-
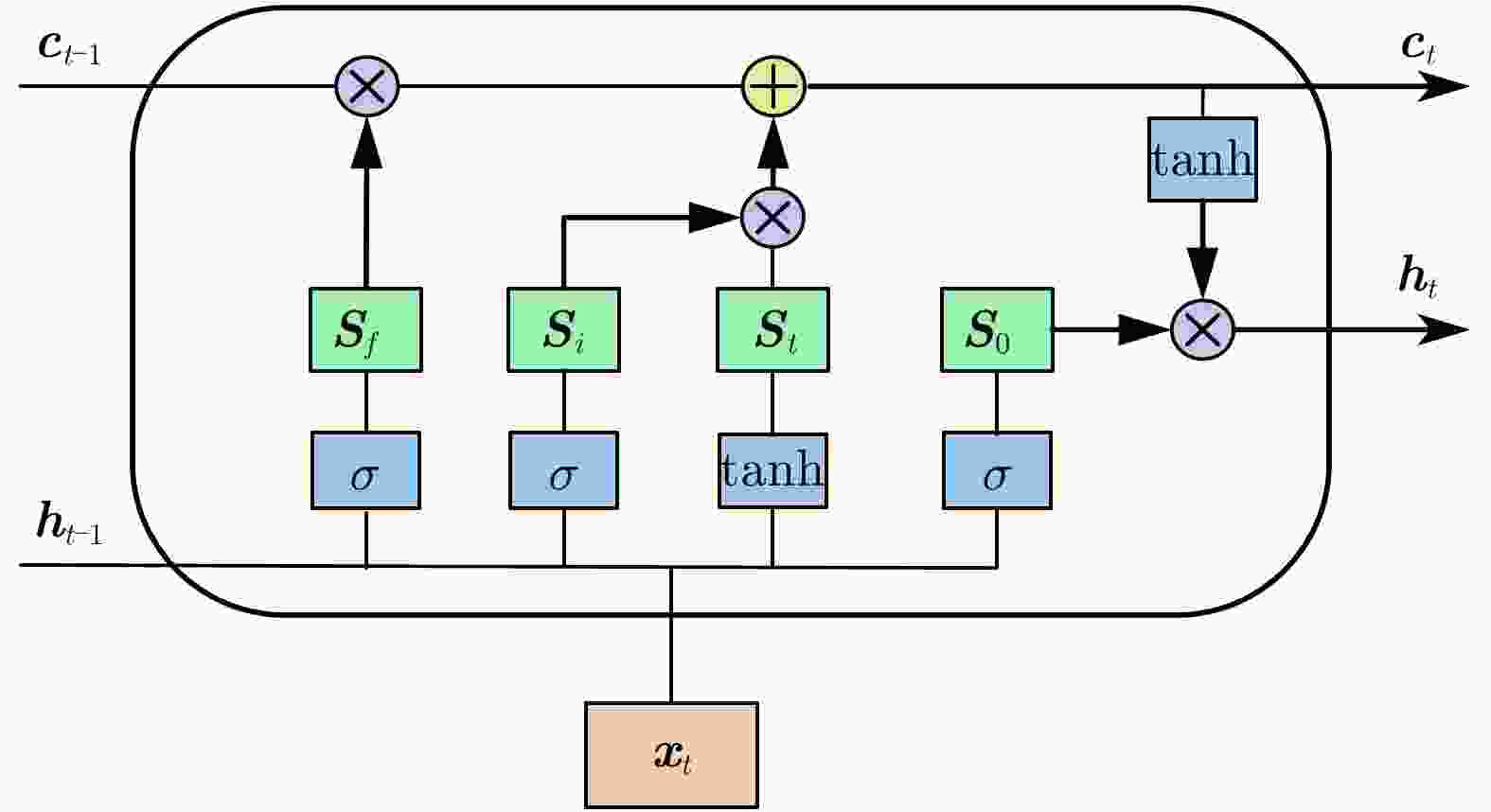
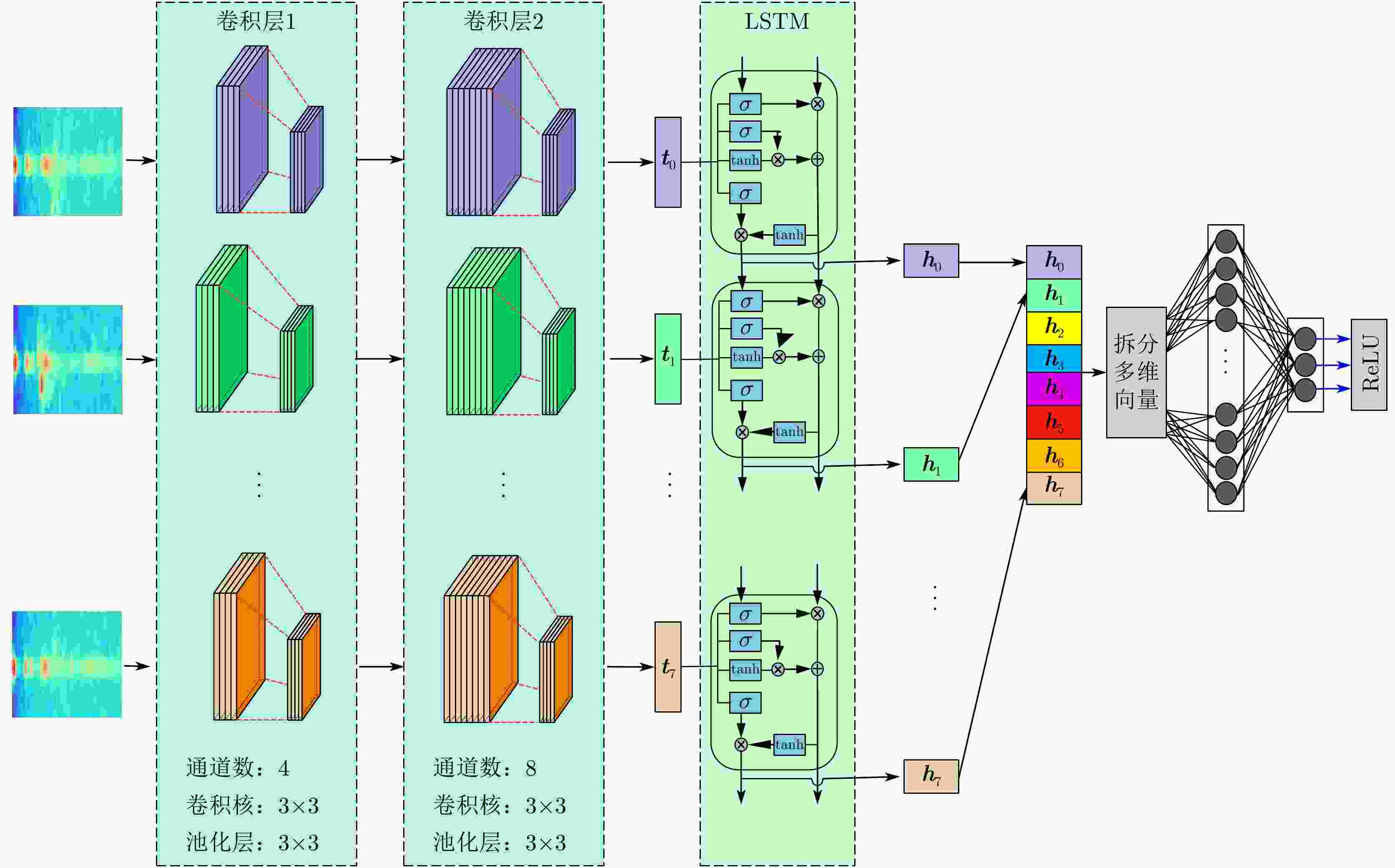
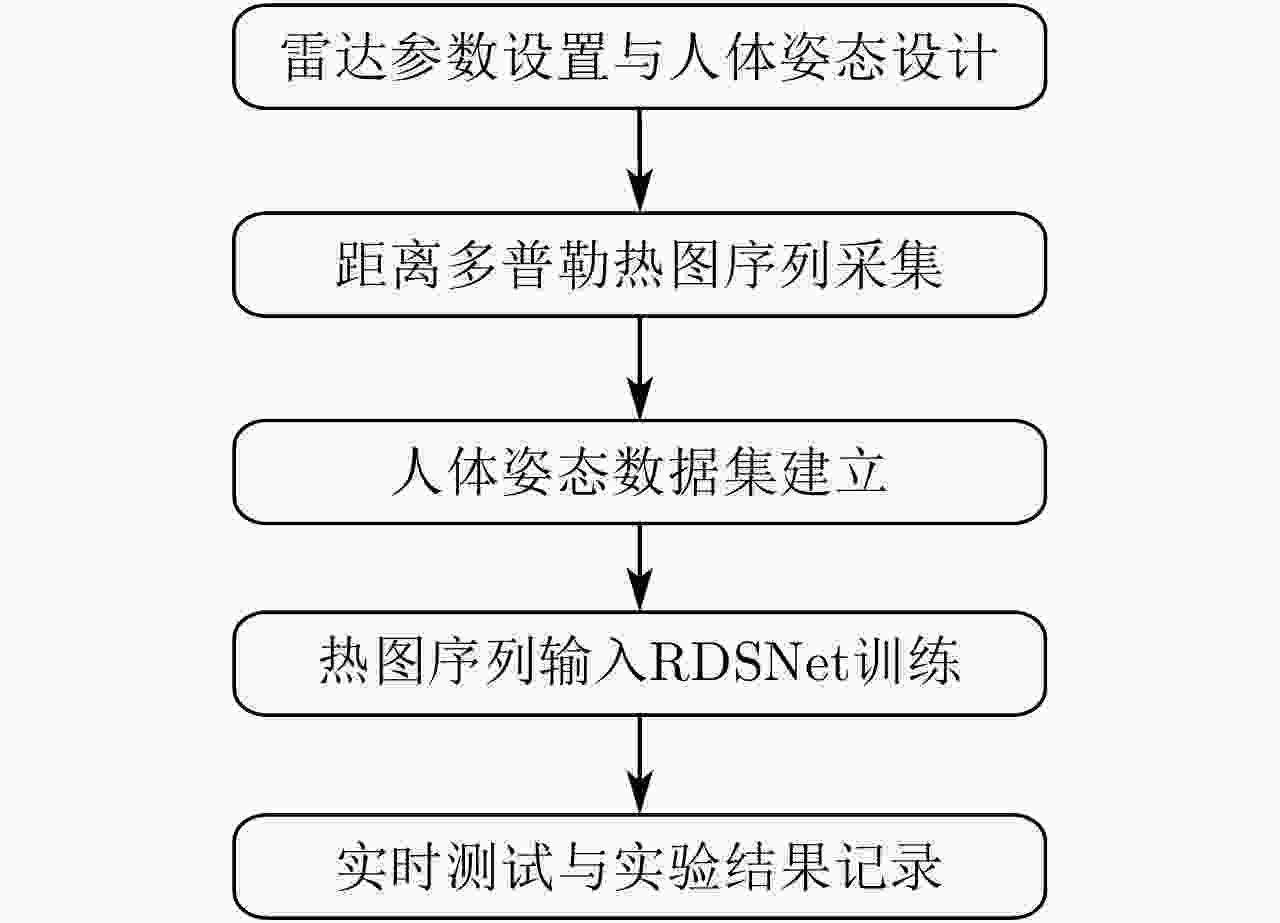
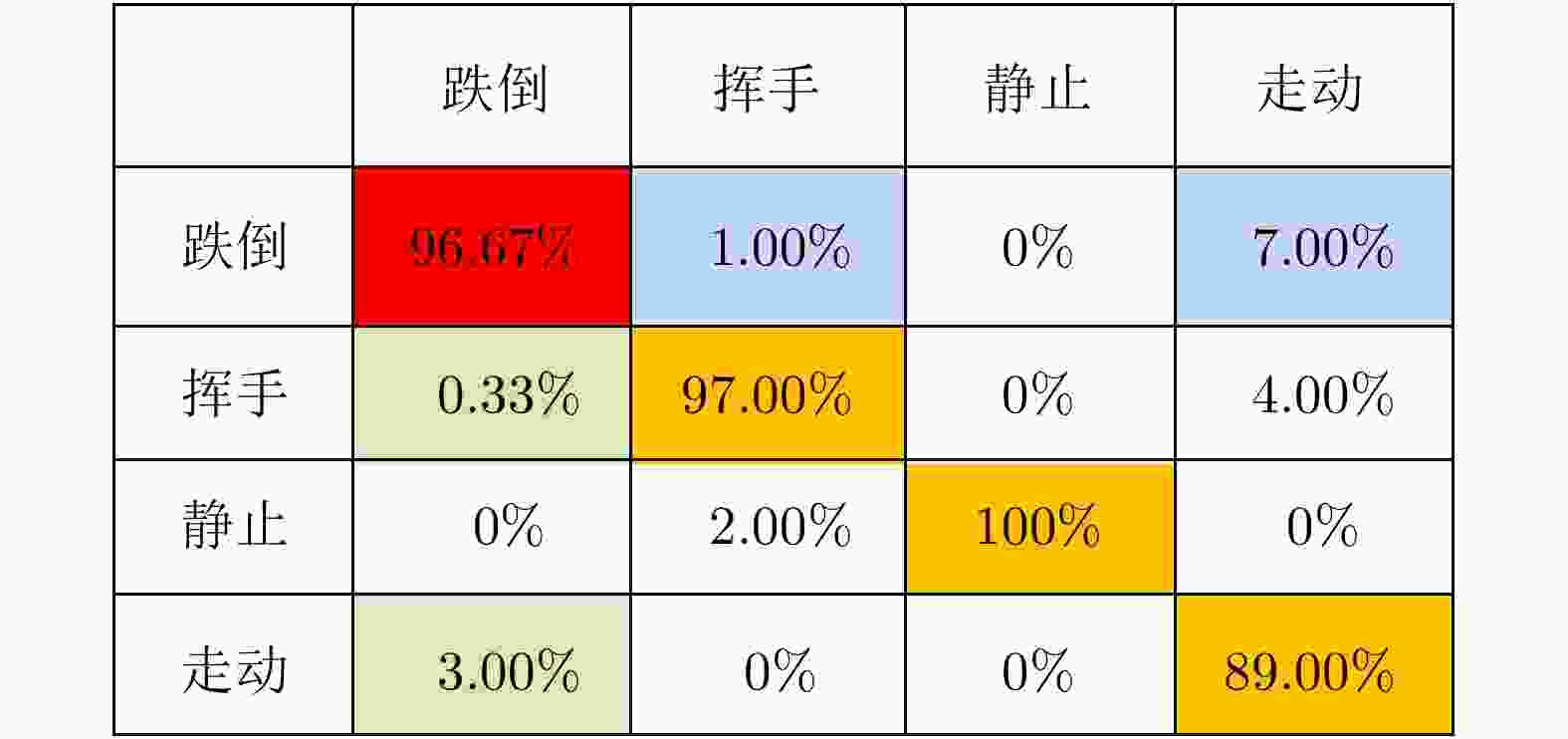
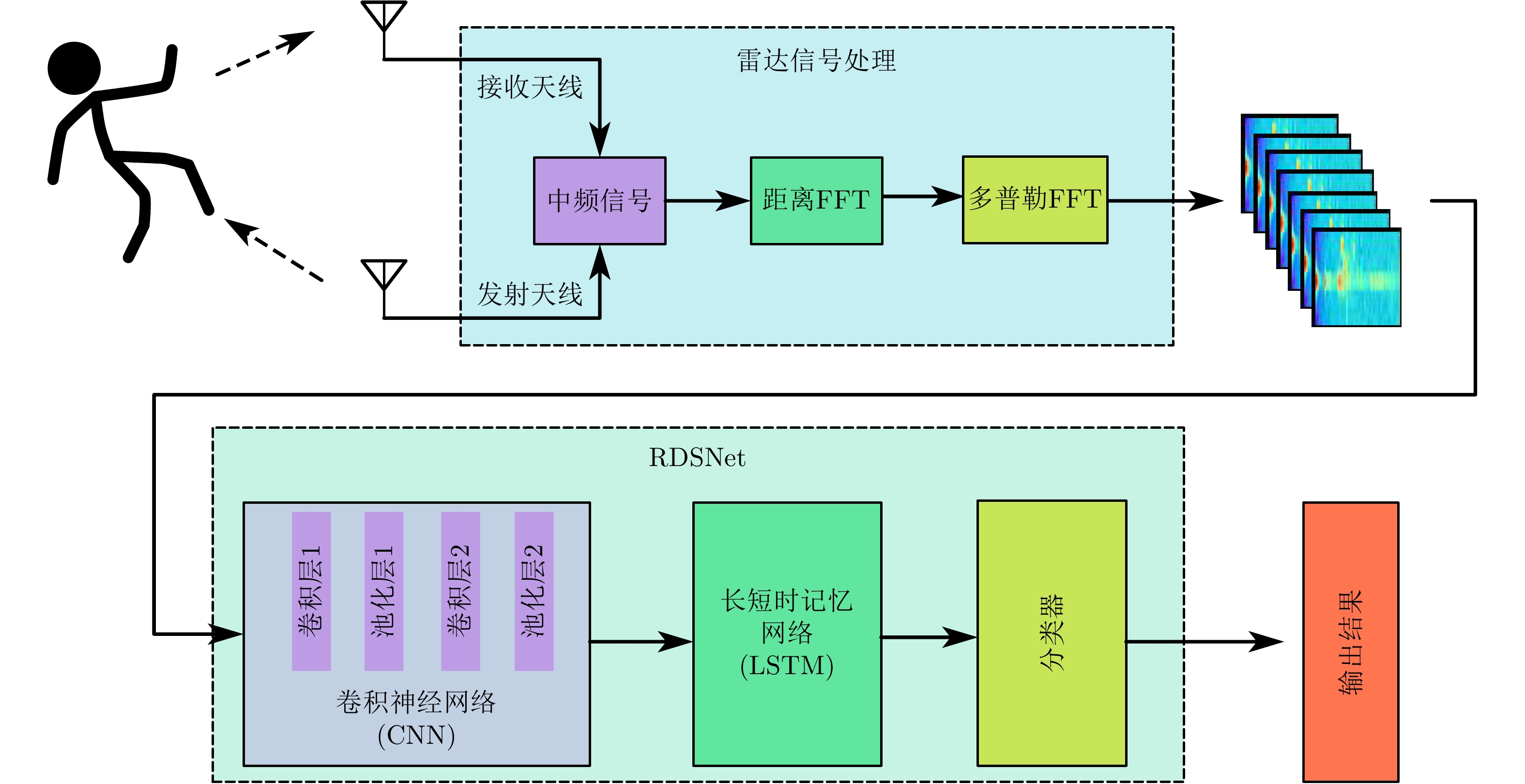
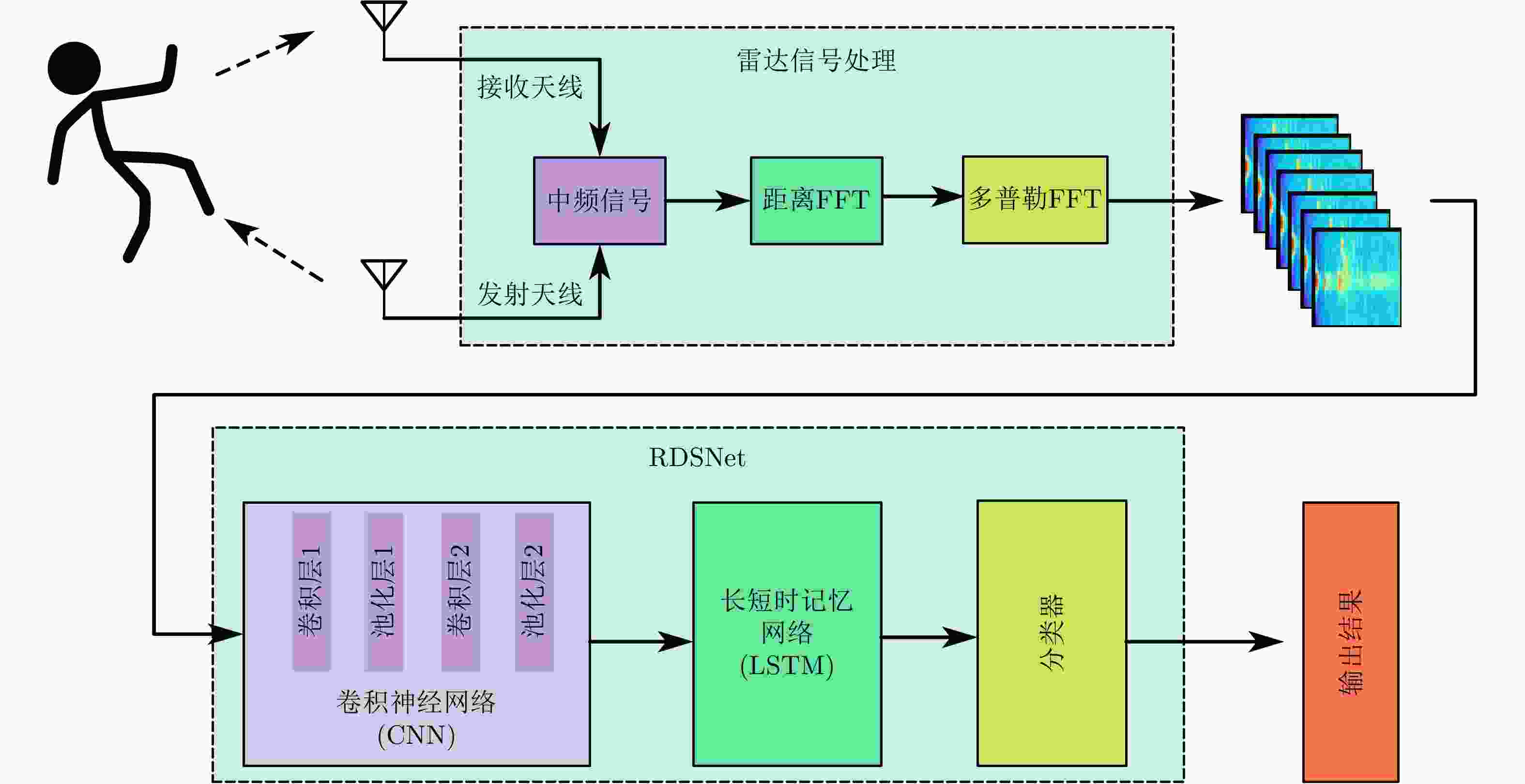
摘要: 随着人口老龄化的到来,跌倒检测逐渐成为研究热点。针对基于毫米波雷达的人体跌倒检测应用,该文提出了一种融合卷积神经网络和长短时记忆网络的距离多普勒热图序列检测网络(RDSNet)模型。首先通过卷积神经网络对距离多普勒热图进行特征提取得到特征向量,然后将动态序列对应的特征向量序列依次输入长短时记忆网络,进而学习得到热图序列的时间相关性信息,最后通过分类器网络得到检测结果。利用毫米波雷达采集了不同对象的多种人体动作,构建了距离多普勒热图数据集。对比试验表明,所提出的RDSNet网络模型检测准确率可达到96.67%,计算时延小于50 ms,而且具有良好的泛化能力,可为跌倒检测和人体姿态识别提供新的技术思路。Abstract: With the advent of the aging population, fall detection has gradually become a research hotspot. Aiming at the detection of human fall using millimeter-wave radar, a Range-Doppler heat map Sequence detection Network (RDSNet) model that combines the convolutional neural network and long short-term memory network is proposed in this study. First, feature extraction is performed using the convolutional neural network. After obtaining the feature vector, the feature vector corresponding to the dynamic sequence is inputted to the long short-term memory network. Subsequently, the time correlation information of the heat map sequence is learned. Finally, the detection results are obtained using the classifier. Moreover, diverse human movement information of different objects is collected using millimeter-wave radar, and a range-Doppler heat map dataset is built in this work. Comparative experiments show that the proposed RDSNet model can reach an accuracy of 96.67% and the calculation delay is not higher than 50 ms. The proposed RDSNet model has good generalization capabilities and provides new technical ideas for human fall detection and human posture recognition.
-
表 1 动作设计及距离多普勒热图序列
Table 1. Motion design and range Doppler heat map sequence
动作 距离多普勒热图序列 跌倒 
挥手 
起立 
静止 
走动 
翻身 
表 2 不同检测方法结果对比
Table 2. Comparative experimental results of different detection methods
分类 方法模型 传感器 动作种类 检测准确率(%) 实时 穿戴式 数据融合检测法[3] 加速度计+RGBD相机 4 99.00 否 基于CNN的手机跌倒检测模型[4] 加速度计+陀螺仪+线性加速度计 2 98.51 是 基于RNN的可穿戴跌倒检测器[21] 加速度计 2 96.70 是 非穿戴式 基于深度学习的多患者行为检测[13] 毫米波雷达 6 84.49 是 基于RGB-D跌倒检测算法[7] RGBD相机 3 98.00 是 复杂场景下的跌倒检测算法[8] RGBD相机 2 89.80 否 基于超宽带雷达的跌倒检测算法[12] 超宽带雷达(3个) 2 90.00 否 智能家居超宽带雷达跌倒检测[11] 超宽带雷达 2 97.50 是 老年人智能检测系统[9] WiFi 6 84.60 否 RDSNet 毫米波雷达 2 98.33 是(<50 ms) 4 96.67 6 93.33 表 3 相同传感器下不同网络结构的结果对比
Table 3. The results of different network structures under the same sensor
表 4 不同网络结构组合结果对比
Table 4. Comparison results of different network structure combinations
CNN(层) LSTM(层) 准确率(%) 漏警率(%) 虚警率(%) 时延(ms) 1 1 89.00 11.00 15 <38 2 1 96.67 3.33 8 <50 3 1 92.67 7.33 6 <69 4 1 67.00 33.00 26 <80 1 2 91.67 8.33 21 >100 2 2 95.33 4.67 11 >100 3 2 84.00 16.00 16 >100 4 2 61.33 38.67 34 >100 -
[1] 师昉, 李福亮, 张思佳, 等. 中国老年跌倒研究的现状与对策[J]. 中国康复, 2018, 33(3): 246–248. doi: 10.3870/zgkf.2018.03.021SHI Fang, LI Fuliang, ZHANG Sijia, et al. The present situation and countermeasures of the study of senile falls in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation, 2018, 33(3): 246–248. doi: 10.3870/zgkf.2018.03.021 [2] DHARUNGEERAN N and JAFARALI J. Sensors-based wearable systems for monitoring of human movement and falls[J]. International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Science, 2014, 1(3): 64–69. [3] GASPARRINI S, CIPPITELLI E, GAMBI E, et al. Proposal and Experimental Evaluation of Fall Detection Solution Based on Wearable and Depth Data Fusion[M]. LOSHKOVSKA S and KOCESKI S. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing. Cham: Springer, 2016, 399: 99–108. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-25733-4_11. [4] 吕艳, 张萌, 姜吴昊, 等. 采用卷积神经网络的老年人跌倒检测系统设计[J]. 浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 53(6): 1130–1138. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2019.06.012LV Yan, ZHANG Meng, JIANG Wuhao, et al. Design of elderly fall detection system using CNN[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Engineering Science, 2019, 53(6): 1130–1138. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2019.06.012 [5] CIPPITELLI E, FIORANELLI F, GAMBI E, et al. Radar and RGB-depth sensors for fall detection: A review[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17(12): 3585–3604. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2697077 [6] ZHANG Jing, LI Wanqing, OGUNBONA P O, et al. RGB-D-based action recognition datasets: A survey[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 60: 86–105. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.05.019 [7] ABOBAKR A, HOSSNY M, ABDELKADER H, et al. RGB-D fall detection via deep residual convolutional LSTM networks[C]. 2018 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Canberra, Australia, 2018: 1–7. doi: 10.1109/DICTA.2018.8615759. [8] FENG Qi, GAO Chenqiang, WANG Lan, et al. Spatio-temporal fall event detection in complex scenes using attention guided LSTM[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 130: 242–249. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2018.08.031 [9] BAO Nan, WU Chengyang, LIANG Qiancheng, et al. The intelligent monitoring for the elderly based on WiFi signals[C]. 18th Pacific-Rim Conference on Advances in Multimedia Information Processing, Harbin, China, 2018: 883–892. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-77380-3_85. [10] HU Yuqian, ZHANG Feng, WU Chenshu, et al. A wifi-based passive fall detection system[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 1723–1727. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9054753. [11] MOKHTARI G, ZHANG Q, and FAZLOLLAHI A. Non-wearable UWB sensor to detect falls in smart home environment[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshop, Kona, Italy, 2017: 274–278. doi: 10.1109/PERCOMW.2017.7917571. [12] MAITRE J, BOUCHARD K, and GABOURY S. Fall detection with UWB radars and CNN-LSTM architecture[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2021, 25(4): 1273–1283. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.3027967 [13] JIN Feng, ZHANG Renyuan, SENGUPTA A, et al. Multiple patients behavior detection in real-time using mmwave radar and deep CNNs[C]. 2019 IEEE Radar Conference, Boston, USA, 2019: 1–6. [14] WANG Bo, GUO Liang, ZHANG Hao, et al. A millimetre-wave radar-based fall detection method using line kernel convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(22): 13364–13370. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3006918 [15] SHRESTHA A, LI Haobo, LE KERNEC J, et al. Continuous human activity classification from FMCW radar with bi-LSTM networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(22): 13607–13619. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3006386 [16] LI Haobo, SHRESTHA A, HEIDARI H, et al. Bi-LSTM network for multimodal continuous human activity recognition and fall detection[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(3): 1191–1201. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2946095 [17] HOCHREITER S and SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735–1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [18] HUBEL D H and WIESEL T N. Receptive fields of single neurones in the cat’s striate cortex[J]. The Journal of Physiology, 1959, 148(3): 574–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006308 [19] 田壮壮, 占荣辉, 胡杰民, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标识别研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037TIAN Zhuangzhuang, ZHAN Ronghui, HU Jiemin, et al. SAR ATR based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037 [20] 韩昭蓉, 黄廷磊, 任文娟, 等. 基于Bi-LSTM模型的轨迹异常点检测算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(1): 36–43. doi: 10.12000/JR18039HAN Zhaorong, HUANG Tinglei, REN Wenjuan, et al. Trajectory outlier detection algorithm based on Bi-LSTM model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(1): 36–43. doi: 10.12000/JR18039 [21] LUNA-PEREJÓN F, DOMÍNGUEZ-MORALES M J, and CIVIT-BALCELLS A. Wearable fall detector using recurrent neural networks[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(22): 4885. doi: 10.3390/s19224885 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: