Techniques and Applications of Spaceborne Time-series InSAR in Urban Dynamic Monitoring
-
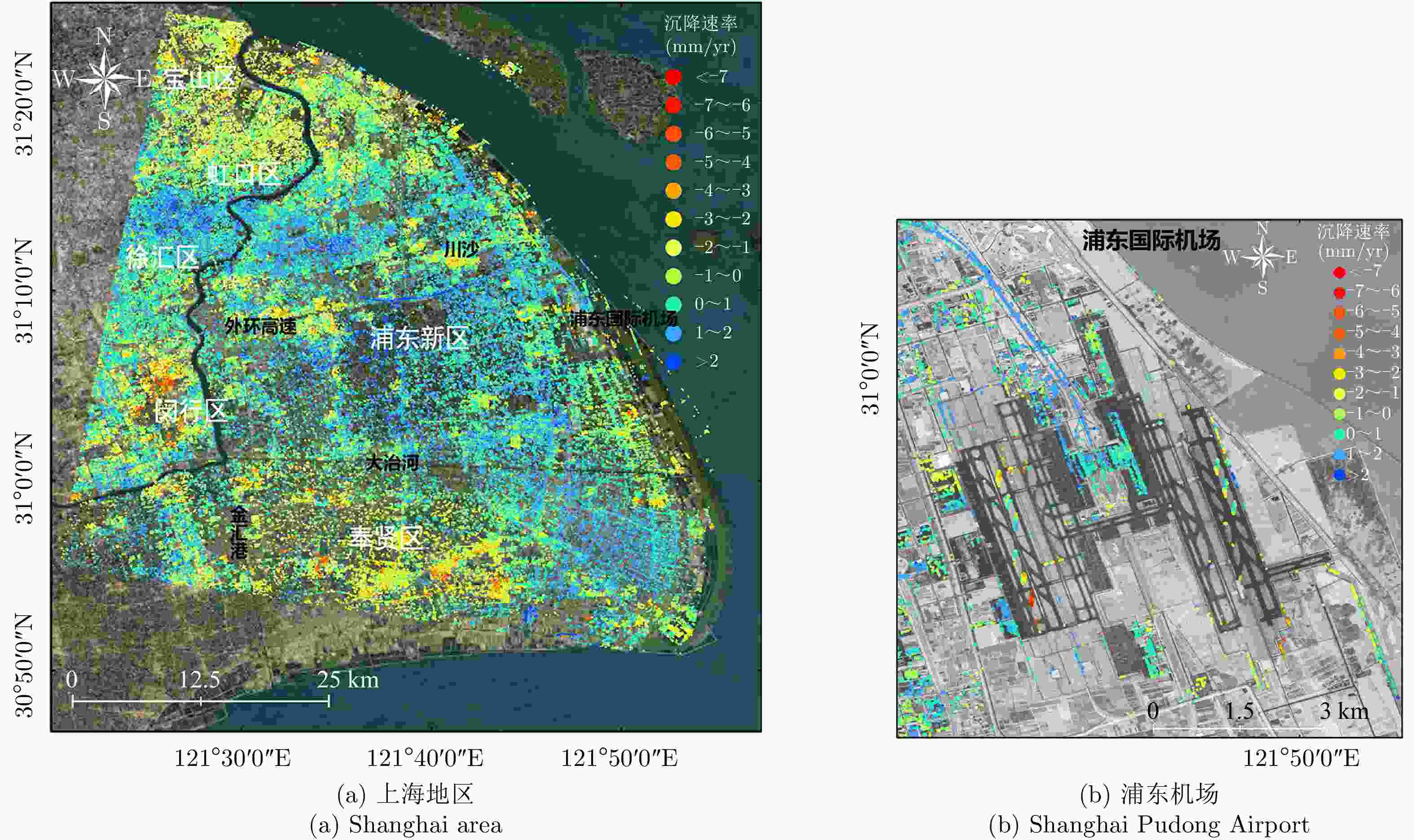
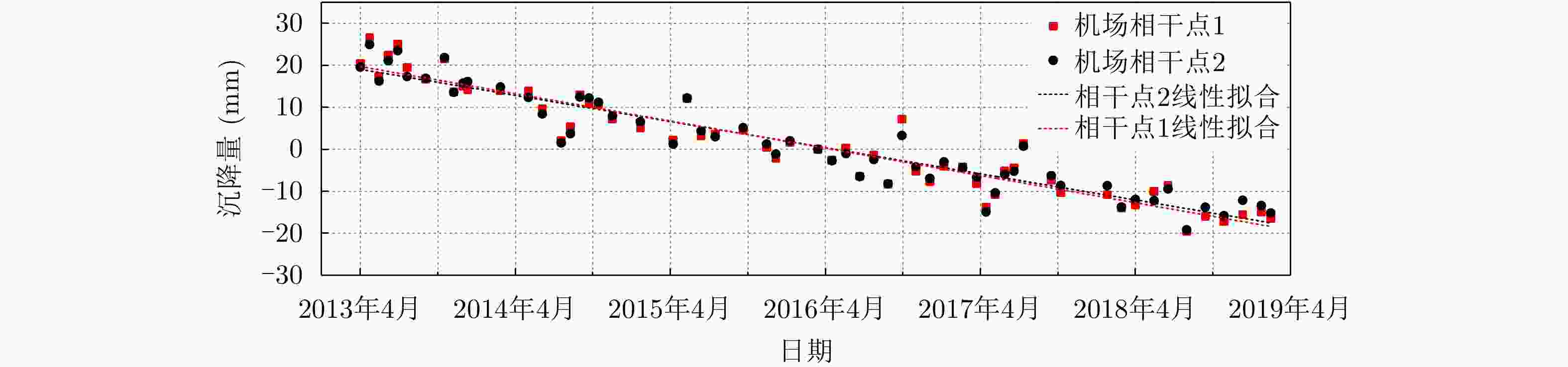
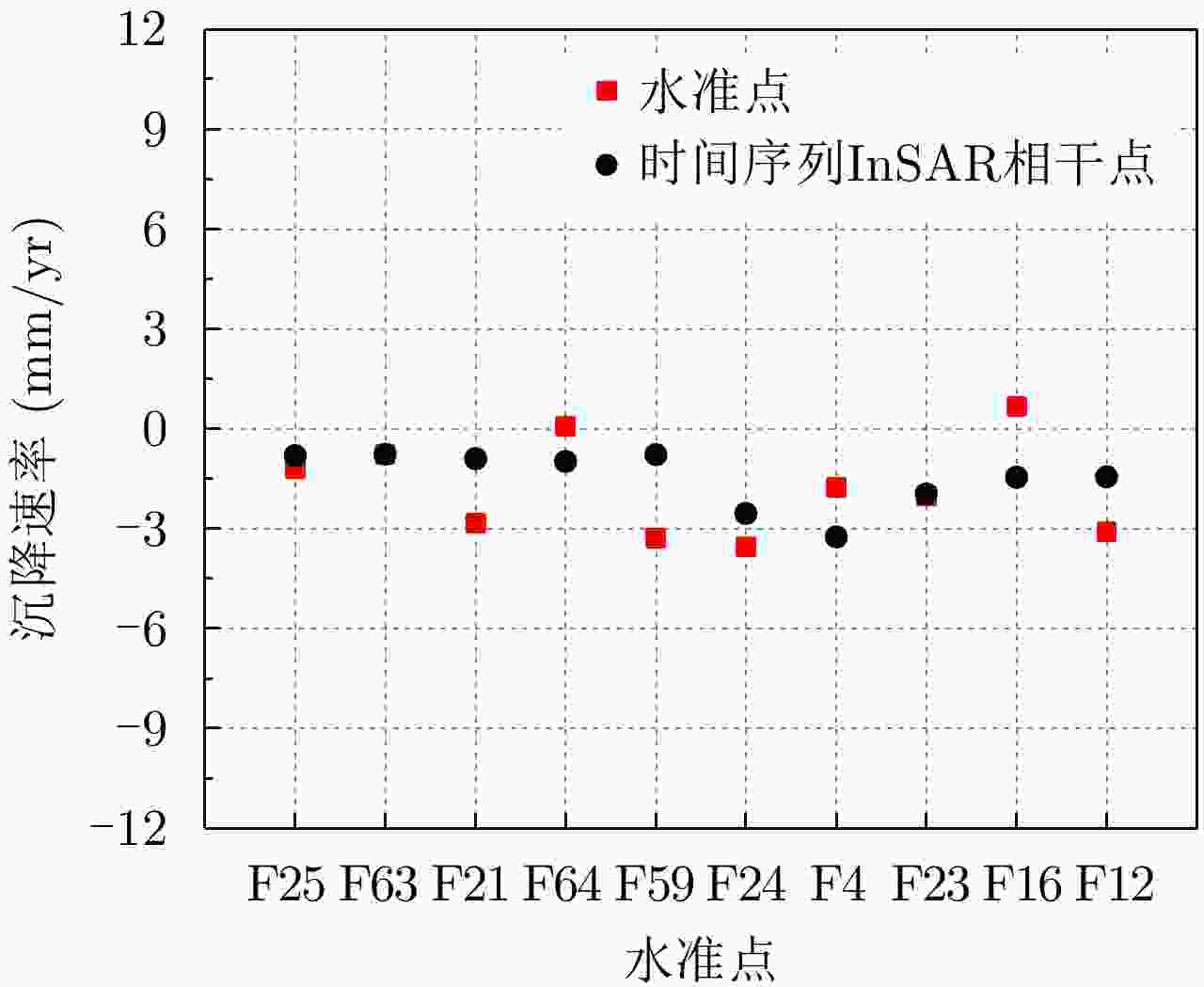
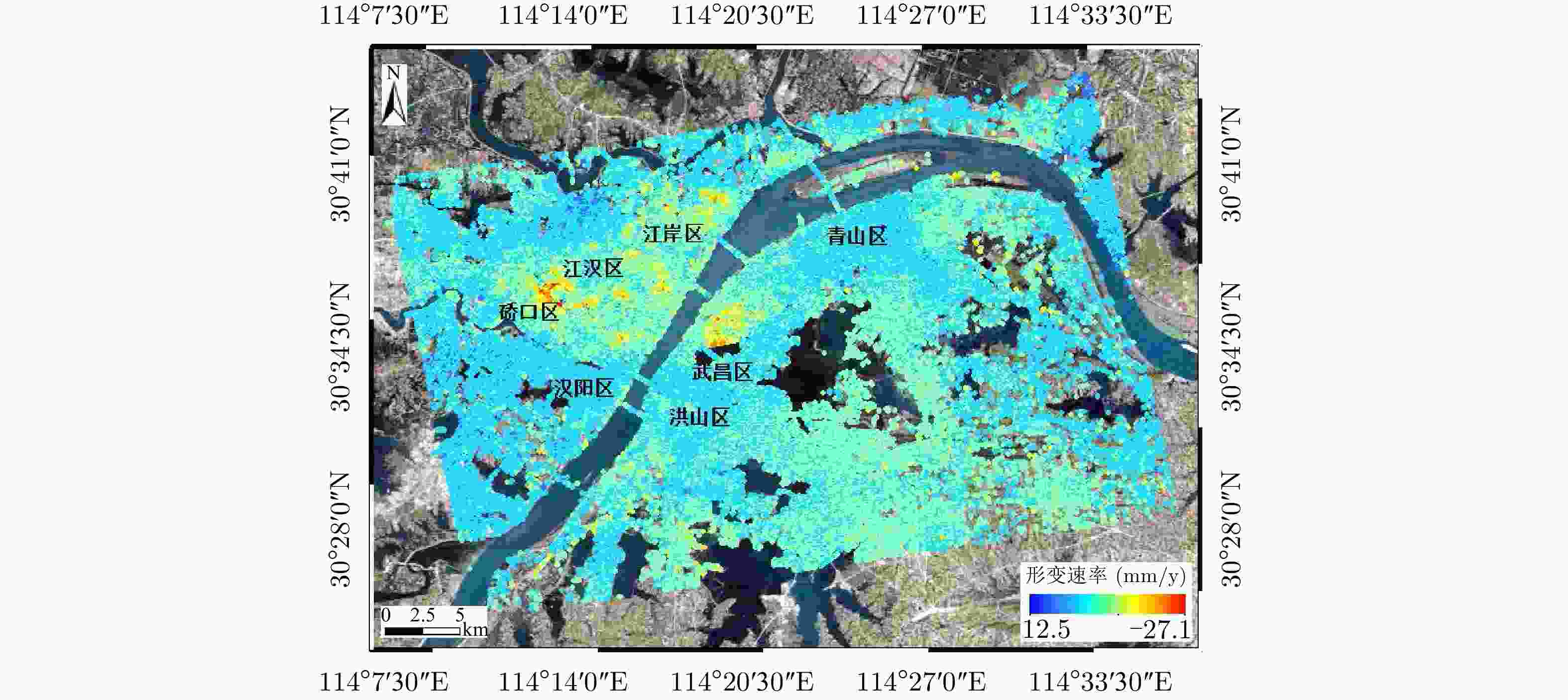
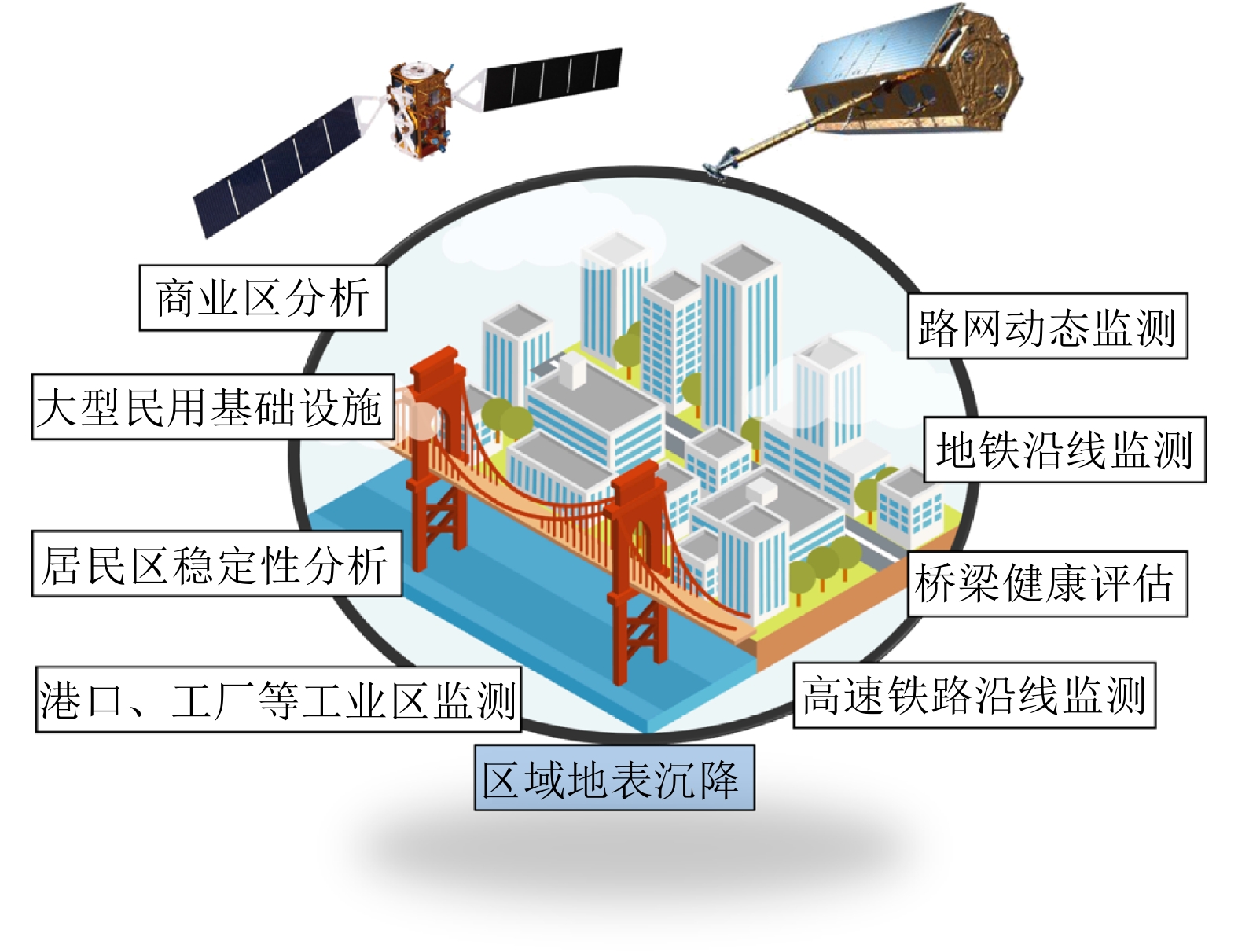
摘要: 城市地表和人工建筑的稳定性监测一直是城市安全的重要监测内容之一。星载合成孔径雷达干涉测量(InSAR)技术以其大范围、高精度、高空间密度的形变获取能力,被广泛用于大范围地表形变监测。近年来,随着星载SAR系统分辨率的不断提高,时序InSAR技术越来越多地应用于重要基础设施的监测。该文结合作者团队长期基于时序InSAR技术在城市地区监测研究经历,总结和回顾了团队关于时序InSAR方法在城市动态监测中的一些典型应用,包括城市机场、高架路网、桥梁、铁路和地铁沿线等,根据多年获取的高分辨率TerraSAR-X影像、Cosmo-SkyMed影像以及后续免费获取的Sentinel-1影像等多种数据以及监测研究中发现的研究问题及相应解决方法,在应用中取得了良好的效果,展现了时序InSAR技术在城区目标精细监测中的潜力。Abstract: The dynamic monitoring of the geological environment in urban areas, including the monitoring of the urban surface stability and detailed monitoring of man-made objects on the surface, is very important for ensuring effective and safe urban development. Spaceborne time-series InSAR technology is widely used to monitor urban deformation due to its large scale, high accuracy, and ability to acquire high-density spatial deformations. In recent years, with the operation of high-resolution satellite missions, time-series InSAR has also been widely used to monitor infrastructures. In this paper based on our long-term monitoring research experience in urban areas using the time-series InSAR technique, we review the application of some typical time-series-InSAR cases to the urban environment, including the monitoring of urban surface displacement and typical large infrastructures, including the airports, elevated road networks, bridges, railways, and subways. Based on various datasets including high-resolution TerraSAR-X images, Cosmo-SkyMed images, and recent Sentinel-1 images obtained at no cost, and the research problems and corresponding solutions identified in published monitoring research, we found good results to have been achieved using this application. With the implementation of more and more satellite missions, this technology will provide more possibilities for urban monitoring.
-
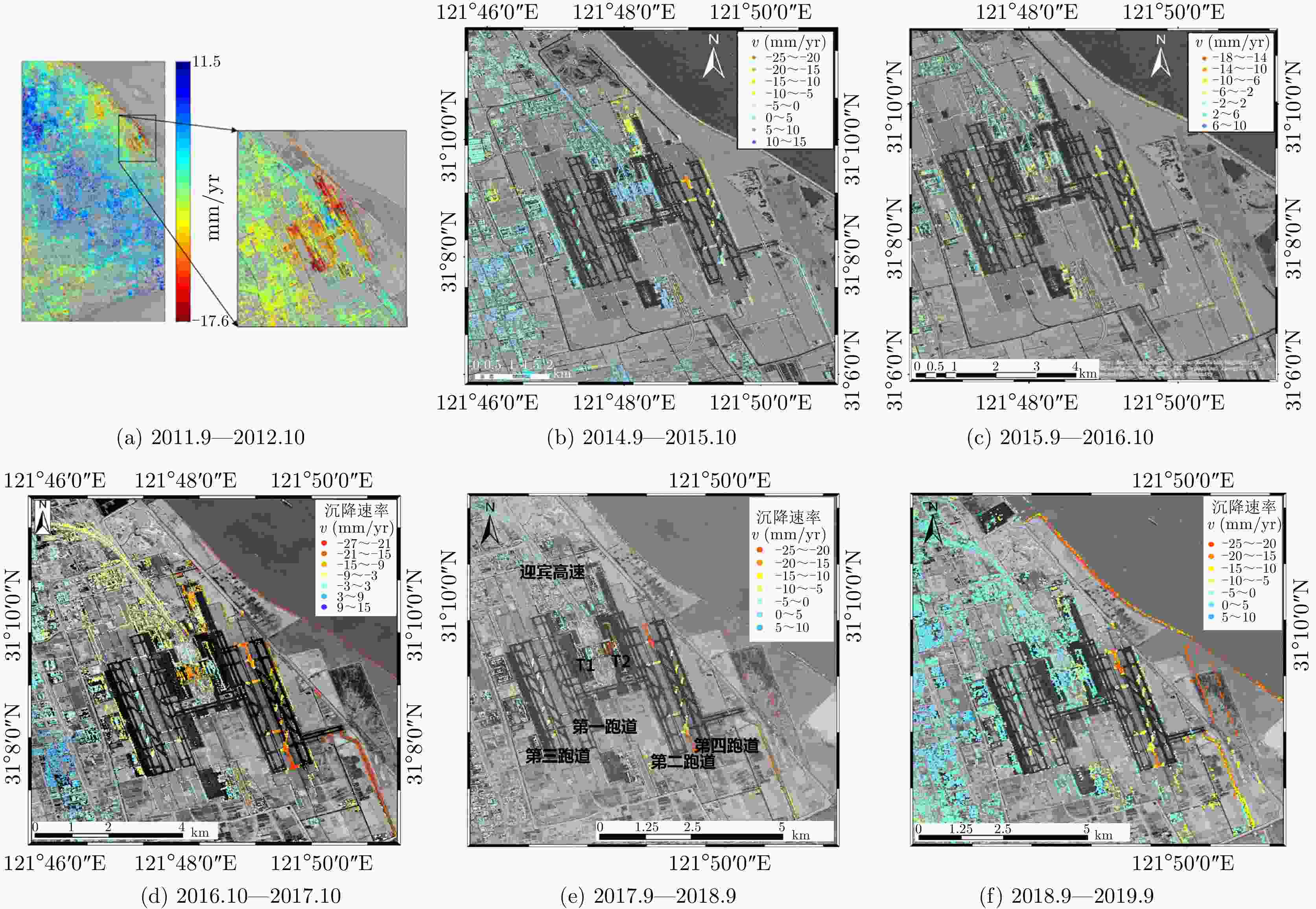
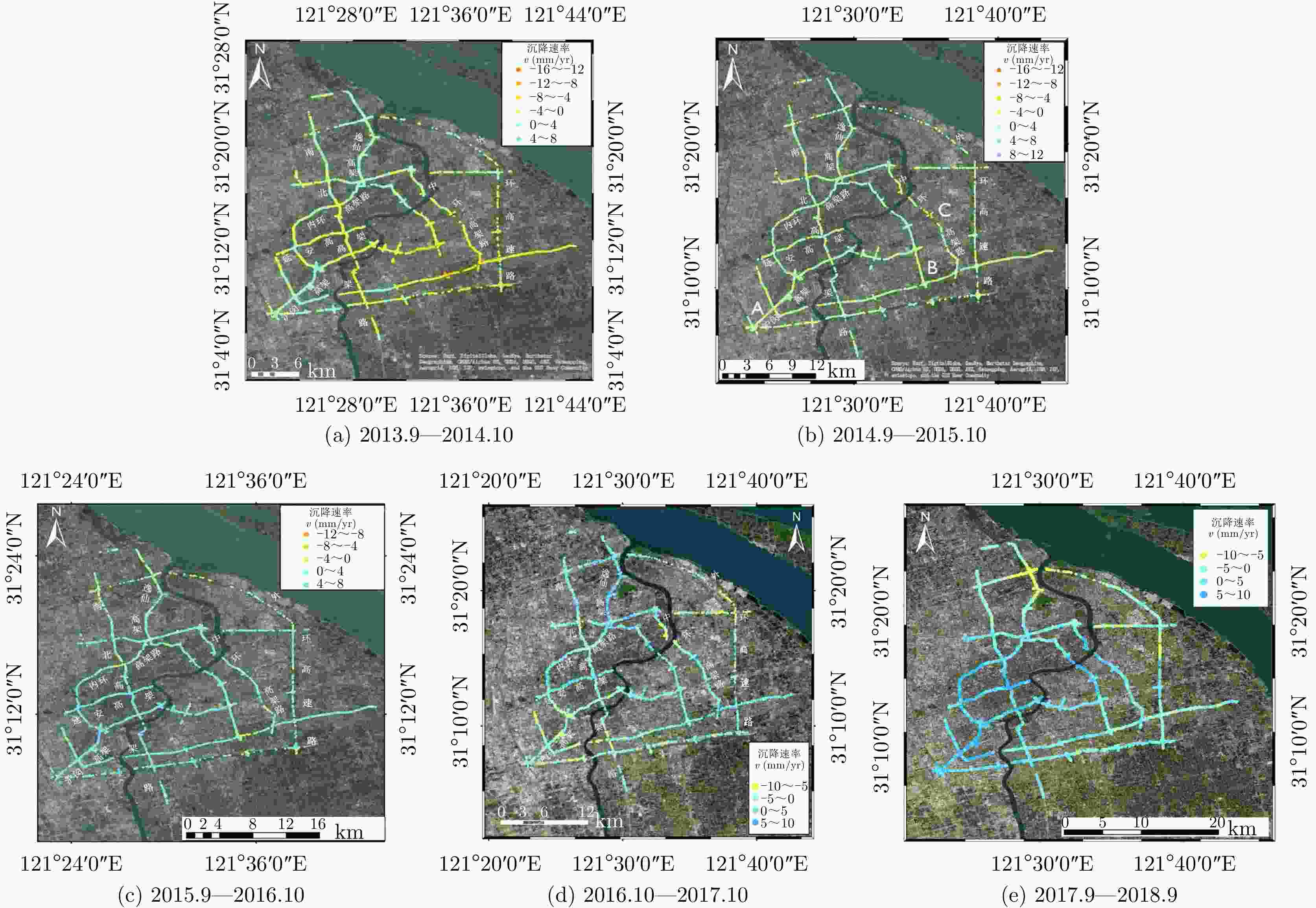
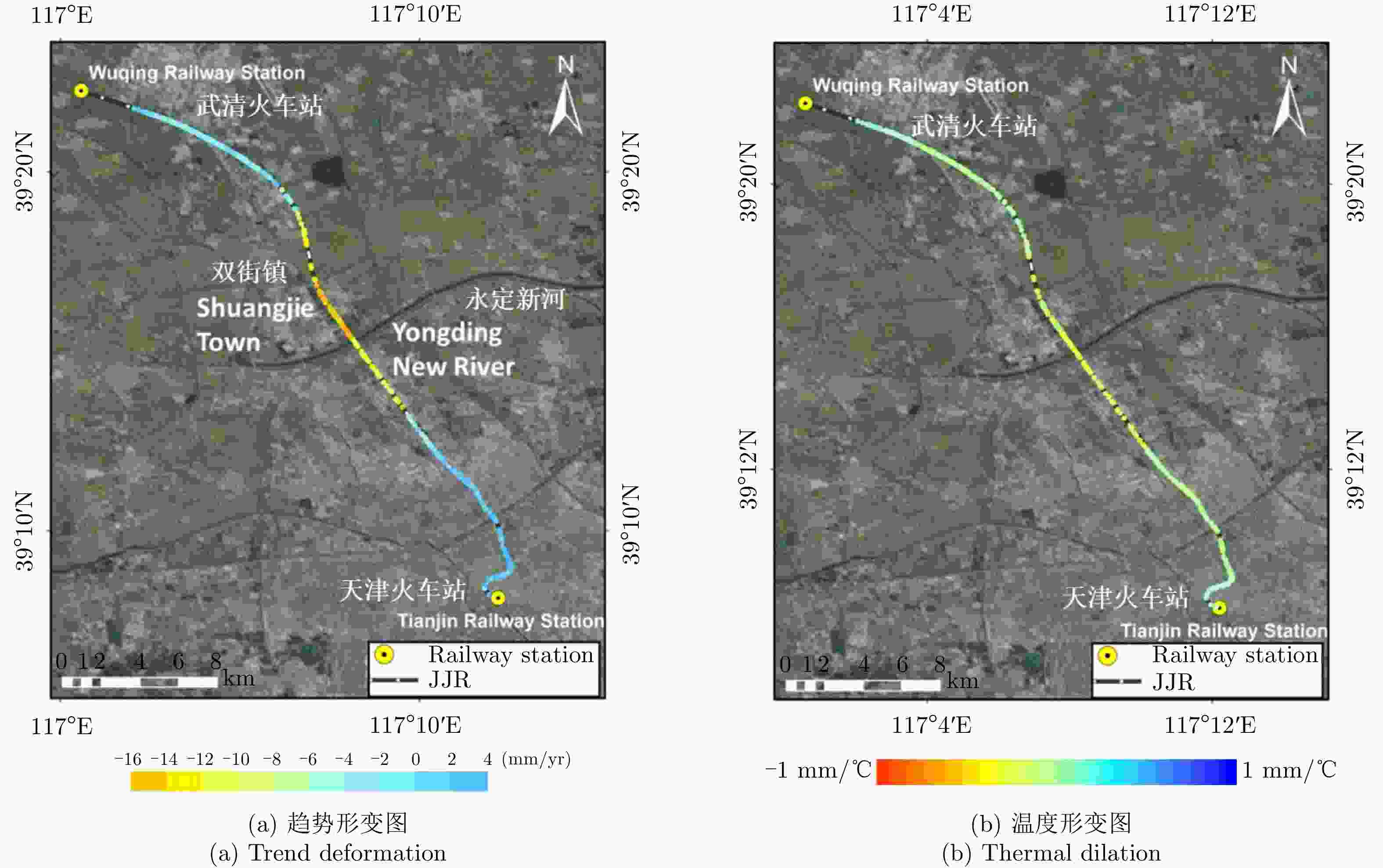
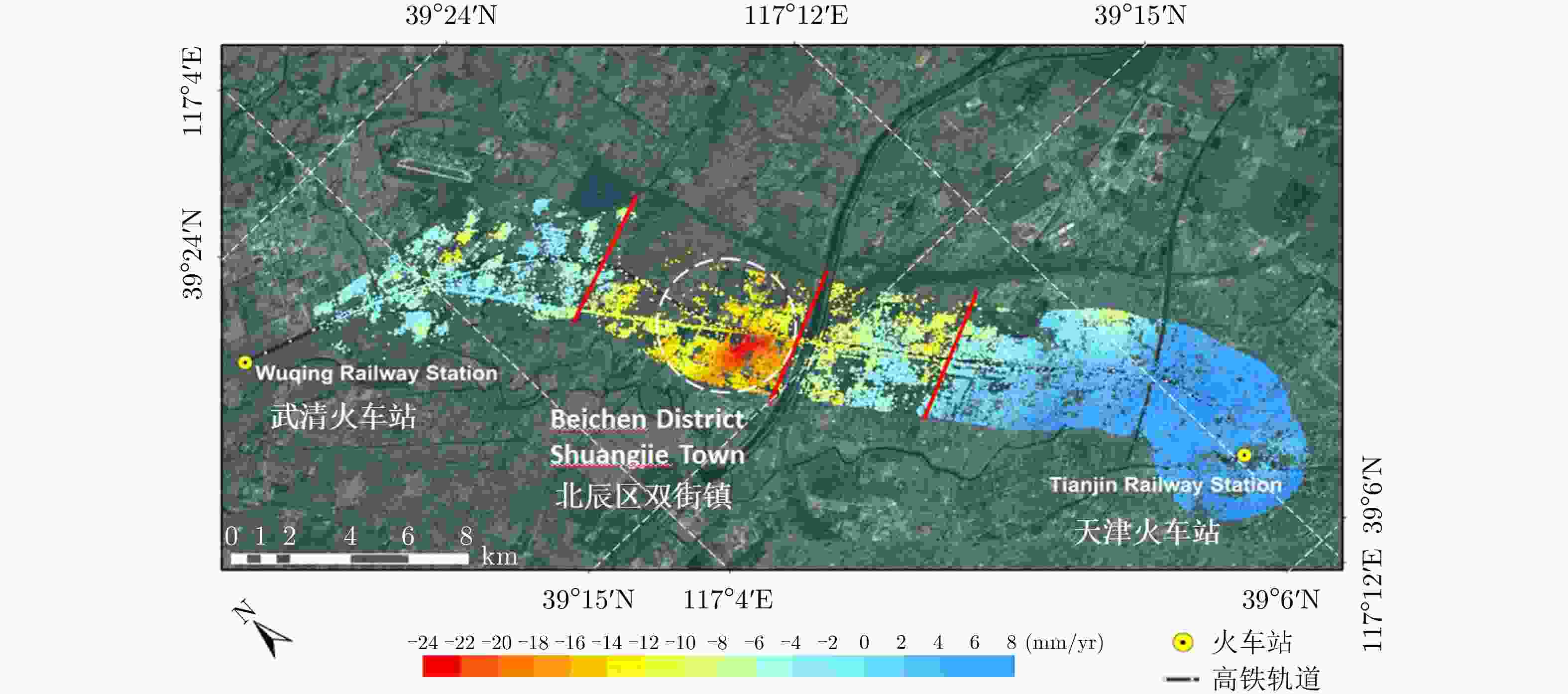
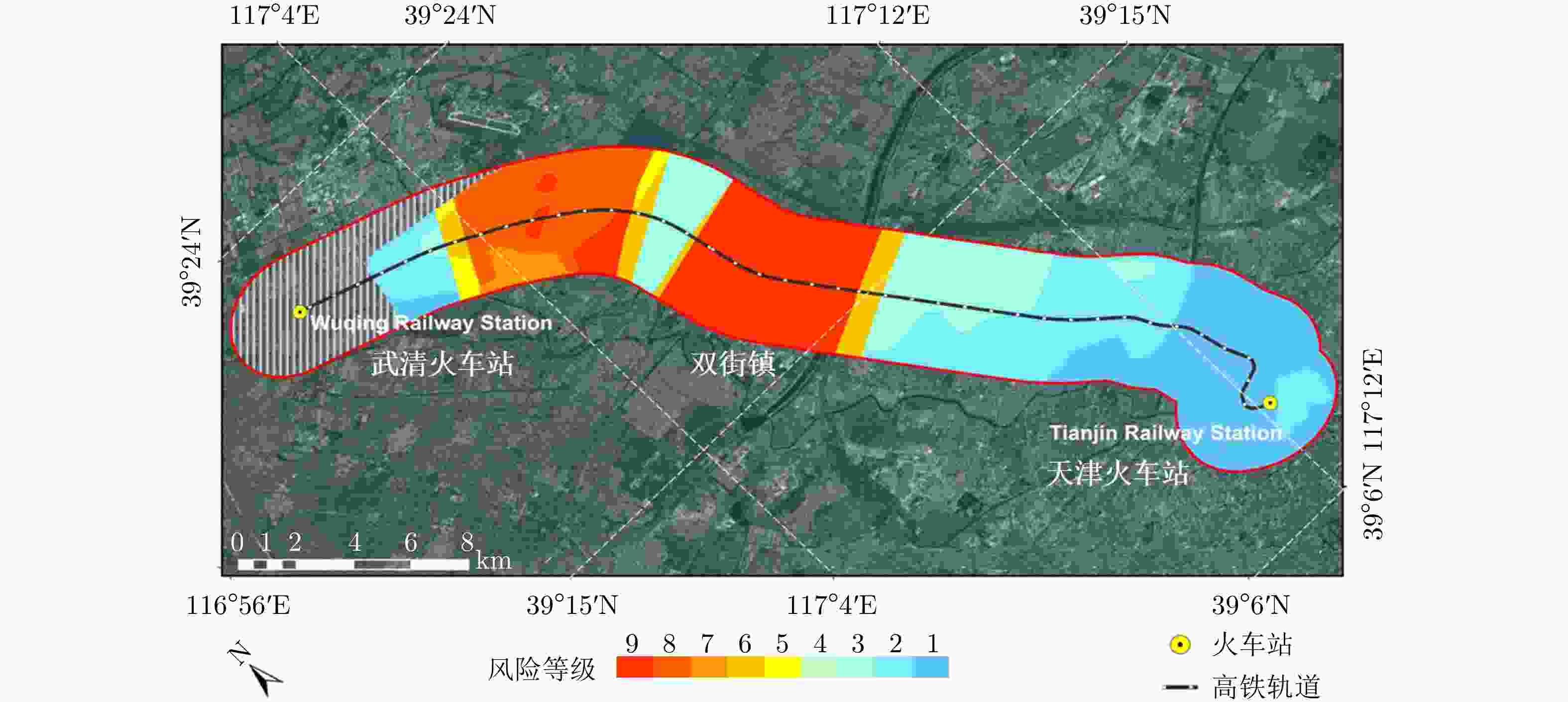
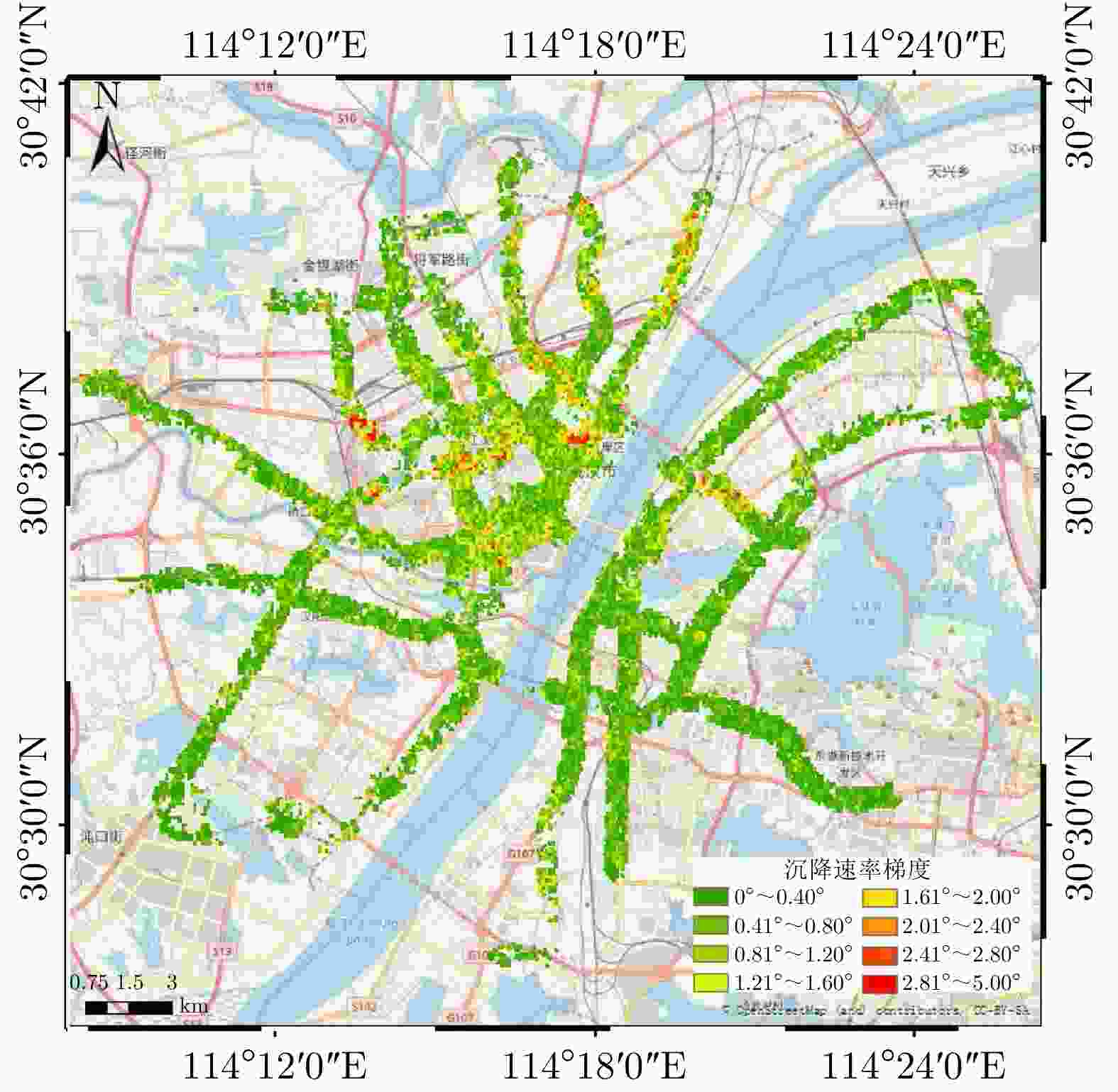
表 1 2013.9—2018.9高架道路沉降情况对比
Table 1. Comparison of the deformation of elevated roads during from September 2013 to September 2018
年份 沉降速率范围(mm/yr) 沉降相干点百分比(%) 沉降点平均速率(mm/yr) 回弹点平均速率(mm/yr) 2013.9—2014.10 –14~8 55.46 –2.651 1.028 2014.9—2015.10 –15~11 46.31 –2.433 0.928 2015.9—2016.10 –14~10 39.54 –1.953 1.039 2016.10—2017.10 –10~10 49.97 –2.932 2.602 2017.9—2018.9 –10~10 29.00 –2.164 2.548 -
[1] MONTGOMERY M R. The urban transformation of the developing world[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5864): 761–764. doi: 10.1126/science.1153012 [2] HANSSEN R F. Satellite radar interferometry for deformation monitoring: a priori assessment of feasibility and accuracy[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2005, 6(3/4): 253–260. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2004.10.004 [3] 廖明生, 林珲. 雷达干涉测量: 原理与信号处理基础[M]. 北京: 测绘出版社, 2003: 1–12.LIAO Mingsheng and LIN Hui. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry: Principle and Singnal Processing[M]. Beijing: Surveying and Mapping Press, 2003: 1–12. [4] FERRETTI A, PRATI C, and ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 8–20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661 [5] BERARDINO P, FORNARO G, LANARI R, et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(11): 2375–2383. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2002.803792 [6] FERRETTI A, SAVIO G, BARZAGHI R, et al. Submillimeter accuracy of InSAR time series: Experimental validation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(5): 1142–1153. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2007.894440 [7] HOOPER A. A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35(16): L16302. doi: 10.1029/2008gl034654 [8] KAMPES B M. Radar Interferometry: Persistent Scatterer Technique[M]. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer, 2006: 21–60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-4723-7. [9] 云烨, 吕孝雷, 付希凯, 等. 星载InSAR技术在地质灾害监测领域的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 73–85. doi: 10.12000/JR20007YUN Ye, LÜ Xiaolei, FU Xikai, et al. Application of spaceborne Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar to geohazard monitoring[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 73–85. doi: 10.12000/JR20007 [10] 廖明生, 王腾. 时间序列InSAR技术与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014: 5–26.LIAO Mingsheng and WANG Teng. Time Series InSAR Technology and Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014: 5–26. [11] 吴立新, 高均海, 葛大庆, 等. 工矿区地表沉陷D-InSAR监测试验研究[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 26(8): 778–782. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2005.08.018WU Lixin, GAO Junhai, GE Daqing, et al. Experimental study on surface subsidence monitoring with D-InSAR in mining area[J]. Journal of Northeastern University:Natural Science, 2005, 26(8): 778–782. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2005.08.018 [12] 汤益先, 张红, 王超. 基于永久散射体雷达干涉测量的苏州地区沉降研究[J]. 自然科学进展, 2006, 16(8): 1015–1020. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008x.2006.08.015TANG Yixian, ZHANG Hong, and WANG Chao. Research on Suzhou subsidence based on permanent scatterer radar interferometry[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2006, 16(8): 1015–1020. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008x.2006.08.015 [13] 王艳, 廖明生, 李德仁, 等. 利用长时间序列相干目标获取地面沉降场[J]. 地球物理学报, 2007, 50(2): 598–604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.02.034WANG Yan, LIAO Mingsheng, LI Deren, et al. Subsidence velocity retrieval from long-term coherent targets in radar interferometric stacks[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2007, 50(2): 598–604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.02.034 [14] 罗小军, 黄丁发, 刘国祥. 基于永久散射体雷达差分干涉测量的城市地面沉降研究—以上海地面沉降监测为例[J]. 测绘通报, 2009, (4): 4–8.LUO Xiaojun, HUANG Dingfa, and LIU Guoxiang. On urban ground subsidence detection based on PS-DInSAR—A case study for Shanghai[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2009(4): 4–8. [15] PERISSIN D and WANG Teng. Time-Series InSAR applications over urban areas in China[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2011, 4(1): 92–100. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2010.2046883 [16] 廖明生, 裴媛媛, 王寒梅, 等. 永久散射体雷达干涉技术监测上海地面沉降[J]. 上海国土资源, 2012, 33(3): 5–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2012.03.006LIAO Mingsheng, PEI Yuanyuan, WANG Hanmei, et al. Subsidence monitoring in Shanghai using the PSInSAR technique[J]. Shanghai Land &Resources, 2012, 33(3): 5–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2012.03.006 [17] 裴媛媛, 廖明生, 王寒梅. 利用时序DInSAR监测填海造陆地区地表沉降[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2012, 37(9): 1092–1095.PEI Yuanyuan, LIAO Mingsheng, and WANG Hanmei. Monitoring subsidence in reclamation area with time series DInSAR images[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2012, 37(9): 1092–1095. [18] 杨梦诗, 廖明生, 史绪国, 等. 联合多平台InSAR数据集精确估计地表沉降速率场[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2017, 42(6): 797–802. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20140924YANG Mengshi, LIAO Mingsheng, SHI Xuguo, et al. Land subsidence monitoring by joint estimation of multi-platform time series InSAR observations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2017, 42(6): 797–802. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20140924 [19] 范景辉, 李梅, 郭小方, 等. 基于PSInSAR方法和ASAR数据监测天津地面沉降的试验研究[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2007, 19(4): 23–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-070x.2007.04.005FAN Jinghui, LI Mei, GUO Xiaofang, et al. A preliminary study of the subsidence in Tianjin area using ASAR images based on PSInSAR technique[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2007, 19(4): 23–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-070x.2007.04.005 [20] LUO Qingli, PERISSIN D, ZHANG Yuanzhi, et al. L- and X-band multi-temporal InSAR analysis of tianjin subsidence[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(9): 7933–7951. doi: 10.3390/rs6097933 [21] 张勤, 赵超英, 丁晓利, 等. 利用GPS与InSAR研究西安现今地面沉降与地裂缝时空演化特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(5): 1214–1222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.05.010ZHANG Qin, ZHAO Chaoying, DING Xiaoli, et al. Research on recent characteristics of spatio-temporal evolution and mechanism of Xi’an land subsidence and ground fissure by using GPS and InSAR techniques[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(5): 1214–1222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.05.010 [22] 陈国浒, 刘云华, 单新建. PS-InSAR技术在北京采空塌陷区地表形变测量中的应用探析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2010, 21(2): 59–63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.02.012CHEN Guohu, LIU Yunhua, and SHAN Xinjian. Application of PS-InSAR technique in the deformation monitoring in mining collapse areas in Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2010, 21(2): 59–63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.02.012 [23] CHEN Mi, TOMÁS R, LI Zhenhong, et al. Imaging land subsidence induced by groundwater extraction in Beijing (China) using satellite radar interferometry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(6): 468. doi: 10.3390/rs8060468 [24] 尹宏杰, 朱建军, 李志伟, 等. 基于SBAS的矿区形变监测研究[J]. 测绘学报, 2011, 40(1): 52–58.YIN Hongjie, ZHU Jianjun, LI Zhiwei, et al. Ground subsidence monitoring in mining area using DInSAR SBAS algorithm[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2011, 40(1): 52–58. [25] 何秀凤, 仲海蓓, 何敏. 基于PS-InSAR和GIS空间分析的南通市区地面沉降监测[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 39(1): 129–134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2011.01.025HE Xiufeng, ZHONG Haibei, and HE Min. Ground subsidence detection of Nantong city based on PS-InSAR and GIS spatial analysis[J]. Journal of Tongji University:Natural Science, 2011, 39(1): 129–134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2011.01.025 [26] 李永生, 张景发, 罗毅, 等. 利用高分辨率聚束模式TerraSAR-X影像的PSInSAR监测地表变形[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2012, 37(12): 1452–1455.LI Yongsheng, ZHANG Jingfa, LUO Yi, et al. Monitoring land deformation using PSInSAR with TerraSAR-X high resolution spotlight SAR images[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2012, 37(12): 1452–1455. [27] NG A H M, GE Linlin, LI Xiaojing, et al. Monitoring ground deformation in Beijing, China with persistent scatterer SAR interferometry[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2012, 86(6): 375–392. doi: 10.1007/s00190-011-0525-4 [28] WANG Huiqiang, FENG Guangcai, XU Bing, et al. Deriving spatio-temporal development of ground subsidence due to subway construction and operation in delta regions with PS-InSAR data: A case study in Guangzhou, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(10): 1004. doi: 10.3390/rs9101004 [29] WANG Ziyun, BALZ T, ZHANG Lu, et al. Using TSX/TDX pursuit monostatic SAR stacks for PS-InSAR analysis in urban areas[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(1): 26. doi: 10.3390/rs11010026 [30] BAI Lin, JIANG Liming, WANG Hansheng, et al. Spatiotemporal characterization of land subsidence and uplift (2009–2010) over Wuhan in Central China revealed by TerraSAR-X InSAR analysis[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(4): 350. doi: 10.3390/rs8040350 [31] TANG Wei and LIAO Mingsheng. Taiyuan city subsidence observed with Persistent Scatterer InSAR[J]. Wuhan University Journal of Natural Sciences, 2014, 19(6): 526–534. doi: 10.1007/s11859-014-1048-7 [32] CHEN Fulong, WU Yuhua, ZHANG Yimeng, et al. Surface motion and structural instability monitoring of ming Dynasty City walls by two-step tomo-PSInSAR approach in Nanjing City, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(4): 371. doi: 10.3390/rs9040371 [33] 林珲, 陈富龙, 江利明, 等. 多基线差分雷达干涉测量的大型人工线状地物形变监测[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2010, 12(5): 718–725.LIN Hui, CHEN Fulong, JIANG Liming, et al. Preliminary research on large-scale man-made linear features deformation monitoring using multi-baseline Differential SAR Interferometry[J]. Geo-Information Science, 2010, 12(5): 718–725. [34] 廖明生, 田馨, 赵卿. TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X雷达遥感计划及其应用[J]. 测绘信息与工程, 2007, 32(2): 44–46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3817.2007.02.019LIAO Mingsheng, TIAN Xin, and ZHAO Qing. Missions and applications of TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X[J]. Journal of Geomatics, 2007, 32(2): 44–46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3817.2007.02.019 [35] 邢孟道, 林浩, 陈溅来, 等. 多平台合成孔径雷达成像算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A review of imaging algorithms in multi-platform-borne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102 [36] 裴媛媛, 廖明生, 王寒梅. 时间序列SAR影像监测堤坝形变研究[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2013, 38(3): 266–269.PEI Yuanyuan, LIAO Mingsheng, and WANG Hanmei. Monitoring levee deformation with repeat-track space-borne SAR images[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2013, 38(3): 266–269. [37] PERISSIN D, WANG Zhiying, and LIN Hui. Shanghai subway tunnels and highways monitoring through Cosmo-SkyMed Persistent Scatterers[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2012, 73: 58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2012.07.002 [38] 秦晓琼, 杨梦诗, 王寒梅, 等. 高分辨率PS-InSAR在轨道交通形变特征探测中的应用[J]. 测绘学报, 2016, 45(6): 713–721. doi: 10.11947/j.agcs.2016.20150440QIN Xiaoqiong, YANG Mengshi, WANG Hanmei, et al. Application of high-resolution PS-InSAR in deformation characteristics probe of urban rail transit[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2016, 45(6): 713–721. doi: 10.11947/j.agcs.2016.20150440 [39] QIN Xiaoqiong, LIAO Mingsheng, ZHANG Lu, et al. Structural health and stability assessment of high-speed railways via thermal dilation mapping with Time-Series InSAR analysis[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(6): 2999–3010. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2719025 [40] QIN Xiaoqiong, YANG Mengshi, ZHANG Lu, et al. Health diagnosis of major transportation infrastructures in Shanghai metropolis using high-resolution Persistent Scatterer Interferometry[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(12): 2770. doi: 10.3390/s17122770 [41] WANG Ru, YANG Tianliang, YANG Mengshi, et al. A safety analysis of elevated highways in Shanghai linked to dynamic load using long-term time-series of InSAR stacks[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 10(12): 1133–1142. doi: 10.1080/2150704x.2019.1648903 [42] CHANG Ling, DOLLEVOET R P B J, and HANSSEN R F. Nationwide railway monitoring using satellite SAR Interferometry[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(2): 596–604. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2016.2584783 [43] 秦晓琼, 廖明生, 杨梦诗, 等. 应用高分辨率PS-InSAR技术监测上海动迁房歪斜形变[J]. 测绘通报, 2016, (6): 18–21, 86. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2016.0181QIN Xiaoqiong, LIAO Mingsheng, YANG Mengshi, et al. Monitoring Shanghai relocation housing skew deformation using high resolution PS-InSAR technology[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2016(6): 18–21, 86. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2016.0181 [44] QIN Xiaoqiong, ZHANG Lu, DING Xiaoli, et al. Mapping and characterizing thermal dilation of civil infrastructures with multi-temporal X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(6): 941. doi: 10.3390/rs10060941 [45] QIN Xiaoqiong, ZHANG Lu, YANG Mengshi, et al. Mapping surface deformation and thermal dilation of arch bridges by structure-driven multi-temporal DInSAR analysis[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 216: 71–90. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2018.06.032 [46] JIANG Yanan, LIAO Mingsheng, WANG Hanmei, et al. Deformation monitoring and analysis of the geological environment of Pudong International Airport with persistent scatterer SAR interferometry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(12): 1021. doi: 10.3390/rs8121021 [47] 廖明生, 魏恋欢, 汪紫芸, 等. 压缩感知在城区高分辨率SAR层析成像中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031LIAO Mingsheng, WEI Lianhuan, WANG Ziyun, et al. Compressive sensing in high-resolution 3D SAR tomography of urban scenarios[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031 [48] YANG Mengshi, LÓPEZ-DEKKER P, DHEENATHAYALAN P, et al. Linking persistent scatterers to the built environment using Ray tracing on urban models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 5764–5776. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2901904 [49] YANG Mengshi, YANG Tianliang, ZHANG Lu, et al. Spatio-temporal characterization of a reclamation settlement in the Shanghai coastal area with time series analyses of X-, C-, and L-Band SAR datasets[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(2): 329. doi: 10.3390/rs10020329 [50] 王飞, 柴波, 徐贵来, 等. 武汉市岩溶塌陷的演化机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2017, 25(3): 824–832. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.03.030WANG Fei, CHAI Bo, XU Guilai, et al. Evolution mechanism of karst sinkholes in Wuhan city[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(3): 824–832. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.03.030 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: