Wavenumber Domain Algorithm Based on the Principle of Chirp Scaling for SAR Imaging
-
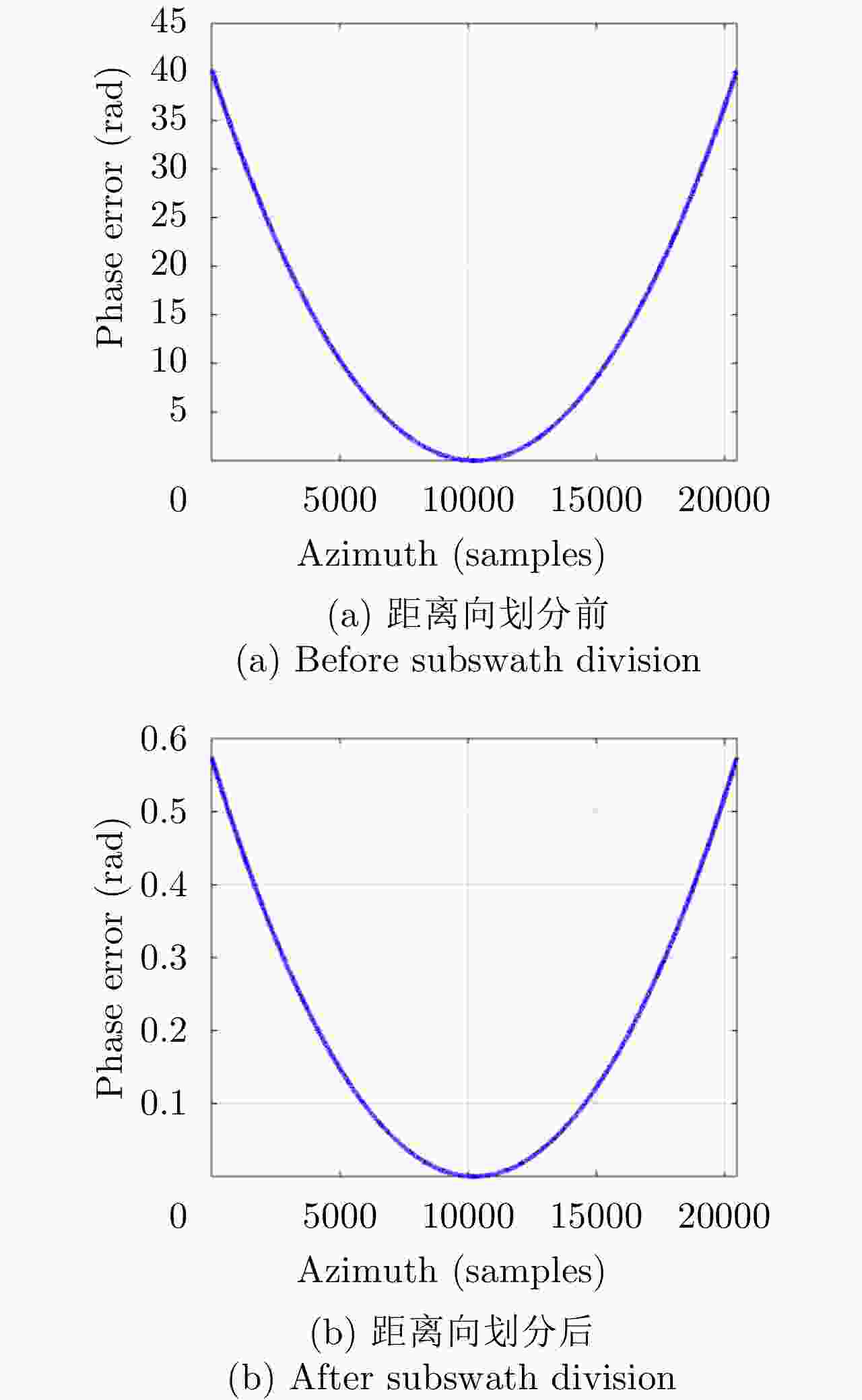
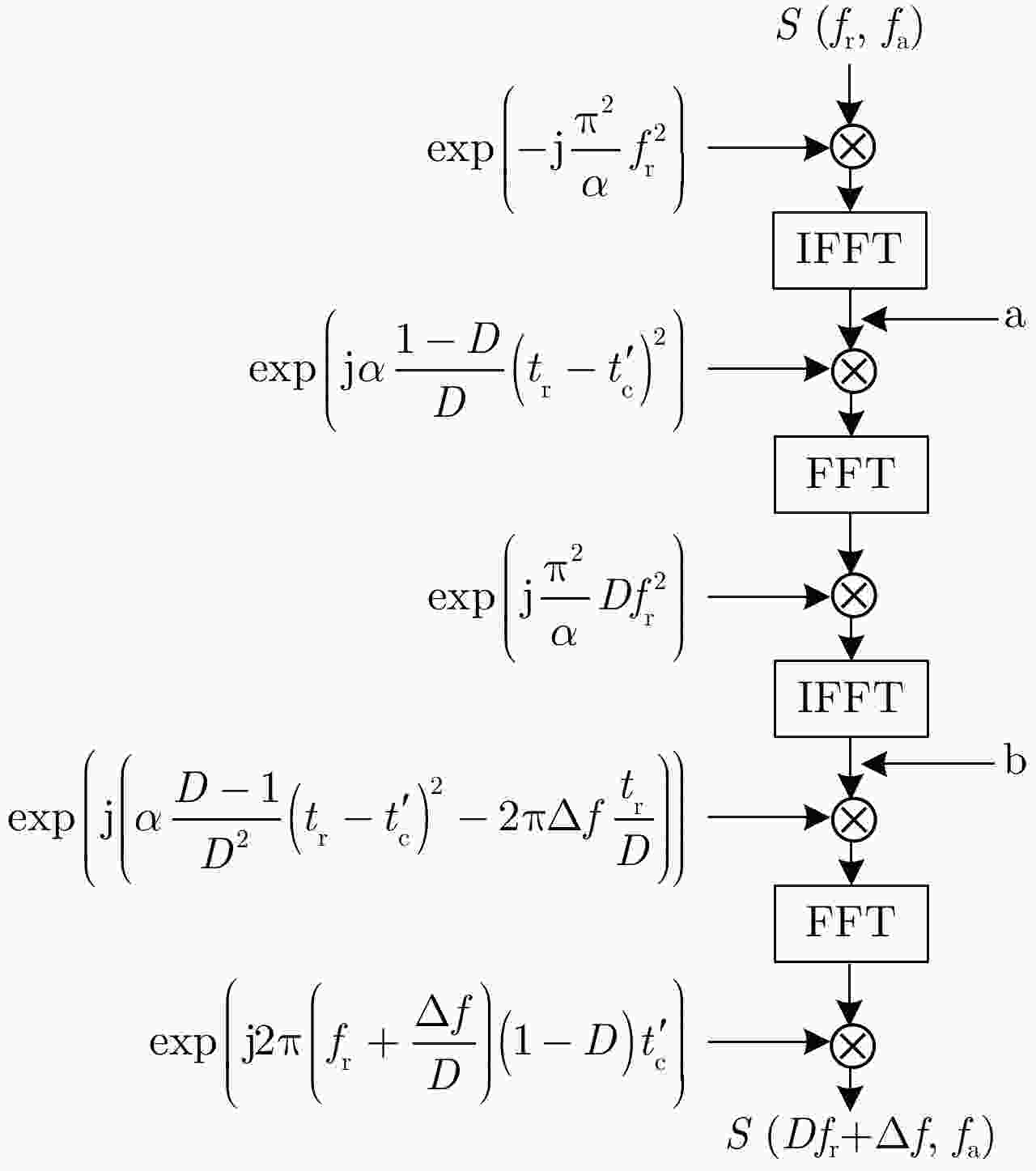
摘要: 距离徙动算法(RMA)作为一种合成孔径雷达(SAR)频域成像算法,理论上能够达到最优性能。然而,该算法采用逐像素点卷积运算实现Stolt映射,其计算效率无法满足SAR大数据量处理需求。据此,该文提出基于尺度变换原理(PCS)的RMA成像算法。首先,将SAR回波数据沿距离向进行划分,利用子带参考距离处2阶距离方位耦合项与高阶项对子带信号进行补偿;然后,转化非线性Stolt映射为线性形式;最后,利用PCS原理实现Stolt插值,以实现高效率的数据重采样。所提PCS-RMA算法仅利用快速傅里叶变换和复矢量相乘操作即可实现改进型Stolt映射,兼具良好的聚焦性能与较高的计算效率。基于多组仿真数据与X波段1.2 GHz带宽的机载SAR实测数据处理结果,验证了所提算法的有效性,同时该算法可进一步应用于弹载/星载/无人机载SAR数据的快速成像处理。Abstract: As a frequency-domain algorithm for Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging, the Range Migration Algorithm (RMA) can theoretically achieve optimal performance. However, because its Stolt mapping is performed using pixel-by-pixel convolution, the computational efficiency of RMA is inadequate for massive SAR data processing requirements. In this paper, we propose a modified RMA based on the Principle of Chirp Scaling (PCS). First, SAR echo data is divided along the range direction, and the subswath signal is compensated by the second-order range-azimuth coupling term and high-order terms at the reference distance. Then, the nonlinear Stolt mapping is modified to become linear. Finally, Stolt interpolation is realized using PCS to efficiently resample the processed data. Demonstrating both well-focused performance and high computational efficiency, the proposed PCS-RMA employs only fast Fourier transforms and complex vector multiplication operations to achieve modified Stolt mapping. The processing results of several simulation data and X-band-measured airborne SAR data with a pulse bandwidth of 1.2 GHz verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. The proposed algorithm can also be employed for the rapid processing of missile-borne, spaceborne, and drone-borne SAR data.
-
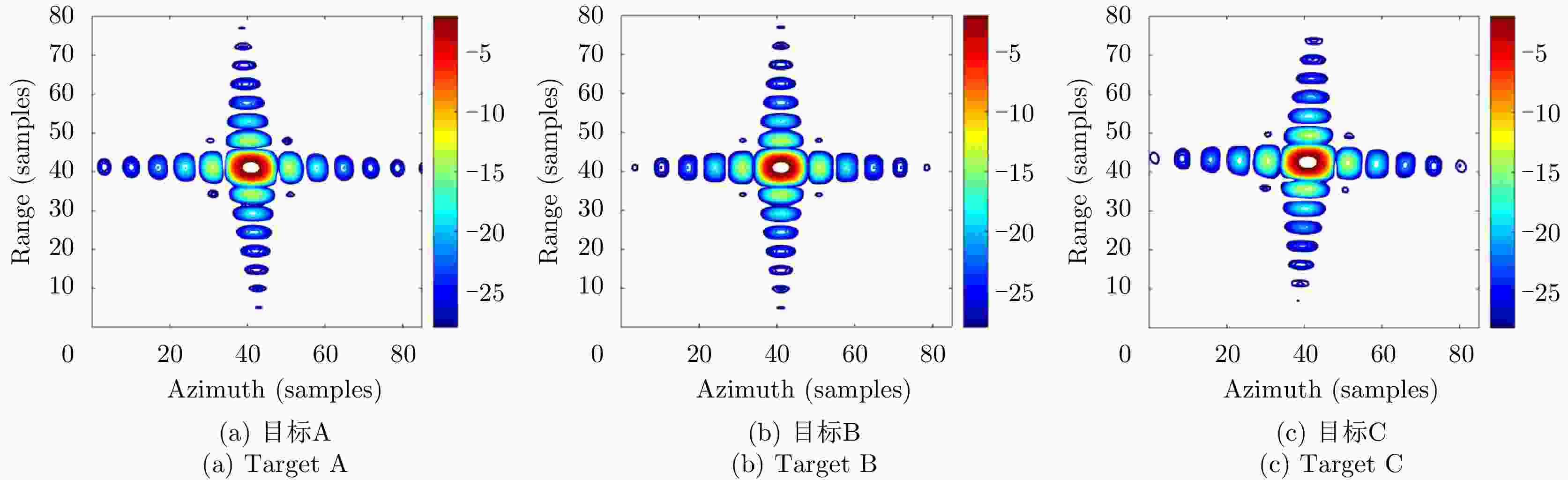
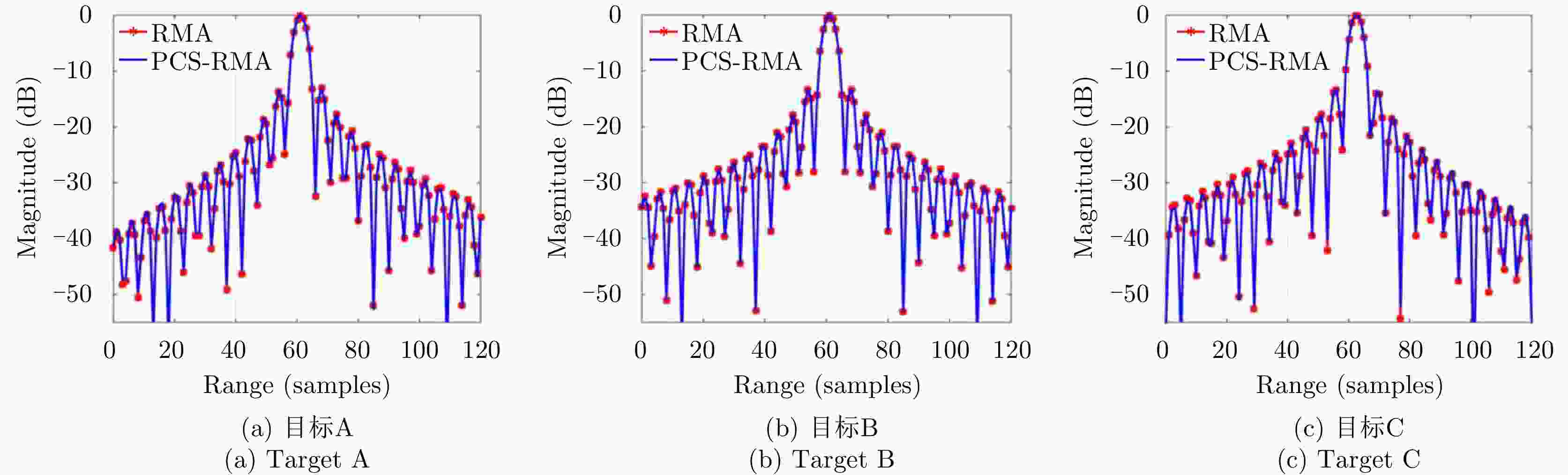
表 1 点目标仿真参数
Table 1. Point target simulation parameters
参数 数值 载频 9.65 GHz 信号带宽 1.5 GHz 脉冲重复频率 1500 Hz 载机速度 100 m/s 中心斜距 10 km 方位向分辨率 0.1 m 表 2 点目标IRF聚焦性能参数
Table 2. Focusing performance parameters of point target IRF
点目标 距离向 方位向 PSLR(dB) ISLR(dB) IRW(m) PSLR(dB) ISLR(dB) IRW(m) A –13.3728 –11.5636 0.0990 –13.2710 –11.1409 0.1017 B –13.4564 –11.5881 0.1001 –13.3030 –11.2275 0.1000 C –13.5875 –9.8772 0.1001 –13.5265 –10.7503 0.1033 -
[1] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 [2] 詹学丽, 王岩飞, 王超, 等. 一种基于脉冲压缩的机载条带SAR重叠子孔径实时成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 199–208. doi: 10.12000/JR14126ZHAN Xueli, WANG Yanfei, WANG Chao, et al. Research on overlapped subaperture real-time imaging algorithm for pulse compression airborne strip SAR system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 199–208. doi: 10.12000/JR14126 [3] 唐江文, 邓云凯, 王宇, 等. 高分辨率滑动聚束SAR BP成像及其异构并行实现[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(4): 368–375. doi: 10.12000/JR16053TANG Jiangwen, DENG Yunkai, WANG Yu, et al. High-resolution slide spotlight SAR imaging by BP algorithm and heterogeneous parallel implementation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(4): 368–375. doi: 10.12000/JR16053 [4] 胡静秋, 刘发林, 周崇彬, 等. 一种新的基于omega-K算法的稀疏场景压缩感知SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(1): 25–33. doi: 10.12000/JR16027HU Jingqiu, LIU Falin, ZHOU Chongbin, et al. CS-SAR imaging method based on inverse omega-K algorithm[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(1): 25–33. doi: 10.12000/JR16027 [5] 王金波, 唐劲松, 张森, 等. 一种宽带大斜视STOLT插值及距离变标补偿方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(7): 1575–1582. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171068WANG Jinbo, TANG Jinsong, ZHANG Sen, et al. Range scaling compensation method based on STOLT interpolation in broadband squint SAS imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(7): 1575–1582. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171068 [6] LIN Yun, HONG Wen, TAN Weixian, et al. Extension of range migration algorithm to squint circular SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(4): 651–655. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2098843 [7] TANG Shiyang, ZHANG Linrang, GUO Ping, et al. An omega-K algorithm for highly squinted missile-borne SAR with constant acceleration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(9): 1569–1573. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2301718 [8] SHIN H S and LIM J T. Omega-K algorithm for spaceborne spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(3): 343–347. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2168380 [9] ZHU Daiyin, YE Shaohua, and ZHU Zhaoda. Polar format agorithm using chirp scaling for spotlight SAR image formation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(4): 1433–1448. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4667720 [10] FAN Bo, QIN Yuliang, YOU Peng, et al. An improved PFA with aperture accommodation for widefield spotlight SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(1): 3–7. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2322858 [11] LUO Xiulian, DENG Yunkai, WANG R, et al. Image formation processing for sliding spotlight SAR with stepped frequency chirps[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(10): 1692–1696. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2306206 [12] LIU Yongcai, WANG Wei, PAN Xiaoyi, et al. Inverse omega-K algorithm for the electromagnetic deception of synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(7): 3037–3049. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2543961 [13] NIE Xin, ZHU Daiyin, MAO Xinhua, et al. The application of the principle of chirp scaling in processing stepped chirps in spotlight SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(4): 860–864. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2027212 [14] PIGNOL F, COLONE F, and MARTELLI T. Lagrange-polynomial-interpolation-based keystone transform for a passive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(3): 1151–1167. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2775924 [15] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Signal Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston, MA, USA: Artech House, 2005: 225–362. [16] LANARI R and FORNARO G. A short discussion on the exact compensation of the SAR range-dependent range cell migration effect[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(6): 1446–1452. doi: 10.1109/36.649799 [17] 吴玉峰, 叶少华, 冯大政. 基于方位相位编码的脉内聚束SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 437–445. doi: 10.12000/JR17114WU Yufeng, YE Shaohua, and FENG Dazheng. Intra-pulse spotlight SAR imaging method based on azimuth phase coding[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 437–445. doi: 10.12000/JR17114 [18] YANG Mingdong, ZHU Daiyin, and SONG Wei. Comparison of two-step and one-step motion compensation algorithms for airborne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Electronics Letters, 2015, 51(14): 1108–1110. doi: 10.1049/el.2015.1350 [19] XING Mengdao, WU Yufeng, ZHANG Y D, et al. Azimuth resampling processing for highly squinted synthetic aperture radar imaging with several modes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4339–4352. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2281454 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公

 下载:
下载: