Statistical Modeling Methods of Single-channel Complex-valued SAR Images for Ship Detection
-
摘要: 合成孔径雷达(SAR)成像模式丰富、覆盖范围广、分辨率高,可以长期、动态、宏观地对海洋进行监测。在完全发展的相干斑假设条件下,传统单通道SAR图像舰船目标检测方法主要研究幅度信息。然而,其部分假设条件在高分辨率情形下并非严格成立,因此无法有效利用单通道SAR图像的相位或复值信息。该文面向舰船目标检测应用,将单通道复值SAR图像统计建模方法划分为幅度、相位和复值统计建模3个部分,首先简要综述了单通道SAR图像幅度统计建模方法,然后详细阐述了单通道SAR图像相位和复值统计建模方法,并重点介绍了其建模过程和参数估计方法。在此基础上,该文给出了作者研究小组在基于复值统计信息的单通道SAR图像舰船目标检测方面的部分最新研究结果,并分析展望了下一步研究方向。Abstract: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), which features rich imaging modes, wide coverage, and high resolution, is an effective technique for long-term, dynamic, and large-scale monitoring of the ocean. Under the assumption of fully developed speckle, traditional ship detection methods in single-channel SAR images focus mainly on amplitude information. Since conventional assumptions are not strictly true in high-resolution situations, this prevents the full investigation of phase or complex-valued information in single-channel SAR images. In this paper, with a focus on ship detection applications, we categories the methods used in the statistical modeling of single-channel complex-valued SAR images as amplitude-, phase-, or complex-valued-based. After providing a brief overview of amplitude statistical modeling methods, we focus on phase and complex-valued statistical modeling methods of single-channel SAR images, describing their modeling processes and parameter estimation methods. We then present the results of our recent ship detection research based on complex-valued statistical information in single-channel SAR images and make suggestions regarding future research.
-
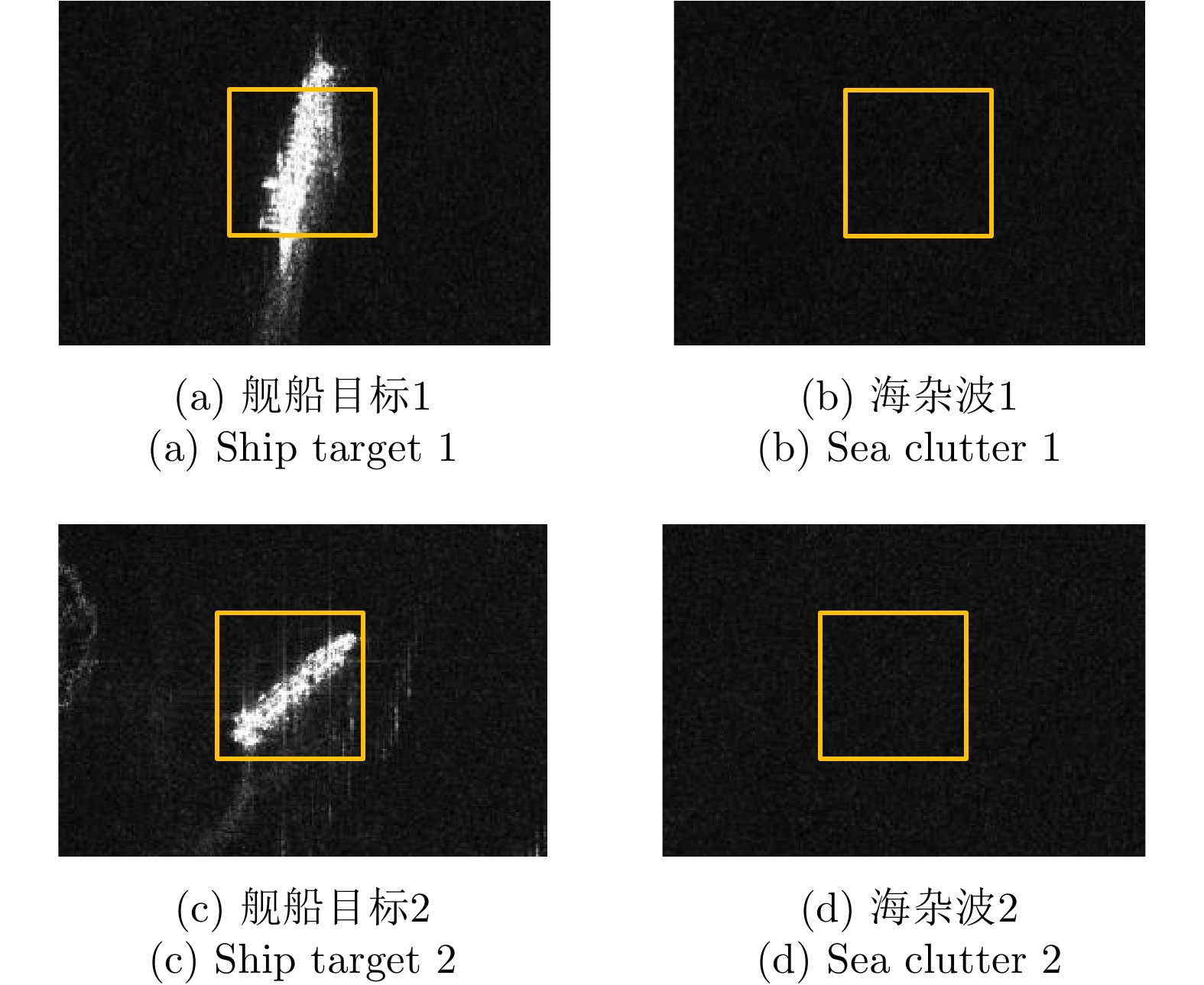
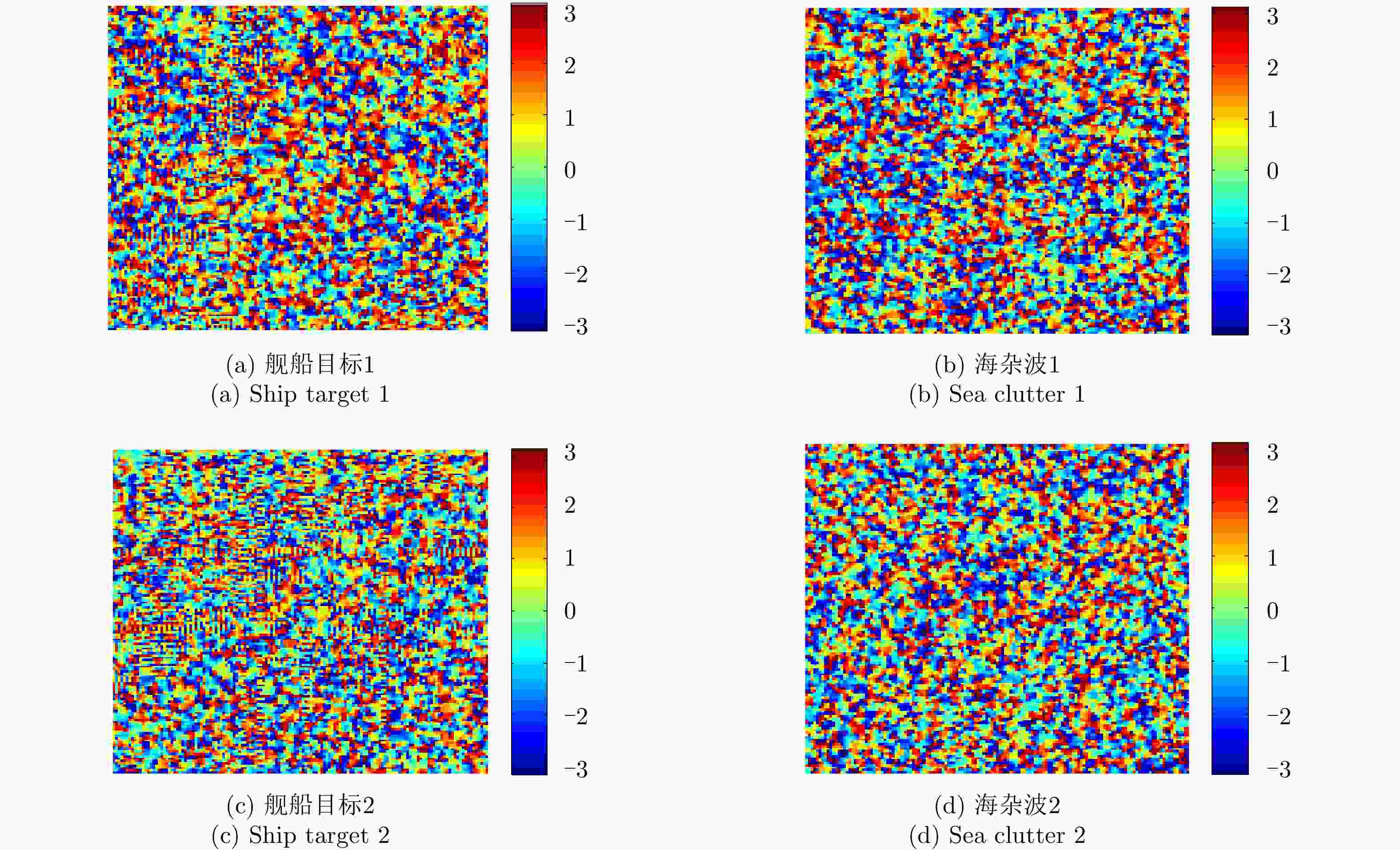
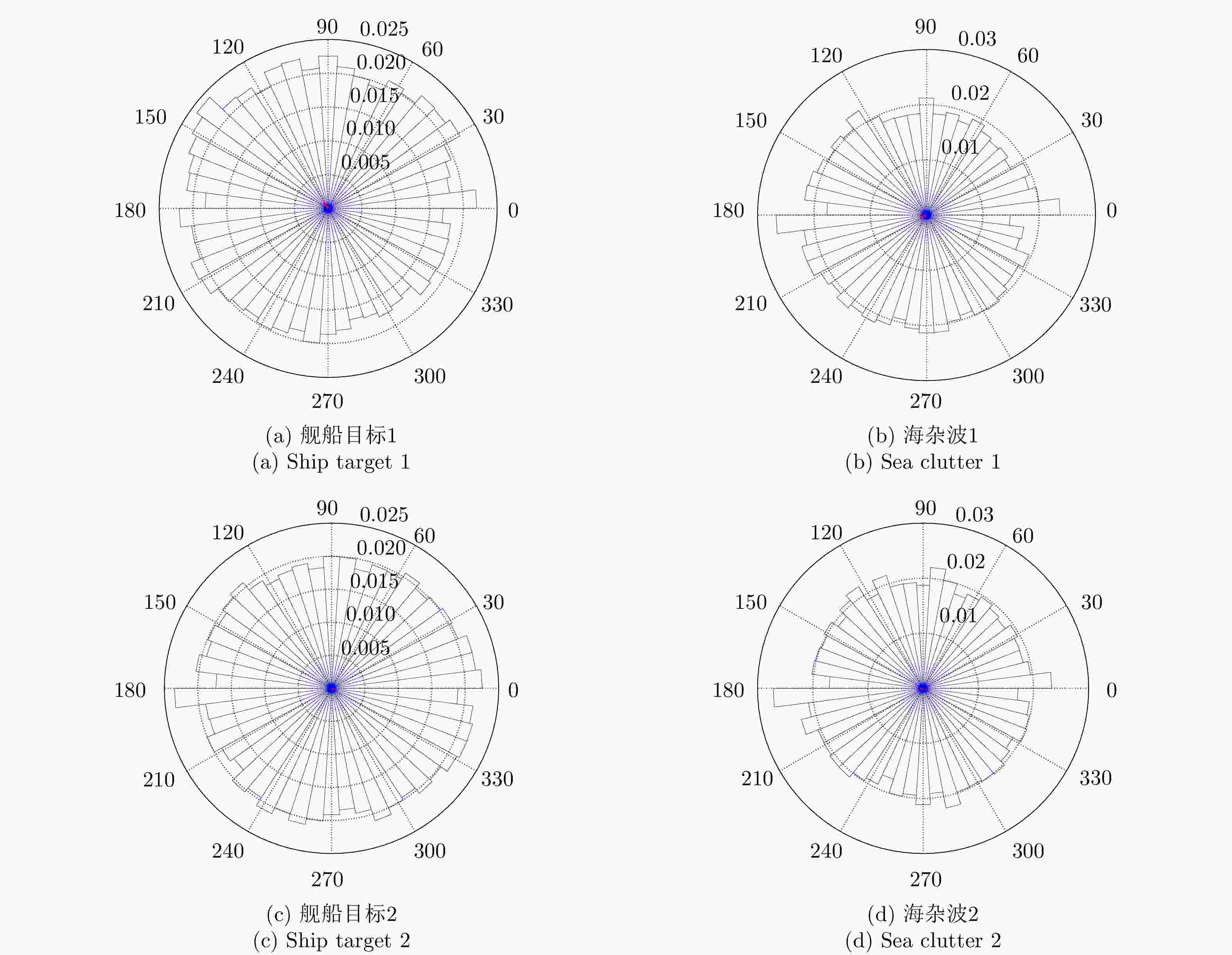
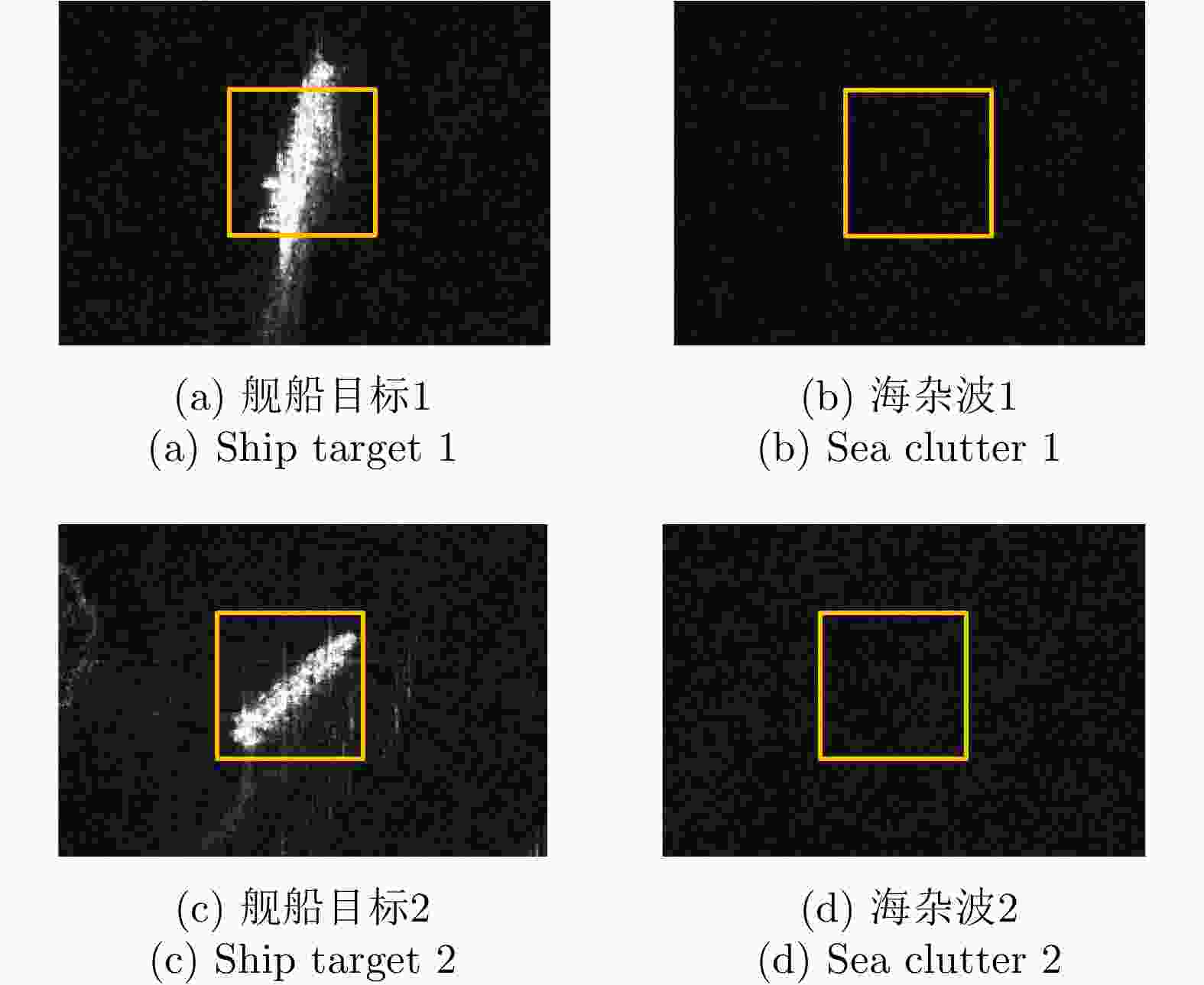
表 1 TerraSAR-X舰船目标和海杂波相位图像循环统计量结果
Table 1. Circular statistical results of TerraSAR-X ship target and sea clutter
循环统计量 均值 方差 标准差 平均长度 偏度 峰度 (a) 舰船目标1 2.21 0.95 2.46 0.05 0 –0.01 (b) 海杂波1 –2.72 0.96 2.49 0.04 –0.01 0.01 (c) 舰船目标2 –0.34 0.98 2.84 0.02 0.01 –0.01 (d) 海杂波2 –2.87 0.98 2.83 0.02 0.01 0 表 2 TerraSAR-X舰船目标和海杂波的邻域相位方向差图像循环统计量结果
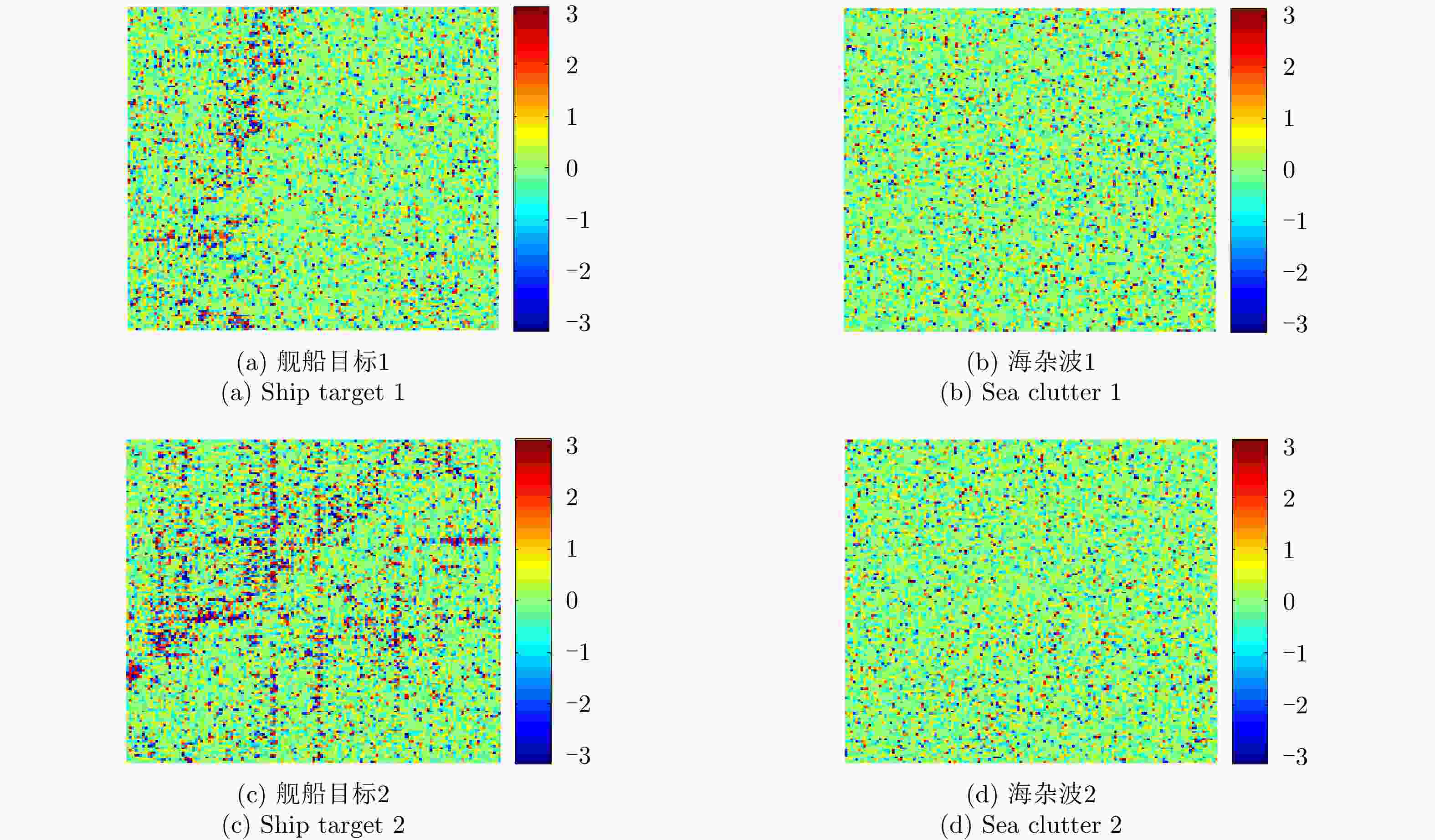
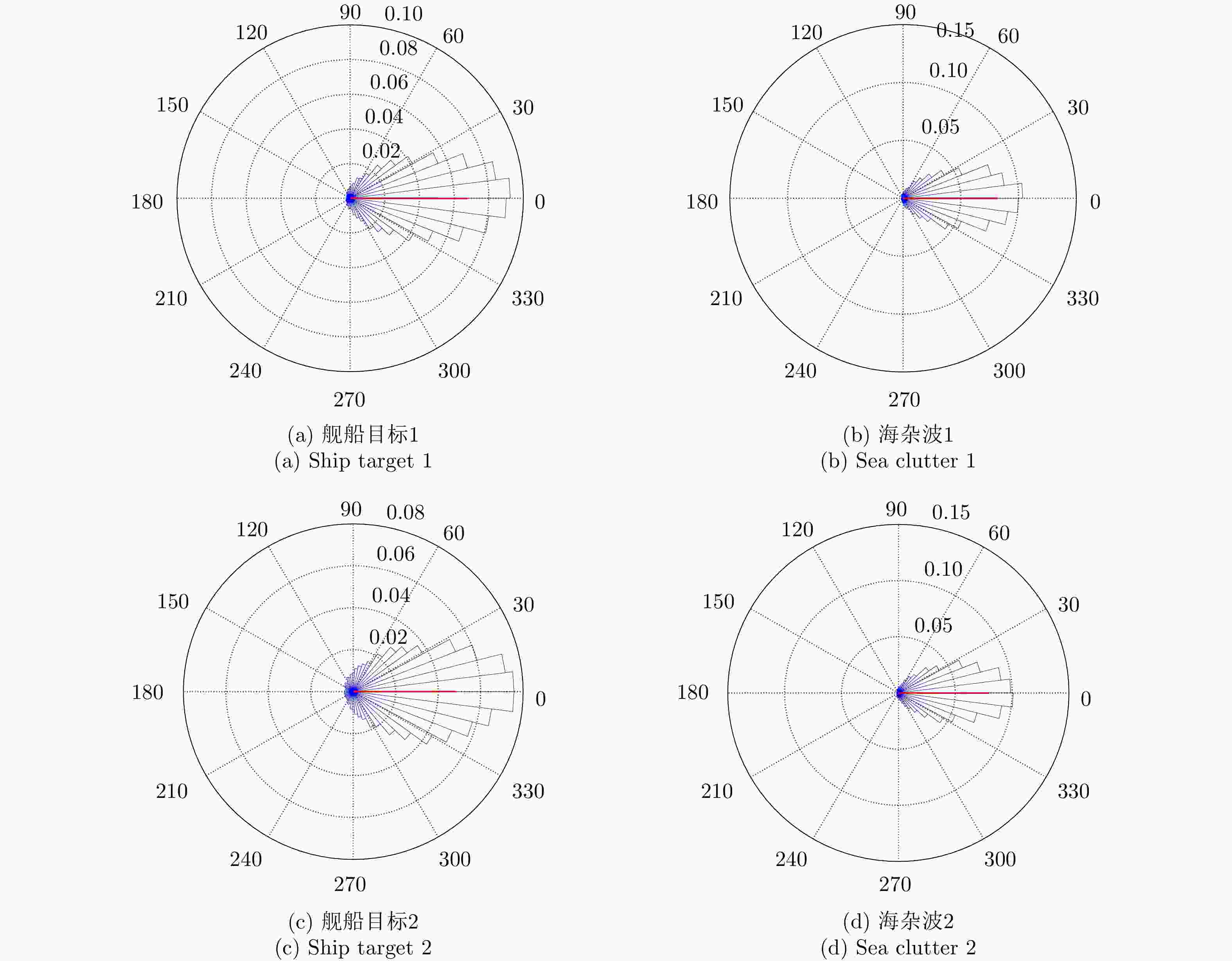
Table 2. Circular statistical results of TerraSAR-X ship target and sea clutter NPDD images
循环统计量 均值 方差 标准差 平均长度 偏度 峰度 (a) 舰船目标1 0 0.27 0.79 0.73 0 0.46 (b) 海杂波1 0 0.21 0.69 0.79 0 0.53 (c) 舰船目标2 0 0.37 0.96 0.63 0 0.35 (d) 海杂波2 0 0.21 0.69 0.79 0.01 0.53 -
[1] LEE J S and POTTIER E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2009. [2] OLIVER C and QUEGAN S. Understanding Synthetic Aperture Radar Images[M]. Boston: SciTech Publishing, 2004. [3] 邓云凯, 赵凤军, 王宇. 星载SAR技术的发展趋势及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015DENG Yunkai, ZHAO Fengjun, and WANG Yu. Brief analysis on the development and application of Spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015 [4] 杨建宇. 雷达对地成像技术多向演化趋势与规律分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099 [5] 金亚秋. 多模式遥感智能信息与目标识别: 微波视觉的物理智能[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083JIN Yaqiu. Multimode remote sensing intelligent information and target recognition: Physical intelligence of microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083 [6] 杜兰, 王兆成, 王燕, 等. 复杂场景下单通道SAR目标检测及鉴别研究进展综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104DU Lan, WANG Zhaocheng, WANG Yan, et al. Survey of research progress on target detection and discrimination of single-channel SAR images for complex scenes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104 [7] CRISP D J. The state-of-the-art in ship detection in synthetic aperture radar imagery[R]. DATO-RR-0272, 2004. [8] GAO G, GAO S, and HE J. Maritime Surveillance with SAR Data[M]. Chapter. Ship Detection. IET book, in publishing. [9] GAO Gui. Statistical modeling of SAR images: A survey[J]. Sensors, 2010, 10(1): 775–795. doi: 10.3390/s100100775 [10] VESPE M and GREIDANUS H. SAR image quality assessment and indicators for vessel and oil spill detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(11): 4726–4734. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2190293 [11] VELOTTO D, SOCCORSI M, and LEHNER S. Azimuth ambiguities removal for ship detection using full polarimetric X-band SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1): 76–88. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2236337 [12] GREIDANUS H, CLAYTON P, INDREGARD M, et al. Benchmarking operational SAR ship detection[C]. 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, USA, 2004: 4215–4218. [13] OUCHI K. Current status on vessel detection and classification by synthetic aperture radar for maritime security and safety[C]. The 38th Symposium on Remote Sensing for Environmental Sciences, Gamagori, Aichi, Japan, 2016: 5–12. [14] PAN Zongxu, LIU Lei, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Fast vessel detection in Gaofen-3 SAR images with ultrafine strip-map mode[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(7): 1578. doi: 10.3390/s17071578 [15] AN Quanzhi, PAN Zongxu, and YOU Hongjian. Ship detection in Gaofen-3 SAR images based on sea clutter distribution analysis and deep convolutional neural network[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 334. doi: 10.3390/s18020334 [16] WANG Shigang, WANG Min, YANG Shuyuan, et al. New hierarchical saliency filtering for fast ship detection in high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 351–362. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2606481 [17] IERVOLINO P and GUIDA R. A novel ship detector based on the generalized-likelihood ratio test for SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(8): 3616–3630. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2692820 [18] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, YANG Kai, et al. A bilateral CFAR algorithm for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(7): 1536–1540. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2412174 [19] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, ZHOU Shilin, et al. An adaptive ship detection scheme for spaceborne SAR imagery[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(9): 1345. doi: 10.3390/s16091345 [20] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, XING Xiangwei, et al. Area ratio invariant feature group for ship detection in SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(7): 2376–2388. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2820078 [21] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Ship detection based on complex signal kurtosis in single-channel SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6447–6461. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2906054 [22] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Discriminating ship from radio frequency interference based on noncircularity and non-Gaussianity in Sentinel-1 SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(1): 352–363. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2854661 [23] EL-DARYMLI K, MCGUIRE P, GILL E W, et al. Characterization and statistical modeling of phase in single-channel synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(3): 2071–2092. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140711 [24] EL-DARYMLI K, MOLONEY C, GILL E, et al. Nonlinearity and the effect of detection on single-channel synthetic aperture radar imagery[C]. OCEANS 2014-TAIPEI, Taipei, China, 2014: 1–7. [25] OLLILA E. On the circularity of a complex random variable[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2008, 15: 841–844. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2008.2005050 [26] OLLILA E, KOIVUNEN V, and POOR H V. Complex-valued signal processing—essential models, tools and statistics[C]. 2011 Information Theory and Applications Workshop, La Jolla, USA, 2011: 1–10. [27] OLLILA E, ERIKSSON J, and KOIVUNEN V. Complex elliptically symmetric random variables—Generation, characterization, and circularity tests[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(1): 58–69. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2083655 [28] ERIKSSON J and KOIVUNEN V. Complex random vectors and ICA models: Identifiability, uniqueness, and separability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(3): 1017–1029. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.864440 [29] ERIKSSON J, OLLILA E, and KOIVUNEN V. Essential statistics and tools for complex random variables[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(10): 5400–5408. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2054085 [30] NOVEY M, ADALI T, and ROY A. Circularity and Gaussianity detection using the complex generalized Gaussian distribution[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2009, 16(11): 993–996. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2009.2028412 [31] NOVEY M, ADALI T, and ROY A. A complex generalized Gaussian distribution—Characterization, generation, and estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(3): 1427–1433. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2036049 [32] NOVEY M, OLLILA E, and ADALI T. On testing the extent of noncircularity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(11): 5632–5637. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2162951 [33] SCHREIER P J and SCHARF L L. Statistical Signal Processing of Complex-valued Data: The Theory of Improper and Noncircular Signals[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010. [34] WU Wenjin, GUO Huadong, LI Xinwu, et al. Urban land use information extraction using the ultrahigh-resolution Chinese airborne SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(10): 5583–5599. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2425658 [35] WU Wenjin, LI Xinwu, GUO Huadong, et al. Noncircularity parameters and their potential applications in UHR MMW SAR data sets[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(10): 1547–1551. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2595762 [36] SOCCORSI M and DATCU M. Stochastic models of SLC HR SAR images[C]. 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 2007: 3887–3890. [37] SOCCORSI M, DATCU M, and GLEICH D. TerraSAR-X: Complex Image Inversion for Feature Extraction[C]. 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, USA, 2008: III-99–III-102. [38] 冷祥光, 计科峰, 周石琳. SAR图像方位模糊去除方法研究[C]. 第五届高分辨率对地观测学术年会论文集, 西安, 2018.LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, and ZHOU Shilin. Research on azimuth ambiguity removal methods in SAR imagery[C]. The 5th China High Resolution Earth Observation Conference, Xi’an, China, 2018. [39] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Azimuth ambiguities removal in littoral zones based on multi-temporal SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(8): 866. doi: 10.3390/rs9080866 [40] JAKEMAN E and PUSEY P. A model for non-Rayleigh sea echo[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1976, 24(6): 806–814. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1976.1141451 [41] GOLDSTEIN G B. False-alarm regulation in log-normal and Weibull clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1973, AES–9(1): 84–92. [42] TRUNK G V and GEORGE S F. Detection of targets in non-Gaussian sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1970, AES–6(5): 620–628. [43] DANA R A and KNEPP D L. The impact of strong scintillation on space based radar design II: Noncoherent detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES–22(1): 34–46. [44] TISON C, NICOLAS J M, TUPIN F, et al. A new statistical model for Markovian classification of urban areas in high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(10): 2046–2057. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.834630 [45] KURUOGLU E E and ZERUBIA J. Modeling SAR images with a generalization of the Rayleigh distribution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 527–533. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.818017 [46] MIGLIACCIO M, FERRARA G, GAMBARDELLA A, et al. A physically consistent speckle model for marine SLC SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2007, 32(4): 839–847. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2007.903985 [47] LIAO Mingsheng, WANG Changcheng, WANG Yong, et al. Using SAR images to detect ships from sea clutter[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(2): 194–198. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.915593 [48] FERRARA G, MIGLIACCIO M, NUNZIATA F, et al. Generalized-K (GK)-based observation of metallic objects at sea in full-resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data: A multipolarization study[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2011, 36(2): 195–204. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2011.2109491 [49] SAHED M, MEZACHE A, and LAROUSSI T. A novel [z log(z)]-based closed form approach to parameter estimation of K-distributed clutter plus noise for radar detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(1): 492–505. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.140180 [50] ROSENBERG L, WATTS S, and BOCQUET S. Application of the K+Rayleigh distribution to high grazing angle sea-clutter[C]. 2014 International Radar Conference, Lille, France, 2014: 1–6. [51] ROSENBERG L and BOCQUET S. Application of the Pareto plus noise distribution to medium grazing angle sea-clutter[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(1): 255–261. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2347957 [52] MIDDLETON D. New physical-statistical methods and models for clutter and reverberation: The KA-distribution and related probability structures[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1999, 24(3): 261–284. doi: 10.1109/48.775289 [53] DONG Yunhan. Distribution of X-band high resolution and high grazing angle sea clutter[R]. DSTO-RR-0316, 2006. [54] ROSENBERG L, CRISP D J, and STACY N J. Analysis of the KK-distribution with medium grazing angle sea-clutter[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2010, 4(2): 209–222. [55] FICHE A, ANGELLIAUME S, ROSENBERG L, et al. Analysis of X-band SAR sea-clutter distributions at different grazing angles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(8): 4650–4660. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2405577 [56] FICHE A, ANGELLIAUME S, ROSENBERG L, et al. Statistical analysis of low grazing angle high resolution X-band SAR sea clutter[C]. 2014 International Radar Conference, Lille, France, 2014: 1–6. [57] 秦先祥. 基于广义Gamma分布的SAR图像统计建模及应用研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2015.QIN Xianxiang. Research on statistical modeling of SAR images and its application based on generalized Gamma distribution[D]. [Ph. D. Dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2015. [58] ACHIM A, KURUOGLU E E, and ZERUBIA J. SAR image filtering based on the heavy-tailed Rayleigh model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(9): 2686–2693. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.877362 [59] RIHACZEK A W and HERSHKOWITZ S J. Theory and Practice of Radar Target Identification[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2000. [60] RIHACZEK A W and HERSHKOWITZ S J. Radar Resolution and Complex-image Analysis[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1996. [61] JAO J K, LEE C E, and AYASLI S. Coherent spatial filtering for SAR detection of stationary targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic systems, 1999, 35(2): 614–626. doi: 10.1109/7.766942 [62] DATCU M, SCHWARZ G, SOCCORSI M, et al. Phase information contained in meter-scale SAR images[C]. SPIE SAR Image Analysis, Modeling, and Techniques IX, Florence, Italy, 2007: 67460H. [63] Circular data analysis[EB/OL]. https://ncss-wpengine.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/themes/ncss/pdf/Procedures/NCSS/Circular_Data_Analysis.pdf. [64] FISHER N I. Statistical Analysis of Circular Data[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1995. [65] MARDIA K V and JUPP P E. Directional Statistics[M]. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2009. [66] EVANS M, HASTINGS N, and PEACOCK B. Statistical Distributions[M]. 3rd ed. New York: Wiley, 2000: 117–118. [67] EL-DARYMLI K, MCGUIRE P, POWER D, et al. Rethinking the phase in single-channel SAR imagery[C]. 2013 14th International Radar Symposium, Dresden, Germany, 2013: 429–436. [68] EL-DARYMLI K, MOLONEY C, GILL E, et al. On circularity/noncircularity in single-channel synthetic aperture radar imagery[C]. 2014 Oceans-St. John’s, St. John’s, Canada, 2014: 1–4. [69] EL-DARYMLI K, MCGUIRE P, GILL E W, et al. Holism-based features for target classification in focused and complex-valued synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52(2): 786–808. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140757 [70] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Fast shape parameter estimation of the complex generalized Gaussian distribution in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, in press. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2960095 [71] FANG Kaitai, KOTZ S, and NG K W. Symmetric Multivariate and Related Distributions[M]. London: Chapman and Hall, 1990. [72] LI Hualiang and ADALI T. A class of complex ICA algorithms based on the kurtosis cost function[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2008, 19(3): 408–420. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2007.908636 [73] DOUGLAS S C. Fixed-point algorithms for the blind separation of arbitrary complex-valued non-Gaussian signal mixtures[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2007, 2007: 036525. doi: 10.1155/2007/36525 [74] LENG X. Fast shape parameter estimation method for CGGD[EB/OL]. https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/69582-shape-paramter-estimation-implementation-for-the-cggd, 2018. [75] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, and ZHOU Shilin. A novel ship segmentation method based on kurtosis test in complex-valued SAR imagery[C]. 2018 10th IAPR Workshop on Pattern Recognition in Remote Sensing, Beijing, China, 2018: 1–4. [76] LENG X. Opensarshipfilter-package-sourcecode[EB/OL]. https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/66929-opensarshipfilter-package-sourcecode, 2018. [77] Shanghai Jiaotong University. Opensar platform[EB/OL]. http://opensar.sjtu.edu.cn/, 2017. [78] HUANG Lanqing, LIU Bin, LI Boying, et al. OpenSARShip: A dataset dedicated to Sentinel-1 ship interpretation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 195–208. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2755672 [79] SANTAMARIA C, ALVAREZ M, GREIDANUS H, et al. Mass processing of Sentinel-1 images for maritime surveillance[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(7): 678. doi: 10.3390/rs9070678 [80] MANSOUR A and JUTTEN C. What should we say about the kurtosis?[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 1999, 6(12): 321–322. doi: 10.1109/97.803435 [81] DUMITRU O C and DATCU M. Information content of very high resolution SAR images: Study of dependency of SAR image structure descriptors with incidence angle[J]. International Journal on Advances in Telecommunications, 2012, 5(3/4): 239–251. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: