Synthetic Aperture Radar Learning-imaging Method Based onData-driven Technique and Artificial Intelligence
-
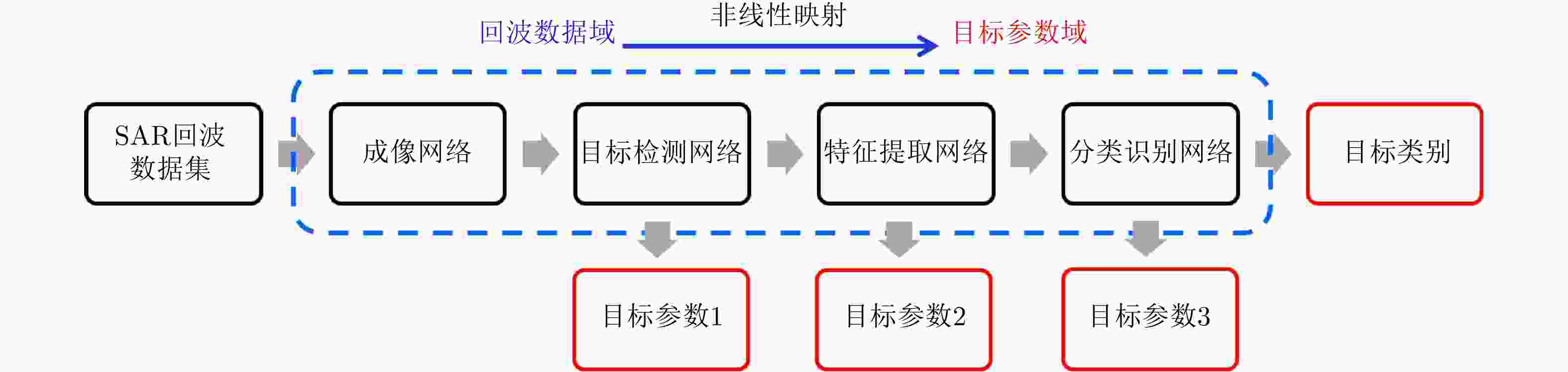
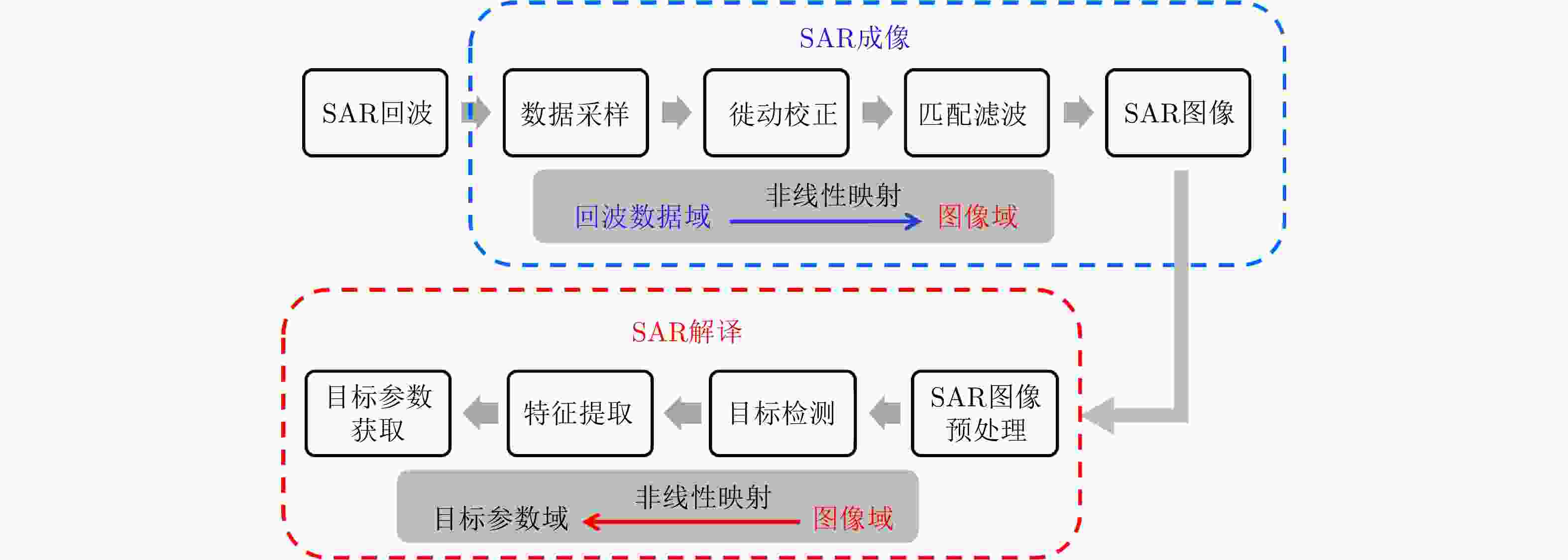
摘要: 对感兴趣目标的数量、位置、型号等参数信息的精确获取一直是合成孔径雷达(SAR)技术中最为重要的研究内容之一。现阶段的SAR信息处理主要分为成像和解译两大部分,两者的研究相对独立。SAR成像和解译各自开发了大量算法,复杂度越来越高,但SAR解译并未因成像分辨率提升而变得简单,特别是对重点目标识别率低的问题并未从本质上得以解决。针对上述问题,该文从SAR成像解译一体化角度出发,尝试利用“数据驱动+智能学习”的方法提升机载SAR的信息处理能力。首先分析了基于“数据驱动+智能学习”方法的SAR成像解译一体化的可行性及现阶段存在的主要问题;在此基础上,提出一种“数据驱动+智能学习”的SAR学习成像方法,给出了学习成像框架、网络参数选取方法、网络训练方法和初步的仿真结果,并分析了需要解决的关键性技术问题。
-
关键词:
- 合成孔径雷达(SAR) /
- SAR成像解译一体化 /
- SAR学习成像 /
- 数据驱动 /
- 深度学习
Abstract: One of the most important research fields in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) technology is to improve the accuracies of the number, location, classification, and other parameters of targets of interest. SAR information processing can be mainly divided into two tasks: imaging and interpretation. At present, research efforts on these two tasks are relatively independent. Many algorithms have been developed for SAR imaging and interpretation, and they have become increasingly complex. However, SAR interpretation has not been made simpler by improvements in the imaging resolution. The low recognition rate of key targets, in particular, has yet to be adequately resolved. In this paper, we use a “data driven + intelligence learning” method to improve the information processing ability of airborne SAR based on SAR imaging & interpretation integration. First, we analyze the feasibility and main problems of SAR imaging & interpretation integration using a “data driven + intelligence learning” method. Based on the results, we propose a SAR learning-imaging method based on “data driven + intelligence learning” with the goal of producing an imaging network. The proposed learning-imaging framework, parameter selection method, network training method, and preliminary simulation results are presented, and the key technical problems to be solved are identified and analyzed. -
表 1 雷达参数和网络参数
Table 1. Parameters of radar and network
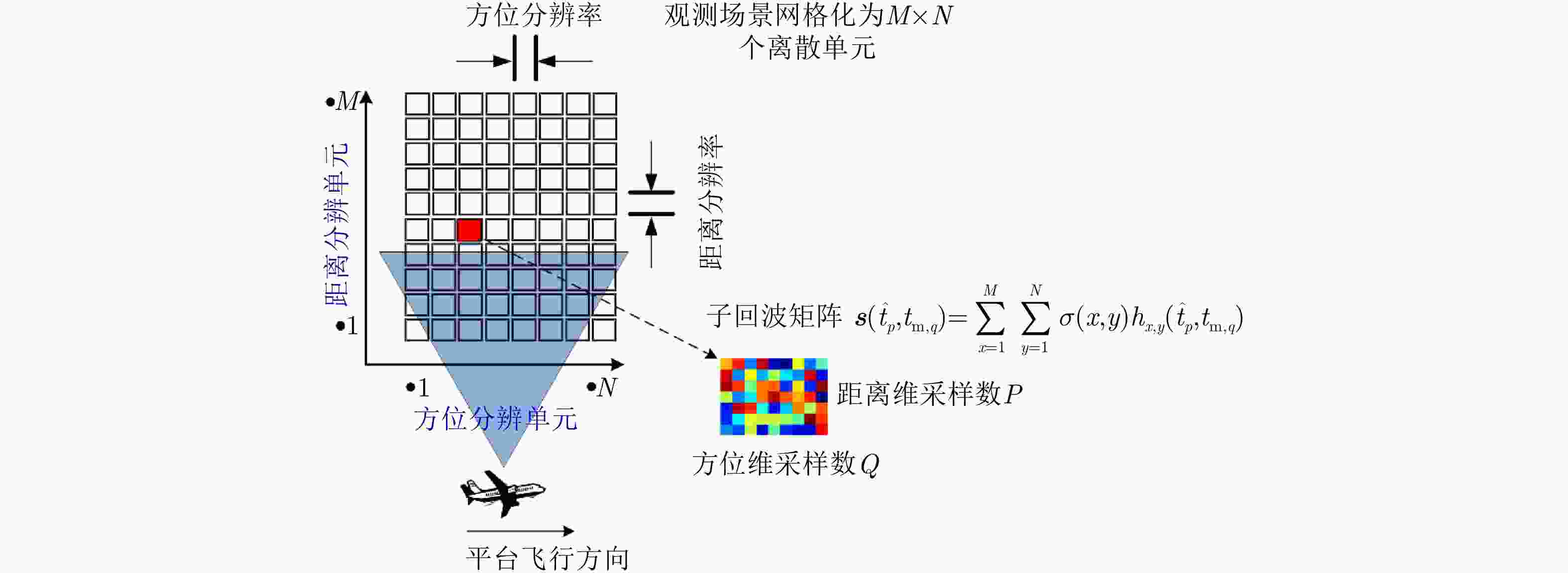
参数 值 雷达参数 载频fc (GHz) 10 带宽Br (MHz) 150 脉冲重复频率PRF (Hz) 500 脉冲持续时间Tr (μs) 1.2 方位向分辨率(m) 2 距离向分辨率(m) 2 平台高度H (m) 10000 平台速度v (m/s) 100 网络参数 网络层数 L 训练样本数量 Ntrain 学习率 η 随机降采样率 γ 表 2 成像质量与成像时间对比
Table 2. Comparison of imaging quality and imaging time
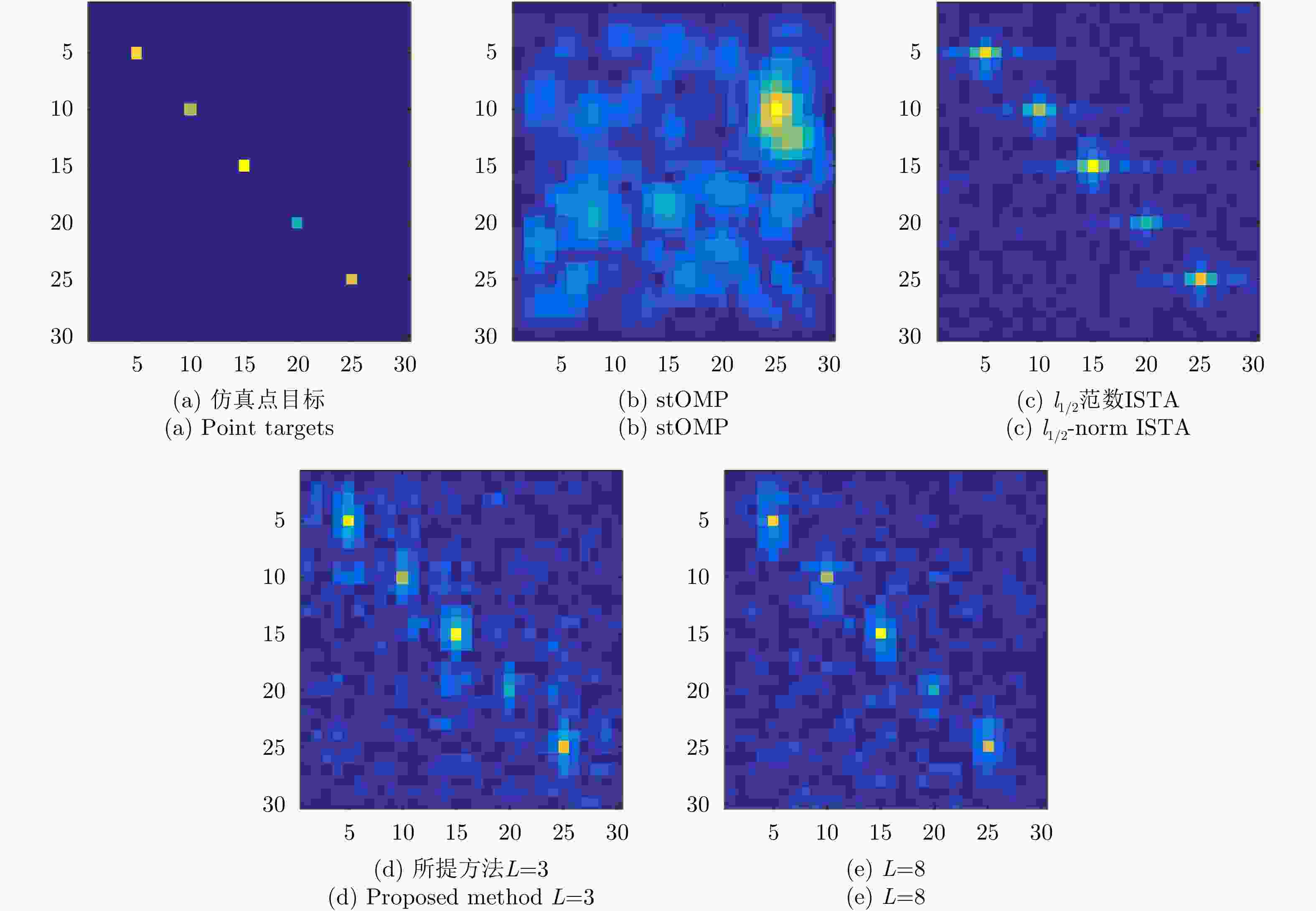
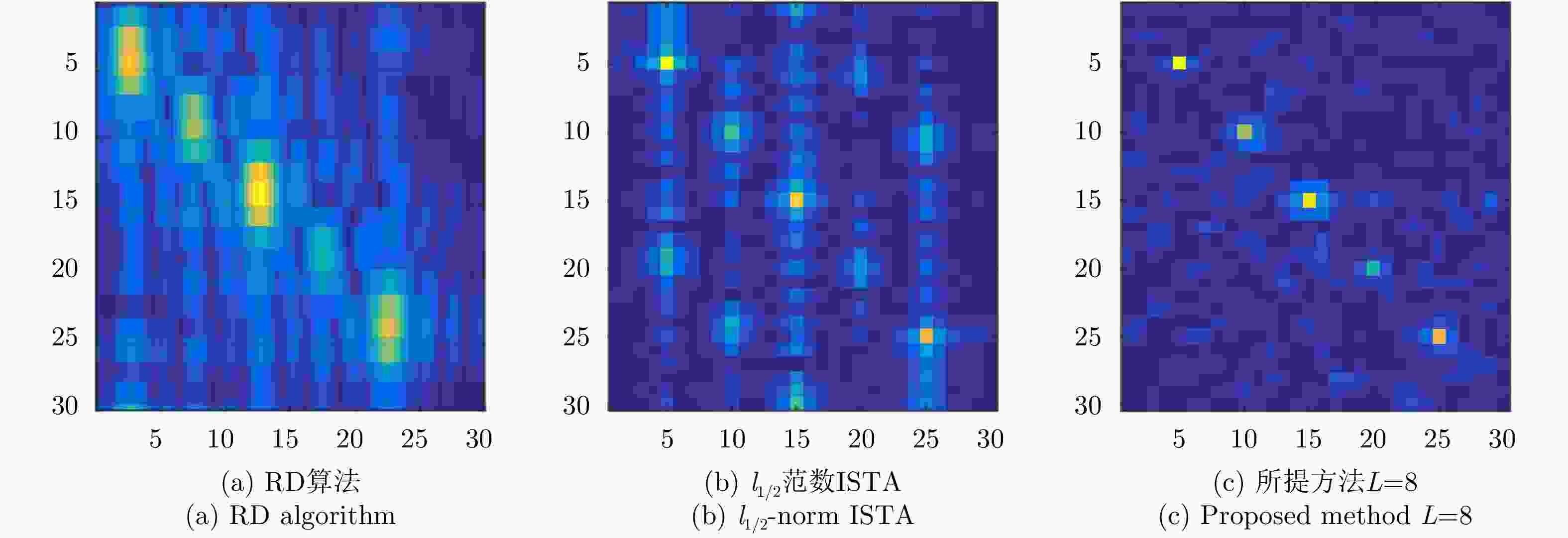
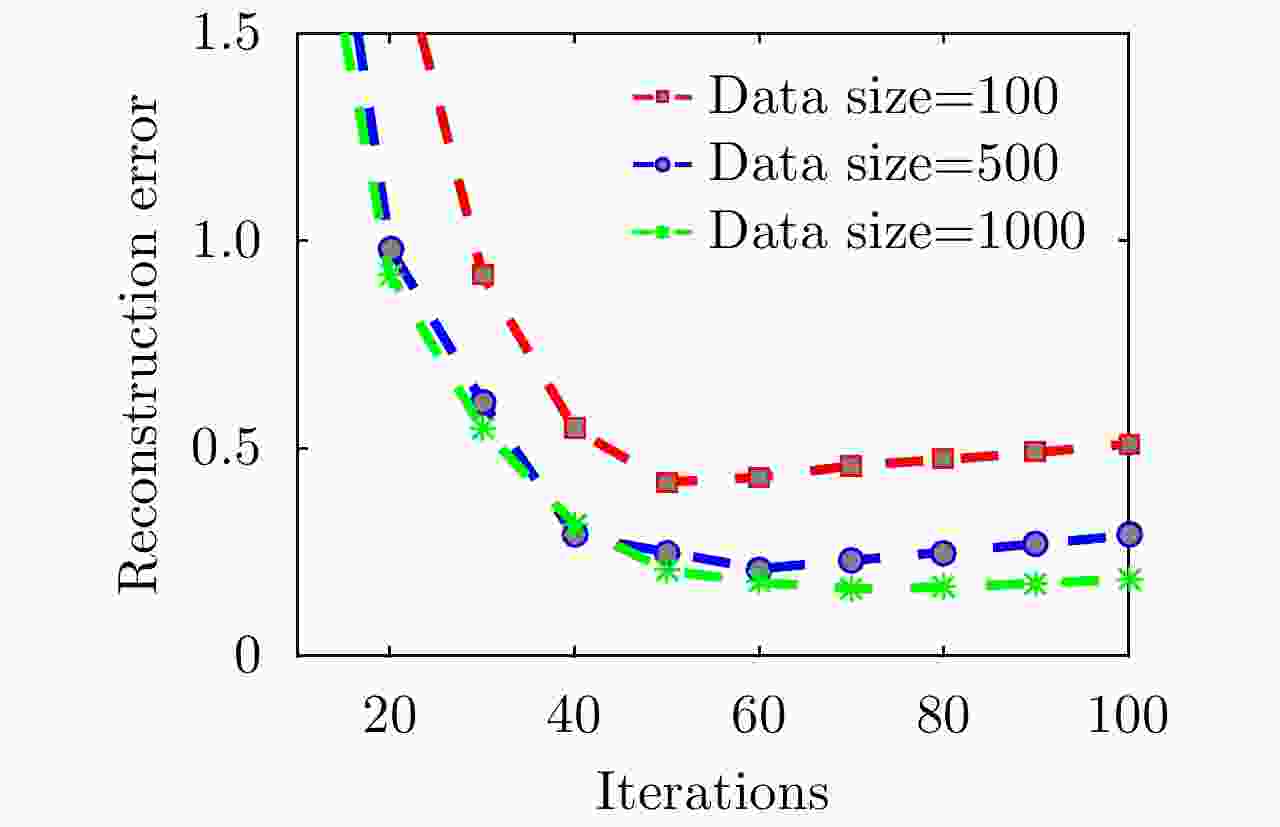
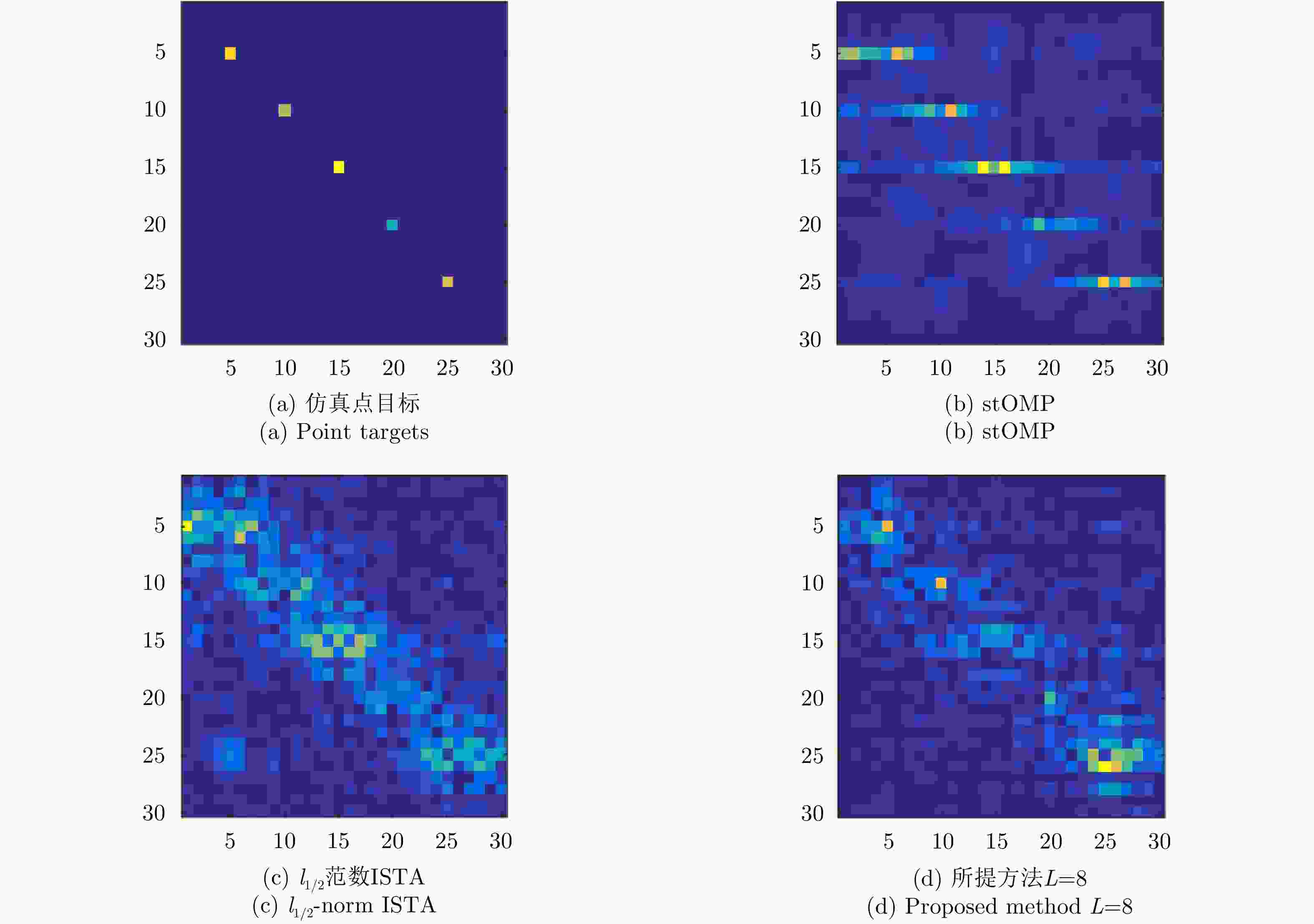
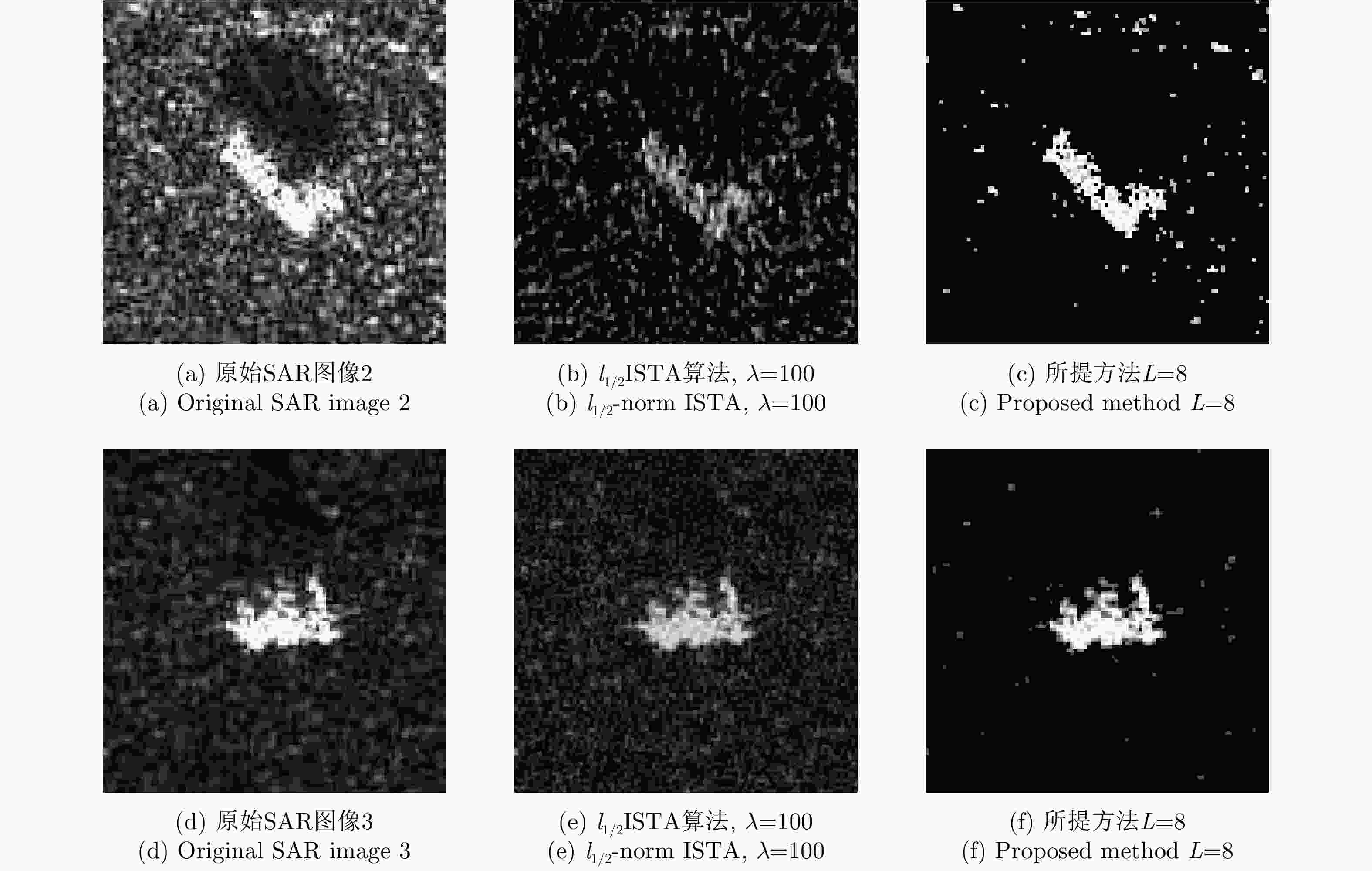
算法 γ=1, 20 dB信噪比 γ=0.1, 5 dB信噪比 PSNR (dB) NMSE PLSR (dB) 成像时间(s) PSNR (dB) NMSE PLSR (dB) 成像时间(s) stOMP 24.61 0.25 –15.55 10.93 –13.05 1.46e3 – 1.20 l1/2范数ISTA 24.44 0.26 –15.69 48.34 21.60 0.50 –13.87 4.83 所提方法L=3 19.95 0.73 –17.40 0.151 19.72 0.77 –13.56 0.012 所提方法L=8 25.58 0.20 –19.49 0.154 22.91 0.37 –16.01 0.012 所提方法L=11 25.80 0.19 –19.52 0.151 22.91 0.37 –16.13 0.012 -
[1] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2006: 1–6.BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Technologies[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2006: 1–6. [2] HONG Wen, WANG Yanping, TAN Weixian, et al. Tomographic SAR and circular SAR experiments in anechoic chamber[C]. The 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2008: 1–6. [3] 洪文, 王彦平, 林赟, 等. 新体制SAR三维成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109HONG Wen, WANG Yanping, LIN Yun, et al. Research progress on three-dimensional SAR imaging techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109 [4] YANG Wei, CHEN Jie, LIU Wei, et al. A modified three-step algorithm for TOPS and sliding spotlight SAR data processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 6910–6921. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2735993 [5] CHEN Siwei, WANG Xuesong, and XIAO Shunping. Urban damage level mapping based on co-polarization coherence pattern using multitemporal polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(8): 2657–2667. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2818939 [6] YANG Jungang, THOMPSON J, HUANG Xiaotao, et al. Random-frequency SAR imaging based on compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(2): 983–994. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2204891 [7] CHEN Yichang, LI Gang, ZHANG Qun, et al. Motion compensation for airborne SAR via parametric sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 551–562. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2611522 [8] 唐禹, 王岩飞, 张冰尘. 滑动聚束SAR成像模式研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(1): 26–29. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2005.00398TANG Yu, WANG Yanfei, and ZHANG Bingchen. A study of sliding spotlight SAR imaging mode[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2007, 29(1): 26–29. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2005.00398 [9] 杨军, 李震宇, 孙光才, 等. 一种新的大斜视TOPS SAR全孔径成像方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 42(1): 42–48, 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2015.01.08YANG Jun, LI Zhenyu, SUN Guangcai, et al. Novel full aperture imaging algorithm for highly squinted TOPS SAR[J]. Journal of Xidian University:Natural Science, 2015, 42(1): 42–48, 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.2015.01.08 [10] ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Tomographic SAR inversion by L1-norm regularization-the compressive sensing approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(10): 3839–3846. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2048117 [11] ZHANG Fubo, LIANG Xingdong, WU Yirong, et al. 3D surface reconstruction of layover areas in continuous terrain for multi-baseline SAR interferometry using a curve model[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(8): 2093–2112. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2015.1030042 [12] TAN Weixian, HUANG Pingping, HAN Kuoye, et al. Array error calibration methods in downward-looking linear-array three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2016, 10(2): 025010. doi: 10.1117/1.jrs.10.025010 [13] 徐丰, 金亚秋. 从物理智能到微波视觉[J]. 科技导报, 2018, 36(10): 30–44. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2018.10.004XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. From the emergence of intelligent science to the research of microwave vision[J]. Science &Technology Review, 2018, 36(10): 30–44. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2018.10.004 [14] 丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像——从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090 [15] LI Gang, XIA Xianggen, XU Jia, et al. A velocity estimation algorithm of moving targets using single antenna SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(3): 1052–1062. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5259182 [16] YANG Jungang, HUANG Xiaotao, THOMPSON J, et al. Compressed sensing radar imaging with compensation of observation position error[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4608–4620. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2013.2283054 [17] CHEN Yichang, ZHANG Qun, YIN Yufu, et al. Estimation of the velocity of a moving ground target using a SAR system, based on a modified multiple-measurement vector model[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 8(10): 937–946. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2017.1339919 [18] ZHANG Bingchen, HONG Wen, and WU Yirong. Sparse microwave imaging: Principles and applications[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2012, 55(3): 1722–1754. doi: 10.1007/s11432-012-4633-4 [19] NI Jiacheng, ZHANG Qun, LUO Ying, et al. Compressed sensing SAR imaging based on centralized sparse representation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(12): 4920–4932. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2831921 [20] NI Jiacheng, ZHANG Qun, YIN Yufu, et al. A novel scan SAR imaging method for maritime surveillance via Lp regularization[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 39(1): 169–190. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2017.1382744 [21] 焦李成, 张向荣, 侯彪, 等. 智能SAR图像处理与解译[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 1–7.JIAO Licheng, ZHANG Xiangrong, HOU Biao, et al. Intelligent SAR Image Processing and Interpretation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 1–7. [22] 张新征, 谭志颖, 王亦坚. 基于多特征-多表示融合的SAR图像目标识别[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 492–502. doi: 10.12000/JR17078ZHANG Xinzheng, TAN Zhiying, and WANG Yijian. SAR target recognition based on multi-feature multiple representation classifier fusion[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 492–502. doi: 10.12000/JR17078 [23] 王俊, 郑彤, 雷鹏, 等. 深度学习在雷达中的研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040WANG Jun, ZHENG Tong, LEI Peng, et al. Study on deep learning in radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(4): 395–411. doi: 10.12000/JR18040 [24] CHANG J H R, LI Chunliang, PÓCZOS B, et al. One network to solve them all-solving linear inverse problems using deep projection models[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 5888–5897. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.627. [25] SHAH V and HEGDE C. Solving linear inverse problems using GAN priors: An algorithm with provable guarantees[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, Canada, 2018: 4609–4613. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8462233. [26] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, CHEN Yunjin, et al. Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3142–3155. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206 [27] MASON E, YONEL B, and YAZICI Y B. Deep learning for SAR image formation[C]. SPIE 10201, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXIV, Anaheim, USA, 2017. doi: 10.1117/12.2267831. [28] BORGERDING M, SCHNITER P, and RANGAN S. AMP-inspired deep networks for sparse linear inverse problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(16): 4293–4308. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2708040 -



 作者中心
作者中心 专家审稿
专家审稿 责编办公
责编办公 编辑办公
编辑办公
 下载:
下载: