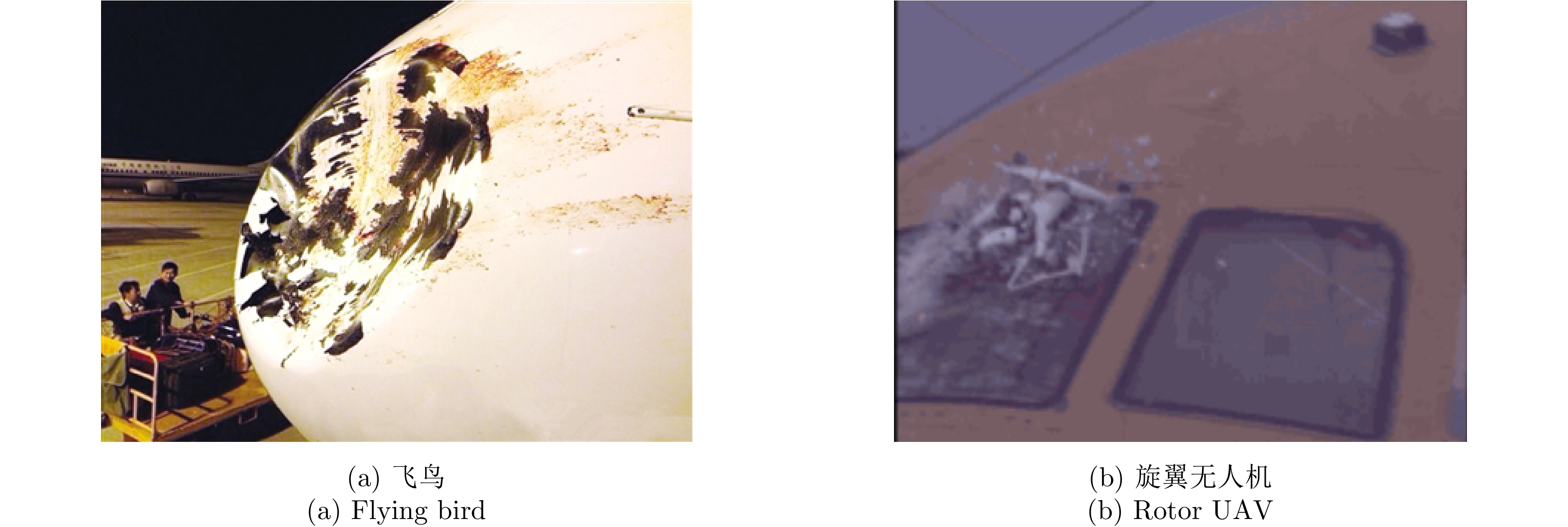
Progress and Prospects of Radar Target Detection and Recognition Technology for Flying Birds and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (in English)
-
摘要:
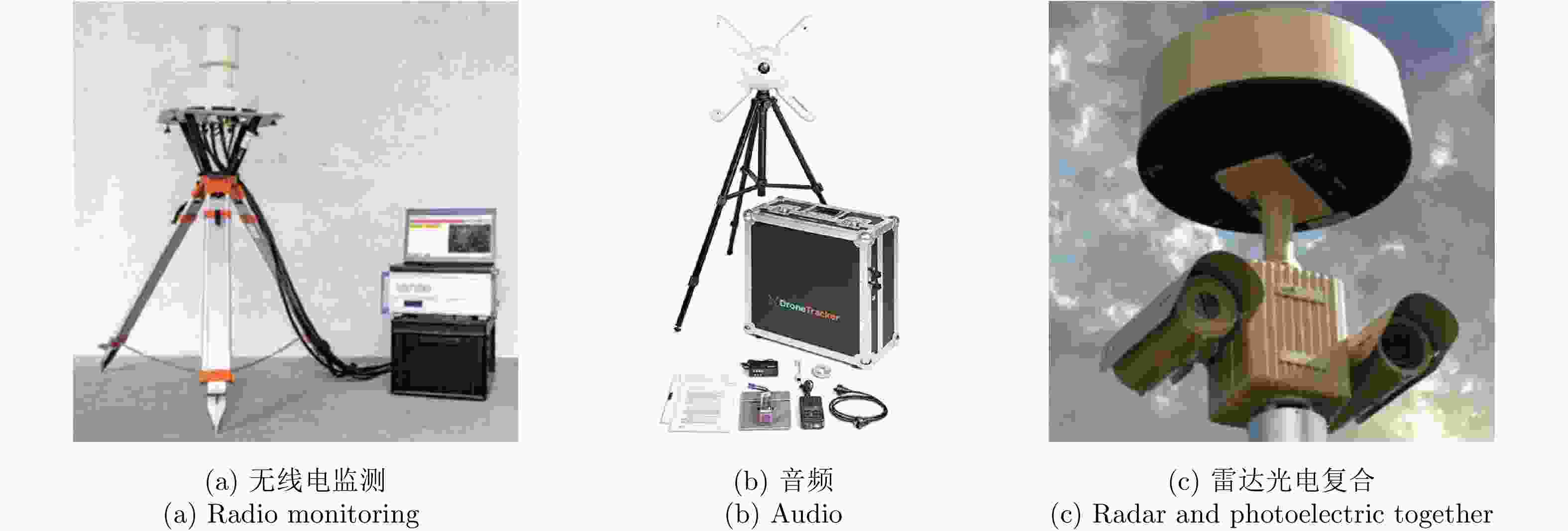
飞鸟和无人机(UAVs)是典型的“低慢小”目标,具有低可观测性,对两者的有效监视和识别成为保障空中航路安全、城市安保等需求迫切需要解决的难题。飞鸟和无人机目标类型多、飞行高度低、机动性强、雷达散射截面积小,加之探测环境复杂,给目标探测带来极大困扰,已成为世界性难题。因此迫切需要研发“看得见(检测能力强)、辨得明(识别概率高)”的无人机、飞鸟等“低慢小”目标监视手段和技术,实现目标的精细化描述和识别。该文集中对近年来复杂场景下旋翼无人机和飞鸟目标检测与识别技术的研究进展进行了归纳总结,介绍了飞鸟和无人机探测的主要手段,从回波建模和微动特性认知、泛探模式下机动特征增强与提取、分布式多视角特征融合、运动轨迹差异、深度学习智能分类等方面给出了检测和识别的有效途径。最后,该文总结了现有研究存在的问题,对未来复杂场景下飞鸟和无人机目标检测与识别技术的发展进行了展望。
Abstract:Flying birds and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are typical “low, slow, and small” targets with low observability. The need for effective monitoring and identification of these two targets has become urgent and must be solved to ensure the safety of air routes and urban areas. There are many types of flying birds and UAVs that are characterized by low flying heights, strong maneuverability, small radar cross-sectional areas, and complicated detection environments, which are posing great challenges in target detection worldwide. “Visible (high detection ability) and clear-cut (high recognition probability)” methods and technologies must be developed that can finely describe and recognize UAVs, flying birds, and “low-slow-small” targets. This paper reviews the recent progress in research on detection and recognition technologies for rotor UAVs and flying birds in complex scenes and discusses effective detection and recognition methods for the detection of birds and drones, including echo modeling and recognition of fretting characteristics, the enhancement and extraction of maneuvering features in ubiquitous observation mode, distributed multi-view features fusion, differences in motion trajectories, and intelligent classification via deep learning. Lastly, the problems of existing research approaches are summarized, and we consider the future development prospects of target detection and recognition technologies for flying birds and UAVs in complex scenarios.
-
图 7 DVB-T passive radar AULOS UAV detection results[35]
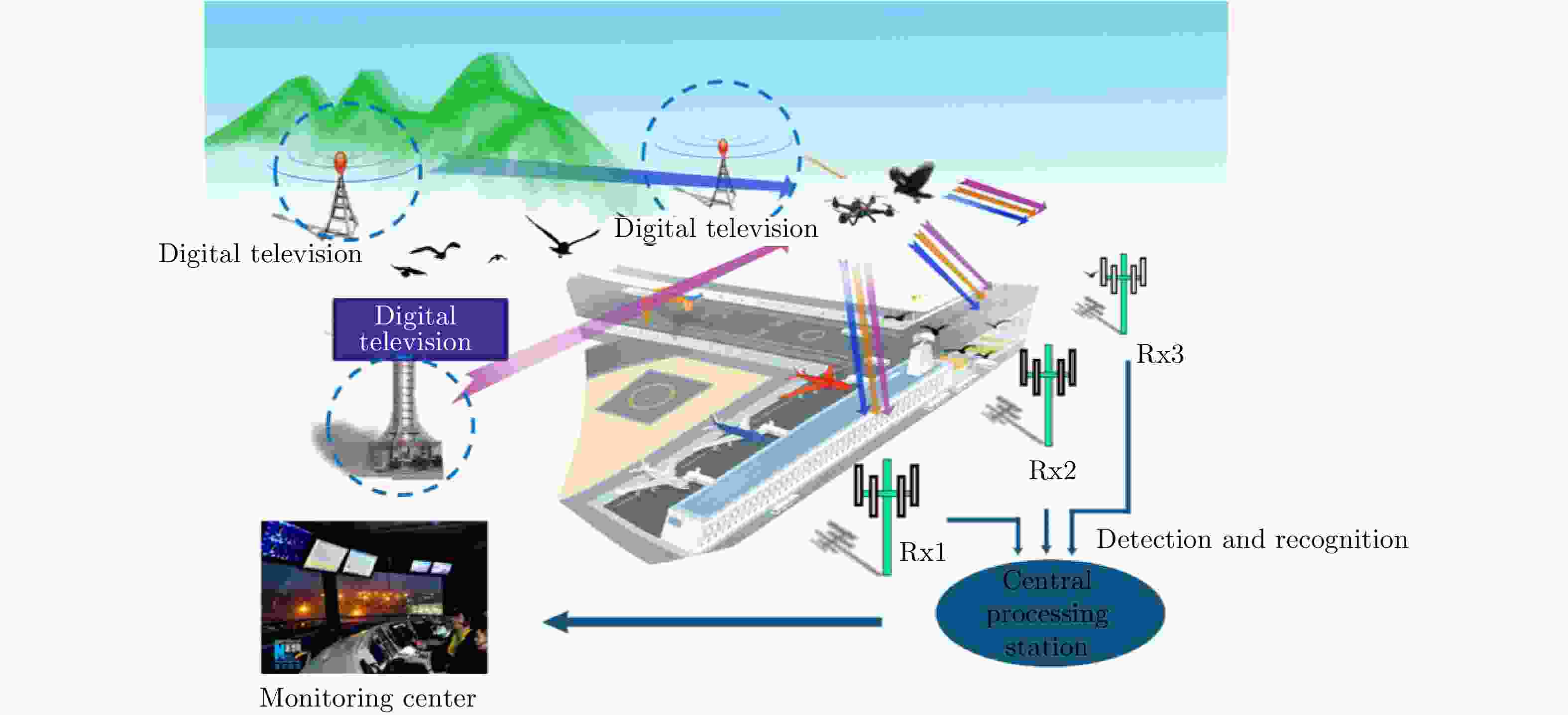
图 8 UAV detection experiment based on DTMB passive radar[38]
图 10 German FHR multi-channel passive radar system GAMMA-2[42]
图 11 NetRAD radar system of university of London[44]
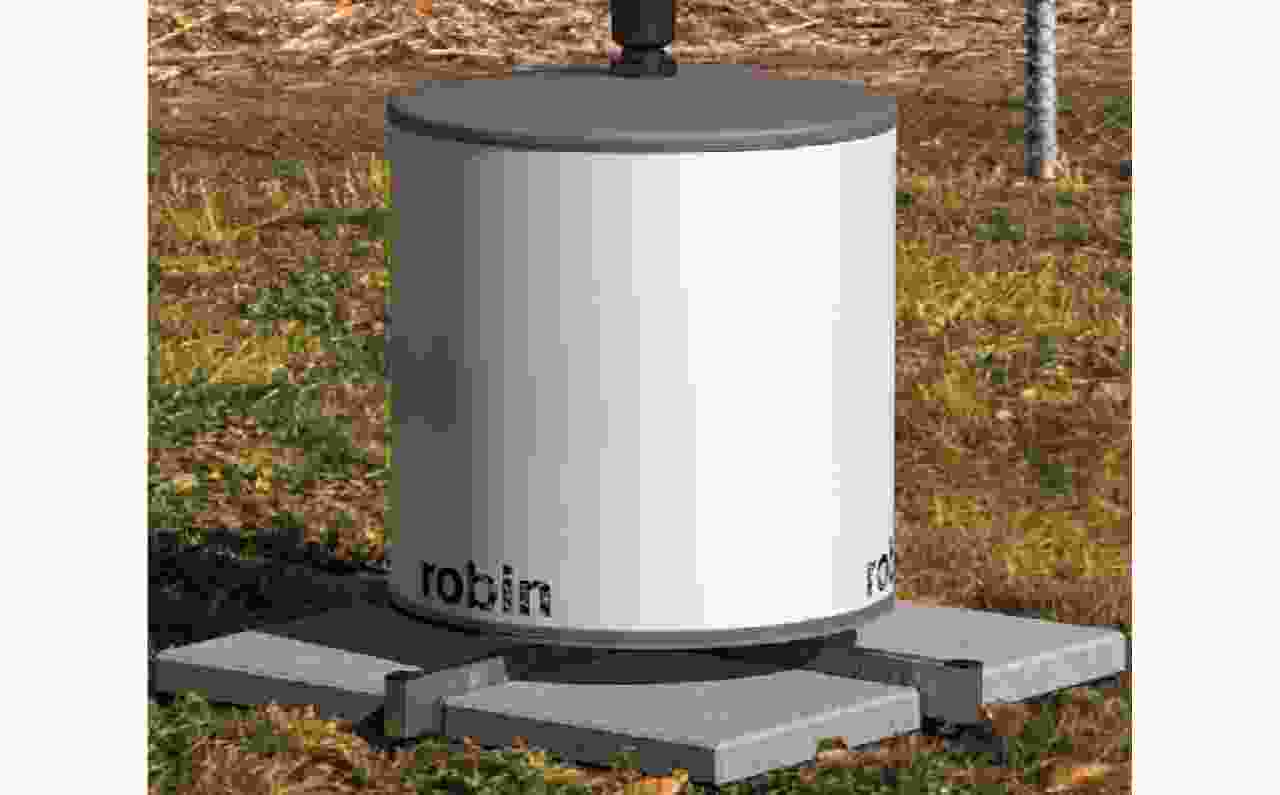
图 12 The Robin birds/UAV recognition radar in Netherlands[45]
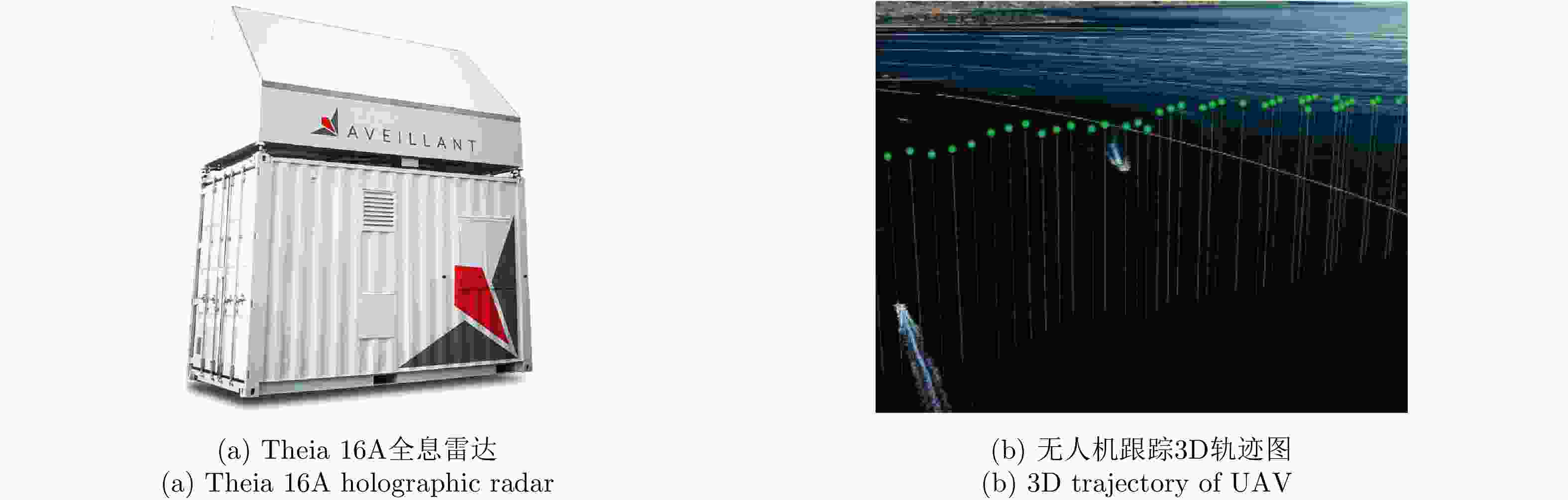
图 13 The holographic radar system from Aveillant, UK[46]
图 14 Micromotion characteristics of six-rotor UAV[53]
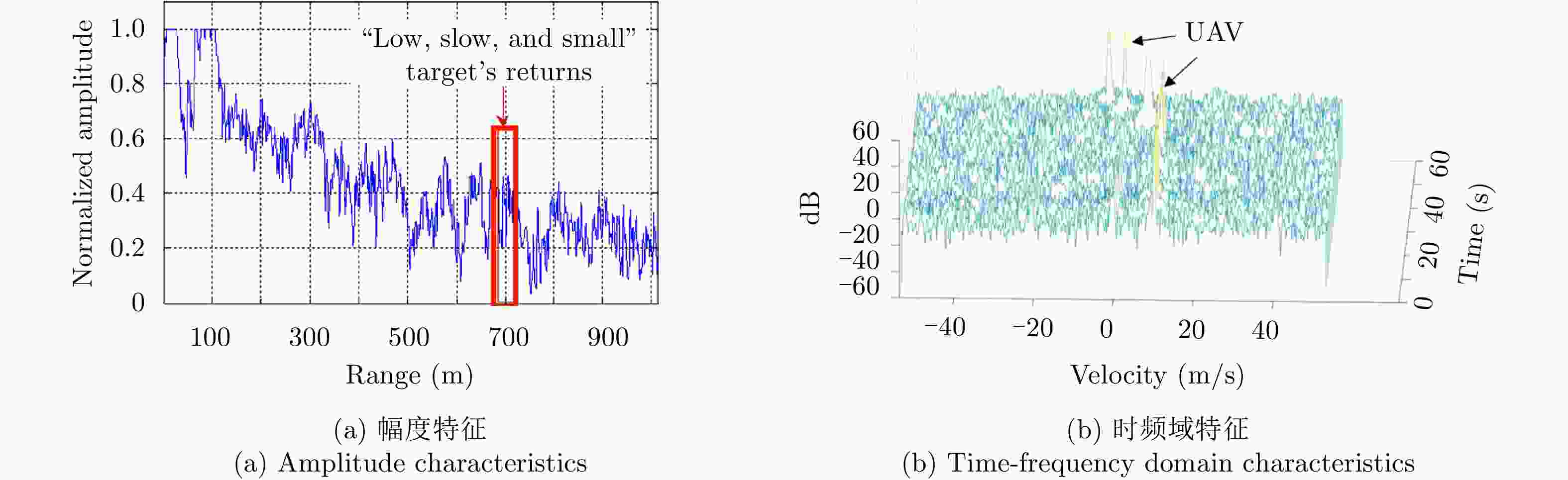
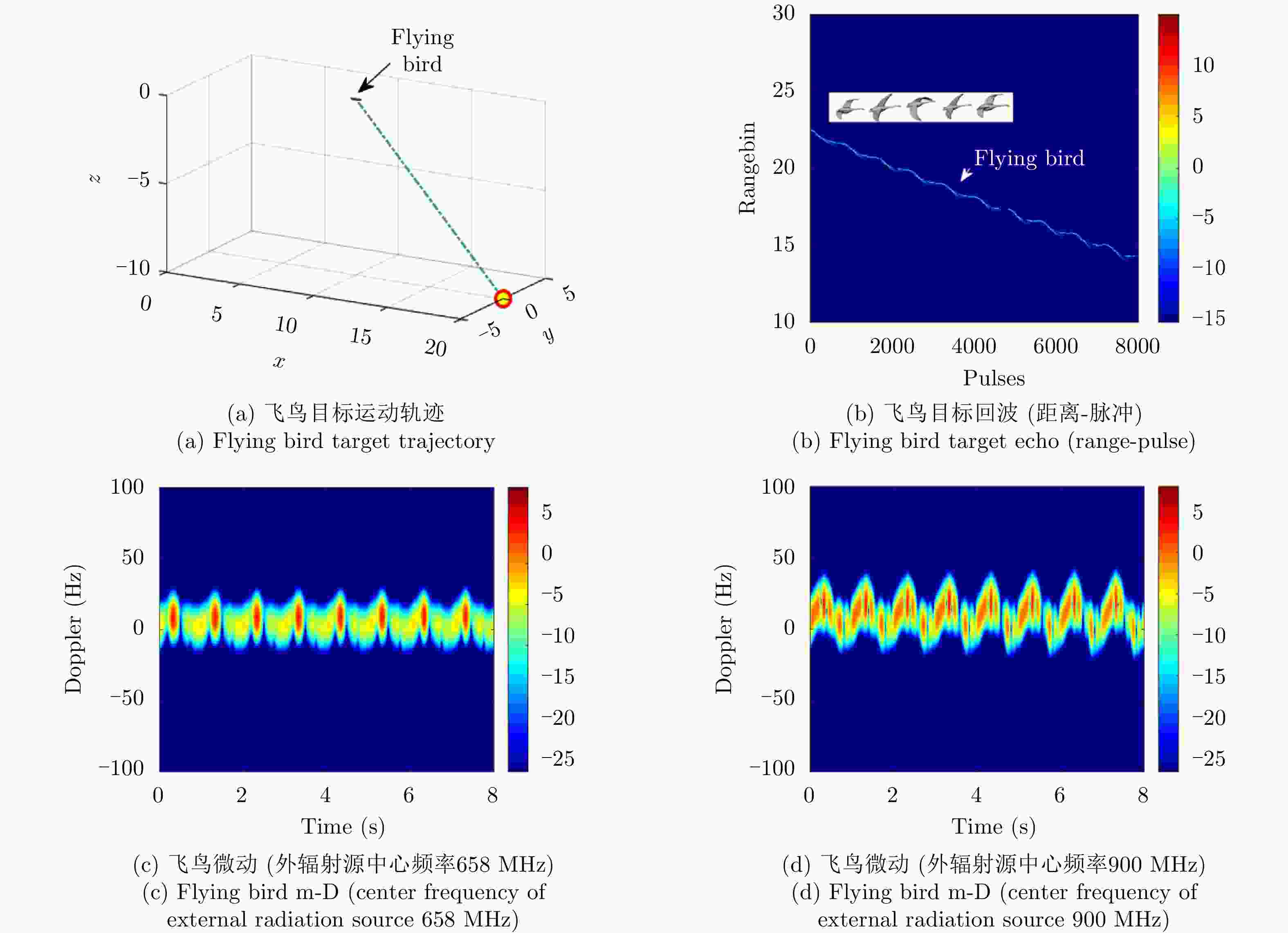
图 17 Analysis of measured m-D characteristics of UAV target (center frequency of external radiation source 658 MHz)[39]
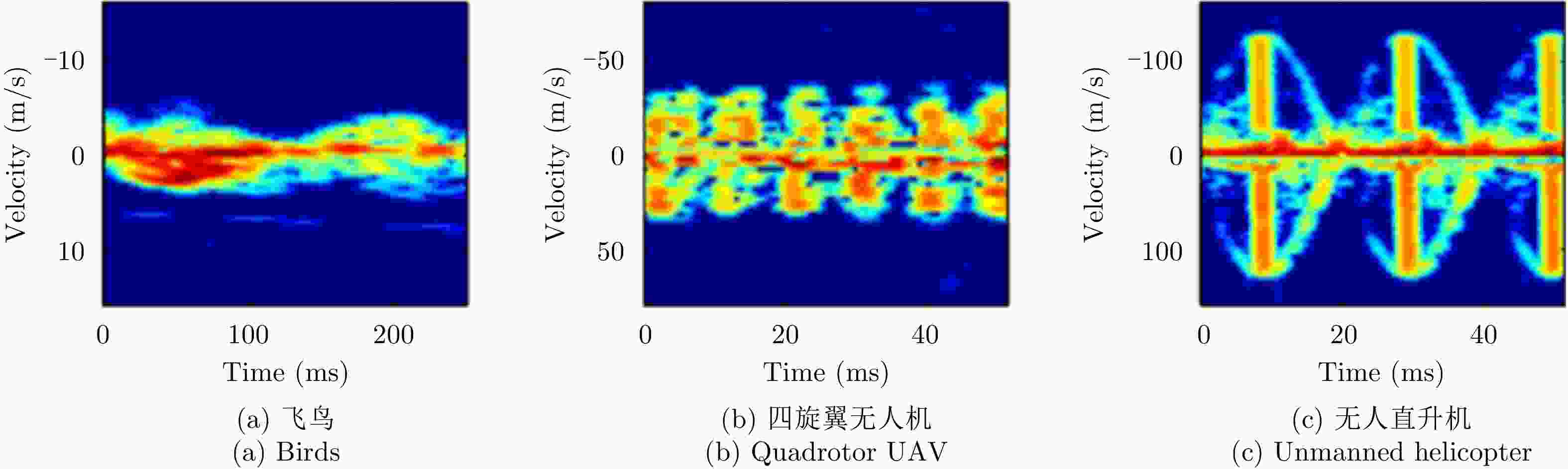
图 18 Micro-Doppler (24 GHz) for UAV and bird targets[54]
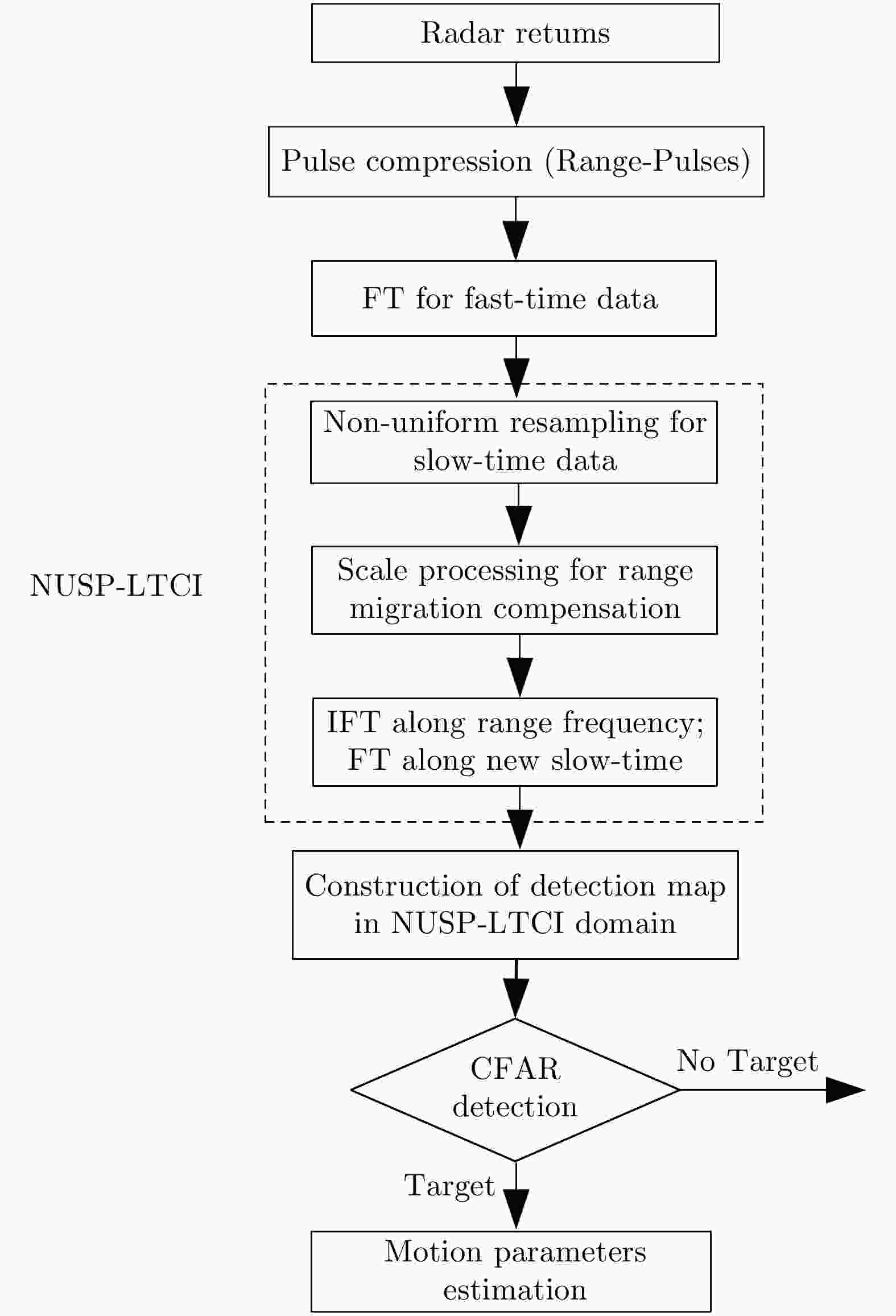
图 20 NUSP-LTCI processing[58]
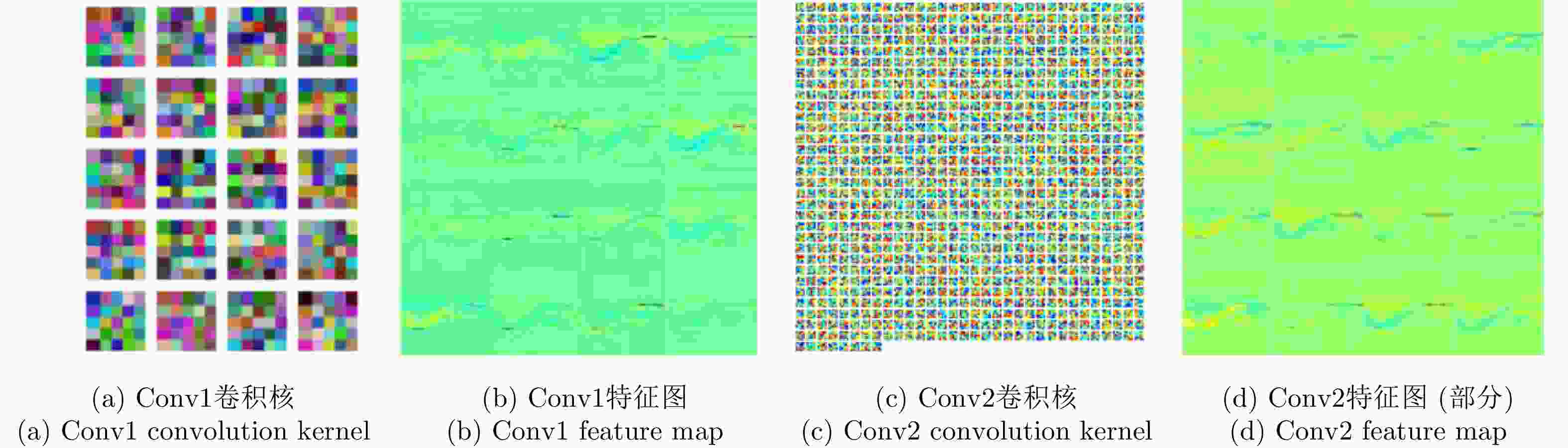
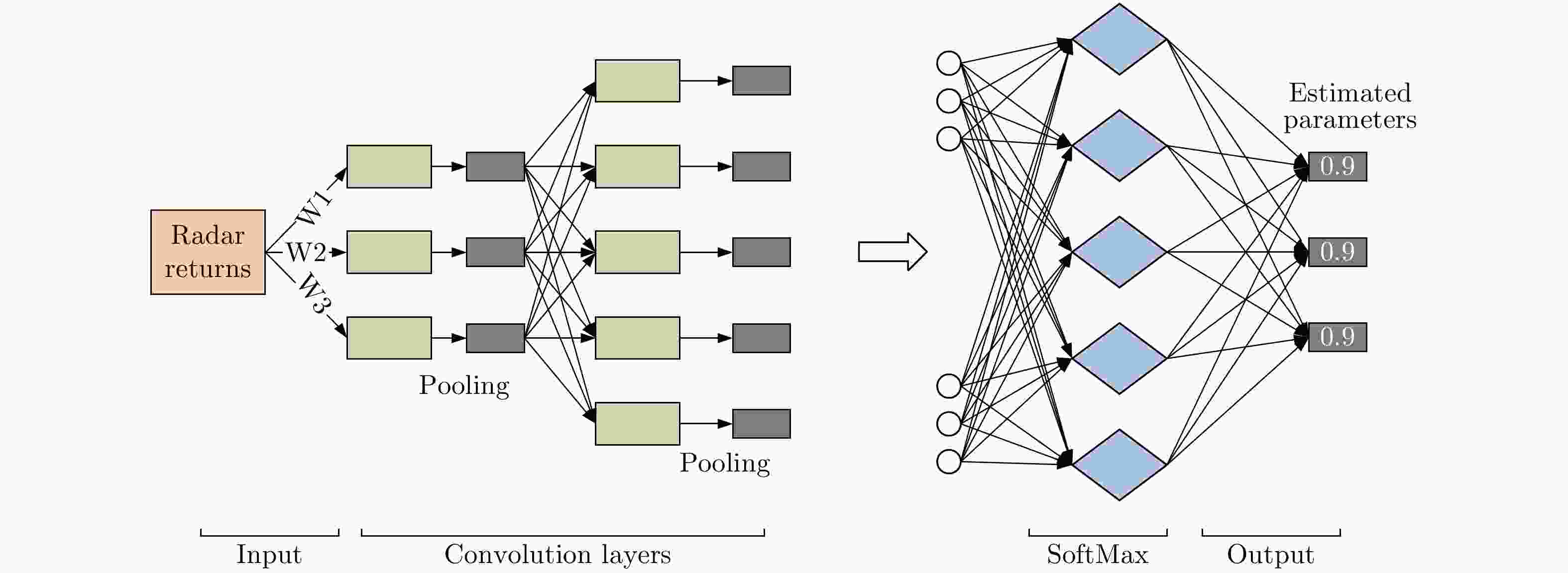
图 23 Data characteristics of convolutional layers in CNN (take LeNet as an example)[73]
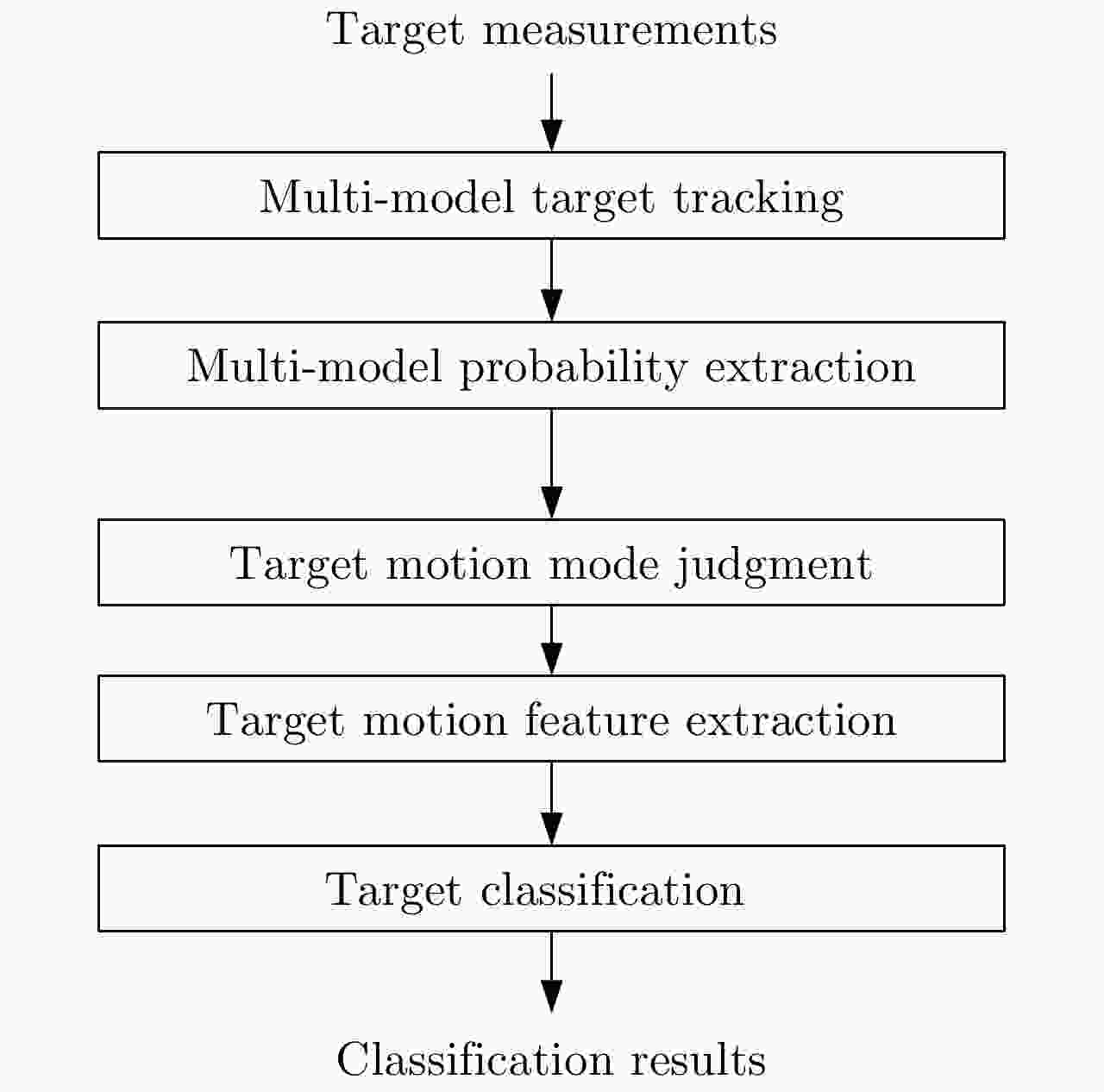
图 26 Recognition results of trajectories of flying birds and UAVs[77]
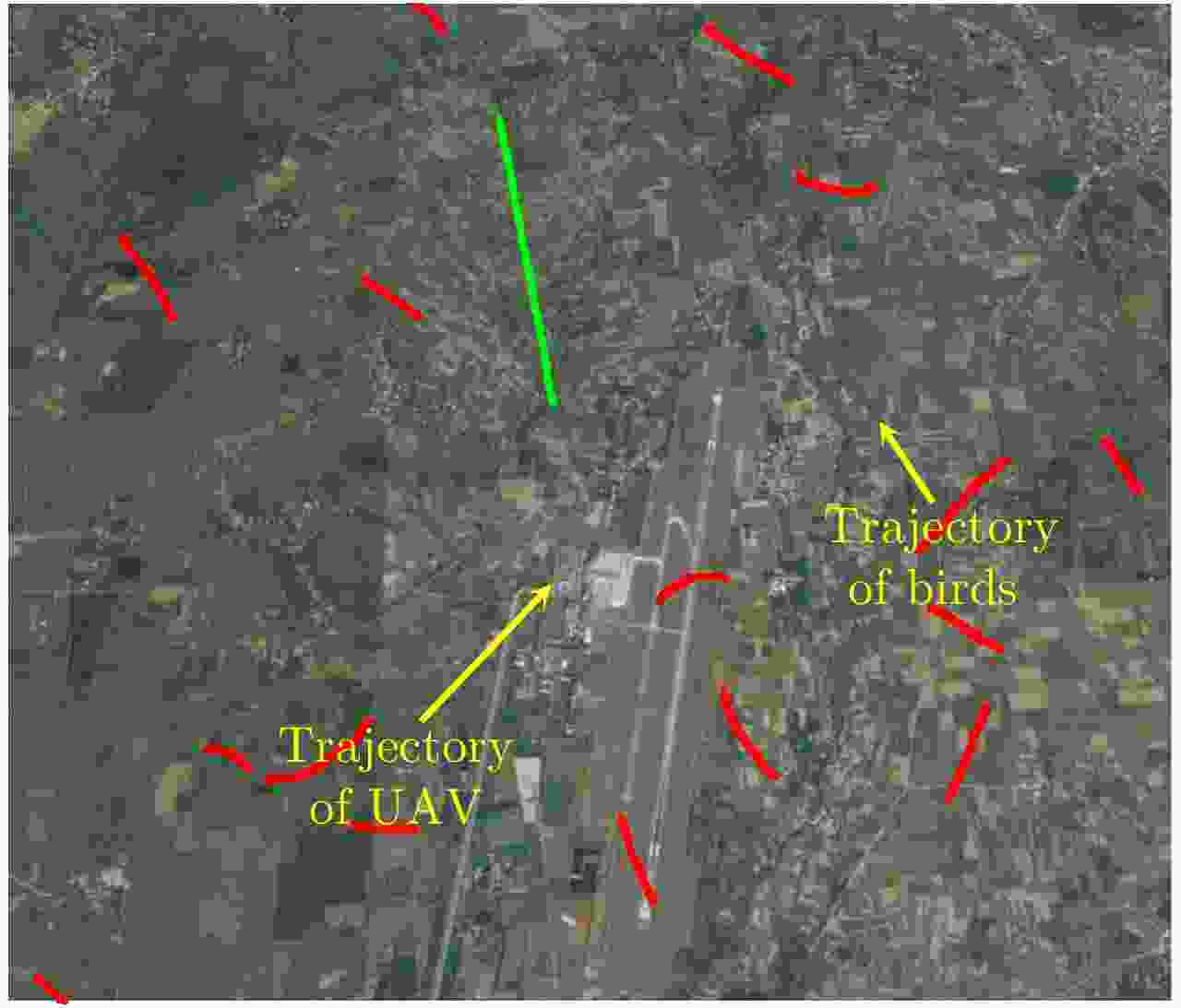
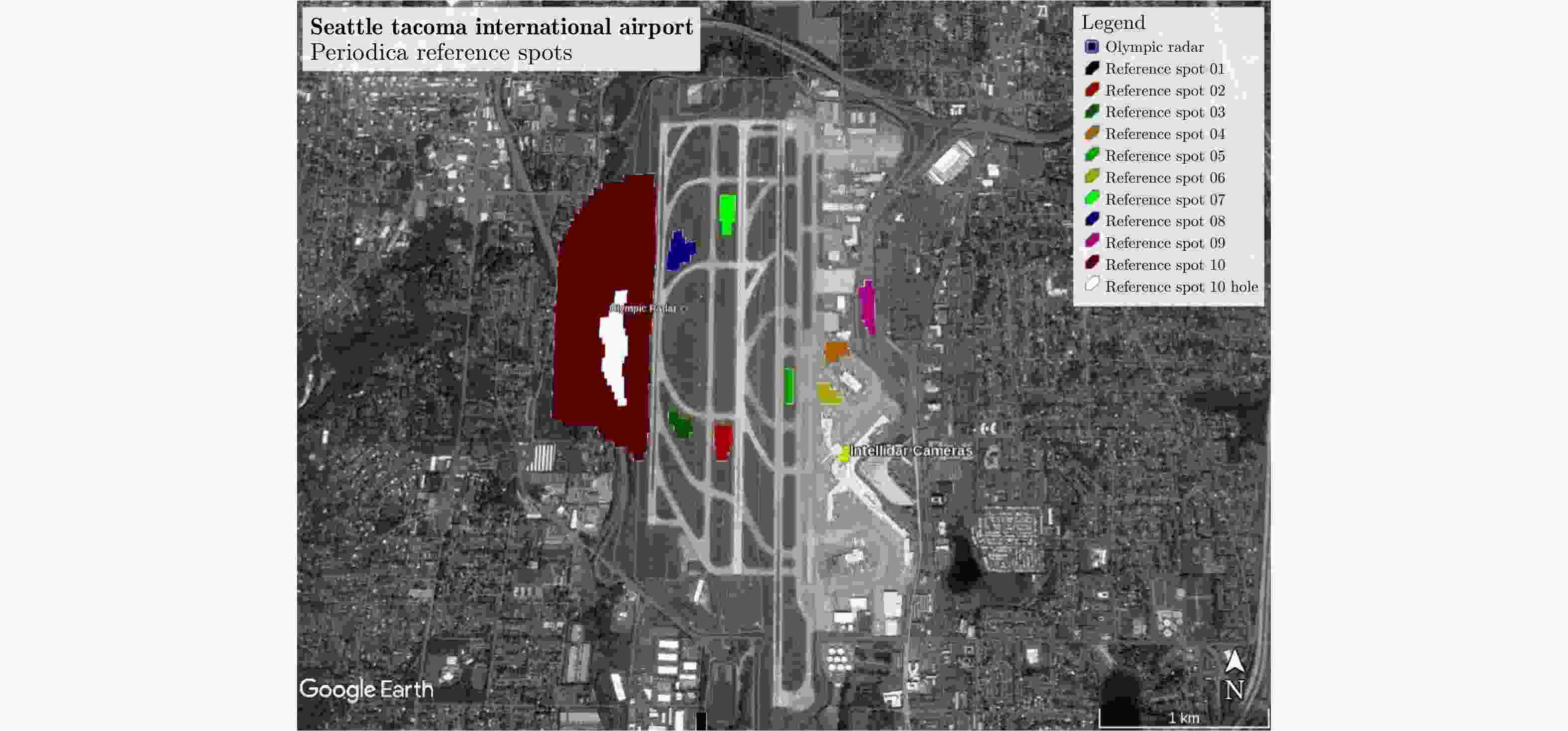
图 27 Statistics of hot spots of birds activity at an airport[79]
表 1 国外3种典型探鸟雷达产品说明
Table 1. Description of three typical foreign avian radar products
产品名称 技术特点 部署方式 Merlin 水平和垂直扫描雷达结合,固态发射机 水平扫描雷达通常部署在靠近机场中心的位置,负责机场周边低空预警;垂直扫描雷达通常部署在每条跑道中心一侧,负责监视航班起降通道;当然,雷达部署是个复杂的系统问题,需要考虑净空障碍物限制面、地物遮挡、供电等多方面因素。 Accipiter 水平和垂直扫描雷达结合,附加抛物面天线 Robin 水平和垂直扫描雷达结合,磁控管发射机 表 2 鸟类热点月度轨迹数量统计
Table 2. Monthly statistics of bird hot spots
热点编号 轨迹数量 百分比(%) 1 7628 0.73 2 30299 2.89 3 22484 2.15 4 16885 1.61 5 21987 2.10 6 15652 1.50 7 29856 2.85 8 33938 3.24 9 21650 2.07 10 846406 80.86 表 1 Description of three typical foreign avian radar products
Product name Merlin Accipiter Robin Technical characteristics Technical features combination of hori-zontal and vertical scanning radar,
solid state transmitterCombination of horizontal and vertical scanning radar, additional parabolic antenna additional parabolic antenna combination of horizontal and vertical scanning radar, magn-etron transmitter Deployment method Horizontal scanning radars are usually deployed close to the center of the airport and are responsible for low-altitude warnings around the airport; vertical scanning radars are usually deployed on the center side of each runway and are responsible for monitoring flight take-off and landing channels; of course, radar deployment is a complex system problem that needs to be considered, there are many factors such as clearance obstacle restriction surface, ground obstruction, power supply and so on. 表 2 Monthly statistics of bird hot spots
Hot number Track number The percentage (%) 1 7628 0.73 2 30299 2.89 3 22484 2.15 4 16885 1.61 5 21987 2.10 6 15652 1.50 7 29856 2.85 8 33938 3.24 9 21650 2.07 10 846406 80.86 -
[1] 王维, 项洪达. 鸟击风险计算方法研究[J]. 中国民航大学学报, 2019, 37(5): 21–24.WANG Wei and XIANG Hongda. Calculation method of aircraft bird strike risk[[J]. Journal of Civil Aviation University of China, 2019, 37(5): 21–24. [2] 于飞, 刘东华, 贺飞扬. 无人机“黑飞”对电磁空间安全的挑战[J]. 中国无线电, 2018, (8): 43–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2018.08.026YU Fei, LIU Donghua, and HE Feiyang. UAV “black flying” challenges the safety of electromagnetic space[J]. China Radio, 2018, (8): 43–44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2018.08.026 [3] 陈唯实. 轻小型无人机监管、探测与干扰技术[J]. 中国民用航空, 2017, (7): 33–34.CHEN Weishi. The supervision, detection and jamming technologies for light and small UAS[J]. China Civil Aviation, 2017, (7): 33–34. [4] 吴小松, 房之军, 陈通海. 民用无人机反制技术研究[J]. 中国无线电, 2018, (3): 55–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2018.03.038WU Xiaosong, FANG Zhijun, and CHEN Tonghai. Research on civil UAV countermeasure technology[J]. China Radio, 2018, (3): 55–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2018.03.038 [5] 罗淮鸿, 卢盈齐. 国外反“低慢小”无人机能力现状与发展趋势[J]. 飞航导弹, 2019, (6): 32–36. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.20180472LUO Huaihong and LU Yingqi. Ability status and development trend of anti-“low, slow and small” UAVs[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2019, (6): 32–36. doi: 10.16338/j.issn.1009-1319.20180472 [6] 陈小龙, 关键, 黄勇, 等. 雷达低可观测目标探测技术[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(11): 30–38. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.11.004CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Radar low-observable target detection[J]. Science&Technology Review, 2017, 35(11): 30–38. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.11.004 [7] 陈小龙, 关键, 黄勇, 等. 雷达低可观测动目标精细化处理及应用[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(20): 19–27. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.002CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, HUANG Yong, et al. Radar refined processing and its applications for low-observable moving target[J]. Science&Technology Review, 2017, 35(20): 19–27. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2017.20.002 [8] NOHARA T J, ENG B, ENG M, et al. An overview of avian radar developments - past, present and future[C]. The 2007 Bird Strike Committee USA/Canada, 9th Annual Meeting, Kingston, Ontario, 2007. [9] BEASON R C, NOHARA T J, and WEBER P. Beware the Boojum: Caveats and strengths of avian radar[J]. Human-Wildlife Interactions, 2013, 7(1): 16–46. [10] BRAUN C E. Techniques for wildlife investigations and management[J]. The Condor, 2007, 109(4): 981–983. doi: 10.1093/condor/109.4.981 [11] 宁焕生, 刘文明, 李敬, 等. 航空鸟击雷达鸟情探测研究[J]. 电子学报, 2006, 34(12): 2232–2237. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2006.12.023NING Huansheng, LIU Wenming, LI Jing, et al. Research on radar avian detection for aviation[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2006, 34(12): 2232–2237. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2006.12.023 [12] 陈唯实, 宁焕生, 刘文明, 等. 基于雷达图像的飞鸟目标检测与信息提取[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2008, 30(9): 1624–1627. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2008.09.006CHEN Weishi, NING Huansheng, LIU Wenming, et al. Flying bird targets detection and information extraction based on radar images[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 30(9): 1624–1627. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2008.09.006 [13] 陈唯实, 李敬. 雷达探鸟技术发展与应用综述[J]. 现代雷达, 2017, 39(2): 7–17. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.02.002CHEN Weishi and LI Jing. Review on development and applications of avian radar technology[J]. Modern Radar, 2017, 39(2): 7–17. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.02.002 [14] 陈唯实, 万显荣, 李敬. 机场净空区非合作无人机目标探测技术[J]. 民航学报, 2018, 2(5): 54–57, 45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4994.2018.05.014CHEN Weishi, WAN Xianrong, and LI Jing. Detection technology of non-cooperative UAV targets in airport clearance area[J]. Journal of Civil Aviation, 2018, 2(5): 54–57, 45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4994.2018.05.014 [15] 蔡亚梅, 姜宇航, 赵霜. 国外反无人机系统发展动态与趋势分析[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2017, 33(2): 59–64. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2017.02.016CAI Yamei, JIANG Yuhang, and ZHAO Shuang. Development status and trend analysis of counter UAV systems[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2017, 33(2): 59–64. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2017.02.016 [16] 罗德与施瓦茨(中国)科技有限公司. 无人机自动识别、定位和压制系统(一)[J]. 中国无线电, 2016, (8): 72–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.08.047Rohde & Schwarz (China) Technology Co., L td. UAV automatic identification, positioning and suppression system (One)[J]. China Radio, 2016, (8): 72–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.08.047 [17] 罗德与施瓦茨(中国)科技有限公司. 无人机自动识别、定位和压制系统(二)[J]. 中国无线电, 2016, (9): 71–72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.09.045Rohde & Schwarz (China) Technology Co., L td. UAV automatic identification, positioning and suppression system (Two)[J]. China Radio, 2016, (9): 71–72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.09.045 [18] 罗德与施瓦茨(中国)科技有限公司. 无人机自动识别、定位和压制系统(三)[J]. 中国无线电, 2016, (10): 72–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.10.044Rohde & Schwarz (China) Technology Co., L td. UAV automatic identification, positioning and suppression system (Three)[J]. China Radio, 2016, (10): 72–73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.10.044 [19] JEON S, SHIN J W, LEE Y J, et al. Empirical study of drone sound detection in real-life environment with deep neural networks[C]. The 2017 25th European Signal Processing Conference, Kos, Greece, 2017. doi: 10.23919/EUSIPCO.2017.8081531. [20] HOMMES A, SHOYKHETBROD A, NOETEL D, et al. Detection of acoustic, electro-optical and RADAR signatures of small unmanned aerial vehicles[C]. SPIE 9997, Target and Background Signatures Ⅱ, Edinburgh, USA, 2016. doi: 10.1117/12.2242180. [21] MEZEI J and MOLNÁR A. Drone sound detection by correlation[C]. The 2016 IEEE 11th International Symposium on Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics, Timisoara, Romania, 2016. doi: 10.1109/SACI.2016.7507430. [22] 陈超帅, 王世勇. 大疆无人机目标红外辐射特性测量及温度反演[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(4): 427–434. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.007CHEN Chaoshuai and WANG Shiyong. Infrared radiation characteristics measurement and temperature retrieval based on DJI unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(4): 427–434. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.007 [23] 郭溪溪. 低空慢速小目标检测识别与威胁度评估[D]. [硕士论文], 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2017.GUO Xixi. Detection and recognition and thread assessment for small target at low altitude and slow speed[D]. [Master dissertation], Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mehcanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. [24] MÜLLER T. Robust drone detection for day/night counter-UAV with static VIS and SWIR cameras[C]. SPIE 10190, Ground/Air Multisensor Interoperability, Integration, and Networking for Persistent ISR VⅢ, Anaheim, USA, 2017. doi: 10.1117/12.2262575. [25] KLARE J, BIALLAWONS O, and CERUTTI-MAORI D. Detection of UAVs using the MIMO radar MIRA-CLE Ka[C]. The EUSAR 2016: 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016. [26] WILLIAMS H. AUDS to target small unmanned intruders[J]. Jane’s International Defense Review, 2015, 48: 22. [27] 郭珊珊. 反无人机技术与产品发展现状[J]. 军事文摘, 2016, (19): 36–39.GUO Shanshan. Anti-UAV technology and product development status[J]. Military Digest, 2016, (19): 36–39. [28] CLEMENTE C and SORAGHAN J J. Passive bistatic radar for helicopters classification: A feasibility study[C]. 2012 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, USA, 2012. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2012.6212273. [29] LIU Yuqi, WAN Xianrong, TANG Hui, et al. Digital television based passive bistatic radar system for drone detection[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944443. [30] SCHÜPbach C, PATRY C, MAASDORP F, et al. Micro-UAV detection using DAB-based passive radar[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944357. [31] TIKKINEN J, HILTUNEN K, MARTIKAINEN K, et al. Helicopter detection capability of passive coherent location (PCL) radar[C]. The 2012 9th European Radar Conference, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2012. [32] TIKKINEN J, HILTUNEN K, and MARTIKAINEN K. Utilization of long coherent integration time in helicopter recognition by passive coherent location (PCL) radar[C]. 2013 European Radar Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 2013. [33] BĄCZYK M K, MISIUREWICZ J, GROMEK D, et al. Analysis of recorded helicopter echo in a passive bistatic radar[C]. 2013 European Radar Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 2013. [34] MAASDORP F D V, CILLIERS J E, INGGS M R, et al. Simulation and measurement of propeller modulation using FM broadcast band commensal radar[J]. Electronics Letters, 2013, 49(23): 1481–1482. doi: 10.1049/el.2013.2875 [35] MARTELLI T, COLONE F, and CARDINALI R. DVB-T based passive radar for simultaneous counter-drone operations and civil air traffic surveillance[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2020, 14(4): 505–515. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2019.0309 [36] MARTELLI T, MURGIA F, COLONE F, et al. Detection and 3D localization of ultralight aircrafts and drones with a WiFi-based passive radar[C]. International Conference on Radar Systems, Belfast, UK, 2017. doi: 10.1049/cp.2017.0423 [37] MUSA S A, RSA R A, SALI A, et al. DVBS based forward scattering radar for drone detection[C]. The 2019 20th International Radar Symposium, Ulm, Germany, 2019. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2019.8767456. [38] LIU Yuqi, YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, et al. Time varying clutter suppression in CP OFDM based passive radar for slowly moving targets detection[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, in press. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2986717 [39] 刘玉琪, 易建新, 万显荣, 等. 数字电视外辐射源雷达多旋翼无人机微多普勒效应实验研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 585–592. doi: 10.12000/JR18062LIU Yuqi, YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, et al. Experimental research on micro-Doppler effect of multi-rotor drone with digital television based passive radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 585–592. doi: 10.12000/JR18062 [40] YI Yucheng, WAN Xianrong, YI Jianxin, et al. polarization diversity technology research in passive radar based on subcarrier processing[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(5): 1710–1719. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2881226 [41] DAN Yangpeng, YI Jianxin, WAN Xianrong, et al. LTE-based passive radar for drone detection and its experimental results[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(20): 6910–6913. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0583 [42] PATEL J S, FIORANELLI F, and ANDERSON D. Review of radar classification and RCS characterisation techniques for small UAVs or drones[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2018, 12(9): 911–919. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.0020 [43] KNOEDLER B, ZEMMARI R, and KOCH W. On the detection of small UAV using a GSM passive coherent location system[C]. The 2016 17th International Radar Symposium, Krakow, Poland, 2016. doi: 10.1109/IRS.2016.7497375. [44] POULLIN D. UAV detection and localization using passive DVB-T radar MFN and SFN[R]. 2016. [45] HOFFMANN F, RITCHIE M, FIORANELLI F, et al. Micro-Doppler based detection and tracking of UAVs with multistatic radar[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.7485236. [46] JAHANGIR M, BAKER C J, and OSWALD G A. Doppler characteristics of micro-drones with L-Band multibeam staring radar[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944360. [47] 张群, 胡健, 罗迎, 等. 微动目标雷达特征提取、成像与识别研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049ZHANG Qun, HU Jian, LUO Ying, et al. Research progresses in radar feature extraction, imaging, and recognition of target with micro-motions[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049 [48] 陈小龙, 关键, 何友. 微多普勒理论在海面目标检测中的应用及展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 123–134. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20102CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, and HE You. Applications and prospect of micro-motion theory in the detection of sea surface target[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 123–134. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20102 [49] 刘凯越, 张晨新, 刘刚, 等. 关于飞机雷达探测飞鸟的RCS建模仿真[J]. 计算机仿真, 2016, 33(5): 120–124, 228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2016.05.025LIU Kaiyue, ZHANG Chenxin, LIU Gang, et al. Modeling and simulation about RCS of aircraft radar detecting bird[J]. Computer Simulation, 2016, 33(5): 120–124, 228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2016.05.025 [50] SINGH A K and KIM Y H. Automatic measurement of blade length and rotation rate of drone using w-band micro-Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(5): 1895–1902. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2785335 [51] 宋晨, 周良将, 吴一戎, 等. 基于自相关-倒谱联合分析的无人机旋翼转动频率估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 255–261. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180399SONG Chen, ZHOU Liangjiang, WU Yirong, et al. An estimation method of rotation frequency of unmanned aerial vehicle based on auto-correlation and cepstrum[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 255–261. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180399 [52] 陈永彬, 李少东, 杨军, 等. 一种旋翼叶片微动特征提取新方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2017, 15(1): 13–18, 28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2017.01.003CHEN Yongbin, LI Shaodong, YANG Jun, et al. A new method for micro-motion signature extraction of rotor blades[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2017, 15(1): 13–18, 28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2017.01.003 [53] JAHANGIR M and BAKER C J. Extended dwell Doppler characteristics of birds and micro-UAS at l-band[C]. The 2017 18th International Radar Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 2017: 1–10. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2017.8008144. [54] RAHMAN S and ROBERTSON D A. Radar micro-Doppler signatures of drones and birds at K-band and W-band[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 17396. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35880-9 [55] CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, LIU Ningbo, et al. Maneuvering target detection via radon-fractional Fourier transform-based long-time coherent integration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(4): 939–953. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2297682 [56] 关键, 陈小龙, 于晓涵. 雷达高速高机动目标长时间相参积累检测方法[J]. 信号处理, 2017, 33(3A): 1–8. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.3A.001GUAN Jian, CHEN Xiaolong, and YU Xiaohan. Long-time coherent integration-based detection method for high-speed and highly maneuvering radar target[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2017, 33(3A): 1–8. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.3A.001 [57] LI Xiaolong, CUI Guolong, YI Wei, et al. Radar maneuvering target detection and motion parameter estimation based on TRT-SGRFT[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 133: 107–116. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2016.10.014 [58] CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, CHEN Weishi, et al. Sparse long-time coherent integration-based detection method for radar low-observable manoeuvring target[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2020, 14(4): 538–546. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2019.0313 [59] DJUROVIĆ I and SIMEUNOVIĆ M. Parameter estimation of 2D polynomial phase signals using NU sampling and 2D CPF[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2018, 12(9): 1140–1145. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2018.5083 [60] CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, WANG Guoqing, et al. Fast and refined processing of radar maneuvering target based on hierarchical detection via sparse fractional representation[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 149878–149889. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2947169 [61] 罗迎, 张群, 封同安, 等. OFD-LFM MIMO雷达中旋转目标微多普勒效应分析及三维微动特征提取[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(1): 8–13. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00234LUO Ying, ZHANG Qun, FENG Tongan, et al. Micro-Doppler effect analysis of rotating target and three-dimensional micro-motion feature extraction in OFD-LFM MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2011, 33(1): 8–13. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00234 [62] 赵双, 鲁卫红, 冯存前, 等. 多视角微多普勒融合的进动目标特征提取[J]. 信号处理, 2016, 32(3): 296–303. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2016.03.006ZHAO Shuang, LU Weihong, FENG Cunqian, et al. Feature extraction of precession targets based on multi-aspect micro-Doppler fusion[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2016, 32(3): 296–303. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2016.03.006 [63] RITCHIE M, FIORANELLI F, BORRION H, et al. Multistatic micro-Doppler radar feature extraction for classification of unloaded/loaded micro-drones[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2017, 11(1): 116–124. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0063 [64] 万显荣, 易建新, 程丰, 等. 单频网分布式外辐射源雷达技术[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(6): 623–631. doi: 10.12000/JR14156WAN Xianrong, YI Jianxin, CHENG Feng, et al. Single frequency network based distributed passive radar technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(6): 623–631. doi: 10.12000/JR14156 [65] 万显荣, 孙绪望, 易建新, 等. 分布式数字广播电视外辐射源雷达系统同步设计与测试[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 65–72. doi: 10.12000/JR16134WAN Xianrong, SUN Xuwang, YI Jianxin, et al. Synchronous design and test of distributed passive radar systems based on digital broadcasting and television[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 65–72. doi: 10.12000/JR16134 [66] CHENG Gong, HAN Junwei, and LU Xiaoqiang. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105(10): 1865–1883. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2017.2675998 [67] 文贡坚, 朱国强, 殷红成, 等. 基于三维电磁散射参数化模型的SAR目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(2): 115–135. doi: 10.12000/JR17034WEN Gongjian, ZHU Guoqiang, YIN Hongcheng, et al. SAR ATR Based on 3D parametric electromagnetic scattering model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(2): 115–135. doi: 10.12000/JR17034 [68] OH B S, GUO Xin, WAN Fangyuan, et al. Micro-Doppler mini-UAV classification using empirical-mode decomposition features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(2): 227–231. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2781711 [69] BIRTCHER C R, BALANIS C A, and DECARLO D. Rotor-blade modulation on antenna amplitude pattern and polarization: Predictions and measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 1999, 41(4): 384–393. doi: 10.1109/15.809828 [70] ZHAO Yichao and SU Yi. Synchrosqueezing phase analysis on micro-Doppler parameters for small UAVs identification with multichannel radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(3): 411–415. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2924266 [71] 田壮壮, 占荣辉, 胡杰民, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的SAR图像目标识别研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037TIAN Zhuangzhuang, ZHAN Ronghui, HU Jiemin, et al. SAR ATR based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(3): 320–325. doi: 10.12000/JR16037 [72] 王俊, 郑彤, 雷鹏, 等. 深度学习在雷达中的研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040WANG Jun, ZHENG Tong, LEI Peng, et al. Study on deep learning in radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040 [73] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的海上微动目标检测与分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Detection and classification of maritime target with micro-motion based on CNNs[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 565–574. doi: 10.12000/JR18077 [74] KIM B K, KANG H S, and PARK S O. Drone classification using convolutional neural networks with merged Doppler images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(1): 38–42. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2624820 [75] MENDIS G J, WEI Jin, and MADANAYAKE A. Deep learning cognitive radar for micro UAS detection and classification[C]. 2017 Cognitive Communications for Aerospace Applications Workshop, Cleveland, USA, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/CCAAW.2017.8001610. [76] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 陈宝欣, 等. 雷达海上目标双通道卷积神经网络特征融合智能检测方法[J]. 现代雷达, 2019, 41(10): 47–52, 57. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.10.009SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Baoxin, et al. Dual-channel convolutional neural networks feature fusion method for radar maritime target intelligent detection[J].Modern Radar, 2019, 41(10): 47–52, 57. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2019.10.009 [77] 陈唯实, 刘佳, 陈小龙, 等. 基于运动模型的低空非合作无人机目标识别[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(4): 687–694. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0447CHEN Weishi, LIU Jia, CHEN Xiaolong, et al. Non-cooperative UAV target recognition in low-altitude airspace based on motion model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(4): 687–694. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0447 [78] 陈唯实, 万健, 李敬. 基于机场探鸟雷达数据的鸟击风险评估[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2013, 39(11): 1431–1436.CHEN Weishi, WAN Jian, and LI Jing. Bird strike risk assessment with airport avian radar data[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(11): 1431–1436. [79] 陈唯实, 张洁, 卢贤锋. 基于探鸟雷达数据的机场鸟情分析[J]. 民用航空, 2020, (1): 43–45.CHEN Weishi, ZHANG Jie, and LU Xianfeng. Airport bird situation analysis based on avian radar data[J]. China Civil Aviation, 2020, (1): 43–45. [80] KIM B K, KANG H S, and PARK S O. Experimental analysis of small drone polarimetry based on micro-Doppler signature[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(10): 1670–1674. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2727824 [81] 章鹏飞, 李刚, 霍超颖, 等. 基于双雷达微动特征融合的无人机分类识别[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 557–564. doi: 10.12000/JR18061ZHANG Pengfei, LI Gang, HUO Chaoying, et al. Classification of drones based on micro-Doppler radar signatures using dual radar sensors[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 557–564. doi: 10.12000/JR18061 [82] 罗迎, 倪嘉成, 张群. 基于“数据驱动+智能学习”的合成孔径雷达学习成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 107–122. doi: 10.12000/JR19103LUO Ying, NI Jiacheng, and ZHANG Qun. Synthetic aperture radar learning-imaging method based on data-driven technique and artificial intelligence[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 107–122. doi: 10.12000/JR19103 [83] 牟效乾, 陈小龙, 苏宁远, 等. 基于时频图深度学习的雷达动目标检测与分类[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2019, 17(1): 105–111. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201901.0105MOU Xiaoqian, CHEN Xiaolong, SU Ningyuan, et al. Radar detection and classification of moving target using deep convolutional neural networks on time-frequency graphs[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2019, 17(1): 105–111. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA201901.0105 [84] SUN Hongbo, OH B S, GUO Xin, et al. Improving the Doppler resolution of ground-based surveillance radar for drone detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 3667–3673. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2895585 [85] 许稼, 彭应宁, 夏香根, 等. 空时频检测前聚焦雷达信号处理方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(2): 129–141. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14023XU Jia, PENG Yingning, XIA Xianggen, et al. Radar signal processing method of space-time-frequency focus-before-detects[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(2): 129–141. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14023 [86] 陈曾平, 张月, 鲍庆龙. 数字阵列雷达及其关键技术进展[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2010, 32(6): 1–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2010.06.001CHEN Zengping, ZHANG Yue, and BAO Qinglong. Advance in digital array radar and its key technologies[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2010, 32(6): 1–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2010.06.001 [87] CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, LI Xiuyou, et al. Effective coherent integration method for marine target with micromotion via phase differentiation and radon-Lv’s distribution[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2015, 9(9): 1284–1295. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0100 [88] KLARE J, BIALLAWONS O, and CERUTTI-MAORI D. UAV detection with MIMO radar[C]. The 2017 18th International Radar Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 2017. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2017.8008140. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: