Inversion of Forest Height Based on ALOS-2 PARSAR-2 Multi-baseline Polarimetric SAR Interferometry Data
-
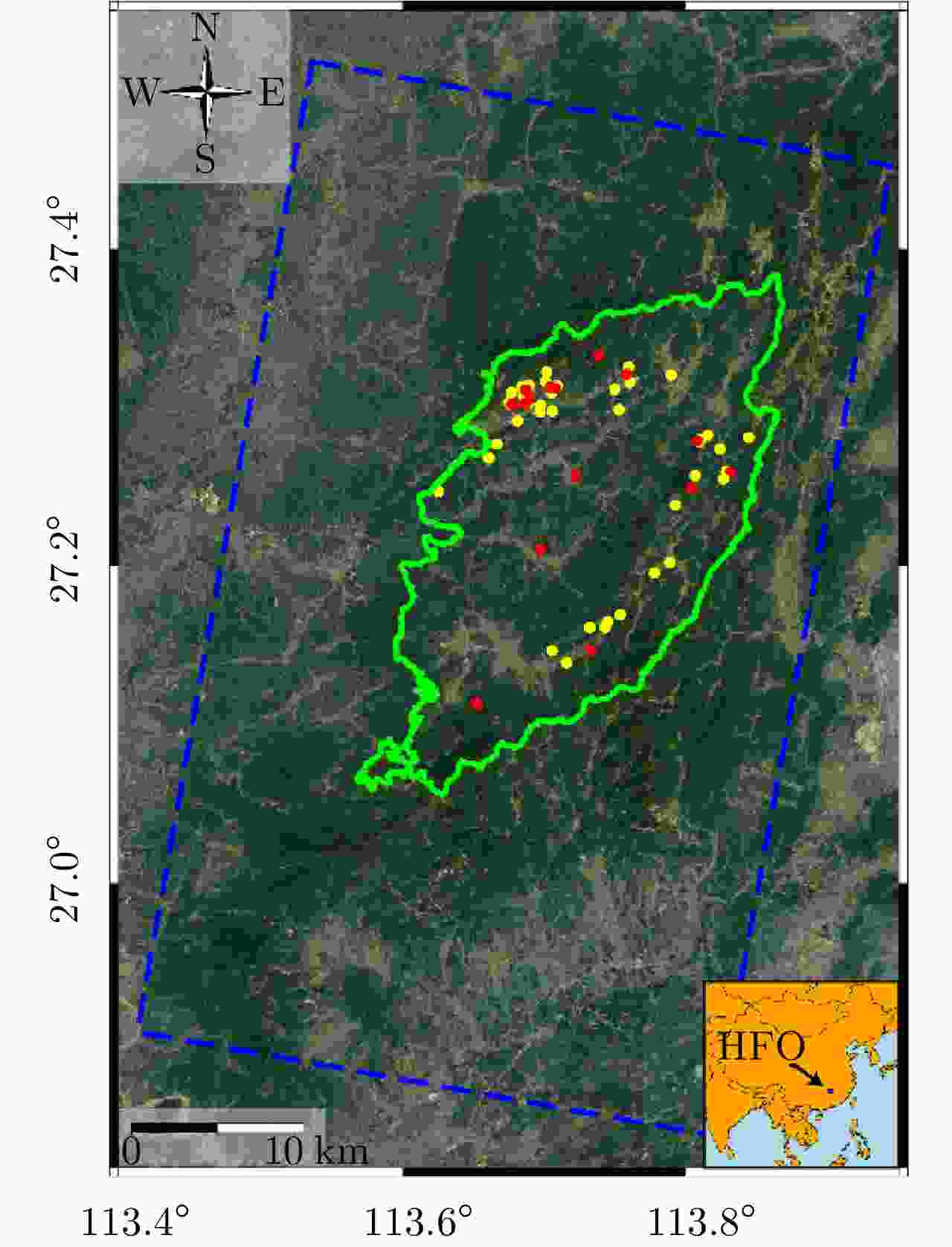
摘要: 为了弥补单基线干涉合成孔径雷达(InSAR)观测信息不足以及几何结构单一限制,该文提出了一种利用ALOS-2 PALSAR-2多基线极化干涉合成孔径雷达(PolInSAR)数据反演森林高度的方法,首先引入相干最大分离算法(MCD)用于寻求极化空间内对体散射最为敏感的极化方式,并利用该极化方式的相干幅度在少量外部已知森林高度数据辅助下对时间去相干半经验散射模型进行解算,然后进一步融合多基线数据用于增加观测几何的多样性,提升反演结果的可靠性。为了验证上述方法的有效性,该文以湖南省攸县黄丰桥国有林场为实验区,采用3对分别具有14天时间基线的ALOS-2 PALSAR-2干涉影像进行实验分析。实验结果表明,该文所提方法有效改善已有方法中的假设和仅适用单基线干涉数据的限制,使反演精度至少提高40%。Abstract: To compensate for the limitations of insufficient observation information and simplistic geometric structure of single-baseline InSAR, this study proposes a new method for extracting forest height from ALOS-2 PARSAR-2 multi-baseline PolInSAR datas. Firstly, the Maximum Coherence Difference (MCD) algorithm is introduced to determine the polarization; this algorithm is very sensitive to volume scattering in the polarization space. Then, with the aid of a small amount of externally known forest height data, the coherence amplitude of the polarization is used to solve the temporal decorrelation semi-empirical scattering model. In addition, multi-baseline datas are further fused to increase the diversity of observation geometry and improve the reliability of the inversion results. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, we selected Huangfengqiao Forestry Center in Hunan, China as the study area and used three pairs of ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 interferometric images with 14-day temporal baseline for the experimental analysis. The experimental results showed that the method proposed in this study effectively improved the assumptions and addressed the limitation of the existing method that is only applicable to single-baseline interferometric data. Thus, the inversion accuracy can be improved by at least 40%.
-
表 1 ALOS-2 PALSAR-2参数信息
Table 1. Parameter information of ALOS-2 PALSAR-2
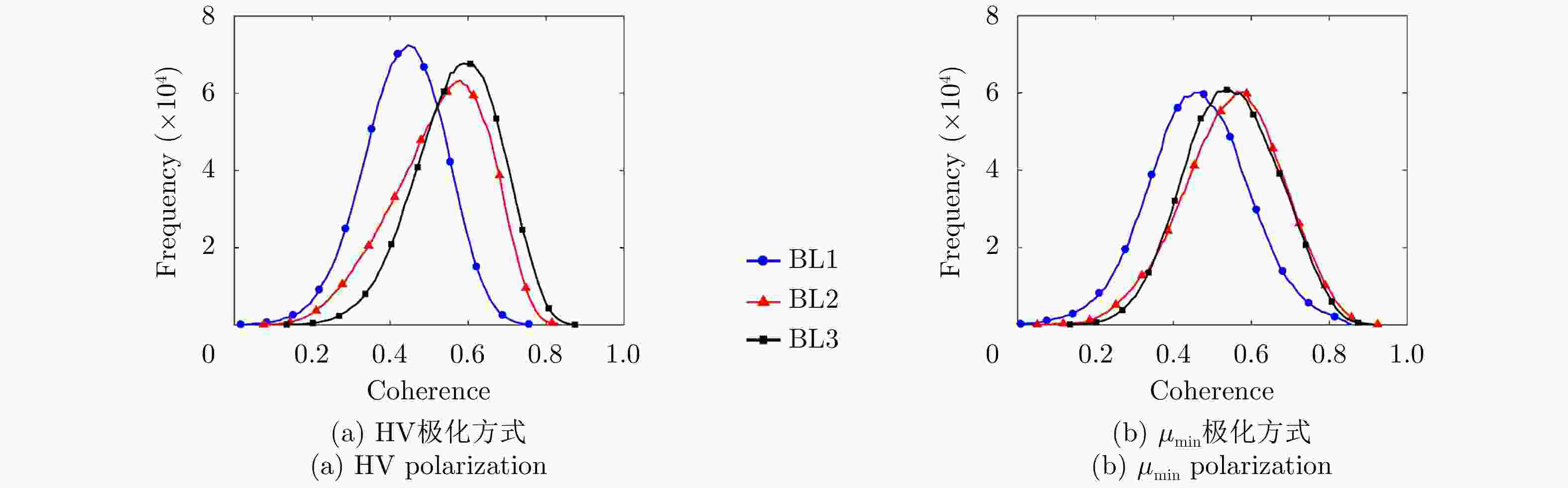
日期(2016年) 垂直有效波数(rad/m) 时间基线(天) 距离向/方位向分辨率(m) 中心入射角 (°) 极化方式 0616—0630 (BL1) 0.013~0.015 0630—0714 (BL2) 0.010~0.011 14 2.86/2.97 38.99 Full 0811—0825 (BL3) 0.009~0.010 表 2 单基线PolInSAR模型参数解算结果
Table 2. Model parameter results of single baseline PolInSAR inversion
模型参数 BL1 BL2 BL3 ${S_{{\rm{scene}}}}$ 0.69 0.78 0.78 ${C_{{\rm{scene}}}}$ 9.88 10.08 11.14 表 3 3个干涉对的相干特性P值以及森林高度值
Table 3. Coherence characteristic P-value and forest heights for three interferometric pairs
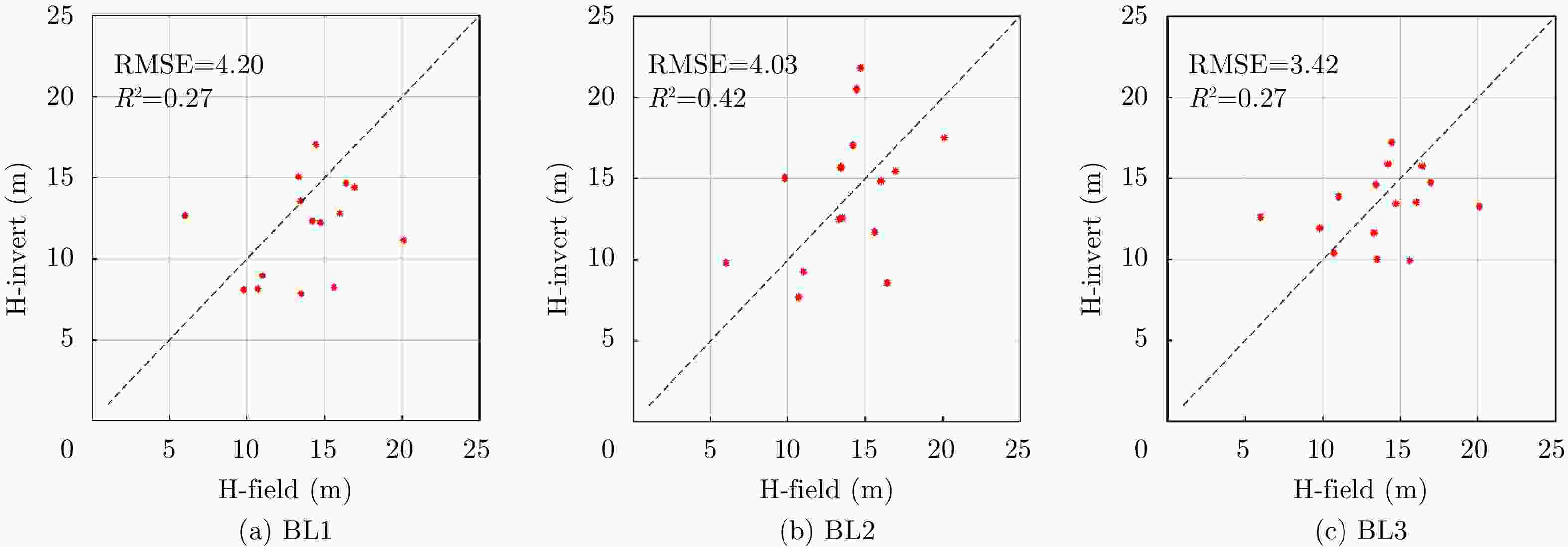
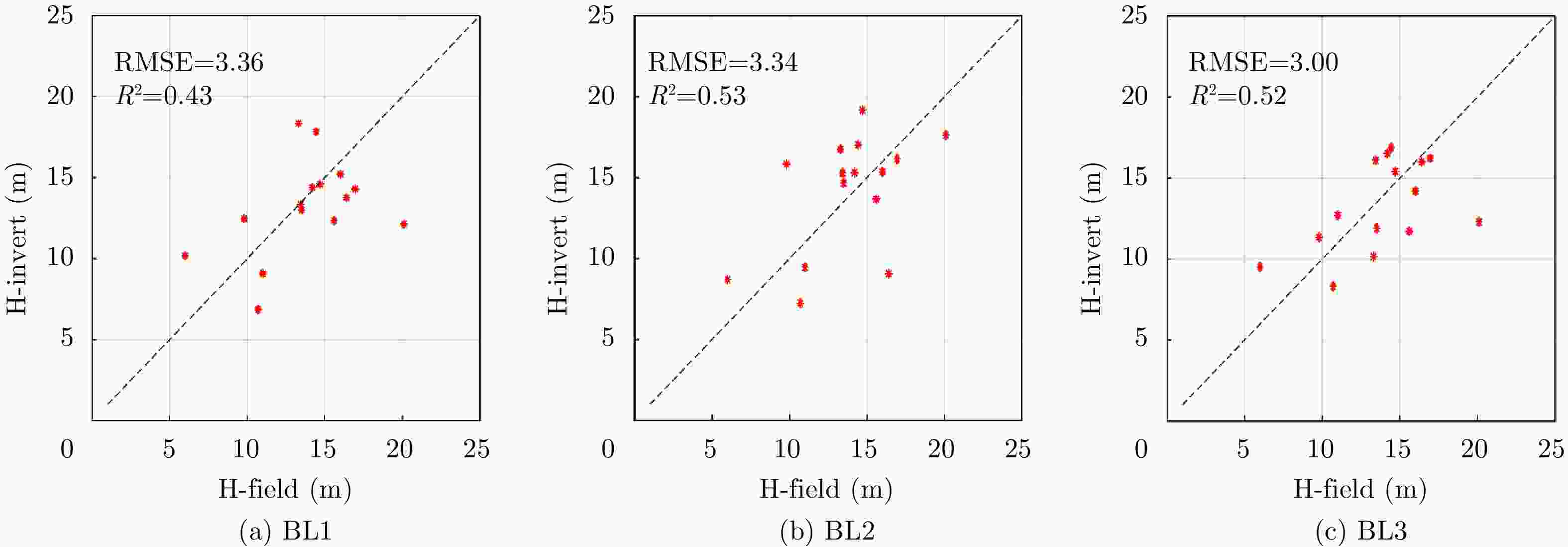
林分样地编号 BL1 P值 / 森林高度(m) BL2 P值 / 森林高度(m) BL3 P值 / 森林高度(m) 多基线融合结果(m) 实测森林高度(m) 1 0.130 / 17.82 0.113 / 17.02 0.081 / 16.89 17.82 14.43 2 0.116 / 14.38 0.104 / 15.30 0.091 / 16.52 14.38 14.20 3 0.092 / 12.46 0.075 / 15.83 0.135 / 11.34 11.34 9.80 4 0.103 / 15.21 0.111 / 15.34 0.119 / 14.19 14.19 16.00 5 0.106 / 6.86 0.106 / 7.24 0.131 / 8.31 8.31 10.70 6 0.110 / 12.98 0.083 / 14.67 0.118 / 11.89 11.89 13.50 7 0.114 / 13.35 0.096 / 15.30 0.101 / 16.10 13.35 13.43 8 0.079 / 14.29 0.106 / 16.15 0.117 / 16.22 16.22 16.95 9 0.069 / 12.12 0.090 / 17.63 0.060 / 12.30 17.63 20.10 10 0.104 / 12.33 0.089 / 13.67 0.102 / 11.72 12.33 15.60 11 0.075 / 18.34 0.103 / 16.75 0.154 / 10.16 10.16 13.30 12 0.113 / 9.08 0.134 / 9.46 0.106 / 12.69 9.46 11.00 13 0.086 / 13.76 0.096 / 9.07 0.109 / 16.00 16.00 16.40 14 0.197 / 10.17 0.230 / 8.71 0.186 / 9.51 8.71 6.00 15 0.103 / 14.59 0.064 / 19.17 0.128 / 15.40 15.40 14.70 -
[1] 郭华东. 雷达对地观测理论与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000: 126–131.GUO Huadong. Radar for Earth Observation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000: 126–131. [2] TREUHAFT R N, MADSEN S N, MOGHADDAM M, et al. Vegetation characteristics and underlying topography from interferometric radar[J]. Radio Science, 1996, 31(6): 1449–1485. doi: 10.1029/96rs01763 [3] PAPATHANASSIOU K P and CLOUDE S R. Single-baseline polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(11): 2352–2363. doi: 10.1109/36.964971 [4] CLOUDE S R and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. Three-stage inversion process for polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(3): 125–134. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030449 [5] PRAKS J, KUGLER F, PAPATHANASSIOU K P, et al. Height estimation of boreal forest: Interferometric model-based inversion at L- and X-band versus HUTSCAT profiling scatterometer[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2007, 4(3): 466–470. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2007.898083 [6] HAJNSEK I, KUGLER F, LEE S K, et al. Tropical-forest-parameter estimation by means of Pol-InSAR: The INDREX-II campaign[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(2): 481–493. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2009437 [7] FU Haiqiang, WANG Changcheng, ZHU Jianjun, et al. Inversion of vegetation height from PolInSAR using complex least squares adjustment method[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2015, 58(6): 1018–1031. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5070-1 [8] LEI Yang and SIQUEIRA P. Estimation of forest height using spaceborne repeat-pass L-band InSAR correlation magnitude over the US state of maine[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(11): 10252–10285. doi: 10.3390/rs61110252 [9] LAVALLE M and HENSLEY S. Extraction of structural and dynamic properties of forests from polarimetric-interferometric SAR data affected by temporal decorrelation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(9): 4752–4767. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2409066 [10] PAPATHANASSIOU K P and CLOUDE S R. The effect of temporal decorrelation on the inversion of forest parameters from Pol-InSAR data[C]. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2003.1294134. [11] LEI Yang, SIQUEIRA P, TORBICK N, et al. Generation of large-scale moderate-resolution forest height mosaic with spaceborne repeat-pass SAR interferometry and lidar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(2): 770–787. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2860590 [12] CLOUDE S R and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(5): 1551–1565. doi: 10.1109/36.718859 [13] NEUMANN M, FERRO-FAMIL L, and REIGBER A. Pol-InSAR coherence set theory and application[C]. The 6th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Dresden, Germany, 2006. [14] 许丽颖, 李世强, 邓云凯, 等. 基于极化干涉SAR反演植被高度的改进三阶段算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(1): 28–34. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13089XU Liying, LI Shiqiang, DENG Yunkai, et al. Improved three-stage algorithm of forest height retrieval with PolInSAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 28–34. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13089 [15] 白璐, 曹芳, 洪文. 相干区域长轴的快速估计方法及其应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(3): 548–553. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00211BAI Lu, CAO Fang, and HONG Wen. Fast approach to estimate the longest axis in coherence region and its applications[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(3): 548–553. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00211 [16] BAMLER R and HARTL P. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Inverse Problems, 1998, 14(4): R1–R54. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/14/4/001 [17] MOON T K and STIRLING W C. Mathematical Methods and Algorithms for Signal Processing[M]. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2000. [18] LAVALLE M, SOLIMINI D, POTTIER E, et al. Forest parameters inversion using polarimetric and interferometric SAR data[C]. 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Cape Town, South Africa, 2009. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2009.5417355. [19] DENBINA M, SIMARD M, and HAWKINS B. Forest height estimation using multibaseline PolInSAR and sparse lidar data fusion[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(10): 3415–5433. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2841388 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: