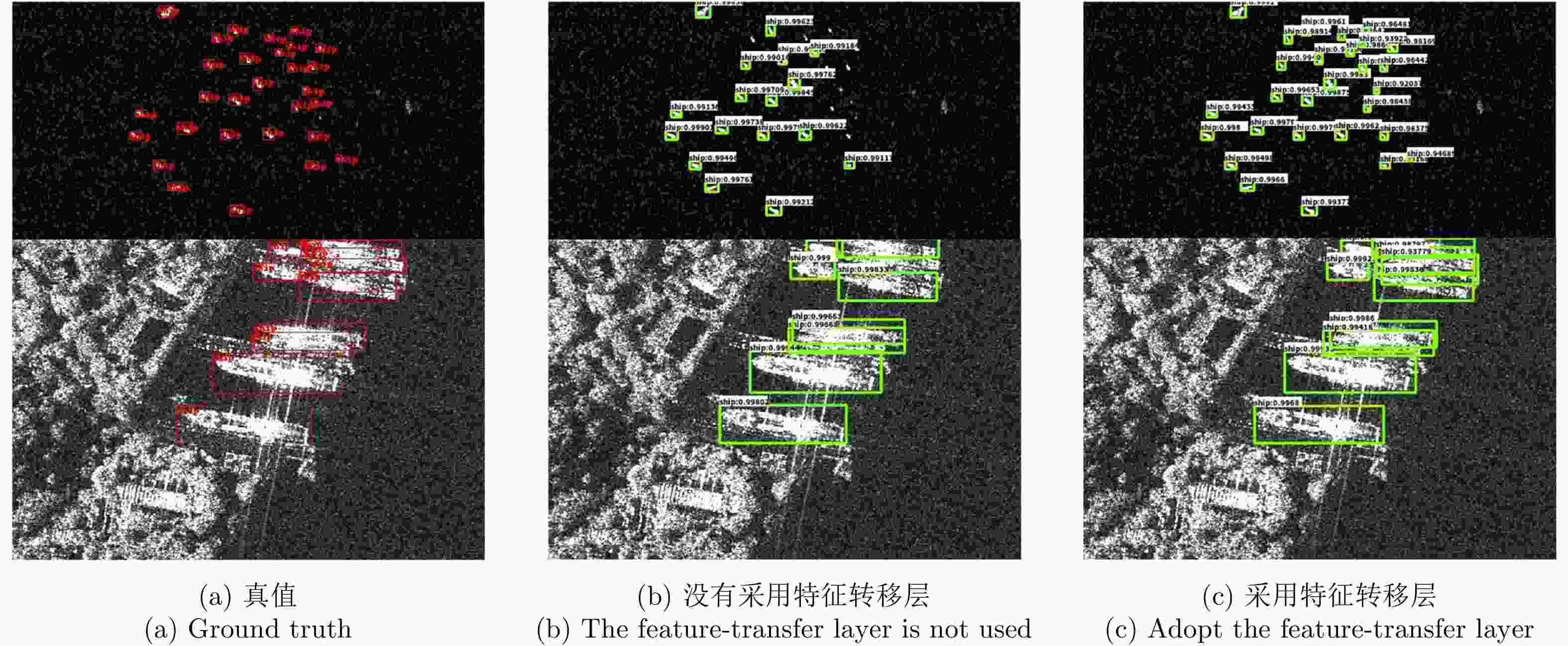
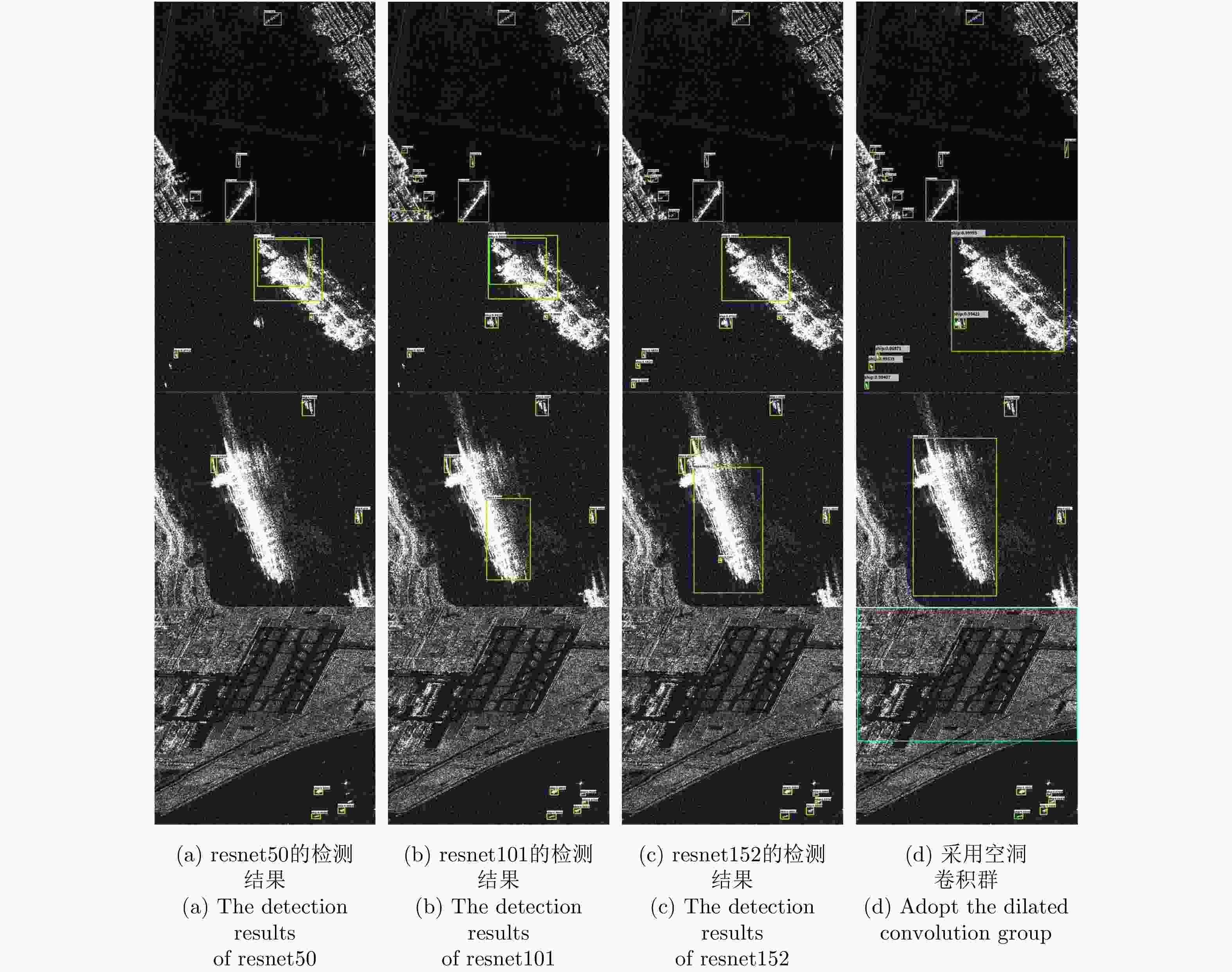
表 1 特征转移层对检测结果的影响
Table 1. The influence of feature-transfer layer on detection results
方法 mAP(%) 没有特征转移层 88.4 本文方法 92.8 表 2 空洞卷积群对检测结果的影响
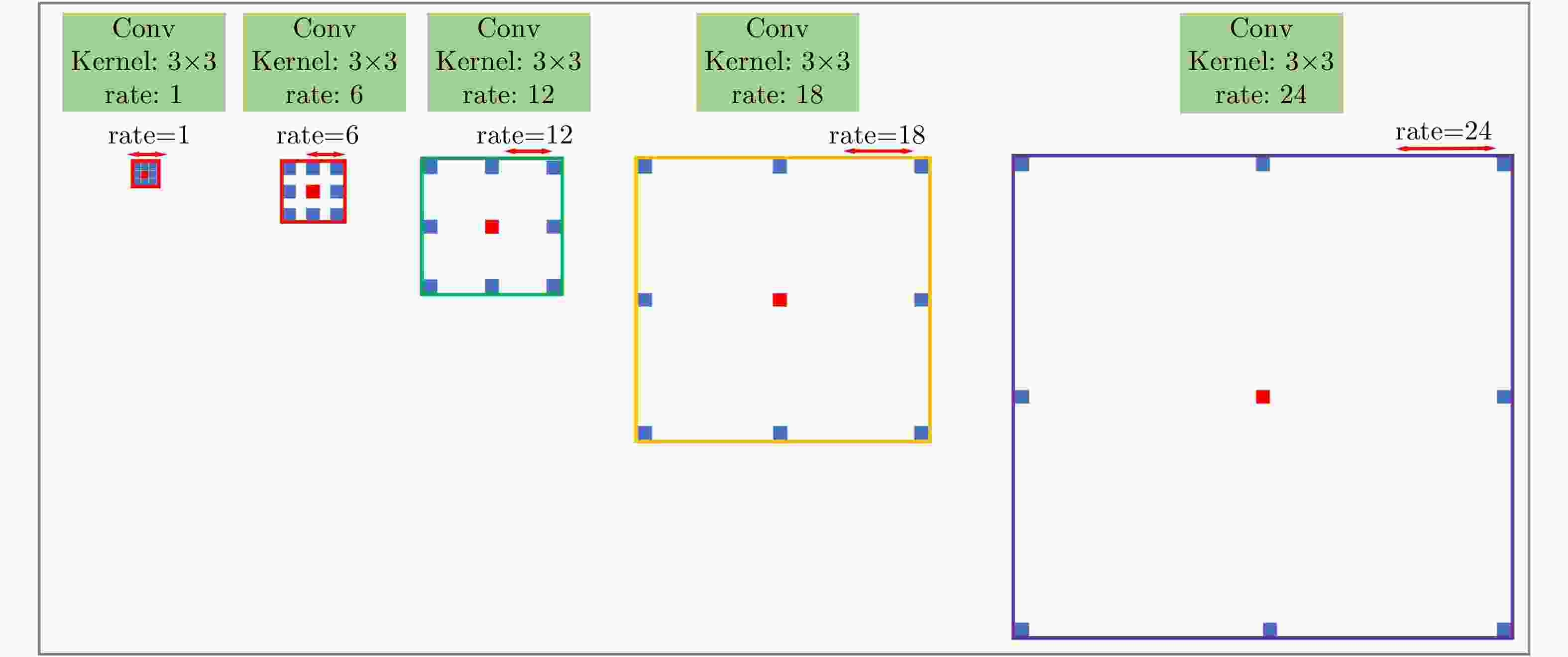
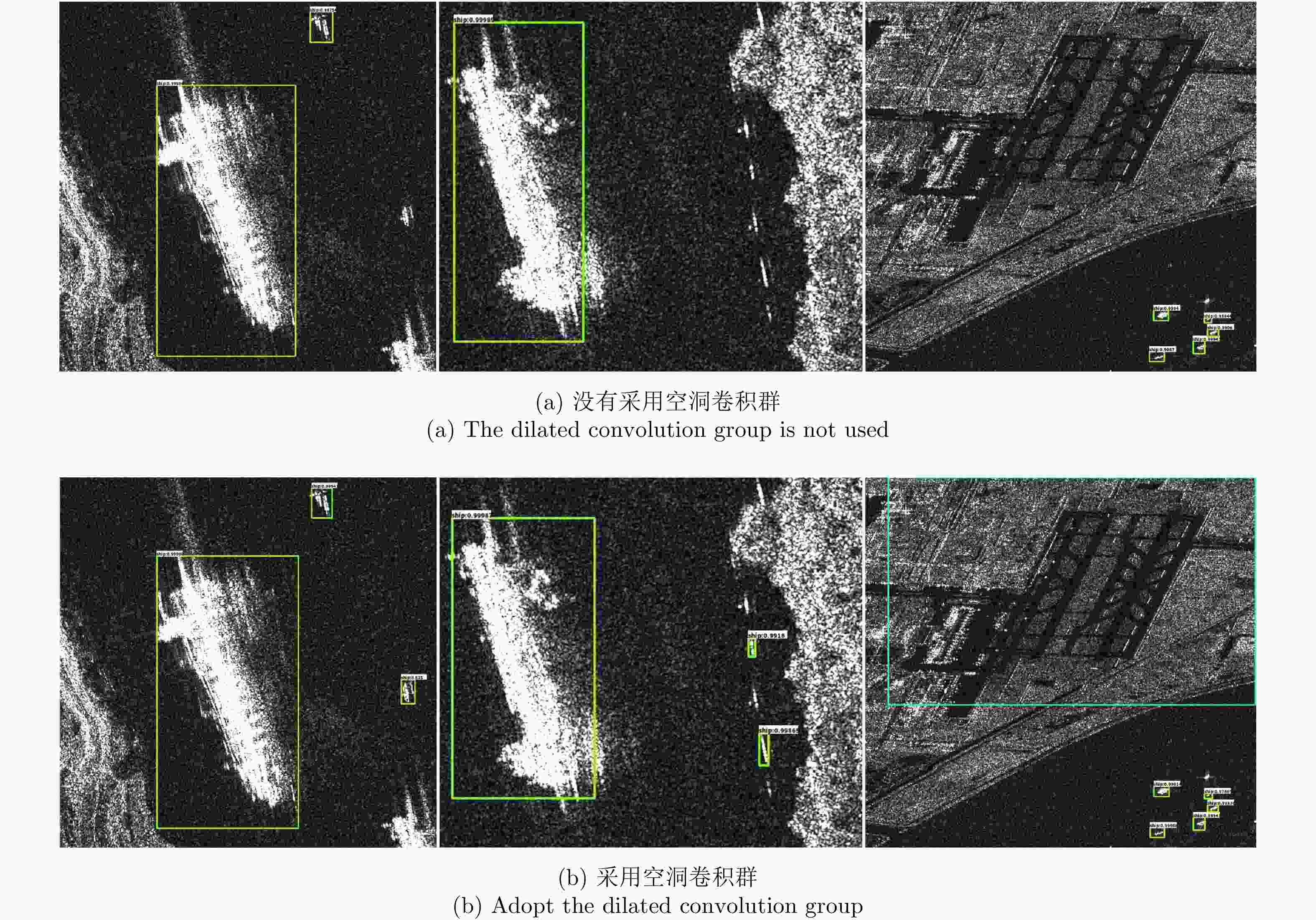
Table 2. Influence of dilated convolution group on detection results
方法 mAP(%) 没有空洞卷积群 88.4 本文方法> 92.1 表 3 与先进的目标检测网络相比
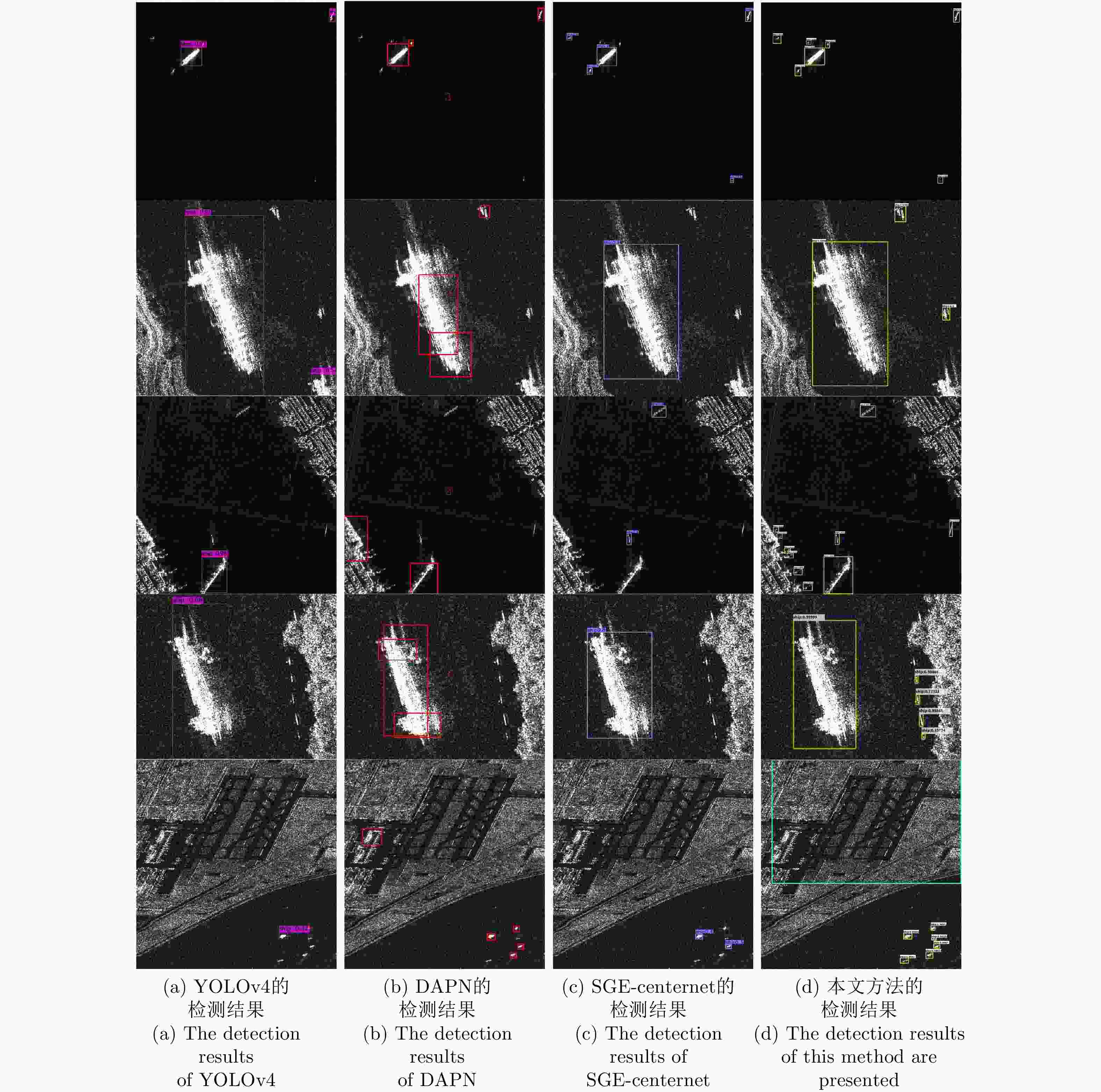
Table 3. Compared with advanced object detection networks
方法 mAP(%) Faster R-CNN 70.1 SSD 78.5 YOLOv4 88.2 YOLOv5 88.5 Improved Faster R-CNN 88.8 DAPN 89.8 PANet 90.8 SGE-centernet 93.9 本文方法 96.5 表 4 机场目标和舰船目标的结果统计
Table 4. Result statistics for airport and ship objects
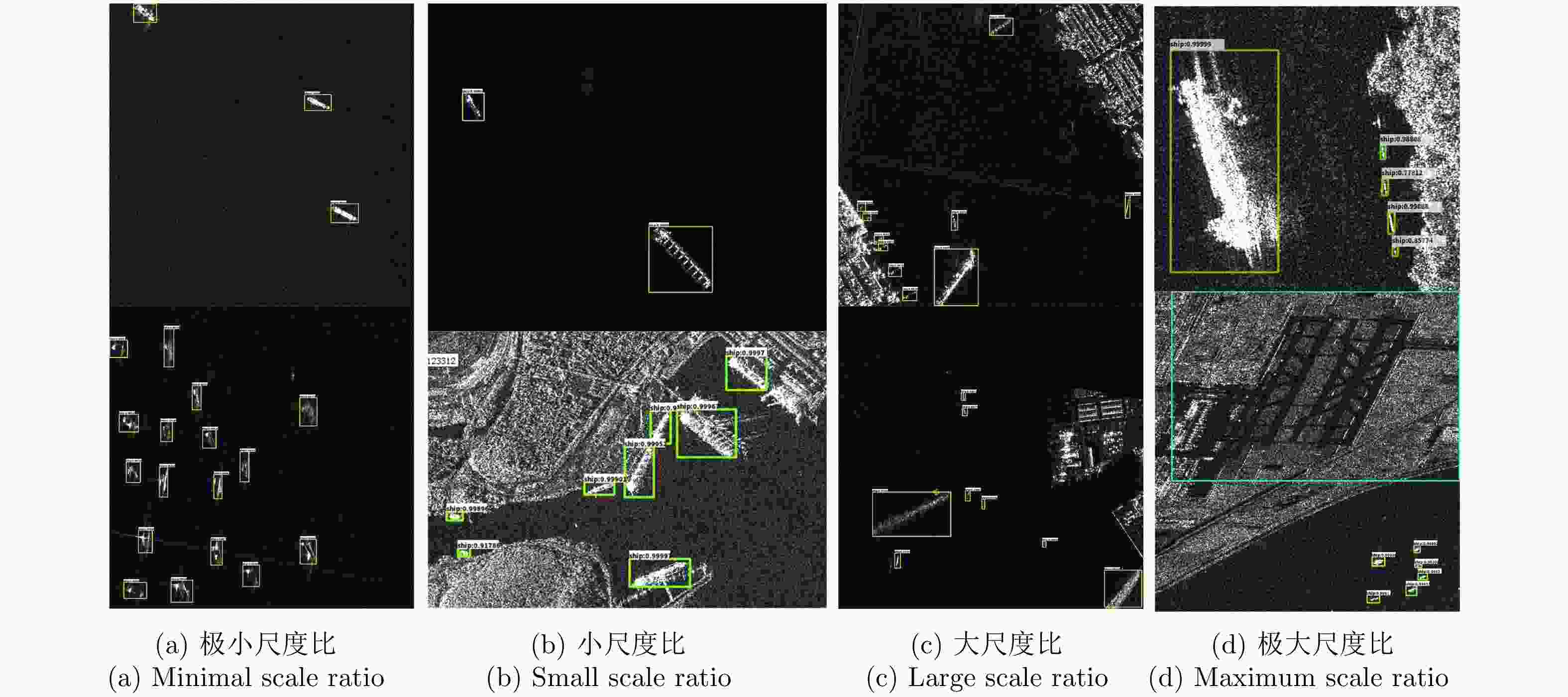
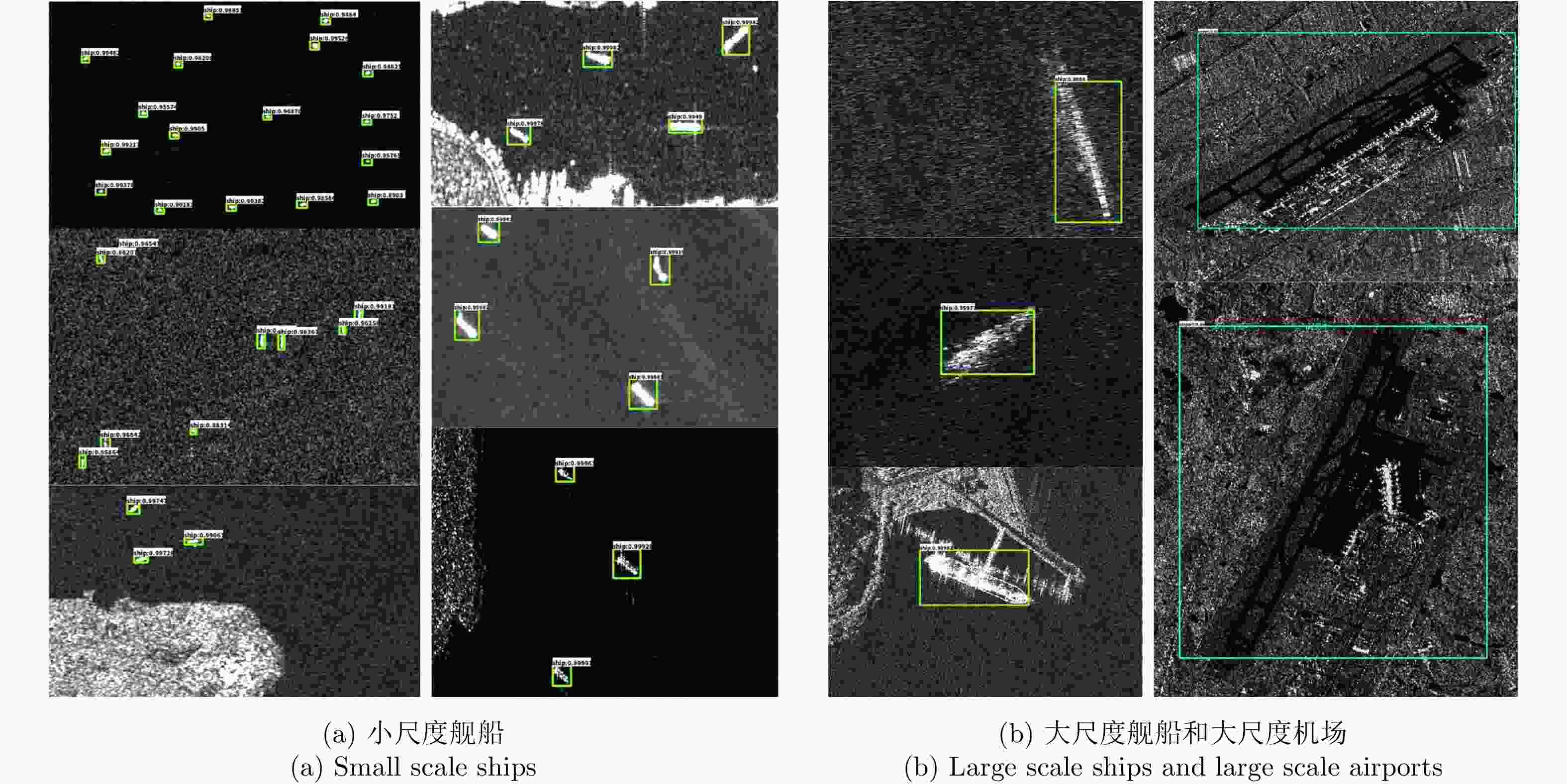
目标类型 N n m f DP(%) MP(%) FP(%) 机场 3 3 0 0 100 0 0 舰船 80 76 4 5 95 5 6.25 表 5 单一尺度目标的检测性能
Table 5. Single scale object detection performance
单一尺度 mAP(%) 小尺度舰船 97.2 大尺度舰船 96.3 大尺度机场 94.4 -
[1] LIU Nengyuan, CAO Zongjie, CUI Zongyong, et al. Multi-scale proposal generation for ship detection in SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(5): 526. doi: 10.3390/rs11050526 [2] AN Wentao, XIE Chunhua, and YUAN Xinzhe. An improved iterative censoring scheme for CFAR ship detection with SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4585–4595. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2282820 [3] LI Tao, LIU Zheng, XIE Rong, et al. An improved superpixel-level CFAR detection method for ship targets in high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 184–194. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2764506 [4] DAI Hui, DU Lan, WANG Yan, et al. A modified CFAR algorithm based on object proposals for ship target detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1925–1929. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2618604 [5] ZHAI Liang, LI Yu, and SU Yi. Inshore ship detection via saliency and context information in high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1870–1874. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2616187 [6] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91. [7] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2. [8] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Region-based convolutional networks for accurate object detection and segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(1): 142–158. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2437384 [9] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.169. [10] 张晓玲, 张天文, 师君, 等. 基于深度分离卷积神经网络的高速高精度SAR舰船检测[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 841–851. doi: 10.12000/JR19111ZHANG Xiaoling, ZHANG Tianwen, SHI Jun, et al. High-speed and High-accurate SAR ship detection based on a depthwise separable convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 841–851. doi: 10.12000/JR19111 [11] HONG Feng, LU Changhua, LIU Chun, et al. A traffic surveillance multi-scale vehicle detection object method base on encoder-decoder[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 47664–47674. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2979260 [12] 陈慧元, 刘泽宇, 郭炜炜, 等. 基于级联卷积神经网络的大场景遥感图像舰船目标快速检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041CHEN Huiyuan, LIU Zeyu, GUO Weiwei, et al. Fast detection of ship targets for large-scale remote sensing image based on a cascade convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 413–424. doi: 10.12000/JR19041 [13] FANG Qingyun, ZHANG Lin, and WANG Zhaokui. An efficient feature pyramid network for object detection in remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 93058–93068. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2993998 [14] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.106. [15] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [16] JIAO Jiao, ZHANG Yue, SUN Hao, et al. A densely connected end-to-end neural network for multiscale and multiscene SAR ship detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 20881–20892. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2825376 [17] 顾佼佼, 李炳臻, 刘克, 等. 基于改进Faster R-CNN的红外舰船目标检测算法[J]. 红外技术, 2021, 43(2): 170–178.GU Jiaojiao, LI Bingzhen, LIU Ke, et al. Infrared ship target detection algorithm based on improved faster R-CNN[J]. Infrared Technology, 2021, 43(2): 170–178. [18] NIE Xuan, DUAN Mengyang, DING Haoxuan, et al. Attention mask R-CNN for ship detection and segmentation from remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 9325–9334. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2964540 [19] 陈华杰, 吴栋, 谷雨. 密集子区域切割的任意方向舰船快速检测[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2021, 26(3): 654–662. doi: 10.11834/jig.200111CHEN Huajie, WU Dong, and GU Yu. Fast detection algorithm for ship in arbitrary direction with dense subregion cutting[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2021, 26(3): 654–662. doi: 10.11834/jig.200111 [20] ZHANG Miaohui, PANG Kangning, GAO Chengcheng, et al. Multi-scale aerial target detection based on densely connected inception ResNet[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 84867–84878. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2992647 [21] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.243. [22] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834–848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [23] LI Jianwei, QU Changwen, and SHAO Jiaqi. Ship detection in SAR images based on an improved faster R-CNN[C]. 2017 SAR in Big Data Era: Models, Methods and Applications (BIGSARDATA), Beijing, China, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/BIGSARDATA.2017.8124934. [24] 孙显, 王智睿, 孙元睿, 等. AIR-SARShip-1.0: 高分辨率SAR舰船检测数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097SUN Xian, WANG Zhirui, SUN Yuanrui, et al. AIR-SARShip-1.0: High-resolution SAR ship detection dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097 [25] WANG Yuanyuan, WANG Chao, ZHANG Hong, et al. A SAR dataset of ship detection for deep learning under complex backgrounds[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(7): 765. doi: 10.3390/rs11070765 [26] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, and LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J]. 2020, in press. [27] LIU Shu, QI Lu, QIN Haifeng, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8759–8768. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00913. [28] CUI Zongyong, LI Qi, CAO Zongjie, et al. Dense attention pyramid networks for multi-scale ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8983–8997. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2923988 [29] CUI Zongyong, WANG Xiaoya, LIU Nengyuan, et al. Ship detection in large-scale SAR images via spatial shuffle-group enhance attention[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(1): 379–391. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2997200 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: