Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar Interpretation and Recognition: Advances and Perspectives
-
摘要:
极化合成孔径雷达(SAR)能够获取目标的全极化信息,在对地观测、灾害评估、侦察监视等民用和军用领域得到广泛应用。国内主要高校、中科院、工业部门和用户单位在该领域开展了卓有成效的工作,取得一大批标志性研究成果。该文简要综述了极化SAR成像解译识别领域的主要研究进展。在解译层面,主要介绍了极化目标分解和极化旋转域解译等理论方法的研究进展。在应用层面,结合研究团队的工作,探讨了上述理论方法在舰船检测、地物分类和建筑物损毁评估等领域的应用成效。最后,对极化SAR目标解译识别技术的研究进行了展望。
-
关键词:
- 极化合成孔径雷达(极化SAR) /
- 极化目标分解 /
- 极化旋转域 /
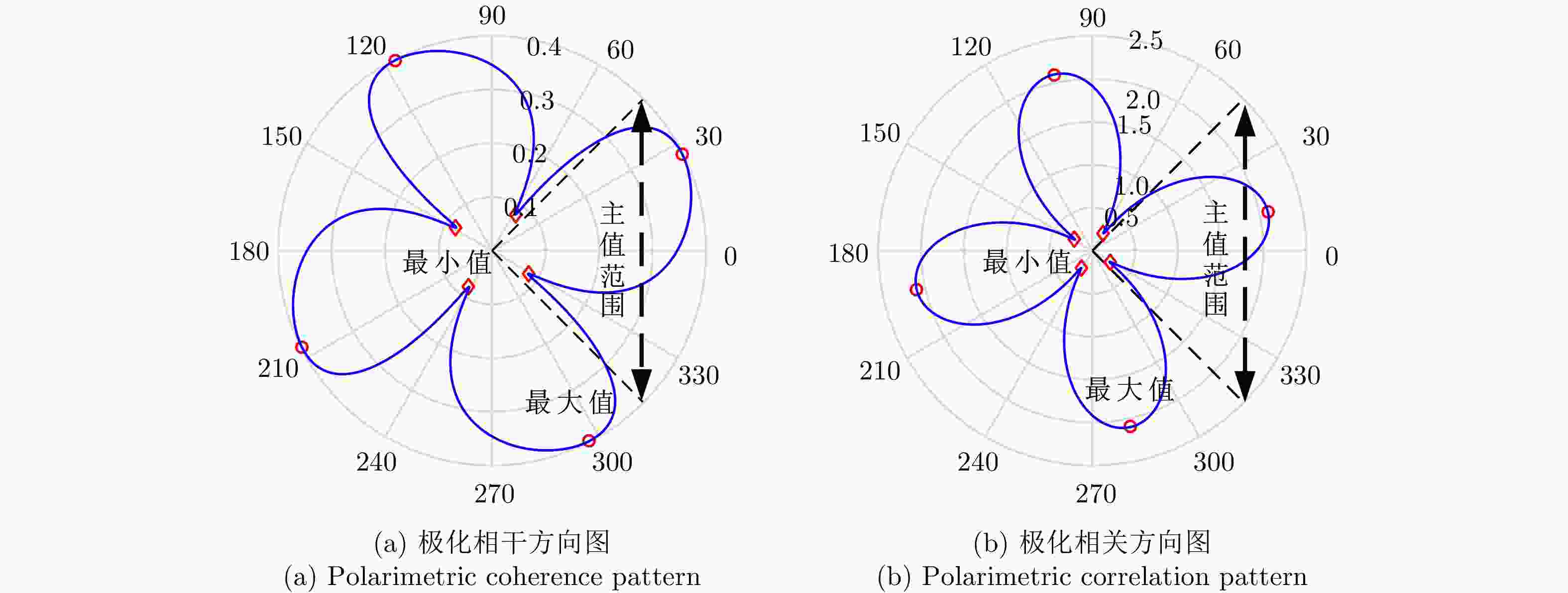
- 散射机理 /
- 目标检测、分类和识别 /
- 灾害评估
Abstract:Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), which can acquire fully polarimetric information, is widely used in civilian and military fields, such as earth observation, damage assessment, and reconnaissance. Major Chinese universities, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the industrial sector, and user units have conducted research in this field and obtained numerous remarkable achievements. This work reviews the recent progress of research in the field of polarimetric SAR imaging interpretation and recognition. For target scattering interpretation, theories of polarimetric target decomposition and polarimetric rotation domain interpretation are introduced. For polarimetric SAR application, the technologies of ship detection, land cover classification, and building damage assessment, which are based on the interpretation tools, are summarized in combination with the authors’ own research. Finally, the future development perspectives of polarimetric SAR interpretation and recognition are briefly discussed.
-
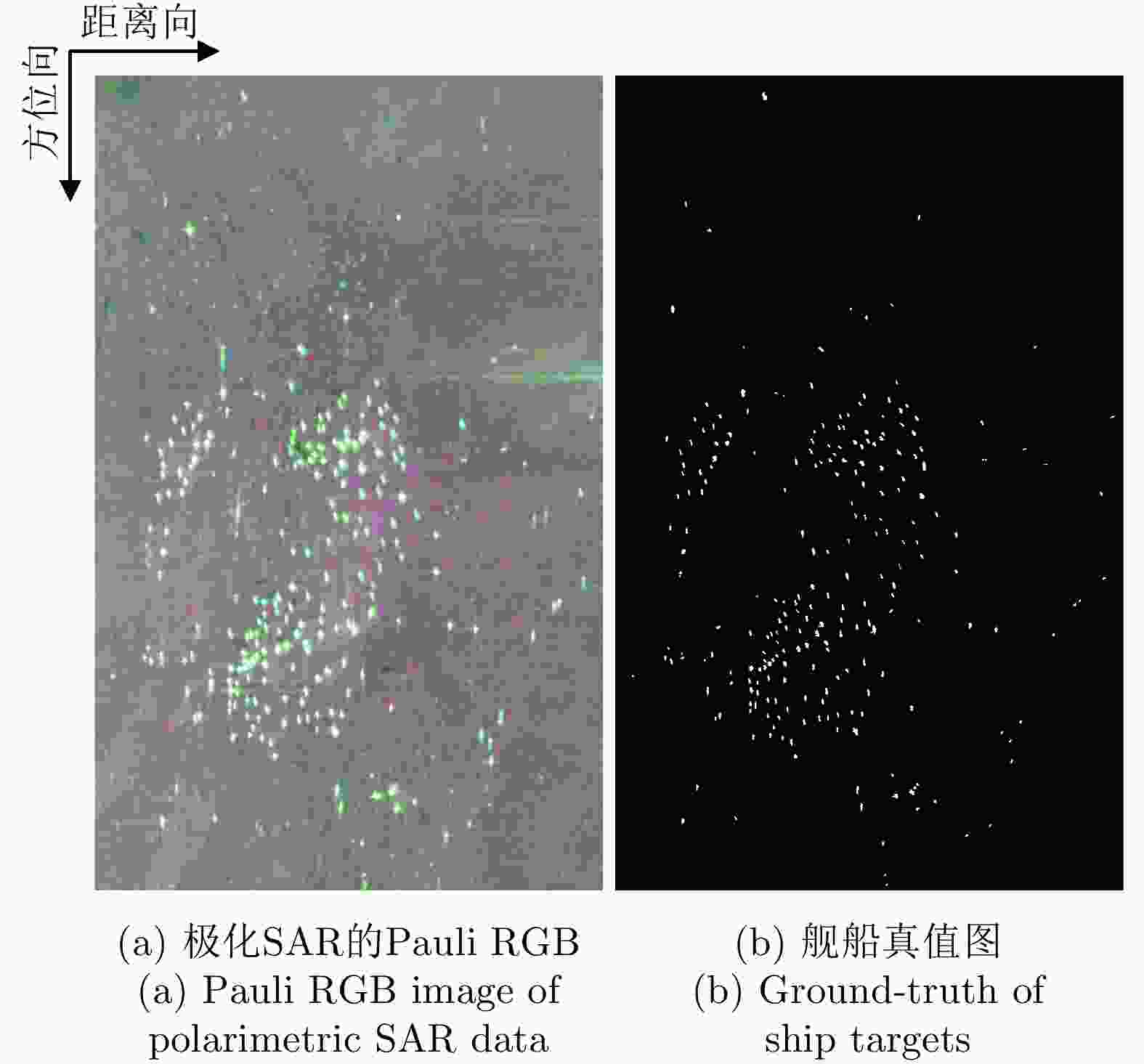
表 1 高分三号极化SAR舰船目标检测结果
Table 1. Ship detection results with GaoFen-3 data
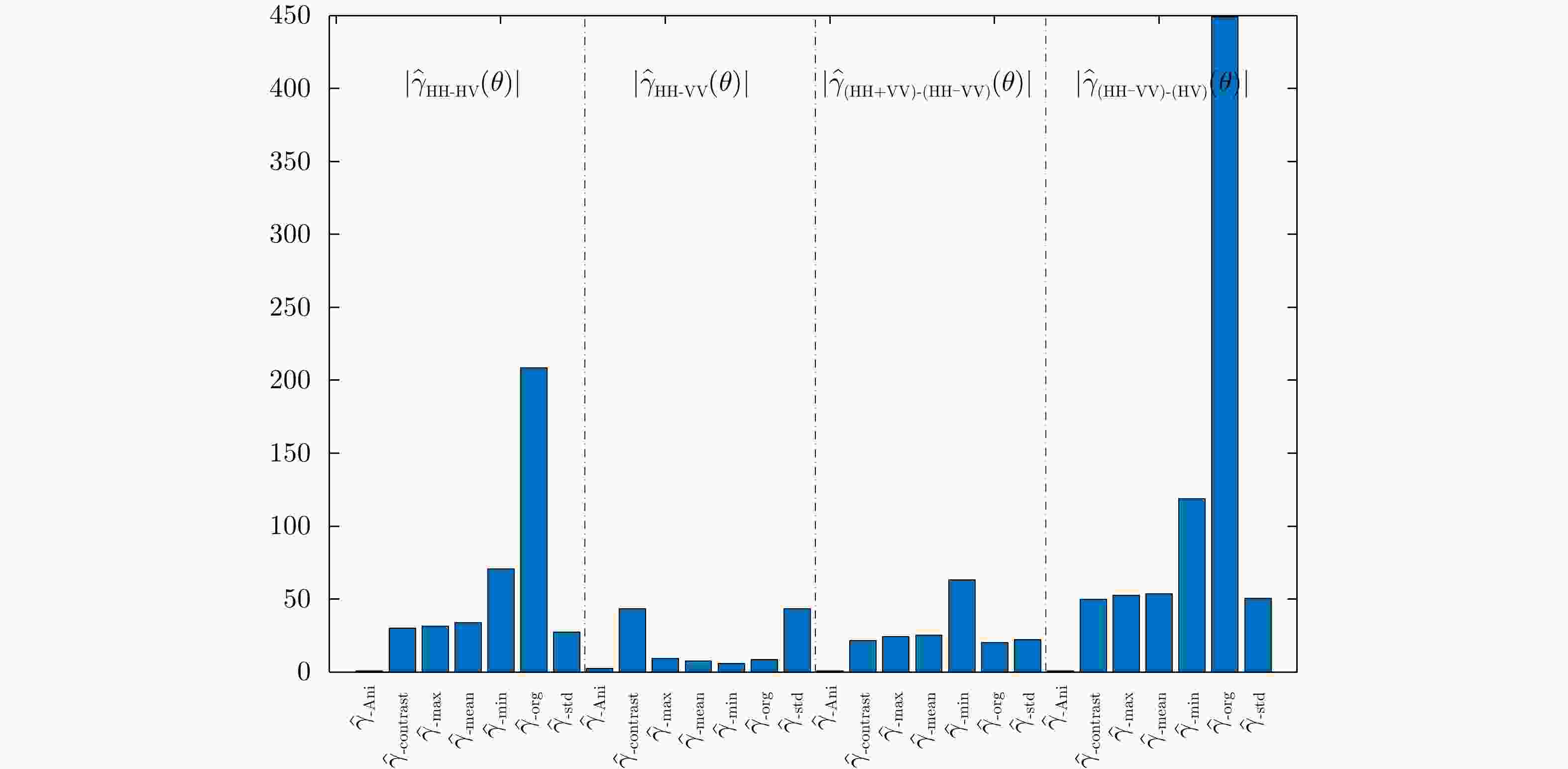
方法 ${N_{\rm{C}}}$ ${N_{\rm{M}}}$ ${N_{{\rm{FA}}}}$ FoM(%) SO-CFAR方法 181 61 0 74.79 Saliency方法 225 17 0 92.98 ${\left| { { {\hat \gamma }_{ {\rm{HH {\text{-}} HV} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|_{ {\rm{org} } } }$ 236 6 3 96.33 ${\left| { { {\hat \gamma }_{({\rm{HH - VV} }){\rm{ {\text{-} } (HV)} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|_{ {\rm{min} } } }$ 235 7 2 96.31 ${\left| { { {\hat \gamma }_{({\rm{HH - VV} }){\rm{ {\text{-} } (HV)} } } }\left( \theta \right)} \right|_{ {\rm{org} } } }$ 237 5 2 97.13 表 2 UAVSAR极化SAR地物分类的总体分类精度(%)
Table 2. The OAs of polarimetric SAR land cover classification results with UAVSAR data (%)
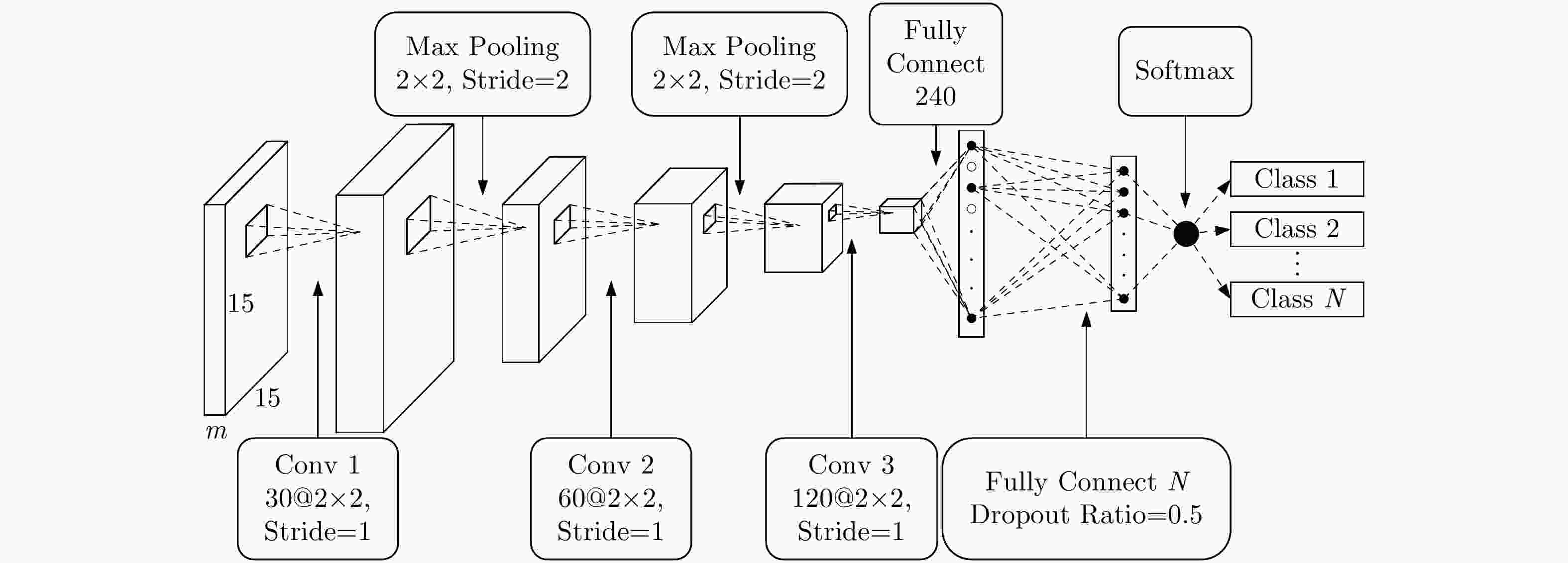
DoY Method Training ratio 10% 5% 1% 169 ${T_3}$+CNN 99.35 99.38 98.92 SF+CNN 99.54 99.43 98.86 174 ${T_3}$+CNN 93.18 93.70 92.37 SF+CNN 98.69 98.11 97.04 175 ${T_3}$+CNN 99.53 99.43 98.87 SF+CNN 99.42 99.23 98.34 -
[1] 王雪松. 雷达极化技术研究现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. doi: 10.12000/JR16039WANG Xuesong. Status and prospects of radar polarimetry techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(2): 119–131. doi: 10.12000/JR16039 [2] BOERNER W M. Recent advances in extra-wide-band polarimetry, interferometry and polarimetric interferometry in synthetic aperture remote sensing and its applications[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(3): 113–124. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030566 [3] 吴一戎. 多维度合成孔径雷达成像概念[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047WU Yirong. Concept of multidimensional space joint-observation SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(2): 135–142. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.13047 [4] TOUZI R, BOERNER W M, LEE J S, et al. A review of polarimetry in the context of synthetic aperture radar: Concepts and information extraction[J]. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 2004, 30(3): 380–407. doi: 10.5589/m04-013 [5] 郭华东, 王心源, 李新武, 等. 多模式SAR玉树地震协同分析[J]. 科学通报, 2010, 55(11): 3499–3503.GUO Huadong, WANG Xinyuan, LI Xinwu, et al. Yushu earthquake synergic analysis using multimodal SAR datasets[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(11): 3499–3503. [6] 郭华东. 对地观测技术与可持续发展[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001.GUO Huadong. Earth Observation Technology and Sustainable Development[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001. [7] 金亚秋, 徐丰. 极化散射与SAR遥感信息理论与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008.JIN Yaqiu and XU Feng. Theory and Approach for Polarimetric Scattering and Information Retrieval of SAR Remote Sensing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008. [8] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, XIAO Shunping, et al. Target Scattering Mechanism in Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar: Interpretation and Application[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2018. [9] CHEN Siwei. Polarimetric coherence pattern: A visualization and characterization tool for PolSAR data investigation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(1): 286–297. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2746662 [10] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, and SATO M. Uniform polarimetric matrix rotation theory and its applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4756–4770. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2013.2284359 [11] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, and XIAO Shunping. Urban damage level mapping based on co-polarization coherence pattern using multitemporal polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(8): 2657–2667. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2818939 [12] 陈思伟, 李永祯, 王雪松, 等. 极化SAR目标散射旋转域解译理论与应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 442–455. doi: 10.12000/JR17033CHEN Siwei, LI Yongzhen, WANG Xuesong, et al. Polarimetric SAR target scattering interpretation in rotation domain: Theory and application[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 442–455. doi: 10.12000/JR17033 [13] LIU Xu, JIAO Licheng, TANG Xu, et al. Polarimetric convolutional network for PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(5): 3040–3054. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2879984 [14] GUO Jiao, WEI Pengliang, LIU Jian, et al. Crop classification based on differential characteristics of H/α scattering parameters for multitemporal quad- and dual-polarization SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 6111–6123. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2832054 [15] 陶臣嵩, 陈思伟, 李永祯, 等. 结合旋转域极化特征的极化SAR地物分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 524–532. doi: 10.12000/JR16131TAO Chensong, CHEN Siwei, LI Yongzhen, et al. Polarimetric SAR terrain classification using polarimetric features derived from rotation domain[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 524–532. doi: 10.12000/JR16131 [16] REIGBER A, SCHEIBER R, JAGER M, et al. Very-high-resolution airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging: Signal processing and applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2013, 101(3): 759–783. doi: 10.1109/jproc.2012.2220511 [17] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, XIAO Shunping, et al. General polarimetric model-based decomposition for coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(3): 1843–1855. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2013.2255615 [18] CHEN Siwei, LI Yongzhen, WANG Xuesong, et al. Modeling and interpretation of scattering mechanisms in polarimetric synthetic aperture radar: Advances and perspectives[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2014, 31(4): 79–89. doi: 10.1109/msp.2014.2312099 [19] CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. A review of target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(2): 498–518. doi: 10.1109/36.485127 [20] CLOUDE S R. Polarisation: Applications in Remote Sensing[M]. London: Oxford University Press, 2009. [21] VAN ZYL J J and KIM Y. Synthetic Aperture Radar Polarimetry[M]. New York: Wiley, 2011. [22] YAMAGUCHI Y, SATO A, BOERNER W M, et al. Four-component scattering power decomposition with rotation of coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(6): 2251–2258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2099124 [23] KROGAGER E. New decomposition of the radar target scattering matrix[J]. Electronics Letters, 1990, 26(18): 1525–1527. doi: 10.1049/el:19900979 [24] CAMERON W L and LEUNG L K. Feature motivated polarization scattering matrix decomposition[C]. IEEE International Conference on Radar, Arlington, USA, 1990: 549-557. [25] CAMERON W L and RAIS H. Conservative polarimetric scatterers and their role in incorrect extensions of the cameron decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(12): 3506–3516. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.879115 [26] CAMERON W L and RAIS H. Derivation of a signed cameron decomposition asymmetry parameter and relationship of cameron to huynen decomposition parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(5): 1677–1688. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2090529 [27] CAMERON W L and RAIS H. Polarization scatterer feature metric space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(6): 3638–3647. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2221466 [28] CLOUDE S R and POTTIER E. An entropy based classification scheme for land applications of polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(1): 68–78. doi: 10.1109/36.551935 [29] LEE J S and POTTIER E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications[M]. Boca Raton, USA: CRC Press, 2009. [30] LOPEZ-MARTINEZ C, POTTIER E and CLOUDE S R. Statistical assessment of eigenvector-based target decomposition theorems in radar polarimetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(9): 2058–2074. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.853934 [31] LEE J S, AINSWORTH T L, KELLY J P, et al. Evaluation and bias removal of multilook effect on entropy/alpha/anisotropy in polarimetric SAR decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(10): 3039–3052. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.922033 [32] ALVAREZ-PEREZ J L. Coherence, polarization, and statistical independence in cloude-pottier’s radar polarimetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 426–441. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2056375 [33] TOUZI R. Target scattering decomposition in terms of roll-invariant target parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(1): 73–84. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2006.886176 [34] PALADINI R, MARTORELLA M, and BERIZZI F. Classification of man-made targets via invariant coherency-matrix eigenvector decomposition of polarimetric SAR/ISAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(8): 3022–3034. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2116121 [35] 张腊梅, 段宝龙, 邹斌. 极化SAR图像目标分解方法的研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3289–3297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160992ZHANG Lamei, DUAN Baolong, and ZOU Bin. Research progress of target decomposition methods for polarimetric SAR images[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3289–3297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160992 [36] FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973. doi: 10.1109/36.673687 [37] YAMAGUCHI Y, MORIYAMA T, ISHIDO M, et al. Four-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR image decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(8): 1699–1706. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.852084 [38] GULAB S and YAMAGUCHI Y. Model-based six-component scattering matrix power decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 5687–5704. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2824322 [39] GULAB S, MALIK R, MOHANTY S, et al. Seven-component scattering power decomposition of POLSAR coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8371–8382. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2920762 [40] VAN ZYL J J, ARII M, and KIM Y. Model-based decomposition of polarimetric SAR covariance matrices constrained for nonnegative eigenvalues[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(9): 3452–3459. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2128325 [41] KUSANO S, TAKAHASHI K, and SATO M. Volume scattering power constraint based on the principal minors of the coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(1): 361–365. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2258654 [42] LIM Y X, BURGIN M S, and VAN ZYL J J. An optimal nonnegative eigenvalue decomposition for the freeman and durden three-component scattering model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(4): 2167–2176. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2637882 [43] CHEN Siwei, OHKI M, SHIMADA M, et al. Deorientation effect investigation for model-based decomposition over oriented built-up areas[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(2): 273–277. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2012.2203577 [44] AN Wentao, CUI Yi, and YANG Jian. Three-component model-based decomposition for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(6): 2732–2739. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2041242 [45] LEE J S and AINSWORTH T L. The effect of orientation angle compensation on coherency matrix and polarimetric target decompositions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 53–64. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048333 [46] NEUMANN M, FERRO-FAMIL L, and REIGBER A. Estimation of forest structure, ground, and canopy layer characteristics from multibaseline polarimetric interferometric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(3): 1086–1104. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2009.2031101 [47] ARII M, VAN ZYL J J, and KIM Y. A general characterization for polarimetric scattering from vegetation canopies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(9): 3349–3357. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2046331 [48] LEE J S, AINSWORTH T L, and WANG Yanting. Generalized polarimetric model-based decompositions using incoherent scattering models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2474–2491. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2262051 [49] HAJNSEK I, JAGDHUBER T, SCHON H, et al. Potential of estimating soil moisture under vegetation cover by means of PolSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(2): 442–454. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2009642 [50] ARII M, VAN ZYL J J, and KIM Y. Adaptive model-based decomposition of polarimetric SAR covariance matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(3): 1104–1113. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2076285 [51] WU Guoqing, CHEN Siwei, and WANG Xuesong. A four-component polarimetric decomposition method based on generalized scattering models[C]. 2019 PhotonIcs & Electromagnetics Research Symposium, Rome, Italy, 2019. [52] SINGH G, YAMAGUCHI Y, and PARK S E. General four-component scattering power decomposition with unitary transformation of coherency matrix[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5): 3014–3022. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2212446 [53] MAURYA H and PANIGRAHI R K. PolSAR coherency matrix optimization through selective unitary rotations for model-based decomposition scheme[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(4): 658–662. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2878654 [54] BHATTACHARYA A, SINGH G, MANICKAM S, et al. An adaptive general four-component scattering power decomposition with unitary transformation of coherency matrix (AG4U)[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(10): 2110–2114. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2451369 [55] CUI Yi, YAMAGUCHI Y, YANG Jian, et al. On complete model-based decomposition of polarimetric SAR coherency matrix data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(4): 1991–2001. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2013.2257603 [56] ZOU Bin, LU Da, ZHANG Lamei, et al. Eigen-decomposition-based four-component decomposition for PolSAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1286–1296. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2513161 [57] AN Wentao and LIN Mingsen. A reflection symmetry approximation of multilook polarimetric SAR data and its application to freeman-durden decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(6): 3649–3660. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2886386 [58] LI Hongzhong, LI Qingquan, WU Guofeng, et al. Adaptive two-component model-based decomposition for polarimetric SAR data without assumption of reflection symmetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 197–211. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2604283 [59] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, LI Yongzhen, et al. Adaptive model-based polarimetric decomposition using PolInSAR coherence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(3): 1705–1718. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2013.2253780 [60] XU Feng, LI Yongchen, and JIN Yaqiu. Polarimetric-anisotropic decomposition and anisotropic entropies of high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(9): 5467–5482. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2565693 [61] XIAO Shunping, CHEN Siwei, CHANG Yuliang, et al. Polarimetric coherence optimization and its application for manmade target extraction in PolSAR data[J]. IEICE Transactions on Electronics, 2014, E97.C(6): 566–574. doi: 10.1587/transele.E97.C.566 [62] CHEN Siwei, LI Yongzhen, and WANG Xuesong. Crop discrimination based on polarimetric correlation coefficients optimization for PolSAR data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(16): 4233–4249. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2015.1079345 [63] TAO Chensong, CHEN Siwei, LI Yongzhen, et al. PolSAR land cover classification based on roll-invariant and selected hidden polarimetric features in the rotation domain[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(7): 660. doi: 10.3390/rs9070660 [64] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, and SATO M. Urban damage level mapping based on scattering mechanism investigation using fully polarimetric SAR data for the 3.11 East Japan earthquake[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(12): 6919–6929. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2588325 [65] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, and SATO M. PolInSAR complex coherence estimation based on covariance matrix similarity test[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(11): 4699–4710. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2192937 [66] CHEN Siwei and TAO Chensong. PolSAR image classification using polarimetric-feature-driven deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(4): 627–631. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2799877 [67] CUI Xingchao, TAO Chensong, SU Yi, et al. PolSAR ship detection based on polarimteric correlation pattern[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters. in press. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2976477. [68] TRUNK G V. Range resolution of targets using automatic detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1978, AES-14(5): 750–755. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1978.308625 [69] ZHAI Liang, LI Yu, and SU Yi. Inshore ship detection via saliency and context information in high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1870–1874. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2616187 [70] CHEN Siwei and SATO M. Tsunami damage investigation of built-up areas using multitemporal spaceborne full polarimetric SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(4): 1985–1997. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2012.2210050 [71] MISHRA P, GARG A, and SINGH D. Critical analysis of model-based incoherent polarimetric decomposition methods and investigation of deorientation effect[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(9): 4868–4877. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2652060 [72] XIE Qinghua, BALLESTER-BERMAN J D, LOPEZ-SANCHEZ J M, et al. Quantitative analysis of polarimetric model-based decomposition methods[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(12): 977. doi: 10.3390/rs8120977 [73] 杨建宇. 雷达对地成像技术多向演化趋势与规律分析[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 669–693. doi: 10.12000/JR19099YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–693. doi: 10.12000/JR19099 [74] 洪文. 圆迹SAR成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(2): 124–135. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20046HONG Wen. Progress in circular SAR imaging technique[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(2): 124–135. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20046 [75] 王杰, 丁赤飚, 梁兴东, 等. 机载同时同频MIMO-SAR系统研究概述[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(2): 220–234. doi: 10.12000/JR17046WANG Jie, DING Chibiao, LIANG Xingdong, et al. Research outline of airborne MIMO-SAR system with same time-frequency coverage[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(2): 220–234. doi: 10.12000/JR17046 [76] 洪文, 王彦平, 林赟, 等. 新体制SAR三维成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109HONG Wen, WANG Yanping, LIN Yun, et al. Research progress on three-dimensional SAR imaging techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109 [77] 洪文. 基于混合极化架构的极化SAR: 原理与应用(中英文)[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 559–595. doi: 10.12000/JR16074HONG Wen. Hybrid-polarity architecture based polarimetric SAR: Principles and applications (in Chinese and in English)[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 559–595. doi: 10.12000/JR16074 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: