Early Identification of Potential Landslide Geohazards in Alpine-canyon Terrain Based on SAR Interferometry—a Case Study of the Middle Section of Yalong River (in English)
-
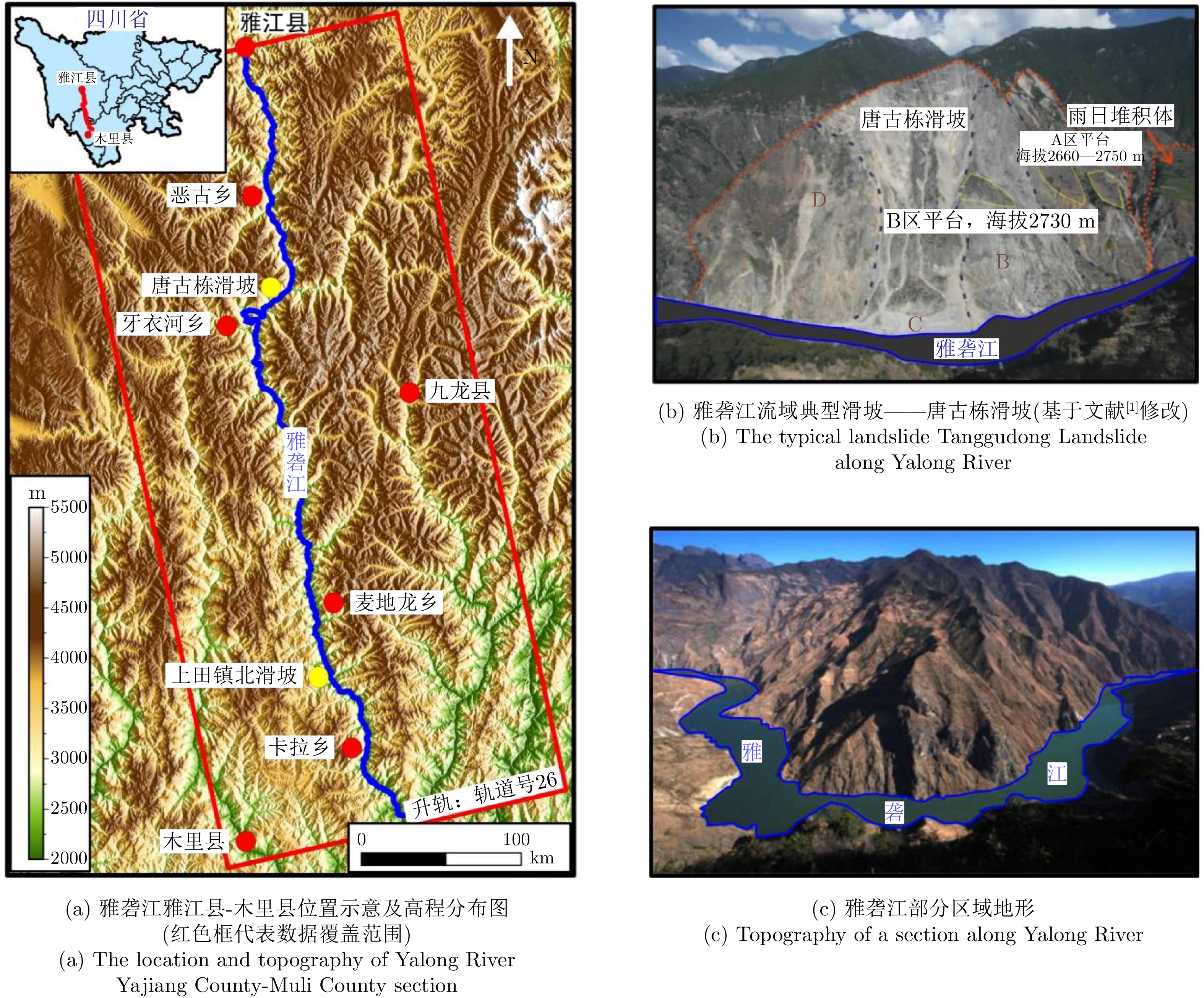
摘要: 我国西部山区滑坡灾害频发,具有强隐蔽性、高突发性、强破坏性等特点,对灾害隐患点进行早期识别是最为有效的防灾减灾措施。西部山区多为高山峡谷区域且范围辽阔,人不易至甚至人不能至,传统的人工排查早期识别方法较难实施。合成孔径雷达干涉测量技术(InSAR)作为新兴雷达遥感测量手段,可以高效准确地对高山峡谷区域进行滑坡灾害隐患早期识别。该文基于欧洲空间局(ESA)的哨兵一号(Sentinel-1)SAR遥感数据,利用时间序列InSAR技术对雅砻江流域雅江县-木里县段的高山峡谷区域进行了滑坡灾害隐患广域早期识别,成功探测到8处隐患区域。并结合滑坡隐患历史资料与光学影像遥感解译对识别结果进行了验证与分析,对灾害点风险等级进行了评定。并探讨了几何畸变因素对高山峡谷区域InSAR技术滑坡灾害隐患广域早期识别的影响。该案例可为当地的防灾减灾提供有力的数据与技术支持,并为高山峡谷区的滑坡灾害隐患早期识别提供思路与参考。
-
关键词:
- 雷达遥感 /
- 时间序列InSAR /
- 高山峡谷区 /
- 滑坡灾害隐患早期识别 /
- 雅砻江
Abstract: Landslide disasters occur frequently in the western mountainous regions of China and are characterized by high concealment, suddenness, and strong destructiveness. Early identification of potential disaster hazards is the most effective prevention and mitigation measure. The western mountainous areas mostly have a wide range of alpine-canyon terrain, which is hard or even impossible to reach. Moreover, traditional early identification methods, such as manual inspection, are difficult to implement in these areas. As an emerging radar remote-sensing method, Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) can efficiently and accurately identify the hidden dangers of landslides. Based on the synthetic aperture radar data of the European Space Agency’s Sentinel-1, this study used time series InSAR technology to identify the potential landslide hazards in the alpine-canyon terrain along the Yajiang-Muli County of the Yalong River; eight potential geohazards were detected. On the basis of the historical data of landslide hazards and the interpretation of optical remote sensing data, the results of early identification were verified and analyzed, and the danger level of the disaster points was evaluated. The influence of geometric distortion in InSAR technology on the early identification of potential landslides in alpine-canyon terrain was also discussed. This case study can provide powerful data and technical support for local disaster prevention and mitigation and provide ideas and references for the early identification of the hidden dangers of landslides in mountain-valley areas. -
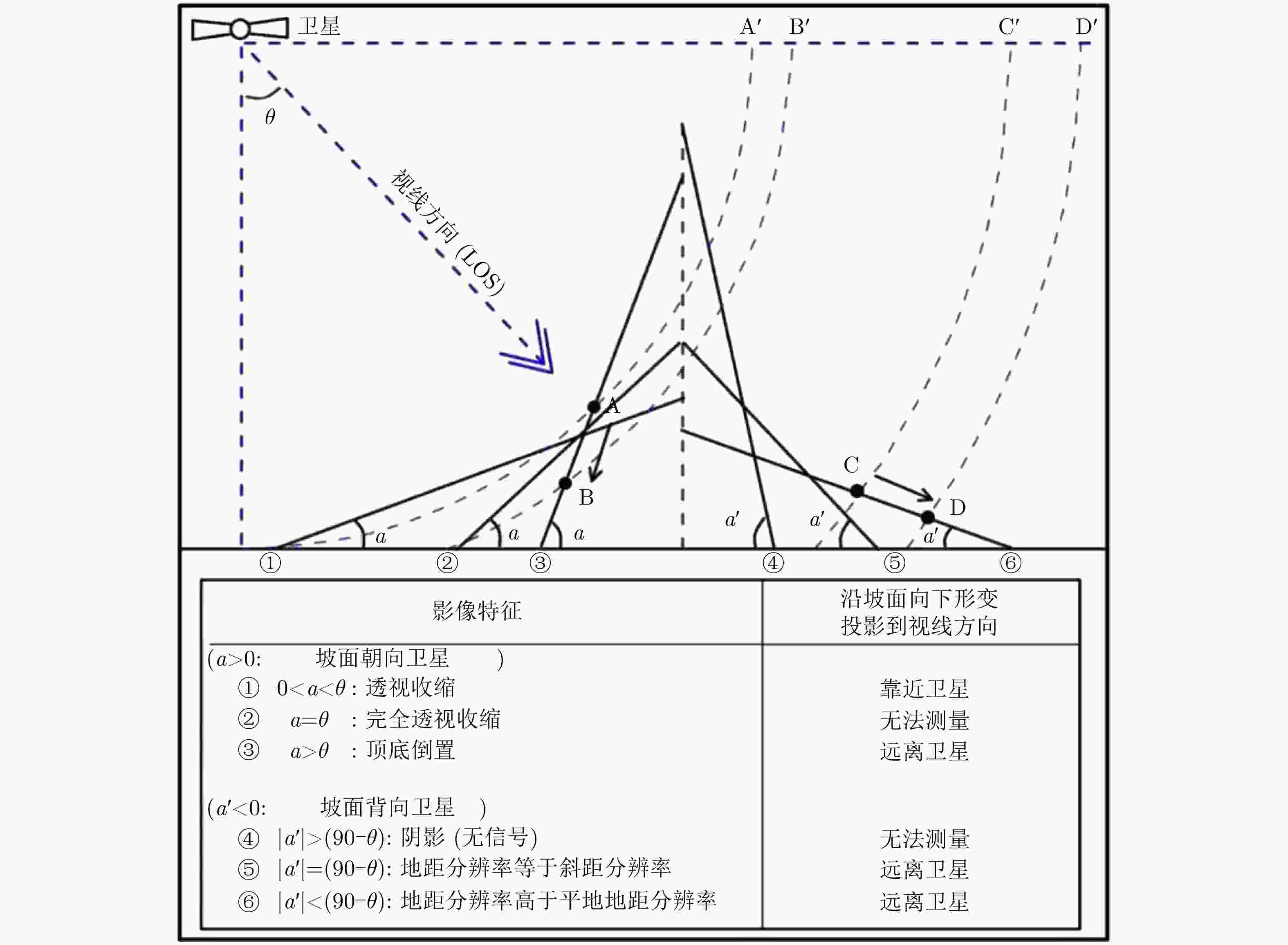
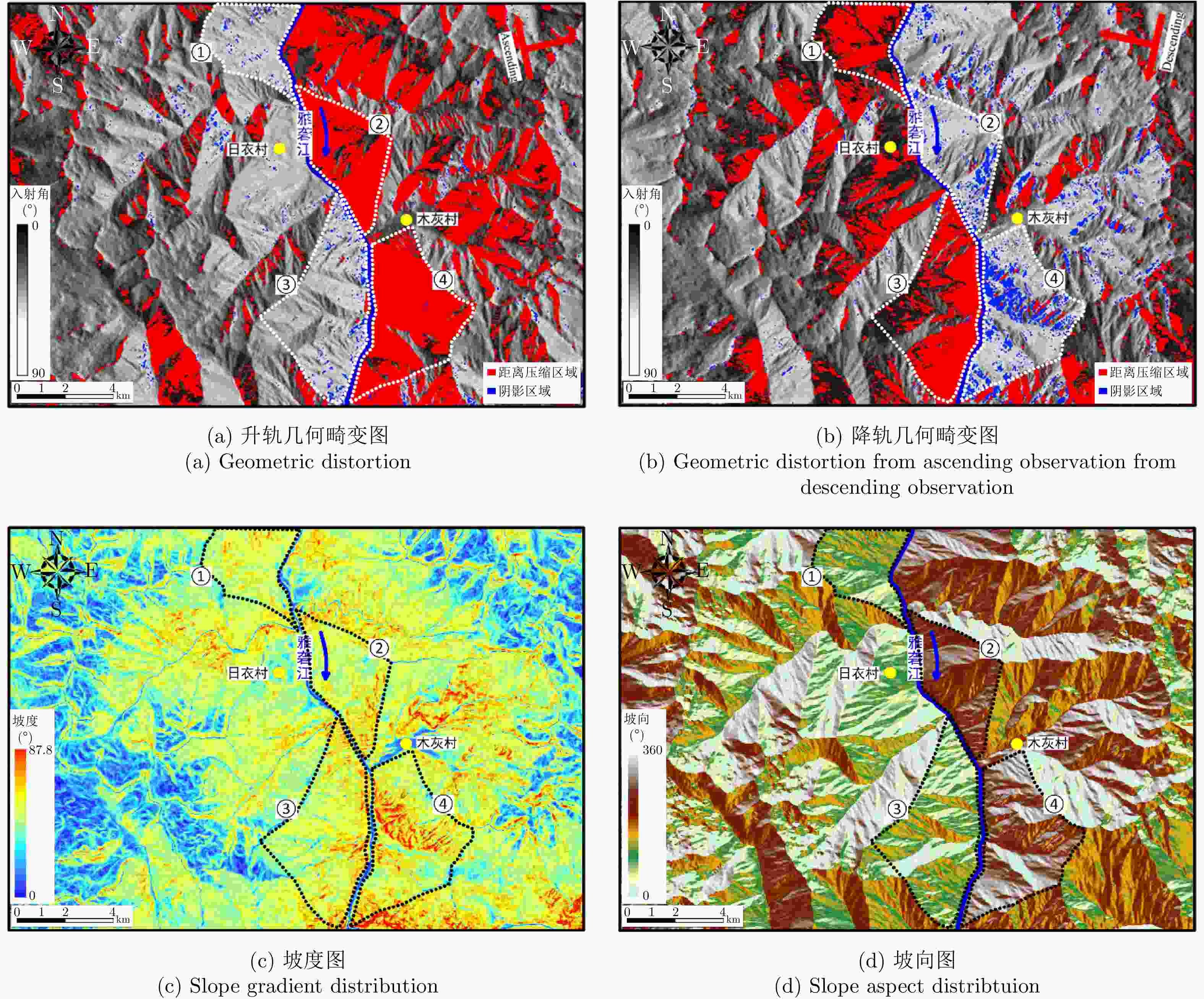
图 8 Relationships between the Line Of Sight (LOS) and the downslope displacements for different slope orientations (adapted from Ref. [22])
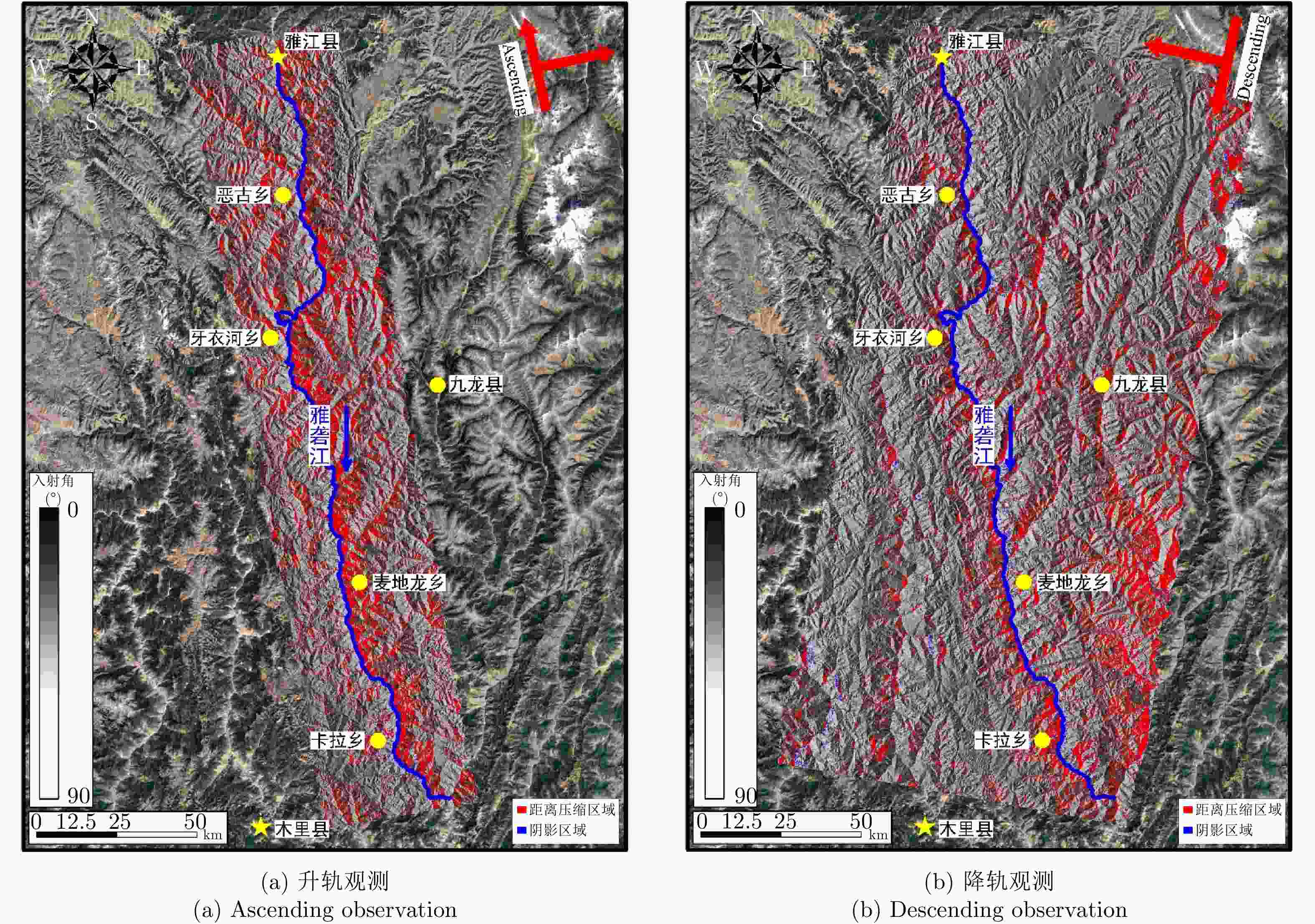
表 1 Sentinel-1卫星SAR影像数据主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of Sentinel-1 SAR datasets
主要参数 Sentinel-1卫星数据 轨道方向 升轨 波段 C 雷达波长(cm) 5.6 空间分辨率(m) 5×20 重访周期(d) 12 入射角(°) 36.8 表 2 雅砻江潜在灾害点早期识别结果列表
Table 2. Early identification results on potential disaster sites along Yalong River
编号 滑坡名 经纬度 变形范围(m) 最大形变速率
(mm/year)平均坡
度(%)高程范围(m) 植被覆
盖情况威胁对象 风险
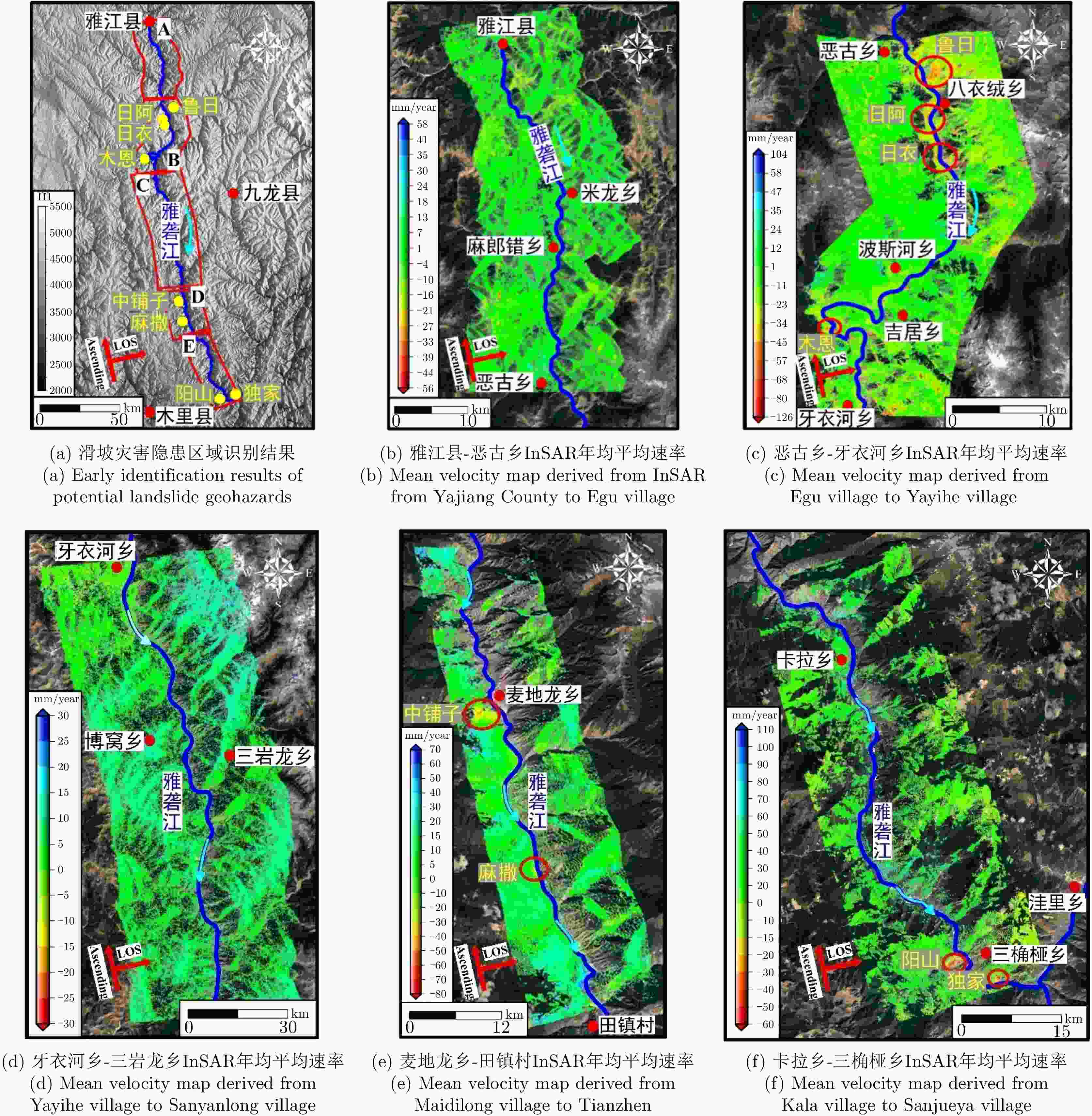
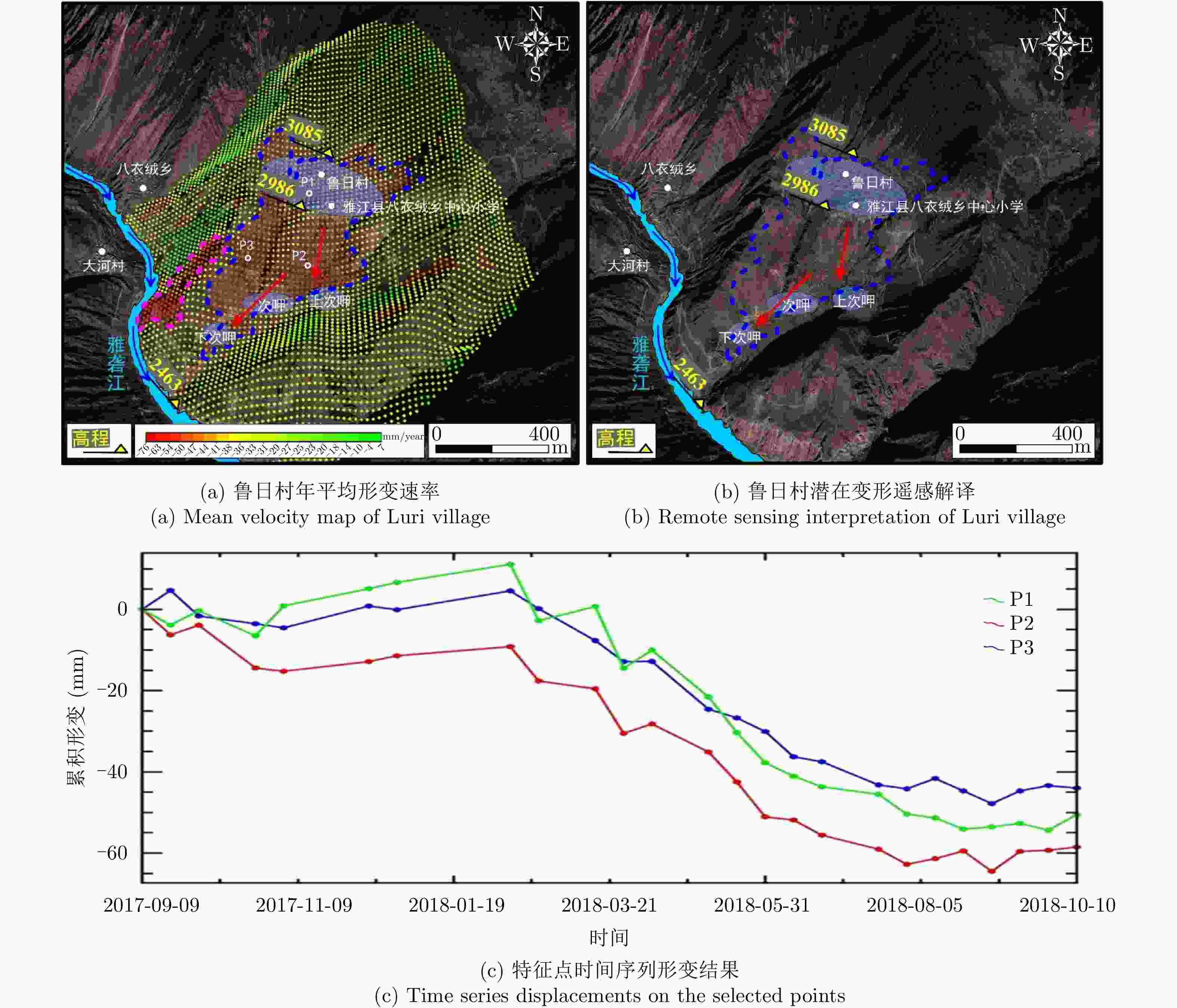
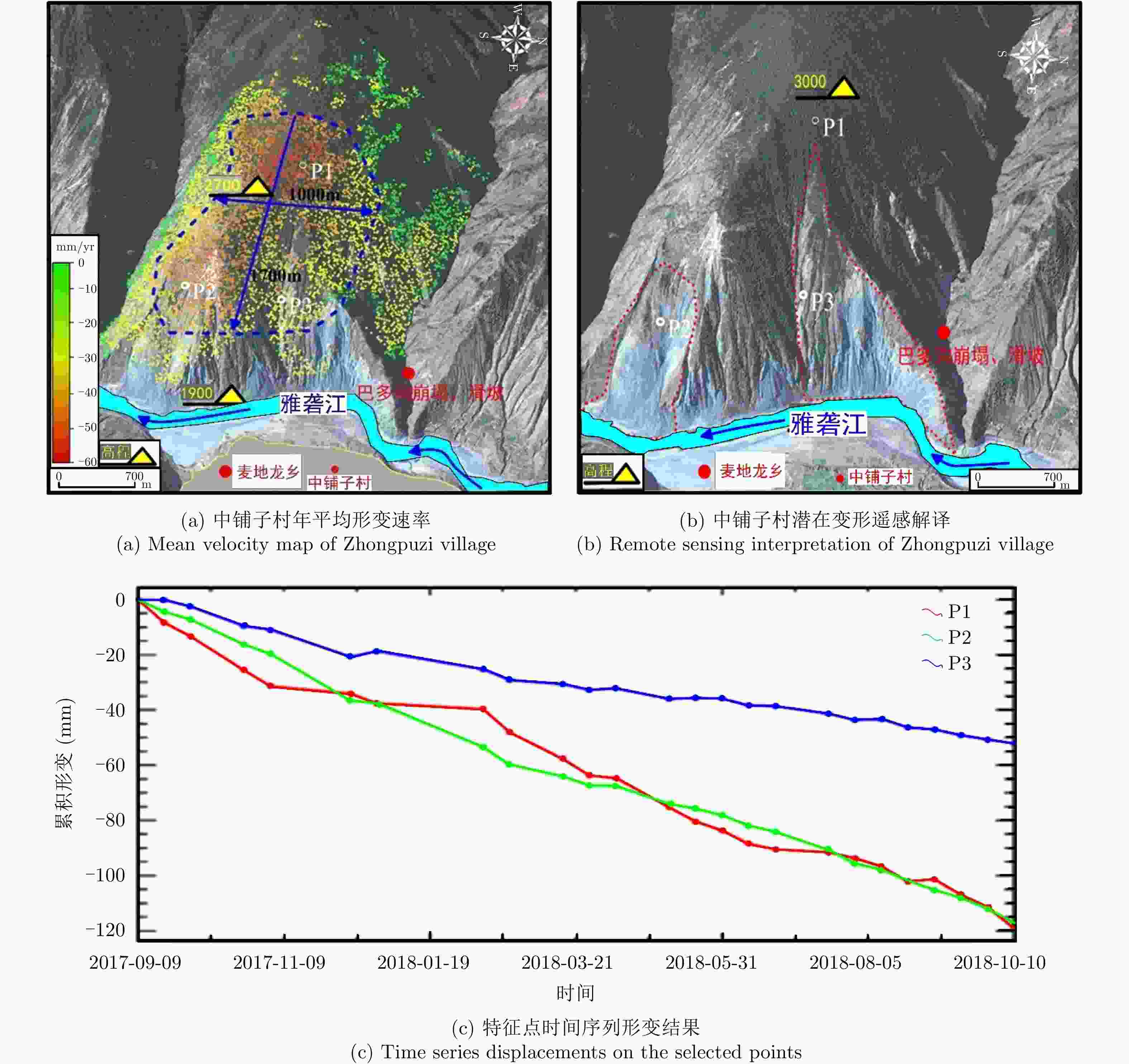
等级1 鲁日村 101°7′ 35″ E 29°34′ 43″ N 1800*1000 76 30 2463~3085 低 村落与雅砻江 高 2 日阿 101°7′ 2″ E 29°32′ 28″ N 2200*900 95 57 2462~3140 低 村落与雅砻江 高 3 日衣 101°7′ 41″ E 29°30′ 29″ N 2100*500 66 57 2452~2896 低 村落与雅砻江 高 4 木恩 101°0′ 37″ E 29°20′ 33″ N 500*800 57 58 2295~2853 低 雅砻江 中 5 中铺子村 101°12′ 30″ E 28°35′ 04″ N 1320*700 73 60 1900~3000 中 村落与雅砻江 高 6 麻撒村 101°14′ 21″ E 28°29′ 07″ N 360*400 46 55 1900~2500 低 村落与雅砻江 高 7 阳山村 101°27′ 32″ E 28°04′ 18″ N 710*1000 53 62 1762~2350 低 雅砻江支流 中 8 独家村 101°30′ 07″ E 28°03′ 31″ N 630*700 60 55 1600~2200 低 雅砻江 中 表 3 雅砻江流域InSAR早期识别验证与对比
Table 3. Verification and comparison on early identification results from InSAR along Yalong River
编号 滑坡名 历史记录 地貌地形特征 威胁对象 危险等级 1 鲁日 古滑坡 可见古滑坡体 村落与雅砻江 高 2 日阿 古滑坡 可见小型古滑坡 村落与雅砻江 高 3 日衣 古滑坡 可见古滑坡体 村落与雅砻江 高 4 木恩 古滑坡 可见古滑坡体 雅砻江 中 5 中铺子村 新发现 可见古滑坡体 村落与雅砻江 高 6 麻撒村 新发现 可见古滑坡体 村落与雅砻江 高 7 阳山村 新发现 无明显特征 雅砻江支流 中 8 独家村 新发现 可见历史崩塌 雅砻江 中 表 1 Main parameters of Sentinel-1 SAR datasets
The main parameters Sentinel-1 SAR data Orbital direction Ascending Bands C Radar wavelength (cm) 5.6 Spatial resolution (m) 5×20 Revisit cycle (d) 12 Incident angle (°) 36.8 表 2 Early identification results on potential disaster sites alongYalongRiver
Number Landslide Latitude and
longitudeDeformation range (m) Maximum deformation rate (mm/year) Average slope (%) Elevation range (m) Vegetation coverage Threat object Risk level 1 Luri ${\rm{101^\circ7'35''E\;29^\circ34'43''N} }$ 1800*1000 76 30 2463~3085 low Villages and Yalong River high 2 Ri’a ${\rm{101^\circ7'2''E\;29^\circ32'28''N} }$ 2200*900 95 57 2462~3140 low Villages and Yalong River high 3 Riyi ${\rm{101^\circ7'41''E\;29^\circ30'29''N} }$ 2100*500 66 57 2452~2896 low Villages and Yalong River high 4 Muen ${\rm{101^\circ0'37''E\;29^\circ20'33''N} }$ 500*800 57 58 2295~2853 low Yalong River middle 5 Zhongpuzi ${\rm{101^\circ12'30''E\;28^\circ35'04''N } }$ 1320*700 73 60 1900~3000 middle Villages and Yalong River high 6 Masa ${\rm{101^\circ14'21''E\;28^\circ29'07''N} }$ 360*400 46 55 1900~2500 low Villages and Yalong River high 7 Yangshan ${\rm{101^\circ27'32''E\;28^\circ04'18''N} }$ 710*1000 53 62 1762~2350 low Yalong River tributary middle 8 Dujia ${\rm{101^\circ30'07''E\;28^\circ03'31''N} }$ 630*700 60 55 1600~2200 low Yalong River middle 表 3 Verification and comparison on early identification results from InSAR along Yalong River
Number Landslide History record Topographic features Threat object Risk level 1 Luri ancient landslide Visible ancient landslide Villages and Yalong River high 2 Ri’a ancient landslide Visible small ancient landslide Villages and Yalong River high 3 Riyi ancient landslide Visible ancient landslide Villages and Yalong River high 4 Muen ancient landslide Visible ancient landslide Yalong River middle 5 Zhongpuzi new discovery Visible ancient landslide Villages and Yalong River high 6 Masa new discovery Visible ancient landslide Villages and Yalong River high 7 Yangshan new discovery No obvious features Yalong River tributary middle 8 Dujia new discovery Visible history collapse Yalong River middle -
[1] 刘哲. 基于GIS的雅砻江流域麦地龙—卡拉段地质灾害危险性评价[D]. [硕士论文], 成都理工大学, 2015.LIU Zhe. Hazard assessment of geological disasters in the Yalong River basin from the Maidilong to Kala based on GIS[D]. [Master dissertation], Chengdu University of Technology, 2015. [2] 常晓军, 魏伦武, 王德伟. 雅砻江流域地质灾害分布特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 灾害学, 2009, 24(3): 83–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2009.03.017CHANG Xiaojun, WEI Lunwu, and WANG Dewei. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of geological hazards in Yalong River basin[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2009, 24(3): 83–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2009.03.017 [3] 王孔伟, 邓成进, 张帆. 中国西南雅砻江流域唐古栋滑坡及雨日堆积体形成机理分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2012, 20(6): 955–970. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.06.007WANG Kongwei, DENG Chengjin, and ZHANG Fan. Formation process of Tanggudong landslide and Yuri accumulation body in Yalong River valley in southwest China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(6): 955–970. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.06.007 [4] 梁瑞锋, 杨敏, 杨栓成, 等. 雅砻江流域卡拉段地质灾害分布特征与影响因素分析[J]. 人民珠江, 2016, 37(11): 13–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2016.11.003LIANG Ruifeng, YANG Min, YANG Shuancheng, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors analysis of geological disasters in Kala section along Yalong River[J]. Pearl River, 2016, 37(11): 13–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9235.2016.11.003 [5] 陆会燕, 李为乐, 许强, 等. 光学遥感与InSAR结合的金沙江白格滑坡上下游滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2019, 44(9): 1342–1354.LU Huiyan, LI Weile, XU Qiang, et al. Early detection of landslides in the upstream and downstream areas of the Baige Landslide, the Jinsha River based on optical remote sensing and InSAR technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(9): 1342–1354. [6] 葛大庆, 戴可人, 郭兆成, 等. 重大地质灾害隐患早期识别中综合遥感应用的思考与建议[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2019, 44(7): 949–956.GE Daqing, DAI Keren, GUO Zhaocheng, et al. Early identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies: Thoughts and recommendations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 949–956. [7] XIA Y. CR-based SAR-interferometry for landslide monitoring[C]. 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, USA, 2008. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2008.4779226. [8] 王腾. 时间序列InSAR数据分析技术及其在三峡地区的应用[D]. [博士论文], 武汉大学, 2010.WANG Teng. Time series InSAR analysis over the Three Gorges Region: Techniques and applications[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Wuhan University, 2010. [9] XU Qiang, YUAN Yong, ZENG Yuping, et al. Some new pre-warning criteria for creep slope failure[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2011, 54(1): 210–220. doi: 10.1007/s11431-011-4640-5 [10] 戴可人, 卓冠晨, 许强, 等. 雷达干涉测量对甘肃南峪乡滑坡灾前二维形变追溯[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2019, 44(12): 1778–1786, 1796.DAI Keren, ZHUO Guanchen, XU Qiang, et al. Tracing the pre-failure two-dimensional surface displacements of Nanyu landslide, Gansu province with radar interferometry[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(12): 1778–1786, 1796. [11] DONG Jie, ZHANG Lu, TANG Minggao, et al. Mapping landslide surface displacements with time series SAR interferometry by combining persistent and distributed scatterers: A case study of Jiaju landslide in Danba, China[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 205: 180–198. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.11.022 [12] 张毅. 基于InSAR技术的地表变形监测与滑坡早期识别研究—以白龙江流域中游为例[D]. [博士论文], 兰州大学, 2018.ZHANG Yi. Detecting ground deformation and investigating landslides using InSAR technique—taking middle reach of Bailong River basin as an example[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Lanzhou University, 2018. [13] 张路, 廖明生, 董杰, 等. 基于时间序列InSAR分析的西部山区滑坡灾害隐患早期识别—以四川丹巴为例[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2018, 43(12): 2039–2049. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20180181ZHANG Lu, LIAO Mingsheng, DONG Jie, et al. Early detection of landslide hazards in mountainous areas of west China using time series SAR interferometry—a case study of Danba, Sichuan[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(12): 2039–2049. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20180181 [14] 张亚迪, 李煜东, 董杰, 等. 时序InSAR技术探测芒康地区滑坡灾害隐患[J]. 遥感学报, 2019, 23(5): 987–996.ZHANG Yadi, LI Yudong, DONG Jie, et al. Landslide hazard detection in Markam with time-series InSAR analyses[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 23(5): 987–996. [15] DAI Keren, CHEN Gang, XU Qiang, et al. Potential landslide early detection near Wenchuan by a qualitatively multi-baseline DInSAR method[C]. ISPRS Technical Commission III Midterm Symposium on "Developments, Technologies and Applications in Remote Sensing", Beijing, China, 2018: 253–256. [16] 李振洪, 宋闯, 余琛, 等. 卫星雷达遥感在滑坡灾害探测和监测中的应用: 挑战与对策[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2019, 44(7): 967–979. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190098LI Zhenhong, SONG Chuang, YU Chen, et al. Application of satellite radar remote sensing to landslide detection and monitoring: challenges and solutions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 967–979. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20190098 [17] 冷伦, 冷荣梅. 雅砻江垮山洪水和历史的教训[J]. 四川水利, 2002, 23(2): 42–44.LENG Lun and LENG Rongmei. Mountain slide flood in Yalong river and historical lesson[J]. Sichuan Water Conservancy, 2002, 23(2): 42–44. [18] 伍超, 冉洪兴, 郑永红, 等. 雅砻江唐古栋垮山堵江溃决洪水过程研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 1999, 11A: 646–652.WU Chao, RAN Hongxing, ZHENG Yonghong, et al. Hydrograph of the dam-break flood of the reservoir formed by mountain collapse in Ya Longjiang[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 1999, 11A: 646–652. [19] 武运泊. 雅砻江卡拉地区滑坡发育规律与成因机制分析[D]. [硕士论文], 成都理工大学, 2015.WU Yunbo. Analysis of development law and genetic mechanism of the landsides in Kala area, Yalong River[D]. [Master dissertation], Chengdu University of Technology, 2015. [20] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(3): 433–454. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001HUANG Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(3): 433–454. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001 [21] BERARDINO P, FORNARO G, LANARI R, et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(11): 2375–2383. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792 [22] DAI Keren, LI Zhenhong, TOMÁS R, et al. Monitoring activity at the Daguangbao mega-landslide (China) using Sentinel-1 TOPS time series interferometry[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 186: 501–513. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.09.009 [23] COLESANTI C and WASOWSKI J. Investigating landslides with space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) interferometry[J]. Engineering Geology, 2006, 88(3/4): 173–199. [24] DAI Keren, LI Zhenhong, XU Qiang, et al. Entering the era of earth observation-based landslide warning systems: A novel and exciting framework[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2020, 8(1): 136–153. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2019.2954395 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: