Super-resolution Reconstruction of SAR Images Based on Feature Reuse Dilated-Residual Convolutional Neural Networks
-
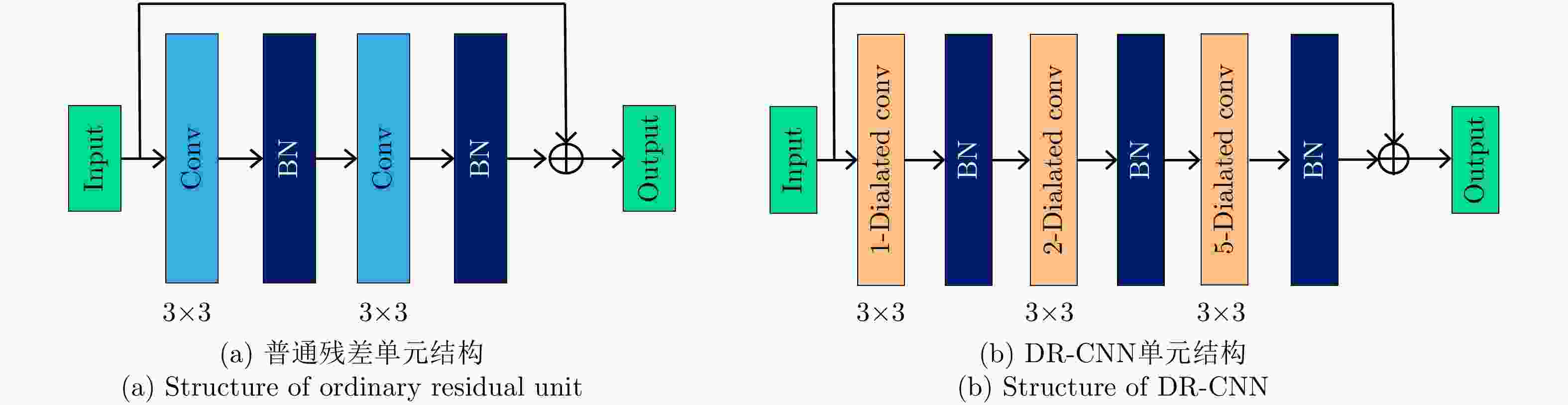
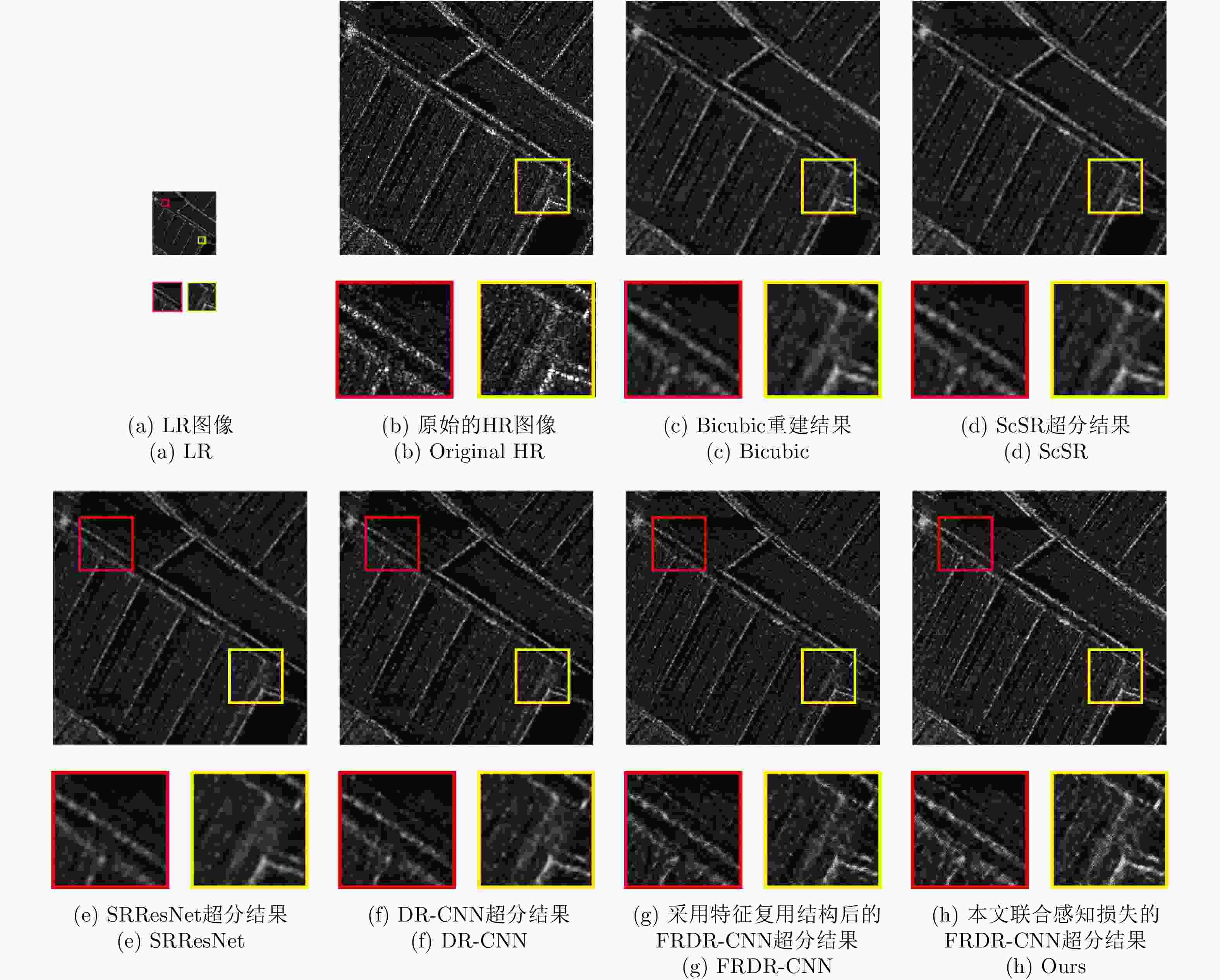
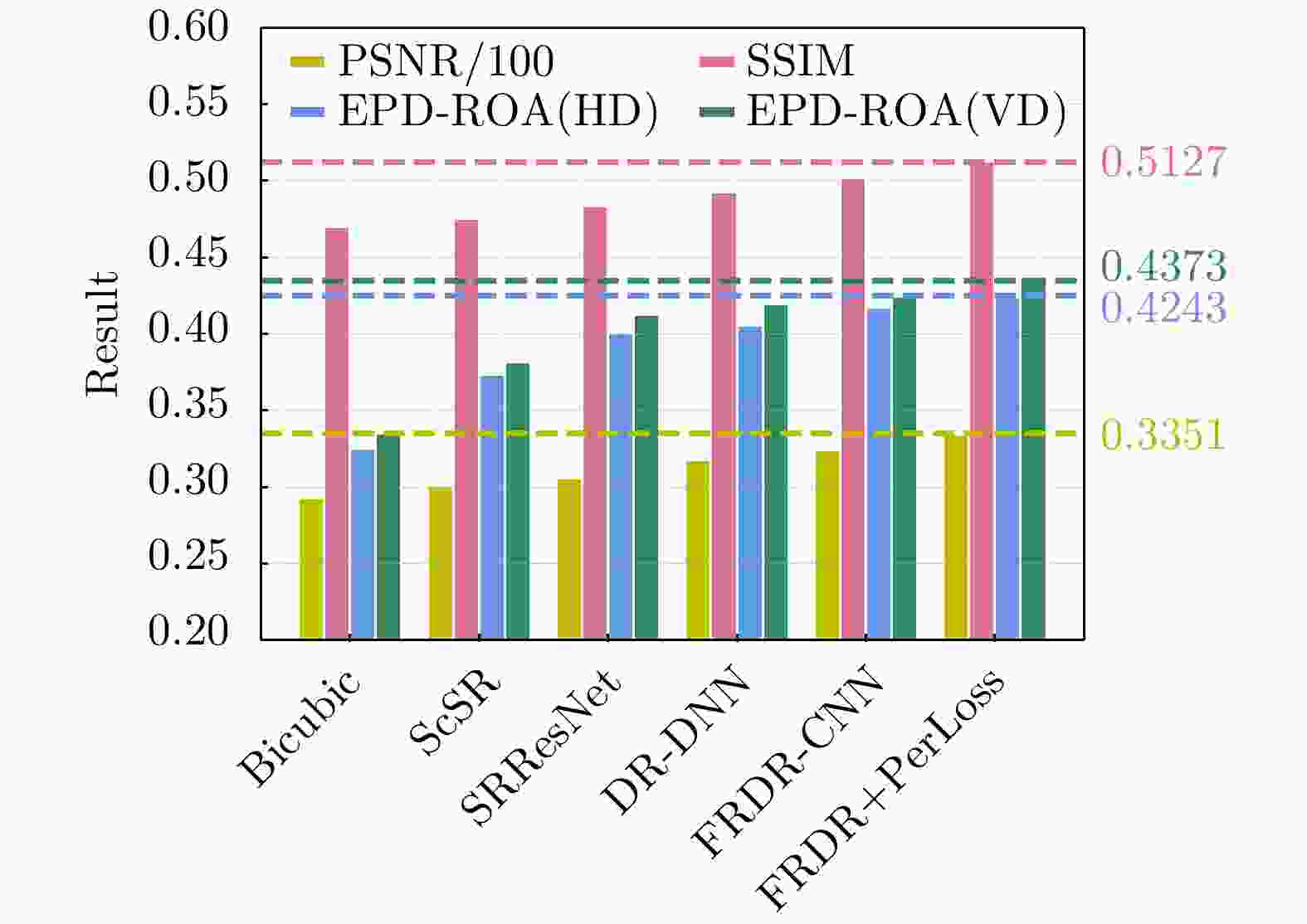
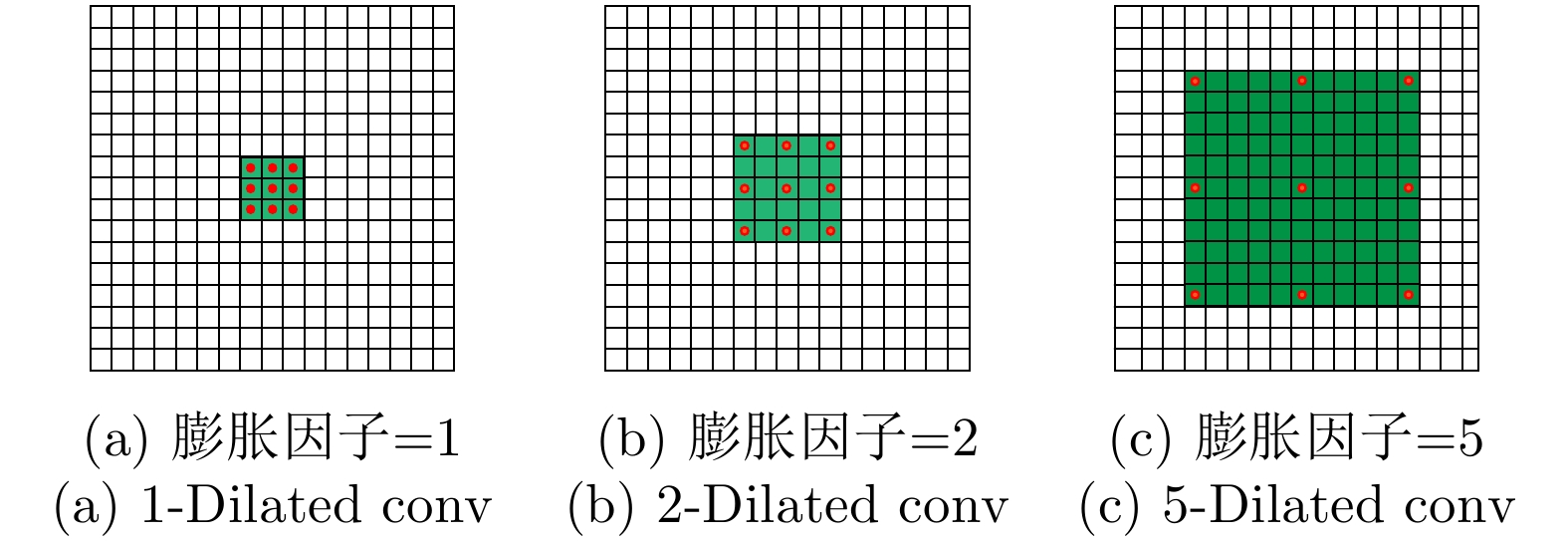
摘要: 对于合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像,传统的超分辨重建方法对视觉特征的人为构造十分依赖,基于普通卷积神经网络(CNN)的超分辨重建方法对微小目标的重建能力较弱,对边缘轮廓的保真度较差。针对以上问题,该文提出一种基于特征复用的膨胀-残差卷积超分辨网络模型,同时引入感知损失,实现了精确的SAR图像4倍语义级超分辨。该方法为增加网络感受野,采用膨胀-残差卷积(DR-CNN)结构用于限制模型中特征图分辨率的严重损失,提高网络对微小细节的敏感度;为实现不同层级的特征最大化利用,将不同层级的特征图进行级联,形成一种特征复用结构(FRDR-CNN),以此大幅度提升特征提取模块的效率,进一步提升超分辨精度;针对SAR图像特殊的相干斑噪声干扰,引入感知损失,使得该方法在恢复图像边缘和精细的纹理信息方面具有优越表现。文中实验表明,与传统算法以及目前较为流行的几种全卷积神经网络超分辨重建算法相比,该文采用的FRDR-CNN模型在视觉上对小物体的超分辨重建能力更强,对边界等轮廓信息的重建更准确,客观指标中的峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似性指数(SSIM)分别为33.5023 dB和0.5127,边缘保持系数(EPD-ROA)在水平和垂直方向上分别为0.4243和0.4373。Abstract: For Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images, traditional super-resolution methods heavily rely on the artificial design of visual features, and super-reconstruction algorithms based on general Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) have poor fidelity to the target edge contour and weak reconstruction ability to small targets. Aiming at the above problems, in this paper, a Dilated-Resnet CNN (DR-CNN) super-resolution model based on feature reuse, i.e., Feature Reuse Dilated-Resnet CNN (FRDR-CNN), is proposed and perceptual loss is introduced, which accurately realizes four times the semantic super-resolution of SAR images. To increase the receptive field, a DR-CNN structure is used to limit the serious loss of the feature map’s resolution in the model, improving the sensitivity to tiny details. To maximize the utilization of features at different levels, the FRDR-CNN cascades the feature maps of different levels, which greatly improves the efficiency of the feature extraction module and further improves the super-resolution accuracy. With the introduction of the perceptual loss, this method has a superior performance in recovering image texture and edge information. Experimental results of the study show that the FRDR-CNN algorithm is more capable of providing small objects’ super-resolution and more accurate in the visual reconstruction of contour details, compared with traditional algorithms and several popular CNN super-resolution algorithms. Objectively, the Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) is 33.5023 dB and Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) is 0.5127, and the Edge Preservation Degreebased on the Ratio Of Average (EPD-ROA) is 0.4243 and 0.4373 in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively.
-
Key words:
- SAR /
- Super resolution construction /
- Dilated convolution /
- Feature reuse /
- Perceptual loss
-
表 1 场景1和场景2的SAR图像重建结果表
Table 1. SAR image reconstruction results table of scene 1 and 2
Results Bicubic ScSR SRResNet DR-CNN FRDR-CNN 本文联合感知损失的FRDR-CNN 场景1 PSNR(dB) 29.2897 29.9867 30.4492 30.5922 31.4015 32.4202 SSIM 0.4755 0.4843 0.4992 0.5023 0.5108 0.5218 EPD-ROA(HD) 0.3302 0.3773 0.4253 0.4298 0.4329 0.4498 EPD-ROA(VD) 0.3425 0.3881 0.4378 0.4380 0.4422 0.4556 场景2 PSNR(dB) 29.3572 30.0634 30.6257 31.7901 32.4717 33.4925 SSIM 0.4532 0.4630 0.4768 0.4796 0.4934 0.5049 EPD-ROA(HD) 0.3189 0.3596 0.4002 0.4085 0.4142 0.4288 EPD-ROA(VD) 0.3349 0.3792 0.4198 0.4217 0.4216 0.4352 -
[1] BI Zhaoqiang, LI Jian, and LIU Zhengshe. Super resolution SAR imaging via parametric spectral estimation methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(1): 267–281. doi: 10.1109/7.745697 [2] GUPTA I J, BEALS M J, and MOGHADDAR A. Data extrapolation for high resolution radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1994, 42(11): 1540–1545. doi: 10.1109/8.362783 [3] BROWN L G. A survey of image registration techniques[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 1992, 24(4): 325–376. doi: 10.1145/146370.146374 [4] YANG Siyoung, KIM Y, and JEONG J. Fine edge-preserving technique for display devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2008, 54(4): 1761–1769. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2008.4711232 [5] DUCHON C E. Lanczos filtering in one and two dimensions[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 1979, 18(8): 1016–1022. doi: 10.1175/1520-0450(1979)018<1016:LFIOAT>2.0.CO;2 [6] YANG Jianchao, WRIGHT J, HUANG T S, et al. Image super-resolution via sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(11): 2861–2873. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2050625 [7] DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295–307. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281 [8] KIM J, KWON LEE J, and MU LEE K. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1646–1654. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.182. [9] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Identity mappings in deep residual networks[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 630–645. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_38. [10] WANG Longgang, ZHENG Mana, DU Wenbo, et al. Super-resolution SAR image reconstruction via generative adversarial network[C]. 2018 12th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation and EM Theory, Hangzhou, China, 2018: 1–4. [11] LI Zhen, YANG Jinglei, LIU Zheng, et al. Feedback network for image super-resolution[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3862–3871. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00399. [12] KIM J, KWON LEE J, and MU LEE K. Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1637–1645. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.181. [13] TAI Ying, YANG Jian, and LIU Xiaoming. Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2790–2798. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.298. [14] LEDIG C, THEIS L, HUSZÁR F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 105–114. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.19. [15] YU F and KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1511.07122, 2015. [16] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4700–4708. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.243. [17] BENGIO Y, LECUN Y, NOHL C, et al. LeRec: A NN/HMM hybrid for on-line handwriting recognition[J]. Neural Computation, 1995, 7(6): 1289–1303. doi: 10.1162/neco.1995.7.6.1289 [18] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. [19] JOHNSON J, ALAHI A, and LI Feifei. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 694–711. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_43. [20] ZHANG Qiang, YUAN Qiangqiang, LI Jie, et al. Learning a dilated residual network for SAR image despeckling[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(2): 196. doi: 10.3390/rs10020196 [21] WANG Panqu, CHEN Pengfei, YUAN Ye, et al. Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation[C]. 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2018: 1451–1460. doi: 10.1109/WACV.2018.00163. [22] SHI Wenzhe, CABALLERO J, HUSZÁR F, et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2016: 1874–1883. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.207. [23] ZEILER M D, TAYLOR G W, and FERGUS R. Adaptive deconvolutional networks for mid and high level feature learning[C]. 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 2018–2025. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2011.6126474. [24] NAIR V and HINTON G E. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines[C]. The 27th International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 2010: 807–814. [25] 王振. 基于学习策略的SAR图像超分辨[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2018.WANG Zhen. SAR image super resolution based on learning strategy[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2018. [26] WANG Qiang and BI Sheng. Prediction of the PSNR quality of decoded images in fractal image coding[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2016, 2016: 2159703. [27] WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [28] 唐伶俐, 江平, 戴昌达, 等. 星载SAR图象斑点噪声消除方法效果的比较研究[J]. 环境遥感, 1996, 11(3): 206–211.TANG Lingli, JIANG Ping, DAI Changda, et al. Evaluation of smoothing filters suppressing speckle noise on SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment China, 1996, 11(3): 206–211. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: