Stochastic Contrast Measures for SAR Data: A Survey
DOI: 10.12000/JR19108 cstr: 32380.14.JR19108
-
Abstract:
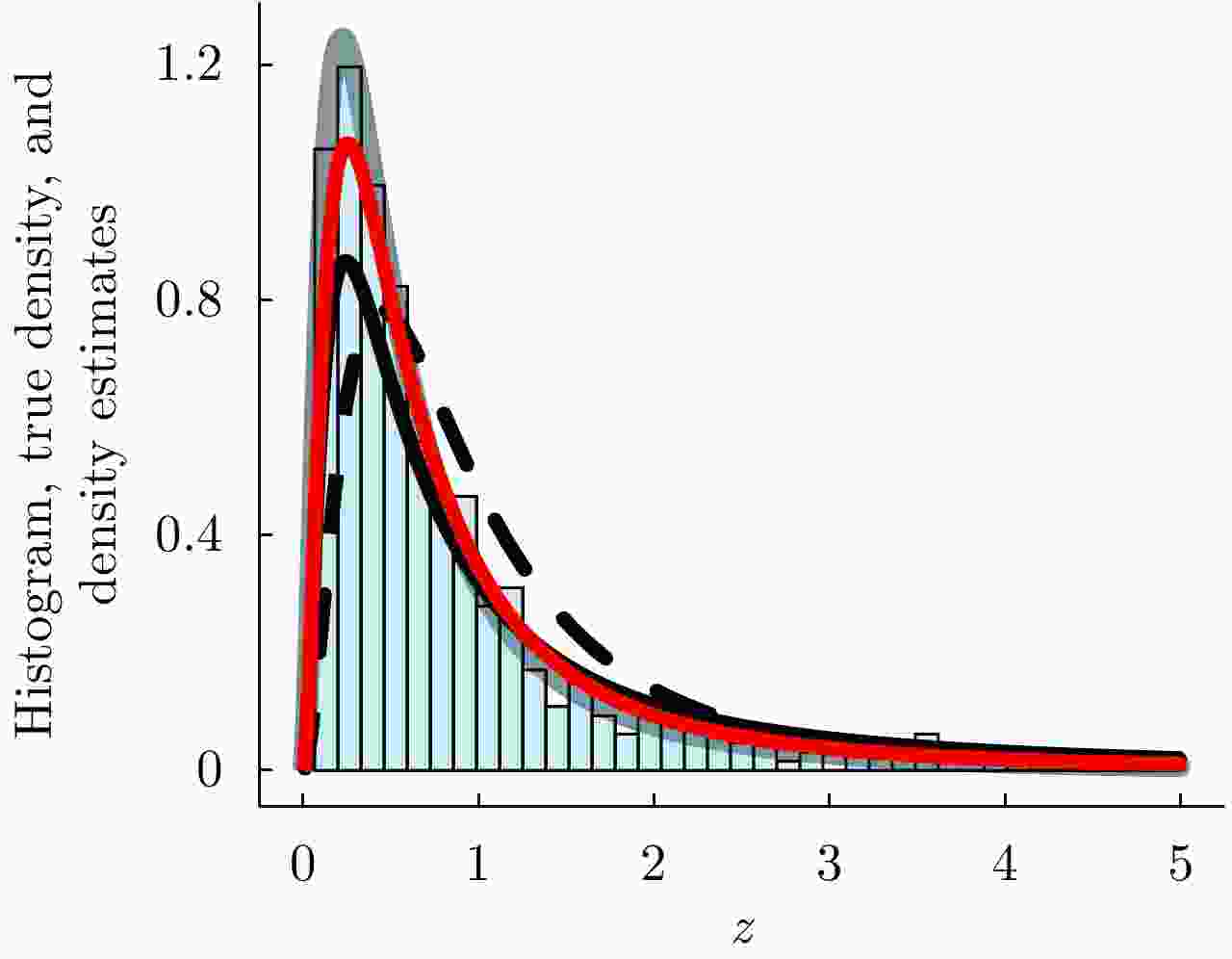
“Contrast” is an generic denomination for “difference”. Measures of contrast are a powerful tool in image processing and analysis, e.g., in denoising, edge detection, segmentation, classification, parameter estimation, change detection, and feature selection. We present a survey on techniques that aim at measuring the contrast between (i) samples of SAR imagery, and (ii) samples and models, with emphasis on those that employ the statistical properties of the data.
-
Key words:
- Contrast /
- Divergence /
- Entropy /
- Geodesic distance /
- Statistics /
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)
-
Table 1. (
$h,\phi$ )-divergences and related functions$\phi$ and$h$ $(h,\phi)$-divergence $h(y)$ $\phi(x)$ Kullback-Leibler $y$ $x\ln(x)$ Rényi (order $\beta$) $\dfrac{1}{\beta-1}\ln\left((\beta-1)y+1\right),\;0\leq y < \dfrac{1}{1-\beta}$ $\dfrac{x^{\beta}-\beta(x-1)-1}{\beta-1},0 < \beta<1$ Hellinger ${y}/{2},0\leq y<2$ $(\sqrt{x}-1)^2$ Bhattacharyya $-\ln(1-y),0\leq y < 1$ $-\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{x+1}{2}$ Jensen-Shannon $y$ $x\ln\left(\dfrac{2x}{x+1}\right)$ Arithmetic-geometric $y$ $\left(\dfrac{x+1}{2}\right)\ln \dfrac{x+1}{2x}$ Triangular $y,\;0\leq y <2$ $\dfrac{(x-1)^2}{x+1}$ Harmonic-mean $-\ln\left(-\dfrac{y}{2}+1\right),\;0\leq y < 2$ $\dfrac{(x-1)^2}{x+1}$ Table 2.
$h$ -$\phi$ entropies and related functions$(h,\phi)$-entropy $h(y)$ $\phi(x)$ Shannon[35] $y$ $-x\ln x$ Restricted Tsallis (order $\beta \in \mathbb{R}_{+}\,:\,\beta\neq 1$)[39] $y$ $\dfrac{x^\beta-x}{1-\beta} $ Rényi (order $\beta \in \mathbb{R}_+\,:\,\beta\neq 1$)[29] $\dfrac{\ln y}{1-\beta}$ $x^\beta$ Arimoto of order $\beta$ $\dfrac{\beta-1}{y^\beta-1}$ $x^{1/\beta}$ Sharma-Mittal of order $\beta$ $ \dfrac{\exp\{(\beta-1)y\} }{\beta-1}$ $ x\ln x$ -
[1] LEE J S and POTTIER E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications[M]. Boca Raton: CRC, 2009. [2] TUR M, CHIN K C, and GOODMAN J W. When is speckle noise multiplicative?[J]. Applied Optics, 1982, 21(7): 1157–1159. doi: 10.1364/AO.21.001157 [3] ARGENTI F, LAPINI A, BIANCHI T, et al. A tutorial on speckle reduction in synthetic aperture radar images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(3): 6–35. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2277512 [4] GOMEZ L, OSPINA R, and FRERY A C. Unassisted quantitative evaluation of despeckling filters[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(4): 389. doi: 10.3390/rs9040389 [5] HARALICK R M. Statistical and structural approaches to texture[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1979, 67(5): 786–804. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1979.11328 [6] VITALE S, COZZOLINO D, SCARPA G, et al. Guided patchwise nonlocal SAR despeckling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6484–6498. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2906412 [7] GOMEZ L, OSPINA R, and FRERY A C. Statistical properties of an unassisted image quality index for SAR imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(4): 385. doi: 10.3390/rs11040385 [8] FRERY A and WU J C. Operational statistics for SAR imagery[EB/OL]. https://github.com/acfrery/Statistics-SAR-Intensity.git, 2019. [9] MANSKI C F. Analog Estimation Methods in Econometrics[M]. New York: Chapman & Hall, 1988. [10] MEJAIL M E, JACOBO-BERLLES J C, FRERY A C, et al. Classification of SAR images using a general and tractable multiplicative model[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2003, 24(18): 3565–3582. doi: 10.1080/0143116021000053274 [11] CINTRA R J, FRERY A C, and NASCIMENTO A D C. Parametric and nonparametric tests for speckled imagery[J]. Pattern Analysis and Applications, 2013, 16(2): 141–161. doi: 10.1007/s10044-011-0249-3 [12] TSYBAKOV A B. Introduction to Nonparametric Estimation[M]. New York: Springer, 2009. [13] WASSERMAN L. All of Nonparametric Statistics[M]. New York: Springer, 2006. [14] GIBBONS J D and CHAKRABORTI S. Nonparametric Statistical Inference[M]. 4th ed. New York: Marcel Dekker, 2003. [15] PALACIO M G, FERRERO S B, and FRERY A C. Revisiting the effect of spatial resolution on information content based on classification results[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 40(12): 4489–4505. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2019.1569278 [16] NEGRI R G, FRERY A C, SILVA W B, et al. Region-based classification of PolSAR data using radial basis kernel functions with stochastic distances[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2019, 12(6): 699–719. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2018.1474958 [17] FRERY A C, SANT’ANNA S J S, MASCARENHAS N D A, et al. Robust inference techniques for speckle noise reduction in 1-look amplitude SAR images[J]. Applied Signal Processing, 1997, 4(2): 61–76. [18] CHAN D, REY A, GAMBINI J, et al. Low-cost robust estimation for the single-look GI0 model using the Pareto distribution[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2956635 [19] BUSTOS O H, LUCINI M M, and FRERY A C. M-estimators of roughness and scale for ${\cal{G}}_A^0 $ -modelled SAR imagery[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2002, 2002(1): 105–114.[20] MOSCHETTI E, PALACIO M G, PICCO M, et al. On the use of Lee’s protocol for speckle-reducing techniques[J]. Latin American Applied Research, 2006, 36(2): 115–121. [21] ALLENDE H, FRERY A C, GALBIATI J, et al. M-estimators with asymmetric influence functions: The ${\cal{G}}_A^0$ distribution case[J]. Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 2006, 76(11): 941–956. doi: 10.1080/10629360600569154[22] CASELLA G and BERGER R L. Statistical Inference[M]. 2nd ed. Pacific Grove: Duxbury, 2002. [23] NASCIMENTO A D C, CINTRA R J, and FRERY A C. Hypothesis testing in speckled data with stochastic distances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(1): 373–385. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2025498 [24] GOUDAIL F and RÉFRÉGIER P. Contrast definition for optical coherent polarimetric images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2004, 26(7): 947–951. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.22 [25] ALI S M and SILVEY S D. A general class of coefficients of divergence of one distribution from another[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological) , 1996, 28(1): 131–142. [26] CSISZÁR I. Information-type measures of difference of probability distributions and indirect observations[J]. Studia Scientiarum Mathematicarum Hungarica, 1967, 2: 299–318. [27] SALICRÚ M, MORALES D, MENÉNDEZ M L, et al. On the applications of divergence type measures in testing statistical hypotheses[J]. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 1994, 51(2): 372–391. doi: 10.1006/jmva.1994.1068 [28] COVER T M and THOMAS J A. Elements of Information Theory[M]. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Son, 1991. [29] RÉNYI A. On measures of entropy and information[C]. The 4th Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Berkeley, USA, 1961: 547–561. [30] FUKUNAGA K. Introduction to Statistical Pattern Recognition[M]. 2nd ed. San Diego: Academic, 1990. [31] DIACONIS P and ZABEL S L. Updating subjective probability[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1982, 77(380): 822–830. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1982.10477893 [32] BURBEA J and RAO C. On the convexity of some divergence measures based on entropy functions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1982, 28(3): 489–495. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1982.1056497 [33] BURBEA J and RAO C R. Entropy differential metric, distance and divergence measures in probability spaces: A unified approach[J]. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 1982, 12(4): 575–596. doi: 10.1016/0047-259X(82)90065-3 [34] SEGHOUANE A K and AMARI S I. The AIC criterion and symmetrizing the Kullback-Leibler divergence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2007, 18(1): 97–106. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2006.882813 [35] SALICRÚ M, MENÉNDEZ M L, MORALES D, et al. Asymptotic distribution of (h, ϕ)-entropy[J]. Communications in Statistics-Theory and Methods, 1993, 22(7): 2015–2031. doi: 10.1080/03610929308831131 [36] PARDO L, MORALES D, SALICRÚ M, et al. Generalized divergence measures: Information matrices, amount of information, asymptotic distribution, and its applications to test statistical hypotheses[J]. Information Sciences, 1995, 84(3/4): 181–198. [37] PARDO L, MORALES D, SALICRÚ M, et al. Large sample behavior of entropy measures when parameters are estimated[J]. Communications in Statistics – Theory and Methods, 1997, 26(2): 483–501. doi: 10.1080/03610929708831929 [38] FRERY A C, CINTRA R J, and NASCIMENTO A D C. Entropy-based statistical analysis of PolSAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(6): 3733–3743. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2222029 [39] HAVRDA J and CHARVÁT F. Quantification method of classification processes: Concept of structural α-entropy[J]. Kybernetika, 1967, 3: 30–35. [40] ATKINSON C and MITCHELL A F S. Rao’s distance measure[J]. Sankhyā: The Indian Journal of Statistics, Series A, 1981, 43(3): 345–365. [41] MENÉNDEZ M L, MORALES D, PARDO L, et al. Statistical tests based on geodesic distances[J]. Applied Mathematics Letters, 1995, 8(1): 65–69. doi: 10.1016/0893-9659(94)00112-P [42] NARANJO-TORRES J, GAMBINI J, and FRERY A C. The geodesic distance between ${\cal{G}}_I^0$ models and its application to region discrimination[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(3): 987–997. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2647846[43] FRERY A C and GAMBINI J. Comparing samples from the ${\cal{G}}^0$ distribution using a geodesic distance[J]. TEST, 2019. doi: 10.1007/s11749-019-00658-2[44] GAO Gui. Statistical modeling of SAR images: A survey[J]. Sensors, 2010, 10(1): 775–795. doi: 10.3390/s100100775 [45] FRERY A C, MÜLLER H J, YANASSE C C F, et al. A model for extremely heterogeneous clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(3): 648–659. doi: 10.1109/36.581981 [46] CHAN D, REY A, GAMBINI J, et al. Sampling from the ${\cal{G}}_I^0$ distribution[J]. Monte Carlo Methods and Applications, 2018, 24(4): 271–287. doi: 10.1515/mcma-2018-2023[47] HORN R. The DLR airborne SAR PROJECT E-SAR[C]. 1996 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Lincoln, USA, 1996: 1624–1628. [48] GAMBINI J, MEJAIL M E, JACOBO-BERLLES J, et al. Feature extraction in speckled imagery using dynamic B-spline deformable contours under the ${\cal{G}}^0$ model[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2006, 27(22): 5037–5059. doi: 10.1080/01431160600702616[49] GAMBINI J, MEJAIL M E, JACOBO-BERLLES J, et al. Accuracy of edge detection methods with local information in speckled imagery[J]. Statistics and Computing, 2008, 18(1): 15–26. doi: 10.1007/s11222-007-9034-y [50] FRERY A C, JACOBO-BERLLES J, GAMBINI J, et al. Polarimetric SAR image segmentation with B-Splines and a new statistical model[J]. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 2010, 21(4): 319–342. doi: 10.1007/s11045-010-0113-4 [51] GAMBINI J, CASSETTI J, LUCINI M M, et al. Parameter estimation in SAR imagery using stochastic distances and asymmetric kernels[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(1): 365–375. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2346017 [52] BUADES A, COLL B, and MOREL J M. A review of image denoising algorithms, with a new one[J]. Multiscale Modeling & Simulation, 2005, 4(2): 490–530. [53] BUADES A, COLL B, and MOREL J M. Image denoising methods: A new nonlocal principle[J]. SIAM Review, 2010, 52(1): 113–147. doi: 10.1137/090773908 [54] TEUBER T and LANG A. A new similarity measure for nonlocal filtering in the presence of multiplicative noise[J]. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2012, 56(12): 3821–3842. doi: 10.1016/j.csda.2012.05.009 [55] PENNA P A A and MASCARENHAS N D A. SAR speckle nonlocal filtering with statistical modeling of Haar wavelet coefficients and stochastic distances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 7194–7208. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2912153 [56] FERRAIOLI G, PASCAZIO V, and SCHIRINZI G. Ratio-based nonlocal anisotropic despeckling approach for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(10): 7785–7798. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2916465 [57] LEE J S, HOPPEL K W, MANGO S A, et al. Intensity and phase statistics of multilook polarimetric and interferometric SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(5): 1017–1028. doi: 10.1109/36.312890 [58] HAGEDORN M, SMITH P J, BONES P J, et al. A trivariate chi-squared distribution derived from the complex Wishart distribution[J]. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 2006, 97(3): 655–674. doi: 10.1016/j.jmva.2005.05.014 [59] DENG Xinping, LÓPEZ-MARTÍNEZ C, CHEN Jinsong, et al. Statistical modeling of polarimetric SAR data: A survey and challenges[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(4): 348. doi: 10.3390/rs9040348 [60] Core Team R. R: A language and environment for statistical computing, R foundation for statistical computing, Vienna, Austria[EB/OL]. https://www.R-project.org/, 2019. [61] ANFINSEN S N, DOULGERIS A P, and ELTOFT T Ø. Estimation of the equivalent number of looks in polarimetric synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(11): 3795–3809. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2019269 [62] FRERY A C, NASCIMENTO A D C, and CINTRA R J. Analytic expressions for stochastic distances between relaxed complex Wishart distributions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(2): 1213–1226. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2248737 [63] MENÉNDEZ M L, MORALES D, PARDO L, et al. (h, $\varPhi $ )-entropy differential metric[J]. Applications of Mathematics, 1997, 42(2): 81–98. doi: 10.1023/A:1022214326758[64] NASCIMENTO A D C, FRERY A C, and CINTRA R J. Detecting changes in fully polarimetric SAR imagery with statistical information theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(3): 1380–1392. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2866367 [65] COELHO D F G, CINTRA R J, FRERY A C, et al. Fast matrix inversion and determinant computation for polarimetric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2018, 119: 109–114. [66] TORRES L, SANT’ANNA S J S, DA COSTA FREITAS C, et al. Speckle reduction in polarimetric SAR imagery with stochastic distances and nonlocal means[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2014, 47(1): 141–157. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2013.04.001 [67] DELEDALLE C A, DENIS L Ï, and TUPIN F. Iterative weighted maximum likelihood denoising with probabilistic patch-based weights[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2009, 18(12): 2661–2672. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2009.2029593 [68] CHEN Jiong, CHEN Yilun, AN Wentao, et al. Nonlocal filtering for polarimetric SAR data: A pretest approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(5): 1744–1754. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2087763 [69] ZHONG Hua, LI Yongwei, and JIAO Licheng. SAR image despeckling using Bayesian nonlocal means filter with sigma preselection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(4): 809–813. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2112331 [70] DELEDALLE C A, DUVAL V, and SALMON J. Non-local methods with shape-adaptive patches (NLM-SAP)[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2012, 43(2): 103–120. doi: 10.1007/s10851-011-0294-y [71] SILVA W B, FREITAS C C, SANT’ANNA S J S, et al. Classification of segments in PolSAR imagery by minimum stochastic distances between Wishart distributions[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2013, 6(3): 1263–1273. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2248132 [72] GOMEZ L, ALVAREZ L, MAZORRA L, et al. Classification of complex Wishart matrices with a diffusion-reaction system guided by stochastic distances[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2015, 373(2056): 20150118. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2015.0118 [73] GOMEZ L, ALVAREZ L, MAZORRA L, et al. Fully PolSAR image classification using machine learning techniques and reaction-diffusion systems[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 255: 52–60. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.08.140 [74] NASCIMENTO A D C, HORTA M M, FRERY A C, et al. Comparing edge detection methods based on stochastic entropies and distances for PolSAR imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(2): 648–663. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2266319 [75] De BORBA A A, MARENGONI M, and FRERY A C. Fusion of evidences for edge detection in PolSAR images[C]. 2019 TENGARSS, Kochi, India, 2019, in press. [76] BHATTACHARYA A, MUHURI A, DE S, et al. Modifying the Yamaguchi four-component decomposition scattering powers using a stochastic distance[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(7): 3497–3506. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2420683 [77] CONRADSEN K, NIELSEN A A, SCHOU J, et al. A test statistic in the complex Wishart distribution and its application to change detection in polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(1): 4–19. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.808066 [78] NIELSEN A A, CONRADSEN K, and SKRIVER H. Change detection in full and dual polarization, single-and multifrequency SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(8): 4041–4048. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2416434 [79] RATHA D, BHATTACHARYA A, and FRERY A C. Unsupervised classification of PolSAR data using a scattering similarity measure derived from a geodesic distance[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(1): 151–155. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2778749 [80] RATHA D, GAMBA P, BHATTACHARYA A, et al. Novel techniques for built-up area extraction from polarimetric SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2914913 [81] RATHA D, MANDAL D, KUMAR V, et al. A generalized volume scattering model-based vegetation index from polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(11): 1791–1795. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2907703 [82] RATHA D, POTTIER E, BHATTACHARYA A, et al. A PolSAR scattering power factorization framework and novel roll-invariant parameters based unsupervised classification scheme using a geodesic distance[J]. arXiv:1906.11577, 2019. [83] FERNANDES D and FRERY A C. Statistical properties of geodesic distances between samples and elementary scatterers in PolSAR imagery[C]. 2019 TENGARSS, Kochi, India, 2019, in press. [84] YUE D X, XU F, FRERY A C, and JIN Q. A generalized Gaussian coherent scatterer model for correlated SAR texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, in press. -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: