-
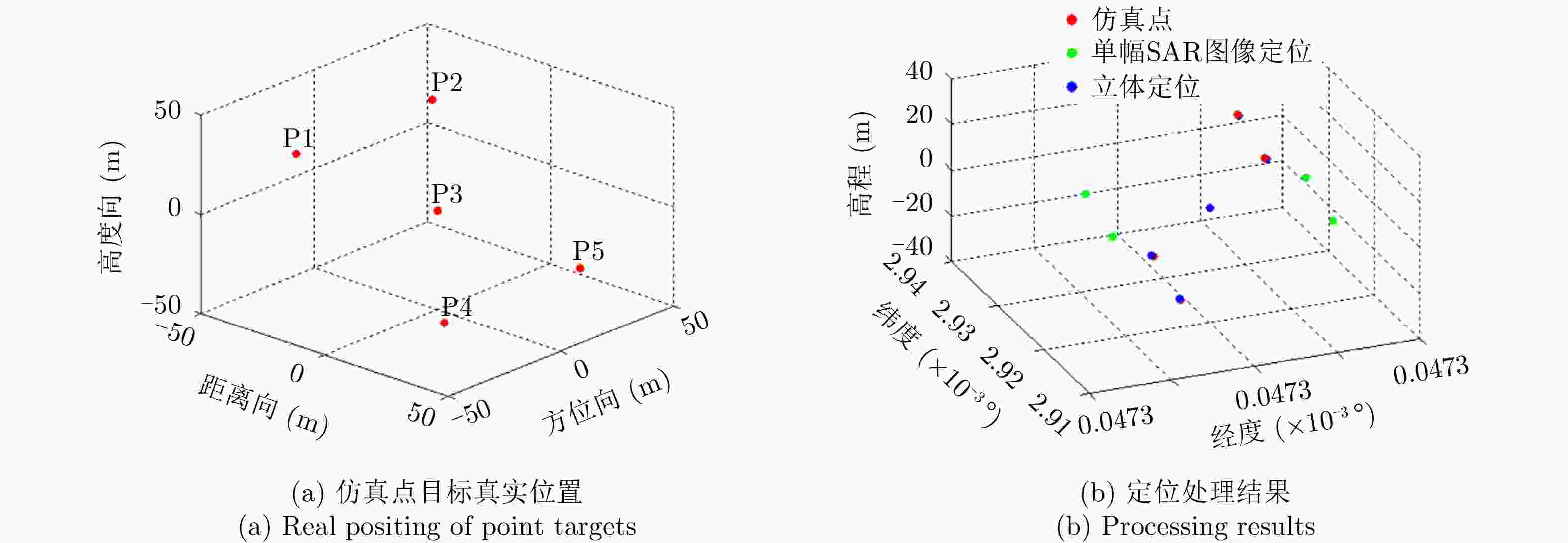
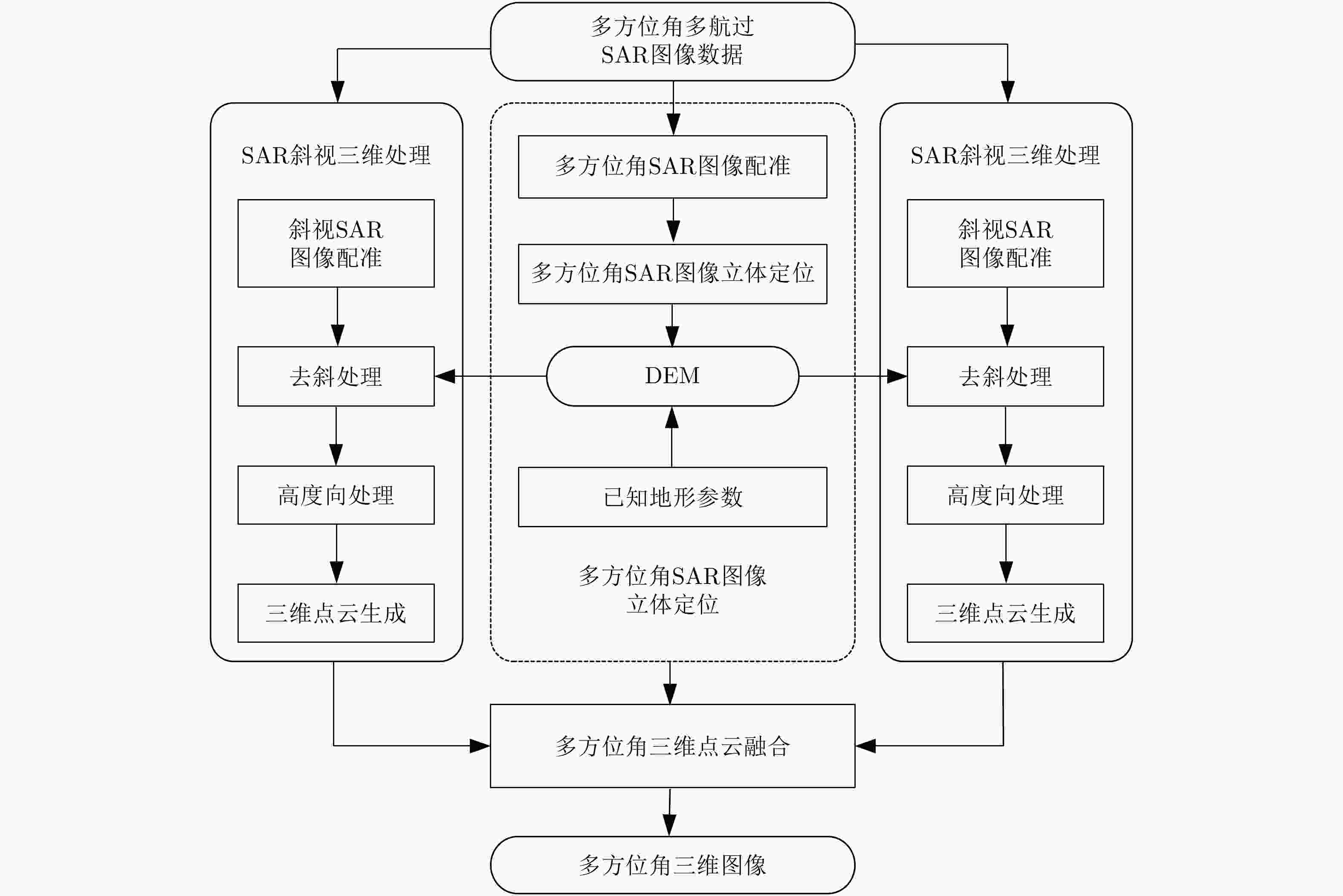
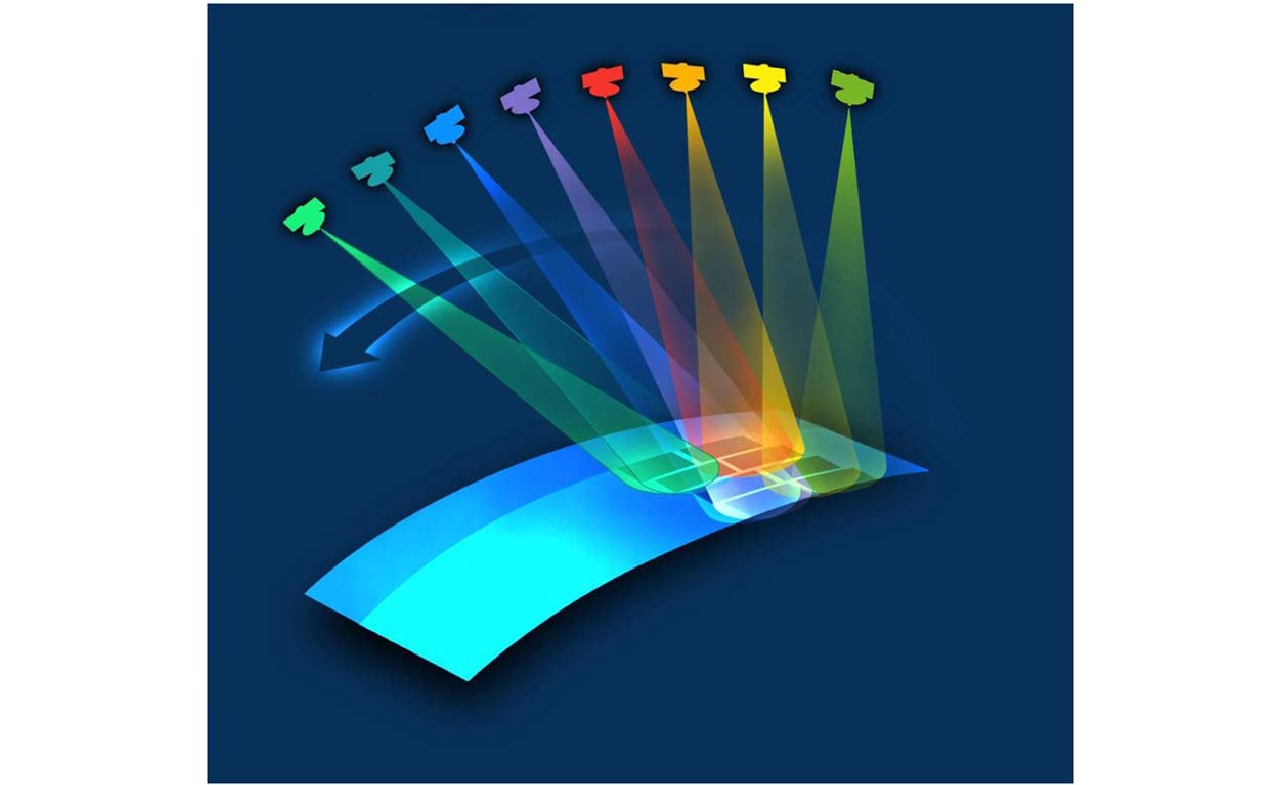
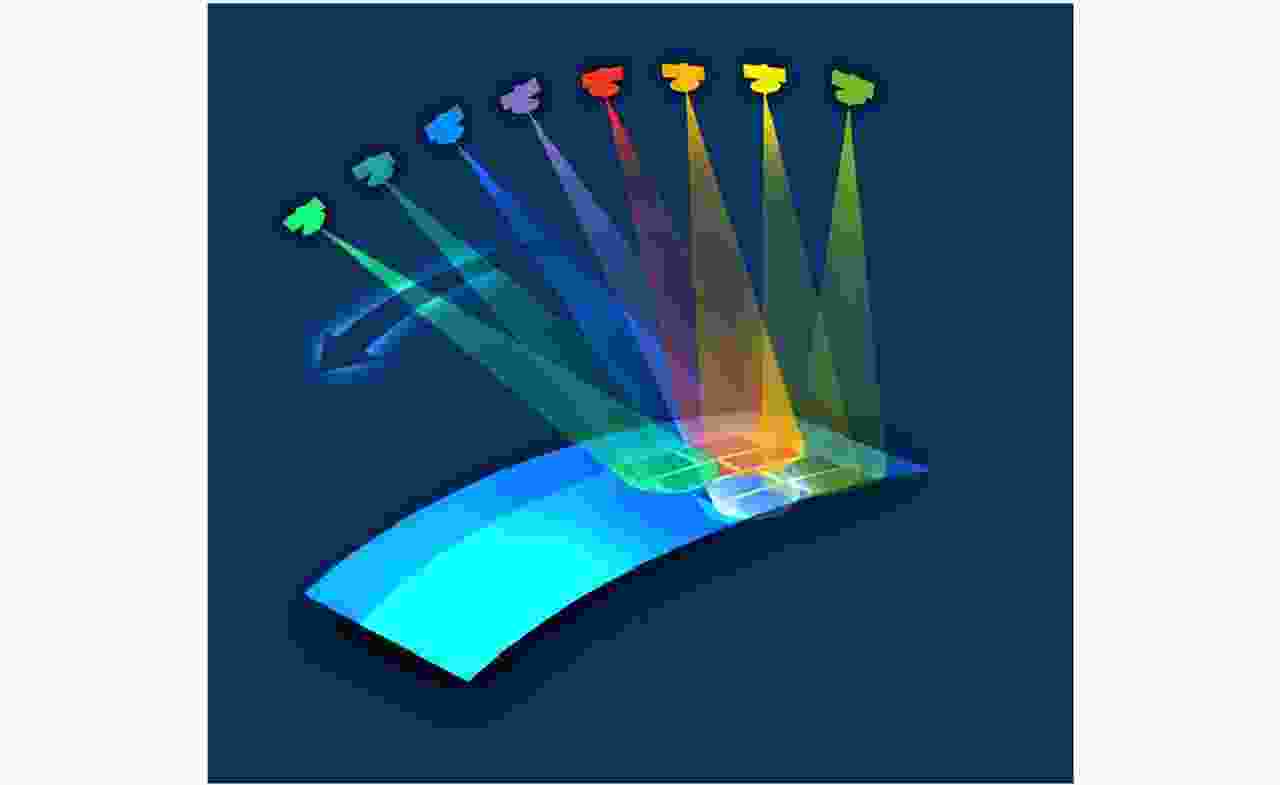
摘要: 该文针对多方位角观测星载SAR新技术进行综述。首先分析了当前国内外SAR卫星发展现状和趋势,并从多个角度对比综述了其对地观测的能力。在此基础上,结合当前应用需求对多方位角观测星载SAR工作新模式进行了综述,解析其工作机理,并结合试验结果总结分析了多方位角观测星载SAR在目标散射信息、几何信息和运动信息获取方面的优势。最后,对多方位角观测星载SAR技术的发展进行了总结和展望。Abstract: This paper reviews the novel azimuthal multi-angle spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) technique. First, the development status and trend of SAR satellites are analyzed, and their observation capacities are compared considering different aspects. Furthermore, the novel azimuthal multi-angle observation SAR imaging modes are presented based on the application requirements, and the imaging mechanism is analyzed in detail. Moreover, the advantages of the azimuthal multi-angle observation spaceborne SAR system for obtaining full scattering information, geometry information, and motion information of ground targets are analyzed. Detailed conclusions are provided, and experiment results are presented. Finally, the azimuthal multi-angle observation spaceborne SAR technique is summarized, and its prospects are highlighted.
-
Key words:
- Spaceborne SAR /
- Azimuthal multi-angles /
- Imaging mode /
- Information acquisition
-
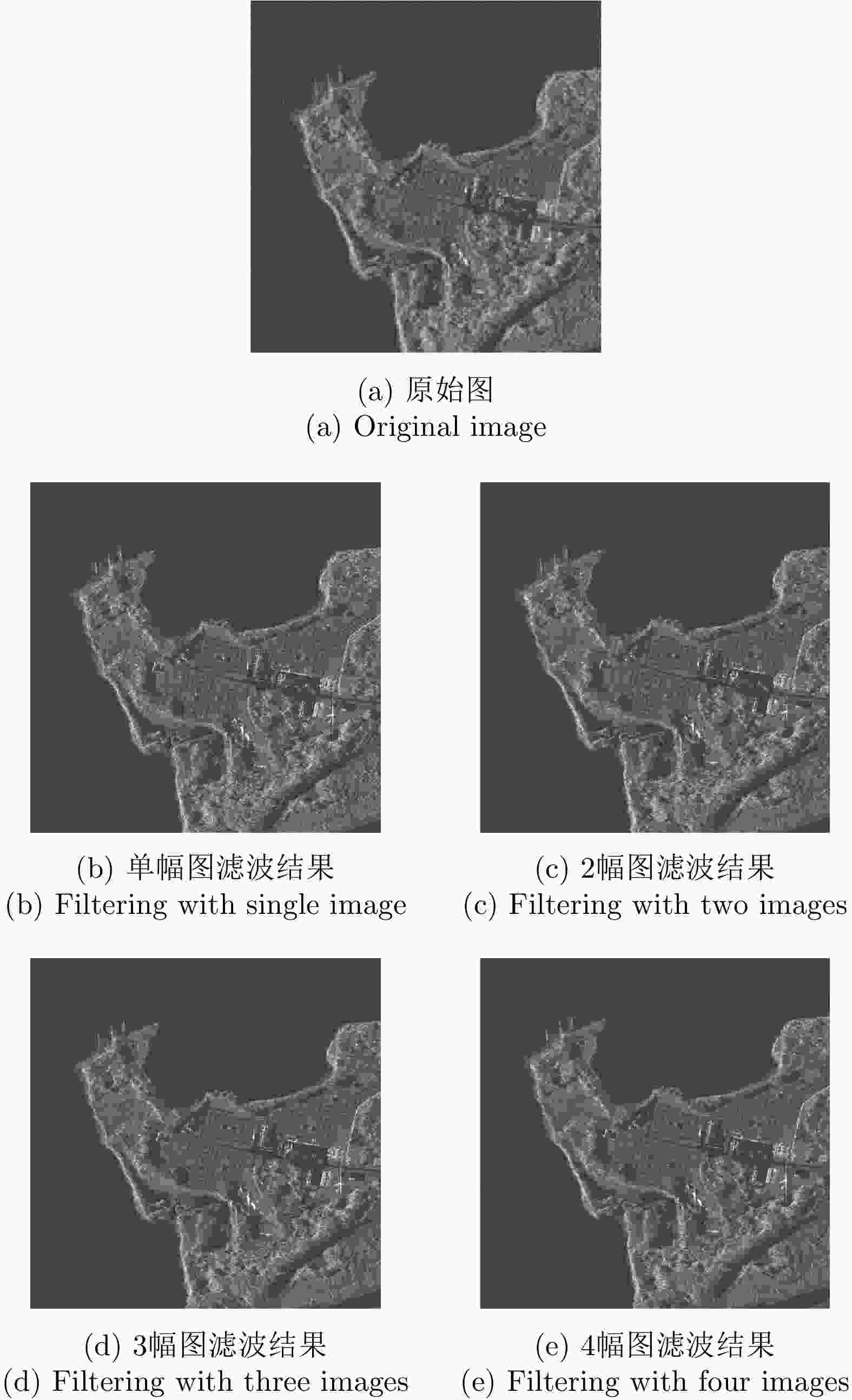
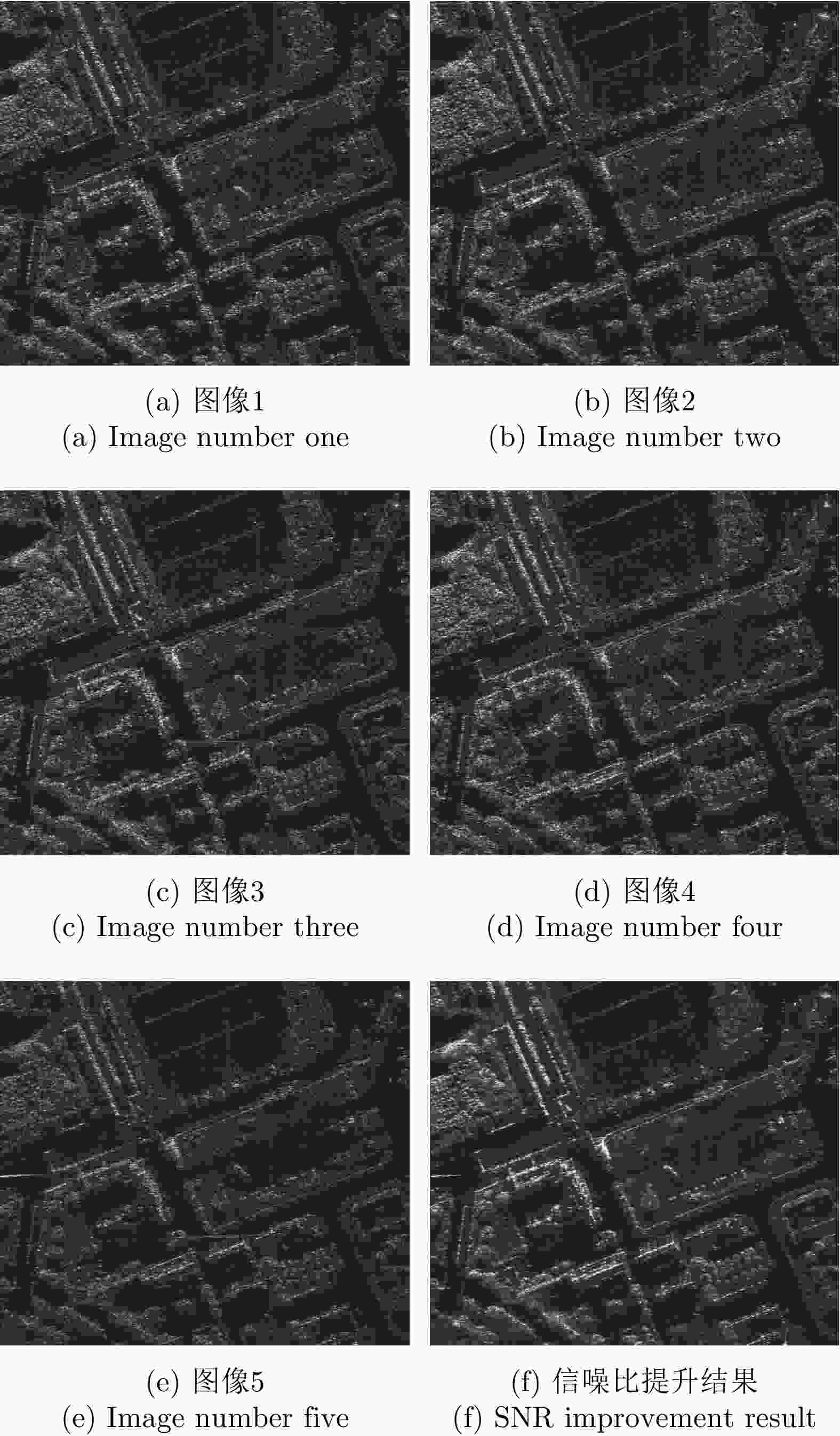
表 1 辐射分辨率分析结果
Table 1. Radiation resolution analysis results
等效视数 辐射分辨率(dB) 原图 0.97 3.03 单帧 5.30 1.56 2幅 29.64 0.73 3幅 43.28 0.61 4幅 52.27 0.56 -
[1] FRANCESCHETTI G, GUIDA R, IODICE A, et al. Efficient simulation of hybrid stripmap/spotlight SAR raw signals from extended scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(11): 2385–2396. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.834763 [2] KRIEGER G, GEBERT N, and MOREIRA A. Unambiguous SAR signal reconstruction from nonuniform displaced phase center sampling[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(4): 260–264. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.832700 [3] PRATS P, SCHEIBER R, MITTERMAYER J, et al. Processing of sliding spotlight and TOPS SAR data using baseband azimuth scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 770–780. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2027701 [4] DE ZAN F and GUARNIERI A M. TOPSAR: Terrain observation by progressive scans[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(9): 2352–2360. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.873853 [5] META A, MITTERMAYER J, STEINBRECHER U, et al. Investigations on the TOPSAR acquisition mode with TerraSAR-X[C]. 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 2007. [6] MITTERMAYER J and WOLLSTADT S. Simultaneous bi-directional SAR acquisition with TerraSAR-X[C]. The 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010. [7] MITTERMAYER J, PRATS P, WOLLSTADT S, et al. Approach to velocity and acceleration measurement in the bi-directional SAR imaging mode[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012. [8] MITTERMAYER J, WOLLSTADT S, PRATS-IRAOLA P, et al. Bidirectional SAR imaging mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 601–614. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2202669 [9] MITTERMAYER J, WOLLSTADT S, PRATS-IRAOLA P, et al. The TerraSAR-X staring spotlight mode concept[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(6): 3695–3706. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2274821 [10] KRAUS T, BRAUTIGAM B, MITTERMAYER J, et al. TerraSAR-X staring spotlight mode optimization and global performance predictions[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1015–1027. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2431821 [11] MITTERMAYER J, KRAUS T, LÓPEZ-DEKKER P, et al. Wrapped staring spotlight SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 5745–5764. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2571340 [12] MOSSING J C and ROSS T D. Evaluation of SAR ATR algorithm performance sensitivity to MSTAR extended operating conditions[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 3370, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery V, Orlando, USA, 1998: 13. [13] ERTIN E, AUSTIN C D, SHARMA S, et al. GOTCHA experience report: Three-dimensional SAR imaging with complete circular apertures[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 6568, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XIV, Orlando, USA, 2007: 656802. [14] 洪文, 王彦平, 林赟, 等. 新体制SAR三维成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109HONG WEN, WANG Yanping, LIN Yun, et al. Research progress on three-dimensional SAR imaging techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109 [15] LIU Min, LI Zhou, and LIU Lu. A novel sidelobe reduction algorithm based on two-dimensional sidelobe correction using D-SVA for squint SAR images[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(783): 783. [16] WANG Yamin, YANG Wei, CHEN Jie, et al. Azimuth sidelobes suppression using multi-azimuth angle synthetic aperture radar images[J]. Sensors, 2018, 19(12): 2764. [17] YANG Wei, CHEN Jie, LIU Wei, et al. Moving target azimuth velocity estimation for the MASA mode based on sequential SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(6): 2780–2790. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2641744 [18] YANG Wei and MA Xiaocong. A novel spaceborne SAR imaging mode for moving target velocity estimation[C]. 2016 International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences, Ansan, South Korea, 2016. [19] ANSARI H, DE ZAN F, PARIZZI A, et al. Measuring 3-D surface motion with future SAR systems based on reflector antennae[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(2): 272–276. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2509440 [20] JUNG H S, LU Zhong, SHEPHERD A, et al. Simulation of the superSAR multi-azimuth synthetic aperture radar imaging system for precise measurement of three-dimensional earth surface displacement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(11): 6196–6206. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2435776 [21] 邓云凯, 禹卫东, 张衡, 等. 未来星载SAR技术发展趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 1–33. doi: 10.12000/JR20008DENG Yunkai, YU Weidong, ZHANG Heng, et al. Forthcoming spaceborne SAR development[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 1–33. doi: 10.12000/JR20008 [22] SHARAY Y and NAFTALY U. TECSAR: Design considerations and programme status[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2006, 153(2): 117–121. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20045124 [23] LEVY-NATHANSOHN R and NAFTALY U. Overview of the TECSAR satellite hardware and mosaic mode[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(3): 423–426. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.915926 [24] NAFTALY U and ORON O. TECSAR-program status[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Microwaves, Communications, Antennas and Electronic Systems, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2013. [25] NAFTALY U and ORON O. TECSAR-program status[C]. The 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, Germany, 2014. [26] HOELLISCH D, BACH K, JANOTH J, et al. On the second generation of TerraSAR-X[C]. The 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010. [27] HEER C and SCHAEFER C. TerraSAR-X next generation: Technology aspects[C]. The 2011 3rd International Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Seoul, South Korea, 2011. [28] GANTERT S, RIEGLER G, TEUFEL F, et al. TerraSAR-X, TanDEM-X, TerraSAR-X2 and their applications[C]. The 2011 3rd International Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Seoul, South Korea, 2011. [29] JANOTH J, GANTERT S, KOPPE W, et al. TerraSAR-X2- Mission overview[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012. [30] JANOTH J, GANTERT S, SCHRAGE T, et al. Terrasar next generation - Mission capabilities[C]. 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 2013. [31] GANTERT S, KERN A, DÜRING R, et al. The future of X-band SAR: TerraSAR-X next generation and WorldSAR constellation[C]. Conference Proceedings of 2013 Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Tsukuba, Japan, 2013. [32] JANOTH J, GANTERT S, SCHRAGE T, et al. From TerraSAR-X towards TerraSAR Next Generation[C]. 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, Germany, 2014. [33] JANOTH J, JOCHUM M, PETRAT L, et al. High resolution wide swath - the next generation X-band mission[C]. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019. [34] SANFOURCHE J P. ‘SAR-lupe’, an important German initiative[J]. Air & Space Europe, 2000, 2(4): 26–27. [35] PETRIE G. Current & future spaceborne SAR systems[C]. VIII International Scientific & Technical Conference “From Imagery to Map: Digital Photogrammetric Technologies, Porec, Croatia, 2008. [36] 孙佳. 国外合成孔径雷达卫星发展趋势分析[J]. 装备指挥技术学院学报, 2007, 18(1): 67–70.SUN Jia. Analysis of the SAR satellite development tendency in the world[J]. Journal of the Academy of Equipment Command &Technology, 2007, 18(1): 67–70. [37] BAYIR I. A glimpse to future commercial spy satellite systems[C]. The 2009 4th International Conference on Recent Advances in Space Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 2009. [38] STRINGHAM C, FARQUHARSON G, CASTELLETTI D, et al. The capella X-band SAR constellation for rapid imaging[C]. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019. [39] 高庆军, 宋泽考. 美国“空间雷达”计划发展动态[J]. 国际太空, 2007(5): 5–8.GAO Qingjun and SONG Zekao. The development of American spaceborne radar program[J]. Space International, 2007(5): 5–8. [40] United States Government Accountability Office. Assessments of selected weapon programs[R]. GAO-15-342SP, 2015. [41] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [42] 王鹏波, 陈杰, 李景文, 等. 一种基于方位非均匀采样的滑动聚束SAR工作体制实现方法[P]. 中国, CN201010051678, 2010.WANG Pengbo, CHEN Jie, LI Jingwen, et al. A realization method of sliding spotlight SAR based on azimuth nonuniform sampling[P]. China, CN201010051678, 2010. [43] WANG Pengbo, LIU Wei, CHEN Jie, et al. A raster scan SAR system for ultra-wide swath imaging[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 5(9): 833–842. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2014.971904 [44] MEN Zhirong, WANG Pengbo, LI Chunsheng, et al. High-temporal-resolution high-spatial-resolution spaceborne SAR based on continuously varying PRF[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(8): 1700. doi: 10.3390/s17081700 [45] ZENG Hongcheng, CHEN Jie, LIU Wei, et al. Modified omega-k algorithm for high-speed platform highly-squint staggered SAR based on azimuth non-uniform interpolation[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(2): 3750–3765. doi: 10.3390/s150203750 [46] 陈世阳, 黄丽佳, 俞雷. 基于改进SINC插值的变PRF采样聚束SAR成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(4): 527–536. doi: 10.12000/JR18095CHEN Shiyang, HUANG Lijia, and YU Lei. A novel sinc interpolation for continuous PRF sampled sequences reconstruction in spotlight SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(4): 527–536. doi: 10.12000/JR18095 [47] MCCORKLE J W and ROFHEART M. Order N2 log(N) backprojector algorithm for focusing wide-angle wide-bandwidth arbitrary-motion synthetic aperture radar[C]. SPIE 2747, Radar Sensor Technology, Orlando, USA, 1996: 25–36. [48] LANARI R, HENSLEY S, and ROSEN P A. Chirp z-transform based SPECAN approach for phase-preserving ScanSAR image generation[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1998, 145(5): 254–261. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19982218 [49] JIN M J Y and WU C. A SAR correlation algorithm which accommodates large-range migration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1984, GE-22(6): 592–597. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.1984.6499176 [50] RANEY R K, RUNGE H, BAMLER R, et al. Precision SAR processing using chirp scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(4): 786–799. doi: 10.1109/36.298008 [51] DAVIDSON G W, CUMMING I G, ITO M R. A chirp scaling approach for processing squint mode SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1996, 32(1): 121–133. doi: 10.1109/7.481254 [52] 王国栋, 周荫清, 李春升. 星载聚束式SAR改进的Frequency Scaling成像算法[J]. 电子学报, 2003, 31(3): 381–385. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2003.03.017WANG Guodong, ZHOU Yinqing, and LI Chunsheng. Refined frequency scaling algorithm for spaceborne spotlight SAR imaging[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2003, 31(3): 381–385. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2003.03.017 [53] 郑义明. 用频率变标算法处理大斜视角SAR数据[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2000, 22(6): 8–11, 65. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2000.06.003ZHENG Yiming. Large squint SAR data processing using frequency scaling algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2000, 22(6): 8–11, 65. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2000.06.003 [54] BAMLER R. A comparison of Range-Doppler and wavenumber domain SAR focusing algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1992, 30(4): 706–713. doi: 10.1109/36.158864 [55] 叶晓东, 朱兆达. 一种分块处理斜视SAR成像方法[J]. 现代雷达, 1997, 19(5): 23–29, 47.YE Xiaodong and ZHU Zhaoda. An approach for squint SAR imaging based on block processing[J]. Modern Radar, 1997, 19(5): 23–29, 47. [56] 曾海彬, 曾涛, 何佩琨. 星载聚束SAR频域极坐标算法研究[J]. 现代雷达, 2006, 28(1): 28–30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2006.01.009ZENG Haibin, ZENG Tao, and HE Peikun. A study on frequency domain polar format algorithm of spaceborne spotlight SAR[J]. Modern Radar, 2006, 28(1): 28–30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7859.2006.01.009 [57] 李春升, 杨威, 王鹏波. 星载SAR成像处理算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 111–122. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20071LI Chunsheng, YANG Wei, and WANG Pengbo. A review of spaceborne SAR algorithm for image formation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 111–122. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20071 [58] CERUTTI-MAORI D and SIKANETA I. A generalization of DPCA processing for multichannel SAR/GMTI radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 560–572. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2201260 [59] SUCHANDT S, RUNGE H, BREIT H, et al. Automatic extraction of traffic flows using TerraSAR-X along-track interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 807–819. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2037919 [60] ROSENBERG L and GRAY D A. Constrained fast-time STAP for interference suppression in multichannel SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(3): 1792–1805. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6558020 [61] MITTERMAYER J and WOLLSTADT S. Simultaneous bi-directional SAR acquisition with TerraSAR-X[C]. 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2010. [62] 张敬. 多源图像超分辨率重建研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2015: 1–30.ZHANG Jing. A study on super-resolution of multi-source images[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2015: 1–30. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: