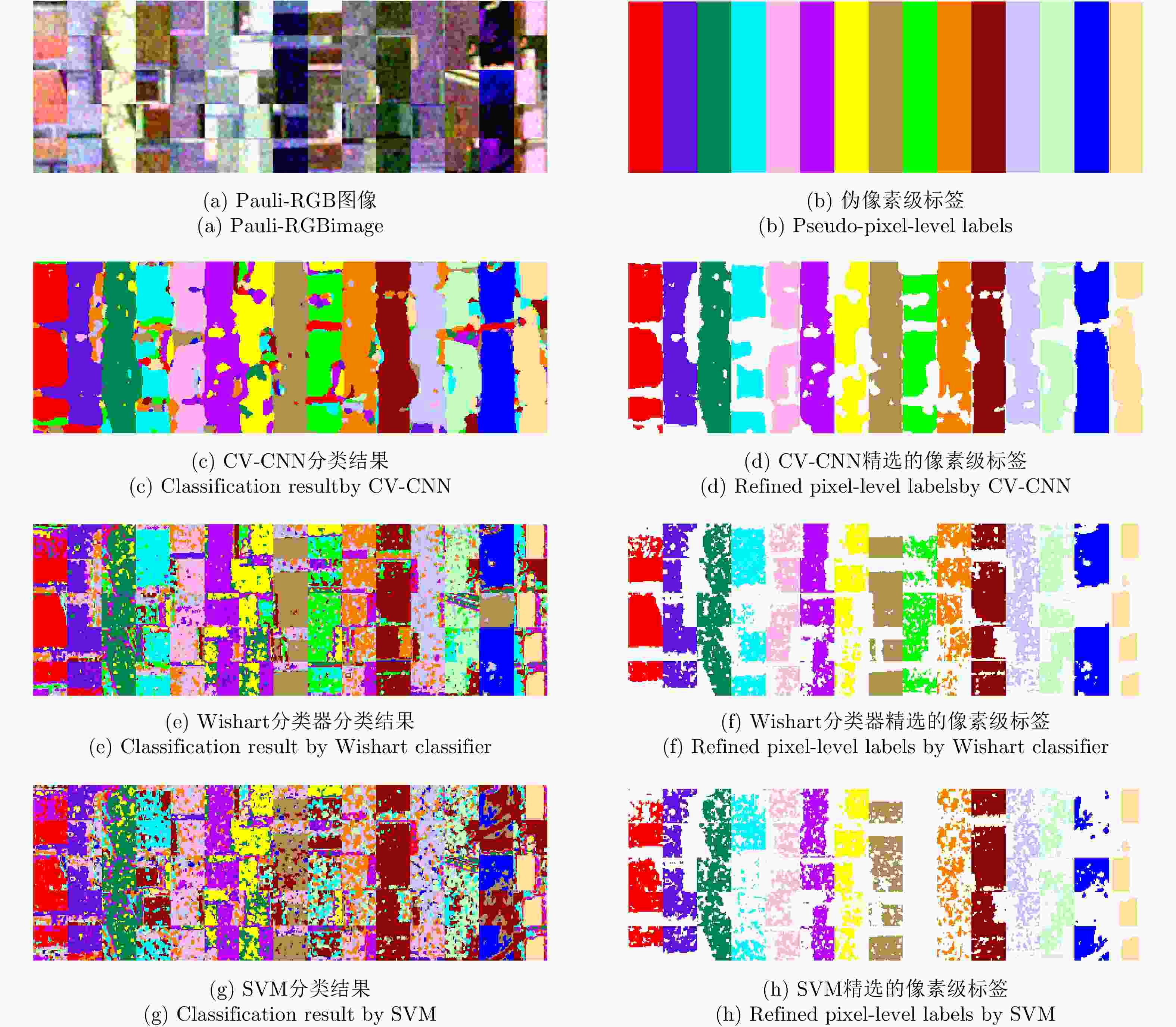
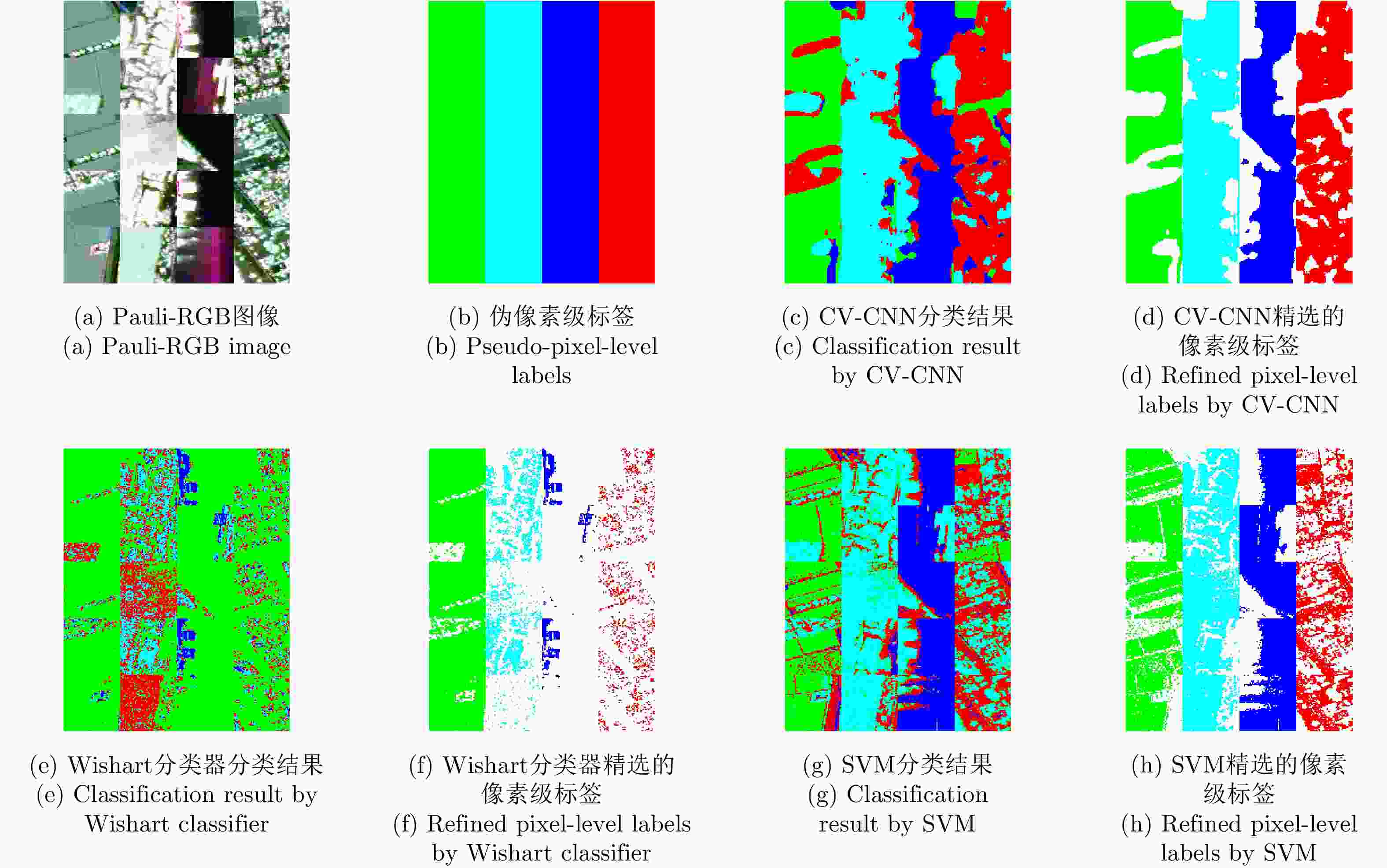
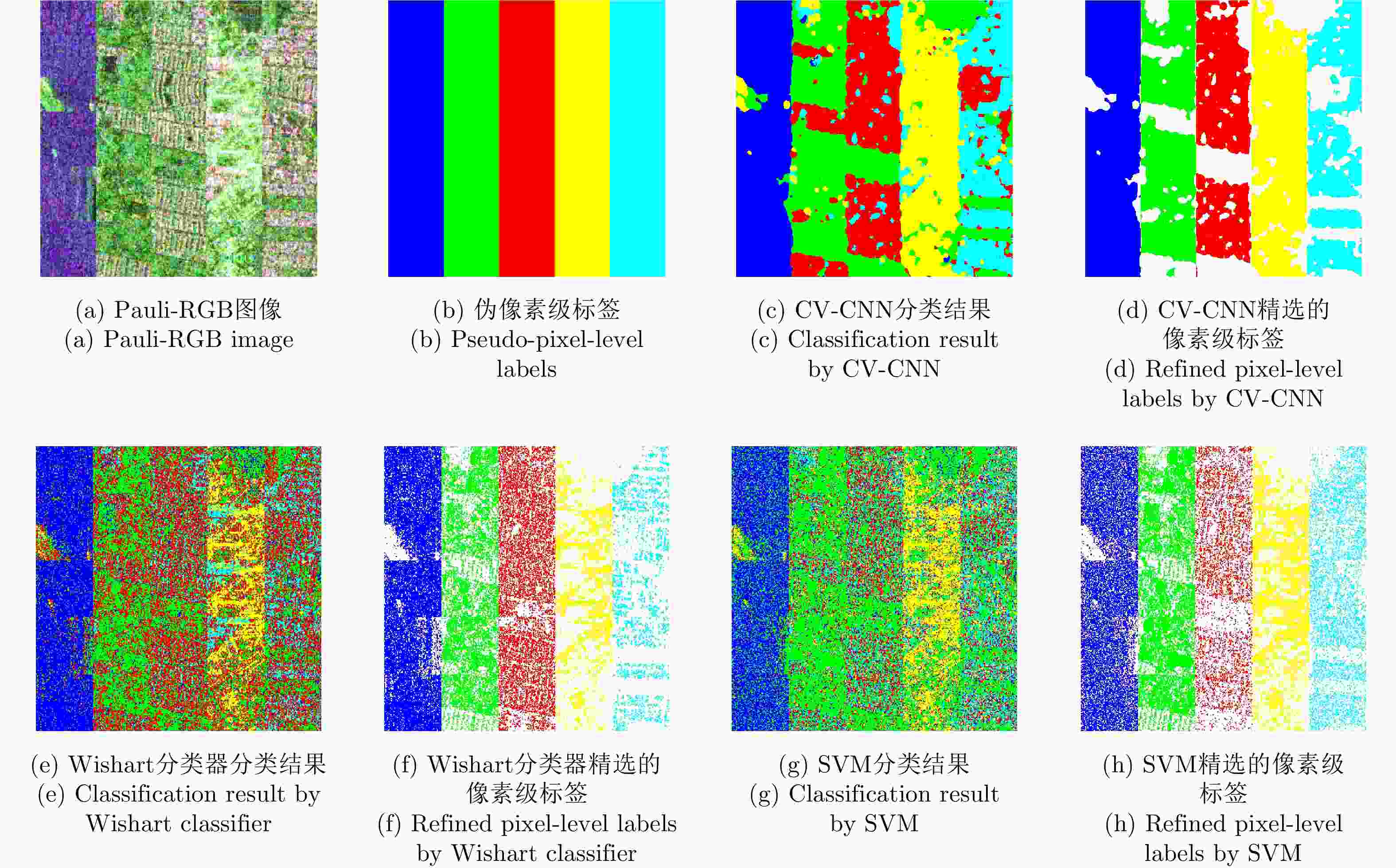
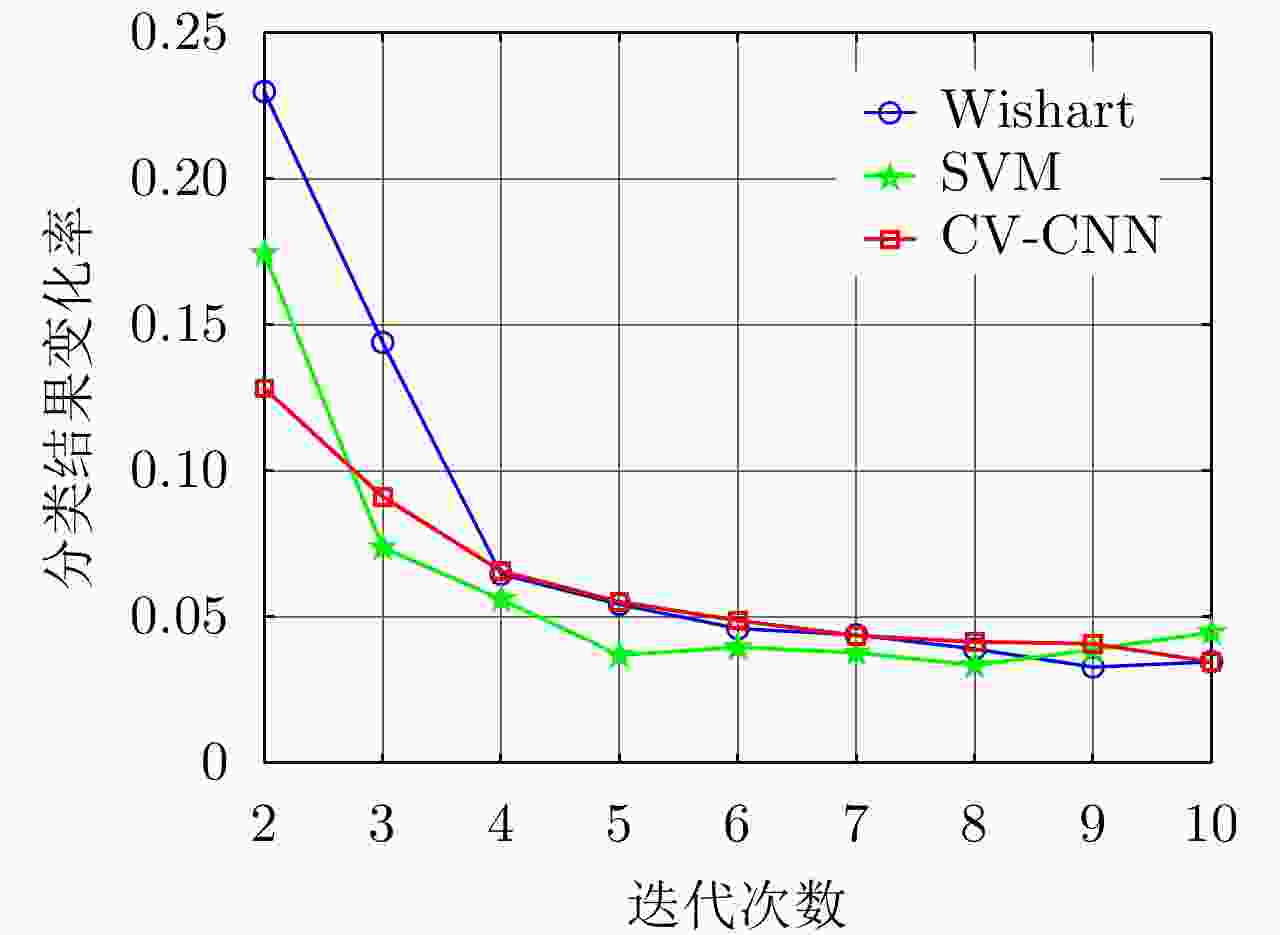
Weakly Supervised Classification of PolSAR Images Based on Sample Refinement with Complex-Valued Convolutional Neural Network
-
摘要:
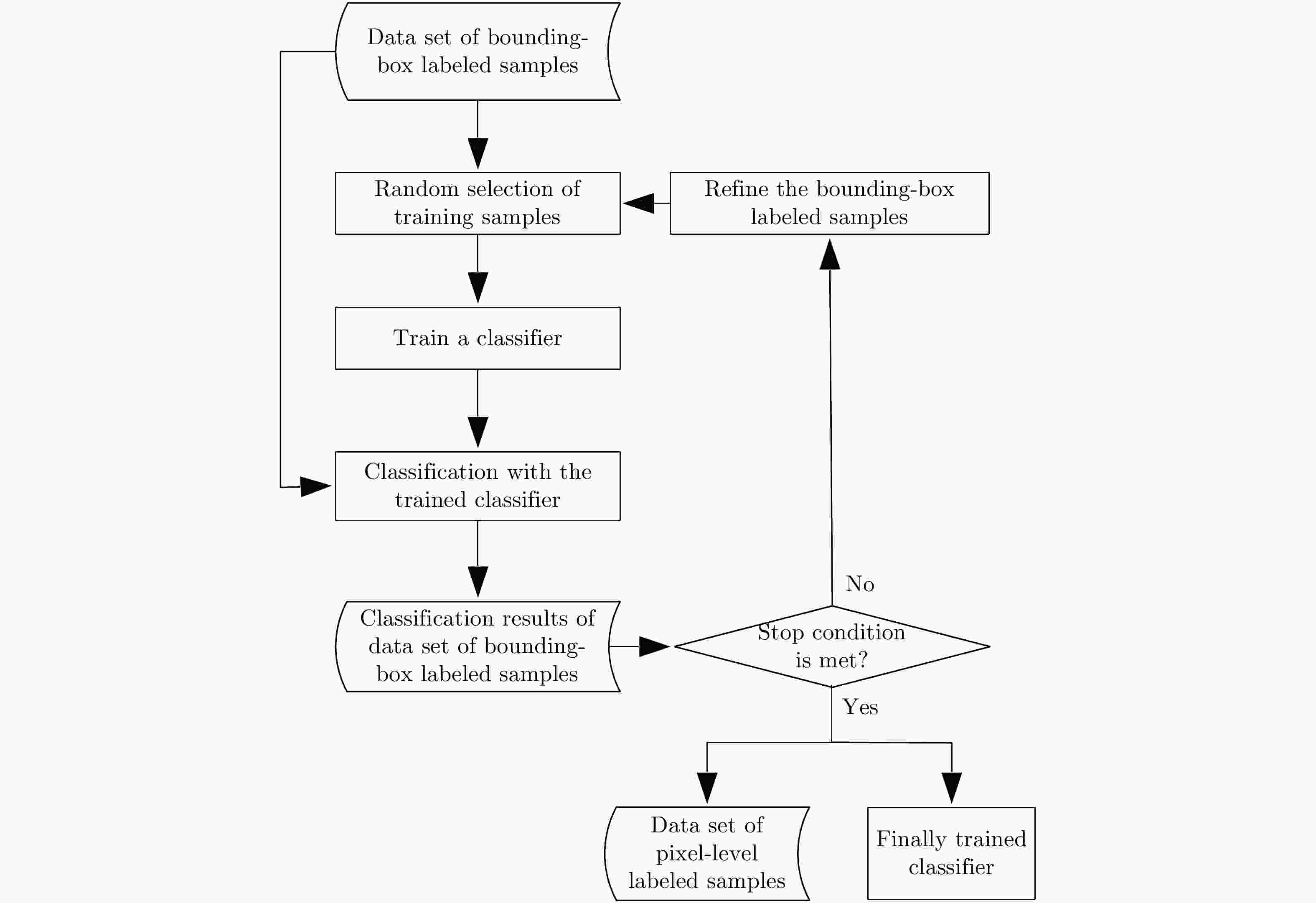
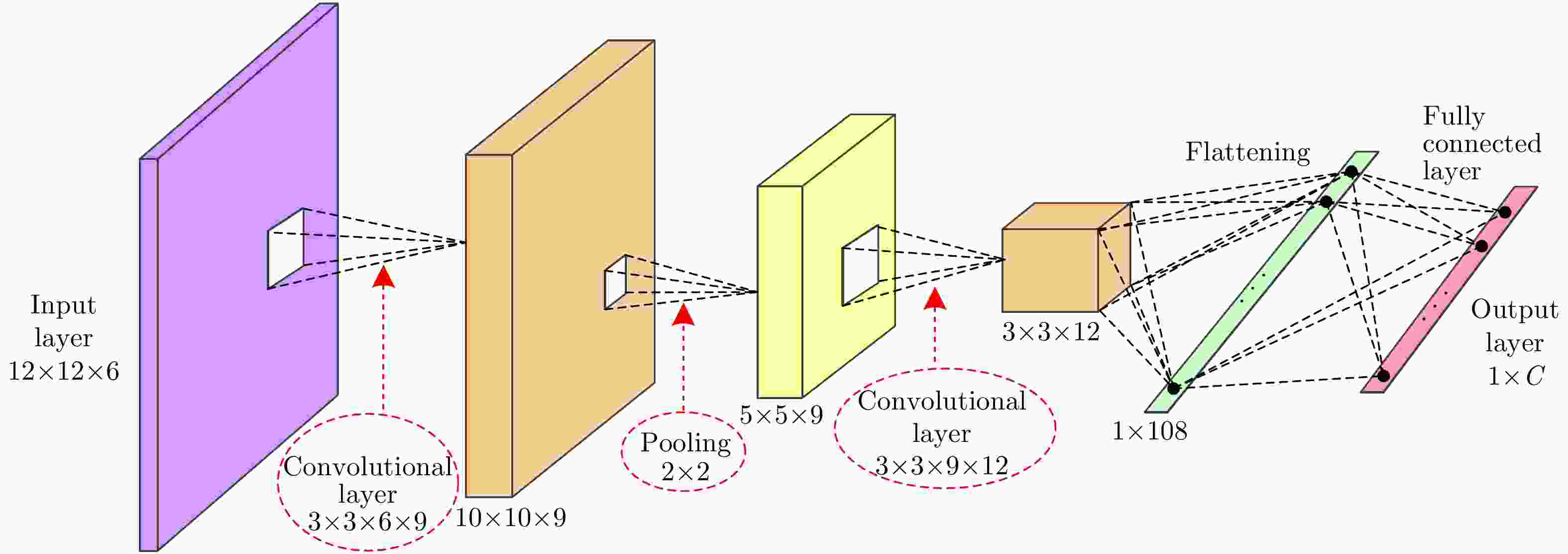
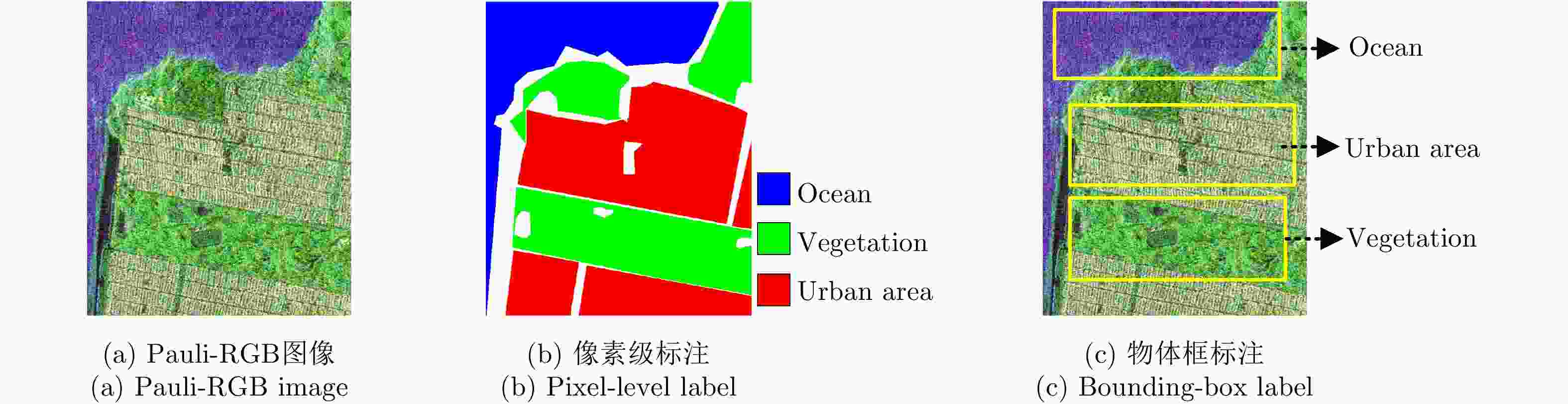
针对物体框标注样本包含大量异质成分的问题,该文提出了一种基于复值卷积神经网络(CV-CNN)样本精选的极化SAR(PolSAR)图像弱监督分类方法。该方法首先采用CV-CNN对物体框标注样本进行迭代精选,并同时训练出可直接用于分类的CV-CNN。然后利用所训练的CV-CNN完成极化SAR图像的分类。基于3幅实测极化SAR图像的实验结果表明,该文方法能够有效剔除异质样本,与采用原始物体框标注样本的传统全监督分类方法相比可以获得明显更优的分类结果,并且该方法采用CV-CNN比采用经典的支持矢量机(SVM)或Wishart分类器性能更优。
Abstract:In this study, a weakly supervised classification method is proposed to classify the Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) images based on sample refinement using a Complex-Valued Convolutional Neural Network (CV-CNN) to solve the problem that the bounding-box labeled samples contain many heterogeneous components. First, CV-CNN is used for iteratively refining the bounding-box labeled samples, and the CV-CNN that can be used for direct classification is trained simultaneously. Then, the given PolSAR image is classified using the trained CV-CNN. The experimental results obtained using three actual PolSAR images demonstrate that the heterogeneous components can be effectively eliminated using the proposed method, obtaining significantly better classification results when compared with those obtained using the traditional fully supervised classification method in which original bounding-box labeled samples are used. Furthermore, the proposed method with CV-CNN is superior to those in which the classical Support Vector Machine(SVM) and Wishart classifier are used.
-
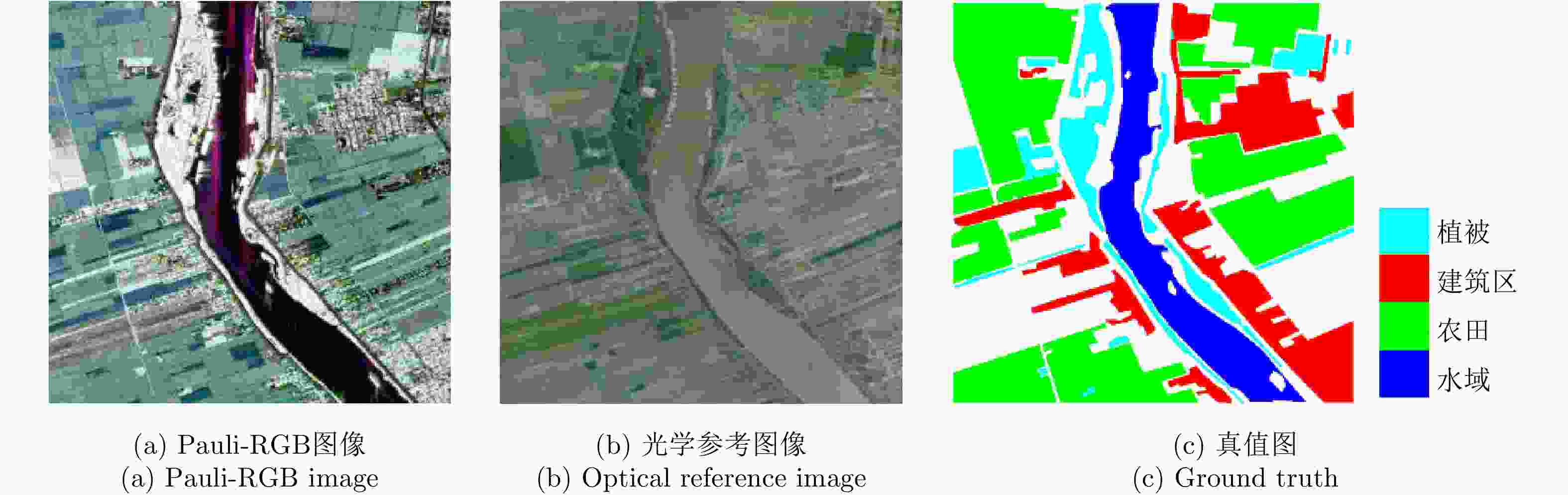
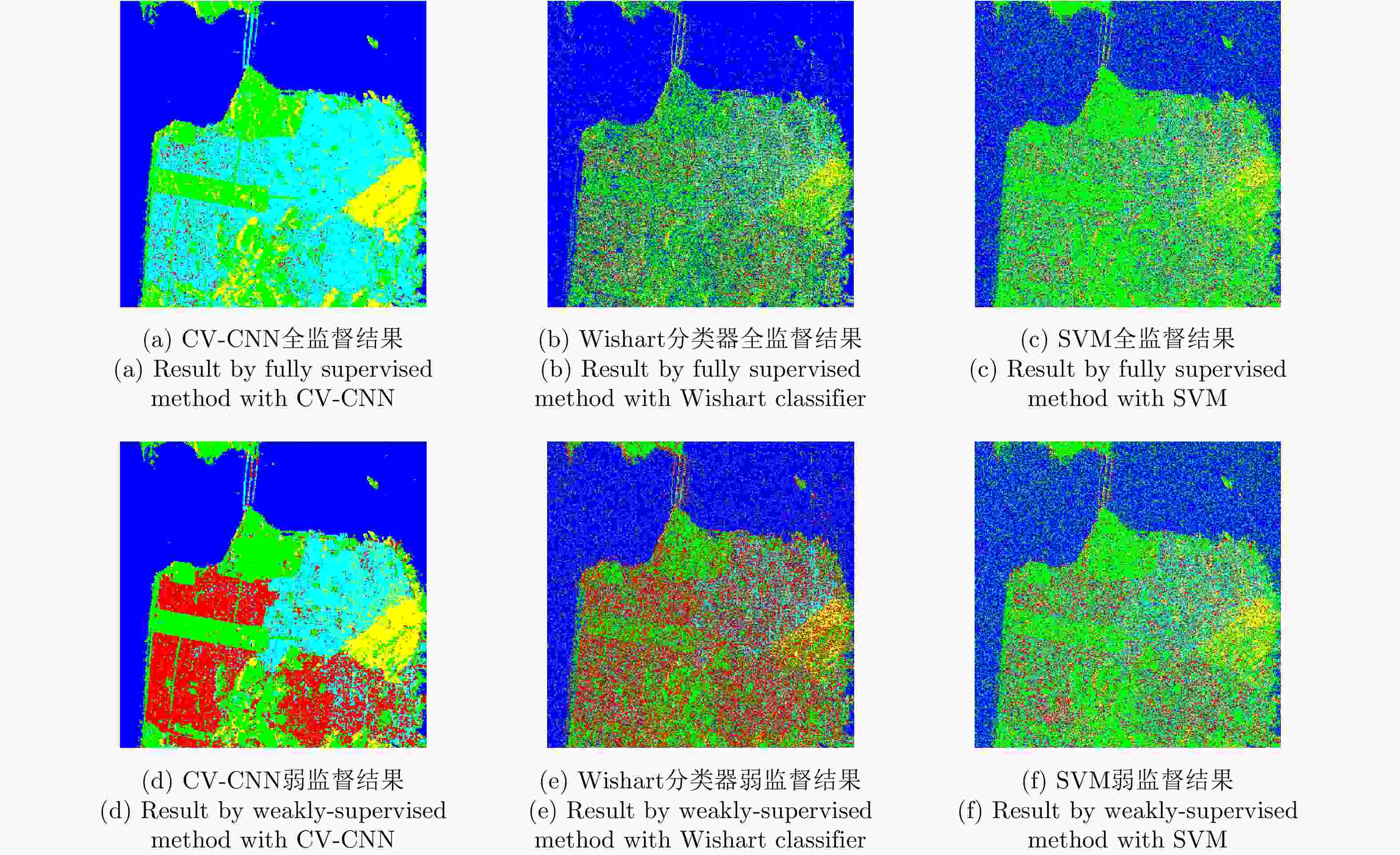
表 1 实验数据1的分类精度(%)、总体精度(%)和Kappa系数
Table 1. Classification accuracy (%), overall accuracy (%) and Kappa coefficient for experimental data 1
方法 蚕豆 豌豆 树林 苜蓿 小麦1 甜菜 土豆 裸地 草地 CV-CNN全监督 56.43 89.02 99.21 20.37 97.12 80.63 49.86 100.00 30.96 CV-CNN弱监督 56.14 98.35 85.18 92.72 88.23 89.00 70.87 100.00 85.56 Wishart全监督 56.51 81.19 88.15 39.88 54.74 35.49 67.11 0.68 0.11 Wishart弱监督 61.63 80.52 81.46 85.90 73.71 91.21 63.84 99.71 62.02 SVM全监督 85.43 74.37 71.80 67.52 68.37 52.59 78.21 21.05 0 SVM弱监督 81.77 73.20 68.44 58.26 61.42 55.45 75.99 27.18 0 方法 油菜籽 大麦 小麦2 小麦3 水域 建筑区 总体精度 Kappa系数 CV-CNN全监督 48.35 95.74 94.36 91.29 90.41 96.22 76.87 0.7473 CV-CNN弱监督 48.21 93.66 95.69 89.81 81.69 99.37 84.58 0.8323 Wishart全监督 19.48 97.48 76.32 53.16 80.51 91.81 58.02 0.5440 Wishart弱监督 44.47 87.02 67.36 68.58 37.47 90.13 69.38 0.6674 SVM全监督 31.42 29.47 39.90 75.97 77.51 67.75 57.09 0.5352 SVM弱监督 36.51 34.76 39.51 70.24 76.72 70.27 56.58 0.5291 表 2 实验数据2的分类精度(%)、总体精度(%)和Kappa系数
Table 2. Classification accuracy (%), overall accuracy (%) and Kappa coefficient for experimental data 2
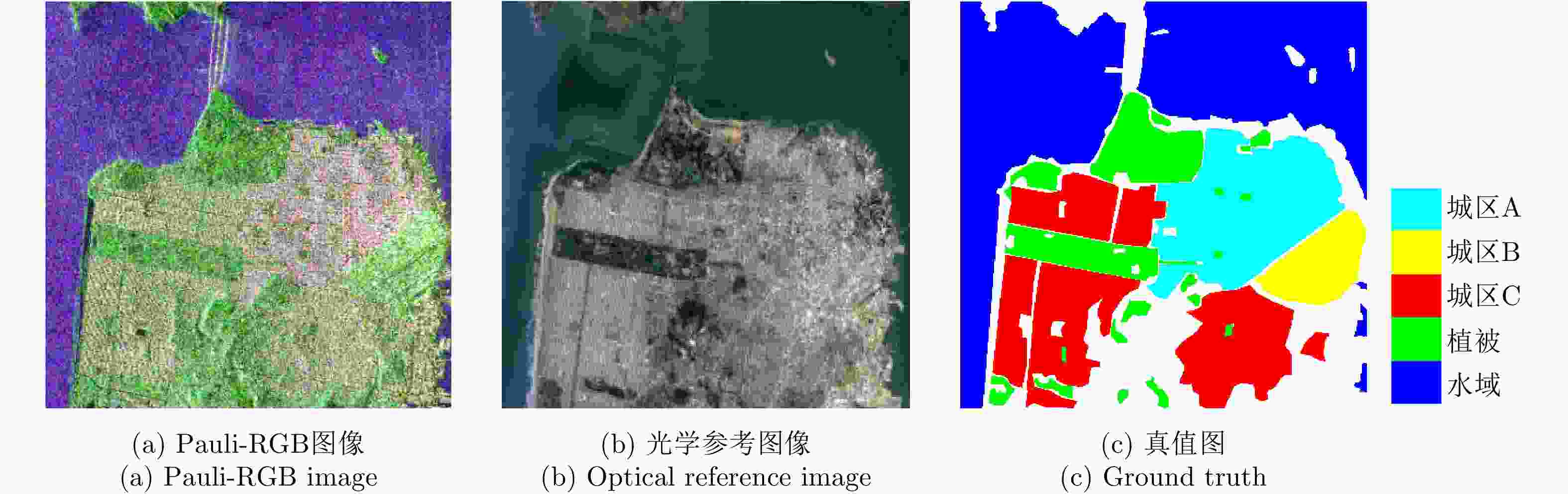
方法 农田 植被 水域 建筑区 总体精度 Kappa系数 CV-CNN全监督 82.42 90.41 98.79 64.91 82.14 0.7458 CV-CNN弱监督 93.34 91.38 98.76 75.88 90.02 0.8537 Wishart全监督 99.76 55.95 0.05 13.07 36.36 0.1515 Wishart弱监督 99.76 34.09 0.01 20.22 34.54 0.1272 SVM全监督 84.33 59.42 71.18 52.22 73.52 0.6073 SVM弱监督 88.07 52.05 93.66 38.79 70.40 0.5797 表 3 实验数据3的分类精度(%)、总体精度(%)和Kappa系数
Table 3. Classification accuracy (%), overall accuracy (%) and Kappa coefficient for experimental data 3
方法 水域 植被 城区A 城区B 城区C 总体精度 Kappa系数 CV-CNN全监督 99.37 82.37 7.55 88.89 91.57 74.56 0.6466 CV-CNN弱监督 99.43 91.98 81.84 80.09 82.84 91.05 0.8731 Wishart全监督 95.58 63.34 23.14 33.05 32.03 45.76 0.3219 Wishart弱监督 86.68 61.32 51.52 24.99 31.77 45.92 0.3239 SVM全监督 85.53 26.71 56.13 23.44 38.99 54.34 0.3802 SVM弱监督 88.51 27.71 56.55 27.44 35.86 54.87 0.3940 -
[1] LEE J S and POTTIER E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications[M]. Boca Raton, USA: CRC Press, 2009. [2] SALEHI M, SAHEBI M R, and MAGHSOUDI Y. Improving the accuracy of urban land cover classification using Radarsat-2 PolSAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(4): 1394–1401. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2273074 [3] VOORMANSIK K, JAGDHUBER T, ZALITE K, et al. Observations of cutting practices in agricultural grasslands using polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(4): 1382–1396. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2503773 [4] YAMAGUCHI Y. Disaster monitoring by fully polarimetric SAR data acquired with ALOS-PALSAR[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2012, 100(10): 2851–2860. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2012.2195469 [5] 折小强, 仇晓兰, 雷斌, 等. 一种极化熵结合混合GEV模型的全极化SAR潮间带区域地物分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 554–563. doi: 10.12000/JR16149SHE Xiaoqiang, QIU Xiaolan, LEI Bin, et al. A classification method based on polarimetric entropy and GEV mixture model for intertidal area of PolSAR image[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 554–563. doi: 10.12000/JR16149 [6] LEE J S, GRUNES M R, AINSWORTH T L, et al. Unsupervised classification using polarimetric decomposition and the complex Wishart classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1999, 37(5): 2249–2258. doi: 10.1109/36.789621 [7] LEE J S, GRUNES M R, POTTIER E, et al. Unsupervised terrain classification preserving polarimetric scattering characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(4): 722–731. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.819883 [8] ZOU Huanxin, LI Meilin, SHAO Ningyuan, et al. Superpixel-oriented unsupervised classification for polarimetric SAR images based on consensus similarity network fusion[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 78347–78366. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2922473 [9] LIU Chi, LI Hengchao, LIAO Wenzhi, et al. Variational textured dirichlet process mixture model with pairwise constraint for unsupervised classification of polarimetric SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(8): 4145–4160. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2906009 [10] 钟能, 杨文, 杨祥立, 等. 基于混合Wishart模型的极化SAR图像非监督分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 533–540. doi: 10.12000/JR16133ZHONG Neng, YANG Wen, YANG Xiangli, et al. Unsupervised classification for polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images based on Wishart mixture models[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 533–540. doi: 10.12000/JR16133 [11] 孙勋, 黄平平, 涂尚坦, 等. 利用多特征融合和集成学习的极化SAR图像分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 692–700. doi: 10.12000/JR15132SUN Xun, HUANG Pingping, TU Shangtan, et al. Polarimetric SAR image classification using multiple-feature fusion and ensemble learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 692–700. doi: 10.12000/JR15132 [12] 胡涛, 李卫华, 秦先祥, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络和条件随机场模型的PolSAR图像地物分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(4): 471–478. doi: 10.12000/JR18065HU Tao, LI Weihua, QIN Xianxiang, et al. Terrain classification of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images based on deep learning and conditional random field model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(4): 471–478. doi: 10.12000/JR18065 [13] 邹焕新, 李美霖, 马倩, 等. 一种基于张量积扩散的非监督极化SAR图像地物分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(4): 436–447. doi: 10.12000/JR19057ZOU Huanxin, LI Meilin, MA Qian, et al. An unsupervised PolSAR image classification algorithm based on tensor product graph diffusion[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(4): 436–447. doi: 10.12000/JR19057 [14] HOU Biao, KOU Hongda, and JIAO Licheng. Classification of polarimetric SAR images using multilayer autoencoders and superpixels[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(7): 3072–3081. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2553104 [15] JIAO Licheng and LIU Fang. Wishart deep stacking network for fast PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(7): 3273–3286. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2567069 [16] ZHOU Yu, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Polarimetric SAR image classification using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1935–1939. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2618840 [17] ZHANG Zhimian, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Complex-valued convolutional neural network and its application in polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7177–7188. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743222 [18] CHEN Siwei and TAO Chensong. PolSAR image classification using polarimetric-feature-driven deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(4): 627–631. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2799877 [19] SALEH F S, ALIAKBARIAN M S, SALZMANN M, et al. Incorporating network built-in priors in weakly-supervised semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(6): 1382–1396. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2713785 [20] 魏云超, 赵耀. 基于DCNN的图像语义分割综述[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2016, 40(4): 82–91. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291.2016.04.013WEI Yunchao and ZHAO Yao. A review on image semantic segmentation based on DCNN[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2016, 40(4): 82–91. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291.2016.04.013 [21] 郑宝玉, 王雨, 吴锦雯, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的弱监督图像语义分割[J]. 南京邮电大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 38(5): 1–12.ZHENG Baoyu, WANG Yu, WU Jinwen, et al. Weakly supervised learning based on deep convolutional neural networks for image semantic segmentation[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 38(5): 1–12. [22] XU Jia, SCHWING A G, and URTASUN R. Learning to segment under various forms of weak supervision[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA, 2015: 3781–3790. [23] PAPANDREOU G, CHEN L C, MURPHY K P, et al. Weakly-and semi-supervised learning of a deep convolutional network for semantic image segmentation[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1742–1750. [24] KHOREVA A, BENENSON R, JAN H, et al. Simple does it: Weakly supervised instance and semantic segmentation[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA, 2017: 876–885. [25] WEI Yunchao, SHEN Zhiqiang, CHENG Bowen, et al. TS2C: Tight box mining with surrounding segmentation context for weakly supervised object detection[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany, 2018. [26] 韩铮, 肖志涛. 基于纹元森林和显著性先验的弱监督图像语义分割方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(3): 610–617. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170472HAN Zheng and XIAO Zhitao. Weakly supervised semantic segmentation based on semantic texton forest and saliency prior[J]. Journal of Electronics&Information Technology, 2018, 40(3): 610–617. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170472 [27] YANG Wen, DAI Dengxin, WU Jun, et al. Weakly supervised Polarimetric SAR image classification with multi-modal Markov aspect model[C]. WAGNER W and SZÉKELY B. ISPRS TC VⅡ Symposium-100 Years ISPRS. Vienna, Austria: IAPRS, 2010: 669–673. [28] YANG Wen, DAI Dengxin, TRIGGS B, et al. SAR-based terrain classification using weakly supervised hierarchical Markov aspect models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(9): 4232–4243. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2199127 [29] GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, and COURVILLE A. Deep Learning[M]. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press, 2016. [30] YU P, QIN A K, and CLAUSI D A. Unsupervised polarimetric SAR image segmentation and classification using region growing with edge penalty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(4): 1302–1317. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2164085 [31] CHANG C C and LIN C J. LIBSVM-a library for support vector machines[EB/OL]. https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/libsvm/. [32] 周晓光. 极化SAR图像分类方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2008.ZHOU Xiaoguang. Polarimetric SAR image classification[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2008. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: