-
摘要: 通过在超表面单元上加载二极管等有源器件,可编程超表面可实现对电磁波的实时灵活调控。通常利用全波仿真软件计算可编程超表面的辐射场,但该方法需要消耗大量的时间,因而降低了设计效率。为了实现准确高效求解给定编码序列计算辐射场,该文首先设计了辐射场自动测试系统,利用该测试系统实测了少量的编码和辐射场数据,其后提出了一个正向深度神经网络,基于实测的数据训练该神经网络,最终实现了给定编码准确高效预测辐射场。对于给定辐射场求解编码的逆问题,该文提出了一个逆向深度神经网络。基于正向网络生成的数据训练所提出的逆向网络,最终实现了给定辐射场实时准确求解编码。该文所提出的方法为雷达波束形成提供了一种新可选方案,在雷达智能波束形成、微波成像等领域有一定的应用价值。Abstract: The Programmable Metasurface (PM) can flexibly manipulate electromagnetic waves in real time using loading active devices on the meta-element. Calculating the radiation fields of the PM with complex structures using full-wave simulation software is time-consuming, which results in design efficiency. To accurately and efficiently solve the mapping relationship from coding schemes to radiation fields, an Auto-Measuring System (AMS) of radiation patterns is designed. A few Code-to-Pattern (C-P) data are measured via the AMS. Then, a forward Deep Neural Network (DNN) is proposed, the DNN is trained by the measured data, and an accurate and efficient prediction of C-P is realized. More C-P data are generated based on the proposed forward neural network, and the data are used to train another proposed inverse DNN and realize the accurate prediction of codes when given patterns in real time. This method provides a new alternative scheme for radar beamforming and has application values in intelligent radar beamforming and microwave imaging.
-
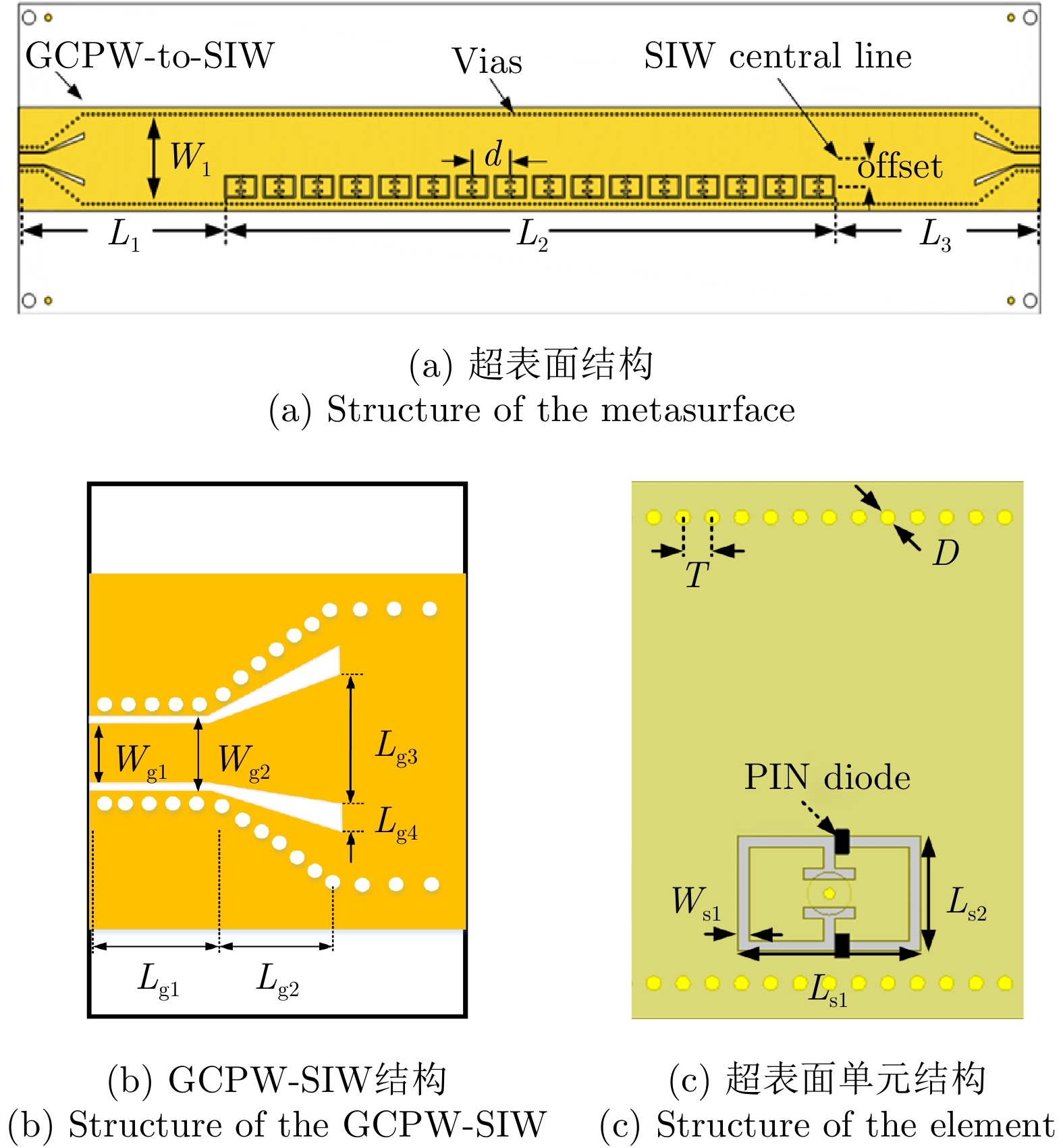
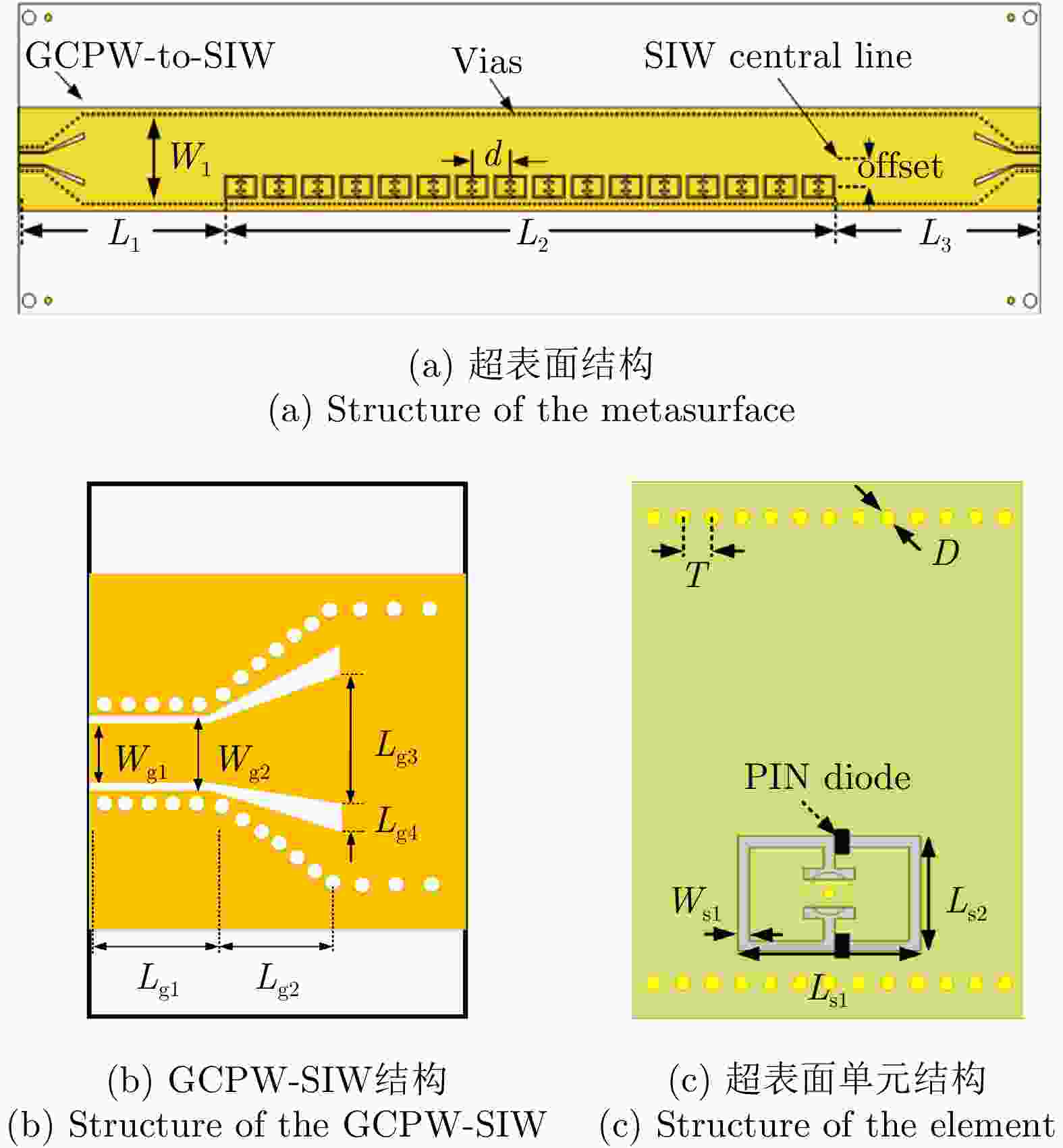
表 1 超表面相关参数(mm)
Table 1. Parameters of the metasurface (mm)
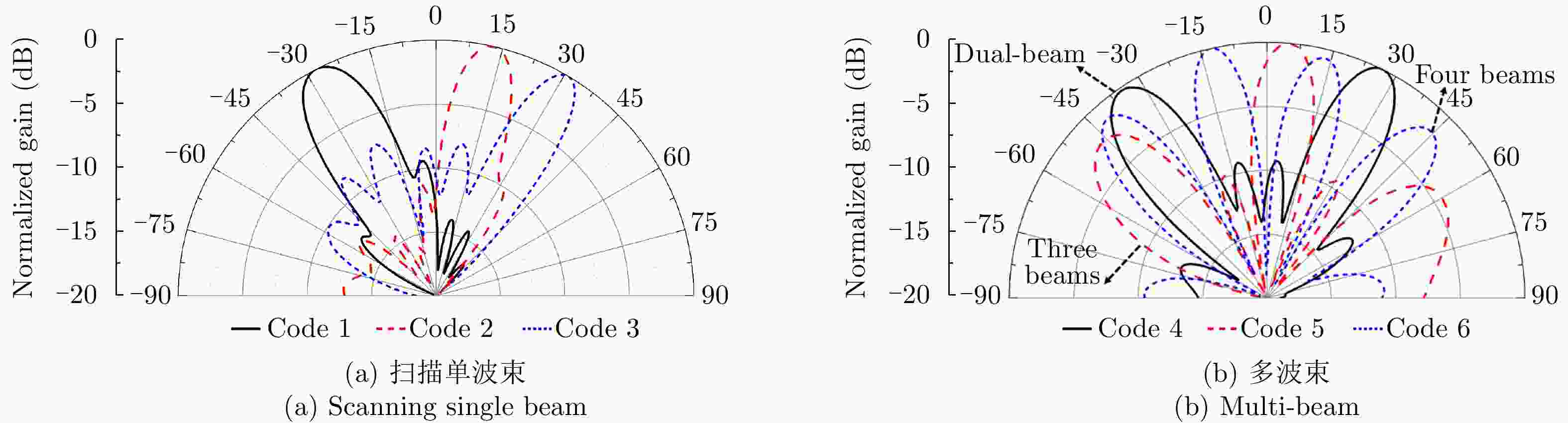
L1 L2 L3 W1 offset d Wfeed Lg1 Lg2 Lg3 32.1 95 32.1 13 4 6 1.65 3.7 6.3 6 Lg4 Wg1 Wg2 Ls1 Ls2 Ws1 T D h1 h2 0.8 1.65 2.05 5 3.2 0.3 0.8 0.4 1.524 0.508 表 2 单波束编码
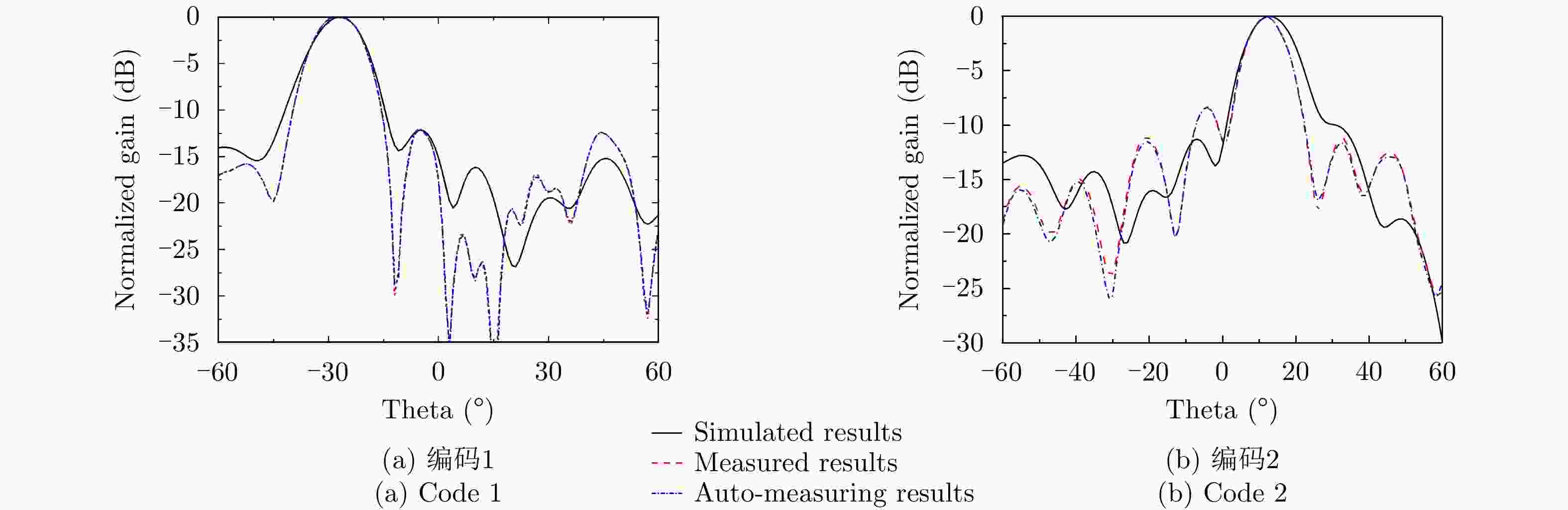
Table 2. Codes for single beams
编码号 编码序列 主瓣指向 波束宽度 Code 1 0101010101010101 –28° 13.5° Code 2 1001001001001001 13° 10.0° Code 3 1001100110011001 31° 8.5° 表 3 多波束编码
Table 3. Codes for multi-beam
编码号 编码序列 波束个数 Code 4 0001000100010001 2 Code 5 0000100001000010 3 Code 6 0000010000010000 4 表 4 计算编码准确率
Table 4. Accuracy for calculated codes
${ {\rm{{A}{c}{c}}}{u} }_{ {\rm{{m}{e}{a}{n}}} }$ ${ {\rm{{A}{c}{c}}}{u} }_{0-{\rm{{b}{i}{t}}} }$ ${ {\rm {{A}{c}{c}}}{u} }_{1-{\rm{{b}{i}{t}}} }$ ${ {\rm {{A}{c}{c}}}{u} }_{2-{\rm {{b}{i}{t}}} }$ ${ {\rm {{A}{c}{c}}}{u} }_{3+{\rm{{b}{i}{t}}} }$ 99.09% 90.25% 6.56% 2.12% 1.07% -
[1] VESELAGO V G and LEBEDEV P N. The electrodynamics of substances with simultaneously negative values of ε and μ[J]. Soviet Physics Uspekhi, 1968, 10(4): 509–514. doi: 10.1070/PU1968v010n04ABEH003699 [2] PENDRY J B, HOLDEN A J, STEWART W J, et al. Extremely low frequency plasmons in metallic mesostructures[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 76(25): 4773–4776. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.76.4773 [3] CUI Tiejun, QI Meiqing, WAN Xiang, et al. Coding metamaterials, digital metamaterials and programmable metamaterials[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2014, 3(10): e218. [4] LI Shangyang, XU Feng, WAN Xiang, et al. Programmable metasurface based on substrate-integrated waveguide for compact dynamic-pattern antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(5): 2958–2962. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3023581 [5] https://www.ni.com/zh-cn/support/model.usb-6212.html. [6] SAINATH T N, MOHAMED A R, KINGSBURY B, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for LVCSR[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, Canada, 2013: 8614–8618. [7] TOMPSON J, JAIN A, LECUN Y, et al. Joint training of a convolutional network and a graphical model for human pose estimation[C]. The 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 1799–1807. [8] PULIDO-MANCERA L M, ZVOLENSKY T, IMANI M F, et al. Discrete dipole approximation applied to highly directive slotted waveguide antennas[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2016, 15: 1823–1826. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2538202 [9] SHAN Tao, PAN Xiaotian, LI Maokun, et al. Coding programmable metasurfaces based on deep learning techniques[J]. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 2020, 10(1): 114–125. doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2020.2972764 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: