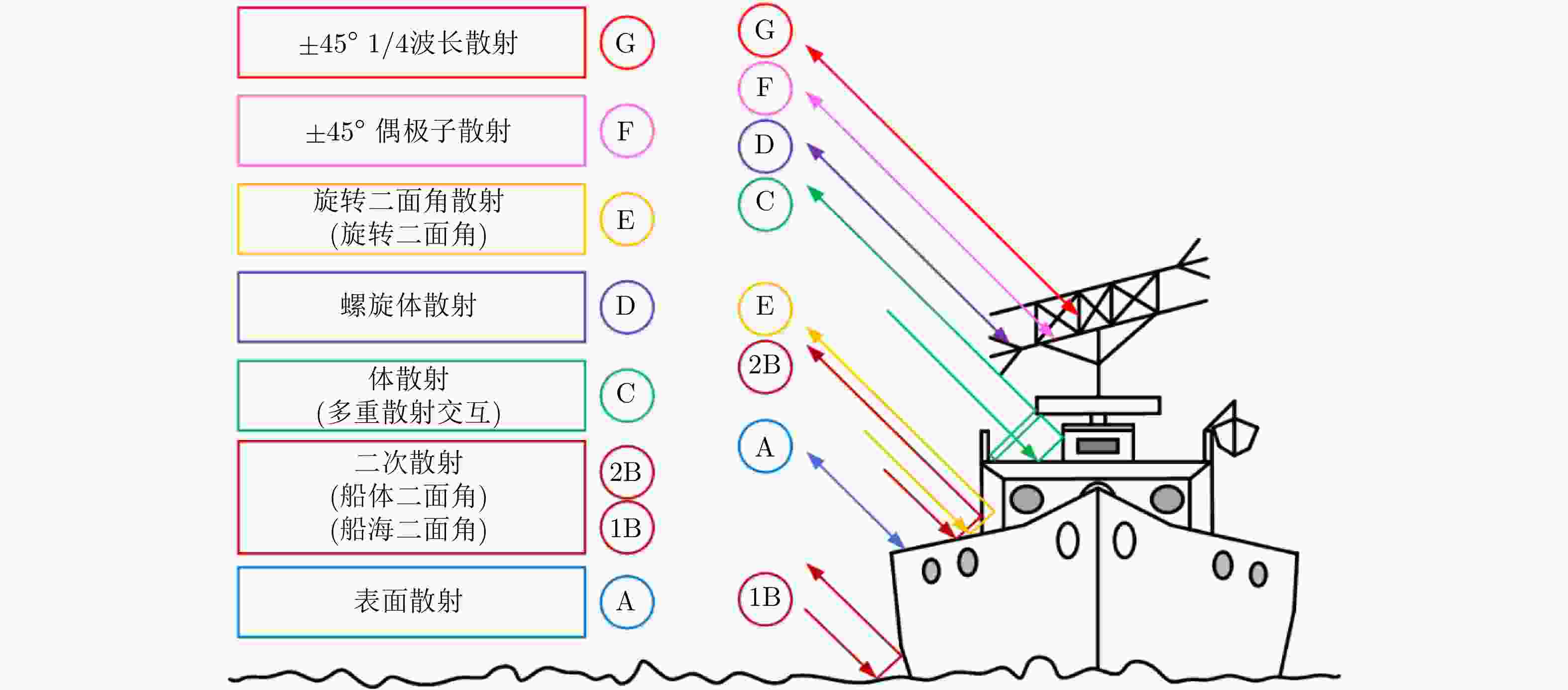
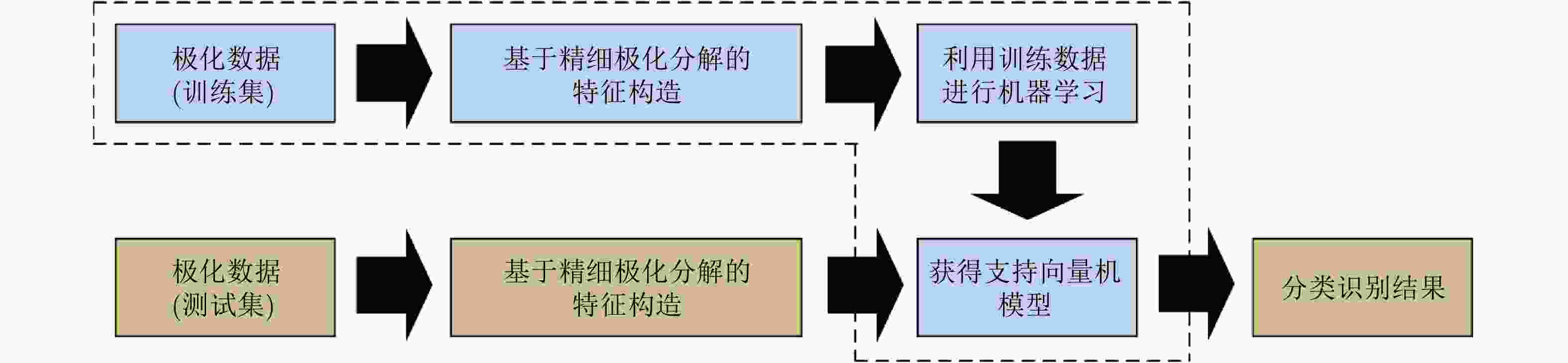
Recognition of Ships and Chaff Clouds Based on Sophisticated Polarimetric Target Decomposition
-
摘要: 用于干扰舰船目标的箔条云通常具有与舰船目标相近的尺寸和雷达散射截面积,这使得舰船与箔条云的识别成为一个非常有挑战性的问题。该文提出一种基于精细极化目标分解的识别方法。为了能够有效地识别舰船目标与箔条云,该文首先结合3种精细化散射模型,提出了一种基于精细散射模型的七成分分解方法。通过这种分解方法可以有效地刻画舰船目标的散射特性。为了将舰船与箔条云的极化特性进行有效的对比和区分,该文根据分解得到的散射成分贡献构造了一个稳健的散射贡献差特征。最后,通过将构造的散射贡献差与极化散射角结合,构造了新的特征矢量并利用支持向量机实现了最终的识别。实验利用仿真和实测的极化雷达数据对所提方法进行了验证,结果表明该方法优于现有的其他方法,并能够达到最高98%的正确识别率。Abstract: The recognition of ships from chaff cloud jamming is challenging because they have similar dimensions and radar cross sections. In this paper, we propose a polarimetric recognition technique with sophisticated polarimetric target decomposition. Three sophisticated scattering models are integrated to constitute a seven-component model-based decomposition method so as to accurately characterize the dominant and local scattering of ships. Based on the concepts of contrast and suppression, a robust scattering contribution difference feature is designed according to the derived scattering contributions. The constructed feature vector, combined with the polarization scattering angle, is inputted into the support vector machine to fulfill the recognition process. Simulated and real polarimetric radar data are utilized to test the proposed method, and the results show that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods by achieving the highest recognition rate of over 98%.
-
表 1 全极化SAR仿真系数
Table 1. Fully polarized SAR simulation parameter
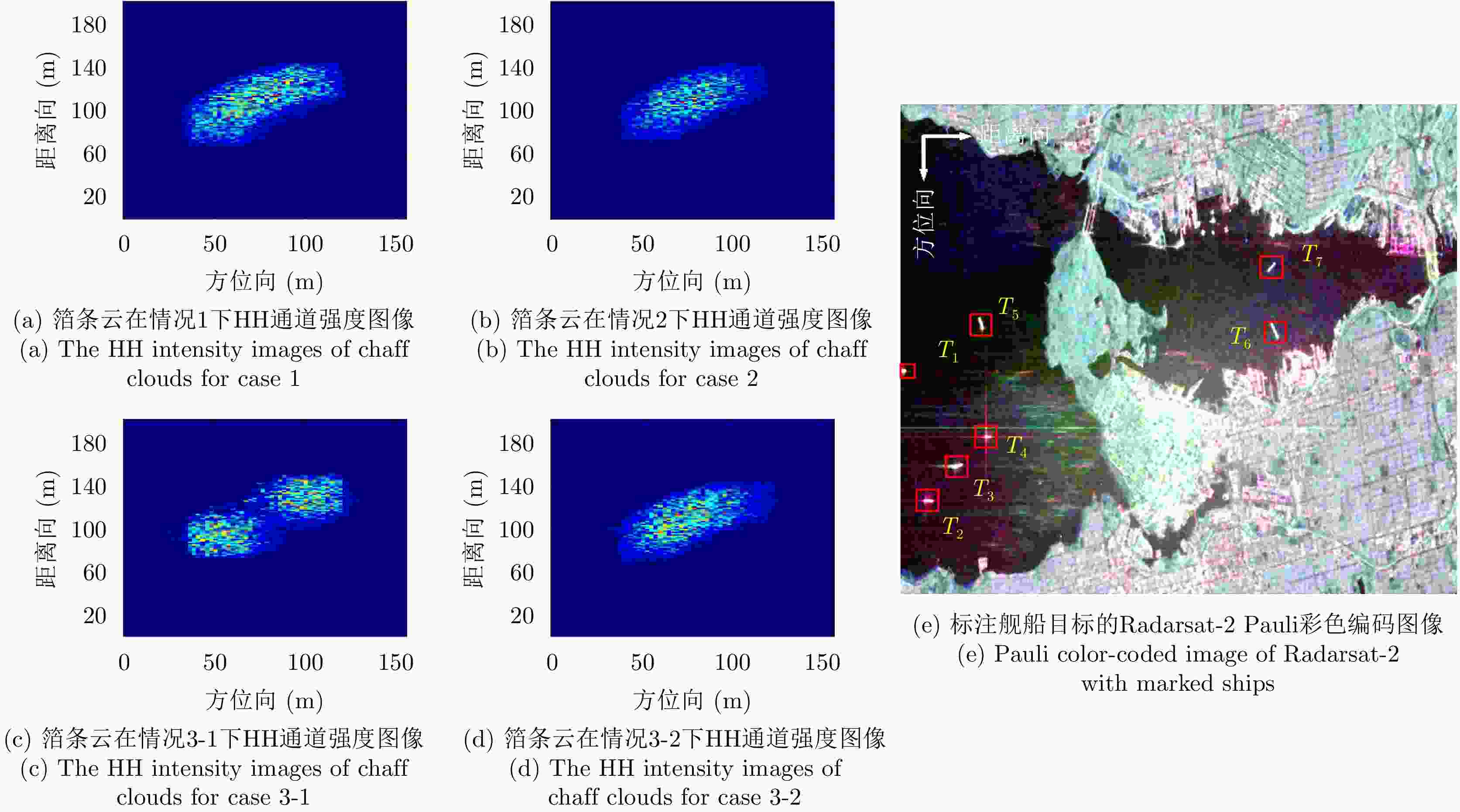
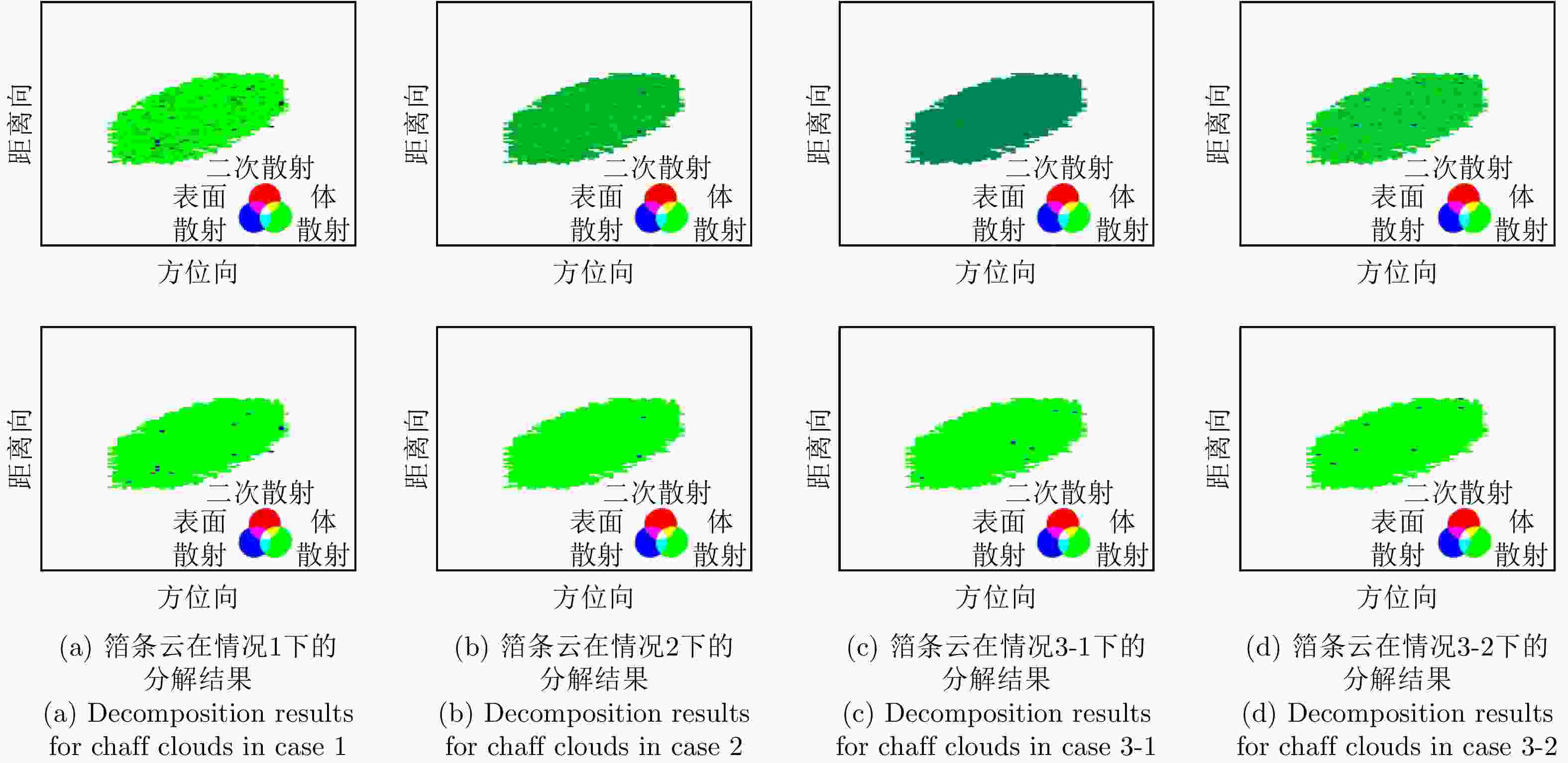
参数 取值 参数 取值 平台速度 400 m/s 方位向波束宽度 0.5° 信号载频 35 GHz 脉冲重复频率 400 Hz 信号带宽 150 MHz 平台高度 20 km 信号脉宽 5 μs 斜视角 70° 最近斜距 20 km 表 2 箔条云散射成分统计结果(%)
Table 2. Scattering contribution statistics for chaff clouds(%)
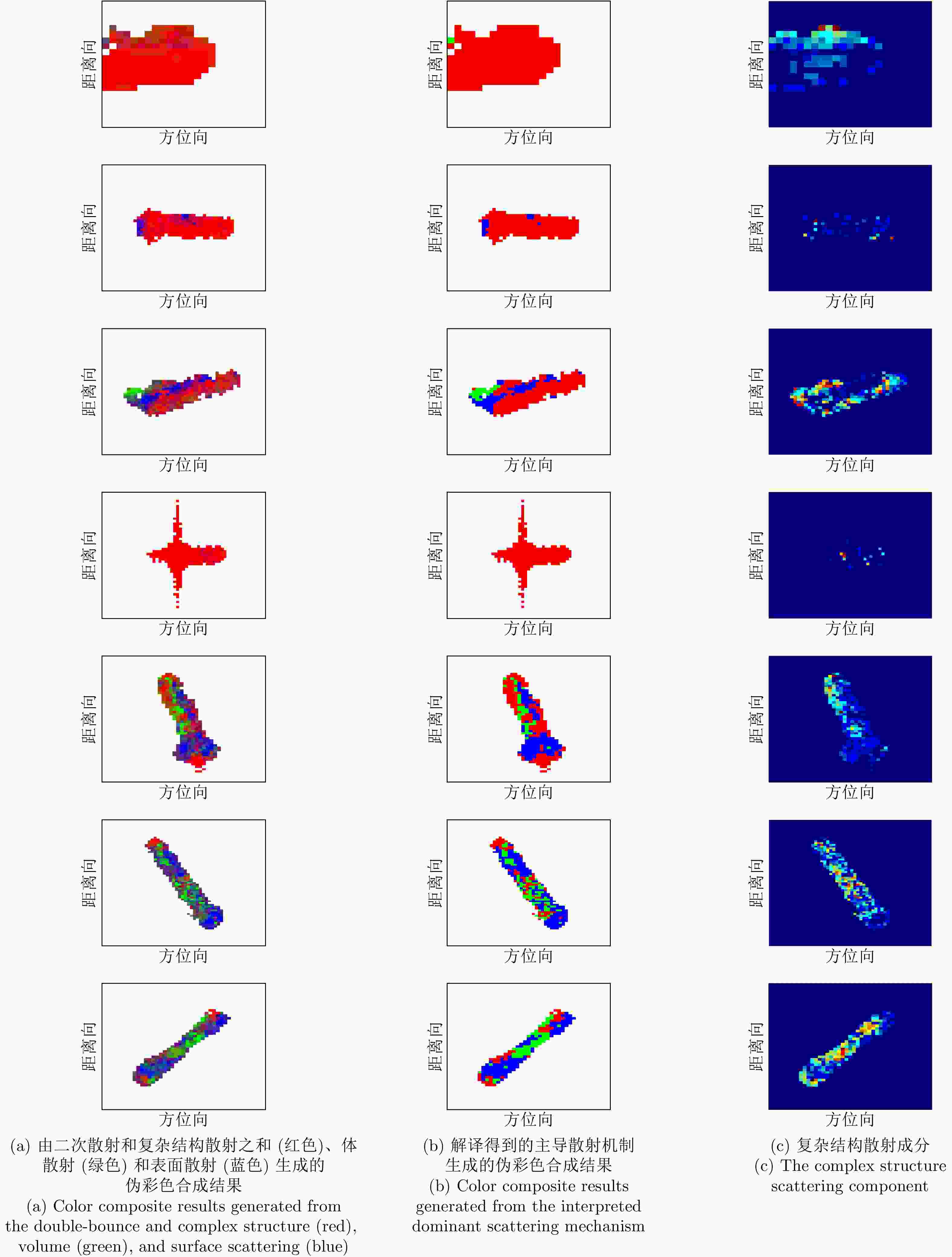
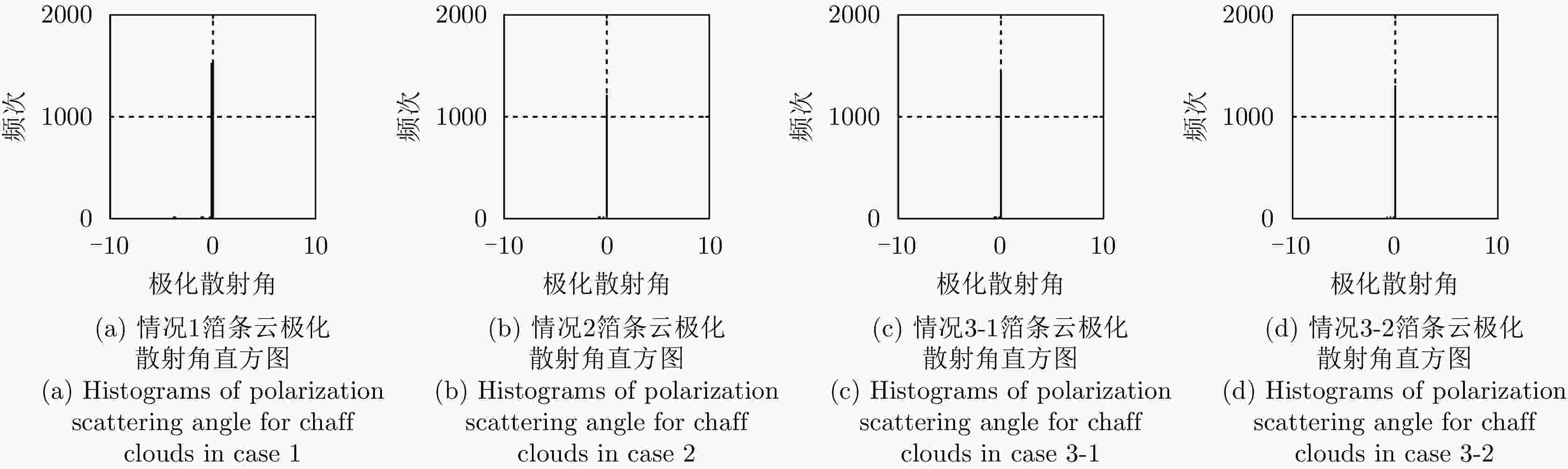
散射类型 情况1 情况2 情况3-1 情况3-2 表面散射 2.71 22.29 38.95 16.91 二次散射 0.86 0.04 0.14 0.08 体散射 93.52 77.13 60.50 82.45 螺旋体散射 0.53 0.40 0.36 0.42 OOD散射 0.55 0.12 0.05 0.06 ±45°OD 散射 0.92 0 0 0.02 ±45°OQW 散射 0.90 0.01 0 0.03 复杂结构散射 2.90 0.53 0.41 0.53 表 3 舰船目标散射成分统计结果(%)
Table 3. Scattering contribution statistics for ships (%)
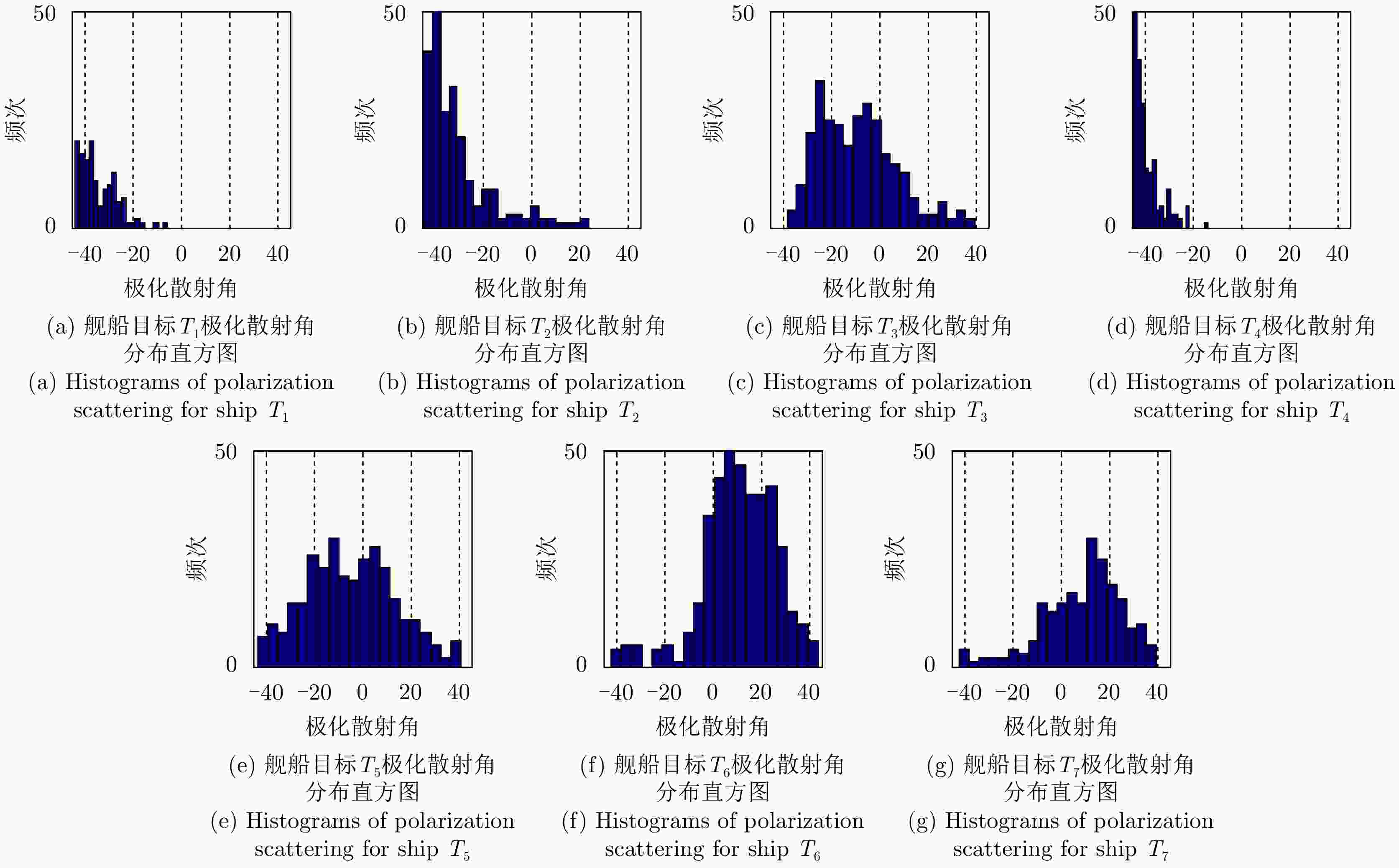
散射类型 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 表面散射 5.030 13.200 31.030 3.840 30.220 42.280 40.830 二次散射 83.560 84.710 55.050 95.300 32.460 12.000 12.080 体散射 5.350 1.530 7.890 0.610 23.830 30.170 33.070 螺旋体散射 2.690 0.120 2.410 0.060 7.410 6.460 9.990 OOD散射 0.300 0.050 0.110 0.030 1.480 0.490 0.060 ±45°OD散射 1.490 0.030 1.040 0.004 2.670 4.370 2.020 ±45°OQW散射 1.190 0.030 2.030 0.008 2.800 4.110 1.710 复杂结构散射 5.670 0.230 5.590 0.100 14.360 15.430 13.780 表 4 不同组合方法定量识别性能(%)
Table 4. Quantitative recognition performance for different composite methods(%)
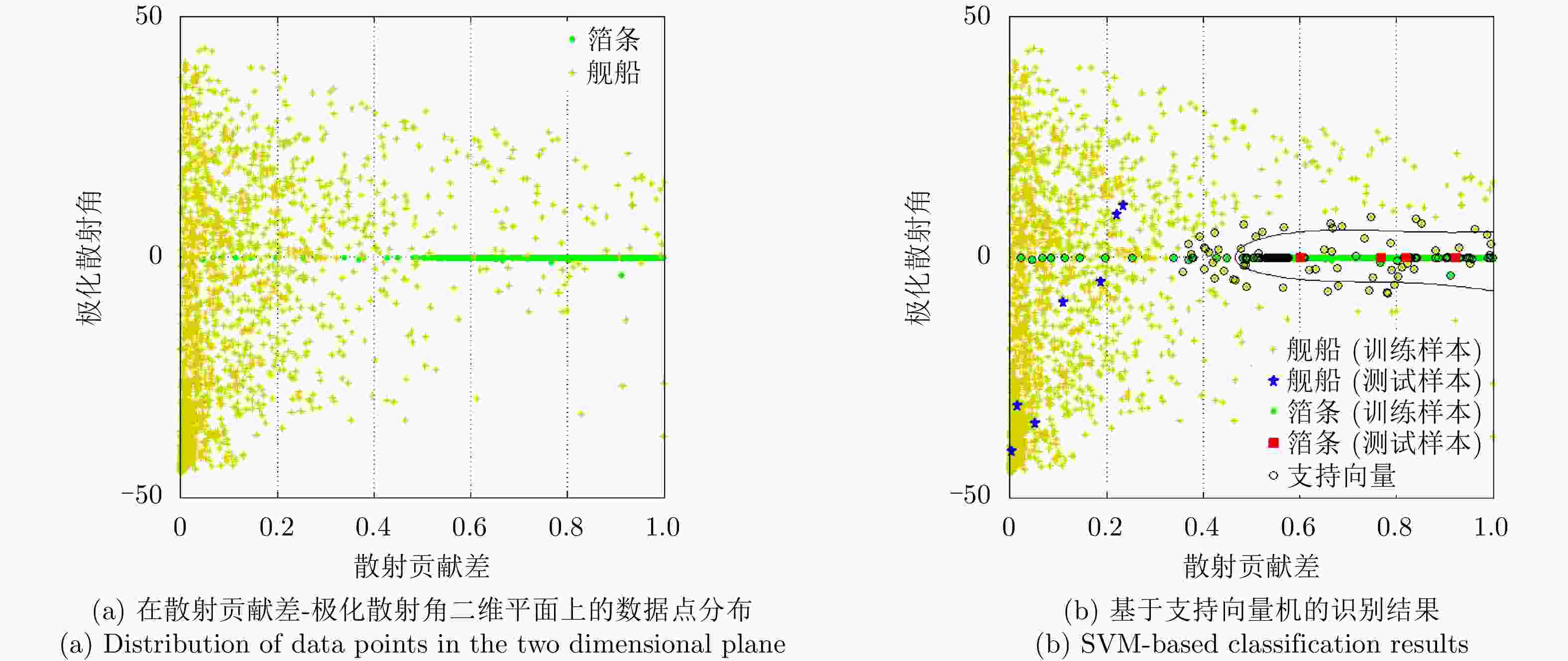
识别方法 正确识别率 漏检率 错误识别率 分类精度 本文方法 98.69 1.31 0.25 100.00 极化比-极化散射角-支持向量机 91.95 8.05 0 90.90 泛化体散射+极化散射角+支持向量机 94.29 5.71 0.89 100.00 散射贡献差-支持向量机 94.94 5.06 3.63 100.00 极化散射角-支持向量机 94.39 5.61 3.91 90.90 -
[1] 陈静. 雷达箔条干扰原理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2007.CHEN Jing. Principles of Radar Chaff Jamming[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2007. [2] MARCUS S W. Dynamics and radar cross section density of chaff clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2004, 40(1): 93–102. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2004.1292145 [3] BENDAYAN M and GARCIA A. Signal modeling of chaff in naval environment simulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(4): 3161–3166. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140922 [4] SEO D W, LEE J H, LEE H S, et al. Estimation of incoherent scattered field by multiple scatterers in random media[J]. ETRI Journal, 2016, 38(1): 141–148. doi: 10.4218/etrij.16.0114.1237 [5] 张杰, 张晰, 范陈清, 等. 极化SAR在海洋探测中的应用与探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 596–606. doi: 10.12000/JR16124ZHANG Jie, ZHANG Xi, FAN Chenqing, et al. Discussion on application of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar in marine surveillance[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 596–606. doi: 10.12000/JR16124 [6] 代大海, 廖斌, 肖顺平, 等. 雷达极化信息获取与处理的研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 143–155. doi: 10.12000/JR15103DAI Dahai, LIAO Bin, XIAO Shunping, et al. Advancements on radar polarization information acquisition and processing[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 143–155. doi: 10.12000/JR15103 [7] 赵春雷, 王亚梁, 阳云龙, 等. 雷达极化信息获取及极化信号处理技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 620–638. doi: 10.12000/JR16092ZHAO Chunlei, WANG Yaliang, YANG Yunlong, et al. Review of radar polarization information acquisition and polarimetric signal processing techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 620–638. doi: 10.12000/JR16092 [8] 杨建宇. 雷达对地成像技术多向演化趋势与规律分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 669–693. doi: 10.12000/JR19099YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–693. doi: 10.12000/JR19099 [9] 王雪松, 陈思伟. 合成孔径雷达极化成像解译识别技术的进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109WANG Xuesong and CHEN Siwei. Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar interpretation and recognition: Advances and perspectives[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(2): 259–276. doi: 10.12000/JR19109 [10] 李永祯, 李棉全, 程旭, 等. 雷达极化测量体制研究综述[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(9): 1873–1877. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.09.12LI Yongzhen, LI Mianquan, CHENG Xu, et al. Summarization of radar polarization measurement modes[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(9): 1873–1877. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2013.09.12 [11] 陈世超, 高鹤婷, 罗丰. 基于极化联合特征的海面目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 664–673. doi: 10.12000/JR20072CHEN Shichao, GAO Heting, and LUO Feng. Target detection in sea clutter based on combined characteristics of polarization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 664–673. doi: 10.12000/JR20072 [12] SHAO Xianhe, XUE Jinghong, and DU Hai. Theoretical analysis of polarization recognition between chaff cloud and ship[C]. 2007 International Workshop on Anti-Counterfeiting, Security and Identification, Xiamen, China, 2007: 125–129. doi: 10.1109/IWASID.2007.373711. [13] SHAO Xianhe, DU Hai, and XUE Jinghong. A target recognition method based on non-Linear polarization transformation[C]. 2007 International Workshop on Anti-Counterfeiting, Security and Identification, Xiamen, China, 2007: 157–163. doi: 10.1109/IWASID.2007.373718. [14] LI Xi, LIN Lianshan, and SHAO Xianhe. A target polarization recognition method for radar echoes[C]. 2010 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Chengdu, China, 2010: 1644–1647. doi: 10.1109/ICMMT.2010.5524748. [15] 李金梁, 曾勇虎, 申绪涧, 等. 改进的箔条干扰极化识别方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2015, 13(4): 350–355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2015.04.004LI Jinliang, ZENG Yonghu, SHEN Xujian, et al. Modified polarization recognition method for chaff jamming[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2015, 13(4): 350–355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2015.04.004 [16] TANG B, LI H M, and SHENG X Q. Jamming recognition method based on the full polarisation scattering matrix of chaff clouds[J]. IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, 2012, 6(13): 1451–1460. doi: 10.1049/iet-map.2012.0297 [17] YANG Yong, XIAO Shunping, FENG Dejun, et al. Polarisation oblique projection for radar seeker tracking in chaff centroid jamming environment without prior knowledge[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8(9): 1195–1202. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0388 [18] CUI Gang, SHI Longfei, MA Jiazhi, et al. Identification of chaff interference based on polarization parameter measurement[C]. The 2017 13th IEEE International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments, Yangzhou, China, 2017: 392–396. doi: 10.1109/ICEMI.2017.8265829. [19] HU Shengliang, WU Lingang, ZHANG Jun, et al. Research on chaff jamming recognition technology of anti-ship missile based on radar target characteristics[C]. The 2019 12th International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Xiangtan, China, 2019: 222–226. doi: 10.1109/ICICTA49267.2019.00054. [20] CRISTIANINI N and SHAWE-TAYLOR J. An Introduction to Support Vector Machines and Other Kernel-based Learning Methods[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2000: 198–216. [21] FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973. doi: 10.1109/36.673687 [22] YAMAGUCHI Y, MORIYAMA T, ISHIDO M, et al. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(8): 1699–1706. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.852084 [23] QUAN Sinong, XIONG Boli, XIANG Deliang, et al. Scattering characterization of obliquely oriented buildings from PolSAR data using eigenvalue-related model[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(5): 581. doi: 10.3390/rs11050581 [24] FAN Hui, QUAN Sinong, DAI Dahai, et al. Seven-component model-based decomposition for PolSAR data with sophisticated scattering models[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(23): 2802. doi: 10.3390/rs11232802 [25] SINGH G and YAMAGUCHI Y. Model-based six-component scattering matrix power decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 5687–5704. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2824322 [26] QUAN Sinong, XIANG Deliang, XIONG Boli, et al. A hierarchical extension of general four-component scattering power decomposition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(8): 856. doi: 10.3390/rs9080856 [27] QUAN Sinong, XIONG Boli, XIANG Deliang, et al. Derivation of the orientation parameters in built-up areas: With application to model-based decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4714–4730. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2835513 [28] YAJIMA Y, YAMAGUCHI Y, SATO R, et al. POLSAR image analysis of wetlands using a modified four-component scattering power decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(6): 1667–1673. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.916326 [29] SATO A, YAMAGUCHI Y, SINGH G, et al. Four-component scattering power decomposition with extended volume scattering model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(2): 166–170. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2011.2162935 [30] QUAN Sinong, XIONG Boli, XIANG Deliang, et al. Eigenvalue-based urban area extraction using polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(2): 458–471. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2787591 [31] LIU Yemin, XING Shiqi, LI Yongzhen, et al. Jamming recognition method based on the polarisation scattering characteristics of chaff clouds[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(11): 1689–1699. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0121 [32] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, XIAO Shunping, et al. General polarimetric model-based decomposition for coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(3): 1843–1855. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2255615 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: