A Novel Clutter Suppression Approach for the Space-borne Multiple Channel in the Azimuth High-resolution and Wide-swath SAR-GMTI System with an Ambiguous Doppler Spectrum
-
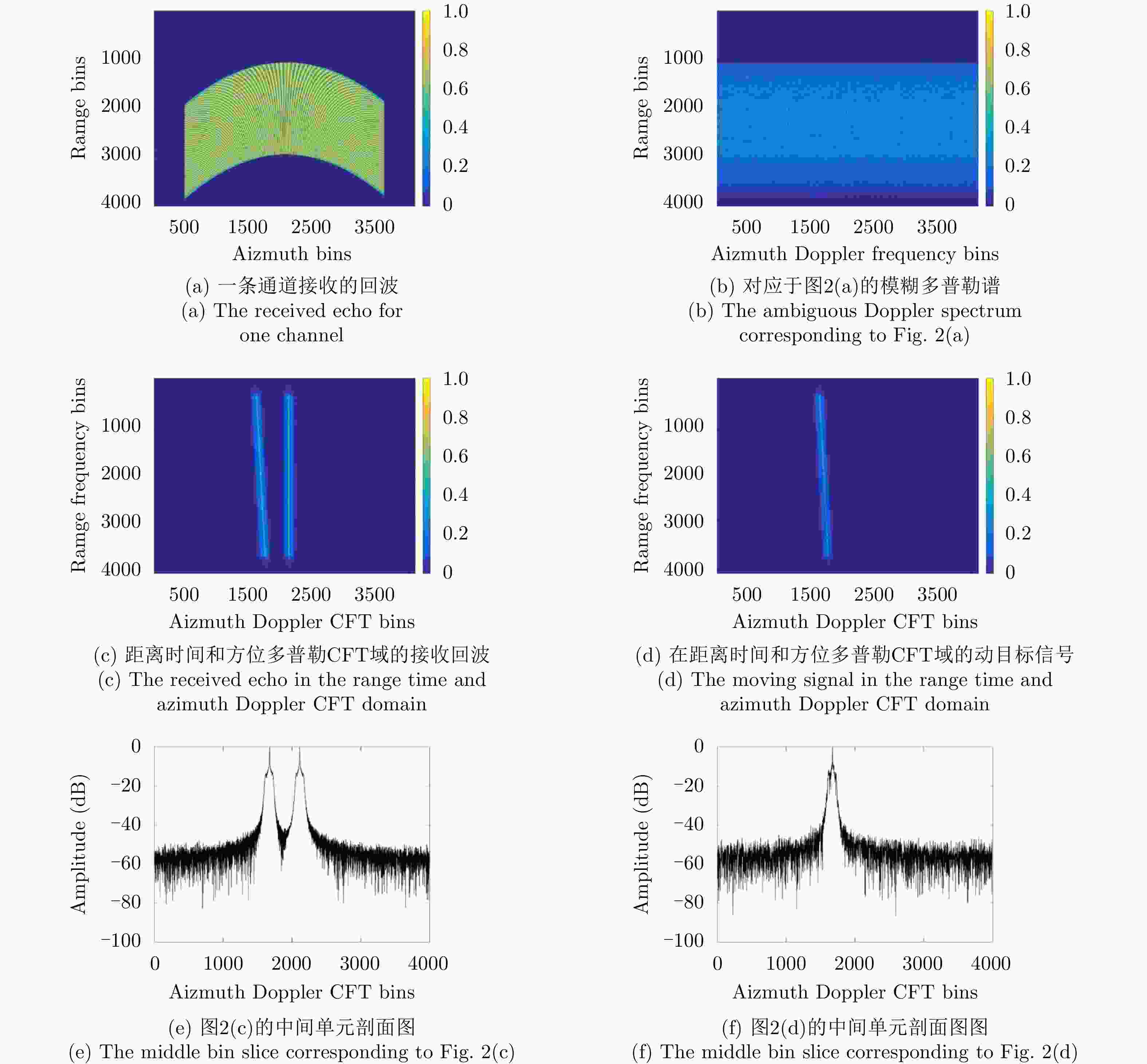
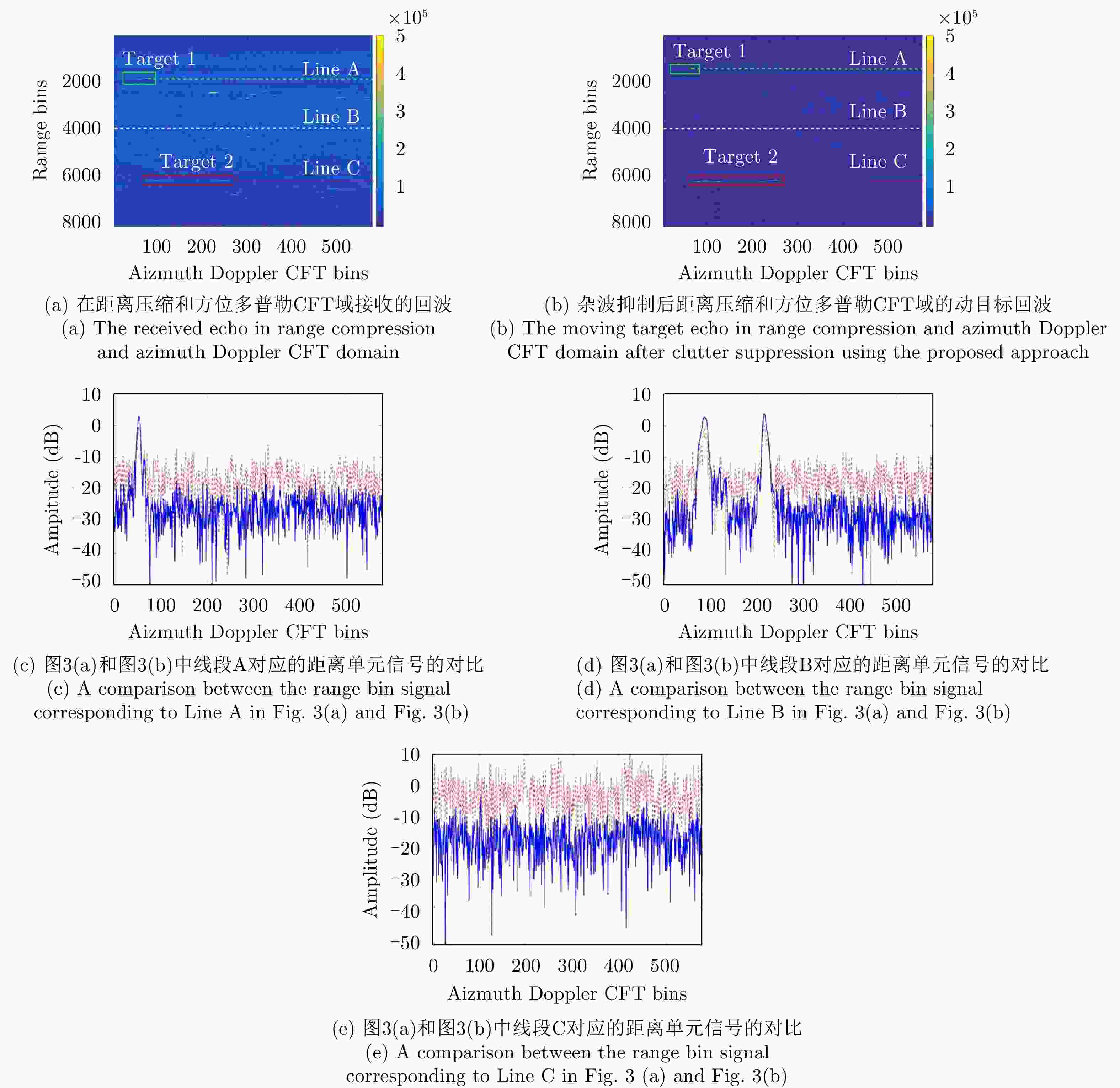
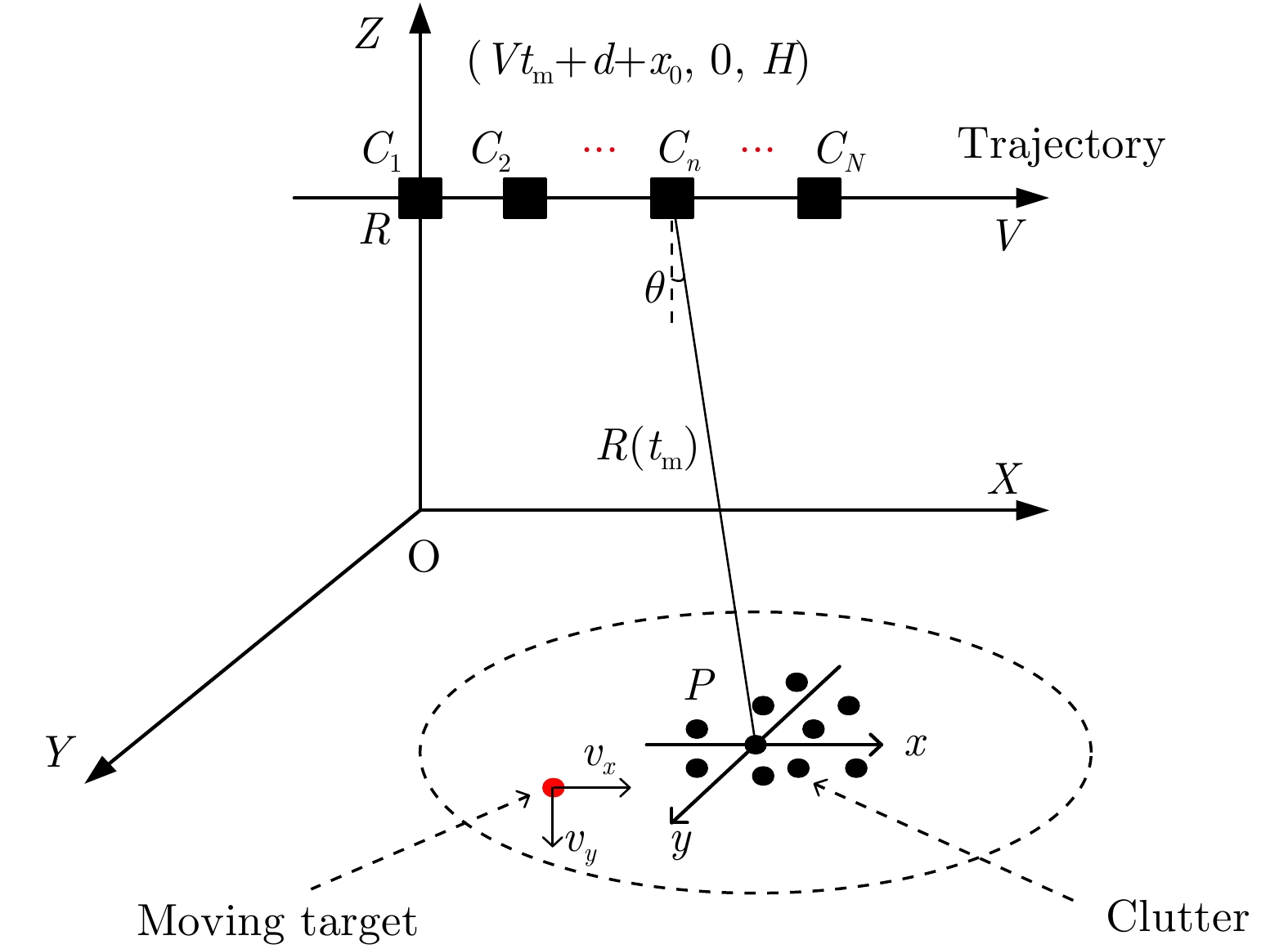
摘要: 该文提出了一种在多普勒频谱模糊情况下的星载方位向多通道高分宽幅合成孔径雷达地面运动目标检测(SAR-GMTI)系统的杂波抑制方法。首先,利用方位解线性调频对方位向多通道(HRWS) SAR-GMTI系统中的回波进行处理,得到杂波和动目标的粗聚焦图像。然后,将多通道SAR系统的粗聚焦图像表示为矩阵形式,并估计出相应的协方差矩阵。之后,用杂波协方差矩阵构造杂波空间的正交矢量,即最小特征值对应的特征向量。该方法需要一个冗余的通道自由度。由于杂波空间的正交矢量与杂波空间向量是正交的,因此可以用来抑制杂波。最后,通过仿真和实测数据实验结果验证该文所提杂波抑制方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 星载方位向多通道合成孔径雷达 /
- 杂波抑制 /
- 高分宽幅(HRWS) /
- 方位解线性调频 /
- 正交矢量
Abstract: A low pulse repletion frequency is required and an ambiguous Doppler spectrum should be considered to obtain a high-resolution and wide-swath Synthetic Aperture Radar-Ground Moving Target Indication (SAR-GMTI) system in the azimuth direction. In this study, we have proposed a novel clutter suppression approach, where the Doppler spectrum of the single channel echo is ambiguous, with respect to the space-borne multiple channels in an azimuth high-resolution and wide-swath SAR-GMTI system. Initially, the azimuth deramping operation is utilized to compress the ambiguous Doppler spectrum, where the signal of clutter or the moving target is focused toward only some azimuth Doppler-frequency bins. Further, a covariance matrix corresponding to the clutter is estimated in the azimuth deramping and range compression domain. Subsequently, the matrix eigenvalue decomposition technique is employed to obtain an eigenvector corresponding to the minimum eigenvalue. Herein, we intend to achieve redundant channel freedom to ensure the suppression of clutter. The obtained eigenvector can be considered to be the orthogonality vector of the clutter space, which denotes the orthogonality with respect to the signal space vector. Hence, we adopt the obtained eigenvector to appropriately suppress the clutter. Simultaneously, the signal of the moving target can be appropriately preserved. Finally, some experiments are conducted to validate the proposed clutter suppression approach. -
表 1 单平台方位向多通道HRWS SAR系统的主要仿真参数
Table 1. Main system parameters for the simulation single-platform multi-channel in azimuth HRWS SAR system
参数 数值 参数 数值 载波频率 5.4 GHz 通道数 7 SAR的有效速度 7552 m/s 平台高度 600 km 中心线距离 800 km 多普勒模糊数 6 脉冲重复频率(PRF) 400 Hz 发送信号的带宽 200 MHz 表 2 实际机载验证系统(单平台方位向多通道HRWS SAR系统)主要参数
Table 2. Main system parameters for the airborne real single-platform multi-channel in azimuth HRWS SAR system
参数 数值 参数 数值 载波频率 5.0 GHz 通道数 6 SAR的有效速度 110 m/s 平台高度 5.5 km 中心线距离 15 km 多普勒模糊数 5 PRF 200 Hz 发送信号的带宽 150 MHz -
[1] GEBERT N. Multi-channel azimuth processing for high-resolution wide-swath SAR imaging[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Fakultät für Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik, 2009. [2] 邢孟道, 林浩, 陈溅来, 等. 多平台合成孔径雷达成像算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A review of imaging algorithms in multi-platform-borne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102 [3] KIM J H, YOUNIS M, PRATS-IRAOLA P, et al. First spaceborne demonstration of digital beamforming for azimuth ambiguity suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(1): 579–590. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2201947 [4] LI Zhenfang, WANG Hongyang, SU Tao, et al. Generation of wide-swath and high-resolution SAR images from multichannel small spaceborne SAR systems[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2005, 2(1): 82–86. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.840610 [5] SIKANETA I, GIERULL C H, and CERUTTI-MAORI D. Optimum signal processing for multichannel SAR: With application to high-resolution wide-swath imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6095–6109. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2294940 [6] 邓云凯, 赵凤军, 王宇. 星载SAR技术的发展趋势及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015DENG Yunkai, ZHAO Fengjun, and WANG Yu. Brief analysis on the development and application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20015 [7] SJÖGREN T K, VU V T, PETTERSSON M I, et al. Suppression of clutter in multichannel SAR GMTI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4005–4013. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2278701 [8] ZHANG Shuangxi, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. Robust clutter suppression and moving target imaging approach for multichannel in azimuth high-resolution and wide-swath synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(2): 687–709. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2327031 [9] WANG H S C. Mainlobe clutter cancellation by DPCA for space-based radars[C]. The 1991 IEEE Aerospace Applications Conference Digest, Crested Butte, USA, 1991: 1–128. doi: 10.1109/AERO.1991.154520. [10] 王肖洋, 高贵, 周石琳, 等. 一种基于双通道DPCA的SAR-GMTI杂波抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2014, 3(2): 241–248. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13121WANG Xiaoyang, GAO Gui, ZHOU Shilin, et al. A clutter suppression approach for SAR-GMTI based on dual-channel DPCA[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(2): 241–248. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13121 [11] KLEMM R. Introduction to space-time adaptive processing[J]. Electronics & Communication Engineering Journal, 1999, 11(1): 5–12. doi: 10.1049/ecej:19990102 [12] TENNETI S V and VAIDYANATHAN P P. iMUSIC: A family of MUSIC-like algorithms for integer period estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(2): 367–382. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2879039 [13] 张兴良, 王可人, 樊甫华. 典型阵列快速MUSIC算法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(2): 149–156. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20026ZHANG Xingliang, WANG Keren, and FAN Fuhua. Study on fast MUSIC algorithm with typical array[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(2): 149–156. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20026 [14] 蒋柏峰, 吕晓德, 向茂生. 基于广义MUSIC 算法的低仰角估计新方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2103, 2(4): 422–429. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13090JIANG Baifeng, LÜ Xiaode, and XIANG Maosheng. A new low-elevation estimation method based on a general MUSIC algorithm[J]. Journal of Radars, 2103, 2(4): 422–429. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13090 [15] ZHANG Shuangxi, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. A robust imaging algorithm for squint mode multi-channel high-resolution and wide-swath SAR with hybrid baseline and fluctuant terrain[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2015, 9(8): 1583–1598. doi: 10.1109/jstsp.2015.2464182 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: