Remote Sensing of Sea Surface Wind and Wave from Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar
-
摘要: 星载合成孔径雷达(SAR)能够全天时、全天候、高空间分辨率、宽刈幅观测海洋表面,是获取海面风场和波浪场信息的重要微波传感器。该文综述了多极化SAR海面风场遥感原理、地球物理模式函数,以及潜在应用(海气边界层现象、海上风能资源开发、台风监测与预警预报),系统总结了传统星载SAR、新型干涉和极化SAR海浪遥感方法和技术。随着雷达卫星编队飞行技术的逐步成熟,未来海洋卫星组网将成为全球海洋和极地观测新趋势,合成孔径雷达海面风场和波浪场定量遥感将从科学研究向业务化海洋动力环境监测发展。Abstract: Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) can observe the ocean surface with high spatial resolution and wide swath under all-weather conditions, day and night. Thus, it is a crucial microwave sensor for obtaining information on sea surface wind and wave fields. This paper reviews various geophysical model functions for wind and wave retrieval and SAR applications in studies of marine atmospheric boundary layer phenomena, offshore wind energy resource development, typhoon monitoring/forecast. The use of traditional SAR and new types of interferometric and polarized SAR data in ocean research are discussed. With the advance of radar satellite technology, the constellation of SAR satellites has become a new trend in the global ocean observations. Many SAR research algorithms have become mature enough to be implemented operationally to provide sea surface wind and wave fields to the scientific communities for ocean dynamic environment monitoring.
-
Key words:
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) /
- Sea surface wind /
- Wave
-
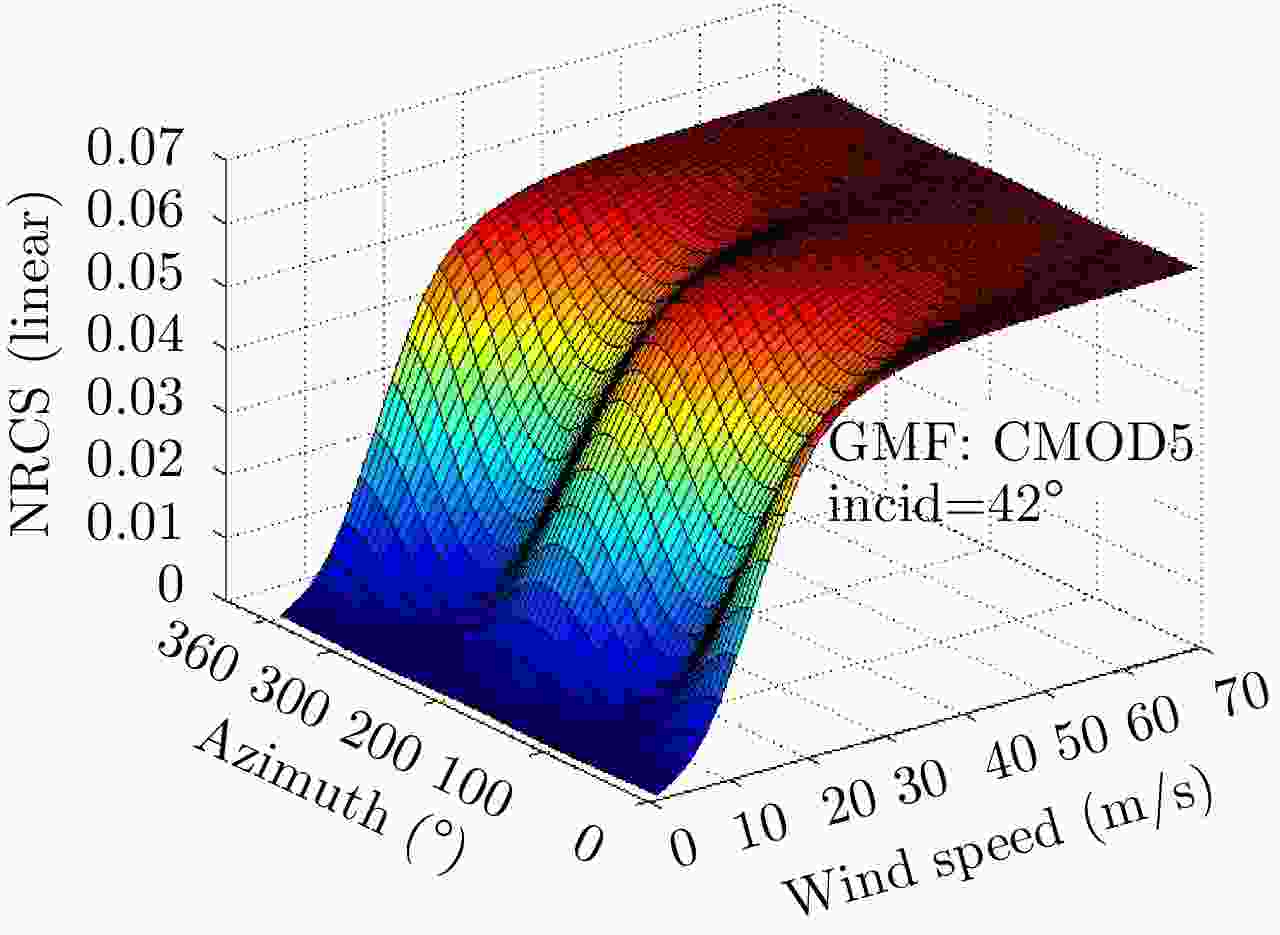
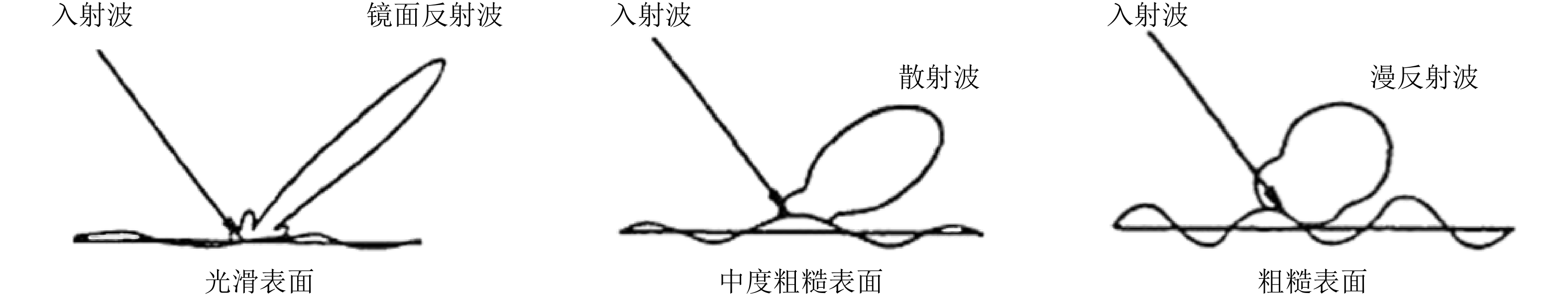
表 1 专用于SAR风场反演的地球物理模式函数汇总表
Table 1. GMFs developed for SAR wind retrievel
表 2 SAR风速遥感误差统计结果汇总表
Table 2. SAR wind speed retrieval statistics
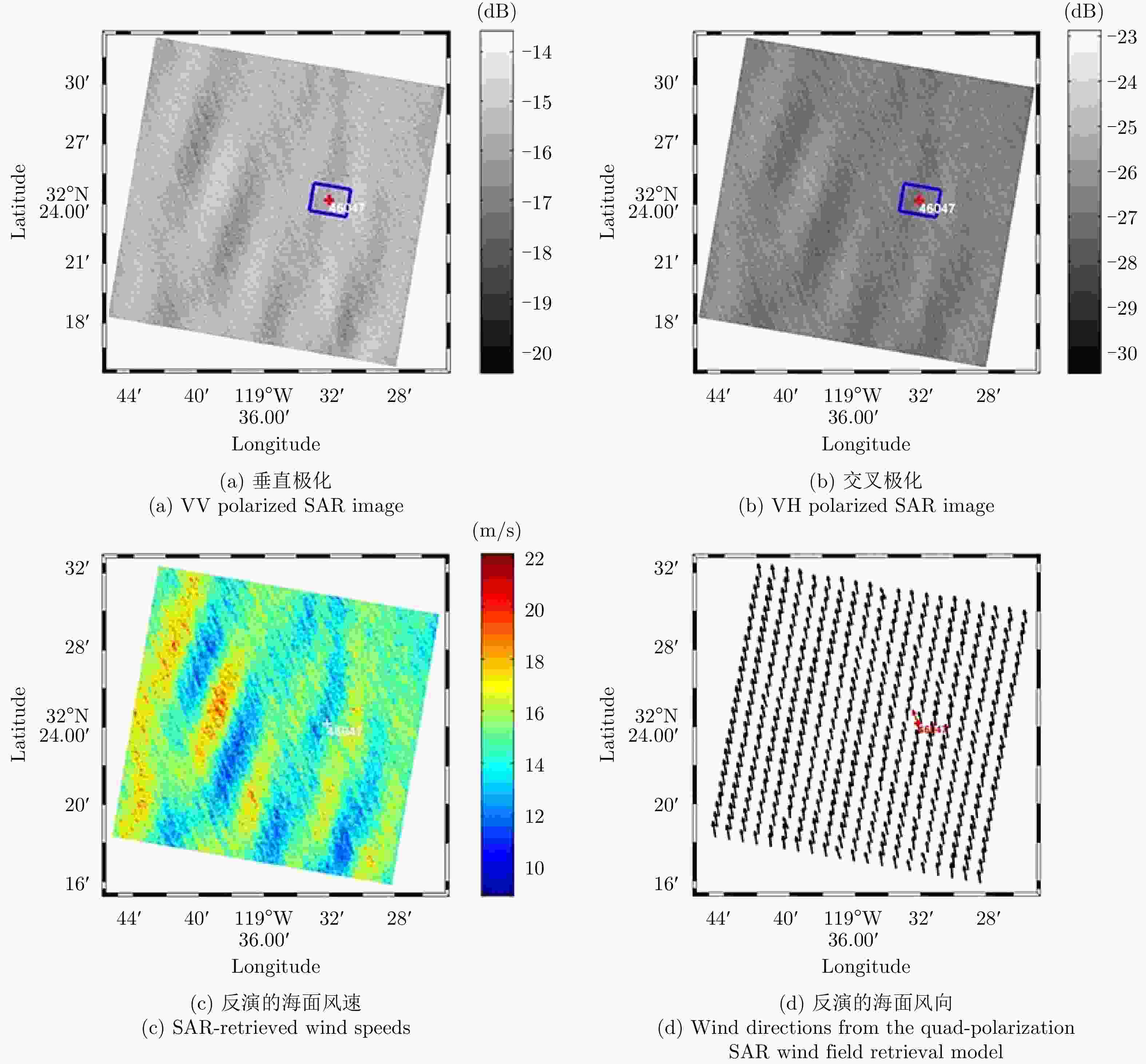
卫星 波段 极化 参考数据 反演误差*(m/s) 风速范围(m/s) 参考文献 RADARSAT-1 C HH 浮标 1.76 <20 Monaldo等人[62],2001 QuikSCAT散射计 1.54 <20 Thompson等人[63],2001 ENVISAT/ASAR C VV 浮标 1.41 <15 Yang等人[64],2011 ASCAT散射计 1.77 <15 NOGAPS数值模式 1.61 <15 Sentienl-1 C VV ASCAT散射计 1.42 <20 Monaldo等人[65],2016 HH ASCAT散射计 1.48 <25 VV+VH SMAP辐射计 2.59 <50 Mouche[66],2017 高分三号 C VV ASCAT散射计 2.04 <20 Ren等人[67],2019 HY2A/SCAT散射计 1.93 <20 HH ASCAT散射计 1.85 <20 HY2A/SCAT 1.73 <20 RADARSAT-2 C VH QuikSCAT 3.63 <40 Zhang等人[55],2014 VH SFMR辐射计 2.81 <40 Zhang等人[42],2017 TS-X/TD-X X VV 浮标 1.44 <20 Li等人[30],2014 HH 浮标 1.79 <15 Shao等人[26],2016 ALOS/PALSAR L HH 浮标 1.87 <20 Isoguchi等人[31],2009 ASCAT散射计 1.85 <25 *注:反演误差指均方根误差或标准偏差。 -
[1] BORN G H, DUNNE J A, LAME D B. Seasat mission overview[J]. Science, 1979, 204(4400): 1405–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.204.4400.1405 [2] STEWART R H. Seasat: Results of the mission[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1988, 69(12): 1441–1447. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1988)069<1441:SROTM>2.0.CO;2 [3] EVANS D L, ALPERS W, CAZENAVE A, et al. Seasat—A 25-year legacy of success[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2005, 94(3): 384–404. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2004.09.011 [4] JACKSON C R and APEL J R. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Marine User’s Manual[M]. Washington: NOAA, 2014: 1–464. [5] LI Xiaofeng, GUO Huadong, CHEN Kunshan, et al. Advances in SAR Remote Sensing of Oceans[M]. Boca Raton, FL 33487, USA: CRC Press, 2018. doi: 10.1201/9781351235822. [6] LI Xiaofeng. Hurricane Monitoring With Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2017:1–398. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-2893-9. [7] MONALDO F M, LI Xiaofeng, PICHEL W G, et al. Ocean wind speed climatology from spaceborne SAR imagery[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2014, 95(4): 565–569. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-12-00165.1 [8] STOPA J E and MOUCHE A. Significant wave heights from Sentinel‐1 SAR: Validation and applications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2017, 122(3): 1827–1848. doi: 10.1002/2016JC012364 [9] WRIGHT J. Backscattering from capillary waves with application to sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1966, 14(6): 749–754. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1966.1138799 [10] CHEN K S, FUNG A K, and WEISSMAN D A. A backscattering model for ocean surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1992, 30(4): 811–817. doi: 10.1109/36.158877 [11] APEL J R. An improved model of the ocean surface wave vector spectrum and its effects on radar backscatter[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1994, 99(C8): 16269–16291. doi: 10.1029/94jc00846 [12] ROMEISER R, ALPERS W, and WISMANN V. An improved composite surface model for the radar backscattering cross section of the ocean surface: 1. Theory of the model and optimization/validation by scatterometer data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(C11): 25237–25250. doi: 10.1029/97jc00190 [13] HWANG P A and PLANT W J. An analysis of the effects of swell and surface roughness spectra on microwave backscatter from the ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115(C4): C04014. doi: 10.1029/2009JC005558 [14] DU Yanlei, YANG Xiaofeng, CHEN Kunshan, et al. An improved spectrum model for sea surface radar backscattering at L-band[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(8): 776. doi: 10.3390/rs9080776 [15] XIE Dengfeng, CHEN Kunshan, and YANG Xiaofeng. Effects of wind wave spectra on radar backscatter from sea surface at different microwave bands: A numerical study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6325–6334. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2905558 [16] PORTABELLA M, STOFFELEN A, and JOHANNESSEN J A. Toward an optimal inversion method for synthetic aperture radar wind retrieval[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107(C8): 3086. doi: 10.1029/2001JC000925 [17] STOFFELEN A and ANDERSON D. Scatterometer data interpretation: Estimation and validation of the transfer function CMOD4[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(C3): 5767–5780. doi: 10.1029/96jc02860 [18] HERSBACH H, STOFFELEN A, and DE HAAN S. An improved C-band scatterometer ocean geophysical model function: CMOD5[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112(C3): C03006. doi: 10.1029/2006JC003743 [19] SOISUVARN S, JELENAK Z, CHANG P S, et al. CMOD5. H—A high wind geophysical model function for C-band vertically polarized satellite scatterometer measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(6): 3744–3760. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2219871 [20] LU Yiru, ZHANG Biao, PERRIE W, et al. A C-band geophysical model function for determining coastal wind speed using synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(7): 2417–2428. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2836661 [21] ZHANG Biao, MOUCHE A, LU Yiru, et al. A geophysical model function for wind speed retrieval from C-band HH-polarized synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(10): 1521–1525. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2905578 [22] LU Yiru, ZHANG Biao, PERRIE W, et al. CMODH validation for C-band synthetic aperture radar HH polarization wind retrieval over the ocean[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2967811 [23] THOMPSON D R, ELFOUHAILY T M, and CHAPRON B. Polarization ratio for microwave backscattering from the ocean surface at low to moderate incidence angles[C]. Sensing and Managing the Environment. 1998 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing. Symposium Proceedings, Seattle, USA, 1998: 1671–1673. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.1998.692411. [24] MOUCHE A, HAUSER D, DALOZE J F, et al. Dual-polarization measurements at C-band over the ocean: Results from airborne radar observations and comparison with ENVISAT ASAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(4): 753–769. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.843951 [25] LIU Guihong, YANG Xiaofeng, LI Xiaofeng, et al. A systematic comparison of the effect of polarization ratio models on sea surface wind retrieval from C-band synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2013, 6(3): 1100–1108. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2013.2242848 [26] SHAO Weizeng, LI Xiaoming, LEHNER S, et al. Development of polarization ratio model for sea surface wind field retrieval from TerraSAR-X HH polarization data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2014, 35(11/12): 4046–4063. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2014.916059 [27] BERGERON T, BERNIER M, CHOKMANI K, et al. Wind speed estimation using polarimetric RADARSAT-2 images: Finding the best polarization and polarization ratio[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2011, 4(12): 896–904. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2011.2158067 [28] MOUCHE A and CHAPRON B. Global C-band Envisat, RADARSAT-2 and Sentinel-1 SAR measurements in copolarization and cross‐polarization[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2015, 120(11): 7195–7207. doi: 10.1002/2015jc011149 [29] REN Yongzheng, LEHNER S, BRUSCH S, et al. An algorithm for the retrieval of sea surface wind fields using X-band TerraSAR-X data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2012, 33(23): 7310–7336. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2012.685977 [30] LI Xiaoming and LEHNER S. Algorithm for sea surface wind retrieval from TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2928–2939. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2267780 [31] ISOGUCHI O and SHIMADA M. An L-band ocean geophysical model function derived from PALSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(7): 1925–1936. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2010864 [32] ZHOU Xuan, CHONG Jinsong, YANG Xiaofeng, et al. Ocean surface wind retrieval using SMAP L-band SAR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(1): 65–74. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2630919 [33] ZHANG Biao, PERRIE W, and HE Yijun. Wind speed retrieval from RADARSAT-2 quad-polarization images using a new polarization ratio model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2011, 116(C8): C08008. doi: 10.1029/2010JC006522 [34] VACHON P W and WOLFE J. C-band cross-polarization wind speed retrieval[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(3): 456–459. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2085417 [35] ZHANG Biao, PERRIE W. Cross-polarized synthetic aperture radar: A new potential measurement technique for hurricanes[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2012, 93(4): 531–541. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00001.1 [36] ZHANG Guosheng, LI Xiaofeng, PERRIE W, et al. A hurricane wind speed retrieval model for C-band RADARSAT-2 cross-polarization ScanSAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(8): 4766–4774. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2699622 [37] TROITSKAYA Y, ABRAMOV V, BAIDAKOV G, et al. Cross-polarization GMF for high wind speed and surface stress retrieval[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2018, 123(8): 5842–5855. doi: 10.1029/2018JC014090 [38] HWANG P A, STOFFELEN A, VAN ZADELHOFF G J, et al. Cross-polarization geophysical model function for C-band radar backscattering from the ocean surface and wind speed retrieval[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2015, 120(2): 893–909. doi: 10.1002/2014JC010439 [39] HWANG P A, PERRIE W, and ZHANG Biao. Cross-polarization radar backscattering from the ocean surface and its dependence on wind velocity[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(12): 2188–2192. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2324276 [40] VAN ZADELHOFF G J, STOFFELEN A, VACHON P W, et al. Retrieving hurricane wind speeds using cross-polarization C-band measurements[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2014, 7(2): 437–449. doi: 10.5194/amt-7-437-2014 [41] YE Xiaomin, LIN Mingsen, ZHENG Quanan, et al. A typhoon wind-field retrieval method for the Dual-polarization SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(10): 1511–1515. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2902418 [42] ZHANG Guosheng, PERRIE W, LI Xiaofeng, et al. A hurricane morphology and sea surface wind vector estimation model based on C-band cross-polarization SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(3): 1743–1751. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2631663 [43] SHAO Weizeng, YUAN Xinzhe, SHENG Yexin, et al. Development of wind speed retrieval from cross-polarization Chinese gaofen-3 synthetic aperture radar in typhoons[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 412. doi: 10.3390/s18020412 [44] GERLING T W. Structure of the surface wind field from the Seasat SAR[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1986, 91(C2): 2308–2320. doi: 10.1029/JC091iC02p02308 [45] LEHNER S, HORSTMANN J, KOCH W, et al. Mesoscale wind measurements using recalibrated ERS SAR images[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1998, 103(C4): 7847–7856. doi: 10.1029/97JC02726 [46] DU Yong, VACHON P W, WOLFE J. Wind direction estimation from SAR images of the ocean using wavelet analysis[J]. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 2002, 28(3): 498–509. doi: 10.5589/m02-029 [47] FICHAUX N and RANCHIN T. Combined extraction of high spatial resolution wind speed and wind direction from SAR images: A new approach using wavelet transform[J]. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 2002, 28(3): 510–516. doi: 10.5589/m02-038 [48] HORSTMANN J, KOCH W, LEHNER S, et al. Ocean winds from RADARSAT-1 ScanSAR[J]. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 2002, 28(3): 524–533. doi: 10.5589/m02-043 [49] HORSTMANN J, KOCH W, and LEHNER S. Ocean wind fields retrieved from the advanced synthetic aperture radar aboard ENVISAT[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2004, 54(6): 570–576. doi: 10.1007/s10236-004-0098-3 [50] KOCH W. Directional analysis of SAR images aiming at wind direction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(4): 702–710. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.818811 [51] ZHOU Lizhang, ZHENG Gang, LI Xiaofeng, et al. An improved local gradient method for sea surface wind direction retrieval from SAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(7): 671. doi: 10.3390/rs9070671 [52] ZHENG Gang, LI Xiaofeng, ZHOU Lizhang, et al. Development of a gray-level co-occurrence matrix-based texture orientation estimation method and its application in sea surface wind direction retrieval from SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(9): 5244–5260. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2812778 [53] WANG He, YANG Jingsong, MOUCHE A, et al. GF-3 SAR ocean wind retrieval: The first view and preliminary assessment[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(7): 694. doi: 10.3390/rs9070694 [54] ZHANG Biao, PERRIE W, VACHON P W, et al. Ocean vector winds retrieval from C-band fully polarimetric SAR measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(11): 4252–4261. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2194157 [55] ZHANG Biao, PERRIE W, ZHANG J A, et al. High-resolution hurricane vector winds from C-band dual-polarization SAR observations[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2014, 31(2): 272–286. doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-13-00006.1 [56] FAN Shengren, ZHANG Biao, MOUCHE A A, et al. Estimation of wind direction in tropical cyclones using C-band dual-polarization synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(2): 1450–1462. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2946885 [57] MONALDO F. The Alaska SAR demonstration and near-real-time synthetic aperture radar winds[J]. Johns Hopkins APL Technical Digest, 2000, 21(1): 75–79. [58] XU Qing, LIN Hui, LI Xiaofeng, et al. Assessment of an analytical model for sea surface wind speed retrieval from spaceborne SAR[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2010, 31(4): 993–1008. doi: 10.1080/01431160902922870 [59] PICHEL W G, LI Xiaofeng, MONALDO F, et al. Envisat ASAR applications demonstrations: Alaska SAR demonstration and Gulf of Mexico hurricane studies[C]. Envisat Symposium 2007, Montreux, Switzerland, 2007: 23–27. [60] YANG Xiaofeng, LI Xiaofeng, ZHENG Quanan, et al. Comparison of ocean-surface winds retrieved from QuikSCAT scatterometer and radarsat-1 SAR in offshore waters of the U. S. west coast[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(1): 163–167. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2053345 [61] VACHON P W and DOBSON F W. Validation of wind vector retrieval from ERS-1 SAR images over the ocean[J]. Global Atmosphere and Ocean System, 1996, 5(2): 177–187. [62] MONALDO F M, THOMPSON D R, BEAL R C, et al. Comparison of SAR-derived wind speed with model predictions and ocean buoy measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(12): 2587–2600. doi: 10.1109/36.974994 [63] THOMPSON D R, MONALDO F M, BEAL R C, et al. Combined estimates improve high-resolution coastal wind mapping[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 2001, 82(41): 469–469. doi: 10.1029/01EO00278 [64] YANG Xiaofeng, LI Xiaofeng, PICHEL W G, et al. Comparison of ocean surface winds from ENVISAT ASAR, MetOp ASCAT scatterometer, buoy measurements, and NOGAPS model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(12): 4743–4750. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2159802 [65] MONALDO F, JACKSON C, LI Xiaofeng, et al. Preliminary evaluation of sentinel-1A wind speed retrievals[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(6): 2638–2642. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2504324 [66] MOUCHE A A, CHAPRON B, ZHANG Biao, et al. Combined co- and cross-polarized SAR measurements under extreme wind conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 6746–6755. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2732508 [67] REN Lin, YANG Jingsong, MOUCHE A A, et al. Assessments of ocean wind retrieval schemes used for Chinese gaofen-3 synthetic aperture radar co-polarized data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 7075–7085. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2911325 [68] TOPOUZELIS K and KITSIOU D. Detection and classification of mesoscale atmospheric phenomena above sea in SAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015, 160(4): 263–272. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.02.006 [69] XU Qing, LI Xiaofeng, BAO Shaowu, et al. SAR observation and numerical simulation of mountain Lee Waves near Kuril islands forced by an extratropical cyclone[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(12): 7157–7165. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2596678 [70] CHUNCHUZOV I, VACHON P W, and LI X. Analysis and modeling of atmospheric gravity waves observed in RADARSAT SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2000, 74(3): 343–361. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(00)00076-6 [71] VACHON P W, JOHANNESSEN O M, and JOHANNESSEN J A. An ERS 1 synthetic aperture radar image of atmospheric lee waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1994, 99(C11): 22483–22490. doi: 10.1029/94JC01392 [72] LI Xiaofeng, DONG Changming, CLEMENTE‐COLÓN P, et al. Synthetic aperture radar observation of the sea surface imprints of upstream atmospheric solitons generated by flow impeded by an island[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2004, 109(C2): C02016. doi: 10.1029/2003JC002168 [73] LIU Shuming, LI Ziwei, YANG Xiaofeng, et al. Atmospheric frontal gravity waves observed in satellite SAR images of the Bohai Sea and Huanghai Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2010, 29(5): 35–43. doi: 10.1007/s13131-010-0061-8 [74] CHENG C and ALPERS W. Investigation of trapped atmospheric gravity waves over the South China Sea using Envisat Synthetic Aperture Radar images[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2010, 31(17/18): 4725–4742. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2010.485145 [75] LI Xiaofeng, ZHENG Weizhong, YANG Xiaofeng, et al. Sea surface imprints of coastal mountain lee waves imaged by synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2011, 116(C2): C02014. doi: 10.1029/2010JC006643 [76] ALPERS W and HUANG Weigen. On the discrimination of radar signatures of atmospheric gravity waves and oceanic internal waves on synthetic aperture radar images of the sea surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(3): 1114–1126. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2072930 [77] LI Xiaofeng, ZHENG Weizhong, YANG Xiaofeng, et al. Coexistence of atmospheric gravity waves and boundary layer rolls observed by SAR[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2013, 70(11): 3448–3459. doi: 10.1175/JAS-D-12-0347.1 [78] LI Xiaofeng, CLEMENTE-COLÓN P, PICHEL W G, et al. Atmospheric vortex streets on a RADARSAT SAR image[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2000, 27(11): 1655–1658. doi: 10.1029/1999GL011212 [79] LI Xiaofeng, ZHENG Weizhong, ZOU Chengzhi, et al. A SAR observation and numerical study on ocean surface imprints of atmospheric vortex streets[J]. Sensors, 2008, 8(5): 3321–3334. doi: 10.3390/s8053321 [80] LI Xiaofeng, ZHENG Weizhong, PICHEL W H, et al. Coastal katabatic winds imaged by SAR[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(3): L03804. doi: 10.1029/2006GL028055 [81] CHELTON D B, FREILICH M H, and ESBENSEN S K. Satellite observations of the wind jets off the pacific coast of Central America. Part I: Case studies and statistical characteristics[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2000, 128(7): 1993–2018. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(2000)128<1993:SOOTWJ>2.0.CO;2 [82] GOHM A and MAYR G J. Numerical and observational case-study of a deep Adriatic bora[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2005, 131(608): 1363–1392. doi: 10.1256/qj.04.82 [83] WINSTEAD N S, COLLE B, BOND N, et al. Using SAR remote sensing, field observations, and models to better understand coastal flows in the gulf of Alaska[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2006, 87(6): 787–800. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-87-6-787 [84] ALPERS W, IVANOV A, and HORSTMANN J. Observations of bora events over the adriatic sea and black sea by spaceborne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2009, 137(3): 1150–1161. doi: 10.1175/2008MWR2563.1 [85] SHIMADA T and KAWAMURA H. Summertime gap winds of the Soya Strait induced by the developed Okhotsk high[J]. Atmospheric Science Letters, 2011, 12(3): 316–320. doi: 10.1002/asl.345 [86] LI Xiaofeng, ZHENG Weizhong, YANG Xiaofeng, et al. Sea fetch observed by synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 272–279. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2605670 [87] SIKORA T D, FRIEDMAN K S, PICHEL W G, et al. Synthetic aperture radar as a tool for investigating polar mesoscale cyclones[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2000, 15(6): 745–758. doi: 10.1175/1520-0434(2000)015<0745:SARAAT>2.0.CO;2 [88] CHUNCHUZOV I, VACHON P W, and RAMSAY B. Detection and characterization of mesoscale cyclones in RADARSAT synthetic aperture radar images of the Labrador sea[J]. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 2000, 26(3): 213–230. doi: 10.1080/07038992.2000.10874771 [89] MOORE G W K and VACHON P W. A polar low over The Labrador Sea: Interactions with topography and an upper-level potential vorticity anomaly, and an observation by RADARSAT-1 SAR[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2002, 29(16): 1773. doi: 10.1029/2001GL014007 [90] FUREVIK B R, SCHYBERG H, NOER G, et al. ASAR and ASCAT in polar low situations[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2015, 32(4): 783–792. doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-14-00154.1 [91] IVANOV A Y. Novaya Zemlya bora and polar cyclones in spaceborne SAR and optical imagery[J]. Izvestiya, Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics, 2016, 52(9): 1142–1154. doi: 10.1134/S0001433816090127 [92] THOMPSON T W, LIU W T, and WEISSMAN D E. Synthetic aperture radar observation of ocean roughness from rolls in an unstable marine boundary layer[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1983, 10(12): 1172–1175. doi: 10.1029/GL010i012p01172 [93] ALPERS W and BRÜMMER B. Atmospheric boundary layer rolls observed by the synthetic aperture radar aboard the ERS-1 satellite[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1994, 99(C6): 12613–12621. doi: 10.1029/94JC00421 [94] MÜLLER G, BRÜMMER B, and ALPERS W. Roll convection within an arctic cold-air outbreak: Interpretation of in situ aircraft measurements and spaceborne SAR imagery by a three-dimensional atmospheric model[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1999, 127(3): 363–380. doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1999)127<0363:RCWAAC>2.0.CO;2 [95] VANDEMARK D, MOURAD P D, BAILEY S A, et al. Measured changes in ocean surface roughness due to atmospheric boundary layer rolls[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2001, 106(C3): 4639–4654. doi: 10.1029/1999JC000051 [96] LEVY G. Boundary layer roll statistics from SAR[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(10): 1993–1995. doi: 10.1029/2000GL012667 [97] HUANG Lanqing, LI Xiaofeng, LIU Bin, et al. Tropical cyclone boundary layer rolls in synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2018, 123(4): 2981–2996. doi: 10.1029/2018JC013755 [98] LI Xiaofeng, YANG Xiaofeng, ZHENG Weizhong, et al. Synergistic use of satellite observations and numerical weather model to study atmospheric occluded fronts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(9): 5269–5279. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2420312 [99] BARTHELMIE R J and PRYOR S C. Can satellite sampling of offshore wind speeds realistically represent wind speed distributions?[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2003, 42(1): 83–94. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(2003)042<0083:CSSOOW>2.0.CO;2 [100] PRYOR S C, NIELSEN M, BARTHELMIE R J, et al. Can satellite sampling of offshore wind speeds realistically represent wind speed distributions? Part II: Quantifying uncertainties associated with distribution fitting methods[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2004, 43(5): 739–750. doi: 10.1175/2096.1 [101] AHSBAHS T, MACLAURIN G, DRAXL C, et al. US East Coast synthetic aperture radar wind atlas for offshore wind energy[J]. Wind Energy Science, 2019. doi: 10.5194/wes-2019-16 [102] WEISSMAN D E, KING D B, and THOMPSON T W. Relationship between hurricane surface winds and l-band radar backscatter from the sea surface[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 1979, 18(8): 1023–1034. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(1979)018<1023:RBHSWA>2.0.CO;2 [103] HORSTMANN J, THOMPSON D R, MONALDO F, et al. Can synthetic aperture radars be used to estimate hurricane force winds?[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005, 32(22): L22801. doi: 10.1029/2005GL023992 [104] KATSAROS K B, VACHON P W, BLACK P G, et al. Wind fields from SAR: Could they improve our understanding of storm dynamics?[J]. Johns Hopkins APL Technical Digest, 2000, 21(1): 86–93. [105] VALENZUELA G R. Theories for the interaction of electromagnetic and oceanic waves—A review[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 1978, 13(1/4): 61–85. doi: 10.1007/bf00913863 [106] KUDRYAVTSEV V, HAUSER D, CAUDAL G, et al. A semiempirical model of the normalized radar cross-section of the sea surface 1. Background model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(C3): 8054. doi: 10.1029/2001jc001003 [107] LI Xiaofeng, ZHANG J A, YANG Xiaofeng, et al. Tropical cyclone morphology from spaceborne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2013, 94(2): 215–230. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00211.1 [108] REPPUCCI A, LEHNER S, SCHULZ-STELLENFLETH J, et al. Tropical cyclone intensity estimated from wide-swath SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(4): 1639–1649. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2037143 [109] ZHOU Xuan, YANG Xiaofeng, LI Ziwei, et al. Estimation of tropical cyclone parameters and wind fields from SAR images[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2013, 56(11): 1977–1987. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4633-2 [110] SHAO Weizeng, LI Xiaofeng, HWANG P, et al. Bridging the gap between cyclone wind and wave by C-band SAR measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2017, 122(8): 6714–6724. doi: 10.1002/2017JC012908 [111] JIN Shaohui, LI Xiaofeng, YANG Xiaofeng, et al. Identification of tropical cyclone centers in SAR imagery based on template matching and particle swarm optimization algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(1): 598–608. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2018.2863259 [112] KHURSHID S, BRADLEY D, and MANORE M. National SAR wind product – user requirements document, meteorological service of Canada[R]. Montreal, QC, Canada: Environment Canada, 2012. [113] YU Yi, YANG Xiaofeng, ZHANG Weimin, et al. Assimilation of sentinel-1 derived sea surface winds for typhoon forecasting[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(8): 845. doi: 10.3390/rs9080845 [114] DUAN Boheng, ZHANG Weimin, YANG Xiaofeng, et al. Assimilation of typhoon wind field retrieved from scatterometer and SAR based on the Huber norm quality control[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(10): 987. doi: 10.3390/rs9100987 [115] HASSELMANN K and HASSELMANN S. On the nonlinear mapping of an ocean wave spectrum into a synthetic aperture radar image spectrum and its inversion[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1991, 96(C6): 10713–10729. doi: 10.1029/91jc00302 [116] ENGEN G and JOHNSEN H. SAR-ocean wave inversion using image cross spectra[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1995, 33(4): 1047–1056. doi: 10.1109/36.406690 [117] MASTENBROEK C and DE VALK C F. A semiparametric algorithm to retrieve ocean wave spectra from synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2000, 105(C2): 3497–3516. doi: 10.1029/1999jc900282 [118] SCHULZ-STELLENFLETH J, KÖNIG T, and LEHNER S. An empirical approach for the retrieval of integral ocean wave parameters from synthetic aperture radar data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112(C3): C03019. doi: 10.1029/2006JC003970 [119] LI Xiaoming, LEHNER S, and BRUNS T. Ocean wave integral parameter measurements using Envisat ASAR wave mode data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 155–174. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2052364 [120] MAROM M, GOLDSTEIN R M, THORNTON E B, et al. Remote sensing of ocean wave spectra by interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Nature, 1990, 345(6278): 793–795. doi: 10.1038/345793a0 [121] LYZENGA D R and BENNETT J R. Estimation of ocean wave spectra using two-antenna SAR systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1991, 29(3): 463–465. doi: 10.1109/36.79437 [122] SHEMER L. On the focusing of the ocean swell images produced by a regular and by an interferometric SAR[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1995, 16(5): 925–947. doi: 10.1080/01431169508954452 [123] BAO Mingquan, BRUNING C, and ALPERS W. Simulation of ocean waves imaging by an along-track interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(3): 618–631. doi: 10.1109/36.581977 [124] BAO Mingquan, ALPERS W, and BRUNING C. A new nonlinear integral transform relating ocean wave spectra to phase image spectra of an along-track interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(1): 461–466. doi: 10.1109/36.739088 [125] HE Yijun and ALPERS W. On the nonlinear integral transform of an ocean wave spectrum into an along-track interferometric synthetic aperture radar image spectrum[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(C6): 3205. doi: 10.1029/2002JC001560 [126] 张彪, 何宜军. 干涉合成孔径雷达海浪遥感研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2006, 21(1): 11–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2006.01.003ZHANG Biao and HE Yijun. The study on remote sensing of ocean wave by interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2006, 21(1): 11–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2006.01.003 [127] ZHANG Biao, HE Yijun, and VACHON P W. Numerical simulation and validation of ocean waves measured by an along-track interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2008, 26(1): 1–8. doi: 10.1007/s00343-008-0001-z [128] ZHANG Biao, PERRIE W, and HE Yijun. Remote sensing of ocean waves by along-track interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2009, 114(C10): C10015. doi: 10.1029/2009JC005310 [129] SCHULZ-STELLENFLETH J and LEHNER S. Ocean wave imaging using an airborne single pass across-track interferometric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 38–45. doi: 10.1109/36.898663 [130] SCHULZ-STELLENFLETH J, HORSTMANN J, LEHNER S, et al. Sea surface imaging with an across-track interferometric synthetic aperture radar: The SINEWAVE experiment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(9): 2017–2028. doi: 10.1109/36.951092 [131] 张彪, 何宜军. 交轨干涉SAR涌浪干涉相位模型及数值模拟[J]. 电波科学学报, 2007, 22(6): 1014–1019, 1028. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2007.06.024ZHANG Biao and HE Yijun. Interferometric phase model and numerical simulations of swell for across-track interferometric SAR[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2007, 22(6): 1014–1019, 1028. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0388.2007.06.024 [132] 张彪. 干涉合成孔径雷达海浪遥感[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 84–86.ZHANG Biao. Remote Sensing of Ocean Wave by Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019: 84–86. [133] SCHULER D L and LEE J S. A microwave technique to improve the measurement of directional ocean wave spectra[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1995, 16(2): 199–215. doi: 10.1080/01431169508954390 [134] SCHULER D L, LEE J S, KASILINGAM D, et al. Measurement of ocean surface slopes and wave spectra using polarimetric SAR image data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2004, 91(2): 198–211. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2004.03.008 [135] HE Yijun, PERRIE W, XIE Tao, et al. Ocean wave spectra from a linear polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(11): 2623–2631. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.836813 [136] HE Yijun, SHEN Hui, and PERRIE W. Remote sensing of ocean waves by polarimetric SAR[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2006, 23(12): 1768–1773. doi: 10.1175/JTECH1948.1 [137] ZHANG Biao, PERRIE W, and HE Yijun. Validation of RADARSAT-2 fully polarimetric SAR measurements of ocean surface waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115(C6): C06031. doi: 10.1029/2009JC005887 [138] 何宜军, 孟雷, 李海艳, 等. 全极化合成孔径雷达海浪遥感方法[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2007, 22(2): 177–182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2007.02.012HE Yijun, MENG Lei, LI Haiyan, et al. Ocean wave measured by fully polarimetric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2007, 22(2): 177–182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2007.02.012 [139] ZHANG Biao, LI Xiaofeng, PERRIE W, et al. Synergistic measurements of ocean winds and waves from SAR[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2015, 120(9): 6164–6184. doi: 10.1002/2015JC011052 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: