Bistatic Synthetic Aperture Radar Two-dimensional Autofocus Approach Based on Prior Knowledge on Phase Structure
-
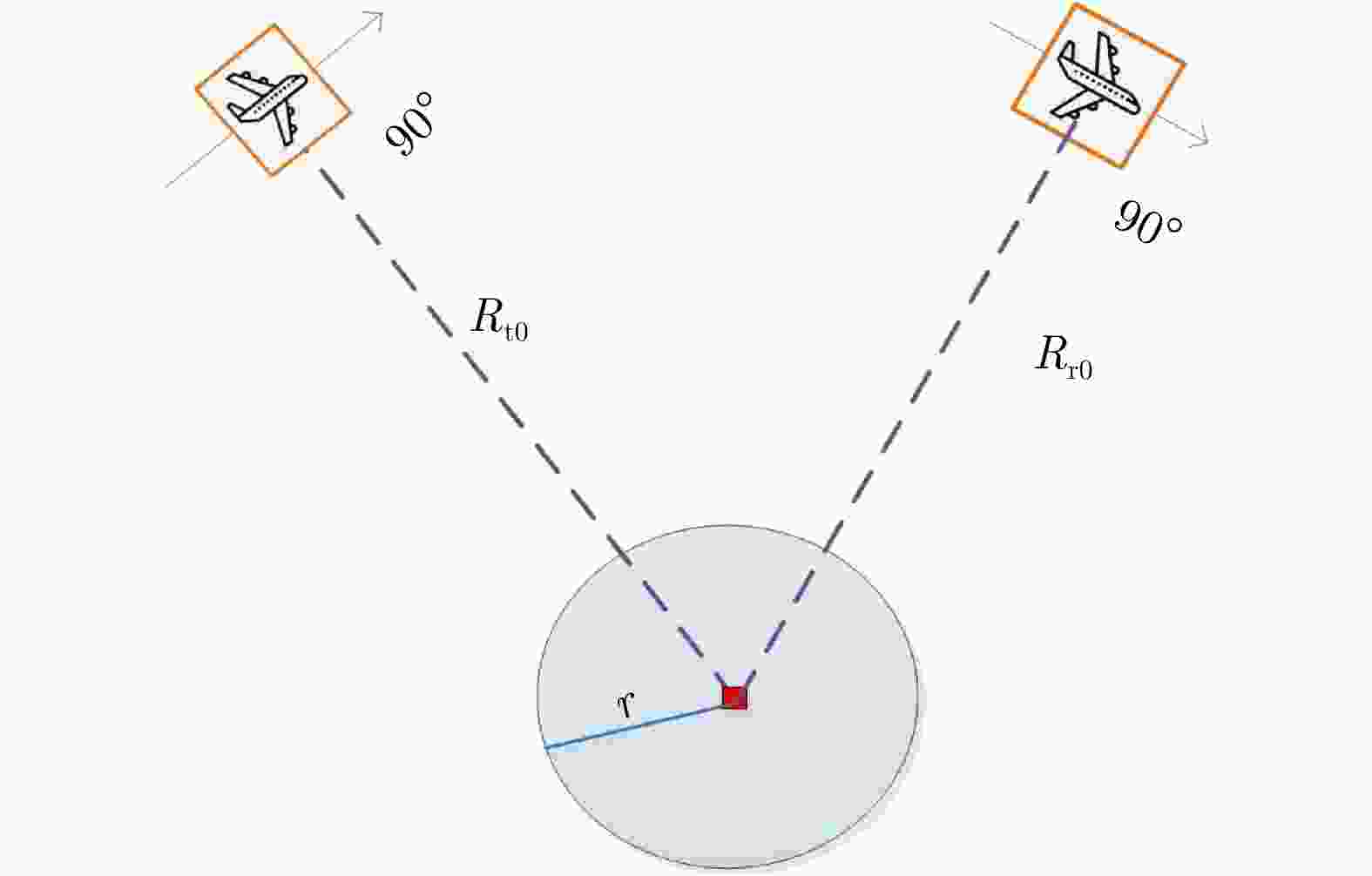
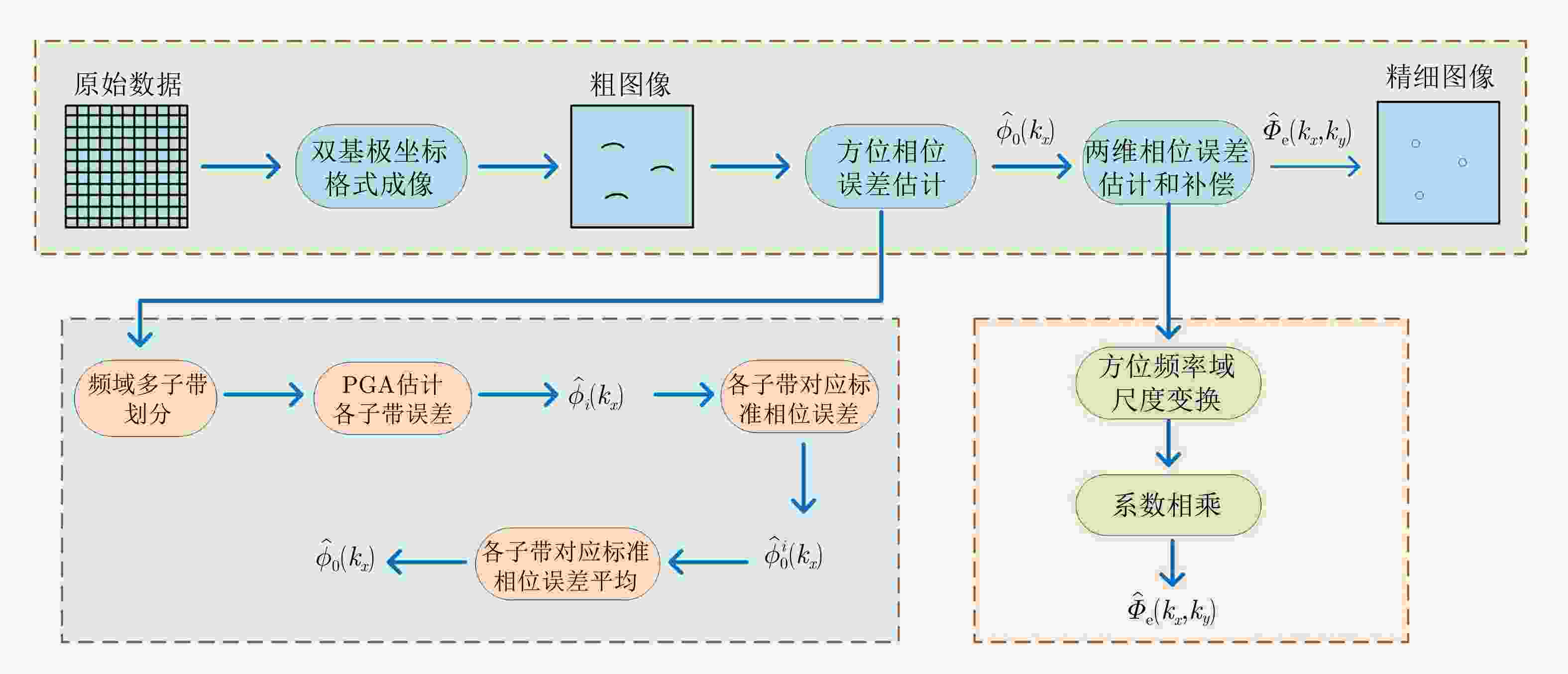
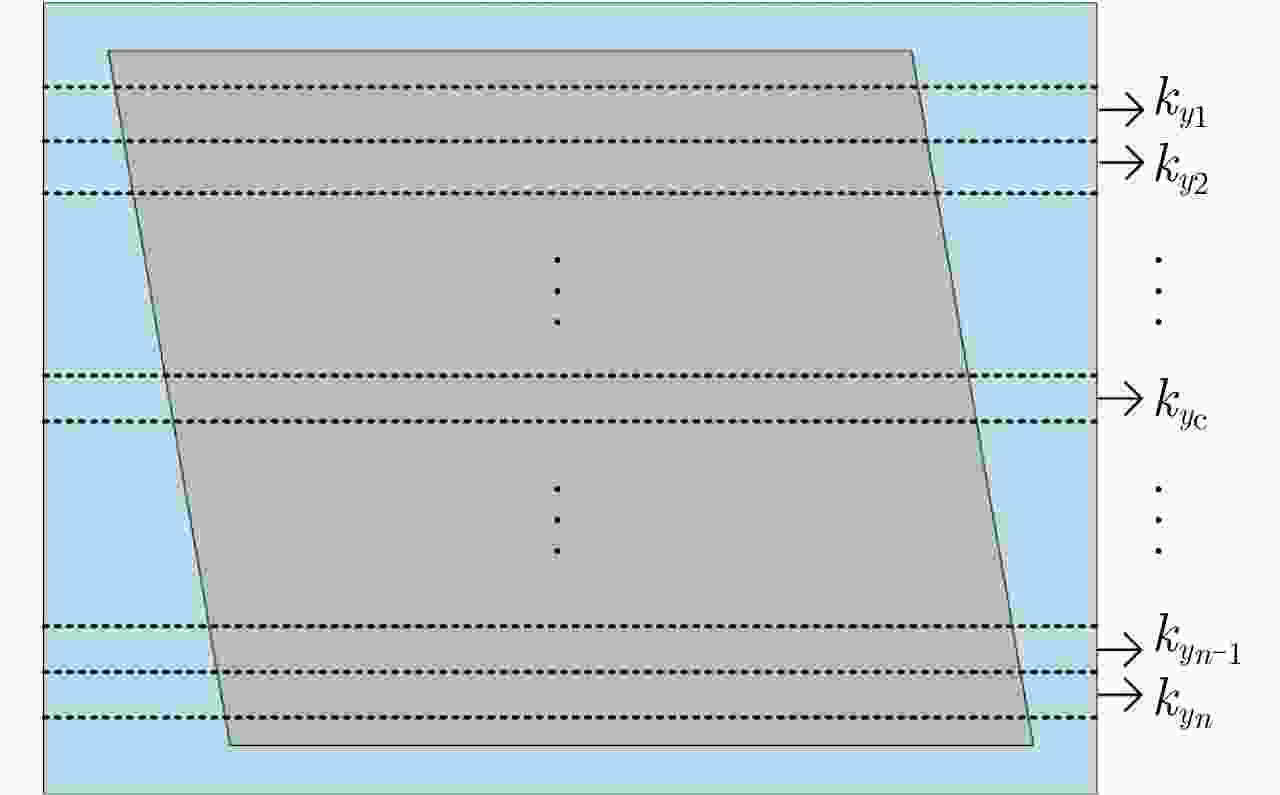
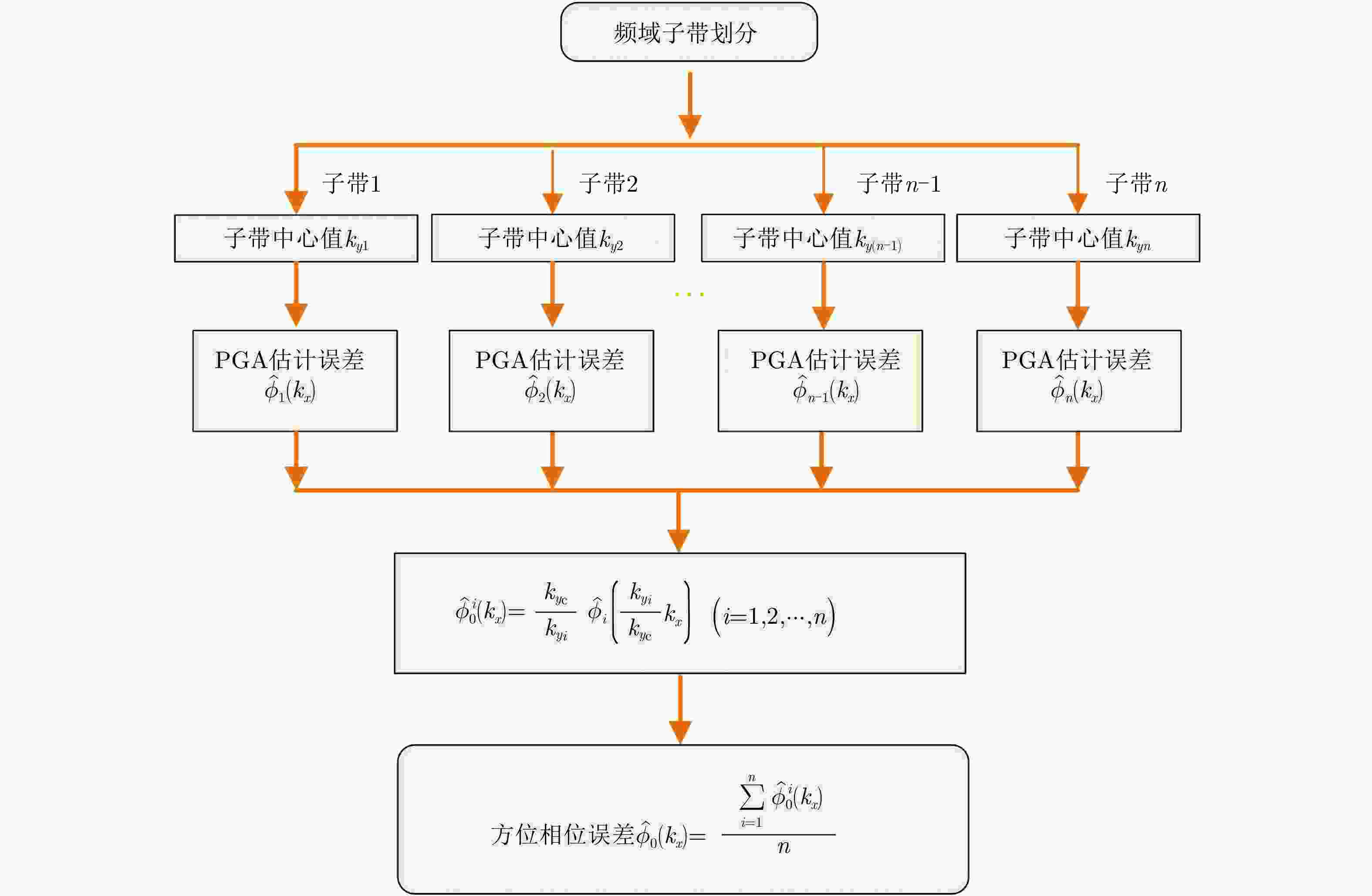
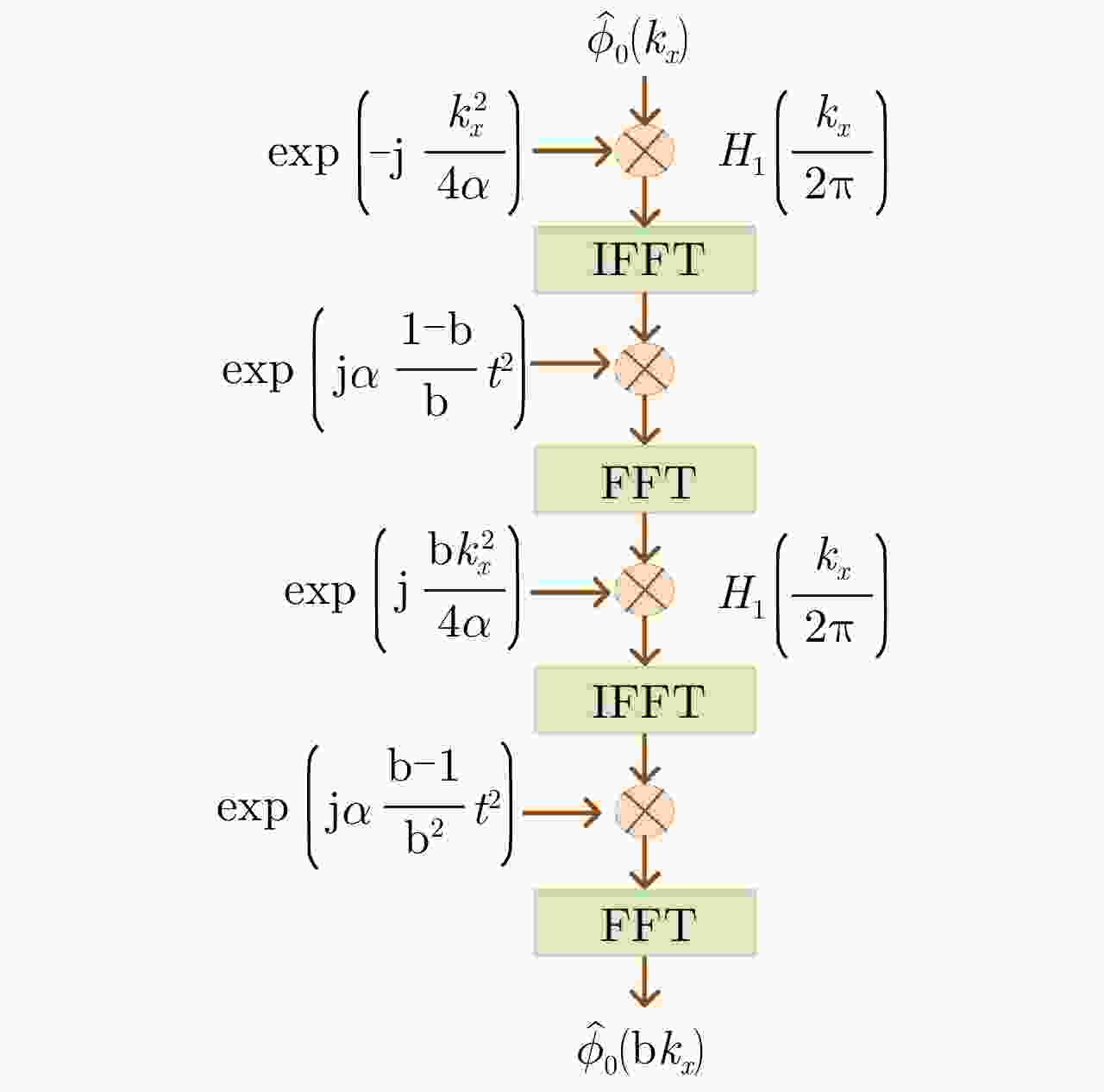
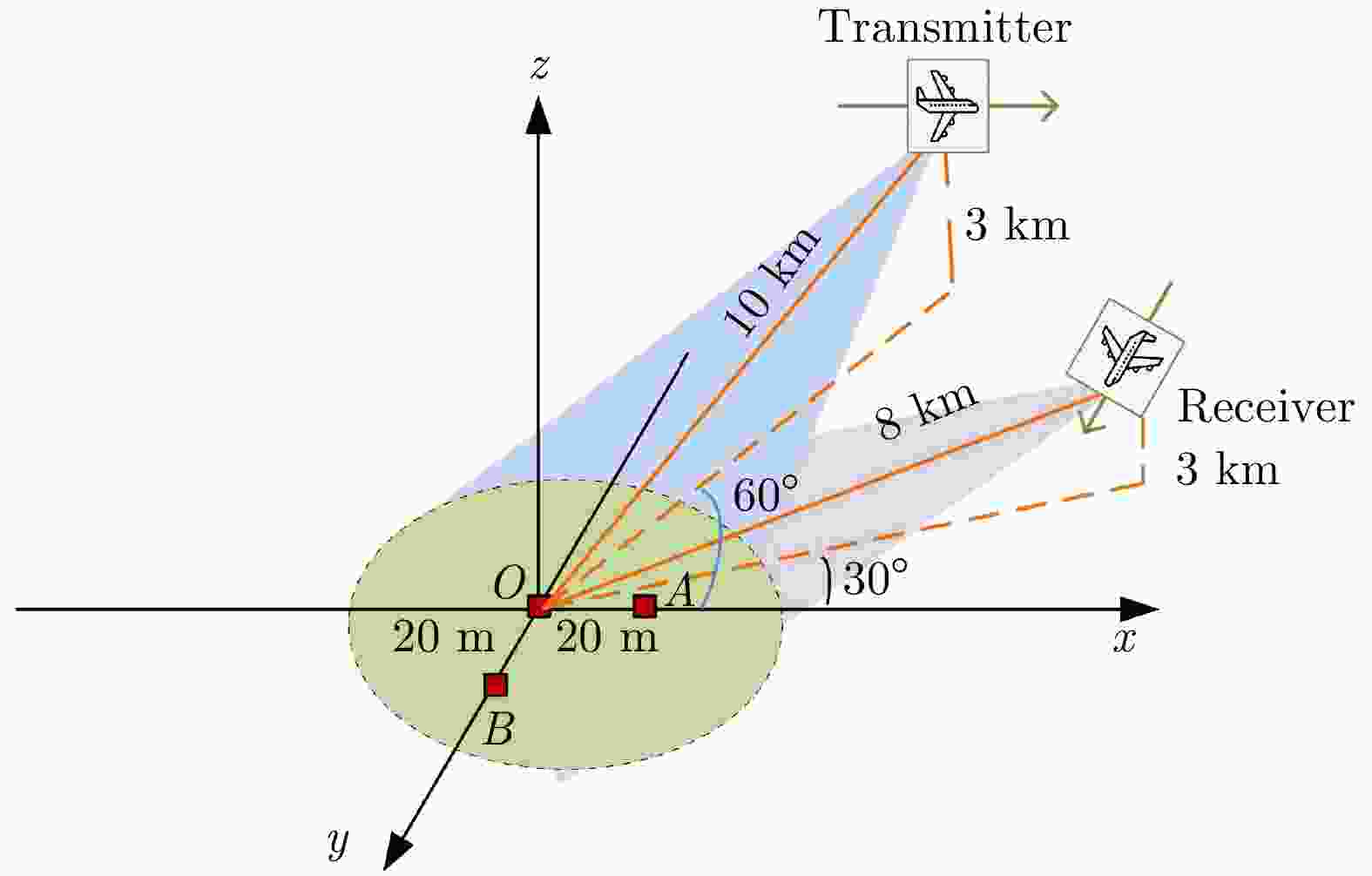
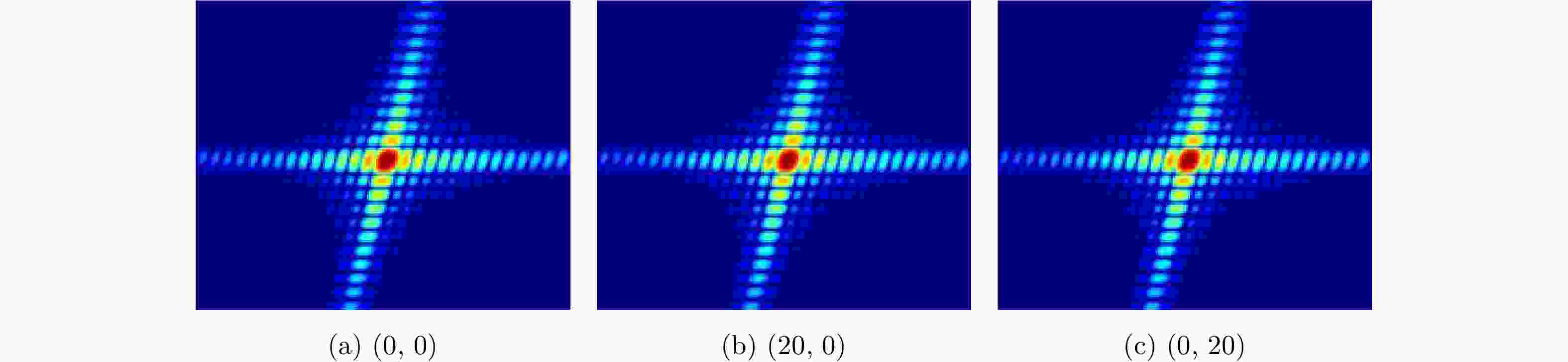
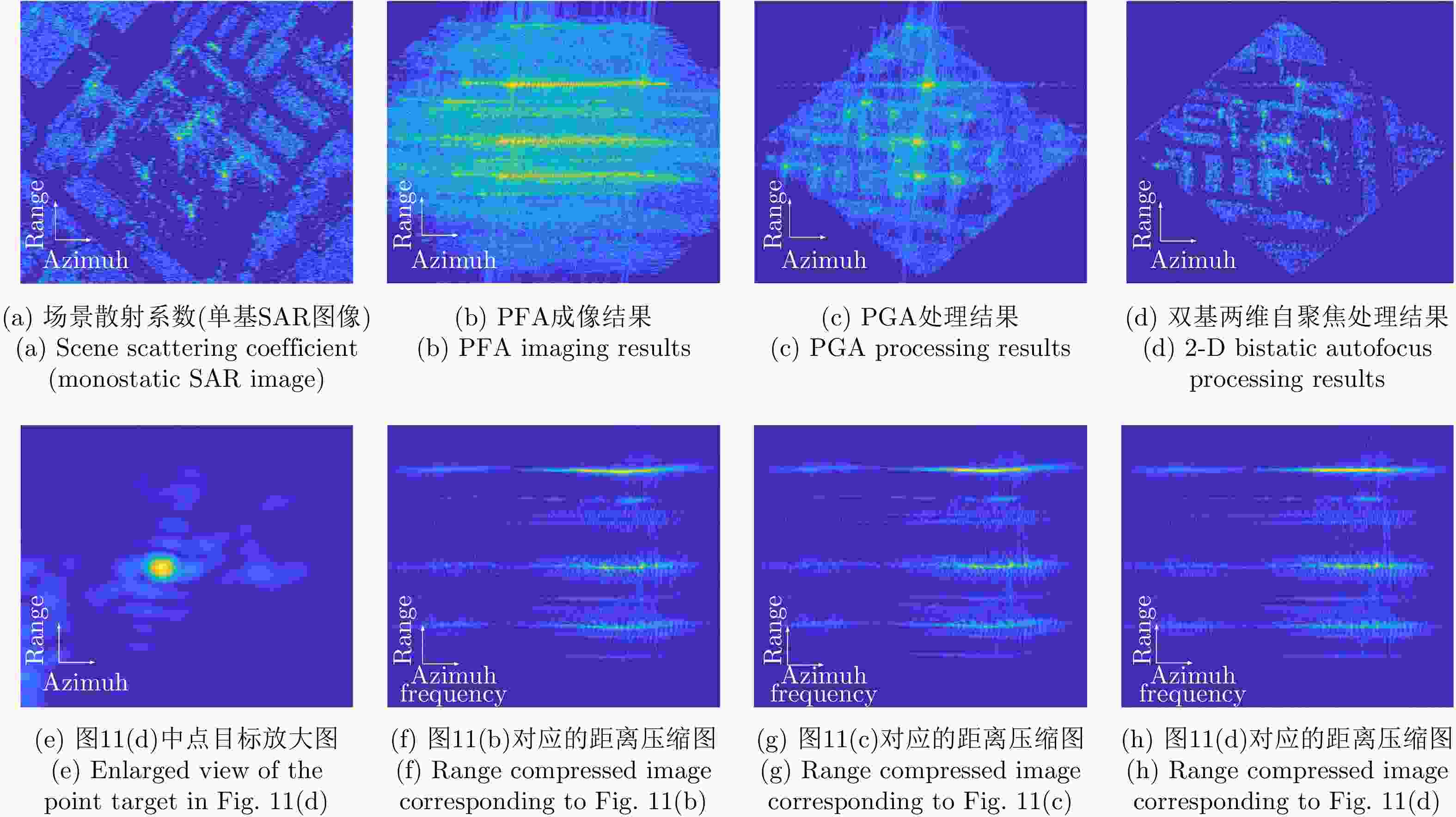
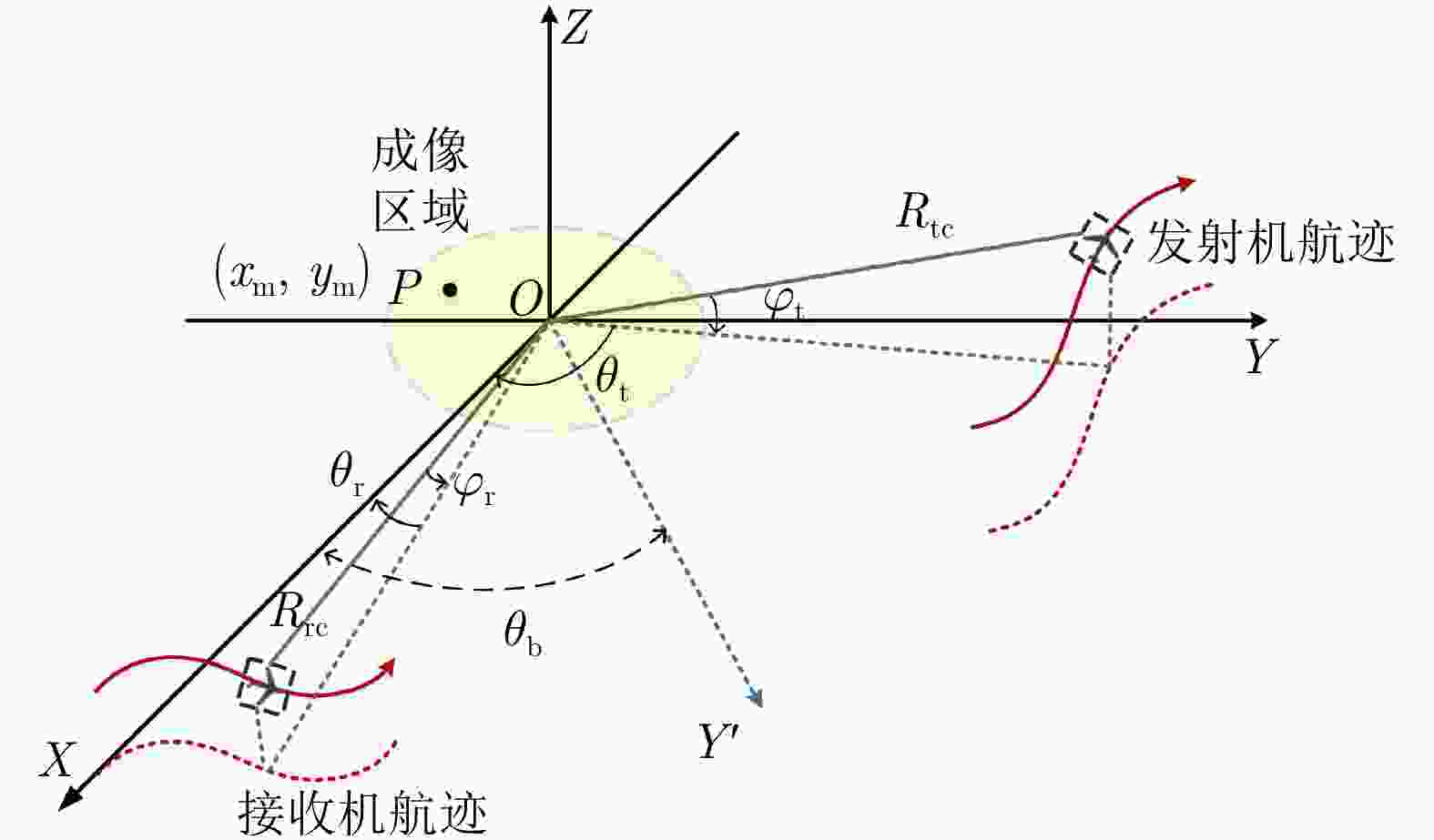
摘要: 两维自聚焦是高机动条件下机载合成孔径雷达(SAR)高分辨率成像的重要保障。现有的双基SAR两维自聚焦算法没有充分利用相位误差的先验结构信息,是对相位误差的一种盲估计,在计算效率和参数估计精度方面仍然存在很大限制。该文从双基SAR极坐标格式成像算法新解释入手,从残留距离徙动(RCM)校正的观点出发,将极坐标格式(PFA)算法的实现解释为距离频率和方位时间两个变量的解耦过程。利用这一观点分析了极坐标格式算法中的距离和方位重采样对两维相位误差的影响,揭示了残留两维相位误差固有的解析结构。基于这一固有的先验信息,该文提出了一种结合先验信息和图像数据的双基SAR两维自聚焦算法。算法通过引入先验知识,将两维相位误差估计降维成一维方位相位误差的估计;同时,在估计方位相位误差时,通过多子带数据平均,充分挖掘了所有数据的信息。相比于已有算法,无论是参数估计精度还是计算效率都有明显改善。实验结果验证了该文理论分析的正确性以及所提两维自聚焦方法的有效性。Abstract: Two-Dimensional (2-D) autofocus is an important guarantee for high-resolution imaging of airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) under high maneuvering conditions. The existing 2-D autofocus approaches for bistatic SAR blindly estimate the phase error and do not fully utilize the prior knowledge on phase structure. In this paper, a new interpretation of the Polar Format Algorithm (PFA) for general bistatic SAR imaging is presented. From the viewpoint of Residual Cell Migration (RCM), PFA is converted into 2-D decoupling. By utilizing this new formulation, we analyze the effect of range and azimuth resampling on the residual 2-D phase error and reveal the inherent structure characteristics of the residual 2-D phase error in the wavenumber domain. The 2-D phase error estimation can reduce to one dimensional azimuth phase error estimation. Based on this prior knowledge, a structure-aided 2-D autofocus approach is proposed. Meanwhile, the information of all the data is fully excavated by averaging sub-band data when the azimuth phase error is being estimated. Compared with the existing algorithms, both the parameter estimation precision and computational efficiency are significantly improved. Experimental results clearly demonstrate the correctness of the theoretical analysis and the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Simulation parameters
参数 值 脉冲宽度 0.2 μs 信号带宽 300 MHz 雷达波长 0.03 m 信号采样频率 360 MHz 脉冲重复频率 600 Hz -
[1] 邓云凯, 王宇. 先进双基SAR技术研究(英文)[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 1–9. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14026DENG Yunkai and WANG R. Exploration of advanced bistatic SAR experiments (in English)[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 1–9. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.14026 [2] BRENNER A R and ENDER J H G. Demonstration of advanced reconnaissance techniques with the airborne SAR/GMTI sensor PAMIR[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2006, 153(2): 152–162. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20050044 [3] CANTALLOUBE H and DUBOIS-FERNANDEZ P. Airborne X-band SAR imaging with 10 cm resolution: Technical challenge and preliminary results[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2006, 153(2): 163–176. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045097 [4] 郭江哲, 朱岱寅, 毛新华. 一种SAR两维自聚焦算法的FPGA实现[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(4): 444–452. doi: 10.12000/JR15092GUO Jiangzhe, ZHU Daiyin, and MAO Xinhua. FPGA implementation of a SAR two-dimensional autofocus approach[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(4): 444–452. doi: 10.12000/JR15092 [5] MAO Xinhua, ZHU Daiyin, and ZHU Zhaoda. Autofocus correction of APE and residual RCM in spotlight SAR polar format imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(4): 2693–2706. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6621846 [6] WAHL D E, EICHEL P H, GHIGLIA D C. Phase gradient autofocus-a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(3): 827–835. doi: 10.1109/7.303752 [7] DING Zegang, ZENG Tao, and YAO Di. Motion measurement errors in bistatic spotlight SAR[C]. 2009 IET International Radar Conference, Guilin, China, 2009. doi: 10.1049/cp.2009.0099. [8] ZHOU Song, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. An Azimuth-dependent Phase Gradient Autofocus (APGA) algorithm for airborne/stationary BiSAR imagery[J]. IEEE geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(6): 1290–1294. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2237749 [9] PU Wei, WU Junjie, HUANG Yulin, et al. Nonsystematic range cell migration analysis and autofocus correction for bistatic forward-looking SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(11): 6556–6570. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2840424 [10] MAO Xinhua and ZHU Daiyin. Two-dimensional autofocus for spotlight SAR polar format imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2016, 2(4): 524–539. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2016.2612945 [11] 丁晶. 单/双基SAR极坐标格式算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2017: 38–44.DING Jing. Study on polar format algorithm for monostatic/Bistatic SAR[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017: 38–44. [12] CARRARA W G, GOODMAN R S, and MAJEWSKI R M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar: Signal Processing Algorithms[M]. Norwood: Artech House, 1995: 56–89. [13] 孙进平, 白霞, 毛士艺. 聚束模式双基地SAR极坐标格式成像算法研究[J]. 电子学报, 2008, 36(12): 2324–2327. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2008.12.010SUN Jinping, BAI Xia, and MAO Shiyi. The PFA imaging algorithm for spotlight mode bistatic SAR[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2008, 36(12): 2324–2327. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2008.12.010 [14] MAO Xinhua, ZHU Daiyin, and WU Di. A new formulation of polar format algorithm for bistatic spotlight SAR[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7130972. [15] 毛新华. PFA在SAR超高分辨率成像和SAR/GMTI中的应用研究[D]. [博士论文], 南京航空航天大学, 2009: 20–30.MAO Xinhua. Study on the application of PFA in SAR ultra-high resolution imaging and SAR/GMTI[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009: 20–30. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: